Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Assignment #3
Title: Design and Implementation of IoT Based Management System
Authors: J. Kokila, K. Gayathri Devi, M. Dhivya and C. Haritha Jose
Date of publication: 2017
This paper focused on the integration of Radio Frequency Identification, sensors, Arduino controller and GSM in solid waste bin and truck monitoring system measured in real time environment.
“The sensors are placed in the garbage bins at the public places. When the pre-defined level of the garbage in the smart bin is reached, indication will be given by the controller to the driver of waste collection truck.” – this statement helped the proponent on the conception on the idea of waste management and how it can be implemented and be further modified.
The literature review was organized in a methodological manner.
Literature Review
The outdated management information systems, lack in the use of modern techniques and best practices, nominal involvement and awareness of the public towards waste management, lack of scientific and skilled manpower, lack of integrated system for the efficient monitoring and disposal of waste, and inappropriate planning for the management of waste lead the development of an integrated system which aims to reduce the operational and environmental cost.
The paper developed a Web based android application interfaced with a web server for the municipality to monitor the cleaning process performed by the workers. The system provided a database containing the bin status, waste amount in the bin, time of the collection of waste. The data collected was processed by graph theory optimization algorithms to find the shortest path in reaching the bin as one of the waste collection strategies to reduce the cost.
The demand for the development of an intelligent alerting system integrated with RFID and IoT for proper innovative management of garbage is increasing day by day as it requires less maintenance in the disposal of waste. The proposed system is very beneficial to the municipal authority in monitoring the waste collection status in real time environment and measuring the performance of yardman, which results in reduced the manual process of monitoring and verification [1].
Title: Smart Trash Can Using Internet of Things
Authors: M. Priya, C. Shiny Sherlin, K. Sathyapriya, F Arshya Banu
Date of publication: May 2017
The paper aims to regulate the waste management system of Municipal in India by using Internet through connecting the trash bins to the internet. It will update the status of the trashcan to the Municipal so that the bins will be cleaned before the waste overflows.
“This project aims to design an IoT enabled trashcan which will automatically and frequently intimate the status of the trashcan to the Municipality.” – this quotation gave the proponent the idea in adding the said functionality to the proposed study and its efficient application to the current dilemma in waste management.
The literature review section of this paper is organized in a thematic way.
Literature Review
Environmental cleanliness is the most important factor to be considered in the developing countries. The study aims to automate the waste management system. Using IoT, the level of the garbage in the trashcan can be automatically projected to the Municipality via the mobile application. Hence, the status of the trashcan can be continuously monitored by the authorized personnel in each local area can covered by the Municipality.
This smart trashcan has three Infrared sensors which are used to find the level of the garbage in the trashcan. If the level reaches the threshold value, Raspberry pi model will send message to a mobile application as well as to an IoT cloud. In addition, the trashcan will have separate section for degradable and non-degradable wastes. The wastes which are thrown to the trashcan will fall on a plate. A capacitive is used to detect the degradable and non- degradable wastes. Initially the trashcan for non-degradable wastes is placed under the plate. If the public put the degradable wastes, a motor will rotate the trashcan for degradable waste under the plate. Then the waste will fall on the correct section. This project will help to improve the waste management system as it also helps avoid manual separation of wastes.
The entire setup of the project is done to manage the wastes in the bus stand, classrooms, and it also can be implemented in the garbage bins which are kept in the streets of the residential areas [2].
Title: IoT-Based Smart Garbage System for Efficient Food Waste Management
Authors: Insung Hong, Sunghoi Park, Beomseok Lee, Jaekeun Lee, Daebeom Jeong, and Sehyun Park
Date of publication: 28 August 2014
In this paper, battery-based smart garbage bins (SGBs) were proposed to reduce the amount of food waste which is IoT-based. SGBs function by exchanging information with each other using wireless mesh networks, the router and a server collect and analyze the information for service provisioning.
“Owing to the recent advances in mobile devices equipped with various sensors and communication modules, together with communication network technologies such as Wi-Fi and LTE, the IoT has gained considerable academic interests.” – as presented by the researcher, the reliability, mobility, service continuity, user convenience, and energy efficiency greatly influenced the utilization of IoT devices.
The literature review of the paper was arranged in a thematic manner.
Literature Review
As a major application field of IoT, waste management has become such an issue. The absence of efficient waste management has caused serious environmental problems and cost issues. In this paper, an IoT-based Smart Garbage Bin (SGS) were developed for replacing existing RFID-based (Radio Frequency Identification) garbage collection systems. The basic system structure of a SGB is a centralized structure where the data gathered in each bin is transferred to the server. HSGB (Header Smart Garbage Bin) we also designed to improve the battery lifetime of each SGB through two types of energy-efficient operations: stand-alone operation and cooperation-based operation. An adaptive user-oriented charge policy was used to motivate residents to reduce their food waste, and Web-based services are provided to achieve more efficiency in the disposal and collection processes.
The system had been operated as a pilot project in Gangnam district, Seoul, Republic of Korea, for a one-year period. The experiment showed that the average amount of food waste could be reduced by 33%. A rate of 16% showed that SGBs can contribute to not only a reduction of food waste but also energy saving. The proposed system along with the adaptive user-oriented charge policy resulted in a reduction of food waste of about 33%, and it is expected that the proposed system will thereby improve the efficiency of food waste management.
Nevertheless, the system requires more maintenance cost than the existing system. As there is a tradeoff owing to the system’s battery-based power structure, photovoltaic power generation is being considered to improve its battery life. Moreover, high-intensity plastic materials are also being considered for durability against external impact and corrosion from humidity [3].
Title: Garbage Monitoring System for Smart Cities
Authors: Lilyan Anthony, Pradnya Chavan , Astrid Ferreira, Prerana Gadhave, Archana Shirke
Date of publication: April 2017
The objective of the system is to optimize waste collection by generating a trigger. The trigger informs the authorities about the overflow of garbage. Thus, fuel emission and consumption usage can be reduced as optimized routes will be undertaken. And essentially, transportation cost will also decrease.
“The system is supposed to work with any type of container and any type of waste, including mixed materials, paper, glass, metals and fluids.” – the quoted sentence added to the abstraction of the innovation of smart garbage bins as the system can be used in hospitals, colleges universities, industries and various other campuses to cover an entire vicinity or city for the convenience of all.
The literature review section of this paper was organized in a thematic manner.
Literature Review
Overflowing garbage bins have been one of the causes of concern for the people in developing countries. With increase in population, the scenario of cleanliness with respect to garbage management is degrading massively. With the already prevailing diseases, the open containers are proving to be a breeding place for germs. The study aims to collect large amount of waste of material in least amount of time along the way.
It is an automatic dustbin monitoring system in order to detect the full condition of the garbage bins. This provides the authorized users timely updates of the status of the garbage bins and thus eliminates the need for periodic manual checks and overflowing garbage bins. This paper also provides an additional feature to add new message receivers or alter the existing authorized users. It also aims at a classification of different waste and thus promoting waste management. Also, the WiMAX technology can be used instead of Bluetooth to cover large areas, but for cost effectiveness, we are implementing this system using Bluetooth [4].
