A personal writing blog for Chek. A stockhouse of all my fiction, fanfiction, writing prompts and writing resources.
Last active 4 hours ago
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Fantasy Guide to Architecture



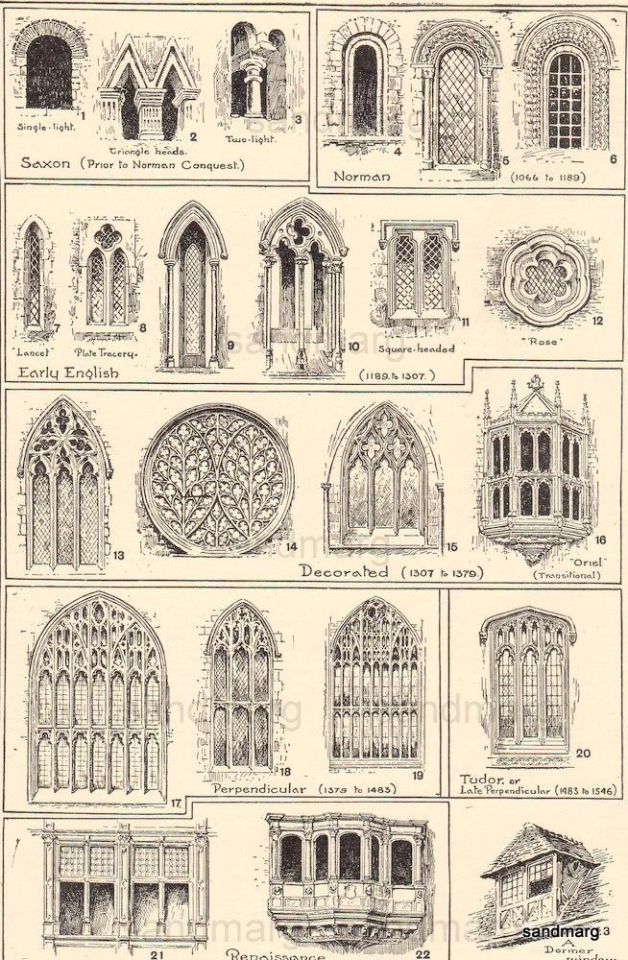


This post has been waiting on the back burner for weeks and during this time of quarantine, I have decided to tackle it. This is probably the longest post I have ever done. I is very tired and hope that I have covered everything from Ancient times to the 19th Century, that will help you guys with your worldbuilding.
Materials
What you build with can be determined by the project you intend, the terrain you build on and the availability of the material. It is one characteristic that we writers can take some some liberties with.
Granite: Granite is an stone formed of Igneous activity near a fissure of the earth or a volcano. Granites come in a wide range of colour, most commonly white, pink, or grey depending on the minerals present. Granite is hard and a durable material to build with. It can be built with without being smoothed but it looks bitchin' and shiny all polished up.
Marble: Probably everyone's go to materials for building grand palaces and temples. Marble is formed when great pressure is placed on limestone. Marble can be easily damaged over time by rain as the calcium in the rock dissolves with the chemicals found in rain. Marble comes in blue, white, green, black, white, red, gray and yellow. Marble is an expensive material to build with, highly sought after for the most important buildings. Marble is easy to carve and shape and polishes to a high gleam. Marble is found at converging plate boundaries.
Obsidian: Obsidian is probably one of the most popular stones mentioned in fantasy works. Obsidian is an igneous rock formed of lava cooling quickly on the earth's surfaces. Obsidian is a very brittle and shiny stone, easy to polish but not quite a good building material but a decorative one.
Limestone: Limestone is made of fragments of marine fossils. Limestone is one of the oldest building materials. Limestone is an easy material to shape but it is easily eroded by rain which leads most limestone monuments looking weathered.
Concrete: Concrete has been around since the Romans. Concrete is formed when aggregate (crushed limstone, gravel or granite mixed with fine dust and sand) is mixed with water. Concrete can be poured into the desired shape making it a cheap and easy building material.
Brick: Brick was one of history's most expensive materials because they took so long to make. Bricks were formed of clay, soil, sand, and lime or concrete and joined together with mortar. The facade of Hampton Court Palace is all of red brick, a statement of wealth in the times.
Glass: Glass is formed of sand heated until it hardens. Glass is an expensive material and for many years, glass could not be found in most buildings as having glass made was very expensive.
Plaster: Plaster is made from gypsum and lime mixed with water. It was used for decoration purposes and to seal walls. A little known fact, children. Castle walls were likely painted with plaster or white render on the interior.
Wattle and Daub: Wattle and daub is a building material formed of woven sticks cemented with a mixture of mud, one of the most common and popular materials throughout time.
Building terms
Arcade: An arcade is a row of arches, supported by columns.
Arch: An arch is a curved feature built to support weight often used for a window or doorway.
Mosaic: Mosaics are a design element that involves using pieces of coloured glass and fitted them together upon the floor or wall to form images.
Frescos: A design element of painting images upon wet plaster.
Buttress: A structure built to reinforce and support a wall.
Column: A column is a pillar of stone or wood built to support a ceiling. We will see more of columns later on.
Eave: Eaves are the edges of overhanging roofs built to allow eater to run off.
Vaulted Ceiling: The vaulted ceilings is a self-supporting arched ceiling, than spans over a chamber or a corridor.
Colonnade: A colonnade is a row of columns joined the entablature.
Entablature: a succession of bands laying atop the tops of columns.
Bay Window: The Bay Window is a window projecting outward from a building.
Courtyard/ Atrium/ Court: The courtyard is an open area surrounded by buildings on all sides
Dome: The dome resembles a hollow half of a sphere set atop walls as a ceiling.
Façade: the exterior side of a building
Gable: The gable is a triangular part of a roof when two intersecting roof slabs meet in the middle.
Hyphen: The hyphen is a smaller building connecting between two larger structures.
Now, let's look at some historical building styles and their characteristics of each Architectural movement.
Classical Style
The classical style of Architecture cannot be grouped into just one period. We have five: Doric (Greek), Ionic (Greek), Corinthian (Greek), Tuscan (Roman) and Composite (Mixed).
Doric: Doric is the oldest of the orders and some argue it is the simplest. The columns of this style are set close together, without bases and carved with concave curves called flutes. The capitals (the top of the column) are plain often built with a curve at the base called an echinus and are topped by a square at the apex called an abacus. The entablature is marked by frieze of vertical channels/triglyphs. In between the channels would be detail of carved marble. The Parthenon in Athens is your best example of Doric architecture.
Ionic: The Ionic style was used for smaller buildings and the interiors. The columns had twin volutes, scroll-like designs on its capital. Between these scrolls, there was a carved curve known as an egg and in this style the entablature is much narrower and the frieze is thick with carvings. The example of Ionic Architecture is the Temple to Athena Nike at the Athens Acropolis.
Corinthian: The Corinthian style has some similarities with the Ionic order, the bases, entablature and columns almost the same but the capital is more ornate its base, column, and entablature, but its capital is far more ornate, commonly carved with depictions of acanthus leaves. The style was more slender than the others on this list, used less for bearing weight but more for decoration. Corinthian style can be found along the top levels of the Colosseum in Rome.
Tuscan: The Tuscan order shares much with the Doric order, but the columns are un-fluted and smooth. The entablature is far simpler, formed without triglyphs or guttae. The columns are capped with round capitals.
Composite: This style is mixed. It features the volutes of the Ionic order and the capitals of the Corinthian order. The volutes are larger in these columns and often more ornate. The column's capital is rather plain. for the capital, with no consistent differences to that above or below the capital.
Islamic Architecture
Islamic architecture is the blanket term for the architectural styles of the buildings most associated with the eponymous faith. The style covers early Islamic times to the present day. Islamic Architecture has some influences from Mesopotamian, Roman, Byzantine, China and the Mongols.
Paradise garden: As gardens are an important symbol in Islam, they are very popular in most Islamic-style buildings. The paradise gardens are commonly symmetrical and often enclosed within walls. The most common style of garden is split into four rectangular with a pond or water feature at the very heart. Paradise gardens commonly have canals, fountains, ponds, pools and fruit trees as the presence of water and scent is essential to a paradise garden.
Sehan: The Sehan is a traditional courtyard. When built at a residence or any place not considered to be a religious site, the sehan is a private courtyard. The sehan will be full of flowering plants, water features snd likely surrounded by walls. The space offers shade, water and protection from summer heat. It was also an area where women might cast off their hijabs as the sehan was considered a private area and the hijab was not required. A sehan is also the term for a courtyard of a mosque. These courtyards would be surrounded by buildings on all sides, yet have no ceiling, leaving it open to the air. Sehans will feature a cleansing pool at the centre, set under a howz, a pavilion to protect the water. The courtyard is used for rituals but also a place of rest and gathering.
Hypostyle Hall: The Hypostyle is a hall, open to the sky and supported by columns leading to a reception hall off the main hall to the right.
Muqarnas : Muqarnas is a type of ornamentation within a dome or a half domed, sometimes called a "honeycomb", or "stalactite" vaulted ceiling. This would be cast from stone, wood, brick or stucco, used to ornament the inside of a dome or cupola. Muqarnas are used to create transitions between spaces, offering a buffer between the spaces.
African Architecture
African Architecture is a very mixed bag and more structurally different and impressive than Hollywood would have you believe. Far beyond the common depictions of primitive buildings, the African nations were among the giants of their time in architecture, no style quite the same as the last but just as breathtaking.
Somali architecture: The Somali were probably had one of Africa's most diverse and impressive architectural styles. Somali Architecture relies heavy on masonry, carving stone to shape the numerous forts, temples, mosques, royal residences, aqueducts and towers. Islamic architecture was the main inspiration for some of the details of the buildings. The Somali used sun-dried bricks, limestone and many other materials to form their impressive buildings, for example the burial monuments called taalo
Ashanti Architecture: The Ashanti style can be found in present day Ghana. The style incorporates walls of plaster formed of mud and designed with bright paint and buildings with a courtyard at the heart, not unlike another examples on this post. The Ashanti also formed their buildings of the favourite method of wattle and daub.
Afrikaner Architecture: This is probably one of the oddest architectural styles to see. Inspired by Dutch settlers (squatters), the buildings of the colony (planters/squatters) of South Africa took on a distinctive Dutch look but with an Afrikaner twist to it making it seem both familiar and strange at the same time.
Rwandan Architecture: The Rwandans commonly built of hardened clay with thatched roofs of dried grass or reeds. Mats of woven reeds carpeted the floors of royal abodes. These residences folded about a large public area known as a karubanda and were often so large that they became almost like a maze, connecting different chambers/huts of all kinds of uses be they residential or for other purposes.
Aksumite Architecture: The Aksumite was an Empire in modern day Ethiopia. The Aksumites created buildings from stone, hewn into place. One only has to look at the example of Bete Medhane Alem to see how imposing it was.
Yoruba Architecture: Yoruba Architecture was made by earth cured until it hardened enough to form into walls, or they used wattle and daub, roofed by timbers slats coated in woven grass or leaves. Each unit divided up parts of the buildings from facilities to residences, all with multiple entrances, connected together.
Igbo Architecture: The Igbo style follows some patterns of the Yoruba architecture, excepting that there are no connected walls and the spacing is not so equal. The closer a unit was to the centre, the more important inhabitants were.
Hausa architecture: Hausa Architecture was formed of monolithic walls coated in plaster. The ceilings and roof of the buildings were in the shape of small domes and early vaulted ceilings of stripped timber and laterite. Hausa Architecture features a single entrance into the building and circular walls.
Nubian Architecture: Nubia, in modern day Ethiopia, was home to the Nubians who were one of the world's most impressive architects at the beginning of the architecture world and probably would be more talked about if it weren't for the Egyptians building monuments only up the road. The Nubians were famous for building the speos, tall tower-like spires carved of stone. The Nubians used a variety of materials and skills to build, for example wattle and daub and mudbrick. The Kingdom of Kush, the people who took over the Nubian Empire was a fan of Egyptian works even if they didn't like them very much. The Kushites began building pyramid-like structures such at the sight of Gebel Barkal
