#webappdevelopmenttechnologies
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Web App Development Technologies in 2024
Struggling to choose the right tech stack for your next web app? This blog post explores the strengths and weaknesses of popular options in 2024, including front-end favorites like React, Vue.js, and Angular, and back-end powerhouses like Node.js and Python. Discover which technology might be the perfect fit for building your next high-performing application!
Blog Link - https://iprogrammer.com/web-app-development-technologies-in-2024/

#webappdevelopment#webapplication#webapplicationdevelopment#webapplicationdevelopmenttechnologies#webappdevelopmenttechnologies#webapplicationdevelopmentservices#webapplicationdevelopmentcompany
0 notes
Text
Web App Development Technologies in 2024

The Right Front End Stack for the Right Project
The landscape of web development is brimming with powerful technologies, each with its own strengths and ideal use cases. There’s no single ‘one size fits all’ answer to the question of the most in-demand stack.
Full-stack developers offer the flexibility to handle both front end and back end development, making them a valuable asset for some projects. However, many organizations choose to hire full stack developers based on specific needs.
This allows them to leverage specialists who are experts in particular technologies within a stack (e.g., front end frameworks like React or back end languages like Python).
Top Front End Technologies for Web App Development in 2024!
React Web Development
React, often referred to as React.js, is more than just a framework — it’s a powerful JavaScript library that has revolutionized front end development. Unlike traditional frameworks with rigid structures, React offers a flexible and component-based approach. This allows developers to create dynamic and interactive user interfaces (UIs) with ease.
React’s popularity stems from its efficiency, performance, and ability to adapt to changing requirements. It empowers developers to build UIs that are:
Component-Based: Complex UIs are broken down into reusable components, promoting code organization and maintainability.
Efficient Rendering: React utilizes a virtual DOM (Document Object Model) to optimize UI updates, ensuring smooth performance.
Flexible & Adaptable: React readily integrates with other libraries and frameworks, allowing for customization to fit specific project needs.
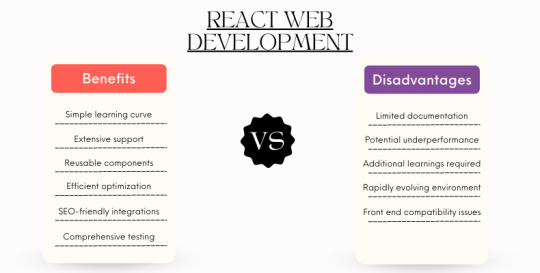
Advantages:
– Simplified Learning Curve: React’s clean syntax and component-based approach make it easier to grasp, even for beginners.
– Extensive Library Support: Leverage a vast ecosystem of pre-built JavaScript libraries to accelerate development and access ready-made functionalities.
– Reusable Components: Build modular and reusable components to streamline development, improve code maintainability, and ensure consistency throughout your application.
– Performance Optimization: React’s virtual DOM enables efficient rendering and updates, resulting in a smoother user experience.
– SEO Friendliness: React applications can be SEO-friendly with proper coding practices and, if needed, server-side rendering techniques.
– Handy Development Tools: Utilize a rich set of tools like Redux, DevTools, and testing frameworks to simplify development, debugging, and code management.
– Dynamic Web Application Development: Build interactive and dynamic web applications that adapt to user behavior with ease.
– Comprehensive Testing Capabilities: The component-based architecture facilitates unit testing, promoting overall code quality.
Disadvantages:
– Limited Official Documentation: While extensive community resources exist, official React documentation can be lacking for specific functionalities, requiring additional research.
– Potential SEO Challenges: Client-side rendering can impact SEO in some scenarios. Careful planning and optimization techniques might be necessary.
– JSX Learning Curve: JSX, a syntax extension for JavaScript, can add an initial learning hurdle for developers unfamiliar with it.
– Rapidly Evolving Ecosystem: The fast pace of React development and its ecosystem necessitates ongoing learning to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements.