Title: A Novel Approach to Garbage Management Using Internet of Things for Smart Cities
Authors: Kasliwal Manasi H., Suryawanshi Smitkumar B.
Date of publication: May 2016
The paper presented the application of Garbage Management using Internet of Things in organizing the waste management, particularly residential or commercial areas of smart cities. The detection of garbage level of the waste materials is through the use of ultrasonic sensor and it will continuously send the gathered data to the authorized control room through GSM module.
“A GUI is also developed to supervise the desired information related to the garbage for various selected locations.” – the quoted statement influenced the addition of the mentioned feature above to the proponent’s idea conception as to monitor the garbage bins placed at the different locations in a city or vicinity. A GUI can be a good visual aid in monitoring the garbage bins can also reduce false reports and pranks.
The literature review of this paper is arranged in a methodological way.
Literature Review
Micro-controller interfaced the sensor system with GSM system.
As wastes in the dustbin increase, the distance measured by the ultrasonic sensor placed at top of dustbin also reduces. When this distance becomes less than 25cm, a message is sent to the control room indicating the overflow along with the floor number of the dustbin. Before sending message to control room ultrasonic sensor check for 10sec whether the garbage level detected is correct or if it is false vale. If the detected vale is false vale, then ultrasonic sensor will not send any value and keep collecting further values. If values are true, then it will send message to control room. In control room there is GUI interface on MATLAB which will show cleaner’s name, his mobile number, dustbin level and location of dustbin. Then, a message is sent to the cleaner of that floor. Also, status of each dustbin (percentage of being filled) is sent to the control room, every passing hour [5].
Title: IoT Based Smart Garbage and Waste Collection Bin
Authors: S. S. Navghane, M. S. Killedar, Dr. V. M. Rohokale
Date of publication: May 2016
The overloaded garbage bins placed at public places created unhygienic conditions to people as well as ugliness to that place leaving bad smell insinuated the implementation of ‘IoT Based Smart Garbage and Waste Collection Bin’ project. The interfaced dustbins with microcontroller had an IR wireless system which are showed on a mobile web browser in a html page through Wi-Fi shows the current status of garbage. Hence, the status will be updated on to the html page.
“And the message can be sent directly to the cleaning vehicle instead of the contractor’s office.” – instead of having a control room per district that can monitor all the bins allotted on that specific location, the message can be sent directly to the garbage collection vehicle designated to that particular place is more efficient. And as suggested by the researchers, the idea of smart garbage bins can be further innovated.
The literatures in the literature review section of this paper are organized in a thematic order.
Literature Review
the application of Internet went beyond just connecting to the web, the tremendous demand and necessity led to the birth of Internet of Things (IoT). Home automation industry and transportation industries are evolving rapidly with IoT. Yet not many articles have been published in this field of study. And so, the paper aims to construct the technology, history and applications of IoT along with various statistics.
Sensors on IoT are deployed everywhere which convert raw physical data into digital signals and transmits them to its control center. By this way we can monitor environment changes remotely from any part of the world via internet. As the system’s architecture would be based on the operations and processes in real-time scenarios, the implementation of smart garbage management system using IR sensor, microcontroller and Wi-Fi module relies heavily on the Wi-Fi module. The system assures the cleaning of dustbins when the garbage level reaches its maximum, record is sent to the higher authority to take appropriate actions if the dustbin is not cleaned at a specific time. The proposed system also helps in monitoring fake reports and thus reduces the total number of trips of garbage collection vehicle which lead to the reduced overall expenditure of the garbage collection. As the smart garbage management system makes the garbage collection more efficient, it is still vulnerable to the different components plundering which needs to be worked on [6].
Title: Smart Garbage Monitoring System using Internet of Things (IOT)
Authors: Prof. Dr. Sandeep M. Chaware, Shriram Dighe, Akshay Joshi, Namrata Bajare, Rohini Korke
Date of publication: January 2017
The detection, monitoring and management of wastes is one of the main dilemma of the present day. The ‘IoT Garbage Monitoring System’ monitors and informs the waste level of garbage bins via web page. The developed web page also sends the information to the garbage collector vehicles designated to collect waste materials.
“The system provided an improved database of garbage collection time and waste amount per location.” – the provision of an improved database by the system is relevant to the proponent’s idea conception as to how the data collected can be further utilized in terms of analysis and forecasting as a basis of the actions that must be taken if circumstances may arise.
The literature review of this paper is arranged in a methodological manner.
Literature Review
One of the primary concerns with our current environment has been solid waste management not only by disrupting the balance of the environment but also the adverse effects on the health of the society. The traditional way of manually monitoring the wastes in waste bins is a complex, troublesome process and needs more human effort, time and cost. The automation of waste management can help avoid the overflow of garbage from the container by monitoring the waste level of garbage bins.
As the system ensures the perfect practice of solid garbage collection process monitoring and management for green environment, the integration of Wi-Fi modem, IoT, GSM, Ultrasonic Sensor introduced an efficient and economic utilization these technologies. The system monitors the garbage bins and informs about the level of garbage collected in the garbage bins via a web page. This web page also sends all information to garbage collection vehicles
The usage of ultrasonic sensors on the bins is able to detect the garbage level and compare it with the garbage bins depth. The system makes use of Arduino family microcontroller, LCD screen, Wi-Fi modem for sending data and a buzzer. The system is powered by a 12V transformer. The LCD screen is used to display the status of the level of garbage collected in the bins.
The developed web page projects the status of the garbage bins by providing a graphical view in color to show the level of garbage collected. The LCD screen shows the status of the garbage level. The system puts on the buzzer when the level of garbage collected crosses the set limit. Thus, the system helps to keep the city clean by informing about the garbage levels of the bins by providing graphical image of the bins via a web page [7].
Title: Intelligent Monitoring System for Garbage Waste Bins Using Arduino
Authors: R. B. Tapase, Ashwini Mohite, Trupti Kadam, Puja Deshmukh
Date of publication: December 2016
Designing an Arduino-based system in monitoring garbage in a particular area to avoid pollution, unhygienic condition, bad smell is the main objective of this proposed project. The dustbins are microcontroller-based interfaced system having ultrasonic sensor showing the current status of garbage on android device.
“We can use video processing, which will improve the reliability of circuit. Also, we can add GPS modem to this project hence, it will help to track the position of dust bin. We can create new application also for garbage monitoring which will show overview of dustbin.” – the stated phrase gave the proponent the concept on how the existing system can be further developed if certain circumstances may arise. For instance, if the device be stolen or misplaced, the GPS modem can locate its position as suggested by the study.
The literature review of this study was organized in a methodological manner.
Literature Review
At present, the garbage bins placed at public area are overflowing due to increase in solid waste everyday which results in unhygienic conditions for all people and disturbing ambiance around the surroundings.