Egyptian Architecture: The Egyptians were the winners of most impressive buildings for s good while. Due to the fact that Egypt was short on wood, Ancient Egyptians returned to building with limestone, granite, mudbrick, sandstone which were commonly painted with bright murals of the gods along with some helpful directions to Anubis's crib. The Egyptians are of course famous for their pyramids but lets not just sit on that bandwagon. Egyptian Architecture sported all kinds of features such as columns, piers, obelisks and carving buildings out of cliff faces as we see at Karnak. The Egyptians are cool because they mapped out their buildings in such a way to adhere to astrological movements meaning on special days if the calendar the temple or monuments were in the right place always. The Egyptians also only build residences on the east bank of the Nile River, for the opposite bank was meant for the dead. The columns of Egyptian where thicker, more bulbous and often had capitals shaped like bundles of papyrus reeds.
Chinese Architecture
Chinese Architecture is probably one of the most recognisable styles in the world. The grandness of Chinese Architecture is imposing and beautiful, as classical today as it was hundreds of years ago.
The Presence of Wood: As China is in an area where earthquakes are common, most of the buildings are were build of wood as it was easy to come across and important as the Ancient Chinese wanted a connection to nature in their homes.
Overhanging Roofs: The most famous feature of the Chinese Architectural style are the tiled roofs, set with wide eaves and upturned corners. The roofs were always tiled with ceramic to protect wood from rotting. The eaves often overhung from the building providing shade.
Symmetrical Layouts: Chinese Architecture is symmetrical. Almost every feature is in perfect balance with its other half.
Fengshui: Fengshui are philosophical principles of how to layout buildings and towns according to harmony lain out in Taoism. This ensured that the occupants in the home where kept in health, happiness, wealth and luck.
One-story: As China is troubled by earthquakes and wood is not a great material for building multi-storied buildings, most Chinese buildings only rise a single floor. Richer families might afford a second floor but the single stories compounds were the norm.
Orientation: The Ancient Chinese believed that the North Star marked out Heaven. So when building their homes and palaces, the northern section was the most important part of the house and housed the heads of the household.
Courtyards: The courtyard was the most important area for the family within the home. The courtyard or siheyuan are often built open to the sky, surrounded by verandas on each side.
Japanese Architecture
Japanese Architecture is famous for its delicacy, smooth beauty and simplistic opulence. Japanese Architecture has been one of the world's most recognisable styles, spanning thousands of years.
Wood as a Common Material: As with the Chinese, the most popular material used by the Japanese is wood. Stone and other materials were not often used because of the presence of earthquakes. Unlike Chinese Architecture, the Japanese did not paint the wood, instead leaving it bare so show the grain.
Screens and sliding doors: The shoji and fusuma are the screens and sliding doors are used in Japanese buildings to divide chambers within the house. The screens were made of light wood and thin parchment, allowing light through the house. The screens and sliding doors were heavier when they where used to shutter off outside features.
Tatami: Tatami mats are used within Japanese households to blanket the floors. They were made of rice straw and rush straw, laid down to cushion the floor.
Verandas: It is a common feature in older Japanese buildings to see a veranda along the outside of the house. Sometimes called an engawa, it acted as an outdoor corridor, often used for resting in.
Genkan: The Genkan was a sunken space between the front door and the rest of the house. This area is meant to separate the home from the outside and is where shoes are discarded before entering.
Nature: As both the Shinto and Buddhist beliefs are great influences upon architecture, there is a strong presence of nature with the architecture. Wood is used for this reason and natural light is prevalent with in the home. The orientation is meant to reflect the best view of the world.
Indian Architecture
India is an architectural goldmine. There are dozens of styles of architecture in the country, some spanning back thousands of years, influenced by other cultures making a heady stew of different styles all as beautiful and striking as the last.
Mughal Architecture: The Mughal architecture blends influences from Islamic, Persian along with native Indian. It was popular between the 16th century -18th century when India was ruled by Mughal Emperors. The Taj Mahal is the best example of this.
Indo-Saracenic Revival Architecture: Indo Saracenic Revival mixes classical Indian architecture, Indo-Islamic architecture, neo-classical and Gothic revival of the 1800s.
Cave Architecture: The cave architecture is probably one of the oldest and most impressive styles of Indian architecture. In third century BC, monks carved temples and buildings into the rock of caves.
Rock-Cut Architecture: The Rock-cut is similar to the cave style, only that the rock cut is carved from a single hunk of natural rock, shaped into buildings and sprawling temples, all carved and set with statues.
Vesara Architecture: Vesara style prevalent in medieval period in India. It is a mixture of the Dravida and the Nagara styles. The tiers of the Vesara style are shorter than the other styles.
Dravidian Architecture: The Dravidian is the southern temple architectural style. The Kovils are an example of prime Dravidian architecture. These monuments are of carved stone, set up in a step like towers like with statues of deities and other important figures adorning them.
Kalinga Architecture: The Kalinga style is the dominant style in the eastern Indian provinces. The Kalinga style is famous for architectural stipulations, iconography and connotations and heavy depictions of legends and myths.
Sikh Architecture: Sikh architecture is probably the most intricate and popular of the styles here. Sikh architecture is famous for its soft lines and details.
Romanesque (6th -11th century/12th)
Romanesque Architecture is a span between the end of Roman Empire to the Gothic style. Taking inspiration from the Roman and Byzantine Empires, the Romanesque period incorporates many of the styles.
Rounded arches: It is here that we see the last of the rounded arches famous in the classical Roman style until the Renaissance. The rounded arches are very popular in this period especially in churches and cathedrals. The rounded arches were often set alongside each other in continuous rows with columns in between.
Details: The most common details are carved floral and foliage symbols with the stonework of the Romanesque buildings. Cable mouldings or twisted rope-like carvings would have framed doorways.
Pillars: The Romanesque columns is commonly plainer than the classical columns, with ornate captials and plain bases. Most columns from this time are rather thick and plain.
Barrel Vaults: A barrel vaulted ceiling is formed when a curved ceiling or a pair of curves (in a pointed ceiling). The ceiling looks rather like half a tunnel, completely smooth and free of ribs, stone channels to strengthen the weight of the ceiling.
Arcading: An arcade is a row of arches in a continual row, supported by columns in a colonnade. Exterior arcades acted as a sheltered passage whilst inside arcades or blind arcades, are set against the wall the arches bricked, the columns and arches protruding from the wall.
Gothic Architecture (12th Century - 16th Century)
The Gothic Architectural style is probably one of the beautiful of the styles on this list and one of most recognisable. The Gothic style is a dramatic, opposing sight and one of the easiest to describe.
Pointed arch: The Gothic style incorporates pointed arches, in the windows and doorways. The arches were likely inspired by pre-Islamic architecture in the east.
Ribbed vault: The ribbed vault of the Gothic age was constructed of pointed arches. The trick with the ribbed vaulted ceiling, is that the pointed arches and channels to bear the weight of the ceiling.
Buttresses: The flying buttress is designed to support the walls. They are similar to arches and are connected to counter-supports fixed outside the walls.
Stained-Glass Window: This is probably one of the most recognisable and beautiful of the Gothic features. They can be set in round rose windows or in the pointed arches.
Renaissance Architecture (15th Century- 17th Century)
Renaissance architecture was inspired by Ancient Roman and Greek Architecture. Renaissance Architecture is Classical on steroids but has its own flare. The Renaissance was a time for colour and grandeur.
Columns and pilasters: Roman and Greek columns were probably the greatest remix of the Renaissance period. The architecture of this period incorporated the five orders of columns are used: Tuscan, Doric, Ionic, Corinthian and Composite. The columns were used to hold up a structure, support ceilings and adorn facades. Pilasters were columns within a chamber, lining the walls for pure decoration purposes.
Arches: Arches are rounded in this period, having a more natural semi-circular shape at its apex. Arches were a favourite feature of the style, used in windows, arcades or atop columns.
Cupola: Is a small dome-like tower atop a bigger dome or a rooftop meant to allow light and air into the chamber beneath.
Vaulted Ceiling/Barrel Vault: Renaissance vaulted ceilings do not have ribs. Instead they are semi-circular in shape, resting upon a square plain rather than the Gothic preference of rectangular. The barrel vault held by its own weight and would likely be coated in plaster and painted.
Domes: The dome is the architectural feature of the Renaissance. The ceiling curves inwards as it rises, forming a bowl like shape over the chamber below. The dome's revival can be attributed to Brunelleschi and the Herculean feat of placing a dome on the Basilica di Santa Maria del Fiore. The idea was later copied by Bramante who built St. Peter's Basilica.
Frescos: To decorate the insides of Renaissance buildings, frescos (the art of applying wet paint to plaster as it dries) were used to coat the walls and ceilings of the buildings. The finest frescos belong to Michelangelo in the Sistine Chapel.
Baroque (1625–1750)
Baroque incorporates some key features of Renaissance architecture, such as those nice columns and domes we saw earlier on. But Baroque takes that to the next level. Everything is higher, bigger, shinier, brighter and more opulent. Some key features of Baroque palaces and buildings would be:
Domes: These domes were a common feature, left over from the Renaissance period. Why throw out a perfectly good bubble roof, I ask you? But Baroque domes were of course, grander. Their interiors were were nearly always painted or gilded, so it drew the eye upwards which is basically the entire trick with Baroque buildings. Domes were not always round in this building style and Eastern European buildings in Poland and Ukraine for example sport pear-shaped domes.
Solomonic columns: Though the idea of columns have been about for years but the solomonic columns but their own twist on it. These columns spiral from beginning to end, often in a s-curved pattern.
Quadratura: Quadratura was the practice of painting the ceilings and walls of a Baroque building with trompe-l'oeil. Most real life versions of this depict angels and gods in the nude. Again this is to draw the eye up.
Mirrors: Mirrors came into popularity during this period as they were a cool way to create depth and light in a chamber. When windows faced the mirrors on the wall, it creates natural light and generally looks bitchin'. Your famous example is the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles.
Grand stairways: The grand sweeping staircases became popular in this era, often acting as the centre piece in a hall. The Baroque staircase would be large and opulent, meant for ceremonies and to smoother guests in grandeur.
Cartouche: The cartouche is a design that is created to add some 3D effect to the wall, usually oval in shape with a convex surface and edged with scrollwork. It is used commonly to outline mirrors on the wall or crest doorways just to give a little extra opulence.
Neoclassical (1750s-19th century)
The Neoclassical Period involved grand buildings inspired by the Greek orders, the most popular being the Doric. The main features of Neoclassical architecture involve the simple geometric lines, columns, smooth walls, detailing and flat planed surfaces. The bas-reliefs of the Neoclassical style are smoother and set within tablets, panels and friezes. St. Petersburg is famous for the Neoclassical styles brought in under the reign of Catherine the Great.
Greek Revival (late 18th and early 19th century)
As travel to other nations became easier in this time period, they became to get really into the Ancient Greek aesthetic. During this architectural movement they brought back the gabled roof, the columns and the entablature. The Greek Revival was more prevalent in the US after the Civil War and in Northern Europe.
Hope this helps somewhat @marril96
27K notes
·
View notes
Text
Words for Skin Tone | How to Describe Skin Color

