#stop code: kernel security check failure
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to Fix a Kernel Security Check Failure BSOD

In a world wherein get right of entry to to a laptop is more essential than ever, a blue display of death (BSOD) errors on a Windows PC can bring that get right of entry to to a grinding halt. Unfortunately, not unusual BSOD mistakes like an unexpected kernel mode trap or vital method died save you your PC from working until you repair the underlying problem.
Another commonplace BSOD errors which can seem, depending on the circumstances, is a “stop code: kernel security check failure” BSOD. This trouble is generally due to corrupted system documents, however it could additionally be due to faulty hardware or old drivers. If you want to restore a kernel security check failure BSOD, right here’s what you’ll want to do.
What Causes a Kernel Security Check Failure BSOD Error on Windows 10?
Some BSOD errors are tough to research, however with a kernel protection take a look at failure BSOD, you may commonly anticipate that it points to certainly one of two things: a hardware trouble or corrupt (or outdated) system documents.
These troubles can reason your PC to attempt to get entry to the Windows kernel incorrectly in a few way. As the most protected of all gadget services, illegal access to the machine kernel reasons an integrity check to fail, together with your PC crashing and showing a BSOD mistakes like this one.
If your gadget documents are corrupted or outdated, you can commonly resolve the difficulty with the aid of jogging Windows Update. This will set up any to be had gadget updates, which include device motive force updates. You may additionally want to run different renovation gear, consisting of System File Checker (SFC) and chkdsk, the use of Windows PowerShell.
Hardware problems, such as defective machine memory, could also be in the back of the hassle. You may also need to check your hardware, and in case you discover faults, recollect changing it. If that doesn’t work, greater drastic movement (which includes resetting Windows) may be your most effective option.
Check for System and Driver Updates
In many instances, a Windows stop code “kernel safety test failure” message is resulting from an old machine with lacking (and necessary) computer virus fixes. To solve the hassle, you’ll need to test Windows Update for brand new device and driver updates.
To begin, proper-click on the Start menu and pick Settings.
In the Settings menu, pick Update & Security > Windows Update and pick Check for Updates to scan for new updates. If any updates are available, choose Download (or Download and Install) to begin the set up process. After installing any to be had updates, restart your PC to complete the process.
While updated drivers must remedy this difficulty, you could locate that new drivers also are at the back of a kernel safety check failure on Windows 10. You can also want to roll back a motive force in case you see this mistake after you’ve currently up to date your tool drivers, either manually or thru Windows Update.
Run the System File Checker and Chkdsk Tools
If Windows machine documents are compromised or corrupted, Windows will forestall running properly. You can help to fix the problem via checking the integrity of your device files and your difficult force’s report machine the use of the System File Checker (SFC) and chkdsk tools.
To do that, open a new Windows PowerShell window by way of proper-clicking the Start menu and choosing the Windows PowerShell (Admin) alternative.
In the PowerShell window, kind sfc /scannow to run the System File Checker device. You’ll want to look ahead to SFC to complete the test of your machine files and, wherein feasible, repair them.
With the SFC tool complete, type chkdsk C: /f to test your machine force’s record gadget integrity. Windows will ask you to time table this to your next reboot, allowing a boot level experiment of your pressure to complete. Type Y and pick the Enter key to verify this, then restart your PC.
Test Your System Memory
Should the SFC and chkdsk gear provide no decision to a kernel safety take a look at failure on Windows 10, you may want to appearance greater intently on the health of your hardware. For instance, memory problems ought to without delay reason a kernel exception message along with this one.
To take a look at the fitness of your machine reminiscence, you’ll need to check it. You can try this the usage of the built-in Windows Memory Diagnostic tool. Start by way of proper-clicking the Start menu and deciding on Run.
In the Run box, type mdsched.Exe and choose OK.
In the Windows Memory Diagnostic window, Windows will ask you for permission to restart. Select Restart now and test for issues to do that without delay or choose Check for issues the next time I begin my computer to delay this until your next restart.
The Memory Diagnostic device will run a stress take a look at of your gadget reminiscence to ensure it’s working effectively. If any troubles are detected, you’ll need to keep in mind replacing your gadget memory to remedy it.
Fixing a Kernel Security Check Failure BSOD Error
The steps above ought to help you fix a windows 10 kernel error , in addition to avoid them in destiny. You have to take a look at your PC’s overall performance regularly to preserve a watch on any similarly issues, keeping your machine up to date to make certain you have the latest worm and protection fixes, and checking for malware regularly.
A PC is only as exact as the hardware it runs on, but. If you’re seeing BSOD mistakes seem at an alarming charge, it can factor to hardware troubles that you could’t resolve. It can be time to improve your PC with new hardware or keep in mind building or buying a brand new PC rather.
0 notes
Text
Ntfs 3g For Mac Os X

Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X Dmg
Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X 10.12.5
Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X 2010.10.2
NTFS-3G for Mac adds drivers to your OS X installation that allow you to read and write to NTFS-formatted thumb and external hard drives as if you're using a Windows machine. The software comes. On October 5, 2009, NTFS-3G for Mac was brought under the auspices of Tuxera Ltd. And a proprietary version called Tuxera NTFS for Mac was made available. On April 12, 2011, it was announced that Ntfsprogs project was merged with NTFS-3G. NTFS-3g added TRIM support in version 2015.3.14. Follow this process to enable NTFS Write Support on Mac OS X Yosemite for FREE. We install three free applications to achieve that. Here are the links for th.
UPD: There is even better way to solve the same issue with native Mac OS X drivers, but it has its own pros and cons. Read at the end for details. UPD (IMPORTANT): Native driver makes NTFS unusable. Read below for details. Mac OS X Lion (10.7) was released recently, in the end of July 2011. And many users had started to complain that their NTFS disks stopped working.
While OS X can natively read and write FAT-formatted drives, it’s a one-way (read-only) street with NTFS—that is, without a little help from Paragon. NTFS for Mac 14 installs a preference pane.
