#java TreeSet tutorial
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Java Collection
Java libraries are indispensable tools that streamline development by providing pre-written code for common tasks. "The Ultimate Guide to Java Libraries" explores a myriad of libraries that enhance Java programming, from handling data structures to implementing complex algorithms.
A key feature covered is collections in Java, which offer efficient ways to manage groups of objects, improving code efficiency and readability.
TpointTech is a valuable resource for developers seeking in-depth tutorials and examples on using these libraries effectively. Leveraging these libraries can significantly reduce development time and improve application performance.
Overview of Java Collections
The Java Collections Framework includes interfaces, implementations, and algorithms. The core interfaces include Collection, List, Set, Queue, and Map, each serving different purposes.
Collection Interface:
The root interface of the framework, representing a group of objects known as elements. It is extended by List, Set, and Queue interfaces.
List Interface:
An ordered collection that allows duplicate elements. Common implementations are ArrayList, LinkedList, and Vector. Lists are ideal when you need to access elements by their index.
ArrayList: Resizable array implementation, offering constant-time positional access but slower for insertion and deletion.
LinkedList: Doubly-linked list implementation, providing efficient insertion and deletion but slower access time.
Vector: Synchronized version of ArrayList, rarely used due to performance overhead.
Set Interface:
A collection that does not allow duplicate elements. It models mathematical sets and provides implementations like HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet.
HashSet: Uses a hash table for storage, offering constant-time performance for basic operations.
LinkedHashSet: Maintains insertion order, slightly slower than HashSet.
TreeSet: Implements the SortedSet interface, ensuring elements are in ascending order, based on their natural ordering or a specified comparator.
Queue Interface:
Designed for holding elements prior to processing, typically ordered in a FIFO (first-in-first-out) manner. Common implementations include LinkedList, PriorityQueue, and ArrayDeque.
PriorityQueue: Elements are ordered according to their natural ordering or a provided comparator, useful for creating priority-based tasks.
ArrayDeque: Resizable-array implementation of the Deque interface, providing efficient insertion and deletion from both ends.
Map Interface:
Represents a collection of key-value pairs, where each key maps to one value. Popular implementations are HashMap, LinkedHashMap, and TreeMap.
HashMap: Provides constant-time performance for basic operations, assuming a good hash function.
LinkedHashMap: Maintains a doubly-linked list of its entries, preserving the order of insertion.
TreeMap: Implements the SortedMap interface, ensuring keys are in ascending order.
Advantages of Java Collections Framework
Reduces Programming Effort: With a set of ready-made data structures and algorithms, JCF eliminates the need for developers to implement complex data structures from scratch.
Increases Program Speed and Quality: Standardized interfaces and optimized implementations ensure high performance and reliability.
Interoperability: Collections can be easily passed across APIs, reducing the complexity of integration.
Ease of Maintenance: Well-documented and widely-used classes make it easier for developers to maintain and enhance code.
Common Algorithms in JCF
Java Collections Framework includes various algorithms to perform routine tasks, such as sorting, searching, and shuffling. These algorithms are static methods in the Collections utility class.
Sorting: Collections.sort(List list), sorts the specified list into ascending order.
Shuffling: Collections.shuffle(List list), randomly permutes the elements in the list.
Searching: Collections.binarySearch(List> list, T key), performs binary search on a sorted list.
Conclusion
The Java Collections Framework is indispensable for any Java developer. It offers a standardized and efficient way to manage groups of objects, making code more robust and maintainable.
By leveraging the various interfaces and implementations, such as lists, sets, queues, and maps, developers can handle data structures effectively.
Understanding collections in Java, as detailed on resources like TpointTech, is crucial for building high-performance applications. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, mastering Java collections will significantly enhance your programming capabilities.
0 notes
Link
Java.util package provides a TreeSet class which is a NavigableSet implementation based on a TreeMap. The elements are ordered using their natural ordering, or by a Comparator provided at set creation time, depending on which constructor is used. The class guarantees that the Map will be in ascending key order and backed by a TreeMap.
0 notes
Text
Write a program in java to demonstrate remove duplication from ArrayList to TreeSet?
Write a program in java to demonstrate remove duplication from ArrayList to TreeSet?