We discussed the issues describing People of Color by means of food in Part I of this guide, which brought rise to even more questions, mostly along the lines of “So, if food’s not an option, what can I use?” Well, I was just getting to that!
This final portion focuses on describing skin tone, with photo and passage examples provided throughout. I hope to cover everything from the use of straight-forward description to the more creatively-inclined, keeping in mind the questions we’ve received on this topic.
Standard Description
Basic Colors

Pictured above: Black, Brown, Beige, White, Pink.
“She had brown skin.”
This is a perfectly fine description that, while not providing the most detail, works well and will never become cliché.
Describing characters’ skin as simply brown or beige works on its own, though it’s not particularly telling just from the range in brown alone.
Complex Colors
These are more rarely used words that actually “mean” their color. Some of these have multiple meanings, so you’ll want to look into those to determine what other associations a word might have.

Pictured above: Umber, Sepia, Ochre, Russet, Terra-cotta, Gold, Tawny, Taupe, Khaki, Fawn.
Complex colors work well alone, though often pair well with a basic color in regards to narrowing down shade/tone.
For example: Golden brown, russet brown, tawny beige…
As some of these are on the “rare” side, sliding in a definition of the word within the sentence itself may help readers who are unfamiliar with the term visualize the color without seeking a dictionary.
“He was tall and slim, his skin a russet, reddish-brown.”
Comparisons to familiar colors or visuals are also helpful:
“His skin was an ochre color, much like the mellow-brown light that bathed the forest.”
Modifiers
Modifiers, often adjectives, make partial changes to a word.The following words are descriptors in reference to skin tone.
Dark - Deep - Rich - Cool
Warm - Medium - Tan
Fair - Light - Pale
Rich Black, Dark brown, Warm beige, Pale pink…
If you’re looking to get more specific than “brown,” modifiers narrow down shade further.
Keep in mind that these modifiers are not exactly colors.
As an already brown-skinned person, I get tan from a lot of sun and resultingly become a darker, deeper brown. I turn a pale, more yellow-brown in the winter.
While best used in combination with a color, I suppose words like “tan” “fair” and “light” do work alone; just note that tan is less likely to be taken for “naturally tan” and much more likely a tanned White person.
Calling someone “dark” as description on its own is offensive to some and also ambiguous. (See: Describing Skin as Dark)
Undertones
Undertones are the colors beneath the skin, seeing as skin isn’t just one even color but has more subdued tones within the dominating palette.

pictured above: warm / earth undertones: yellow, golden, copper, olive, bronze, orange, orange-red, coral | cool / jewel undertones: pink, red, blue, blue-red, rose, magenta, sapphire, silver.
Mentioning the undertones within a character’s skin is an even more precise way to denote skin tone.
As shown, there’s a difference between say, brown skin with warm orange-red undertones (Kelly Rowland) and brown skin with cool, jewel undertones (Rutina Wesley).
“A dazzling smile revealed the bronze glow at her cheeks.”
“He always looked as if he’d ran a mile, a constant tinge of pink under his tawny skin.”
Standard Description Passage
“Farah’s skin, always fawn, had burned and freckled under the summer’s sun. Even at the cusp of autumn, an uneven tan clung to her skin like burrs. So unlike the smooth, red-brown ochre of her mother, which the sun had richened to a blessing.”
-From my story “Where Summer Ends” featured in Strange Little Girls
Here the state of skin also gives insight on character.
Note my use of “fawn” in regards to multiple meaning and association. While fawn is a color, it’s also a small, timid deer, which describes this very traumatized character of mine perfectly.
Though I use standard descriptions of skin tone more in my writing, at the same time I’m no stranger to creative descriptions, and do enjoy the occasional artsy detail of a character.
Creative Description
Whether compared to night-cast rivers or day’s first light…I actually enjoy seeing Characters of Colors dressed in artful detail.
I’ve read loads of descriptions in my day of white characters and their “smooth rose-tinged ivory skin”, while the PoC, if there, are reduced to something from a candy bowl or a Starbucks drink, so to actually read of PoC described in lavish detail can be somewhat of a treat.
Still, be mindful when you get creative with your character descriptions. Too many frills can become purple-prose-like, so do what feels right for your writing when and where. Not every character or scene warrants a creative description, either. Especially if they’re not even a secondary character.
Using a combination of color descriptions from standard to creative is probably a better method than straight creative. But again, do what’s good for your tale.
Natural Settings - Sky

Pictured above: Harvest Moon -Twilight, Fall/Autumn Leaves, Clay, Desert/Sahara, Sunlight - Sunrise - Sunset - Afterglow - Dawn- Day- Daybreak, Field - Prairie - Wheat, Mountain/Cliff, Beach/Sand/Straw/Hay.
Now before you run off to compare your heroine’s skin to the harvest moon or a cliff side, think about the associations to your words.
When I think cliff, I think of jagged, perilous, rough. I hear sand and picture grainy, yet smooth. Calm. mellow.
So consider your character and what you see fit to compare them to.
Also consider whose perspective you’re describing them from. Someone describing a person they revere or admire may have a more pleasant, loftier description than someone who can’t stand the person.
“Her face was like the fire-gold glow of dawn, lifting my gaze, drawing me in.”
“She had a sandy complexion, smooth and tawny.”
Even creative descriptions tend to draw help from your standard words.
Flowers

Pictured above: Calla lilies, Western Coneflower, Hazel Fay, Hibiscus, Freesia, Rose
It was a bit difficult to find flowers to my liking that didn’t have a 20 character name or wasn’t called something like “chocolate silk” so these are the finalists.
You’ll definitely want to avoid purple-prose here.
Also be aware of flowers that most might’ve never heard of. Roses are easy, as most know the look and coloring(s) of this plant. But Western coneflowers? Calla lilies? Maybe not so much.
“He entered the cottage in a huff, cheeks a blushing brown like the flowers Nana planted right under my window. Hazel Fay she called them, was it?”
Assorted Plants & Nature