NTFS-3GDeveloper(s)Tuxera Inc.Stable releaseWritten inCOperating systemUnix-like, HaikuTypeLicenseDual-licensed GNU GPL/Proprietary[citation needed]Websitewww.tuxera.com/community/open-source-ntfs-3g/
NTFS-3G is an open-sourcecross-platform implementation of the Microsoft WindowsNTFS file system with read/write support. NTFS-3G often uses the FUSEfile system interface, so it can run unmodified on many different operating systems. It is runnable on Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenSolaris, illumos, BeOS, QNX, WinCE, Nucleus, VxWorks, Haiku,[1]MorphOS, Minix, macOS[2] and OpenBSD.[3][4] It is licensed under the GNU General Public License. It is a partial fork of ntfsprogs and is under active maintenance and development.
NTFS-3G was introduced by one of the senior Linux NTFS developers, Szabolcs Szakacsits, in July 2006. The first stable version was released on February 21, 2007, as version 1.0. The developers of NTFS-3G later formed a company, Tuxera Inc., to further develop the code. NTFS-3G is now the free 'community edition',[1][failed verification] while Tuxera NTFS is the proprietary version.
Features[edit]
NTFS-3G supports all operations for writing files: files of any size can be created, modified, renamed, moved, or deleted on NTFS partitions. Transparent compression is supported, as well as system-level encryption.[5] Support to modify access control lists and permissions is available.[6] NTFS partitions are mounted using the Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE) interface. NTFS-3G supports hard links, symbolic links, and junctions. With the help of NTFS reparse point plugins, it can be made to read chunk-deduplicated files, system-compressed files, and OneDrive files.[7] NTFS-3G provides complete support and translation of NTFS access control list (ACL) to POSIX ACL permissions. A 'usermap' utility is included to record the mapping from UIDs to Windows NT SIDs.
NTFS-3G supports partial NTFS journaling, so if an unexpected computer failure leaves the file system in an inconsistent state, the volume can be repaired. As of 2009, a volume having an unclean journal file is recovered and mounted by default. The ‘norecover’ mount option can be used to disable this behavior.[8]

Performance[edit]
Benchmarks show that the driver's performance via FUSE is comparable to that of other filesystems' drivers in-kernel,[9] provided that the CPU is powerful enough. On embedded or old systems, the high processor usage can severely limit performance. Tuxera sells optimized versions of the driver that claims to have improved CPU utilization for embedded systems and MacOS.[10]
The slowness of NTFS-3G (and FUSE in general) on embedded systems is attributed to the frequent context switching associated with FUSE calls. Some open-source methods provided to reduce this overhead include:[11]
The underlying FUSE layer has an option called big_writes to use larger blocks when writing. Using a larger block means fewer context switches. This is in fact a solution recommended by Tuxera.[12] A patch is available to use an even larger block.[13]
There is also a Linux kernel option called lazytime to reduce the writes on file access.
Synology Inc. uses a modified NTFS-3G on their NAS systems. It replaces the ntfs-3g inode caching CACHE_NIDATA_SIZE with a different mechanism with unsure benefit. (It also includes an alternative Security Identifier translation for the NAS.)
History[edit]

NTFS-3G forked from the Linux-NTFS project on October 31, 2006.
On February 21, 2007, Szabolcs Szakacsits announced 'the release of the first open-source, freely available, stable read/write NTFS driver, NTFS-3G 1.0.'
On October 5, 2009, NTFS-3G for Mac was brought under the auspices of Tuxera Ltd. and a proprietary version called Tuxera NTFS for Mac was made available.[14]
On April 12, 2011, it was announced that Ntfsprogs project was merged with NTFS-3G.[15]
NTFS-3g added TRIM support in version 2015.3.14.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
^ abc'STABLE Version 2017.3.23 (March 28, 2017)'. Tuxera. Tuxera. 2017-03-23. Retrieved 2017-03-23.
^NTFS-3G for Mac OS X ('Catacombae')
^'OpenBSD adds fuse(4) support for adding file systems in userland'. OpenBSD Journal. 2013-11-08. Retrieved 2013-11-08.
^'ntfs_3g-2014.2.15 – FUSE NTFS driver with read/write support'. OpenBSD ports. 2014-01-05. Retrieved 2015-02-14.
^NTFS-3G FAQ
^NTFS-3G: NTFS Driver with Ownership and permissions
^André, Jean-Pierre (March 1, 2019). 'NTFS-3G: Junction Points, Symbolic Links and Reparse Points'. jp-andre.pagesperso-orange.fr.
^'NTFS-3G 2009.2.1 changelog'. Archived from the original on 2009-03-23. Retrieved 2012-09-10.
^Comparing NTFS-3G to ZFS-FUSE for FUSE Performance
^Performance at Tuxera
^Gothe, Markus. 'On Linux NTFS Performance'. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
^'NTFS-3G Questions'. Tuxera. Workaround: using the mount option “big_writes” generally reduces the CPU usage, provided the software requesting the writes supports big blocks.
^Wang, M. 'linux - Disadvantages of ntfs-3g `big_writes` mount option'. Unix & Linux Stack Exchange. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
^NTFS-3G for Mac OS X is now Tuxera NTFS for Mac
^Release: NTFS-3G + NTFSPROGS 2011.4.12
External links[edit]
Retrieved from 'https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=NTFS-3G&oldid=958820922'
3 Free NTFS Solution
UPD 21.08.2011: There is even better way to solve the same issue with native Mac OS X drivers, but it has its own pros and cons. Read at the end for details.
UPD 12.09.2011 (IMPORTANT): Native driver makes NTFS unusable. Read below for details.
Mac OS X Lion (10.7) was released recently, in the end of July 2011. And many users had started to complain that their NTFS disks stopped working. And the much worse problem is that “old” solutions do not work well.
Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X Dmg
But after one or two weeks of researching of this issue, I’ve managed to make NTFS work in Mac OS X Lion (10.7). The key here is a proper combination of software versions.
So I will shortly describe the usual choices for external data storages, and what problems arises with each of them. And later I will show how you can get the most universal way — NTFS — to work where it does not work by default, with links and pictures.
Data Storages
The only reason to worry about this problem is an ability to access external storage drives. Even if these are your own drives and you can select a filesystem to use, that choice is not easy.