Angular Web Development
Launched in 2010 by Google, Angular has become a popular framework for front-end development. It leverages TypeScript, a superset of JavaScript, for enhanced code maintainability and type safety. While AngularJS, an earlier version, laid the groundwork, Angular (without the JS suffix) has emerged as the preferred choice for modern development.
Why Angular for Enterprise Applications?
Angular’s strengths make it particularly well-suited for building enterprise-grade web applications:
Scalability: Angular applications are designed to handle the complexity and growing data demands of large-scale enterprise applications.
Structure and Maintainability: The use of TypeScript and a component-based architecture promote clean code, easier maintenance, and reduced development overhead for large projects.
Rich Ecosystem and Support: Angular benefits from a vast ecosystem of libraries, tools, and a large developer community, providing extensive support and resources.
Angular 13: The Latest and Greatest?
Angular releases regular updates, and Angular 13 is the latest iteration. While not necessarily the absolute “future” of web development, it offers several advancements over previous versions, including:
– Improved Performance: Optimizations in Angular 13 ensure smoother user experiences for even demanding applications.
– Enhanced Developer Experience: New features and tooling improvements streamline development workflows.
– Staying Up-to-Date: Upgrading to the latest version ensures access to the newest features and security patches. Angular Development Advantages:
Trusted Foundation: Developed and maintained by Google, Angular offers stability and ongoing support.
Extensive Community: Benefit from a large and active developer community for knowledge sharing, troubleshooting, and finding pre-built components.
Streamlined Development: Two-way data binding simplifies data flow between your application’s model and view, reducing development complexity.
Rapid Prototyping: Angular’s features facilitate iterative development, enabling faster creation and testing of prototypes.
Familiar Templates: Utilize familiar HTML templates for building user interfaces, making it easier for developers with HTML experience to pick up.
Enhanced Code Quality: TypeScript, used with Angular, enforces type safety and promotes cleaner, more maintainable code.
Modular Design: The component-based architecture promotes code reusability and simplifies development of complex applications.
Rich Ecosystem: Angular leverages a vast ecosystem of libraries, tools, and frameworks to extend functionalities and streamline development.
Angular Development Disadvantages:
Steeper Learning Curve: While conceptually similar to HTML, Angular introduces new concepts and patterns that might require more effort to learn for beginners.
Potential for Complexity: Angular’s structure and features can lead to complex codebases for smaller projects, potentially requiring more development effort.
Memory Consumption: In some cases, Angular applications can have a higher memory footprint compared to simpler frameworks.
Enforced Structure: The hierarchical tree-like structure can be less flexible for specific use cases compared to some other frameworks.
Migration Challenges:: Upgrading between major Angular versions can involve significant code changes, requiring careful planning and effort. VueJS Web Developement
VueJS Web Developement
Vue.js has emerged as a compelling contender in the front-end development landscape. This open-source JavaScript framework empowers sweb app developers to create user interfaces and single-page applications (SPAs) with ease.
Key Advantages of Vue.js:
Lightweight and approachable: Compared to some frameworks, Vue.js boasts a gentler learning curve for beginners due to its intuitive nature and focus on core web development concepts.
MVVM Architecture: Vue.js leverages the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) architectural pattern, promoting clean separation of concerns and simplified code management.
Flexibility for Migration: Migrating existing web applications can be smoother with Vue.js, thanks to its compatibility with existing HTML structures and the potential for incremental adoption.
Rich HTML Functionality: Vue.js seamlessly integrates with HTML, allowing developers to leverage their existing web development knowledge and avoid complex syntax.
Modern Tooling: Vue utilizes Vite.js, a next-generation bundler, for efficient development workflows and faster build times.
While Vue.js offers many advantages, it’s important to consider some potential drawbacks:
Managing Reactivity: Vue.js’s reactive system can be complex for large-scale applications, requiring careful planning and attention to potential performance bottlenecks.
