#species are going extinct before our eyes but sure let’s attack the organizations actually doing real conservation work
Text
Five critically endangered northern right whales dead from boat strikes and netting entanglements, and representatives are introducing a bill to Congress to… ban aquarium belugas from breeding.
#ban baby belugas 2k24#and orcas and… pilot whales and false killer whales?#which aren’t even bred!?#species are going extinct before our eyes but sure let’s attack the organizations actually doing real conservation work#this is the swims act again… it was shot down in 2022 and they’re trying to bring it back#gonna monitor this and draft some letters if necessary#swims act#northern right whale#belugas#whales#conservation
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here are 9 of the most badass animals ever to swim

Art by Tyson Whiting
Say hello to some horrifying sea monsters
This article was originally published on SB Nation a while ago, but was always intended for a Secret Base-y audience. So if you haven’t seen it yet, here you go!
The Earth has some very cool aquatic predators swimming about. Thanks to their intelligence and pack-hunting techniques, orcas are, perhaps, the most dangerous hunters ever to swim the ocean. Saltwater crocodiles are bulletproof murder tanks. And the great white shark, of course, needs no introduction. But now that we’re talking about terrifying underwater murder-beasts, why just settle for just the ones we have around now?
Underwater murder-beasts have a long and distinguished (pre-)history, and I thought it would be fun to introduce y’all to some new pals. TO THE IMAGINARY TIME MACHINE!
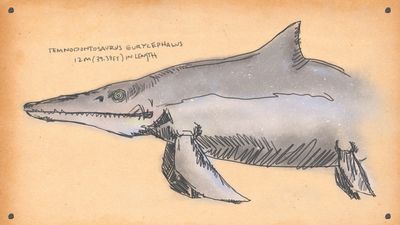
Temnodontosaurus eurycephalus
Grumpy croco-dolphin
Ichthyosaurs evolved 250 million years ago. In the aftermath of the Permian extinction, which killed off a frankly horrifying number of creatures, a group of terrestrial reptiles took to the depleted seas. Fast-forward a little bit and you have primitive ichthyosaurs, creatures so well adapted to oceanic life that they ended up looking like a cross between a crocodile and an extremely ill-tempered, extremely large dolphin.
Fast-forward even further, to the early Jurassic (175 million years ago), and you have Temnodontosaurus eurycephalus. It’s not the largest ichthyosaur ever to grace the seas, but it’s up there, and it’s a far more developed predator than its giant forebears. Somewhere around 30 feet long, T. emnodontosaurus was a powerful swimmer with strong jaws, well-equipped to chow down on other Jurassic swimmers. One closely-related species possessed the largest eyes of any known animal, perfect for hunting in deeper oceanic waters; another has been found with the remains of a different ichthyosaur in is stomach.
This monster considered 13-foot oceanic reptiles a delicious snack. It was also fast. Spare a thought for the poor ocean-going creatures minding their own business before one of these huge assholes rams into them from below at speed, opens those long, toothy jaws and turns them into lunch.

Deinosuchus hatcheri
Dinosaur hunter
Take a saltwater crocodile. Actually, it’s probably best not to. They are, after all, 20-foot, 2,000-pound apex predators more than happy to eat anything they come across, including you. Salties are strong, fast and surprisingly smart. They are at home in the open ocean as well as along the coast. Like all crocodiles, they’re ambush predators who use water as cover to attack their prey. Unlike most crocodiles they’re capable of jumping clear out of the water to get to it. They have the strongest bite of any living animal.
Right. Now that you have a saltwater crocodile in your head, make one, oh, twice as big. Yeah, like that. Decently boat-sized. Terrifying teeth in terrifying, dino-crushing jaws. Armored skin thick enough to turn aside more or less anything.
Your terrifying vision is Deinosuchus hatcheri, a crocodile adapted to more or less the exact same situation as a modern saltwater but in a world inhabited by giant dinosaurs. During the late Cretaceous (80 million years ago), North America was split by a shallow sea, the Western Interior Seaway. D. hatcheri was present on both the western side of the seaway (a slightly smaller species dominated the east), happily chowing through dinosaurs who were foolish enough to get too close.