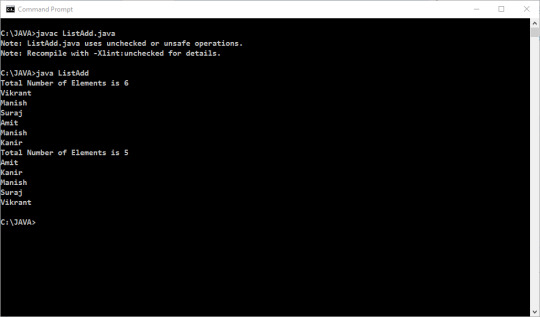
import java.util.*; public class ListAdd { public static void main(String arg[]) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); ArrayList ls=new ArrayList(); TreeSet set=newTreeSet(); ls.add("Vikrant"); ls.add("Manish"); ls.add("Suraj"); ls.add(3,"Amit"); ls.add("Manish"); …
View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Link
Start Learning Java Programming Step By Step with 200+ code examples. 250 Amazing Steps For Absolute Java Beginners!
What you’ll learn
You will Learn Java the MODERN WAY – Step By Step – With 200 HANDS-ON Code Examples
You will Understand the BEST PRACTICES in Writing High Quality Java Code
You will Solve a Wide Range of Hands-on Programming EXERCISES with Java
You will Learn to Write AWESOME Object Oriented Programs with Java
You will Acquire ALL the SKILLS to demonstrate an EXPERTISE with Java Programming in Your Job Interviews
You will learn ADVANCED Object Oriented Programming Concepts – Abstraction, Inheritance, Encapsulation and Polymorphism
You will learn the Basics of Object Oriented Programming – Interfaces, Inheritance, Abstract Class and Constructors
You will learn the Basics of Programming – variables, choosing a data type, conditional execution, loops, writing great methods, breaking down problems into sub problems and implementing great Exception Handling
You will learn Basics of Functional Programming with Java
You will gain Expertise in using Eclipse IDE and JShell
You will learn the basics of MultiThreaded Programming – with Executor Service
You will learn about a wide variety of Java Collections – List, Map, Set and Queue Interfaces
Requirements
You have an attitude to learn while having fun 🙂
You have ZERO Programming Experience and Want to Learn Java
Description
Zero Java Programming Experience? No Problem.
Do you want to take the first steps to Become a Great Java Programmer? Do you want to Learn Java Step By Step in a Fail Safe in28Minutes Way? Do you want to Learn to Write Great Java Programs?
******* Some Amazing Reviews From Our Learners *******
★★★★★ it’s an awesome course , i was a complete beginner and it helped me a lot. One of the best courses i have every taken on Udemy.
★★★★★ This is the best Java course I’ve come across. It’s straight to the point without any missing details. You can get an idea of what you’re getting into working with Java fast with this course. I really like it.
★★★★★ The experienece was extremely amazing. The course was highly detailed and comprehensive and all the topic were covered properly with due examples to their credit. The instructor is passionateabout what he is doing and hence it makes the course much more worth to learn. Kudos to the instructor for such an amazing job.
★★★★★ Never thought taking an online course will be so helpful. The instructor is quite engaging, gives good amount of exercises.
★★★★★ This course is wonderful! I really enjoy it. It really is for beginners, so it’s very helpful for people which don’t know nothing about programming.
★★★★★ Very comprehensive and detail course the instructor takes the patience to explain everything and goes a step forward in thinking what kind of errors could happen to the students really good instructor!
★★★★★ It’s very well thought out. I enjoy the constant exercises and the challenge they present to make things happen.
******* Course Overview *******
Java is one of the most popular programming languages. Java offers both object oriented and functional programming features.
We take an hands-on approach using a combination of JShell and Eclipse as an IDE to illustrate more than 200 Java Coding Exercises, Puzzles and Code Examples. This course assumes no previous ( beginner ) programming or Java experience. If you’ve never programmed a computer before, or if you already have experience with another programming language and want to quickly learn Java, this is a perfect course for you.
In more than 250 Steps, we explore the most important Java Programming Language Features
Basics of Java Programming – Expressions, Variables and Printing Output
Java Operators – Java Assignment Operator, Relational and Logical Operators, Short Circuit Operators
Java Conditionals and If Statement
Methods – Parameters, Arguments and Return Values
Object Oriented Programming – Class, Object, State and Behavior
Basics of OOPS – Encapsulation, Abstraction, Inheritance and Polymorphism
Basics about Java Data Types – Casting, Operators and More
Java Built in Classes – BigDecimal, String, Java Wrapper Classes
Conditionals with Java – If Else Statement, Nested If Else, Java Switch Statement, Java Ternary Operator
Loops – For Loop, While Loop in Java, Do While Loop, Break and Continue
Immutablity of Java Wrapper Classes, String and BigDecimal
Java Dates – Introduction to LocalDate, LocalTime and LocalDateTime
Java Array and ArrayList – Java String Arrays, Arrays of Objects, Primitive Data Types, toString and Exceptions
Introduction to Variable Arguments
Basics of Designing a Class – Class, Object, State and Behavior. Deciding State and Constructors.