Balancing Flexibility: The framework’s flexibility can be a double-edged sword. While it allows for customization, it can also lead to inconsistent code structures in large projects if not managed effectively.
Memory Usage Considerations: In some cases, Vue.js applications might have a slightly higher memory footprint compared to certain minimal frameworks. Optimization strategies might be required for memory-constrained environments.
Developer Availability: While the developer community is growing, it might still be smaller compared to some other established frameworks. Finding highly experienced Vue.js developers for large projects could require a wider search.
Resource Ecosystem: The ecosystem of third-party libraries and plugins for Vue.js is still expanding. While extensive resources are available, it might not be as comprehensive as those for more mature frameworks.

ASP .NET Web Development
ASP.NET Core, the open-source and powerful web framework for building modern web applications, excels in backend development. While primarily focused on web application development, ASP.NET Core can be leveraged with other .NET technologies to create various applications.
.NET leverages the Common Language Runtime (CLR) to achieve platform independence. This, along with its strong focus on best practices, empowers developers to build robust applications using their preferred languages. The open-source nature of .NET adds another advantage — you can join a vast and active developer community constantly improving the framework.
Benefits of ASP.NET Core:
Clean Code Structure Encourages separation of concerns, keeping your code organized and maintainable.
Faster Development Provides pre-built features to jumpstart development, saving you coding time.
Flexible and Adaptable Offers extensive customization options and extensibility for unique project needs.
Enhanced Security Built-in security features help protect your web applications from vulnerabilities.
Simplified Management Streamlines monitoring and management processes for your applications.
Cross-Platform Freedom Develop and deploy applications seamlessly across Windows, macOS, and Linux environments.
Considerations for ASP.NET Core:
Learning Curve ASP.NET Core, while well-documented, might require additional learning compared to some very established frameworks due to its evolving nature.
Migration Costs Migrating existing projects from a different framework to ASP.NET Core can involve some investment in time and resources.
Node.js Web Development
Node.js is a highly popular open-source runtime environment built on Chrome’s JavaScript engine (V8). This empowers web development teams to create fast, scalable web applications using JavaScript on both the front-end and back-end.
Node.js paves the way for innovative approaches to server-side development with its unique event-driven architecture.
While Node.js wasn’t necessarily the most used programming language in 2020 (reports may vary on usage statistics), it has gained significant traction among developers for its unique strengths.
Benefits of Node.js:
Effortless Scalability Node.js excels at handling growing applications. Its architecture allows for easy scaling to meet increasing user demands.
Quick Start for Developers JavaScript proficiency translates well to Node.js, making it a breeze for developers to learn and become productive quickly.
Full-Stack Flexibility Embrace JavaScript for both front-end and back-end development, streamlining your workflow and reducing the need for multiple languages.
Thriving Community Benefit from a vast and active community of Node.js developers who contribute libraries, tools, and support.
Real-Time Advantage Node.js excels at handling concurrent requests efficiently, making it ideal for real-time applications like chat or collaborative tools.
Speedy Performance Node’s event-driven architecture minimizes waiting time, leading to faster application performance and improved user experience.
Intelligent Caching Node.js allows for efficient caching mechanisms, further reducing load times and enhancing application responsiveness.
Considerations for Node.js:
Evolving API While uncommon, breaking changes can occur in the Node.js API, requiring developers to adapt their code. Staying updated with the latest releases helps mitigate this.
Asynchronous Mindset Shift Node.js utilizes an asynchronous programming model, which can require a different approach compared to traditional synchronous coding. While powerful, it might have a learning curve for some developers.
CPU-Intensive Tasks Node.js performs best with I/O bound tasks (tasks involving waiting for data). For computationally heavy operations, other technologies might be better suited.
Performance in Specific Scenarios While generally performant, Node.js might not always be the optimal choice for highly complex calculations. Consider the specific needs of your application.
Maturity of Libraries While the Node.js ecosystem is vast, some specialized libraries might not be as mature or widely adopted compared to older, more established languages.
