#whatisblockchaintechnology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Blockchain Technology: What is it? and Understanding of Inner Workings
A blockchain technology is a distributed ledger made up of expanding lists of entries, or blocks, that are safely connected by cryptographic hashes.A timestamp, transaction data (usually shown as a Merkle tree with data nodes represented by leaves), and a cryptographic hash of the preceding block are all contained in each block. Each new block links to the ones before it, forming an effective chain since each block carries information about the one before it (see linked list data structure). As a result, blockchain transactions are irreversible since, once they are recorded, it is impossible to change the data in a single block backward without also changing all blocks that follow it.

A blockchain is a distributed, decentralized, and frequently public digital ledger made up of documents called blocks that are used to log transactions across numerous computers. This ensures that any block that is involved cannot be changed backwards without also changing all other blocks that come after it. This enables the parties to independently and reasonably cheaply check and audit transactions. A distributed timestamping server and a peer-to-peer network are used to manage a blockchain database independently. They are verified by widespread cooperation motivated by group self-interest.
primarily on earlier work by Stuart Haber, W. Scott Stornetta, and Dave Bayer, a person (or group of individuals) going by the name (or pseudonym) Satoshi Nakamoto constructed a blockchain in 2008 to function as the public distributed ledger for bitcoin cryptocurrency transactions.Due to the blockchain's integration, bitcoin is the first virtual money that can prevent double-spending without the aid of a central server or reliable authority. The design of bitcoin has served as an inspiration for other publicly readable applications and blockchains that are utilized by cryptocurrencies. The blockchain could be viewed as a particular kind of payment rail. What is Blockchain Technology? I find blockchain technology to be a groundbreaking innovation that is revolutionizing various industries. Here are key points to understand about blockchain: - Definition: Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that securely records transactions across a network of computers. - Blocks and Chains: Transactions are grouped into blocks, which are then linked together in chronological order to form a chain, hence the name "blockchain." - Decentralization: One of the key characteristics of blockchain is its decentralized nature. There is no central authority; instead, all participants have a copy of the ledger, ensuring transparency and security. - Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions, making it tamper-proof. Once a block is added to the chain, altering it is extremely difficult due to the consensus mechanism. - Consensus Mechanisms: To validate transactions, blockchain networks use consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms ensure agreement among all participants. - Smart Contracts: Blockchain platforms like Ethereum allow the execution of smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. This automates processes and eliminates the need for intermediaries. - Applications: Blockchain is employed in various fields such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and voting systems due to its transparency, immutability, and security features. Understanding blockchain technology is crucial in grasping its potential to transform traditional processes and create new opportunities in the digital era.
The History and Evolution of Blockchain
I will begin by taking a deeper dive into the history and evolution of blockchain technology: - Origins: Blockchain technology was first conceptualized by an individual or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. Nakamoto outlined the core principles of blockchain in a whitepaper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System." - Bitcoin: The release of Bitcoin in 2009 marked the first successful implementation of blockchain technology. Bitcoin, a decentralized digital currency, utilizes blockchain to record transactions securely and transparently without the need for a central authority. - Expansion: Following the success of Bitcoin, developers began exploring ways to apply blockchain technology beyond cryptocurrencies. This led to the creation of alternative blockchains, such as Ethereum, which introduced smart contracts - self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. - Diversification: Over time, blockchain technology has diversified into various industries, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more. Companies have started leveraging blockchain for increased transparency, security, and efficiency in their operations. - Evolution: As blockchain technology continues to evolve, new advancements such as permissioned blockchains, interoperability between different blockchains, and scalability solutions are being developed. These innovations aim to address the limitations of early blockchain networks, such as scalability issues and energy consumption. - Future Outlook: The future of blockchain technology holds promise for further innovation and adoption across industries. As more use cases are discovered and refined, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize how data is stored, verified, and shared in a secure and decentralized manner. Understanding the history and evolution of blockchain provides valuable insights into the development and potential future applications of this transformative technology.