Understanding Object Composition and Inheritance
Java Abstract Class and Interfaces. Introduction to Polymorphism.
Java Collections – List Interface(ArrayList, LinkedList and Vector), Set Interface (HashSet, LinkedHashSet and TreeSet), Queue Interface (PriorityQueue) and Map Interface (HashMap, HashTable, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap() – Compare, Contrast and Choose
Generics – Why do we need Generics? Restrictions with extends and Generic Methods, WildCards – Upper Bound and Lower Bound.
Functional Programming – Lambda Expression, Stream and Operations on a Stream (Intermediate Operations – Sort, Distinct, Filter, Map and Terminal Operations – max, min, collect to List), Functional Interfaces – Predicate Interface,Consumer Interface, Function Inteface for Mapping, Method References – static and instance methods
Introduction to Threads and MultiThreading – Need for Threads
Implementing Threads – Extending Thread Class and Implementing Runnable Interface
States of a Thread and Communication between Threads
Introduction to Executor Service – Customizing number of Active Threads. Returning a Future, invokeAll and invokeAny
Introduction to Exception Handling – Your Thought Process during Exception Handling. try, catch and finally. Exception Hierarchy – Checked Exceptions vs Unchecked Exceptions. Throwing an Exception. Creating and Throwing a Custom Exception – CurrenciesDoNotMatchException. Try with Resources – New Feature in Java 7.
List files and folders in Directory with Files list method, File walk method and find methods. Read and write from a File.
******* What You Can Expect from Every in28Minutes Course *******
in28Minutes created 20 Best Selling Courses providing Amazing Learning Experiences to 250,000 Learners across the world.
Each of these courses come with
✔ Amazing Hands-on Step By Step Learning Experiences
✔ Real Project Experiences using the Best Tools and Frameworks
✔ Awesome Troubleshooting Guides with 200+ FAQs Answered
✔ Friendly Support in the Q&A section
✔ Free Udemy Certificate of Completion on Completion of Course
✔ 30 Day “No Questions Asked” Money Back Guarantee!
~~~ Here are a Few Reviews on The in28Minutes Way ~~~
★★★★★ Excellent, fabulous. The way he has prepared the material and the way he teaches is really awesome. What an effort .. Thanks a million
★★★★★ A lot of preparation work has taken place from the teacher and this is visible throughout the course.
★★★★★ This guy is fantastic. Really. Wonderful teaching skills, and goes well out of his way to make sure that everything he is doing is fully understood. This is the kind of tutorial that gets me excited to work with a framework that I may otherwise not be.
★★★★★ The best part of it is the hands-on approach which the author maintained throughout the course as he had promised at the beginning of the lecture. He explains the concepts really well and also makes sure that there is not a single line of code you type without understanding what it really does.
★★★★★ I also appreciate the mind and hands approach of teaching something and then having the student apply it. It makes everything a lot clearer for the student and uncovers issues that we will face in our project early.
★★★★★ Amazing course. Explained super difficult concepts (that I have spent hours on the internet finding a good explanation) in under 5 minutes.
Zero risk. 30 day money-back guarantee with every purchase of the course. You have nothing to lose!
Start Learning Now. Hit the Enroll Button!