Anomalocaris canadensis
Nightmare Shrimp
So far we’ve had a dolphin analogue in Temnodontosaurus and an actual crocodile. Cool, but nowhere near the sort of weirdness the past can provide. So let’s go to the deep, deep past, revealed wonderfully by the Burgess Shale. Here we shall find the NIGHTMARE SHRIMP.
One of the problems with studying the very earliest phase of animal life — we’re talking half a billion years at this point — is that it’s squishy, and squishy is not of much benefit when it comes to preserving fossils. Thanks to a fluke of geology, the conditions that produced the Burgess Shale were also capable of preserving soft tissue, giving palaeontologists a rare chance to look into what the seas looked like during the first days of the animal kingdom.
They looked extremely weird. The fauna found in the Burgess Shale was almost obnoxiously uncategorisable. One famous example is the worm Hallucigenia, which so confused everyone involved that it was reconstructed upside-down for the better part of a decade. Another is Opabinia, which looks sort of like a five-eyed miniature vacuum cleaner. I promise I am not making this up.
Anyway, all these critters were apparently food for the ocean’s first proper predator.
With good eyes set on flexible stalks and a surprising turn of speed, Anomalocaris canadensis cruised the Pre-Cambrian seas in death-shrimp mode. It was a full meter long, dwarfing most of its companions in the Burgess Shale. It was also delightfully strange-looking. It is so odd, in fact, that when it was discovered its various body parts were assigned to several different animals.
A. canadensis would be higher on this list if we could be sure of what it actually ate. Long-held to be a trilobite-hunter, recent studies have shown it would probably have had to restrict itself to soft-bodied prey due to relatively flimsy mouthparts, and therefore could only have actually eaten a trilobite just after a moult. But it’s much more fun to imagine this guy roaming the seafloor chomping down on everything, so that’s what we’ll do.
Disclaimer: an old friend of mine is a paleontologist who specializes in the Burgess Shale fossils. I did not contact him for this story, because I am consumed by envy whenever I so much as think about him.

Cameroceras
Spiky death-squid
Back in the Palaeozoic and Mesozoic, cephalopods were armored critters, much like our modern nautilus. The most famous of them, and one of the most widely known extinct animals ever, is the spiral-shelled ammonite. Since they had hard shells, they’re extremely common in marine strata. They also got surprisingly large. The biggest-known ammonite was two meters across. Imagine that thing trying to swim.
Ammonites weren’t the only armored cephalopod prowling the ancient seas, however. The orthocones were straight-shelled versions, and some of those got really, really big. Like Cameroceras. Current estimates put Cameroceras’s shell at upwards of six meters long. That’s three average-sized men stacked on each others’ shoulders.
Somehow this monster was still able to get about in the Ordovician seas. It’s quite hard to imagine it chasing anything around, so it presumably surprised trilobites etc. at nighttime or dug it out of the mud, but since paleoecology is at least in part about imagination, right now I’m enjoying Cameroceras retracting its head deep into its shell and pretending to be a cave before trying to eat whatever entered. It wouldn’t be quite big enough to swallow the Millennium Falcon, buuuuuuuuut ...

Carcharocles megalodon
The shark that eats planets
Megalodon needs no introduction. The great white shark has a profound hold on popular culture, but its long-gone big sister isn’t far behind. Megalodon made even the most vicious shark in today’s seas look like a toy. Since sharks are mostly soft tissue, they don’t fossilize as well as we’d like, but their teeth do, and Megalodon’s tell a terrifying story.
Megalodon died out only relatively recently. It wasn’t quite contemporaneous with human beings, but its extinction was recent enough that there are plenty of folks willing to tell tall tales of how it might still be swimming somewhere in the depths of the ocean. If it was, probably best not to get anywhere near it — a Megalodon may have had a bite force of up to 10 times the strength of a great white. That’d be a bad day.
What were those huge jaws for? Whales. Apparently, these things liked to swim up from underneath its prey and bite through their chest to reach their internal organs. The ability to kill a whole-ass whale with one bite is honestly horrifying, even if whales in Megalodon’s day were a little smaller than the current batch of great rorquals.