By implementing this project, monitoring the garbage level in the dust bins placed at public places, we can collect garbage which will avoid the waste overflow in helping reduce pollution as well as different hazards to health. When waste reaches the level of sensor, a signal will be given to the microcontroller unit then the microcontroller sends signal to the user through GSM. This system will reduce the expenditure of fuel by reducing number of trips of garbage collection vehicle. Hence, intelligent garbage monitoring system will make the garbage collection more efficient [8].
Title: Automatic Waste Segregator and Monitoring System
Authors: Aleena V.J., Kavya Balakrishnan, Rosmi T.B., Swathy Krishna K.J., Sreejith S, T.D. Subha
Date of publication: January 2016
This paper proposed a cheap and easy to use automatic waste segregator for households. Automatic waste segregator is designed to sort the waste into three main categories namely; metallic, organic and plastic. Ultrasonic sensors are used in monitoring waste collection process. If the waste level reaches the sensor placed in all garbage bins, a signal will be then sent to the microcontroller. The microcontroller will give indication to the driver of garbage collection truck by sending SMS using GSM technology.
“The system sorts waste into three different categories, namely metal, plastic and organic waste.” – this quote gave the proponent how the proposed study determines degradable and non-degradable waste materials.
The literatures in the literature review section of this paper are organized in a methodological manner.
Literature Review
The segregation, transport, handling and disposal of waste must be managed properly in metro cities and urban areas to minimize the risks to the public, and to the environment. The “Automatic Waste Segregator and Monitoring System” segregates wastes materials into three different categories; metal, plastic and the wet waste.
The system was tested on household wastes which yielded the following result: the system is able to monitor the solid waste collection process and management of the overall collection process. The waste segregator can segregate the waste into three major classes: plastic, organic, metallic. The inlet section is provided with open and close mechanism to regulate the flow of waste on to the conveyor. Inductive proximity sensor is used to detect the metallic waste. A blower mechanism is used to segregate dry and wet waste. The timing and movement of the conveyor belt is controlled by Arduino Uno. Continuous and unnecessary operation of any particular section is thus avoided.
Separating our waste is essential as the amount of waste being generated today causes immense problem [9].
Title: Smart Garbage Management System
Authors: Vikrant Bhor, Pankaj Morajkar, Maheshwar Gurav, Dishant Pandya
Date of publication: March 2015
The proposal of ‘smart garbage management system’ which detects the level of waste in the dustbins using sensor systems, and communicates to the authorized control room through GSM system to assist overflowing dustbins. Microcontroller is used to interface the sensor system with GSM system. A GUI is also to oversee the waste collection efficiently at chosen areas.
“A GSM Module is connected to the computer of the control room through microcontroller. The same GSM Module is used to send the message to the personnel in charge of cleaning the dustbin.” – the abstraction of how the GSM and microcontroller work together gave the proponent the plausible idea of the mechanism of the proposed study.
The literature review portion of this paper are written in a methodological manner.
Literature Review
The paper presents the implementation of smart garbage management system using IR sensor, microcontroller and GSM module. The system guarantees the cleaning of dustbins when the waste reaches its maximum level. If the dustbin is not cleaned in a particular time, the record is then sent to the higher authority who can take fitting action against the concerned contractor. Moreover, the system can monitor fake reports which reduces the total number of trips of garbage collection vehicle and hence the reduction of the total expenditure associated with garbage collection. Therefore, the smart garbage management system makes the garbage collection more efficient. The paper also recommends the use of solar panels to reduce the energy consumption [10].
References:
[1] J. Kokila, K. Gayathri Devi, M. Dhivya and C. Haritha Jose , “Design and Implementation of IoT Based Waste Management System,” Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 995-1000, 2017
[2] I. Hong, S. Park, B. Lee, J. Lee, D. Jeong, and S. Park, “IoT-Based Smart Garbage System for Efficient Food Waste Management,” The Scientific World Journal, pp. 13, 2014, Retrived from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/646953
[3] L. Anthony, P. Chavan, A. Ferreira, P. Gadhave, A. Shirke, “Garbage Monitoring System for Smart Cities,” International Journal of Adavanced Technology in engineering and Science vol. 5, no. 4, April 2017
[4] M. H. Kasliwal, S. B. Suryawanshi, “A Novel Approach to Garbage Management Using Internet of Things for Smart Cities,” International Journal of Current Trends in Engineering & Research, vol. 2 no. 5, pp. 348 – 353, May 2016, Retrieved from: http://www.ijcter.com
[5] S. S. Navghane, M. S. Killedar, Dr. V. M. Rohokale, “IoT Based Smart Garbage and Waste Collection Bin,” International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Communication Engineering, vol. 5, no. 5, May 2016
[6] Prof. Dr. S. M. Chaware, S. Dighe, A. Joshi, N. Bajare, R. Korke, “Smart Garbage Monitoring System using Internet of Things (IOT),” International Journal of Innovative Research in Electrical, Electronics, Instrumentation and Control Engineering, vol. 5, no. 1, January 2017
[7] R.B.Tapase, A. Mohite, T. Kadam, P. Deshmukh, “Intelligent Monitoring System for Garbage Waste Bins Using Arduino,” International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology, vol. 5 no. 12, December 2016, Available @ http://ijret.org
[8] V.J. Aleena, K. Balakrishnan, T.B. Rosmi, S. K.J. Krishna, S. Sreejith, T.D. Subha, “Automatic Waste Segregator and Monitoring System,” Journal of Microcontroller Engineering and Applications, vol. 3, no. 2, January 2016, Retrieved from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317720527
[9] V. Bhor, P. Morajkar, M. Gurav, D. Pandya, “Smart Garbage Management System,” International Journal of Advanced Research Methodology in Engineering & Technology, vol. 4, no. 3, March 2015
[10] F. A. Banu, M. Priya C. ShinySherlin, K. Sathyapriya, “Smart Trash Can Using Internet of Things,” International Journal of Advanced Research Methodology in Engineering & Technology, vol. 1, no. 3, May 2017
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Assignment #2
1. Based on your previous readings, identify a topic that you would want to work on a thesis.
The topic that the proponent came up with after the previous readings was ‘Smart Garbage Bins or USeP’ that can detect the overflow of waste materials in the garbage bins located at USeP which can be monitored on the phone web browser of the janitors via internet. The proposed tittle aims to determine and segregate waste materials from degradable and non-degradable.
3.
The selected journals follow a certain outline, starting from introduction, materials and methods, results, discussion, conclusion, and acknowledgements and references. Each paper may have an architectural framework of the system or a flow chart. The selected papers also presented figures of the devices and materials that will be used. Sample data can also be found from each paper from their developed prototype.
The following are the terms and concepts which were unknown to the blogger which are therefore defined:
1. GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) - is a digital mobile telephony system which uses variation of time division multiple access (TDMA). GSM digitizes and compresses data, then sends it down a channel with two other streams of user data, each in its own time slot [1].
2.Ultrasonic Sensor - is a device which measures the distance to an object by using sound waves. It measures distance by sending out a sound wave at a specific frequency and listening for that sound wave to bounce back. By recording the elapsed time between the sound wave being generated and the sound wave bouncing back, it is possible to calculate the distance between the sonar sensor and the object. To find the distance to the object, simply divide the round-trip distance in half [2].