******* Step By Step Details *******
Introduction to Java Programming with Jshell using Multiplication Table
Step 00 – Getting Started with Programming Step 01 – Introduction to Multiplication Table challenge Step 02 – Launch JShell Step 03 – Break Down Multiplication Table Challenge Step 04 – Java Expression – An Introduction Step 05 – Java Expression – Exercises Step 06 – Java Expression – Puzzles Step 07 – Printing output to console with Java Step 08 – Printing output to console with Java – Exercise Statements Step 09 – Printing output to console with Java – Exercise Solutions Step 10 – Printing output to console with Java – Puzzles Step 11 – Advanced Printing output to console with Java Step 12 – Advanced Printing output to console with Java – Exercises and Puzzles Step 13 – Introduction to Variables in Java Step 14 – Introduction to Variables in Java – Exercises and Puzzles Step 15 – 4 Important Things to Know about Variables in Java Step 16 – How are variables stored in memory? Step 17 – How to name a variable? Step 18 – Understanding Primitive Variable Types in Java Step 19 – Understanding Primitive Variable Types in Java – Choosing a Type Step 20 – Java Assignment Operator Step 21 – Java Assignment Operator – Puzzles on Increment, Decrement and Compound Assignment Step 23 – Java Conditionals and If Statement – Introduction Step 24 – Java Conditionals and If Statement – Exercise Statements Step 25 – Java Conditionals and If Statement – Exercise Solutions Step 26 – Java Conditionals and If Statement – Puzzles Step 27 – Java For Loop to Print Multiplication Table – Introduction Step 28 – Java For Loop to Print Multiplication Table – Exercise Statements Step 29 – Java For Loop to Print Multiplication Table – Exercise Solutions Step 30 – Java For Loop to Print Multiplication Table – Puzzles Step 31 – Programming Tips : JShell – Shortcuts, Multiple Lines and Variables TODO Move up Step 32 – Getting Started with Programming – Revise all Terminology
Introduction to Method with Multiplication Table
Step 00 – Section 02 – Methods – An Introduction Step 01 – Your First Java Method – Hello World Twice and Exercise Statements Step 02 – Introduction to Java Methods – Exercises and Puzzles Step 03 – Programming Tip – Editing Methods with JShell Step 04 – Introduction to Java Methods – Arguments and Parameters Step 05 – Introduction to Java Method Arguments – Exercises Step 06 – Introduction to Java Method Arguments – Puzzles and Tips Step 07 – Getting back to Multiplication Table – Creating a method Step 08 – Print Multiplication Table with a Parameter and Method Overloading Step 09 – Passing Multiple Parameters to a Java Method Step 10 – Returning from a Java Method – An Introduction Step 11 – Returning from a Java Method – Exercises Step 99 – Methods – Section Review
Introduction to Java Platform
Step 00 – Section 03 – Overview Of Java Platform – Section Overview Step 01 – Overview Of Java Platform – An Introduction – java, javac, bytecode and JVM Step 02 – Java Class and Object – First Look Step 03 – Create a method in a Java class Step 04 – Create and Compile Planet.java class Step 05 – Run Planet calss with Java – Using a main method Step 06 – Play and Learn with Planet Class Step 07 – JDK vs JRE vs JVM
Introduction to Eclipse – First Java Project
Step 01 – Creating a New Java Project with Eclipse Step 02 – Your first Java class with Eclipse Step 03 – Writing Multiplication Table Java Program with Eclipse Step 04 – Adding more methods for Multiplication Table Program Step 05 – Programming Tip 1 : Refactoring with Eclipse Step 06 – Programming Tip 2 : Debugging with Eclipse Step 07 – Programming Tip 3 : Eclipse vs JShell – How to choose?
Introduction To Object Oriented Programming
Step 00 – Introduction to Object Oriented Programming – Section Overview Step 01 – Introduction to Object Oriented Programming – Basics Step 02 – Introduction to Object Oriented Programming – Terminology – Class, Object, State and Behavior Step 03 – Introduction to Object Oriented Programming – Exercise – Online Shopping System and Person Step 04 – Create Motor Bike Java Class and a couple of objects Step 05 – Exercise Solutions – Book class and Three instances Step 06 – Introducing State of an object with speed variable Step 07 – Understanding basics of Encapsulation with Setter methods Step 08 – Exercises and Tips – Getters and Generating Getters and Setters with Eclipse Step 09 – Puzzles on this and initialization of member variables Step 10 – First Advantage of Encapsulation Step 11 – Introduction to Encapsulation – Level 2 Step 12 – Encapsulation Exercises – Better Validation and Book class Step 13 – Introdcution to Abstraction Step 14 – Introduction to Java Constructors Step 15 – Introduction to Java Constructors – Exercises and Puzzles Step 16 – Introduction to Object Oriented Programming – Conclusion