Jaekelopterus rhenaniae
Sea Scorpion
Did you know ‘sea scorpions’ were a thing? Sea scorpions were a thing. Since eurypterids (to give them their proper name) went extinct hundreds of millions of years ago, we don’t have very good comparisons for what these things were like. So let’s get creative. Let’s take a lobster. Despite their ferocious armament, lobsters are relatively placid creatures. They’re not averse to grabbing a fish here or a mollusk there, but they’re not built for hunting. Let’s make the required tweaks.
We need to add eyes. Let’s make them big and sensitive and set for stereoscopic vision, which allows those pincers to be used more effectively to grab prey. Let’s make them better swimmers, too — we’ll add some paddles for agility and short bursts of speed. Let’s make their claws spikier, just for sheer scare value.
Oh and let’s make them 10 feet long and perfectly happy to eat you alive. Now you have a Jaekelopterus. Aren’t you glad they’re dead?

Dunkleosteus terrelli
A, uh, fish-tank
When evolution first came up with bone, it got a little bit carried away. Well, a lot carried away. The era of armored fishes is one of the most fabulously strange in the entire history of the planet. (A personal favorite of mine is Lunapsis, which looks like a fish had a baby with Batman’s utility belt.) With bone-plated heads and upper bodies, these fish probably didn’t swim very well, but who cares? They looked cool as hell, and with that body armor they were well protected against predators.
Which, as it turns out, is the sort of inspiration nature needs to come up with some better predators*. Enter Dunkleosteus, a monster armored fish with a set of jaws which could rip straight through the armor of any other fish slowly swimming through the Devonian ocean. Known to be 20 feet long, it didn’t really have teeth so much as a huge bony beak, which honestly makes the whole contraption even more frightening, like some sort of mobile oceanic guillotine.
*I’m being overly teleological here. Forgive me. Nature, of course, does not ‘come up with’ anything.

Mosasaurus hoffmanni
For whatever reason, the fauna of Cretaceous period got big. Really, really big. On land, we had Tyrannosaurus Rex. In the skies, azhdarchids the size of small aircraft coasted from thermal to thermal. And in the shallow seas, we had another monster: Mosasaurus.
Mosasaurus was essentially an enormous — estimates have it as almost 60 feet long — ocean-going lizard. Its legs were replaced with bladed paddles for maneuverability and it had a powerful tail for direct propulsion. Mosasaurus ate everything it could get in its mouth, which was a) double-hinged for extra capacity and b) already pretty capacious to begin with.
It would have hung around near the surface of the ocean, where there was an abundance of prey. Mosasaurus could have waited for other marine reptiles (such as Archelon, the largest turtle known) to come up to breathe, grab low-flying pterosaurs on fishing expeditions, or simply have picked off the many large fish that swam the Cretaceous seas.

Livyatan Melvilli
Moby-Dick’s even-scarier dad
In 1820, the Essex was lost in the southern Pacific Ocean. The ship had been sent out to hunt for sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus, since you asked), but soon had the tables turned when it was attacked and sunk by a ferocious bull. Of the 20 crew, only eight survived, and the incident went on to inspire a famous book about whales which you may have heard of.
What you probably haven’t heard of is Livyatan. Modern sperm whales are enormous creatures, but very rare boat attacks aside, they’re only really dangerous to their favorite prey, deep-swimming squid. But not so long ago, geographically speaking, there were also a group of ‘macroraptorial’ sperm whales. These didn’t eat squid. Instead, they competed with Megalodon to hunt other great whales.
Livyatan’s teeth are some of the most awe-inspiring fossils in the world. The biggest ones are 12 inches long and look like artillery shells. Estimates have Livyatan as sitting a touch smaller than its modern friends, but those teeth indicate that it would have been significantly more vicious, fully capable of cutting a sperm whale into very bloody chunks.
It’s not clear whether or not Livyatan hunted alone or in packs, like a modern killer whale, but it had the power and size to be able to plausibly compete with Megalodon even solo. The crew of the Essex found out that a bull sperm whale could be a formidable opponent; one suspects Livyatan would have left even fewer survivors.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here are 9 of the most badass animals ever to swim