Key Components of Blockchain Technology
I. Decentralized Network: - In a blockchain network, there is no central authority governing the system. Nodes or computers participating in the network validate and record transactions, ensuring transparency and security. II. Blocks: - Blocks are collections of transactions that are bundled together and added to the blockchain. Each block contains a unique code called a hash, the hash of the previous block, and the transaction data. III. Immutable Ledger: - The blockchain ledger is immutable, meaning that once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature ensures the integrity and reliability of the recorded data. IV. Consensus Mechanism: - Consensus mechanisms are protocols used to achieve agreement among nodes in the network regarding the validity of transactions. Common mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). V. Smart Contracts: - Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute and enforce the terms when predefined conditions are met. VI. Public and Private Keys: - Public and private keys are cryptographic keys that allow users to interact securely with the blockchain. The public key is visible to others and is used to receive funds, while the private key should be kept confidential and is used for transaction signing. VII. Cryptographic Hash Function: - Blockchain uses cryptographic hash functions to secure data by converting input data into a fixed-size string of bytes. Any change in the input data will result in a different hash, making it easy to detect tampering. VIII. Distributed Ledger: - The ledger in blockchain is distributed across multiple nodes in the network, making it transparent, resilient to failures, and resistant to tampering. IX. Peer-to-Peer Network: - Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network where nodes communicate directly with each other, eliminating the need for intermediaries and promoting direct interaction between participants.
Understanding Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
I have learned that blockchain consensus mechanisms are algorithms used to achieve an agreement on a single data value or a single state of the network among distributed processes or multi-agent systems. There are several consensus mechanisms that different blockchain networks employ, including Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), and more.
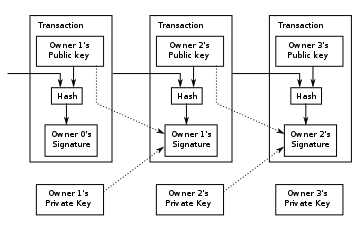
- Proof of Work (PoW): In PoW, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks on the blockchain. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block and is rewarded with cryptocurrency. This mechanism is energy-intensive but is known for its security. - Proof of Stake (PoS): Unlike PoW, PoS does not require miners to solve complex puzzles. Instead, new blocks are created and added to the blockchain based on the number of coins a miner holds. The more cryptocurrency a miner has, the more likely they are to be chosen to create the next block. - Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): DPoS is a variation of PoS where coin holders vote for delegates who are responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks. This mechanism is known for its scalability and efficiency. - Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): In PBFT, a network reaches consensus through a series of rounds where a leader is chosen to propose the next block, which is then confirmed by other nodes in the network. This mechanism is fast and efficient but requires a predetermined set of nodes. Understanding these consensus mechanisms is crucial in grasping how blockchain networks operate securely and efficiently. Each mechanism has its strengths and weaknesses, influencing factors such as decentralization, scalability, security, and energy consumption.
Cryptographic Principles in Blockchain
When it comes to understanding the inner workings of blockchain technology, cryptographic principles play a fundamental role. Here are key aspects to consider: - Hash Functions: In blockchain, hash functions are crucial for creating secure and tamper-proof connections between blocks. These functions take an input (data) and produce a fixed-size string of characters. Any slight change in the input data will result in a drastically different output, making it easy to detect alterations in the blockchain. - Public Key Cryptography: Public key cryptography is at the core of blockchain security. It involves using a pair of cryptographic keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. When a transaction is made, the sender uses the recipient's public key to encrypt the transaction, ensuring that only the recipient can decrypt and access the funds with their private key. - Digital Signatures: Digital signatures verify the authenticity of transactions in a blockchain. They are created using the sender's private key and can be verified with the sender's public key. This process ensures that transactions are secure, unaltered, and traceable back to the sender. - Consensus Algorithms: Cryptography is also instrumental in achieving consensus among network participants in blockchain. By utilizing algorithms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, blockchain networks can confirm transactions, agree on the order of blocks, and maintain the integrity of the distributed ledger. In summary, cryptographic principles form the backbone of blockchain technology, providing security, integrity, and transparency to decentralized networks. Understanding how these principles work is essential for grasping the complex yet innovative nature of blockchain systems.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications (DApps)
I find smart contracts fascinating as they are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Using blockchain technology, smart contracts facilitate and verify the performance of credible transactions without the need for intermediaries. When a certain set of predefined conditions are met, the contract executes automatically, ensuring security and efficiency. Some key points to understand about smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) include: - Code-based Agreements: Smart contracts operate based on code, ensuring transparency, immutability, and autonomy in the execution of contracts. - Decentralized Applications (DApps): DApps are applications that run on a decentralized network rather than a single server. They leverage blockchain technology and smart contracts to provide secure and transparent functionality. - Benefits of Smart Contracts: Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, reduce transaction costs, enhance security, and enable faster transaction processing. - Challenges: While smart contracts offer numerous advantages, they also present challenges such as code vulnerabilities, regulatory compliance, and scalability issues that need to be addressed. Understanding the implications and potential of smart contracts and DApps is crucial in comprehending the transformative power of blockchain technology. By enabling secure, trustless, and efficient transactions, smart contracts are revolutionizing traditional contract agreements and paving the way for decentralized applications to disrupt various industries.