There are few possible choices for large (~1TB) file storages, but each has very unpleasant limitations and issues:
* HFS+/HFSX (or “Mac OS Extended”/”Mac OS Extended (case sensitive)”) — okay with big volumes and big files, but works natively under Mac OS X and Linuxes only. Windows need third-party software, which is either free file browser/extractor or paid low-level drivers.
* FAT32 work in each and every OS now, but has limitation for file size up to 4GB (so, you cannot store DVD image, which is usually 4.5+ GB).
* FAT64 (exFAT) is a new solution, but it works natively only in Mac OS X and Windows 7. Older Windows systems (Vista, XP) require Service Packs and updates to support exFAT. Linuxes do not support exFAT yet at all. More on that, it has only one file table, so if this only place will be corrupted on write, I will get all the data lost.
* NTFS. Okay with big files an bug volumes. Works natively in all Windows systems. Works fluently in all Linux systems. Has native read-only support in Mac OS X. But has not write support under Mac OS X.
As you can see, in terms of cross-compativility, NTFS is the best choice: it works almost everywhere, and with no limitations. The only issue is write mode in Mac OS X.
Taking into account that you probably have a lot of friends with NTFS volumes, who can visit you and bring you something interesting there, you actually have no choice except as try to make NTFS working.
So, let’s do it.
Paid NTFS Solutions
But first, in case you want to make your own research, or you are looking for a solution that just works out of the box, and you are ready to pay for it, you can give a try to Paragon NTFS for Max OS X 9.0 for $19.99 (5-days trial). That is much cheaper than Tuxera NTFS for Mac for $36.02 (with 15-days trial).
The former one definitely works �� I’ve tried it in trial. Just install and get everything ready: both read and write modes, auto-mount, and also NTFS formatting in Disk Utility, disk checking, etc.
I haven’t tested the latter one, so you can leave a comment here about your experience with Tuxera paid solution.
Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X 10.12.5
Free NTFS Solution
This free solution requires some efforts. Not so much, of course. Well, if you are going to make your own research, it can be lots of efforts, since the situation with NTFS-3G is not very clear now.
But if you are just about a ready, copy-n-install solution, it will be easy, and requires only these two or three steps:
* MacFUSE 64-bit.
* NTFS-3G stable.
* “15 seconds” error work-around (optional).
MacFUSE 64-bit
First, you need MacFUSE with 64 bit support. That is the main problem with Mac OS X Lion — it uses 64-bit kernel, and all previous version of Mac OS X used 32-bit one. So, old MacFUSE binaries won’t work anymore.
You can get Tuxera MacFUSE 2.2 image for free (could not find a page with it, just a download links) or try to compile OSXFUSE from sources. I’ve used the former one.
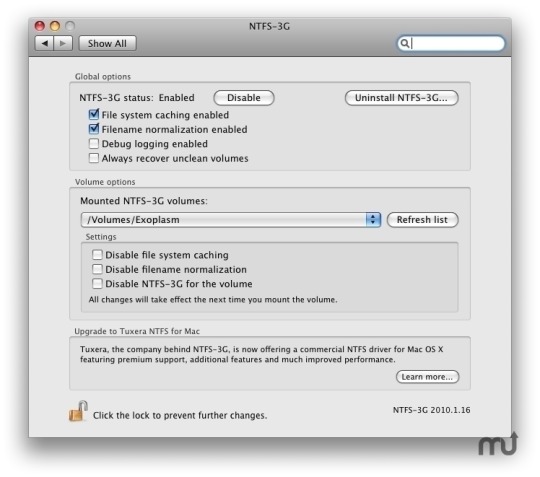
You can see MacFUSE preferences in “System Preferences”. Well, actually these are not preferences, but only “update” and “uninstall” actions, and current version info:
NTFS-3G stable
Second, you will need working copy of NTFS-3G. Long story short, NTFS-3G is either already dead or is going to die. There is its ancestor: Tuxera NTFS for Mac (paid).
But we are going to use old version of NTFS-3G — the one from 2010. I’ve got one from here. But you can try googling for it, or browse here for this exact version (not 2011 — I’m not sure they work).
I also tried to install later version from MacPorts, but it does not work too: mounts something that stills unreadable. That is in addition to an error in installation process (“mv” does not see the libntfs-3g file or so).
Now, when you have installed two binary packages, you can restart Mac OS X and try to attach the drive. It should work.
NTFS-3G preferences pane looks populated and interesting:
“15 seconds” error work-around
But it will show you the error message saying that there were not signal in 15 seconds:
This is not a big problem, because everything works fine. Only annoying message box is a problem.
So the third, optional step is to address this issue. You can follow this link: https://gist.github.com/1100318 (see first and the only comment under the code). You just download this attached C file, run “gcc” command line from the comment, and replaces the “fuse_wait” binary as said there. Yes, you will need “gcc” here.
And voila! Now you have working NTFS filesystem for free with no “15 seconds” error message. Profit!
Problems
Nevertheless, Mac OS X is a Unix-based system. And Unix-based system is a big problem when they work as desktop OS (earlier I thought that on Linux-based system because of community-driven and crowd-based development concept). This solution has some problems too. Though they are not about the solution itself, but about the components used.
The most important problem now is the speed: with this NTFS-3G on MacBook Air (4GB, i7 CPU) write speed for USB 2.0 drive is about 3.3 MB/s. Just to compare, the same drive in the same port, but with exFAT/FAT64 partition can write with ~38 MB/s (or fast enough to make exact estimation; will try larger files later).
Also, immediately following the mount of a drive, there is a line in system log with an error message saying:
Ntfs-3g For Mac Os X 2010.10.2
8/21/1112:48:43.000AM kernel:NTFS-fs error(device/dev/disk1s1,pid4859):ntfs_system_inodes_get():$LogFile isnotclean.Mounting read-only.Mount inWindows.
All the “cons” can be solved by installing NTFS-3G and keeping it disabled all the time, except when you need to format new volume, or to mount a problematic volume. Actually, it is better to enable NTFS-3G, mount it with NTFS-3G, then unmount, disable NTFS-3G, and mount it with native drivers; or use “ntfsfix” if you are not afraid of command line after all these hacks ;-)
IMPORTANT UPD 12.09.2011: Please read comments below: people say that this driver makes NTFS filesystem corrupted and unusable.