Art by Tyson Whiting
Say hello to some horrifying sea monsters
The Earth has some very cool aquatic predators swimming about. Thanks to their intelligence and pack-hunting techniques, orcas are, perhaps, the most dangerous hunters ever to swim the ocean. Saltwater crocodiles are bulletproof murder tanks. And the great white shark, of course, needs no introduction. But now that we’re talking about terrifying underwater murder-beasts, why just settle for just the ones we have around now?
Underwater murder-beasts have a long and distinguished (pre-)history, and I thought it would be fun to introduce y’all to some new pals. TO THE IMAGINARY TIME MACHINE!
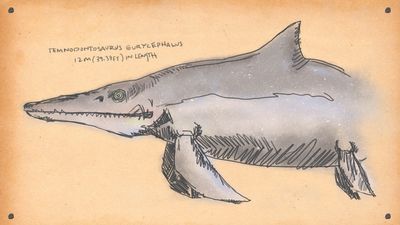
Temnodontosaurus eurycephalus
Grumpy croco-dolphin
Ichthyosaurs evolved 250 million years ago. In the aftermath of the Permian extinction, which killed off a frankly horrifying number of creatures, a group of terrestrial reptiles took to the depleted seas. Fast-forward a little bit and you have primitive ichthyosaurs, creatures so well adapted to oceanic life that they ended up looking like a cross between a crocodile and an extremely ill-tempered, extremely large dolphin.
Fast-forward even further, to the early Jurassic (175 million years ago), and you have Temnodontosaurus eurycephalus. It’s not the largest ichthyosaur ever to grace the seas, but it’s up there, and it’s a far more developed predator than its giant forebears. Somewhere around 30 feet long, T. emnodontosaurus was a powerful swimmer with strong jaws, well-equipped to chow down on other Jurassic swimmers. One closely-related species possessed the largest eyes of any known animal, perfect for hunting in deeper oceanic waters; another has been found with the remains of a different ichthyosaur in is stomach.
This monster considered 13-foot oceanic reptiles a delicious snack. It was also fast. Spare a thought for the poor ocean-going creatures minding their own business before one of these huge assholes rams into them from below at speed, opens those long, toothy jaws and turns them into lunch.

Deinosuchus hatcheri
Dinosaur hunter
Take a saltwater crocodile. Actually, it’s probably best not to. They are, after all, 20-foot, 2,000-pound apex predators more than happy to eat anything they come across, including you. Salties are strong, fast and surprisingly smart. They are at home in the open ocean as well as along the coast. Like all crocodiles, they’re ambush predators who use water as cover to attack their prey. Unlike most crocodiles they’re capable of jumping clear out of the water to get to it. They have the strongest bite of any living animal.
Right. Now that you have a saltwater crocodile in your head, make one, oh, twice as big. Yeah, like that. Decently boat-sized. Terrifying teeth in terrifying, dino-crushing jaws. Armored skin thick enough to turn aside more or less anything.
Your terrifying vision is Deinosuchus hatcheri, a crocodile adapted to more or less the exact same situation as a modern saltwater but in a world inhabited by giant dinosaurs. During the late Cretaceous (80 million years ago), North America was split by a shallow sea, the Western Interior Seaway. D. hatcheri was present on both the western side of the seaway (a slightly smaller species dominated the east), happily chowing through dinosaurs who were foolish enough to get too close.