Pictured above: Cattails, Seashell, Driftwood, Pinecone, Acorn, Amber
These ones are kinda odd. Perhaps because I’ve never seen these in comparison to skin tone, With the exception of amber.
At least they’re common enough that most may have an idea what you’re talking about at the mention of “pinecone.“
I suggest reading out your sentences aloud to get a better feel of how it’ll sounds.
“Auburn hair swept past pointed ears, set around a face like an acorn both in shape and shade.”
I pictured some tree-dwelling being or person from a fantasy world in this example, which makes the comparison more appropriate.
I don’t suggest using a comparison just “cuz you can” but actually being thoughtful about what you’re comparing your character to and how it applies to your character and/or setting.
Wood

Pictured above: Mahogany, Walnut, Chestnut, Golden Oak, Ash
Wood can be an iffy description for skin tone. Not only due to several of them having “foody” terminology within their names, but again, associations.
Some people would prefer not to compare/be compared to wood at all, so get opinions, try it aloud, and make sure it’s appropriate to the character if you do use it.
“The old warlock’s skin was a deep shade of mahogany, his stare serious and firm as it held mine.”
Metals

Pictured above: Platinum, Copper, Brass, Gold, Bronze
Copper skin, brass-colored skin, golden skin…
I’ve even heard variations of these used before by comparison to an object of the same properties/coloring, such as penny for copper.
These also work well with modifiers.
“The dress of fine white silks popped against the deep bronze of her skin.”
Gemstones - Minerals