I had the same experience: my NTFS volume become only partially readable in Mac OS X, and completely unusable in Windows. More on that, when I tried to attach the drive, Windows kernel started to use 100% CPU, and did not stop to do so even when the drive were detached. Drive letter never appeared.
Luckily for me, I had two backups of the whole volume (I do so when experimenting with new drives, since I once lost my whole photo archive due to burned out new drive). To solve the whole problem of NTFS@Mac, I’ve finally bought Paragon NTFS for Mac.

0 notes
Text
Stefan Hajnoczi: Determining why a Linux syscall failed
One is often left wondering what caused an errno value when a system call fails. Figuring out the reason can be tricky because a single errno value can have multiple causes. Applications get an errno integer and no additional information about what went wrong in the kernel.
There are several ways to determine the reason for a system call failure (from easiest to most involved):
Check the system call's man page for the meaning of the errno value. Sometimes this is enough to explain the failure.
Check the kernel log using dmesg(1). If something went seriously wrong (like a hardware error) then there may be a detailed error information. It may help to increase the kernel log level.
Read the kernel source code to understand various error code paths and identify the most relevant one.
Use the function graph tracer to see which code path was taken.
Add printk() calls, recompile the kernel (module), and rerun to see the output.
Reading the man page and checking dmesg(1) are fairly easy for application developers and do not require knowledge of kernel internals. If this does not produce an answer then it is necessary to look closely at the kernel source code to understand a system call's error code paths.
This post discusses the function graph tracer and how it can be used to identify system call failures without recompiling the kernel. This is useful because running a custom kernel may not be possible (e.g. due to security or reliability concerns) and recompiling the kernel is slow.
An example
In order to explore some debugging techniques let's take the io_uring_setup(2) system call as an example. It is failing with ENOMEM but the system is not under memory pressure, so ENOMEM is not expected.
The io_uring_setup(2) source code (fs/io_uring.c) contains many ENOMEM locations but it is not possible to conclusively identify which one is failing. The next step is to determine which code path is taken using dynamic instrumentation.
The function graph tracer
The Linux function graph tracer records kernel function entries and returns so that function call relationships are made apparent. The io_uring_setup(2) system call is failing with ENOMEM but it is unclear at which point in the system call this happens. It is possible to find the answer by studying the function call graph produced by the tracer and following along in the Linux source code.
Since io_uring_setup(2) is a system call it's not an ordinary C function definition and has a special symbol name in the kernel ELF file. It is possible to look up the (architecture-specific) symbol for the currently running kernel:
# grep io_uring_setup /proc/kallsyms ... ffffffffbd357130 T __x64_sys_io_uring_setup
Let's trace all __x64_sys_io_uring_setup calls:
# cd /sys/kernel/debug/tracing # echo '__x64_sys_io_uring_setup' > set_graph_function # echo 'function_graph' >current_tracer # cat trace_pipe >/tmp/trace.log ...now run the application in another terminal... ^C
The trace contains many successful io_uring_setup(2) calls that look like this:
1) | __x64_sys_io_uring_setup() { 1) | io_uring_setup() { 1) | capable() { 1) | ns_capable_common() { 1) | security_capable() { 1) 0.199 us | cap_capable(); 1) 7.095 us | } 1) 7.594 us | } 1) 8.059 us | } 1) | kmem_cache_alloc_trace() { 1) | _cond_resched() { 1) 0.244 us | rcu_all_qs(); 1) 0.708 us | } 1) 0.208 us | should_failslab(); 1) 0.220 us | memcg_kmem_put_cache(); 1) 2.201 us | } ... 1) | fd_install() { 1) 0.223 us | __fd_install(); 1) 0.643 us | } 1) ! 190.396 us | } 1) ! 216.236 us | }
Although the goal is to understand system call failures, looking at a successful invocation can be useful too. Failed calls in trace output can be identified on the basis that they differ from successful calls. This knowledge can be valuable when searching through large trace files. A failed io_uring_setup(2) call aborts early and does not invoke fd_install(). Now it is possible to find a failed call amongst all the io_uring_setup(2) calls:
2) | __x64_sys_io_uring_setup() { 2) | io_uring_setup() { 2) | capable() { 2) | ns_capable_common() { 2) | security_capable() { 2) 0.236 us | cap_capable(); 2) 0.872 us | } 2) 1.419 us | } 2) 1.951 us | } 2) 0.419 us | free_uid(); 2) 3.389 us | } 2) + 48.769 us | }
The fs/io_uring.c code shows the likely error code paths:
account_mem = !capable(CAP_IPC_LOCK); if (account_mem) { ret = io_account_mem(user, ring_pages(p->sq_entries, p->cq_entries)); if (ret) { free_uid(user); return ret; } } ctx = io_ring_ctx_alloc(p); if (!ctx) { if (account_mem) io_unaccount_mem(user, ring_pages(p->sq_entries, p->cq_entries)); free_uid(user); return -ENOMEM; }
But is there enough information in the trace to determine which of these return statements is executed? The trace shows free_uid() so we can be confident that both these code paths are valid candidates. By looking back at the success code path we can use the kmem_cache_alloc_trace() as a landmark. It is called by io_ring_ctx_alloc() so we should see kmem_cache_alloc_trace() in the trace before free_uid() if the second return statement is taken. Since it does not appear in the trace output we conclude that the first return statement is being taken!
When trace output is inconclusive
Function graph tracer output only shows functions in the ELF file. When the compiler inlines code, no entry or return is recorded in the function graph trace. This can make it hard to identify the exact return statement taken in a long function. Functions containing few function calls and many conditional branches are also difficult to analyze from just a function graph trace.
We can enhance our understanding of the trace by adding dynamic probes that record function arguments, local variables, and/or return values via perf-probe(2). By knowing these values we can make inferences about the code path being taken.
If this is not enough to infer which code path is being taken, detailed code coverage information is necessary.
