Text


52K notes
·
View notes
Text

Daily marine animal #12
More whale sharks :) they a big hit and I love em too!
342 notes
·
View notes
Text
Did You Know??
Sharks are the apex fish predators. However, they are scared of another even deadlier animal called the Orca.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sometimes I forget to switch accounts :')
1 note
·
View note
Text

Daily marine animal #3
Today's creature is a whale shark!!
Tag list: no one yet! Let me know if you wanna be added!
137 notes
·
View notes
Text
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Along the coast of Gujarat, India, a renowned spiritual leader is inspiring fishermen to become guardians of the world’s biggest fish: the endangered whale shark.
When the fishing community here saw their traditional stocks decline, they began to target whale sharks as a new source of meat and valuable oil. The high demand for these products in Asian markets made the sharks lucrative to hunt, and contributed to a steep decline in their numbers. In just 75 years, the worldwide population of whale sharks was cut in half.
In response, the Indian government added legal protections, although the new laws were a challenge to enforce and poaching continued when fishermen encountered these gentle giants out at sea. The Wildlife Trust of India then launched an awareness campaign to teach the community about the sharks and show how to save them if they became trapped in their nets — but by far the biggest shift began when spiritual leader Morari Bapu joined the campaign and spread the message that the whale sharks were like daughters returning home to give birth. His voice led to a change of heart in the local community, and has helped finally turn the community of fishers into a growing army of whale shark conservationists.
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
me and the bitches i pulled by being massive

4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Wet Beast Wednesday: whale shark
So I may have committed a cardinal sin last week because I didn't realize it was shark week and instead of a shark, I covered hagfish. This was clearly a terrible oversight and to make up for it, I'm going to talk about the biggest shark of all: the mighty whale shark.

(Image: a whale shark seen from the side. It is a very large shark with a flattened head and three ridges running down its side. The skin in grey and covered in white spots. Smaller sharks and remoras are swimming alongside it. End ID)
Whale sharks (Rhincodon typus) are carpet sharks, meaning they are members of the order Orectolobiformes. The carpet sharks most people are familiar with are the wobbegongs, who are ventrally flattened sharks they typically stick near the seafloor, but Orectolobiformes is a pretty diverse clade containing a large variety of sharks with diverse body plans. Whale sharks are the only living member of the family Rhinocodontidae, making them effectively cousins of the wobbegongs. While there is only one living species of whale shark, we know of another few in the fossil record and there were likely more extinct species and relatives that we don't know about. Because shark skeletons are made of cartilage, they rarely fossilize, leaving only their teeth as fossils. Whale sharks have very tiny teeth and smaller things are less likely to fossilize than large things. Add in that fossilization is very rare and it's very possible there were whale sharks and other similar things in the past we will never know about because they never fossilized.

(Image: a whale shark seen from the front. Its mouth is open, very wide, and apparently toothless. End ID)
Whale sharks are the largest living sharks and the largest living animals that aren't whales. Whale sharks can reach an average adult size of 14.5 meters (48 ft) and 18,600 kg (41,000 lbs), with males being larger. The largest whale shark on record was measured to be 18.8 m (62 ft). Whale sharks have broad, flattened heads and unlike most sharks, their mouths are on the front of the head instead of beneath the snout. The mouth can be over 2 meters across in an adult and is lined with approximately 300 rows of tiny teeth. These teeth are vestigial and do not play a role in feeding. Instead, the shark uses a structure at the back of the mouth composed of 20 fleshy pads that are coated with a thin mesh and held in place with connective tissue. More on feeding below. Whale sharks are grey in color, with white bellies and white spots covering the body. Each whale shark has a unique pattern of spots that scientists can use for identification. The spots will reappear in areas where damaged skin has healed instead of being scarred over. Whale sharks also have some regenerative ability, being able to recover from major wounds and possibly regrow sections of lost fin. Each side of the body has three long ridges that may help with streamlining.
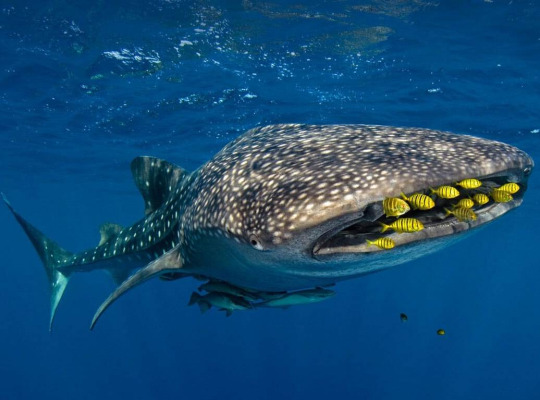