Pictured above: Onyx, Obsidian, Sard, Topaz, Carnelian, Smoky Quartz, Rutile, Pyrite, Citrine, Gypsum
These are trickier to use. As with some complex colors, the writer will have to get us to understand what most of these look like.
If you use these, or any more rare description, consider if it actually “fits” the book or scene.
Even if you’re able to get us to picture what “rutile” looks like, why are you using this description as opposed to something else? Have that answer for yourself.
“His skin reminded her of the topaz ring her father wore at his finger, a gleaming stone of brown, mellow facades.”
Physical Description
Physical character description can be more than skin tone.
Show us hair, eyes, noses, mouth, hands…body posture, body shape, skin texture… though not necessarily all of those nor at once.
Describing features also helps indicate race, especially if your character has some traits common within the race they are, such as afro hair to a Black character.
How comprehensive you decide to get is up to you. I wouldn’t overdo it and get specific to every mole and birthmark. Noting defining characteristics is good, though, like slightly spaced front teeth, curls that stay flopping in their face, hands freckled with sunspots…
General Tips
Indicate Race Early: I suggest indicators of race be made at the earliest convenience within the writing, with more hints threaded throughout here and there.
Get Creative On Your Own: Obviously, I couldn’t cover every proper color or comparison in which has been “approved” to use for your characters’ skin color, so it’s up to you to use discretion when seeking other ways and shades to describe skin tone.
Skin Color May Not Be Enough: Describing skin tone isn’t always enough to indicate someone’s ethnicity. As timeless cases with readers equating brown to “dark white” or something, more indicators of race may be needed.
Describe White characters and PoC Alike: You should describe the race and/or skin tone of your white characters just as you do your Characters of Color. If you don’t, you risk implying that White is the default human being and PoC are the “Other”).
PSA: Don’t use “Colored.” Based on some asks we’ve received using this word, I’d like to say that unless you or your character is a racist grandmama from the 1960s, do not call People of Color “colored” please.
Not Sure Where to Start? You really can’t go wrong using basic colors for your skin descriptions. It’s actually what many people prefer and works best for most writing. Personally, I tend to describe my characters using a combo of basic colors + modifiers, with mentions of undertones at times. I do like to veer into more creative descriptions on occasion.
Want some alternatives to “skin” or “skin color”? Try: Appearance, blend, blush, cast, coloring, complexion, flush, glow, hue, overtone, palette, pigmentation, rinse, shade, sheen, spectrum, tinge, tint, tone, undertone, value, wash.
Skin Tone Resources
List of Color Names
The Color Thesaurus
Skin Undertone & Color Matching
Tips and Words on Describing Skin
Photos: Undertones Described (Modifiers included)
Online Thesaurus (try colors, such as “red” & “brown”)
Don’t Call me Pastries: Creative Skin Tones w/ pics I
Writing & Description Guides
WWC Featured Description Posts
WWC Guide: Words to Describe Hair
Writing with Color: Description & Skin Color Tags
7 Offensive Mistakes Well-intentioned Writers Make
I tried to be as comprehensive as possible with this guide, but if you have a question regarding describing skin color that hasn’t been answered within part I or II of this guide, or have more questions after reading this post, feel free to ask!
~ Mod Colette
170K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing a Blind or Visually Impaired Character
A Multi-Step Guide Written by a Visually Impaired Writer and Blogger
I’m hoping this blog will over time develop its own following, and when it does people will inevitably see my bio and notice what I included: I’m visually impaired.
Yes, a visually impaired writer, and I’ve written with two blind characters before so I have some practice in the field.
So, inevitably, someone is going to ask how to write a blind character.
Or, at least, I hope you’ll ask someone who’s actually blind or visually impaired about writing a blind character before you get too involved with your new WIP.
All parts will be tagged #blindcharacter in my blog, and I will add links to every post as I finish each part. Follow my blog for more writing advice.
Note, this post updates fairly often and old versions are still floating around out there. The most current version of this post is pinned to my blog with any new guides or links you might of missed.
As of 24 January 2021, this is the most extensive and screen reader friendly version of this post.
Part One: Crafting the Blind Character
In which I tell you how to begin making a blind character who is more than a cardboard cutout
Part Two: Narrative Choice, Visual Description, Verbal Description, Social Interaction
In which I give you a basic rundown on how to write from the perspective of a character who can’t see and still make the narration descriptive
Part Three: Tropes and Clichés to Avoid
Your blind readers will thank you for not being the 5000th person to do this and manage to actually finish your story. (Do you have any idea how many stories I’ve noped out of within two chapters because of these clichés? A Lot.)
-New- Part Four: Canes, Guide Dogs, and O&M
Everything I can tell you about 1) how to learn how to use a cane 2) how a cane works 3) how to describe what your character experiences with their cane 4) everything I know on guide dogs
Part Five: Small Aspects of being Blind You Never Thought Of
5 January 2021 Edit: This link has been fixed to correspond with the correct post
Or, really, very normal everyday things for blind people, the inclusion of which will make your characters more real and authentic. It’s the tiny details.
Part Six: Should You Cure Your Character’s Blindness? (Short Answer: No)
There’s no way to write a cure for your blind character that doesn’t make blind readers hate you. Sorry. We came here to finally experience a relatable character who experiences the world like us, but none of us are getting cured so seeing this character we learned to love become something alien from us in the end feels like a slap in the face
Why I’m Blind and What I See -NEW-
I thought I’d finally make a post explaining the complicated situation about my vision. Includes an explanation of visual snow and exotropia, two of the three causes for my vision issues.
Writing Blind Characters Falling in Love, an Advice Post:
Someone asked what being blind and falling in love have to do with each other. Honestly, blindness changes your perspective on everything and it makes an impact on every relationship you have. This includes some things that you definitely do not want your character’s love interest to be/do.
Writing Blind Jokes (Should You Do It?)
You know those flow charts of “should you do x?” going around? It’s like that, but screen reader friendly. Should you write blind jokes. It’s pretty complicated and there are a lot of possible scenarios and details to consider.
Advice for Writing Toph Beifong -NEW-
In this I discuss what I would like to see done in fanfiction with Toph’s character after ten years of reading Avatar the Last Airbender fanfiction
A small essay addressing the frequently asked question on giving your blind character a superpower to help them “see.”
It’s became a popular question, so to make the answer easier/faster for everyone to access, I wrote what will usually be my initial answer. Below there are a few links to some notable past questions on this subject.
Mourning My Vision, it’s More than Depression.
A small personal essay addressing the nuances of the mourning period you experience with a new disability. The mourning period is mentioned in other guides, but this is more detailed.
Dealing with Heightened Senses, a video by Molly Burke with additional commentary by me
While Molly talks about the myths and truths about heightened senses, I talk about the correlation with blindness and neuro-divergency and how co-morbid disorders/disabilities might affect sensory processing.
Satirical Commentary on the phrase “that blank look in their eyes” used too often in fiction to identify a blind character
a:tla, I’m looking at you (and my eyes aren’t blank)
I Found a Lost Piece of Blindness History
My grandmother told me about her blind aunt and how she sent letters. It led me to speculate about all the O&M things people develop on their own but never get a chance to pass onto other blind people. Technology and techniques are lost in history and reinvented, including the white cane ad guide dogs.
Includes a little history on the introduction of guide dogs into the 20th century
The Following are Answered Anon Questions
Making Your Blog More Accessible
Making Links Accessible to Screen Readers
Reblogging to Add an Image Description to Someone Else’s Image
Why I Write Image Descriptions
Writing Blind Characters
Advice for a Character Who was Born Blind
Over-Protective Parents of a Blind Character, Why They’re Over-Protective and How to Avoid Crossing a Line
A Blind Character in Victorian Era Historical Fiction
Is It Bad Not to Have Guide Dogs in a Fantasy/Historical Setting Without Guide Dogs (short answer: it’s not bad)
Someone Asked About My Thoughts on a Medusa-like Character Blinding Herself to Avoid Hurting Anyone
-New- Characters Who Have Recently Gone Blind and Avoiding Inspiration Porn
Talking about Popular Blind Characters In Media
Does Daredevil’s Echolocation Negate His Blindness
Someone Else was Asked How to Write Daredevil Fanfiction
Blind Characters with Superpowers/Fighting Styles
World Setting where the General Population has a Superpower
Superpowers that don’t involve sight, Five questions to ask yourself if this superpower is a bad idea or a good one
-New- Your character would not use a cane as a weapon, it’s a bad idea
D&D/Roleplaying Blind Characters
-New- Animal Familiars Acting as Service Animals and Advice for Communicating with Your DM
-New- Portraying Older Blind Characters + Causes for Vision Loss with Old Age
32K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Create a Mythological System
Hey guys! Once again, this is an original post by yours truly— @thecomfywriter — so if you would like to repost it (though no one has tried to lol), make sure to tag me [insta: @tovwriter and tumblr: @thecomfywriter). If you like this post, reblog, like and comment what you’d like to see next.
———————————————————————————————————
Creating a mythological system in my book was probably the best thing I could have done because it enhanced the story and the world by SO MUCH. It turned my regular old story about a hero on a quest in a magical lands into a Cairoyas in Soilaila on a quest to slay Mother Dragon— believed to be descendant of the gods — as a way to pay tribute to his mother’s morals, values and faith. It brought the culture of Soilaila to life. It created a history within the lands and brought motivation to the characters, as well as gave them a moral compass similar to the moral compass faith gives people. It also just made it cooler lol. It was like an interesting subplot. A whole other universe or backstory that built upon my existing backstory and world. IT WAS JUST REALLY COOL. So, without further ado, How to create a mythological system:
Establish the origin story
Think of it in the perspective of the people in your culture. How would you interpret the world around you? How would you imagine it to have started? Are you thinking about how our world was born, or the entire universe? Who is involved in this origin story? Was it controlled by some higher power god or goddess that is established in your mythology, or is it a happy accident of the world?
Some cultures even have an ambiguous beginning to their world. They accept the idea that whatever happened before the beginning is unknown, or better yet, a secret for only the gods to know. Maybe that’s how the people in your culture reach enlightenment (if that concept exists at all): by discovering the truth of before.
Whatever you choose, decide on how your people believe the world/universe began.
Create the main gods/goddesses
These deities will be your main cast of characters. The recurring gods, so important they seem to be featured in every myth, or highly regarded in some shape or manner of worship. I like to think of my gods and goddesses as characters, and build on them like that too. Give them personalities, roles, responsibilities, motives. What makes these gods important? Why are they so highly worshipped or talked about in comparison to say, some other deity? How much power do they have? What do they do with that power?
Note: if you have a monothestic culture, you might have one main god/goddess, and that’s okay. Just apply these questions to that god(ess). What makes them so special, that an entire culture was convinced to worship them?
Think of things in nature, and try to explain them using your gods/goddesses.
The very first myth (apart from my origin story) I created was why the sun rose and set every day and night. It featured one of the main gods — Yozar (who is one of my FAVOURITE CHARACTERS after Evan) — and how he was the god of the sun, the carrier of the Flame and the carrier of the dead. It was, in a way, his origin story. The most famous story in regards to his name. If someone in this culture said Yozar’s name, you could immediately respond with “oh, he’s the reason why the sun dances across the sky!”
Notice the small things in nature that we usually explain by science, or we don’t explain at all. Remember: mythology and religion was originally created as an explanation to understand the mysteries and fascination of the world, long before any other scientific or other explanations existed. People didn’t know that rainbows were created by refractions of light in water droplets; they used to think it was a bridge to the Spirit World. Other cultures used to think that volcanoes erupting was the anger of the gods, or the hammer of Hephestus, or believe lightning bolts were the byproduct of Zeus’s wrath. Try to explain nature in the perspective of your culture using the gods/goddesses you made. Be creative with it :) there’s no wrong answer
Create DRAMA
This is probably my favourite part. There is no way in hell all these all-powerful gods live happily and peaceful amongst each other. Maybe in their form of heaven (if that exists in your culture), but you need to explain why human suffering occurs. Most of the time, that is explained through the drama of the gods/goddesses.
I’ll give you an example. In Soilailan Mythology (from my book), the reason why infertility and/or miscarriages happen is because the goddess of fertility (Flaera) was so angry at the god of mischief (Morohav) for threatening her brother’s life and trying to kill him, that she cursed his wife to never be able to conceive a child, because she knew it was his one dream in life to have his own child. Is it fair? No. Does it have to be? No. Your gods/goddesses don’t have to be benevolent. They can be petty. They can be cruel. They can be bad people and wrong.
Of course, there also has to be a reason why your people worship them. If you just look at the fact that Flaera caused Morohav’s wife so much heartbreak and suffering in order to get revenge on him, she seems like a nasty person. But when you consider the background of Morohav and all the cruel things he had done to Flaera, there is almost a sense of justice felt— at least to the people in my culture. Even if it is controversial, if it can be argued, it can exist.
Also, the drama of your mythology, apart from explaining human suffering, can also create popularity. Think of Greek Mythology; do you know how much people shit on Zeus for being such a horn dog? His affairs created half the myths, all because he couldn’t keep it in his pants. It’s entertaining. Your culture probably has arts, which means it has a form of entertainment. Sometimes, you gotta make some filler myths just because some poets in the ancient history of your culture got bored and decided to drunkenly write a ballad about the infidelities of the gods. YOLO, lol.
—————————————————————————————————–
Aight, that’s all I got for now. I might make a part two when I think of some more, but yeah! Anyways, let me know if this helped, or if you want a part 2, or if you would even like to know the basics of my own mythology system. There is so much drama and myths created, I can lowkey make a spinoff series about it. Or even a show. Or a comic! I dunno lol. M’kay bye!
Happy Writing!
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Make Your Descriptions Less Boring
We’ve all been warned about the dangers of using too much description. Readers don’t want to read three paragraphs about a sunset, we’re told. Description slows down a story; it’s boring and self-indulgent. You should keep your description as short and simple as possible. For those who take a more scientific approach to writing fiction, arbitrary rules abound: One sentence per paragraph. One paragraph per page. And, for god’s sake, “Never open a book with weather” (Elmore Leonard).
But what this conventional wedding wisdom fails to take into account is the difference between static and dynamic description. Static description is usually boring. It exists almost like a painted backdrop to a play. As the name suggests, it doesn’t move, doesn’t interact or get interacted with.
There were clouds in the sky. Her hair was red with hints of orange. The house had brown carpeting and yellow countertops.
In moderation, there’s nothing wrong with static description. Sometimes, facts are facts, and you need to communicate them to the reader in a straightforward manner.
But too much static description, and readers will start to skim forward. They don’t want to read about what the house looks like or the stormy weather or the hair color of each of your protagonist’s seventeen cousins.
Why? Because they can tell it’s not important. They can afford to skip all of your description because their understanding of the story will not be impacted.
That’s where dynamic description comes in. Dynamic description is a living entity. It’s interactive, it’s relevant. It takes on the voices of your narrators and characters. In short, it gives us important information about the story, and it can’t be skimmed over.
So how do you make your description more dynamic so that it engages your readers and adds color and excitement to your story? Here are a few tips.
(I have a TON more tips about setting and description. These are just a few. But I’m trying to keep this short, so if you have any questions or want more advice about this, please feel free to ask me.)
Keep reading
25K notes
·
View notes
Text
92K notes
·
View notes
Text
Lucasfilm did not fire Gina Carano from The Mandalorian for being Transphobic:
She got fired for being Anti-Semitic.
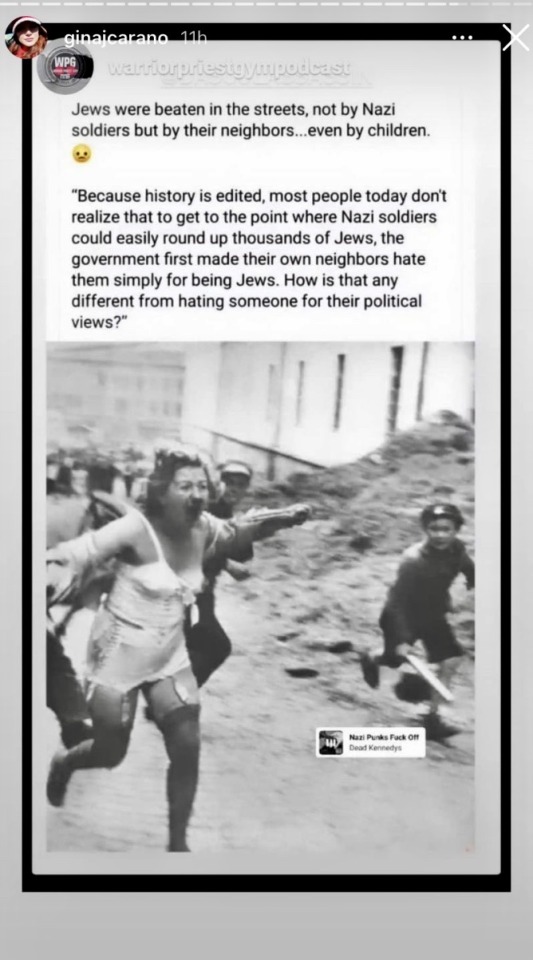
Her being Transphobic is not at all okay either but,
Anti-Semitism is not talked about enough.
She basically just compared Holocaust victims to being a Republican. Do you realize how fucked up that is?!
I’m Jewish. I really don’t like when someone compares the genocide of 6 million of my people to being a Republican. When was the last time 6 million Republicans were murdered via gas chambers?
People need to know that this was why she got fired. Don’t you dare just like this post!
REBLOG IT
41K notes
·
View notes
Text
Resources for Writing Injuries