Primitive Data Types And Alternatives
Step 00 – Primitive Data Types in Depth – Section Overview Step 01 – Basics about Java Integer Data Types – Casting, Operators and More Step 02 – Java Integer Data Types – Puzzles – Octal, Hexadecimal, Post and Pre increment Step 03 – Java Integer Data Types – Exercises – BiNumber – add, multiply and double Step 04 – Java Floating Point Data Types – Casting , Conversion and Accuracy Step 05 – Introduction to BigDecimal Java Class Step 06 – BigDecimal Puzzles – Adding Integers Step 07 – BigDecimal Exercises – Simple Interest Calculation Step 08 – Java Boolean Data Type – Relational and Logical Operators Step 09 – Java Boolean Data Type – Puzzles – Short Circuit Operators Step 10 – Java Character Data Type char – Representation and Conversion Step 11 – Java char Data Type – Exercises 1 – isVowel Step 12 – Java char Data Type – Exercises 2 – isDigit Step 13 – Java char Data Type – Exercises 3 – isConsonant, List Upper Case and Lower Case Characters Step 14 – Primitive Data Types in Depth – Conclusion
Conditionals
Step 00 – Conditionals with Java – Section Overview Step 01 – Introduction to If Else Statement Step 02 – Introduction to Nested If Else Step 03 – If Else Statement – Puzzles Step 04 – If Else Problem – How to get User Input in Java? Step 05 – If Else Problem – How to get number 2 and choice from user? Step 06 – If Else Problem – Implementing with Nested If Else Step 07 – Java Switch Statement – An introduction Step 08 – Java Switch Statement – Puzzles – Default, Break and Fall Through Step 09 – Java Switch Statement – Exercises – isWeekDay, nameOfMonth, nameOfDay Step 10 – Java Ternary Operation – An Introduction Step 11 – Conditionals with Java – Conclusion
Loops
Step 00 – Java Loops – Section Introduction Step 01 – Java For Loop – Syntax and Puzzles Step 02 – Java For Loop – Exercises Overview and First Exercise Prime Numbers Step 03 – Java For Loop – Exercise – Sum Upto N Numbers and Sum of Divisors Step 04 – Java For Loop – Exercise – Print a Number Triangle Step 05 – While Loop in Java – An Introduction Step 06 – While Loop – Exericises – Cubes and Squares upto limit Step 07 – Do While Loop in Java – An Introduction Step 08 – Do While Loop in Java – An Example – Cube while user enters positive numbers Step 09 – Introduction to Break and Continue Step 10 – Selecting Loop in Java – For vs While vs Do While
Reference Types
Step 00 – Java Reference Types – Section Introduction Step 01 – Reference Types – How are they stored in Memory? Step 02 – Java Reference Types – Puzzles Step 03 – String class – Introduction and Exercise – Print each word and char on a new line Step 04 – String class – Exercise Solution and Some More Important Methods Step 05 – Understanding String is Immutable and String Concat, Upper Case, Lower Case, Trim methods Step 06 – String Concatenation and Join, Replace Methods Step 07 – Java String Alternatives – StringBuffer and StringBuilder Step 08 – Java Wrapper Classes – An Introduction – Why and What? Step 09 – Java Wrapper Classes – Creation – Constructor and valueOf Step 10 – Java Wrapper Classes – Auto Boxing and a Few Wrapper Constants – SIZE, BYTES, MAX_VALUE and MIN_VALUE Step 11 – Java Dates – Introduction to LocalDate, LocalTime and LocalDateTime Step 12 – Java Dates – Exploring LocalDate – Creation and Methods to play with Date Step 13 – Java Dates – Exploring LocalDate – Comparing Dates and Creating Specific Dates Step 14 – Java Reference Types – Conclusion
Arrays and ArrayLists
Step 00 – Introduction to Array and ArrayList – Section Introduction with a Challenge Step 01 – Understanding the need and Basics about an Array Step 02 – Java Arrays – Creating and Accessing Values – Introduction Step 03 – Java Arrays – Puzzles – Arrays of Objects, Primitive Data Types, toString and Exceptions Step 04 – Java Arrays – Compare, Sort and Fill Step 05 – Java Arrays – Exercise – Create Student Class – Part 1 – Total and Average Marks Step 06 – Java Arrays – Exercise – Create Student Class – Part 2 – Maximum and Minimum Mark Step 07 – Introduction to Variable Arguments – Need Step 08 – Introduction to Variable Arguments – Basics Step 09 – Introduction to Variable Arguments – Enhancing Student Class Step 10 – Java Arrays – Using Person Objects and String Elements with Exercises Step 11 – Java String Arrays – Exercise Solutions – Print Day of Week with Most number of letters and more Step 12 – Adding and Removing Marks – Problem with Arrays Step 13 – First Look at ArrayList – An Introduction Step 14 – First Look at ArrayList – Refactoring Student Class to use ArrayList Step 15 – First Look at ArrayList – Enhancing Student Class with Add and Remove Marks Step 16 – Introduction to Array and ArrayList – Conclusion
Object Oriented Programming Again