Python Web Development
Both Node.js and Python are popular back end development languages, each with their strengths and weaknesses. The best choice depends on your project’s specific requirements.
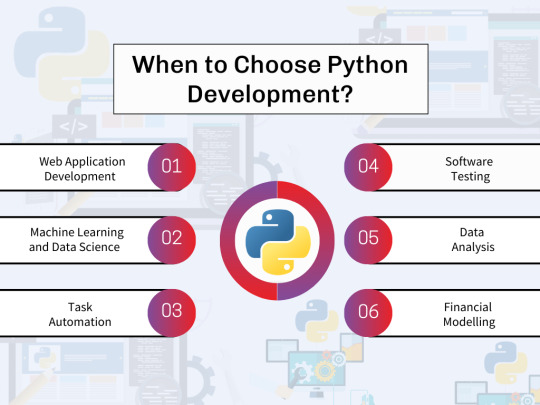
1. Web Application Development Python excels in building feature-rich websites and web applications, thanks to its robust frameworks like Django and Flask.
2. Machine Learning and Data Science Python reigns supreme in these fields due to its extensive libraries like NumPy, pandas, and scikit-learn. These tools make data manipulation, analysis, and machine learning model creation a breeze.
3. Task Automation Python’s ability to automate repetitive tasks makes it a valuable asset for streamlining workflows across various domains.
4. Software Testing Python’s readability and vast testing frameworks like Pytest empower developers to write efficient and maintainable test suites.
Beyond traditional programming, Python’s easy-to-learn nature makes it accessible to non-programmers as well. Scientists, accountants, and other professionals can leverage Python for tasks like:
– Data Analysis: Python simplifies data cleaning, exploration, and visualization, making it easier to extract insights from data.
– Financial Modeling: Python’s libraries enable the creation of complex financial models for better decision-making.
With its versatility and ease of use, Python remains a top choice for programmers and non-programmers alike.
Benefits of Python for Developers:
Boost Productivity Python’s clean syntax and focus on readability allow web app developers to write code quickly and maintain it easily. This translates to faster development cycles and more efficient use of time.
Rich Ecosystem of Libraries The vast Python Package Index (PyPI) offers a library for nearly any task imaginable. From data science (NumPy, Pandas) to web development (Django, Flask) and machine learning (scikit-learn), you’ll find powerful tools to streamline your development process.
Gentle Learning Curve Python’s clear and concise structure makes it one of the easiest programming languages to learn. This low barrier to entry makes it ideal for beginners and allows experienced developers to pick it up quickly for new projects.
Integration Powerhouse Python integrates seamlessly with various languages and frameworks, enabling developers to leverage existing components and avoid reinventing the wheel. Additionally, built-in features like modules and packages promote code organization and reusability.
Fine-Grained Control Python offers a good balance between high-level abstraction and low-level control. Developers can work at a level of detail appropriate for the task, making it suitable for various development needs.
Object-Oriented Approach Python supports object-oriented programming principles, allowing developers to create well-structured, maintainable, and reusable code. This promotes modularity and simplifies complex project management.
Web Development Friendly Python’s robust web frameworks like Django and Flask provide powerful tools for building modern and scalable web applications. With these frameworks, developers can focus on core functionalities without getting bogged down in low-level details.
Considerations for Python Development:
Potential Integration Challenges While Python integrates well with many languages, complex integrations with some non-Python systems might require additional effort.
Performance Considerations Compared to compiled languages like C++, Python can be slower for computationally intensive tasks. However, for many applications, Python’s speed is sufficient.
Database Access Options Python has database access layers, but they might not be as mature or optimized as those in languages specifically designed for database interaction. Consider the project’s database needs when choosing a language.
Runtime Errors Python’s dynamic typing can lead to runtime errors if data types aren’t handled carefully during development. Implementing robust testing practices helps mitigate this risk.