One way to approximate code coverage is using a sampling CPU profiler, like perf(1), and letting it run under load for some time to gather statistics on which code paths are executed frequently. This is not as precise as code coverage tools, which record each branch encountered in a program, but it can be enough to observe code paths in functions that are not amenable to the function graph tracer due to the low number of function calls.
This is done as follows:
Run the system call in question in a tight loop so the CPU is spending a significant amount of time in the code path you wish to observe.
Start perf record -a and let it run for 30 seconds.
Stop perf-record(1) and run perf-report(1) to view the annotated source code of the function in question.
The error code path should have a significant number of profiler samples and it should be prominent in the pref-report(1) annotated output.
Conclusion
Determining the cause for a system call failure can be hard work. The function graph tracer is helpful in shedding light on the code paths being taken by the kernel. Additional debugging is possible using perf-probe(2) and the sampling profiler, so that in most cases it's not necessary to recompile the kernel with printk() just to learn why a system call is failing.
from http://blog.vmsplice.net/2019/08/determining-why-linux-syscall-failed.html
0 notes
Text
Identify security hotspots in your apps and STOP hackers from exploiting you
The story behind Equifax: one of their most exposed web application was using an unpatched version of Apache Struts 2. This lead to a critical security breach which was exploited by hackers who didn't even need to be authenticated and stole millions of Equifax's customer data. The breach made headlines and caused a myriad of issues for both Equifax and Apache. The most important lesson learned is we need to be more proactive and know our vulnerabilities before it's too late. This article explains how CAST Highlight can help you detect and mitigate vulnerabilities before hackers find them, thanks to 2 important features: automated framework discovery feature and continuous CVE database lookup.
What is a CVE?
A CVE (Common Vulnerabilities & Enumerations) is “a weakness in the computational logic (e.g., code) found in software and hardware components that, when exploited, results in a negative impact to confidentiality, integrity, or availability. Mitigation of the vulnerabilities in this context typically involves coding changes, but could also include specification changes or even specification deprecations (e.g., removal of affected protocols or functionality in their entirety)” (source: NIST).
In other words, a CVE is a known/documented issue or flaw in a specific version of a software component. Whether it is commercial or open source, your application is at risk from a security standpoint if it's in your production environment.
Launched by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and regularly updated by the MITRE, the National Vulnerability Database references around 100K vulnerabilities distributed across 2300 software products. Some of them are very famous like Linux Kernel with the highest number of vulnerabilities. Android with the highest number of CVEs found in 2017, others are less known by a larger audience but maybe used somewhere in your applications. For instance, Yassl had issues, it was embedded into some versions of the well-known MySQL database and exposed software to DoS attacks.
The amazing thing about this CVE database is that the information is structured the same way across all entries and allows us to categorize the vulnerabilities:
A unique CVE Idendifier and status – E.g. CVE-2017-5638
Product and Vendor – E.g. Apache / Struts
Version(s) where the issue is found – E.g. 2.3.5.*, 2.5.3.*
The kind of issue (mapping with CWE classification) – E.g. CWE-20 (Input Validation)
a CIA (confidentiality, integrity, availability) impact categorization – E.g. C:High, I:High, A:High
a characterization of what is needed to exploit the vulnerability – Eg: Attack Vector (Network), Complexity (Low), Privileges (None), User Interaction (None)
References to advisories, solutions and tools: E.g. Mitigation provided by Apache
The organization having referenced the CVE (e.g. US-CERT/NIST), date, last revision, etc.
A global score that helps InfoSec and development teams prioritize actions (e.g. 10 out of 10 / CRITICAL)
CVE detection and reporting in CAST Highlight
CAST Highlight detects hundreds of frameworks and third-party components and (most of the time) the version used in the application. The CVE feature in Highlight is all about crossing this information with the vulnerability database detailed above. Highlight queries the CVE database to verify if a detected framework and version (e.g. apache.struts 1.3) has known security issues and helps the development teams to quantify and prioritize mitigations within a given application. The CVE count is distributed across four levels of severity: critical, high, medium and low. You're just one click away of knowing which components you should quickly upgrade to close doors to black hats.
At the framework level, users can also quickly see if CVEs have been found, the precise version number and the severity levels. A simple click reveals a quick overview of the issue. From here, you can learn more about the issue itself, impacted versions, communication from the vendor and/or security expert communities, and finally decide whether this issue is relevant or not in the context of your application. As seen for Equifax and their unpatched version of Apache Struts, most of the time a simple upgrade to a safe version would be enough to mitigate the risk and secure the application.
And because we absolutely want application insights the most reliable for your organization, users can also report a false positive if they consider our framework search algorithm didn't match with a CVE item. This request will be analyzed by the product team and considered to enrich the search algorithm.
How to use the feature: Put InfoSec insights and CVEs into your app portfolio context
Now you're able to detect frameworks' vulnerabilities your applications may embed, that's the perfect moment to take a step back and consider what probably most of InfoSec teams lack nowadays where they sometimes miss the point: what is the business context of the application? Is it important enough to the business to justify the additional and unexpected cost of a framework migration? Is this specific application even exposed to attackers over the standard networks?
We don't want Highlight to be a security pure player but it has nice arguments to catch the attention of your DevSecOps teams though. Highlight builds software analytics at the portfolio level and is able to conciliate both and technical worlds with organizational indicators like the Business Impact. This metric, which is derived from survey questions on the importance of an application in the business context (e.g. define the level of impact of an application failure on your company's image: very high, high, medium, low), could definitely help you prioritize the most urgent upgrades you'll have to perform. Highlight also gathers valuable information through surveys sent to application owners, to let IT managers arbitrate on the opportunity to fix all the leaks (you would be surprise by the number) or rationalize the effort.
Would you personally take the decision to upgrade (and re-test) an application which can be used only in your walls and without any sensitive data in it? InfoSec ayatollahs are not going to be pleased but the organization should be able to rationalize their security effort.
Security is a speed race!
Securing and protecting your software against hackers is a speed race and the only way you will avoid a malicious attack is to be aware of the possible breach at the earliest. That's exactly where the planets align perfectly with the other features of CAST Highlight. In order to ensure your application is not exposed too long (or ideally not at all) to vulnerabilities, you need to frequently control your software at the first stages in the build chain – even before it's shipped in production.