Step 00 – Object Oriented Programming – Level 2 – Section Introduction Step 01 – Basics of Designing a Class – Class, Object, State and Behavior Step 02 – OOPS Example – Fan Class – Deciding State and Constructors Step 03 – OOPS Example – Fan Class – Deciding Behavior with Methods Step 04 – OOPS Exercise – Rectangle Class Step 05 – Understanding Object Composition with Customer Address Example Step 06 – Understanding Object Composition – An Exercise – Books and Reviews Step 07 – Understanding Inheritance – Why do we need it? Step 08 – Object is at top of Inheritance Hierarchy Step 09 – Inheritance and Overriding – with toString() method Step 10 – Java Inheritance – Exercise – Student and Employee Classes Step 11 – Java Inheritance – Default Constructors and super() method call Step 12 – Java Inheritance – Puzzles – Multiple Inheritance, Reference Variables and instanceof Step 13 – Java Abstract Class – Introductio Step 14 – Java Abstract Class – First Example – Creating Recipes with Template Method Step 15 – Java Abstract Class – Puzzles Step 16 – Java Interface – Example 1 – Gaming Console – How to think about Intefaces? Step 17 – Java Interface – Example 2 – Complex Algorithm – API defined by external team Step 18 – Java Interface – Puzzles – Unimplemented methods, Abstract Classes, Variables, Default Methods and more Step 19 – Java Interface vs Abstract Class – A Comparison Step 20 – Java Interface Flyable and Abstract Class Animal – An Exercise Step 21 – Polymorphism – An introduction
Collections
Step 01 – Java Collections – Section Overview with Need For Collections Step 02 – List Interface – Introduction – Position is King Step 03 – List Inteface – Immutability and Introduction of Implementations – ArrayList, LinkedList and Vector Step 04 – List Inteface Implementations – ArrayList vs LinkedList Step 05 – List Inteface Implementations – ArrayList vs Vector Step 06 – List Inteface – Methods to add, remove and change elements and lists Step 07 – List and ArrayList – Iterating around elements Step 08 – List and ArrayList – Choosing iteration approach for printing and deleting elements Step 09 – List and ArrayList – Puzzles – Type Safety and Removing Integers Step 10 – List and ArrayList – Sorting – Introduction to Collections sort static method Step 11 – List and ArrayList – Sorting – Implementing Comparable Inteface in Student Class Step 12 – List and ArrayList – Sorting – Providing Flexibility by implementing Comparator interface Step 13 – List and ArrayList – A Summary Step 14 – Set Interface – Introduction – No Duplication Step 15 – Understanding Data Structures – Array, LinkedList and Hashing Step 16 – Understanding Data Structures – Tree – Sorted Order Step 17 – Set Interface – Hands on – HashSet, LinkedHashSet and TreeSet Step 18 – Set Interface – Exercise – Find Unique Characters in a List Step 19 – TreeSet – Methods from NavigableSet – floor,lower,upper, subSet, head and tailSet Step 20 – Queue Interface – Process Elements in Order Step 21 – Introduction to PriorityQueue – Basic Methods and Customized Priority Step 22 – Map Interface – An Introduction – Key and Value Step 23 – Map Interface – Implementations – HashMap, HashTable, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap Step 24 – Map Interface – Basic Operations Step 25 – Map Interface – Comparison – HashMap vs LinkedHashMap vs TreeMap Step 26 – Map Interface – Exercise – Count occurances of characters and words in a piece of text Step 27 – TreeMap – Methods from NavigableMap – floorKey, higherKey, firstEntry, subMap and more Step 28 – Java Collections – Conclusion with Three Tips
Generics
Step 01 – Introduction to Generics – Why do we need Generics? Step 02 – Implementing Generics for the Custom List Step 03 – Extending Custom List with a Generic Return Method Step 04 – Generics Puzzles – Restrictions with extends and Generic Methods Step 05 – Generics and WildCards – Upper Bound and Lower Bound
Introduction to Functional Programming
Step 01 – Introduction to Functional Programming – Functions are First Class Citizens Step 02 – Functional Programming – First Example with Function as Parameter Step 03 – Functional Programming – Exercise – Loop a List of Numbers Step 04 – Functional Programming – Filtering – Exercises to print odd and even numbers from List Step 05 – Functional Programming – Collect – Sum of Numbers in a List Step 06 – Functional Programming vs Structural Programming – A Quick Comparison Step 07 – Functional Programming Terminology – Lambda Expression, Stream and Operations on a Stream Step 08 – Stream Intermediate Operations – Sort, Distinct, Filter and Map Step 09 – Stream Intermediate Operations – Exercises – Squares of First 10, Map String List to LowerCase and Length of String Step 10 – Stream Terminal Operations – 1 – max operation with Comparator Step 11 – Stream Terminal Operations – 2 – min, collect to List, Step 12 – Optional class in Java – An Introduction Step 13 – Behind the Screens with Functional Interfaces – Implement Predicate Interface Step 14 – Behind the Screens with Functional Interfaces – Implement Consumer Interface Step 15 – Behind the Screens with Functional Interfaces – Implement Function Inteface for Mapping Step 16 – Simplify Functional Programming code with Method References – static and instance methods Step 17 – Functions are First Class Citizens Step 18 – Introduction to Functional Programming – Conclusion