(Image: a whale shark seen form the front with its mouth closed. There are remoras attached to its underbelly and a group of small yellow fish with black stripes swimming near the mouth, possibly acting as cleaner fish. End ID)
Whale shark skin can be up to 15 cm thick and is covered with tiny, tooth-like scales called dermal denticles. Having tiny teeth where bony fish have scales is normal for sharks. What is not normal is having them on your eyes, but the whale shark does anyway. Let me repeat: whale sharks have teeth on their eyeballs. I like body horror and I'm creeped out by that. The eyes can be retracted into the head and these two adaptations are believed to protect the eyes from predators and parasites. Another adaptations the eyes (which, again, HAVE TEETH ON THEM) have is a mutated version of rhodopsin, the pigment the rod sells of the yes use to see. this mutation makes the eyes good at seeing blue light, but the rhodopsin becomes unstable in warm temperatures. In humans, this mutation leads to a degenerative eye condition that can result in blindness. Whale sharks have a solution, though. When in warm, shallow water, the pigment can be turned off to keep the eyes from degenerating. When the shark dives to deep water, the pigment is reactivated, granting the shark better vision as blue light is the most common in the deep sea.

(Image: a close-up of a whale shark eye. It is a small, black, lidless eyeball surrounded by gray skin. End ID)
While whale sharks are huge, they aren't hunters. They are one of three living species of filter-feeding shark, the others being the basking shark (which I covered previously) and the awesomely-named megamouth shark. The majority of a whale shark's diet consists of plankton: primarily copepods, krill, eggs and larvae, and small fish, squid, and jellyfish. The shark can feed either by ram feeding (swimming forward with the mouth open) or creating suction to draw water into the mouth. The mouth is shaped like a funnel and forces water through the filtration pads. The pads, which likely evolved from gill rakers, capture food particles, which are then swallowed as the water is forced out through the gills. The filtration pads are extremely efficient and resistant to being clogged up with debris, though whale sharks have been observed performing a coughing-like behavior that is speculated to help clean the pads. Whale sharks spend up to 8 hours a day near the surface of the ocean, feeding on an estimated 2.7 kg (6 lbs) of plankton per hour.

(Image: an artistic diagram of the feeding pads and gills of a whale shark and how water flows through the mouth and out the gills. Source: EmilyDamstra.com. End ID)
Whale sharks live in temperate and tropical oceans worldwide and can be found in both the open ocean and coastal regions. They are gentle giants who swim slowly and bask at the surface of the ocean, not threatening anything bigger than a sardine. While they spend a lot of time at the surface, whale sharks periodically dive in search of food. Most of these dives are less than 200 meters (660 ft) deep, but they will occasionally dive over 500 m (1,600 ft) deep. The deepest recorded dive reached 1,928 m (6,325 ft), the deepest recorded dive of any fish. Whale sharks are known to practice different feeding behavior based on available food in their region. There are two subpopulations of whale shark based on location: the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific populations. 75% of the whale shark population lives in the Indo-Pacific. Whale sharks seasonally migrate following warm waters and food and may also migrate to mate. Multiple places around the world host seasonal gatherings of whale shark, making them to best place to reliably see them.