Patreon || Ko-Fi || Masterlist || Work In Progress
–
Head Injuries
General Information | More
Hematoma
Hemorrhage
Concussion
Edema
Skull Fracture
Diffuse Axonal Injury
Neck
General Information
Neck sprain
Herniated Disk
Pinched Nerve
Cervical Fracture
Broken Neck
Chest (Thoracic)
General Information
Aortic disruption
Blunt cardiac injury
Cardiac tamponade
Flail chest
Hemothorax
Pneumothorax (traumatic pneumothorax, open pneumothorax, and tension pneumothorax)
Pulmonary contusion
Broken Ribs
Broken Collarbone
Abdominal
General Information
Blunt trauma
Penetrating injuries (see also, gunshot wound & stab wound sections)
Broken Spine
Lung Trauma
Heart (Blunt Cardiac Injury)
Bladder Trauma
Spleen Trauma
Intestinal Trauma
Liver Trauma
Pancreas Trauma
Kidney Trauma
Arms/Hands/Legs/Feet
General Information | More
Fractures
Dislocations
Sprains
Strains
Muscle Overuse
Muscle Bruise
Bone Bruise
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Tendon pain
Bruises
Injuries to ligaments
Injuries to tendons
Crushed Hand
Crushed Foot
Broken Hand
Broken Foot
Broken Ankle
Broken Wrist
Broken Arm
Shoulder Trauma
Broken elbow
Broken Knee
Broken Finger
Broken Toe
Face
General Information
Broken Nose
Corneal Abrasion
Chemical Eye Burns
Subconjunctival Hemorrhages (Eye Bleeding)
Facial Trauma
Broken/Dislocated jaw
Fractured Cheekbone
Skin & Bleeding
General Information (Skin Injuries) | More (Arteries)
femoral artery (inner thigh)
thoracic aorta (chest & heart)
abdominal aorta (abdomen)
brachial artery (upper arm)
radial artery (hand & forearm)
common carotid artery (neck)
aorta (heart & abdomen)
axillary artery (underarm)
popliteal artery (knee & outer thigh)
anterior tibial artery (shin & ankle)
posterior tibial artery (calf & heel)
arteria dorsalis pedis (foot)
Cuts/Lacerations
Scrapes
Abrasions (Floor burns)
Bruises
Gunshot Wounds
General Information
In the Head
In the Neck
In the Shoulders
In the Chest
In the Abdomen
In the Legs/Arms
In the Hands
In The Feet
Stab Wounds
General Information
In the Head
In the Neck
In the Chest
In the Abdomen
In the Legs/Arms
General Resources
Guide to Story Researching
A Writer’s Thesaurus
Words To Describe Body Types and How They Move
Words To Describe…
Writing Intense Scenes
–
Masterlist | WIP Blog
If you enjoy my blog and wish for it to continue being updated frequently and for me to continue putting my energy toward answering your questions, please consider Buying Me A Coffee, or pledging your support on Patreon, where I offer early access and exclusive benefits for only $5/month.
Shoutout to my $15+ patrons, Jade Ashley and Douglas S.!
64K notes
·
View notes
Photo
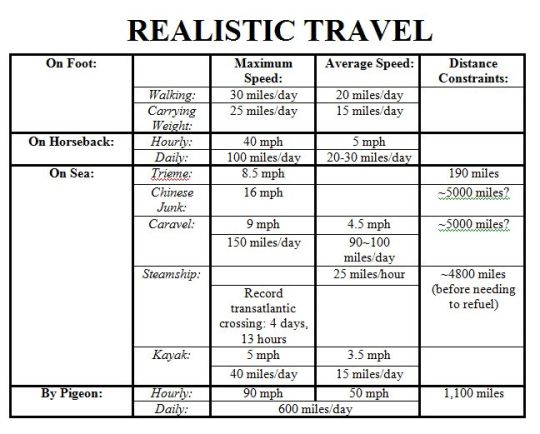
Writing a historical novel means knowing how far they can travel on a horse, This is good info right here.
(via Pinterest)
125K notes
·
View notes
Text

Writing with Color: Description Guide - Words for Skin Tone
We discussed the issues describing People of Color by means of food in Part I of this guide, which brought rise to even more questions, mostly along the lines of “So, if food’s not an option, what can I use?” Well, I was just getting to that!
This final portion focuses on describing skin tone, with photo and passage examples provided throughout. I hope to cover everything from the use of straight-forward description to the more creatively-inclined, keeping in mind the questions we’ve received on this topic.
So let’s get to it.
S T A N D A R D D E S C R I P T I O N
B a s i c C o l o r s

Pictured above: Black, Brown, Beige, White, Pink.
“She had brown skin.”
This is a perfectly fine description that, while not providing the most detail, works well and will never become cliché.
Describing characters’ skin as simply brown or beige works on its own, though it’s not particularly telling just from the range in brown alone.
C o m p l e x C o l o r s
These are more rarely used words that actually “mean” their color. Some of these have multiple meanings, so you’ll want to look into those to determine what other associations a word might have.

Pictured above: Umber, Sepia, Ochre, Russet, Terra-cotta, Gold, Tawny, Taupe, Khaki, Fawn.
Complex colors work well alone, though often pair well with a basic color in regards to narrowing down shade/tone.
For example: Golden brown, russet brown, tawny beige…
As some of these are on the “rare” side, sliding in a definition of the word within the sentence itself may help readers who are unfamiliar with the term visualize the color without seeking a dictionary.
“He was tall and slim, his skin a russet, reddish-brown.”
Comparisons to familiar colors or visuals are also helpful:
“His skin was an ochre color, much like the mellow-brown light that bathed the forest.”
M o d i f i e r s
Modifiers, often adjectives, make partial changes to a word.The following words are descriptors in reference to skin tone.
D a r k - D e e p - R i c h - C o o l
W a r m - M e d i u m - T a n
F a i r - L i g h t - P a l e
Rich Black, Dark brown, Warm beige, Pale pink…
If you’re looking to get more specific than “brown,” modifiers narrow down shade further.
Keep in mind that these modifiers are not exactly colors.
As an already brown-skinned person, I get tan from a lot of sun and resultingly become a darker, deeper brown. I turn a pale, more yellow-brown in the winter.
While best used in combination with a color, I suppose words like “tan” “fair” and “light” do work alone; just note that tan is less likely to be taken for “naturally tan” and much more likely a tanned White person.
Calling someone “dark” as description on its own is offensive to some and also ambiguous. (See: Describing Skin as Dark)
U n d e r t o n e s
Undertones are the colors beneath the skin, seeing as skin isn’t just one even color but has more subdued tones within the dominating palette.

Mentioning the undertones within a character’s skin is an even more precise way to denote skin tone.
As shown, there’s a difference between say, brown skin with warm orange-red undertones (Kelly Rowland) and brown skin with cool, jewel undertones (Rutina Wesley).
“A dazzling smile revealed the bronze glow at her cheeks.”
“He always looked as if he’d ran a mile, a constant tinge of pink under his tawny skin.”
Standard Description Passage
“Farah’s skin, always fawn, had burned and freckled under the summer’s sun. Even at the cusp of autumn, an uneven tan clung to her skin like burrs. So unlike the smooth, red-brown ochre of her mother, which the sun had richened to a blessing.”
-From my story “Where Summer Ends” featured in Strange Little Girls
Here the state of skin also gives insight on character.
Note my use of “fawn” in regards to multiple meaning and association. While fawn is a color, it’s also a small, timid deer, which describes this very traumatized character of mine perfectly.
Though I use standard descriptions of skin tone more in my writing, at the same time I’m no stranger to creative descriptions, and do enjoy the occasional artsy detail of a character.
C R E A T I V E D E S C R I P T I O N
Whether compared to night-cast rivers or day’s first light…I actually enjoy seeing Characters of Colors dressed in artful detail.
I’ve read loads of descriptions in my day of white characters and their “smooth rose-tinged ivory skin”, while the PoC, if there, are reduced to something from a candy bowl or a Starbucks drink, so to actually read of PoC described in lavish detail can be somewhat of a treat.
Still, be mindful when you get creative with your character descriptions. Too many frills can become purple-prose-like, so do what feels right for your writing when and where. Not every character or scene warrants a creative description, either. Especially if they’re not even a secondary character.
Using a combination of color descriptions from standard to creative is probably a better method than straight creative. But again, do what’s good for your tale.
N A T U R AL S E T T I N G S - S K Y

Pictured above: Harvest Moon -Twilight, Fall/Autumn Leaves, Clay, Desert/Sahara, Sunlight - Sunrise - Sunset - Afterglow - Dawn- Day- Daybreak, Field - Prairie - Wheat, Mountain/Cliff, Beach/Sand/Straw/Hay.
Now before you run off to compare your heroine’s skin to the harvest moon or a cliff side, think about the associations to your words.
When I think cliff, I think of jagged, perilous, rough. I hear sand and picture grainy, yet smooth. Calm. mellow.
So consider your character and what you see fit to compare them to.
Also consider whose perspective you’re describing them from. Someone describing a person they revere or admire may have a more pleasant, loftier description than someone who can’t stand the person.
“Her face was like the fire-gold glow of dawn, lifting my gaze, drawing me in.”
“She had a sandy complexion, smooth and tawny.”
Even creative descriptions tend to draw help from your standard words.
F L O W E R S

Pictured above: Calla lilies, Western Coneflower, Hazel Fay, Hibiscus, Freesia, Rose
It was a bit difficult to find flowers to my liking that didn’t have a 20 character name or wasn’t called something like “chocolate silk” so these are the finalists.
You’ll definitely want to avoid purple-prose here.
Also be aware of flowers that most might’ve never heard of. Roses are easy, as most know the look and coloring(s) of this plant. But Western coneflowers? Calla lilies? Maybe not so much.
“He entered the cottage in a huff, cheeks a blushing brown like the flowers Nana planted right under my window. Hazel Fay she called them, was it?”
A S S O R T E D P L A N T S & N A T U R E