Mobile App Development While Python can be used for mobile app development with frameworks like Kivy, it’s not the most common choice for native mobile app development. Consider the target platforms and desired user experience when selecting a language.
Memory Management Python’s automatic memory management can lead to higher memory usage compared to some languages. However, for most web development scenarios, this isn’t a major concern. If memory optimization is critical, explore alternative approaches within Python or consider other languages.
Top Databases in 2024!
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
AWS is a powerful and ever-expanding cloud computing platform from Amazon. It provides a one-stop shop for businesses and individuals to leverage a variety of services to build, deploy, and manage applications in the cloud.
Launched in 2006 by Amazon, AWS has become a dominant force in cloud computing.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a powerful cloud computing platform, not just a database. It provides a secure and scalable foundation for organizations to build, deploy, and manage a wide range of applications, regardless of their size or industry-
Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness AWS allows you to scale your computing resources (like storage and processing power) up or down as needed. This flexibility ensures you only pay for what you use, leading to significant cost savings compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Robust Security AWS prioritizes security with a layered approach that includes encryption, access controls, and threat detection. This empowers organizations to safeguard their sensitive data and applications.
Broad Applicability AWS caters to diverse industries and application types. From building web applications and mobile backends to running complex data analytics or machine learning workloads, AWS offers the tools and services needed.
Simplified Management AWS offers a user-friendly interface and well-documented services, making it easy for businesses to get started and manage their cloud resources without needing extensive cloud expertise.
Enhanced Speed and Agility AWS empowers businesses to deploy applications and services faster. The scalable nature of AWS cloud resources allows businesses to react quickly to changing market conditions and innovate at an accelerated pace.
Considerations for Using AWS:
Security is a Shared Responsibility While AWS offers robust security features, it’s important to remember that security is a shared responsibility. Businesses must configure and manage their cloud resources securely to maximize protection.
Potential Support Costs While AWS provides basic customer support, in-depth technical assistance might require additional fees. Carefully evaluate your support needs when budgeting for AWS.
Amazon EC2 Resource Constraints AWS imposes limitations on resources allocated to a single EC2 instance (virtual server) in certain regions. However, requesting higher limits is usually an option. For very demanding workloads, alternative AWS services or configurations might be more suitable.
General Cloud Considerations Cloud computing introduces inherent considerations like potential vendor lock-in, reliance on internet connectivity, and managing costs associated with data egress (transferring data out of AWS). Evaluate your project needs and risk tolerance when deciding if cloud computing is the right fit.
Firebase
In today’s mobile development landscape, selecting a suitable backend solution is crucial for your app’s success. Two popular options are Firebase and AWS. Both offer a comprehensive suite of services but cater to different needs.
This comparison will explore the key features of each platform to help you make an informed decision.
Developed by Google, Firebase is a Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) platform designed to simplify mobile and web app development. It offers a variety of tools and services to streamline various aspects of the development process, potentially helping you build high-quality applications and expand your user base.

Robust Database Solutions Firebase offers flexible NoSQL databases that store and manage data in JSON-like documents. This structure is ideal for frequently changing or complex data, often encountered in modern applications.
Cost-Effective Development Firebase provides a generous free tier for many of its services, making it a cost-effective option for startups and businesses of all sizes. This allows for building core functionalities without upfront investment.
Effortless Static Hosting Firebase simplifies web content hosting with its built-in static hosting capabilities. This eliminates the need to manage separate web servers, saving development time and resources.
Clear and Comprehensive Documentation Firebase boasts excellent documentation with tutorials, code samples, and clear explanations. This comprehensive library of resources empowers developers to learn and leverage Firebase features effectively.
Intuitive User Interface Firebase’s user interface is well-designed and easy to navigate. This allows developers to quickly access and manage their projects and cloud resources without a steep learning curve.
Seamless Integration Firebase integrates smoothly with various Google products and development tools, streamlining workflows and simplifying development processes.