Anomalocaris canadensis
Nightmare Shrimp
So far we’ve had a dolphin analogue in Temnodontosaurus and an actual crocodile. Cool, but nowhere near the sort of weirdness the past can provide. So let’s go to the deep, deep past, revealed wonderfully by the Burgess Shale. Here we shall find the NIGHTMARE SHRIMP.
One of the problems with studying the very earliest phase of animal life — we’re talking half a billion years at this point — is that it’s squishy, and squishy is not of much benefit when it comes to preserving fossils. Thanks to a fluke of geology, the conditions that produced the Burgess Shale were also capable of preserving soft tissue, giving palaeontologists a rare chance to look into what the seas looked like during the first days of the animal kingdom.
They looked extremely weird. The fauna found in the Burgess Shale was almost obnoxiously uncategorisable. One famous example is the worm Hallucigenia, which so confused everyone involved that it was reconstructed upside-down for the better part of a decade. Another is Opabinia, which looks sort of like a five-eyed miniature vacuum cleaner. I promise I am not making this up.
Anyway, all these critters were apparently food for the ocean’s first proper predator.
With good eyes set on flexible stalks and a surprising turn of speed, Anomalocaris canadensis cruised the Pre-Cambrian seas in death-shrimp mode. It was a full meter long, dwarfing most of its companions in the Burgess Shale. It was also delightfully strange-looking. It is so odd, in fact, that when it was discovered its various body parts were assigned to several different animals.
A. canadensis would be higher on this list if we could be sure of what it actually ate. Long-held to be a trilobite-hunter, recent studies have shown it would probably have had to restrict itself to soft-bodied prey due to relatively flimsy mouthparts, and therefore could only have actually eaten a trilobite just after a moult. But it’s much more fun to imagine this guy roaming the seafloor chomping down on everything, so that’s what we’ll do.
Disclaimer: an old friend of mine is a paleontologist who specializes in the Burgess Shale fossils. I did not contact him for this story, because I am consumed by envy whenever I so much as think about him.

Cameroceras
Spiky death-squid
Back in the Palaeozoic and Mesozoic, cephalopods were armored critters, much like our modern nautilus. The most famous of them, and one of the most widely known extinct animals ever, is the spiral-shelled ammonite. Since they had hard shells, they’re extremely common in marine strata. They also got surprisingly large. The biggest-known ammonite was two meters across. Imagine that thing trying to swim.
Ammonites weren’t the only armored cephalopod prowling the ancient seas, however. The orthocones were straight-shelled versions, and some of those got really, really big. Like Cameroceras. Current estimates put Cameroceras’s shell at upwards of six meters long. That’s three average-sized men stacked on each others’ shoulders.
Somehow this monster was still able to get about in the Ordovician seas. It’s quite hard to imagine it chasing anything around, so it presumably surprised trilobites etc. at nighttime or dug it out of the mud, but since paleoecology is at least in part about imagination, right now I’m enjoying Cameroceras retracting its head deep into its shell and pretending to be a cave before trying to eat whatever entered. It wouldn’t be quite big enough to swallow the Millennium Falcon, buuuuuuuuut ...

Carcharocles megalodon
The shark that eats planets
Megalodon needs no introduction. The great white shark has a profound hold on popular culture, but its long-gone big sister isn’t far behind. Megalodon made even the most vicious shark in today’s seas look like a toy. Since sharks are mostly soft tissue, they don’t fossilize as well as we’d like, but their teeth do, and Megalodon’s tell a terrifying story.
Megalodon died out only relatively recently. It wasn’t quite contemporaneous with human beings, but its extinction was recent enough that there are plenty of folks willing to tell tall tales of how it might still be swimming somewhere in the depths of the ocean. If it was, probably best not to get anywhere near it — a Megalodon may have had a bite force of up to 10 times the strength of a great white. That’d be a bad day.
What were those huge jaws for? Whales. Apparently, these things liked to swim up from underneath its prey and bite through their chest to reach their internal organs. The ability to kill a whole-ass whale with one bite is honestly horrifying, even if whales in Megalodon’s day were a little smaller than the current batch of great rorquals.