3. Raspberry Pi - is a low cost, credit card-sized computer that plugs into a computer monitor or TV, and uses a standard keyboard and mouse that enables people of all ages to explore computing, and to learn how to program in languages like Scratch and Python. Creator Eben Upton's aimed to create a low-cost device that would improve programming skills and hardware understanding at the pre-university level [3].
4. Infrared Sensor - An infrared sensor is an electronic instrument used to sense certain characteristics of its surroundings by either emitting and/or detecting infrared radiation. Infrared sensors are also capable of measuring the heat being emitted by an object and detecting motion. Thermal and Quantum infrared sensors are the two main types of infrared sensors [4].
5. Arduino - is an open-source platform used for building electronics projects. Arduino consists of both a microcontroller and an IDE that runs on your computer to write and upload computer code to the physical board. Additionally, the Arduino IDE uses a simplified version of C++ [5].
Claims from each selected paper with supporting evidences:
1. Design and Implementation of IoT Based Management System
“However, the group of the people involved in collecting and transporting the wastes are usually not responsible enough to make the job well done.” – this claim lead to the author’s conclusion on “Very often the wastes are not collected from each and every waste bin properly due to driver’s attitude lethargy” which was further supported by Md. Liakot Ali et. al [41, 6].
“The NIR reflectance spectroscopy helps to distinguish and eliminate plastic item from MSW and provides all biodegradable substance that can be further used in biogas plant.” – the introduction of NIR spectroscopy further discussed its usability to the proposed system as cited in [41, 7].
“Implementation of the above smart bin can prevent lumping of the trash for a longer period of time thereby preventing the widespread of diseases to a great extent and promising a clean environment in the city [41, 8].” – as this statement is one of the major objectives of the proposed paper, this claim adequately supports the implementation of the system and its underlying good outcomes.
2. IoT-Based Smart Garbage System for Efficient Food Waste Management
“The term Internet of Things was introduced by Kevin Ashton, who was the director of the Auto-ID Center of MIT in 1999 [42, 9].” – the author cited the introduction of internet of things (IoT) as its basic idea were primarily discussed.
“For IoT applications performing these functions, a variety of researches on IoT services including environmental monitoring [42, 10, 11], object tracking [42, 12], traffic management [42, 13], health care [42, 14], and smart home technology [42, 15, 16] are being conducted.” – this claim fully utilized today’s technology, particularly IoT devices which insinuated the pursue of this proposal.
“To handle these problems, various researches into waste management based on IoT technology have been conducted, from studies on RFID technology to studies on waste management platforms and systems [42, 17-21].” – as this claimed was cited by many references, it highly proved the dilemma in waste management and the need for innovation concerning food waste management.
3. Garbage Monitoring System for Smart Cities
“In [43, 22], they came to a point It is important to understand the societal concerns over the increased rate of resource consumption and waste production.” - the paper presented how law makers were urged to impose recycling and reuse strategies in reducing the demand for raw materials and the waste quantity.
“In [43, 23], it is being proposed in this paper that introduction of an integrated system combined with an integrated system of Radio Frequency Identification, Global Position System, General Packet Radio Service, Geographic Information System and web camera will solve the problem of solid waste.” – this claim was supported when the data of the actual performance of the system were gathered and analyzed.
“The present garbage management system is not efficient enough to take care of the large amount of waste matter that is generated every day because the garbage bins are overflowing. This causes air and water pollution. This also increases number of diseases as large number of insects and mosquitoes breed on this waste [43, 24].” – the paper presented the effect of the current dilemma if left unattended which was cited above. Thus, this urged the development of an efficient garbage management system.
4. A Novel Approach to Garbage Management Using Internet of Things for Smart Cities
“Proper management of waste materials is important to maintain healthy and hygienic environment to live [44, 25].” – this claim is a positive counter of the preceding sentences that people are investing less in waste management relates software due to the rapid increase of population and the lack of public awareness.
“As per the research of Central Public Health and Environmental Engineering Organization, the total amount of waste generated in India is approximately 1.3 pounds per person every single day” – this claim was countered by “This figure is comparatively less compared to 4.6 pounds of waste generated per person every day in the United States [44, 26]”, to show the immense and immediate response to an efficient garbage management system.
“But the U.S. population was approximately 307 million in July 2009, whereas India’s population was 1.2 billion.” – this claim is supported by “These statistics shows that India is generating almost 27 million more tons of waste than the U.S. every year [44, 27]”, to present realism of the situation in numbers.
5. IoT Based Smart Garbage and Waste Collection Bin
“A review on Internet of Things gave the idea of IoT subject and addition details about IoT. The proper smart environment and various applications [45, 28].”
“A study by Arkady Zaslavsky, Dimitrios Georgakopoulos. This paper gave us the details about mobile analysis and sensor information management helped in data segregation of various dustbins [45, 29].”
“Smart Garbage management System by Vikrant Bhor et al provided additional details and designs needed for flow and management of garbage while collection [45, 30].”
These claims added up and paved the way to the proposal of the said system.
6. Smart Garbage Monitoring System using Internet of Things (IOT)
“It can prevent pollution and also prevent the consumption of the spread-out garbage by the street animals [46, 31].” – this claim is the conclusion deducted by the author prior to how smart dustbins can prevent the accumulation of the garbage along the roadside to a great extent thereby controlling the widespread of many diseases.
“The zig bee and GSM system would be able to monitor the solid waste collection process [46, 32].” – this statement was deduced by the author after presenting the usability of the devices to used; “The range of communication of the zig bee is almost 50 meters. They use for range GSM Module, analyzing the image we get an idea about level of garbage.”
“The dynamic routing of GCV compared with static solution is much more efficient and will be much effective when more than one dustbin fills up at the same time [46, 33].” – this claim is further innovated by the idea of " The initial planned route is saved so that when real-time data is received only portion of the planned path may be changed,” which lead to this sophisticated system proposal.
7. Intelligent Monitoring System for Garbage Waste Bins Using Arduino
“[47, 34]. The waste bin monitoring system using integrated technologies placed the sensor in the garbage bin at maximum level, if that level is crossed by garbage in bin, then sensor will sense that and communicate to ARM7 controller through Zig Bee technology.”
“[47, 34]. City garbage collection indicator using RF(ZigBee) and GSM technology gave transmission of data to receiver side and also the main channel flow of the project.”
“[47, 34]. A review about Garbage and street light monitoring system using internet of things include garbage as well as street light monitoring which avoids accident during night.”
The stated claims above gave the idea or the abstraction of how the system should work in terms of the sensors to be used, and the principles that can be used in other ways to reduce power consumption and manpower.
8. Automatic Waste Segregator and Monitoring System
“When the waste is segregated into basic streams such as plastic, metallic and organic, the waste has a higher potential of recovery, and then, recycled and reused [48, 35].”
“The organic waste is converted either into compost or methane-gas or both [48, 36].”
