#miterature
Photo

Translations (like wives) are seldom strictly faithful if they are in the least attractive.
- Roy Campbell, poet (1901-1957)
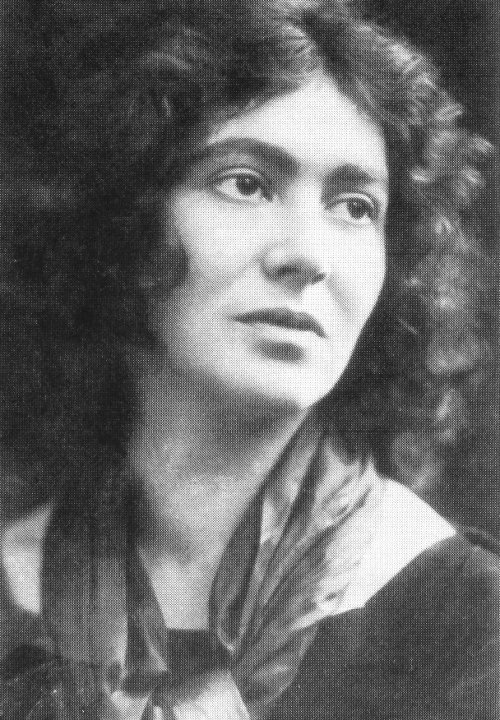
Roy Campbell was a South African poet and satirist and to this day remains criminally under appreciated. He was considered by T. S. Eliot, Dylan Thomas and Edith Sitwell to have been one of the best poets of the period between the First and Second World Wars. Campbell's vocal attacks upon both Stalinism and Freudianism, and support for Francisco Franco's Nationalists during the Spanish Civil War, has caused him to be labeled a Fascist and left out of modern poetry anthologies.
Roy Campbell, was born in Durban, South Africa, and moved to England soon after he graduated from high school. An accomplished horseman and fisherman, he also became fluent in Zulu. He left the Union of South Africa in December 1918 for Oxford University, where he arrived early in 1919. However, he failed the entrance examination. Reporting this to his father, he took a philosophical stance, telling him that "university lectures interfere very much with my work", which was writing poetry.
Campbell left Oxford for London in 1920. Holidays spent in wandering through France and along the Mediterranean coast alternated with periods in Bohemian London. In 1922 he married without parental consent and forfeited, for a time, the generous parental allowance. His wife was Mary Margaret Garman, eldest of the Garman sisters, was part of the famous literary Bloomsbury group that incuded Virginia Woolf. Mary would go on to have a scandalous lesbian love affair with Vita Sackville-West. Both she and Roy had two daughters, Teresa (Tess) and Anna.

In England, Roy befriended poets such as Wyndham Lewis, who based a character in his novel The Apes of God on Campbell. Campbell’s first book, The Flaming Terrapin (1924), brought him immediate acclaim; as T.S. Eliot does in The Waste Land, to which Campbell’s book is sometimes compared, Campbell rebels against postwar cynicism and apathy. And like Eliot, Campbell eventually converted to Catholicism.
Elizabethan dramatists such as Marlowe, Chapman, and Dekker inspired Campbell’s poetry, and his work fit uneasily into the socially conscious turn affected by many English poets in the 1930s. His second book, The Wayzgoose (1928), satirized South African intellectuals, and his third, The Georgiad (1931), attacked the mores and pretentions of Bloomsbury, whose members Campbell called “intellectuals without intellect.” He also wrote more lyrical collections, including Adamastor (1930), Flowering Reeds (1933), and Talking Bronco (1946).
Campbell led an adventurous life; after The Flaming Terrapin was published, he traveled back to South Africa to edit the literary magazine Voorslag with William Plomer and Laurens van der Post. Campbell soon returned to Europe. In the 1930s, Mary and Roy Campbell moved to the south of France among Augustus John, Aldous Huxley, Sybille Bedford and Nancy Cunard.