Pictured above: Cattails, Seashell, Driftwood, Pinecone, Acorn, Amber
These ones are kinda odd. Perhaps because I’ve never seen these in comparison to skin tone, With the exception of amber.
At least they’re common enough that most may have an idea what you’re talking about at the mention of “pinecone.“
I suggest reading out your sentences aloud to get a better feel of how it’ll sounds.
“Auburn hair swept past pointed ears, set around a face like an acorn both in shape and shade.”
I pictured some tree-dwelling being or person from a fantasy world in this example, which makes the comparison more appropriate.
I don’t suggest using a comparison just “cuz you can” but actually being thoughtful about what you’re comparing your character to and how it applies to your character and/or setting.
W O O D

Pictured above: Mahogany, Walnut, Chestnut, Golden Oak, Ash
Wood can be an iffy description for skin tone. Not only due to several of them having “foody” terminology within their names, but again, associations.
Some people would prefer not to compare/be compared to wood at all, so get opinions, try it aloud, and make sure it’s appropriate to the character if you do use it.
“The old warlock’s skin was a deep shade of mahogany, his stare serious and firm as it held mine.”
M E T A L S

Pictured above: Platinum, Copper, Brass, Gold, Bronze
Copper skin, brass-colored skin, golden skin…
I’ve even heard variations of these used before by comparison to an object of the same properties/coloring, such as penny for copper.
These also work well with modifiers.
“The dress of fine white silks popped against the deep bronze of her skin.”
G E M S T O N E S - M I N E R A LS

Pictured above: Onyx, Obsidian, Sard, Topaz, Carnelian, Smoky Quartz, Rutile, Pyrite, Citrine, Gypsum
These are trickier to use. As with some complex colors, the writer will have to get us to understand what most of these look like.
If you use these, or any more rare description, consider if it actually “fits” the book or scene.
Even if you’re able to get us to picture what “rutile” looks like, why are you using this description as opposed to something else? Have that answer for yourself.
“His skin reminded her of the topaz ring her father wore at his finger, a gleaming stone of brown, mellow facades.”
P H Y S I C A L D E S C R I P T I ON
Physical character description can be more than skin tone.
Show us hair, eyes, noses, mouth, hands…body posture, body shape, skin texture… though not necessarily all of those nor at once.
Describing features also helps indicate race, especially if your character has some traits common within the race they are, such as afro hair to a Black character.
How comprehensive you decide to get is up to you. I wouldn’t overdo it and get specific to every mole and birthmark. Noting defining characteristics is good, though, like slightly spaced front teeth, curls that stay flopping in their face, hands freckled with sunspots…
G E N E R A L T I P S
Indicate Race Early: I suggest indicators of race be made at the earliest convenience within the writing, with more hints threaded throughout here and there.
Get Creative On Your Own: Obviously, I couldn’t cover every proper color or comparison in which has been “approved” to use for your characters’ skin color, so it’s up to you to use discretion when seeking other ways and shades to describe skin tone.
Skin Color May Not Be Enough: Describing skin tone isn’t always enough to indicate someone’s ethnicity. As timeless cases with readers equating brown to “dark white” or something, more indicators of race may be needed.
Describe White characters and PoC Alike: You should describe the race and/or skin tone of your white characters just as you do your Characters of Color. If you don’t, you risk implying that White is the default human being and PoC are the “Other”).
PSA: Don’t use “Colored.” Based on some asks we’ve received using this word, I’d like to say that unless you or your character is a racist grandmama from the 1960s, do not call People of Color “colored” please.
Not Sure Where to Start? You really can’t go wrong using basic colors for your skin descriptions. It’s actually what many people prefer and works best for most writing. Personally, I tend to describe my characters using a combo of basic colors + modifiers, with mentions of undertones at times. I do like to veer into more creative descriptions on occasion.
Want some alternatives to “skin” or “skin color”? Try: Appearance, blend, blush, cast, coloring, complexion, flush, glow, hue, overtone, palette, pigmentation, rinse, shade, sheen, spectrum, tinge, tint, tone, undertone, value, wash.
Skin Tone Resources
List of Color Names
The Color Thesaurus
Things that are Brown (blog)
Skin Undertone & Color Matching
Tips and Words on Describing Skin
Photos: Undertones Described (Modifiers included)
Online Thesaurus (try colors, such as “red” & “brown”)
Don’t Call me Pastries: Creative Skin Tones w/ pics 3 2 1
Writing & Description Guides
WWC Featured Description Posts
WWC Guide: Words to Describe Hair
Writing with Color: Description & Skin Color Tags
7 Offensive Mistakes Well-intentioned Writers Make
I tried to be as comprehensive as possible with this guide, but if you have a question regarding describing skin color that hasn’t been answered within part I or II of this guide, or have more questions after reading this post, feel free to ask!
~ Mod Colette
170K notes
·
View notes
Text
When To Stop Planning