Both claims presented the common method of waste disposal where it can be hazardous to human health, plant, and life as metallic and organic waste have a higher potential of recovery, and how organic waste can be converted either compost or methane-gas or both.
“The philosophy of “waste management hierarchy” has been adopted by most nations as the step for developing municipal solid waste (MSW) management strategies [48, 37].” – this statement is an attempt to address the preceding text; “In India about 60 million tons of waste is being generated every year. Ten million tons of garbage is generated in metropolitan cities.”
9. Smart Garbage Management System
“For communication purpose ZigBee technology can also be used in the transmitter section [49, 38].” – this claim is supported by the definition and the wide range of applications of ZigBee technology by the author.
“Government of India have struggled for years to find a way to manage the country’s ever-increasing amount of trash [49, 39].” – this claim was proved by the author through laying these sentences: “According to the survey carried out in 1994 the garbage produced in Mumbai is 5800 tons per day. Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (MCGM) operates a huge fleet of 983 Municipal and Private Vehicles for collection of waste making 1396 number of trips each day. Solid Waste Management (SWM) expenditure outlay in the year 2007-08 is Rs.10479.3 Million.”
“A GSM Module is connected to the computer of the control room through microcontroller [49, 40].” – this statement is very well supported by an existing system as to how the model of this system is devised.
10. Smart Trash Can Using Internet of Things
“With the existence of many diseases in our Nation, the open containers are proving to be a breeding place for germs [50].” – this claim was countered by how municipalities operate on weekly routes to pick up waste in the garbage bins on designated days. This supporting text was again countered by this phrase; “but regardless of whether the containers are full or not, municipalities collect waste on designated days” which clearly showed the need for the modification of the existing waste management system.
“It will update the status of the trashcan to the Municipal so that the garbage will be cleaned earlier to the overflow stage [50].” – this statement is further supported by the technical capability of the three Infrared sensors to find the garbage level in the trashcan.
“The trashcan will have separate section for degradable and non-degradable wastes [50].” – such claim is supported by the use of the plate acting as a capacitive in determining non-degradable from degradable waste and vice versa. For instance, if an individual place the degradable waste, a motor will rotate the trashcan for degradable waste under the plate. Then the waste will fall on the correct section.
References:
[1] “What is GSM (Global System for Mobile communication)? - Definition from WhatIs.com,” SearchMobileComputing. [Online]. Available: http://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/GSM. [Accessed: 03-Feb-2018].
[2] “Ultrasonic Sensor | What is an Ultrasonic Sensor?” [Online]. Available: http://education.rec.ri.cmu.edu/content/electronics/boe/ultrasonic_sensor/1.html. [Accessed: 03-Feb-2018].
[3] “What is a Raspberry Pi?,” Raspberry Pi. .
[4] “The Working Principle and Key Applications of Infrared Sensors,” AZoSensors.com, 07-Oct-2013. [Online]. Available: https://www.azosensors.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=339. [Accessed: 03-Feb-2018].
[5] “What is an Arduino? - learn.sparkfun.com.” [Online]. Available: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/what-is-an-arduino. [Accessed: 03-Feb-2018].
[6] Md. L. Ali, M. Alam and Md. Abu N. R. Rahaman, 2012. RFID based E-monitoring System for Municipal Solid Waste Management, 7th International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering. Bangladesh. Proceedings, pp: 474-477.
[7] S. Thakker and R. Narayanamoorthi, 2015. Smart and Wireless Waste Management an innovative way to manage waste and also produce energy, IEEE Sponsored International conference on Innovations in Information Embedded and communication Systems, Proceedings, pp: 1-4.
[8] Twinkle Sinha, K. Mugesh Kumar and P. Saisharan, 2015. Smart dustbin, International Journal Industrial Electronics and Electrical Engineering, 3: 1-4.
[9] K. Ashton, “That “internet of things” thing,” RFiD Journal, vol. 22, pp. 97–114, 2009.
[10] M. T. Lazarescu, “Design of a WSN platform for long-term environmental monitoring for IoT applications,” IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 45–54, 2013.
[11] S. D. T. Kelly, N. K. Suryadevara, and S. C. Mukhopadhyay, “Towards the implementation of IoT for environmental condition monitoring in homes,” IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 3846–3853, 2013.
[12] K. Gama, L. Touseau, and D. Donsez, “Combining heterogeneous service technologies for building an internet of things middleware,” Computer Communications, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 405–417, 2012.
[13] L. Foschini, T. Taleb, A. Corradi, and D. Bottazzi, “M2M-based metropolitan platform for IMS-enabled road traffic management in IoT,” IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 49, no. 11, pp. 50–57, 2011.
[14] A. J. Jara, M. A. Zamora, and A. F. G. Skarmeta, “An internet of things-based personal device for diabetes therapy management in ambient assisted living (AAL),” Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 431–440, 2011.
[15] S. Tozlu, M. Senel, W. Mao, and A. Keshavarzian, “Wi-Fi enabled sensors for internet of things: a practical approach,” IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 134–143, 2012.
[16] X. Li, R. Lu, X. Liang, X. Shen, J. Chen, and X. Lin, “Smart community: an internet of things application,” IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 49, no. 11, pp. 68–75, 2011.
[17] I. Nielsen, M. Lim, and P. Nielsen, “Optimizing supply chain waste management through the use of RFID technology,” in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on RFIDTechnology and Applications, pp. 296–301, Guangzhou, China, June 2010.
[18] Z. Lizong, A. Anthony, and H. Yu, “Knowledge management application of internet of things in construction waste logistics with RFID technology,” International Journal of Computing Science and Communication Technologies, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 760–767, 2012.
[19] B. Chowdhury and M. U. Chowdhury, “RFID-based realtime smart waste management system,” in Proceedings of the Telecommunication Networks and Applications Conference, pp. 175–180, December 2007.
[20] M. A. Hannan, M. Arebey, R. A. Begum, and H. Basri, “Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and communication technologies for solid waste bin and truck monitoring system,” Waste Management, vol. 31, no. 12, pp. 2406–2413, 2011.
[21] P. Pratheep and M. A. Hannan, “Solid waste bins monitoring system using RFID technologies,” Journal of Applied Sciences Research, vol. 7, no. 7, pp. 1093–1101, 2011.
[22] M. Al-Maadeed, N. K. Madi, Ramazan Kahraman, A. Hodzic, N. G. Ozerkan , An Overview of Solid Waste Management and Plastic Recycling in Qatar, Springer Journal of Polymers and the Environment, March 2012, Volume 20, Issue 1, pp 186-194
[23] Islam, M.S. Arebey, M.; Hannan, M.A. ; Basri, H,”Overview for solid waste bin monitoring and collection system"Innovation Management and Technology Research (ICIMTR), 2012 International Conference, Malacca, 258 – 262.
[24] Latifah, A., Mohd, A. A., & Nur Ilyana, M. (2009). Municipal solid waste management in Malaysia: Practices and challenges. Waste Management, 29, 2902-2906.
[25] “Microsoft Excel Dashboard & Reports”, of Michael Alexander, John Walkenbach and Wiley.