Introduction to Threads And Concurrency
Step 01 – Introduction to Threads and MultiThreading – Need for Threads Step 02 – Creating a Thread for Task1 – Extending Thread Class Step 03 – Creating a Thread for Task2 – Implement Runnable Interface Step 04 – Theory – States of a Thread Step 05 – Placing Priority Requests for Threads Step 06 – Communication between Threads – join method Step 07 – Thread utility methods and synchronized keyword – sleep, yield Step 08 – Need for Controlling the Execution of Threads Step 09 – Introduction to Executor Service Step 10 – Executor Service – Customizing number of Threads Step 11 – Executor Service – Returning a Future from Thread using Callable Step 12 – Executor Service – Waiting for completion of multiple tasks using invokeAll Step 13 – Executor Service – Wait for only the fastest task using invokeAny Step 14 – Threads and MultiThreading – Conclusion
Introduction to Exception Handling
Step 01 – Introduction to Exception Handling – Your Thought Process during Exception Handling Step 02 – Basics of Exceptions – NullPointerException and StackTrace Step 03 – Basics of Handling Exceptions – try and catch Step 04 – Basics of Handling Exceptions – Exception Hierarchy, Matching and Catching Multiple Exceptions Step 05 – Basics of Handling Exceptions – Need for finally Step 06 – Basics of Handling Exceptions – Puzzles Step 07 – Checked Exceptions vs Unchecked Exceptions – An Example Step 08 – Hierarchy of Errors and Exceptions – Checked and Runtime Step 09 – Throwing an Exception – Currencies Do Not Match Runtime Exception Step 10 – Throwing a Checked Exception – Throws in method signature and handling Step 11 – Throwing a Custom Exception – CurrenciesDoNotMatchException Step 12 – Write less code with Try with Resources – New Feature in Java 7 Step 13 – Basics of Handling Exceptions – Puzzles 2 Step 14 – Exception Handling – Conclusion with Best Practices
Files and Directories
Step 01 – List files and folders in Directory with Files list method Step 02 – Recursively List and Filter all files and folders in Directory with Step Files walk method and Search with find method Step 03 – Read content from a File – Files readAllLines and lines methods Step 04 – Writing Content to a File – Files write method Step 05 – Files – Conclusion
More Concurrency with Concurrent Collections and Atomic Operations
Step 01 – Getting started with Synchronized Step 02 – Problem with Synchronized – Less Concurrency Step 03 – Enter Locks with ReEntrantLock Step 04 – Introduction to Atomic Classes – AtomicInteger Step 05 – Need for ConcurrentMap Step 06 – Implementing an example with ConcurrentHashMap Step 07 – ConcurrentHashMap uses different locks for diferrent regions Step 08 – CopyOnWrite Concurrent Collections – When reads are more than writes Step 09 – Conclusion
Java Tips
Java Tip 01 – Imports and Static Imports Java Tip 02 – Blocks Java Tip 03 – equals method Java Tip 04 – hashcode method Java Tip 05 – Class Access Modifiers – public and default Java Tip 06 – Method Access Modifiers – public, protected, private and default Java Tip 07 – Final classes and Final methods Java Tip 08 – Final Variables and Final Arguments Java Tip 09 – Why do we need static variables? Java Tip 09 – Why do we need static methods? Java Tip 10 – Static methods cannot use instance methods or variables Java Tip 11 – public static final – Constants Java Tip 12 – Nested Classes – Inner Class vs Static Nested Class Java Tip 13 – Anonymous Classes Java Tip 14 – Why Enum and Enum Basics – ordinal and values Java Tip 15 – Enum – Constructor, variables and methods Java Tip 16 – Quick look at inbuild Enums – Month, DayOfWeek
Zero risk. 30 day money-back guarantee with every purchase of the course. You have nothing to lose!
Start Learning Now. Hit the Enroll Button!
Who this course is for:
You have ZERO programming experience and want to learn Java Programming
You are a Beginner at Java Programming and want to Learn to write Great Java Programs
You want to learn the Basics of Object Oriented Programming with Java
You want to learn the Basics of Functional Programming with Java
Created by in28Minutes Official Last updated 1/2019 English English [Auto-generated]
Size: 2.80 GB
Download Now
https://ift.tt/2A4bRbM.