(Image: a whale shark from the side, swimming with its mouth open. Other fish can be seen in the background. End ID)
Not much is known about Whale shark mating. It has only been seen a few times in Saint Helena Island in the Atlantic and off the coast of Australia. Mating likely occurs during the seasonal aggregations. Female whale sharks are believed to travel to regional pupping grounds to give birth, but where exactly these are is an open question as juvenile whale sharks are rarely seen. The youngest whale shark ever observed was discovered having been captured and tied to a stake on a beach in Pilar, the Philippines. It was measured at 38 cm (15 in) and was released after being measured. This discovery likely means there is a pupping ground in the area. Whale sharks are ovoviviparous, meaning their eggs hatch internally and the young are born live. Whale shark females are believed to be able to reserve sperm and impregnate themselves repeatedly between matings, rather than bearing all their young at once. It is not clear how long it takes whale sharks to mature or how long they can live, though some estimates put them at sexually mature at around 25 years old and with a maximum lifespan between 50 and 150 years. It is estimated that only 10% of whale sharks live long enough to reach sexual maturity. Adult whale sharks have no natural predators.

(Image: a baby whale shark that was rescued from a gill net in India. It looks like a smaller version of the adult, but with a proportionately larger head. A human (out of frame) is holding it just above the water. ENd ID)
Whale sharks are classified as endangered by the IUCN. They are threatened by fishing, poaching, bycatch, and boat strikes. Whale sharks are hunted for their skin, liver oil, and meat, though countries worldwide are increasingly regulating or banning whale shark hunting. Whale sharks also ingest large quantities of microplastics. The health effects of this are not understood currently. Whale sharks are kept in captivity in less than 20 aquariums worldwide. They need very large tanks and have special feeding requirements that makes it difficult to keep them healthy. Wild whale sharks pose no threat to humans though there have been reports of them ramming sport fishing boats after being provoked. In places where whale sharks seasonally aggregate, snorkeling or SCUBA diving alongside them has become a major ecotourism industry. Touching the sharks can hurt them and is illegal in most places. Some tourism agencies have been known to lure in young whale sharks by feeding them shrimp, something which is discouraged by naturalists as it can foster dependence on humans and potentially introduce dangerous chemicals to the sharks' diets.

(Image: a person in a pink swimsuit wearing goggles and a snorkel swimming next to a whale shark just beneath the surface of the water. Two other whale sharks are in the background. End ID)
171 notes
·
View notes
Text

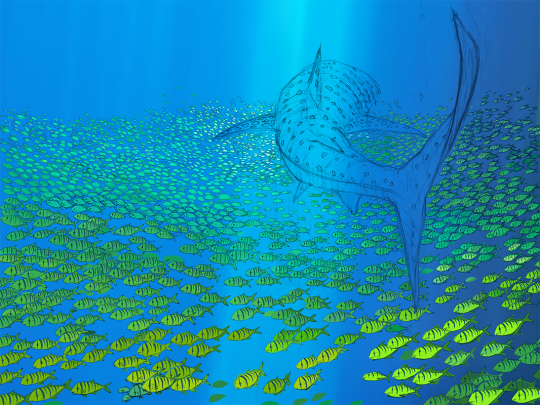

First sketch > Flat Colors > Finish | x
341 notes
·
View notes
Text

Each whale shark's spot pattern is unique like fingerprints.
814 notes
·
View notes
Text



✩°。. ⋆⸜ 🎧 ✮ 💿

whale sharks ⋆.ೃ࿔*:・⋆.ೃ࿔*:・
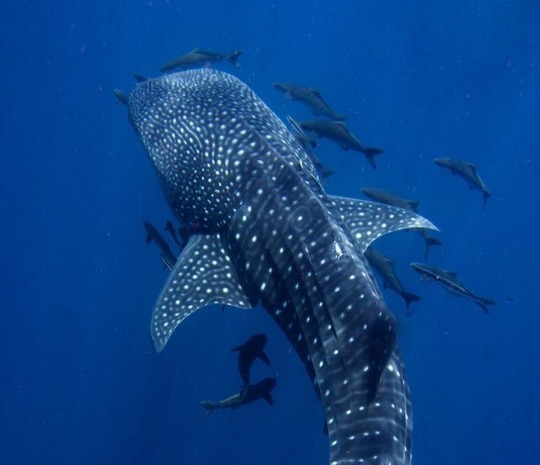




2K notes
·
View notes
Note
um pls I NEED shark pics
Greenland sharks and whale sharks
thankyouthankyouthankyou
🦈




whale and green :)
and may i introduce you to the greenland's brother, the pacific sleeper!! (they're from the same genus and go :D)

318 notes
·
View notes