The Role of Nodes and Miners in Blockchain
I play a crucial role in the blockchain network as a node. When I am a node, I maintain a copy of the entire blockchain ledger. This means I hold a record of every transaction that has ever occurred on the blockchain. My presence as a node is essential for the security and decentralization of the network. As a node, I validate transactions by checking them against the rules of the blockchain protocol. Once validated, I broadcast these transactions to other nodes in the network. This process ensures that all nodes have a consistent copy of the blockchain, promoting transparency and trust among participants. Miners, on the other hand, are another key component of the blockchain ecosystem. Miners play a vital role in securing the network and validating transactions. When I am tasked with mining, I compete with other miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets the opportunity to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain. Mining is resource-intensive, requiring significant computational power. However, it is a necessary process to ensure the integrity of the blockchain. By participating in mining, I contribute to the consensus mechanism that validates transactions and maintains the immutability of the ledger. In summary, nodes and miners are integral to the functioning of a blockchain network. As a node, I uphold the integrity of the ledger by maintaining a copy of the blockchain and validating transactions. When I take on the role of a miner, I contribute to securing the network and adding new blocks to the blockchain. Both nodes and miners work together to ensure the efficiency and security of the blockchain ecosystem.
Security and Privacy in Blockchain Technology
When it comes to security in blockchain technology, the decentralized nature of blockchain networks plays a significant role. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating a secure chain that makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to alter the data. This immutability factor is a core strength of blockchain technology in ensuring data integrity and security. In terms of privacy, blockchain technology offers a transparent yet secure way of conducting transactions. While the details of transactions are visible on the blockchain, the identities of the transacting parties are often pseudonymous. This pseudonymity provides a level of privacy, but it's essential to note that transactions on a public blockchain are still visible to anyone who has access to the network. Moreover, cryptographic techniques like hashing, digital signatures, and encryption add layers of security to blockchain transactions. Hash functions ensure data integrity, digital signatures authenticate the participants in a transaction, and encryption secures the data being transmitted. When it comes to private blockchains, additional privacy measures can be implemented. These may include permissioned access, where participants need authorization to join the network, and zero-knowledge proofs, which allow for verification of transactions without revealing any sensitive information. Overall, security and privacy are fundamental aspects of blockchain technology. By leveraging cryptographic tools and the decentralized nature of blockchain networks, we can ensure that data remains secure and transactions are conducted with a reasonable level of privacy.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain
I. Scalability: - Blockchain technology faces challenges when it comes to scalability. As more transactions are added to a blockchain, the network can become slow and inefficient. This is a significant limitation for blockchain applications looking to handle high volumes of transactions. II. Energy Consumption: - The process of validating transactions on a blockchain requires significant computational power, leading to high energy consumption. This has raised concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain technology, particularly in the case of networks using proof-of-work consensus algorithms. III. Security Concerns: - While blockchain is known for its security features, it is not entirely immune to attacks. Some common security concerns include the 51% attack, where a single entity gains control of the majority of the network's mining power, and smart contract vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors. IV. Regulatory Challenges: - The decentralized nature of blockchain technology can pose challenges when it comes to regulatory compliance. Government entities around the world are still grappling with how to regulate blockchain-based applications, which can create uncertainty for businesses operating in this space. V. Interoperability: - Interoperability between different blockchain networks and traditional systems is a significant challenge. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
What does Yschool bring to the table?