[26] “Trash Plant: India”, by Marian Look earth911B.
[27] Feature of “Solid waste Management Project”.
[28] P.Suresh1J. Vijay Daniel2, Dr.V.Parthasarathy4” A state of the art review on the Internet of Things (IoT)” International Conference on Science, Engineering and Management Research (ICSEMR 2014)
[29] Arkady Zaslavsky, Dimitrios Georgakopoulos” Internet of Things: Challenges and State-of-the-art solutions in Internet-scale Sensor Information Management and Mobile Analytics” 2015 16th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management.
[30] Vikrant Bhor, Pankaj Morajkar, Maheshwar Gurav, Dishant Pandya4 “Smart Garbage Management System” International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) ISSN: 2278-0181 IJERTV4IS031175 Vol. 4 Issue 03, March-2015
[31] Twinkle sinha, k.mugesh Kumar, p.saisharan, “SMART DUSTBIN”, International Journal of Industrial Electronics and Electrical Engineering, ISSN: 2347-6982 Volume-3, Issue-5, May2015.
[32] Kanchan Mahajan, Prof.J.S.Chitode, “Waste Bin Monitoring System Using Integrated Technologies”, International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology (An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization) Vol. 3, Issue 7, July 2014.
[33] Richu Sam Alex, R Narciss Starbell, “Energy Efficient Intelligent Street Lighting System Using ZIGBEE and Sensors”, International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 2249 – 8958, Volume-3, Issue-4, April 2014.
[34] Ms. Ashwini Mohite, Student,Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Engineering, Annasaheb Dange College of Engineering and Technology Ashta, Maharashtra, India.
[35] Pushpa MK, et al. Microcontroller Based Automatic Waste Segregator. International Journal of Innovative Research in Electrical, Electronics, Instrumentation and Control Engineering (IJIREEICE). May 2015; 3(5).
[36] N. Kothari. Waste to Wealth. New Delhi: NSWAI; Jul 2013.
[37] D. Hoornweg, et al. What a Waste: A Global Review of Solid Waste Management. Washington, DC: Urban Development & Local Government Unit World Bank, No.15; Mar 2012.
[38] Hindustan Embedded System, “City Garbage collection indicator using RF (ZigBee) and GSM technology”.
[39] Basic Feature, “Solid waste Management Project by MCGM”.
[40] Z embedded, “GSM modem interfacing with 8051 for SMS” August 2012.
[41] J. Kokila, K. Gayathri Devi, M. Dhivya and C. Haritha Jose , “Design and Implementation of IoT Based Waste Management System,” Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 995-1000, 2017
[42] I. Hong, S. Park, B. Lee, J. Lee, D. Jeong, and S. Park, “IoT-Based Smart Garbage System for Efficient Food Waste Management,” The Scientific World Journal, pp. 13, 2014, Retrived from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/646953
[43] L. Anthony, P. Chavan, A. Ferreira, P. Gadhave, A. Shirke, “Garbage Monitoring System for Smart Cities,” International Journal of Adavanced Technology in engineering and Science vol. 5, no. 4, April 2017
[44] M. H. Kasliwal, S. B. Suryawanshi, “A Novel Approach to Garbage Management Using Internet of Things for Smart Cities,” International Journal of Current Trends in Engineering & Research, vol. 2 no. 5, pp. 348 – 353, May 2016, Retrieved from: http://www.ijcter.com
[45] S. S. Navghane, M. S. Killedar, Dr. V. M. Rohokale, “IoT Based Smart Garbage and Waste Collection Bin,” International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Communication Engineering, vol. 5, no. 5, May 2016
[46] Prof. Dr. S. M. Chaware, S. Dighe, A. Joshi, N. Bajare, R. Korke, “Smart Garbage Monitoring System using Internet of Things (IOT),” International Journal of Innovative Research in Electrical, Electronics, Instrumentation and Control Engineering, vol. 5, no. 1, January 2017
[47] R.B.Tapase, A. Mohite, T. Kadam, P. Deshmukh, “Intelligent Monitoring System for Garbage Waste Bins Using Arduino,” International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology, vol. 5 no. 12, December 2016, Available @ http://ijret.org
[48] V.J. Aleena, K. Balakrishnan, T.B. Rosmi, S. K.J. Krishna, S. Sreejith, T.D. Subha, “Automatic Waste Segregator and Monitoring System,” Journal of Microcontroller Engineering and Applications, vol. 3, no. 2, January 2016, Retrieved from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317720527
[49] V. Bhor, P. Morajkar, M. Gurav, D. Pandya, “Smart Garbage Management System,” International Journal of Advanced Research Methodology in Engineering & Technology, vol. 4, no. 3, March 2015
[50] F. A. Banu, M. Priya C. ShinySherlin, K. Sathyapriya, “Smart Trash Can Using Internet of Things,” International Journal of Advanced Research Methodology in Engineering & Technology, vol. 1, no. 3, May 2017
1 note
·
View note
Text
Audio Compression Technique
Due to the rise of the internet, computers, embedded systems, decreasing memory cost and increasing internet bandwidth, the market is in highly demand of small, high-quality, and convenient formats of audio signals. Since original, uncompressed digital recordings are very large in size, efficient and lossless formats are needed to retain the original audio signals. This blog compares the topic laid out with the different study from various authors with regards to the efficiency of the various audio compression techniques under different constraints like various transmission errors, channel noises and huge data size, which increases channel congestion and transmission delay which the topic is interested to shape in.
The widespread use of high-speed internet, consumers can download and transfer audio files. Audio compression, also known as lossy audio compression techniques make this po ssible by removing inaudible information to the original audio file (e.g. .wav file .aiff file) with minor or no quality loss. However, an encoded audio file can never be recovered.
In order to keep an exact copy of the original file, lossless audio compression must be used. For example, an uncompressed three-minute Wave file, consuming 30.3 Mb of memory, can be reduced to 50 – 60% of its original size, without quality loss and can always possible to obtain the exact original file if needed.
A case study by Rivero and Mishra (2008), which studies dictionary-based compression techniques to see if Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC) can be improved directly or by employing compression techniques from other domains by conducting tests on nineteen quality benchmarks.
The study concluded that the improvement to the FLAC method must come from another domain as results provided only slight improvement. FLAC can be likely improved in the residual coding section by testing other error encoding means. Furthermore, the file size may be possibly reduced using bitmask-based compression in matching data patterns that are not identical using bitmasks.
And as suggested, studying FLAC in order to incorporate near-lossless audio compression to provide the highest quality audio possible by removing unnecessary characteristics of the audio signal is an interesting path to study.
A study by Yen Pan entitled ‘Digital Compression’ (1993) also tackles the various audio compression techniques of different levels of complexity, compressed audio quality, and amount compressed data to provide useful information to of all levels of readers unto digital audio processing. The paper summarized the basic audio digitization process and the detailed descriptions of two relatively simple approaches to audio compression: µ-law and adaptive differential pulse code modulation. The paper also provided an overview of the Motion Picture Experts Group (MPEG).