They soon grew tired and moved to Spain. They had initially arrived in Barcelona in the autumn of 1933, having lived for several years in Provence. Their arrival coincided with the anarchist strikes that had followed the Right-wing victory in the recent elections. “For the Catalonians, as with the Irish, politics is a national industry,” Campbell wrote to a friend. In spite of the turbulence of the times, the Campbells fell in love with Spain and Spanish culture. Mary’s enduring love for the figure of St Teresa of Avila had fired her imagination for Spain since her youth, and she had evidently passed this imaginative fire infectiously to her husband, as is evidenced by the poetry about Spain that he wrote after his arrival in the country.
Campbell wrote: “From the very beginning my wife and I understood the real issues in Spain. There could be no compromise… between the east and the west, between credulity and faith, between irresponsible innovation… and tradition, between the emotions (disguised as reason) and the intelligence.”
Tired of the brief interlude of urban life, the Campbells moved to the village of Altea, near Alicante, in May 1934. It was here that the whole family was received into the Catholic Church.
Fr Gregorio, the village priest, was delighted that a whole family of “English” was being won over to the Church. Two years later, the priest would be murdered by militiamen sent from Valencia. By this time, as we have seen, the Campbells had moved to Toledo, which Campbell eulogised in one of his poems as a “sacred city of the mind”.

Fighting in the Spanish Civil War and World War II and serving in East and North Africa and the East gave him the inspiration to write his more haunting poetry. Campbell published two autobiographies during his lifetime: Broken Record (1934) and Light on a Dark Horse (1951). He also translated work by Spanish, Portuguese, and French writers, including St. John of the Cross, Baudelaire, and Lorca, and novels by de Quevedo, among others.
In April 1957, Roy and his wife Mary set off in their tiny Fiat 600 from their home in Portugal, destined for the Holy Week celebrations in Seville. En route they stopped off for several days in Toledo, “this heavenly place which means more than all the world to me”, as Campbell described it in a postcard sent to a friend. Throughout the week of processions in Seville, Mary noticed that her husband was unusually quiet and particularly serious in his devotions.

On April 23 they set off back to Portugal, crossing the border in the early afternoon. A front tyre burst, and the car swerved out of control and hit a tree. Mary survived - she would die in 1979 - but Roy died at the scene of the crash. Thus ended, at the age of 55, the life of one of the finest and most controversial poets of the 20th century, a poet who counted George Orwell, Aldous Huxley, T S Eliot, Evelyn Waugh, J R R Tolkien and C S Lewis among his friends.
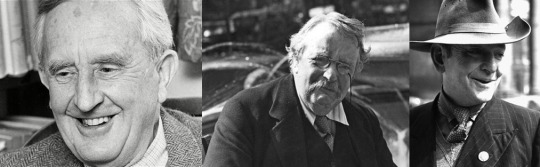
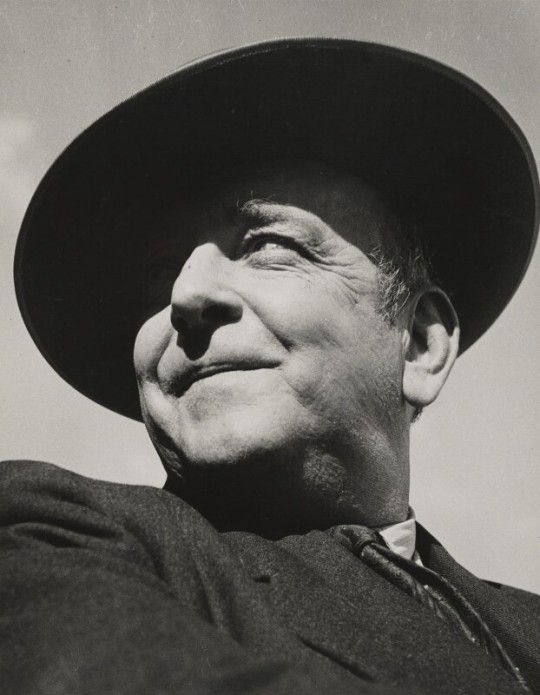
As regards his friendship with Tolkien, it is one of Campbell’s intriguing claims to fame that he was part of the inspiration for the character of Aragorn, who was played by Viggo Mortenson in the movie version of The Lord of the Rings.
Tolkien first encountered Campbell as a mysterious stranger in a pub in Oxford in 1944 who was listening intently to the conversation of C S Lewis. As Campbell peered intently at Lewis from under a wide-brimmed hat, he reminded Tolkien of Aragorn, the mysterious stranger who eavesdropped on the conversation of the hobbits in the Prancing Pony, the pub in the story in which the hobbits first meet Aragorn. Since Tolkien was in the midst of writing The Lord of the Rings at the time, and was deeply impressed by the adventurous life that Campbell had lived in Spain and elsewhere, it seems likely that Campbell helped to shape Aragorn’s character in Tolkien’s imagination.
#campbell#roy campbell#quote#poet#south africa#britain#tolkien#CS lewis#oxford#poetry#spanish civil war#war#miterature
25 notes
·
View notes