In the recent version of Highlight, we introduced our command line which enables code scan and result upload automation. In other words, it provides you the appropriate tooling to automatically verify the integrity of the software produced by your CI/CD chain, without any human effort. This way, you'll be able to anticipate framework patches and upgrades even before your application is publicly released (and exposed to hackers).
More importantly, CAST Highlight's CVE insights look at the past (i.e. old CVEs your third-party libraries might still have) and are always up to date at the same time. Indeed, the feature check your application against issues from 2002 to today, and is refreshed with new (or newly updated known issues) every 12 hours.
The post Identify security hotspots in your apps and STOP hackers from exploiting you appeared first on CAST Highlight.
0 notes
Text
Debian 8.6 update release
The Debian project is pleased to announce the sixth update of its stable distribution Debian 8 (codename jessie). This update mainly adds corrections for security problems to the stable release, along with a few adjustments for serious problems. Security advisories were already published separately and are referenced where available.
Please note that this update does not constitute a new version of Debian 8 but only updates some of the packages included. There is no need to throw away old jessie CDs or DVDs but only to update via an up-to-date Debian mirror after an installation, to cause any out of date packages to be updated.
Those who frequently install updates from security.debian.org won't have to update many packages and most updates from security.debian.org are included in this update.
New installation media and CD and DVD images containing updated packages will be available soon at the regular locations.
Upgrading to this revision online is usually done by pointing the aptitude (or apt) package tool (see the sources.list(5) manual page) to one of Debian's many FTP or HTTP mirrors. A comprehensive list of mirrors is available at:
https://www.debian.org/mirror/list
Miscellaneous Bug Fixes
This stable update adds a few important corrections to the following packages:
Package
Reason
adblock-plus
New upstream release, compatible with firefox-esr
apache2
Fix race condition and logical error in init script; remove links to manpages.debian.org in default index.html; mod_socache_memcache: Increase idle timeout to 15s to allow keep-alive connections; mod_proxy_fcgi: Fix wrong behaviour with 304 responses; correct systemd-sysv-generator behaviour; mod_proxy_html: Add missing config file mods-available/proxy_html.conf
audiofile
Fix buffer overflow when changing both sample format and number of channels [CVE-2015-7747]
automake-1.14
Avoid insecure use of /tmp/ in install-sh
backintime
Add missing dependency on python-dbus
backuppc
Fix regressions from samba update to 4.2
base-files
Update for the point release
biber
Fix breakage triggered by point release update of perl
cacti
Fix sql injection in tree.php [CVE-2016-3172] and graph_view.php [CVE-2016-3659]; fix authentication bypass [CVE-2016-2313]
ccache
Upstream bug-fix release
clamav
Don't fail if AllowSupplementaryGroups is still set in the configuration file
cmake
Fix FindOpenSSL module to detect OpenSSL 1.0.1t
conkeror
Support Firefox 44 and later
debian-edu-config
Move from Iceweasel to Firefox ESR; adjust ldap-tools/ldap-debian-edu-install to be compliant with systemd now that unit samba.service is masked; dhclient-exit-hooks.d/hostname: adjust for the case of a dedicated LTSP server; adjust cf.krb5client to ensure that cfengine runs are idempotent; move code to cleanup /usr/share/pam-configs/krb5 diversion from postinst to preinst to ease upgrades from old wheezy installations; don't purge libnss-mdns as cups now needs mdns for automatic printer detection
debian-edu-doc
Update Debian Edu jessie and wheezy manuals from the wiki
debian-installer
Rebuild against proposed-updates
debian-installer-netboot-images
Rebuild for the point release
debian-security-support
Update included support data; add support for marking packages as losing support at a future date
dietlibc
Fix insecure default PATH
dwarfutils
Security fixes [CVE-2015-8538 CVE-2015-8750 CVE-2016-2050 CVE-2016-2091 CVE-2016-5034 CVE-2016-5036 CVE-2016-5038 CVE-2016-5039 CVE-2016-5042]
e2fsprogs
Disable prompts for time skew which is fudged in e2fsck; fix potential corruption of Hurd file systems by e2fsck, pointer bugs that could cause crashes in e2fsck and resize2fs
exim4
Fix cutthrough bug with body lines having a single dot; fix crash on exim -be '${if crypteq{xxx}{\$aaa}{yes}{no}}'; improve NEWS file; backport missing upstream patch to actually make $initial_cwd expansion work
file
Fix buffer over-write in finfo_open with malformed magic file [CVE-2015-8865]
firegestures
New upstream release, compatible with firefox-esr
flashplugin-nonfree
Update-flashplugin-nonfree: Delete old get-upstream-version.pl from cache
fusionforge
Remove dependency on Mediawiki plugin from fusionforge-full metapackage
gdcm
Fix integer overflow [CVE-2015-8396] and denial of service [CVE-2015-8397]
glibc