In conclusion, digital audio compression techniques include µ -law and adaptive differential pulse code modulation both apply low-complexity, low-compression, and medium audio quality algorithms to audio signals. The audio compression algorithm MPEG, is an ISO standard for high-fidelity audio compression. The MPEG has three layers of successive complexity for improved compression performance.
Data loss during big data transmission is one of the aspects stressed by the topic at hand. And so, the use of efficient data compression technique must be highly considered. Data compression can be categorized as lossy and lossless. Lossy technique degrades data quality during compression while lossless compression retains the quality of the input. Lossy compression is generally used for video, audio and image compression like MP3, Mpeg and Jpeg. Variable length coding (VLC) and fixed length coding (FLC) are the two types of lossless compression. Among these two types, VLC is much more efficient as it offers poor robustness against various errors and channel noises during transmission.
Another study by Bhattacharjee et. al (2015) stressed on the solution to the problem of compression efficiency, robustness and time delay in big data transmission. And as mentioned above, the study proposed a FLC based compression technique. The efficiency of the proposed technique under various terms are tested and measured using standard files of various types and size inputs.
The said study found that channel congestion and transmission errors are the major cause of data loss as the big size of data increases the channel congestion during transmission and transmission delay. The proposed fixed length coding based compression technique showed positive results as it offers better compression efficiencies by producing lower compression ratio and better compression percentage than other existing techniques. Its capacity to produce better signal to noise ratio (SNR) and throughput justify its capacity to increase robustness and reduce time delay.
Another study by Dangarwala and Shah (2010) which covers wave audio file format and algorithm of silence compression and companding method in comparing how these methods compress and decompress wave audio file.
The study differentiated that more compression may be achieved using silence compression if more silence values were present in the input audio file. And by decompressing the audio file, the original size can be recovered but not the original data using silence method. On the other hand, companding method is able to adjust compression ratio according to requirement. In decompressing an audio file using companding method, the original size and the original data can be recovered with only minor losses and audio quality.
And finally, the ‘A Comparative Analysis of Data Compression Techniques’ by Souley et. al (2014) which examined Lossless compression and lossy algorithms. The study provided a comparative analysis of the Huffman, Lempel-Ziv and RunLength Encoding compression techniques.
Results revealed that the Lempel-Ziv technique has been proven to be most effective, and works better for Notepad and web documents. The proposed study also stressed that the full implementation of the application could help in effectively handling data transfer and storage by reducing as storage space and transmission bandwidth consumption as these algorithms have been proven to be more effective on notepad, text, web documents, PDF, images and sound. The study also developed a compression and decompression tool to carry out the comparison analysis.
The first study correlates negatively with the topic at hand as it tries to improve FLAC and this blog tries to evaluate the efficiency of existing audio compression techniques. Although the study included the discussion on dictionary-based audio compression, it was not clearly assed and evaluated as this blog aims to correlate the topic at hand and the study of Rivero and Mishra.
The second study correlates positively with the topic at hand as it discusses the different audio compression techniques. On the other hand, the topic at hand aims to evaluate the efficiency of existing audio compression techniques under different constraints like bandwidth over the network speed, and etc. yet, the study only discusses these techniques above the said constraints. Nonetheless, the study also tackled real-time software implorations.
‘A Lossless Compression Technique to Increase Robustness in Big Data Transmission’ by Bhattacharjee et al correlates with topic at hand in terms of trying to resolve the problem about compression efficiency, robustness and time delay on the grounds of big data transmission. As the study introduced variable length encoding and proposed fixed length encoding technique inclines outward the topic at hand as it aims to investigate the efficiency of existing audio compression algorithms.
Dangarwala and Shah study is inclined with the topic at hand as how original wave audio file is compressed and decompressed. However, the topic at hand is focused on what is the most efficient algorithms must be used for compression and decompression of audio files.
Souley et. al correlates exactly as the topic at hand as the study tries to discuss lossless and lossy algorithms. Furthermore, the paper provided a comparative analysis on encoding compression techniques.
As technology keeps upgrading, a lossless compression technique may be achieved in a few years with increasing memory space and decreasing memory cost and increasing internet bandwidth. As I have reviewed, the existing data compression algorithm frames a new algorithm with an unending cycle of building and improving. And so researches such as these are very significant in upgrading the present technology for the optimum utilization of our current resources and the creating of an ever efficient desired outcome; Lossless audio compression technique.
References:
Battacharjee, S. , Rahim, L.B.Ab. , & Aziz, I.B.A. (2015, November) A Lossless Compression Technique to Increase Robustness in Big Data Transmission System. 7(4), 3.
Souley, B. , Das, P. , Tanko, S. (2014). A Comparative Analysis of Data Compression Techniques. Nigeria: New Dehli Publishers
Dangarwala, K. , Shah, J. (2010, Marach) C Implementation & Comparison of Companding & Audio Compression Techniques. 7(2), 3.
Rivero, C. , Mishra, P. (2008). Lossless Audio Compression: Case Study (Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering, Technical Report No. 08-415). Gainesville, FL: University of Florida.
Yen Pan, D. (1993). Digital Audio Compression. 5(2), 2.
0 notes
Text
Decision Tree-Data Mining Modeling Technique RRL
The earliest record of decision tree analysis was created by J. Ross Quinlan. John Ross Quinlan is a computer science researcher in data mining and decision theory. He has contributed greatly to the decision tree algorithms development, including inventing the canonical C4.5 and ID3 algorithms. The Iterative Dichotomiser 3 (ID3) generate decision trees based on Occam's razor principle in attempting to create the smallest, most efficient decision tree possible. Quinlan also developed C4.5 algorithm, and the C5.0 algorithm. (Ross Quinlan 2017)
Decision tree is defined by the Foundations of Operations Management as: “A schematic model of alternatives available to the decision maker, along with their possible consequences.”
Decision tree is an analysis diagram that gives the decision maker an overview of the multiple conditions as an aid in making a wide variety of simple and complex choices. This allows decision makers to predict, explain, describe, or classify an outcome by projecting possible outcomes (DECISION TREE: OPMT n.d.).
It is a decision support tool that uses a tree-like graph or model where the internal node represents a "test", the branch represents the outcome of the test, and each leaf node represents the decision taken after computing all attributes. The paths from root to leaf represent classification rules. Decision tree only have splitting paths and paths never converge (Decision Tree 2017).
Decision tree is one of the many ways to display an algorithm that only contains conditional control statements. It is commonly used in operations research like decision analysis and operations management.
Decision analysis and influence diagram are visual and analytical decision support tool used as a descriptive means for calculating conditional probabilities. The process of calculating the value of each node is known as “folding back” the tree.
Trees are robust in the presence of missing data and offer multiple ways of incorporating missing data in the resulting models. Although trees are powerful, they are also flexible and easy to use methods. This assures the production of high quality results that require few assumptions to deploy. (de Ville 2013)
Lucidchart (What Is a Decision Tree Diagram 2017) presented decision tree symbols as the following:

To illustrate decision tree clearly, the outlook dataset will be used using RapidMiner. The outlook dataset contains the following.