1) High-Quality Content
All learners will have a personalised digital learning experience.
2) Courses at Reasonable Prices
Our learning platform is the most cost-effective solution available in the country, with significantly greater benefits.
3) Extensive Analytics
Through our AI technology, our platform delivers precise metrics for students to assess their accuracy and speed.
4) Support is available 24 hours a day, seven days a week, for all of our students via App / Whatsapp.
Learn what abilities you'll need to develop your blockchain networks at scale. Yschool will assist you in deciphering the jargon around Blockchain, Bitcoin, and Cryptocurrency.
Why is Yschool all you need? Carry win-win survival techniques with you to secure proactive dominance. A new reality that has emerged from generation X is on the horizon.
Master future technology by learning blockchain with us and advancing your career path!
Download the YSchool App Right Away!
Blockchain, Physics, Math, Chemistry, and Biology enthusiasts will enjoy this learning app. Engaging 1000+ video courses, Reward-based learning, Performance metrics, and an unlimited number of mock exams
#blockchaintechnology
#whatisblockchain
#whatisblockchaintechnology
#blockchaindeveloper
0 notes
Link
Blockchain technology is evolving and is sure to dominate in the near future. Read here to know more about what is blockchain technology and how does it work.
0 notes
Text
What Is Blockchain Technology
What Is Blockchain Technology in Hindi
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8PgkkuFMgMQ
youtube
0 notes
Text
What's the big deal about blockchain technology?

There have been numerous attempts to generate virtual currency, but they have all failed.
The dominant issue is one of trust. How can we believe that if someone invents a new money called the X dollar, they will not give themselves a million X dollars or steal your X dollars?
Bitcoin was intended to overcome this issue by employing a blockchain, a database type. Most conventional databases, such as Database systems, contain an administrator who can execute modifications to the records (e.g., giving themselves a thousand X dollars). Blockchain is unusual because no one governs it; instead, it is controlled by the individuals who use it. Additionally, bitcoins cannot be falsified or exploited.
Blockchain development is one of the most rapidly rising industries. Companies are searching for blockchain developers to help them create effective and immediate implementations, enhance their existing systems, and stay ahead of the competition.
As a result, now is the most significant moment to become a blockchain developer.
Blockchain is a new area and market that is predicted to grow fast in the future years, with a market size of 163.83 billion by 2029. There are numerous factors contributing to blockchain's current popularity. One of them is the security it provides in transactions. Another critical reason is the data traceability offered by blockchain.
Blockchain can appear to be a complex technology to grasp owing to its perceived complexity. You may, nevertheless, grasp this technology and explore an exciting new job if you have the necessary prerequisite abilities. Such skills can be acquired through the comprehensive solutions provided by Yschool.