Fix assertion failure with unconnectable name server addresses (regression introduced by CVE-2015-7547 fix); fix *context functions on s390x; fix a buffer overflow in the glob function [CVE-2016-1234], a stack overflow in nss_dns_getnetbyname_r [CVE-2016-3075], a stack overflow in getaddrinfo function [CVE-2016-3706], a stack overflow in Sun RPC clntudp_call() [CVE-2016-4429]; update from upstream stable branch; fix open and openat functions with O_TMPFILE; fix backtrace hang on armel/armhf, possibly causing a minor denial of service vulnerability [CVE-2016-6323]; fix mtr on systems using only IPv6 nameservers
gnome-maps
New upstream release; use the Mapbox tile server, instead of the no longer supported MapQuest server
gnome-sudoku
Don't generate the same puzzle sequence every time
gnupg
gpgv: Tweak default options for extra security; g10: Fix checking key for signature validation
gnupg2
gpgv: Tweak default options for extra security; g10: Fix checking key for signature validation
greasemonkey
New upstream release, compatible with firefox-esr
intel-microcode
New upstream release
jakarta-jmeter
Really install the templates; fix an error with libxstream-java >= 1.4.9 when loading the templates
javatools
Return correct architecture string for ppc64el in java-arch.sh
kamailio
Fix libssl version check
libbusiness-creditcard-perl
Adjust to changes in credit card ranges and processing of various companies
libcss-dom-perl
Work around Encode changes included in perl and libencode-perl stable updates
libdatetime-timezone-perl
Update included data to 2016e; new upstream release
libdevel-declare-perl
Fix breakage caused by change in perl stable update
libnet-ssleay-perl
Fix build failure with openssl 1.0.1t-1+deb8u1
libquota-perl
Adapt platform detection to work with Linux 4.x
libtool
Fix multi-arch co-installability [amd64 i386]
libxml2
Fix a problem unparsing URIs without a host part like qemu:///system; this unbreaks libvirt, libsys-virt-perl and others
linux
New upstream stable release
lxc
Make sure stretch/sid containers have an init system, after init 1.34 dropped the 'Essential: yes' header
mariadb-10.0
New upstream release, including security fix [CVE-2016-6662]
mozilla-noscript
New upstream release, compatible with firefox-esr
nullmailer
Do not keep relayhost data in debconf database longer than strictly needed
open-iscsi
Init script: wait a bit after iSCSI devices have appeared, working around a race condition in which dependent devices can appear only after the initial udev settle has returned; open-iscsi-udeb: update initramfs after copying configuration to target system
openssl
Fix length check for CRLs; enable asm optimisation for s390x
ovirt-guest-agent
Install ovirt-guest-agent.py executable; change owner of log directory to ovirtagent in postinst
piuparts
Fix build failure (don't test the current Debian release status, tracking that is distro-info-data's problem)
policykit-1
Several bug-fixes: fix heap corruption [CVE-2015-3255], local authenticated denial of service [CVE-2015-4625] and issue with invalid object paths in RegisterAuthenticationAgent [CVE-2015-3218]
publicsuffix
New upstream release
pypdf2
Fix infinite loop in readObject() function
python-django
Bug-fix update to 1.7.11
python2.7
Address StartTLS stripping attack in smtplib [CVE-2016-0772], integer overflow in zipimporter [CVE-2016-5636], HTTP header injection [CVE-2016-5699]
quassel
Fix remote DoS in quassel core with invalid handshake data [CVE-2016-4414]
ruby-eventmachine
Fix remotely triggerable crash due to FD handling
ruby2.1
dl::dlopen should not open a library with tainted library name in safe mode [CVE-2009-5147]; Fiddle handles should not call functions with tainted function names [CVE-2015-7551]
sendmail
Do not abort with an assertion if the connection to an LDAP server is lost; ensure sendmail {client_port} is set correctly on little endian machines
sqlite3
Fix tempdir selection vulnerability [CVE-2016-6153], segfault following heavy SAVEPOINT usage
systemd
Use the right timeout for stop processes we fork; don't reset log level to NOTICE if we get quiet on the kernel cmdline; fix prepare priority queue comparison function in sd-event; update links to kernel.org cgroup documentation; don't start console-getty.service when /dev/console is missing; order systemd-user-sessions.service after nss-user-lookup.target and network.target
tabmixplus
New upstream release, compatible with firefox-esr
tcpreplay
Handle frames of 65535 octets size, add a size check [CVE-2016-6160]
tor
Update the set of authority directory servers
tzdata
New upstream release; update to 2016e
unbound
Init script fixes: add pidfile magic comment; call start-stop-daemon with --retry for 'stop' action
util-vserver
Rebuild against dietlibc 0.33~cvs20120325-6+deb8u1, fixing insecure default PATH
vorbis-tools
Fix large alloca on bad AIFF input to oggenc [CVE-2015-6749], Validate count of channels in the header [CVE-2014-9638 CVE-2014-9639], fix segmentation fault in vcut
vtk
Rebuild to fix Java paths [ppc64el]
wget
By default, on server redirects to a FTP resource, use the original URL to get the local file name [CVE-2016-4971]
wpa
Security updates relating to invalid characters [CVE-2016-4476, CVE-2016-4477]
yaws
Fix HTTP_PROXY cgi env injection [CVE-2016-1000108]
zabbix
Fix mysql.size shell command injection in zabbix-agent [CVE-2016-4338]
The mariadb-10.0 package failed to build on the powerpc architecture, but has been included in the point release to allow quicker release of the fix for CVE-2016-6662, which had not been disclosed at the time of the upload. If a fix for the build failure becomes available before the next mariadb-10.0 DSA, an updated package may be released via jessie-updates.