Jaekelopterus rhenaniae
Sea Scorpion
Did you know ‘sea scorpions’ were a thing? Sea scorpions were a thing. Since eurypterids (to give them their proper name) went extinct hundreds of millions of years ago, we don’t have very good comparisons for what these things were like. So let’s get creative. Let’s take a lobster. Despite their ferocious armament, lobsters are relatively placid creatures. They’re not averse to grabbing a fish here or a mollusk there, but they’re not built for hunting. Let’s make the required tweaks.
We need to add eyes. Let’s make them big and sensitive and set for stereoscopic vision, which allows those pincers to be used more effectively to grab prey. Let’s make them better swimmers, too — we’ll add some paddles for agility and short bursts of speed. Let’s make their claws spikier, just for sheer scare value.
Oh and let’s make them 10 feet long and perfectly happy to eat you alive. Now you have a Jaekelopterus. Aren’t you glad they’re dead?

Dunkleosteus terrelli
A, uh, fish-tank
When evolution first came up with bone, it got a little bit carried away. Well, a lot carried away. The era of armored fishes is one of the most fabulously strange in the entire history of the planet. (A personal favorite of mine is Lunapsis, which looks like a fish had a baby with Batman’s utility belt.) With bone-plated heads and upper bodies, these fish probably didn’t swim very well, but who cares? They looked cool as hell, and with that body armor they were well protected against predators.
Which, as it turns out, is the sort of inspiration nature needs to come up with some better predators*. Enter Dunkleosteus, a monster armored fish with a set of jaws which could rip straight through the armor of any other fish slowly swimming through the Devonian ocean. Known to be 20 feet long, it didn’t really have teeth so much as a huge bony beak, which honestly makes the whole contraption even more frightening, like some sort of mobile oceanic guillotine.
*I’m being overly teleological here. Forgive me. Nature, of course, does not ‘come up with’ anything.

Mosasaurus hoffmanni
For whatever reason, the fauna of Cretaceous period got big. Really, really big. On land, we had Tyrannosaurus Rex. In the skies, azhdarchids the size of small aircraft coasted from thermal to thermal. And in the shallow seas, we had another monster: Mosasaurus.
Mosasaurus was essentially an enormous — estimates have it as almost 60 feet long — ocean-going lizard. Its legs were replaced with bladed paddles for maneuverability and it had a powerful tail for direct propulsion. Mosasaurus ate everything it could get in its mouth, which was a) double-hinged for extra capacity and b) already pretty capacious to begin with.
It would have hung around near the surface of the ocean, where there was an abundance of prey. Mosasaurus could have waited for other marine reptiles (such as Archelon, the largest turtle known) to come up to breathe, grab low-flying pterosaurs on fishing expeditions, or simply have picked off the many large fish that swam the Cretaceous seas.

Livyatan Melvilli
Moby-Dick’s even-scarier dad
In 1820, the Essex was lost in the southern Pacific Ocean. The ship had been sent out to hunt for sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus, since you asked), but soon had the tables turned when it was attacked and sunk by a ferocious bull. Of the 20 crew, only eight survived, and the incident went on to inspire a famous book about whales which you may have heard of.
What you probably haven’t heard of is Livyatan. Modern sperm whales are enormous creatures, but very rare boat attacks aside, they’re only really dangerous to their favorite prey, deep-swimming squid. But not so long ago, geographically speaking, there were also a group of ‘macroraptorial’ sperm whales. These didn’t eat squid. Instead, they competed with Megalodon to hunt other great whales.
Livyatan’s teeth are some of the most awe-inspiring fossils in the world. The biggest ones are 12 inches long and look like artillery shells. Estimates have Livyatan as sitting a touch smaller than its modern friends, but those teeth indicate that it would have been significantly more vicious, fully capable of cutting a sperm whale into very bloody chunks.
It’s not clear whether or not Livyatan hunted alone or in packs, like a modern killer whale, but it had the power and size to be able to plausibly compete with Megalodon even solo. The crew of the Essex found out that a bull sperm whale could be a formidable opponent; one suspects Livyatan would have left even fewer survivors.
0 notes