Actionable Insights with Analytics Firebase Analytics provides valuable insights into user behavior and app performance. This data empowers developers to make data-driven decisions and optimize their applications for better user engagement.
Enhanced App Quality with Testing Tools Firebase offers robust testing services that help developers identify and fix bugs before release. This ensures high-quality applications that deliver a positive user experience.
Serverless Functions for Scalability Firebase’s serverless functions enable developers to build scalable back-end logic without managing servers. This simplifies development and reduces infrastructure overhead.
Integration of Machine Learning Firebase allows integration with Google’s machine learning capabilities, enabling developers to add intelligent features to their applications without extensive machine learning expertise.
MongoDB
MongoDB is a popular NoSQL database known for its scalability and flexibility. Unlike traditional relational databases, MongoDB stores data in JSON-like documents, offering several advantages:
– Schema Flexibility: Documents can have different structures, allowing you to store data with varying fields without rigid table definitions. This makes MongoDB a good fit for evolving data models and complex data structures.
– High Performance: MongoDB excels at handling large datasets and offers efficient querying capabilities. This makes it suitable for applications that require frequent data updates and retrieval.
– Horizontal Scalability: MongoDB scales horizontally by adding more servers, making it easy to accommodate growing data volumes.
However, it’s important to consider these factors when evaluating MongoDB for your project:
1. Data Relationships
Modeling complex relationships between data points might require additional design considerations in MongoDB compared to relational databases.
2. Schema Enforcement
Without a predefined schema, data consistency might require more development effort compared to strictly typed databases.
Who Uses MongoDB?
While not a one-size-fits-all solution, MongoDB is a popular choice for various applications and industries due to its flexibility and performance:
Real-time Applications: MongoDB’s responsiveness makes it suitable for applications requiring real-time data updates and retrieval.
Content Management Systems (CMS): The schema flexibility allows for storing diverse content types efficiently.
E-commerce Platforms: MongoDB can handle the high volume and variety of data associated with e-commerce transactions.
MongoDB offers a robust query language that allows developers to retrieve specific data efficiently.
Here are some key features:
Precise Field Selection Queries can target specific fields within documents, returning only the data you need. This improves performance and reduces the amount of data transferred.
Range-Based Queries MongoDB allows querying documents based on a range of values for a particular field. This is useful for filtering data within specific boundaries, like dates or product prices.
Regular Expression Support MongoDB supports regular expressions for pattern matching within fields. This enables powerful searches for text data that might have variations or specific patterns.
Flexible Return Options Queries can return entire documents, specific fields, or even random samples of data depending on your needs. This level of control allows developers to optimize their queries for different use cases.
By leveraging these capabilities, developers can write efficient queries that retrieve the exact data they need, optimizing performance and reducing unnecessary data transfer.

Selecting the optimal technology stack is a critical decision that lays the groundwork for any web application development project. To make an informed choice, consider these key factors:
Project Requirements: Clearly define your project’s goals, functionalities, and target audience. The tech stack should align with the specific needs of your application.
Team Expertise: Evaluate your development team’s skills and experience. Choosing a stack that leverages their existing knowledge can streamline development and reduce the learning curve.
Market Landscape: Consider current technology trends and the availability of resources like libraries and frameworks for your chosen stack. A mature stack with a large community often offers more extensive support.
Scalability and Maintainability: Think about the long-term vision for your application. The tech stack should be able to accommodate future growth and simplify ongoing maintenance efforts.
Security Considerations: Prioritize security throughout the development process. Choose technologies with a strong track record of security and ensure your team follows security best practices.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make a well-informed decision about the tech stack that will empower your team to build a successful and sustainable web application.
Tech Stack Decisions: Driven by Project Needs
The functionalities and features you envision for your project significantly influence the technology choices you make. For instance, building a real-time chat application necessitates technologies like WebSockets to ensure seamless communication.
When it comes to performance and scalability, some programming languages and frameworks excel. Microservices architecture, containerization (like Docker), and cloud services work together to handle high workloads and enable horizontal scaling for applications that require it.