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Linux Debian
Support Firefox 44 and later
debian-edu-config
Move from Iceweasel to Firefox ESR; adjust ldap-tools/ldap-debian-edu-install to be compliant with systemd now that unit samba.service is masked; dhclient-exit-hooks.d/hostname: adjust for the case of a dedicated LTSP server; adjust cf.krb5client to ensure that cfengine runs are idempotent; move code to cleanup /usr/share/pam-configs/krb5 diversion from postinst to preinst to ease upgrades from old wheezy installations; don't purge libnss-mdns as cups now needs mdns for automatic printer detection
debian-edu-doc
Update Debian Edu jessie and wheezy manuals from the wiki
debian-installer
Rebuild against proposed-updates
debian-installer-netboot-images
Rebuild for the point release
debian-security-support
Update included support data; add support for marking packages as losing support at a future date
dietlibc
Fix insecure default PATH
dwarfutils
Security fixes [CVE-2015-8538 CVE-2015-8750 CVE-2016-2050 CVE-2016-2091 CVE-2016-5034 CVE-2016-5036 CVE-2016-5038 CVE-2016-5039 CVE-2016-5042]
e2fsprogs
Disable prompts for time skew which is fudged in e2fsck; fix potential corruption of Hurd file systems by e2fsck, pointer bugs that could cause crashes in e2fsck and resize2fs
exim4
Fix cutthrough bug with body lines having a single dot; fix crash on exim -be '${if crypteq{xxx}{\$aaa}{yes}{no}}'; improve NEWS file; backport missing upstream patch to actually make $initial_cwd expansion work
file
Fix buffer over-write in finfo_open with malformed magic file [CVE-2015-8865]
firegestures
New upstream release, compatible with firefox-esr
flashplugin-nonfree
Update-flashplugin-nonfree: Delete old get-upstream-version.pl from cache
fusionforge
Remove dependency on Mediawiki plugin from fusionforge-full metapackage
gdcm
Fix integer overflow [CVE-2015-8396] and denial of service [CVE-2015-8397]
glibc
Fix assertion failure with unconnectable name server addresses (regression introduced by CVE-2015-7547 fix); fix *context functions on s390x; fix a buffer overflow in the glob function [CVE-2016-1234], a stack overflow in nss_dns_getnetbyname_r [CVE-2016-3075], a stack overflow in getaddrinfo function [CVE-2016-3706], a stack overflow in Sun RPC clntudp_call() [CVE-2016-4429]; update from upstream stable branch; fix open and openat functions with O_TMPFILE; fix backtrace hang on armel/armhf, possibly causing a minor denial of service vulnerability [CVE-2016-6323]; fix mtr on systems using only IPv6 nameservers
gnome-maps
New upstream release; use the Mapbox tile server, instead of the no longer supported MapQuest server
gnome-sudoku
Don't generate the same puzzle sequence every time
gnupg
gpgv: Tweak default options for extra security; g10: Fix checking key for signature validation
gnupg2
gpgv: Tweak default options for extra security; g10: Fix checking key for signature validation
greasemonkey
New upstream release, compatible with firefox-esr
intel-microcode
New upstream release
jakarta-jmeter
Really install the templates; fix an error with libxstream-java >= 1.4.9 when loading the templates
javatools
Return correct architecture string for ppc64el in java-arch.sh
kamailio
Fix libssl version check
libbusiness-creditcard-perl
Adjust to changes in credit card ranges and processing of various companies
libcss-dom-perl
Work around Encode changes included in perl and libencode-perl stable updates
libdatetime-timezone-perl
Update included data to 2016e; new upstream release
libdevel-declare-perl
Fix breakage caused by change in perl stable update
libnet-ssleay-perl
Fix build failure with openssl 1.0.1t-1+deb8u1
libquota-perl
Adapt platform detection to work with Linux 4.x
libtool
Fix multi-arch co-installability [amd64 i386]
libxml2
Fix a problem unparsing URIs without a host part like qemu:///system; this unbreaks libvirt, libsys-virt-perl and others
linux
New upstream stable release
lxc
Make sure stretch/sid containers have an init system, after init 1.34 dropped the 'Essential: yes' header
mariadb-10.0
New upstream release, including security fix [CVE-2016-6662]
mozilla-noscript
New upstream release, compatible with firefox-esr
nullmailer
Do not keep relayhost data in debconf database longer than strictly needed
open-iscsi
Init script: wait a bit after iSCSI devices have appeared, working around a race condition in which dependent devices can appear only after the initial udev settle has returned; open-iscsi-udeb: update initramfs after copying configuration to target system
openssl
Fix length check for CRLs; enable asm optimisation for s390x
ovirt-guest-agent
Install ovirt-guest-agent.py executable; change owner of log directory to ovirtagent in postinst
piuparts
Fix build failure (don't test the current Debian release status, tracking that is distro-info-data's problem)
policykit-1
Several bug-fixes: fix heap corruption [CVE-2015-3255], local authenticated denial of service [CVE-2015-4625] and issue with invalid object paths in RegisterAuthenticationAgent [CVE-2015-3218]
publicsuffix
New upstream release
pypdf2
Fix infinite loop in readObject() function
python-django
Bug-fix update to 1.7.11
python2.7
Address StartTLS stripping attack in smtplib [CVE-2016-0772], integer overflow in zipimporter [CVE-2016-5636], HTTP header injection [CVE-2016-5699]
quassel
Fix remote DoS in quassel core with invalid handshake data [CVE-2016-4414]
ruby-eventmachine
Fix remotely triggerable crash due to FD handling
ruby2.1
dl::dlopen should not open a library with tainted library name in safe mode [CVE-2009-5147]; Fiddle handles should not call functions with tainted function names [CVE-2015-7551]
sendmail
Do not abort with an assertion if the connection to an LDAP server is lost; ensure sendmail {client_port} is set correctly on little endian machines
sqlite3
Fix tempdir selection vulnerability [CVE-2016-6153], segfault following heavy SAVEPOINT usage
systemd
Use the right timeout for stop processes we fork; don't reset log level to NOTICE if we get quiet on the kernel cmdline; fix prepare priority queue comparison function in sd-event; update links to kernel.org cgroup documentation; don't start console-getty.service when /dev/console is missing; order systemd-user-sessions.service after nss-user-lookup.target and network.target
tabmixplus
New upstream release, compatible with firefox-esr
tcpreplay
Handle frames of 65535 octets size, add a size check [CVE-2016-6160]
tor
Update the set of authority directory servers
tzdata
New upstream release; update to 2016e
unbound
Init script fixes: add pidfile magic comment; call start-stop-daemon with --retry for 'stop' action
util-vserver
Rebuild against dietlibc 0.33~cvs20120325-6+deb8u1, fixing insecure default PATH
vorbis-tools
Fix large alloca on bad AIFF input to oggenc [CVE-2015-6749], Validate count of channels in the header [CVE-2014-9638 CVE-2014-9639], fix segmentation fault in vcut
vtk
Rebuild to fix Java paths [ppc64el]
wget
By default, on server redirects to a FTP resource, use the original URL to get the local file name [CVE-2016-4971]
wpa
Security updates relating to invalid characters [CVE-2016-4476, CVE-2016-4477]
yaws
Fix HTTP_PROXY cgi env injection [CVE-2016-1000108]
zabbix
Fix mysql.size shell command injection in zabbix-agent [CVE-2016-4338]
The mariadb-10.0 package failed to build on the powerpc architecture, but has been included in the point release to allow quicker release of the fix for CVE-2016-6662, which had not been disclosed at the time of the upload. If a fix for the build failure becomes available before the next mariadb-10.0 DSA, an updated package may be released via jessie-updates.
0 notes