The post Java Programming for Complete Beginners – Learn in 250 Steps appeared first on Free Course Lab.
0 notes
Text
http://www.sudotutorials.com
Check http://www.sudotutorials.com/ for all java tutorials
http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/contents.html : Table of Contents http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-hello-world.html : Write a Java Program http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-operator.html : Learn Java Operators http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-literals.html : Java Literals http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-datatypes.html : Java Data Types http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-class-object.html : Create Class and Object in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-constructor.html : Java Constructor http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-control-statement.html : Java Control Statement http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-access-control.html : Access Control in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-inheritance.html : Java Inheritance Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-method-overloading.html : Java Method Overloading Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-method-overriding.html : Java Method Overriding Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-package.html : Java Package Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-interface.html : Java Interface Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-abstract-class.html : Java Abstract Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-composition.html : Java Composition Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-exception-handling.html : Exception Handling in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-custom-exception.html : Create Custom Exception Class in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-chained-exception.html : Chained Exception in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-static-method.html : Static Method in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-final-keyword.html : Use of final Keyword in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/contents.html : Table of Contents http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-collection-interface.html : Java Collection Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-set-interface.html : Java Set Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-hashset-class.html : Java HashSet Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-treeset-class.html : Java TreeSet Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-linkedhashset-class.html : Java LinkedHashSet Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-navigableset-interface.html : Java NavigableSet Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-sortedset-interface.html : Java SortedSet Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-queue-interface.html : Java Queue Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-deque-interface.html : Java Deque Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-list-interface.html : Java List Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-arraylist-class.html : Java ArrayList Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-linkedlist-class.html : Java LinkedList Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-hashmap-class.html : Java HashMap Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/how-hashmap-works-internally-in-java.html : How HashMap Works Internally in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-linkedlist-vs-arraylist.html : Java LinkedList vs ArrayList Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-comparable-interface.html : Java Comparable Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/use-comparator-for-custom-sorting.html : Use Comparator For Custom Sorting http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/comparator-vs-comparable-in-java.html : Difference Between Comparator and Comparable Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/contents.html : Table of Contents http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/what-is-stream-in-java.html : What is Stream in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/byte-stream-in-java.html : Java Byte Stream Classes http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-inputstream-class.html : Java InputStream Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-outputstream-class.html : Java OutputStream Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-fileinputstream-class.html : Java FileInputStream Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-fileoutputstream-class.html : Java FileOutputStream Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-bytearrayinputstream-class.html : Java ByteArrayInputStream Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/character-stream-in-java.html : Java Character Stream Classes http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-reader-class.html : Java Reader Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-writer-class.html : Java Writer Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-filereader-class.html : Java FileReader Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-filewriter-class.html : Java FileWriter Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/contents.html : Table of Contents http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/create-thread-in-java.html : Create Thread in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/create-multiple-thread-in-java.html : Create Multiple Thread in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-thread-lifecycle.html : Java Thread Lifecycle http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/thread-priority-in-java.html : Thread Priority in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/what-is-daemon-thread-in-java.html : Daemon Thread in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/synchronization-in-java.html : Thread Synchronization in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/difference-between-synchronized-block-and-method-in-Java.html : Difference Between Synchronized Block and Method in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-thread-interthread-communication.html : Java Interthread Communiction http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-thread-join-isalive-method.html : Java Thread join(), isAlive() Method http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-use-of-volitile-variable-in-thread.html : Use of Volatile Variable in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/object-level-locking-vs-class-level-locking-in-java.html : Object Level Locking and Class Level Locking in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/difference-between-wait-sleep-yield-in-java.html : Difference Between wait(), sleep() and yield() in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/how-to-create-a-immutable-class-in-java.html : How to Create Immutable Class in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-concurrent-api.html : Java Concurrent API http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-semaphore.html : Semaphore in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-countdownlatch.html : Java CountdownLatch Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-cyclicbarrier.html : Java CyclicBarrier Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-thread-exchanger.html : Java Exchanger in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-phaser.html : The Java Phaser Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-executor-interface.html : Java Executor Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-concurrent-collection.html : Java Concurrent Collection http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-blocking-queue.html : Java BlockingQueue Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-concurrent-map.html : Java Concurrent Map http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-concurrentnavigablemap.html : Java ConcurrentNavigableMap Concurrent Collection http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-fork-join-framework.html : Java Fork/Join Framework http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-locks.html : The Lock object in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-atomicinteger.html : Java AtomicInteger Class
0 notes