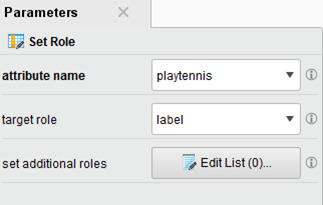
Before adding the decision tree operator, the Set Role operator must be placed. The Set Role operator needs two parameters: attribute name and target role. We set the attribute name as playtennis and label as its target role. Label is needed for the proceeding steps. This is also because we want to know if a player will play tennis or not under different weather conditions.
Add the decision tree operator and connect the example set output to the training set port of the decision tree operator. After which, add the Apply Model operator. Connect the model output of the decision tree as the input model of the Apply Model operator.

But then, the operator will still have a mandatory input as the unlabeled data. and that’s where the same dataset will be added. And finally, connect both the output (labeled data, model) of Apply Model to the result port.

The data produced the following:


The original dataset was added with predicted label of ‘yes’ and ‘no’, and two columns of yes and no confidence value of 1 and 0. And that concludes the discussion regarding decision trees.
Decision Trees in Machine Learning and Data Mining
A decision tree can be applied in machine learning, data mining, and statistics known as decision tree learning.
In these decision trees, nodes represent data. This type of tree is also known as a classification tree. Each branch contains a set of attributes, or classification rules, that are associated with a particular class label, which is found at the end of the branch.
These rules (decision rules) are expressed in an if-then clause, with each decision or data value forming a clause. For instance, “if conditions 1, 2 and 3 are fulfilled, then outcome x will be the result with y certainty.” Decision trees with continuous, infinite possible outcomes are called regression trees.
Sometimes multiple trees are grouped together in ensemble methods:
Bagging creates multiple trees by resampling the source data, then has those trees vote to reach consensus.
A Random Forest classifier consists of multiple trees designed to increase the classification rate
Boosted trees that can be used for regression and classification trees.
The trees in a Rotation Forest are all trained by using PCA (principal component analysis) on a random portion of the data
A decision tree is considered optimal when it represents the most data with the fewest number of levels or questions. A decision tree can also be created by building association rules, placing the target variable on the right. Common methods in determining the best way to split the data at each level include measuring the Gini impurity, information gain, and variance reduction (What Is a Decision Tree Diagram 2017).
Overfitting
A large set of features results to a large number of split, which in turn gives a huge tree. Such trees are complex and can lead to overfitting. Setting the minimum number of training inputs on each leaf, and setting maximum depth of your model to avoid such occurrence. Maximum depth refers to the length of the longest path from a root to a leaf.
Pruning
Pruning can increase the performance of a tree by removing the branches with low importance to reduce the complexity of tree, and thus increasing its predictive power by reducing overfitting. Pruning can start at either root or the leaves. This method is also called reduced error pruning. More sophisticated pruning methods can be used such as cost complexity pruning where a learning parameter (alpha) is used to weigh whether nodes can be removed based on the size of the sub-tree. This is also known as weakest link pruning (Gupta 2017).
Advantages of decision trees:
Easy to understand and interpret for any reader.
Flexible; allows the addition of new possible scenarios, work well with multi stage/phase decisions, and can handle both numerical and categorical data.
Help determine worst, best and expected values for different scenarios.
Can be combined with other decision techniques.
Small details that may have been missed are taken into consideration.
Saves time; requires little data preparation.
Possible to validate a model using statistical tests.
Disadvantages of decision trees:
Calculations can be very complex if many values are uncertain and/or if many outcomes are linked.
Overfitting can occur where the tree does not generalize the data well. Mechanisms such as pruning (not currently supported).
Decision trees can be unstable because small variations in the data might result in a completely different tree being generated.
Decision tree learners create biased trees if some classes dominate.
Bibliography: Decision Tree 2017 Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Decision_tree&oldid=811274714, accessed December 3, 2017.
DECISION TREE: OPMT N.d. DECISION TREE. http://decisiontreemodel.blogspot.com/2008/01/opmt.html, accessed December 3, 2017.
Gupta, Prashant 2017 Decision Trees in Machine Learning. Towards Data Science. https://towardsdatascience.com/decision-trees-in-machine-learning-641b9c4e8052, accessed December 3, 2017.
Ross Quinlan 2017 Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Ross_Quinlan&oldid=800005606, accessed December 3, 2017.
de Ville, Barry 2013 Decision Trees. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics 5(6): 448–455.
What Is a Decision Tree Diagram 2017 Lucidchart. https://www.lucidchart.com/pages/decision-tree, accessed December 3, 2017.
0 notes
Text
Free Elective
I am Sheena May I. Halog. 19 years old. I live in Dumalag 1, Matina
Aplaya, Davao City. I completed my elementary education at Matina
Central Special Science Pilot Elementary School and took up my secondary
education at Daniel R. Aguinaldo National High School. I am the second
offspring among the three siblings of my parents Marilyn I. Halog and
Anastacio S. Halog Jr. My elder brother Sefred Jay I. Halog is
currently working as a welder at a machinery company. While my
younger sister Salome Ann I. Halog is currently a grade 10 student at
Daniel R. Aguinaldo National High School
When I was in grade 1, I belong to the special class but because I am
very demure. Seeing that they were all very competitive unlike me, I
was kicked out from that class. But I was always one of the honor
students when I was in the general class. in high school, our TLE
subject was drafting. So, I have little knowledge with architecture
and fine arts. We were given the chance to do t-shirt printing with
fairytail logo's, and draw anime characters. I am not saying this
to brag but I was one of the best in our class but I bet professionals
and students who took up the proper course are far more better than me.
And I admit I am not good with software tools like AutoCAD, photoshop or
anything as we were taught to do things manually: painting, line drawing,
sketch, portrait and etc. That is why I can relate to the different house and
infrastructure designs, the difficulty of drawing a perfect square or making a
house miniature.
What I expect from this subject is that the lesson be delivered well and be
well understood by all especially I who have a hard time comprehending
without practical application. I bet the subject matter will be all
lecture but I hope it will not be reported by our own classmates
for I am afraid that the topic will not be delivered well. For the subject
to not be gloomy and boring, I suggest that we should have activities
either group or individual like quiz bee where the students should
study individually for no one knows who will be called to represent
the group and their grade. I expect that the lessons be presented
through power point and be uploaded to the fb group for future
references. from this blog article, I assume we will be asked to pass
such requirements where our comprehension regarding the topic will
be checked. as for the grades, lol Have Mercy O God!
Business intelligence is what I prefer because having knowledge aside
from computers gives a programmer the advantage in global competition.
in the said preferred elective, retrieval and visualization of data
may be tackled as well as data science and data analytics in knowing the
degree of the needs of the customers. Pattern recognition may also be
discussed to know the trend of the business and what to expect or
what to do to counterpart a declining business. The business world
is wide and has many branches, and I believe that indulging in such
matter give us amateurs the idea on how to deal business problems
if such circumstances may come.
0 notes