On the other hand, if your project is a smaller, simpler application with minimal anticipated changes, a monolithic architecture and a straightforward language like PHP can be a cost-effective option for both development and future maintenance.
In essence, the ideal tech stack aligns with your project’s specific requirements, striking a balance between functionality, performance, and long-term maintainability.
Building on Your Team’s Strengths:
Leveraging your development team’s existing knowledge is a strategic move. When developers work with familiar technologies, they experience:
Enhanced Productivity: Reduced learning curves lead to faster development cycles and quicker time-to-market.
Efficient Coding: Existing knowledge translates to cleaner, more maintainable code.
Stronger Decision-Making: Experience with the technology allows for better-informed technical choices.
However, new project requirements or evolving trends might necessitate the introduction of new technologies. Here are two approaches to consider:
Hybrid Team Approach: Engage external specialists to collaborate with your core team. This allows for knowledge transfer and skill development within your team while leveraging the specialist’s expertise in the new technology.
Strategic Outsourcing: Partner with a reputable IT staff augmentation company specializing in projects like yours. This can be ideal for complex projects or situations where in-house expertise is limited.
The key takeaway?
Align the chosen approach with your team’s existing skillset and project complexity. This minimizes the learning curve, maximizes efficiency, and keeps your team motivated throughout the development process.
The Power of Market Trends
Staying attuned to current market trends can give your project a significant edge. Here’s how:
Competitive Advantage: Leveraging trending technologies can translate into innovative features, a more engaging user experience, or enhanced security, differentiating your project from competitors.
Talent Pool: A tech stack in high demand means a larger pool of skilled developers familiar with the chosen technologies. This simplifies the recruitment process and ensures access to qualified personnel for ongoing maintenance or future development.
Streamlined Development: Popular tech stacks often benefit from a wider range of readily available third-party integrations and libraries. These tools can streamline development workflows and accelerate project completion.
However, it’s important to strike a balance. While staying current is valuable, don’t chase fleeting trends. Focus on technologies that demonstrably align with your project’s goals and offer long-term value.
How the Right
Web Application Development Technology
Drives Success
Building a Unified Team Through Technology
A standardized tech stack, with the same programming languages, frameworks, and tools across the team, offers a powerful advantage: enhanced collaboration. Here’s how:
Shared Knowledge and Support: Developers can readily understand and contribute to each other’s code, fostering knowledge sharing and mutual support. This streamlines development processes and reduces roadblocks.
Streamlined Communication: A common language of technology eliminates confusion and allows for clearer communication within the team. Discussions about code become more efficient and productive.
Consistent Best Practices: Standardized tools and frameworks often lead to well-documented best practices and coding guidelines. These serve as a shared reference point, ensuring code consistency and simplifying onboarding for new team members.
By leveraging a unified tech stack, your team can work together more effectively, achieve better results, and lay the foundation for long-term project success.
Performance Gains with the Right Tech Stack
A well-considered tech stack goes beyond just functionality. It lays the groundwork for a high-performing application:
Scalability and Efficiency: The chosen technologies should be able to handle a growing user base and increasing data demands without compromising performance. This ensures your application can adapt and thrive as it scales.
Performance Optimization: The tech stack should include tools and technologies that are known for their efficiency and speed. This translates to a smoother user experience for your application’s end users.
Ongoing Improvement: Selecting technologies with a strong track record of regular updates ensures access to performance enhancements and security patches for a future-proof application.
By prioritizing performance through your tech stack choices, you can create a product that delivers a consistently smooth and responsive user experience, even as your user base grows.
Optimizing Development Costs: The Benefits of a Standardized Tech Stack
A standardized tech stack delivers benefits beyond streamlined development. It translates to significant cost savings in several ways:
Reduced Development Time: Familiarity with the chosen technologies allows your team to work efficiently and develop code faster. This translates directly to lower labor costs associated with development.