#blockchaintechnology
#whatisblockchain
#whatisblockchaintechnology
#blockchaindeveloper
0 notes
Text

#Blockchain, #NFTs, #DeFi & #yschool #learning #schoollearning #blockchainlearning #blockchaintechnology #whatisblockchain #whatisblockchaintechnology #blockchaindeveloper #blockchainmeaning
#Blockchain#NFTs#DeFi &#yschool#learning#schoollearning#blockchainlearning#blockchaintechnology#whatisblockchain#whatisblockchaintechnology#blockchaindeveloper#blockchainmeaning
0 notes
Text

#Blockchain, #NFTs, #DeFi & #yschool #learning #schoollearning #blockchainlearning #blockchaintechnology #whatisblockchain #whatisblockchaintechnology #blockchaindeveloper #blockchainmeaning
#Blockchain#NFTs#DeFi &#yschool#learning#schoollearning#blockchainlearning#blockchaintechnology#whatisblockchain#whatisblockchaintechnology#blockchaindeveloper#blockchainmeaning
0 notes
Text

#Blockchain, #NFTs, #DeFi & #yschool #learning #schoollearning #blockchainlearning #blockchaintechnology #whatisblockchain #whatisblockchaintechnology #blockchaindeveloper #blockchainmeaning
#Blockchain#NFTs#DeFi &#yschool#learning#schoollearning#blockchainlearning#blockchaintechnology#whatisblockchain#whatisblockchaintechnology#blockchaindeveloper#blockchainmeaning
0 notes
Text

#Blockchain, #NFTs, #DeFi & #yschool #learning #schoollearning #blockchainlearning #blockchaintechnology #whatisblockchain #whatisblockchaintechnology #blockchaindeveloper #blockchainmeaning
#Blockchain#NFTs#DeFi &#yschool#learning#schoollearning#blockchainlearning#blockchaintechnology#whatisblockchain#whatisblockchaintechnology#blockchaindeveloper#blockchainmeaning
0 notes
Text

#Blockchain, #NFTs, #DeFi & #yschool #learning #schoollearning #blockchainlearning #blockchaintechnology #whatisblockchain #whatisblockchaintechnology #blockchaindeveloper #blockchainmeaning
#Blockchain#NFTs#DeFi &#yschool#learning#schoollearning#blockchainlearning#blockchaintechnology#whatisblockchain#whatisblockchaintechnology#blockchaindeveloper#blockchainmeaning
0 notes
Text

#Blockchain, #NFTs, #DeFi & #yschool #learning #schoollearning #blockchainlearning #blockchaintechnology #whatisblockchain #whatisblockchaintechnology #blockchaindeveloper #blockchainmeaning
#Blockchain#NFTs#DeFi &#yschool#learning#schoollearning#blockchainlearning#blockchaintechnology#whatisblockchain#whatisblockchaintechnology#blockchaindeveloper#blockchainmeaning
0 notes
Text
Blockchain is a powerful tool that can streamline many processes and make them more secure. With a better understanding of how it works, you can utilize this technology to its full potential.
https://yschool.in/
#Blockchain, #NFTs, #DeFi & #yschool #learning #schoollearning #blockchainlearning #blockchaintechnology #whatisblockchain #whatisblockchaintechnology #blockchaindeveloper #blockchainmeaning
#Blockchain#NFTs#DeFi &#yschool#learning#schoollearning#blockchainlearning#blockchaintechnology#whatisblockchain#whatisblockchaintechnology#blockchaindeveloper#blockchainmeaning
0 notes
Text
You can learn such competencies through the comprehensive solutions offered here at Yschool.
https://yschool.in/
#Blockchain, #NFTs, #DeFi & #yschool #learning #schoollearning #blockchainlearning #blockchaintechnology #whatisblockchain #whatisblockchaintechnology #blockchaindeveloper #blockchainmeaning
#Blockchain#NFTs#DeFi &#yschool#learning#schoollearning#blockchainlearning#blockchaintechnology#whatisblockchain#whatisblockchaintechnology#blockchaindeveloper#blockchainmeaning
0 notes
Text
Blockchain
With the right prerequisite skills, you can master blockchain technology and pursue an exciting new career.
https://yschool.in/
#Blockchain, #NFTs, #DeFi & #yschool #learning #schoollearning #blockchainlearning #blockchaintechnology #whatisblockchain #whatisblockchaintechnology #blockchaindeveloper #blockchainmeaning
#Blockchain#NFTs#DeFi &#yschool#learning#schoollearning#blockchainlearning#blockchaintechnology#whatisblockchain#whatisblockchaintechnology#blockchaindeveloper#blockchainmeaning
0 notes
Text
Blockchain Technology: The Future Of Employment - Learn Here
https://yschool.in
#Blockchain, #NFTs, #DeFi & #yschool #learning #schoollearning #blockchainlearning #blockchaintechnology #whatisblockchain #whatisblockchaintechnology #blockchaindeveloper #blockchainmeaning
#Blockchain#NFTs#DeFi &#yschool#learning#schoollearning#blockchainlearning#blockchaintechnology#whatisblockchain#whatisblockchaintechnology#blockchaindeveloper#blockchainmeaning
0 notes