Minimized Troubleshooting: Popular tech stacks often benefit from active developer communities and robust support systems. When issues arise, developers can quickly find solutions, reducing troubleshooting time and associated expenses.
Automation Advantages: Modern tech stacks frequently include built-in automation tools for deployment, testing, and monitoring. This frees up valuable developer time, minimizes manual effort, and ultimately leads to cost savings.
By leveraging a standardized tech stack, you can optimize your development process, reduce overall project costs, and free up your team to focus on innovation.
How Tech Stack Decisions Shape Industry Leaders
Choosing the right tech stack is fundamental to creating a sustainable and scalable product. Many of today’s tech giants credit their success, in part, to well-informed tech stack decisions.
Here are some real-world examples:
Netflix
This streaming giant leverages a powerful combination of technologies:
Frontend: React (user interfaces) and Redux (state management) for a dynamic and responsive user experience.
Backend: A mix of Java, Spring Boot, and Node.js allows for efficient web application development and global content delivery.
Databases: Netflix utilizes various databases like Cassandra, MySQL, and Elasticsearch to cater to different data storage requirements.
This strategic tech stack empowers Netflix to:
– Manage a Large User Base: The microservices architecture facilitates easier maintenance and scaling as the user base grows.
Deliver Global Streaming: The backend combination enables seamless streaming experiences worldwide.
Create an Engaging User Interface: React and Redux contribute to a rich and interactive experience that keeps users engaged.
Handle Diverse Data: Different databases effectively manage various data types, from user profiles to content recommendations.
Airbnb: A Tech Stack Tailored for User Experience and Growth
Similar to Netflix, Airbnb has achieved success in part due to its strategic tech stack choices. Here’s a breakdown of their key technologies:
Frontend: Airbnb prioritizes a user-friendly interface with a combination of JavaScript, React, and Redux. This trio enables a dynamic and responsive user experience that keeps users engaged.
Backend: Airbnb leverages a diverse backend stack:
Ruby on Rails: This framework powers the main website and services, offering a developer-friendly environment for rapid feature updates.
Python: Airbnb utilizes Python for machine learning capabilities, enabling data-driven insights and personalization.
Node.js: This JavaScript runtime environment handles specific microservices within the application.
Databases: Airbnb utilizes a multi-database approach, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Redshift. Each database caters to specific data needs, allowing Airbnb to efficiently collect, analyze, and gain valuable insights from vast amounts of user data.
This combination empowers Airbnb to:
– Prioritize User Experience: The front end tech stack ensures a dynamic and user-friendly interface.
– Maintain Development Agility: Ruby on Rails and Node.js facilitate rapid feature updates and innovation.
– Unlock Data-Driven Decisions: The use of Python for machine learning and diverse databases allows Airbnb to leverage data for informed decision-making.
By carefully selecting each technology to address specific needs, Airbnb has built a tech stack that supports their user experience, growth, and data-driven approach.
IProgrammer as Your Web Application Development Company
Here’s why partnering with us for your web application tech stack selection is the secret sauce to your web app’s success:
Seasoned Expertise: We don’t just follow trends; we understand the nuances of each technology and its impact on your specific project.
Future-Proof Foundations: We build with scalability and long-term maintainability in mind, ensuring your web app can adapt and thrive as your business grows.
Performance Optimization: Our team prioritizes speed, security, and a seamless user experience, delivering web applications that delight your audience.
Ready to cook up something extraordinary with iProgrammer’s Web Application Development Services?
Contact our experts today and craft the perfect tech stack recipe for your next web application development masterpiece.
Blog Reference Link — https://www.iprogrammer.com/web-app-development-technologies-in-2024/
#iprogrammer#webappdevelopment#webapplication#webapplicationdevelopment#webapplicationdevelopmenttechnologies#webappdevelopmenttechnologies#webapplicationdevelopmentservices#webapplicationdevelopmentcompany
0 notes