– A lot of asks have come in recently asking about when it’s time to stop planning and start writing and what you should know before you start the first draft vs what you should develop along the way. This is pretty much a checklist of things you should have generally figured out before you begin the first draft. Once you have the following things fleshed out, you should be pretty ready to go. There is always a point in the planning phase where you must accept that 90% of story development happens along the way and partially on accident. I hope this helps you feel more confident in starting your first draft after what I’m sure has been lots of over-planning. Happy writing!
Plot
What plot structure are you following?
What is the main conflict of your story?
Who is the protagonist?
Who or what is the antagonist?
What are the subplots in your story?
What events caused the conflict in your story?
What about the plot will interest your reader the most?
Where does the plot twist(s) occur in your story and how do they affect the it?
What is original or different about your plot that the reader has never experienced before?
What is your story, as a whole, primarily about? Family? Good vs. Evil? The change a character endures? Mirroring reality? Social commentary?
World/Setting
Where is your story taking place?
What areas or locations do the majority of your story take place in?
Is the story based on Earth, an alternate Earth, or a completely different place?
What are the rules of science/magic in your story?
What is the history of the world in your story?
What is society like in your world?
What is the government/economics like in your world?
What level of technology is there in your world?
What is the geography like?
What are some cultures/cultural aspects that will come into play during your story?
Characters
What role does the character play in your story?
What motivates your character?
What are your character’s strengths and weaknesses?
How will your character change throughout the story?
What is your character’s backstory?
How do they impact the plot?
What are their relationships with other characters?
What drives their actions?
What is in the way of them accomplishing their goals?
What Do They..
- Think they want - Truly want - Need
Representation/Symbolism/Theme
What are the major subtextual messages you want to get across throughout your story?
Have you created a cast of characters that represent any minorities?
What are the major symbols in your story?
How are you going to display these symbols to your audience?
How relevant are the symbols to your actual plot?
What is/are the major theme(s) in your story?
Are the themes of your story being conveyed through your setting, characters, or plot?
Is the conflict parallel with a real social issue that you’re commenting on?
How can your representation, symbolism, and theme be enhanced at this point in the writing process?
Have you run your ideas and plans by someone who could give you critiques in order to improve the representation, theme, and symbolism in your story?
I just want to emphasize that it is super important to maintain flexibility when you’re writing a fictional story. Details will change, your preference will change, characters will start to make their own choices, and you will be tempted to change things as you go. Let it happen. Be willing to let go of your past decisions if they no longer satisfy you or your narrative.
Support Wordsnstuff!
If you enjoy my blog and wish for it to continue being updated frequently and for me to continue putting my energy toward answering your questions, please consider Buying Me A Coffee.
Request Resources, Tips, Playlists, or Prompt Lists
Instagram // Twitter //Facebook //#wordsnstuff
FAQ //monthly writing challenges // Masterlist
MY CURRENT WORK IN PROGRESS (Check it out, it’s pretty cool. At least I think it is.)
4K notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey, I love your work btw, it has a flow I really admire. I was wondering if you have any advice to make writing sound less juvenile. I know that practise makes perfect, but I'm more looking for specific advice that I can implement. Thanks!
Thank you very much! You’re right that practice makes perfect, but I totally understand the need for specific points. My writing wouldn’t be where it’s at today without the advice I received from friends, family, and other authors!
It’s hard to say what point will help your writing specifically (since there might be some things you already excel at that I don’t), but here’s a list of points that helped my writing develop (and still develop) a more mature tone.
1) Not all your characters can say what they’re thinking.
People don’t run around spouting out their motivations in real life. While it’s true that characters tend to run around spouting out their motivations in fiction, having too many in one space can make a scene really two dimensional.
“I don’t want him to leave,” he cries. “He’s like a brother to us!”
“I want him out of my city,” she growls. “Every second he’s here increases the danger. I love him too, but love can’t be my priority. You should think about everyone else’s safety.” She throws the saddle onto her horse.
“You’re always telling me what to do,” he says. He wipes at his eyes. “I hate it and I’ll leave before I’m parted from him.”
“No,” she says, “I want you to stay. Please stay. The city comes first, it has to, you know that.”
Seems fine, right? And it is, in small doses. But if the entire conversation goes on like that, you make the scene lose the urgency and tension it needs.
“I don’t want him to leave,” he cries. “He’s like a brother to us!”
“He’s leaving,” she growls. “Tonight.” She throws the saddle onto her horse.
“Then I’ll leave,” he says. He wipes at his eyes. “I’ll leave before I’m parted from him.”
She stills, hands pausing on the leather straps. She wants to tell him to stay, to explain, but can’t. The city comes first. “Do what you want.”
“It’s like you don’t even care,” he says, the words a whisper at her back.
See how there’s so much more to explore this way? How the tension stays through each line of dialogue? How their relationship is put in jeopardy by her silence?
Keep reading
751 notes
·
View notes
Text
There is a specific and terrifying difference between “never were” monsters and “are not anymore” monsters
“The thing that was not a deer” implies a creature which mimics a deer but imperfectly and the details which are wrong are what makes it terrifying
“The thing that was not a deer anymore” on the other hand implies a thing that USED to be a deer before it was somehow mutated, possessed, parasitically controlled or reanimated improperly and what makes THAT terrifying is the details that are still right and recognizable poking out of all the wrong and horrible malformations.
193K notes
·
View notes
Link
Are you still stuck for ideas for National Novel Writing Month? Or are you working on a novel at a more leisurely pace? Here are 102 resources on Character, Point of View, Dialogue, Plot, Conflict, Structure, Outlining, Setting, and World Building, plus some links to generate Ideas and Inspiration.
CHARACTER, POINT OF VIEW, DIALOGUE
10 Days of Character Building
Name Generators
Name Playground
The Universal Mary Sue Litmus Test
Priming the idea pump (A character checklist shamlessly lifted from acting)
How to Create a Character
Seven Common Character Types
Handling a Cast of Thousands – Part I: Getting to Know Your Characters
It’s Not What They Say …
Establishing the Right Point of View: How to Avoid “Stepping Out of Character”
How to Start Writing in the Third Person
Web Resources for Developing Characters
What are the Sixteen Master Archetypes?
Character: A compilation of guidance from classical and contemporary experts on creating great dramatic characters
Building Fictional Characters
Fiction Writer’s Character Chart
Character Building Workshop
Tips for Characterization
Fiction Writer’s Character Chart
Villains are People, Too, But …
Top 10 Tips for Writing Dialogue
Speaking of Dialogue
Dialogue Tips
Advantages, Disadvantages and Skills (character traits)
How to Write a Character Bible
Character Development Exercises
All Your Characters Sounds the Same — And They’re Not a Hivemind!
Medieval Names Archive
Sympathy Without Saintliness
Writing the Other: Bridging Cultural Difference for Successful Fiction
Family Echo (family tree website)
Interviewing Characters: Follow the Energy
100 Character Development Questions for Writers
Behind the Name
Lineage Chart Layout Generator
PLOT, CONFLICT, STRUCTURE, OUTLINE
How to Write a Novel: The Snowflake Method
Effectively Outlining Your Plot
Conflict and Character within Story Structure
Outlining Your Plot
Ideas, Plots & Using the Premise Sheets
How to Write a Novel
Creating Conflict and Sustaining Suspense
Plunge Right In … Into Your Story, That Is!
Fiction Writing Tips: Story Grid
Tips for Creating a Compelling Plot
Writer’s “Cheat Sheets”
The Thirty-six (plus one) Dramatic Situations
The Evil Overlord Devises a Plot: Excerpt from Stupid Plotting Tricks
Conflict Test
What is Conflict?
Monomyth
The Hero’s Journey: Summary of the Steps
Outline Your Novel in Thirty Minutes
Plotting Without Fears
Novel Outlining 101
Writing the Perfect Scene
Fight Scenes 101
Basic Plots in Literature
One-Page Plotting
The Great Swampy Middle
SETTING, WORLD BUILDING
Magical World Builder’s Guide
I Love the End of the World
World Building 101
The Art of Description: Eight Tips to Help You Bring Your Settings to Life
Creating the Perfect Setting – Part I
Creating a Believable World
An Impatient Writer’s Approach to Worldbuilding
Fantasy Worldbuilding Questions
Setting
Character and Setting Interactions
Creating Fantasy and Science Fiction Worlds
Creating Fantasy Worlds
Questions About Worldbuilding
Maps Workshop — Developing the Fictional World Through Mapping
World Builder Projects
IDEAS, INSPIRATION
Quick Story Idea Generator
Solve Your Problems Simply by Saying Them Out Loud
Busting Your Writing Rut
Writing Inspiration, or Sex on a Bicycle
Creative Acceleration: 11 Tips to Engineer a Productive Flow
The Seven Major Beginner Mistakes
Complete Your First Book with these 9 Simple Writing Habits
Free Association, Active Imagination, Twilight Imaging
Random Book Title Generator
Finishing Your Novel
Story Starters and Idea Generators
REVISION
How to Rewrite
One-Pass Manuscript Revision: From First Draft to Last in One Cycle
Editing Recipe
Cliche Finder
Revising Your Novel: Read What You’ve Written
Writing 101: So You Want to Write a Novel Part 3: Revising a Novel
TOOLS and SOFTWARE
My Writing Nook (online text editor; free)
Bubbl.us (online mind map application; free)
Freemind (mind map application; free; Windows, Mac, Linux, portable)
XMind (mind map application; free; Windows, Mac, Linux, portable)
Liquid Story Binder (novel organization and writing software; free trial, $45.95; Windows, portable)
Scrivener (novel organization and writing software; free trial, $39.95; Mac)
SuperNotecard (novel organization and writing software; free trial, $29; Windows, Mac, Linux, portable)
yWriter (novel organization and writing software; free; Windows, Linux, portable)
JDarkRoom (minimalist text editor; free; Windows, Mac, Linux, portable)
AutoRealm (map creation software; free; Windows, Linux with Wine)
114K notes
·
View notes
Text
Are These Filter Words Weakening Your Story?
After putting my writing on hold for several weeks, I decided to jump back in. I expected to find all sorts of problems with my story–inconsistencies in the plot, lack of transitions, poor characterization–the works. But what began to stick out to me was something to which I’d given little thought in writing.
Filter words.
What are Filter Words?
Actually, I didn’t even know these insidious creatures had a name until I started combing the internet for info.
Filter words are those that unnecessarily filter the reader’s experience through a character’s point of view. Dark Angel’s Blog says:
“Filtering” is when you place a character between the detail you want to present and the reader. The term was started by Janet Burroway in her book On Writing.
In terms of example, you should watch out for:
To see
To hear
To think
To touch
To wonder
To realize
To watch
To look
To seem
To feel (or feel like)
Can
To decide
To sound (or sound like)
To know
I’m being honest when I say my manuscript is filled with these words, and the majority of them need to be edited out.
What do Filter Words Look Like?
Let’s imagine a character in your novel is walking down a street during peak hour.
You might, for example, write:
Sarah felt a sinking feeling as she realized she’d forgotten her purse back at the cafe across the street. She saw cars filing past, their bumpers end-to-end. She heard the impatient honk of horns and wondered how she could quickly cross the busy road before someone took off with her bag. But the traffic seemed impenetrable, and she decided to run to the intersection at the end of the block.
Eliminating the bolded words removes the filters that distances us, the readers, from this character’s experience:
Sarah’s stomach sank. Her purse—she’d forgotten it back at the cafe across the street. Cars filed past, their bumpers end-to-end. Horns honked impatiently. Could she make it across the road before someone took off with her bag? She ran past the impenetrable stream of traffic, toward the intersection at the end of the block.
Are Filter Words Ever Acceptable?
Of course, there are usually exceptions to every rule.
Just because filter words tend to be weak doesn’t mean they never have a place in our writing. Sometimes they are helpful and even necessary.
Susan Dennard of Let The Words Flow writes that we should use filter words when they are critical to the meaning of the sentence.
If there’s no better way to phrase something than to use a filter word, then it’s probably okay to do so.
Want to know more?
Read these other helpful articles on filter words and more great writing tips:
Filter Words and Distancing Point of View
The Reasons Editors reject Manuscripts
Filter Those words and Strengthen Your Writing
44K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Plot a Complex Novel in One Day

Now first, I have to say, that the plot you’re able to come up with in one day is not going to be without its flaws, but coming up with it all at once, the entire story unfolds right in front of you and makes you want to keep going with it. So, where to begin?
What is your premise and basic plot? Pick your plot. I recommend just pulling one from this list. No plots are “original” so making yours interesting and complicated will easily distract from that fact, that and interesting characters. Characters will be something for you to work on another day, because this is plotting day. You’ll want the main plot to be fairly straight forward, because a confusing main plot will doom you if you want subplots.
Decide who the characters will be. They don’t have to have names at this point. You don’t even need to know who they are other than why they have to be in the story. The more characters there are the more complicated the plot will be. If you intend to have more than one subplot, then you’ll want more characters. Multiple interconnected subplots will give the illusion that the story is very complicated and will give the reader a lot of different things to look at at all times. It also gives you the chance to develop many side characters. The plot I worked out yesterday had 13 characters, all were necessary. Decide their “roles” don’t bother with much else. This seems shallow, but this is plot. Plot is shallow.
Now, decide what drives each character. Why specifically are they in this story? You can make this up. You don’t even know these characters yet. Just so long as everyone has their own motivations, you’re in the clear.
What aren’t these characters giving away right off the bat? Give them a secret! It doesn’t have to be something that they are actively lying about or trying to hide, just find something that perhaps ties them into the plot or subplot. This is a moment to dig into subplot. This does not need to be at all connected to their drive to be present in the story. Decide who is in love with who, what did this person do in the 70’s that’s coming back to bite them today, and what continues to haunt what-his-face to this very day. This is where you start to see the characters take shape. Don’t worry much about who they are or what they look like, just focus on what they’re doing to the story.
What is going to change these characters? Now this will take some thinking. Everyone wants at least a few of the characters to come out changed by the end of the story, so think, how will they be different as a result of the plot/subplot? It might not be plot that changes them, but if you have a lot of characters, a few changes that are worked into the bones of the plot might help you.
Now list out the major events of the novel with subplot in chronological order. This will be your timeline. Especially list the historical things that you want to exist in backstory. List everything you can think of. Think about where the story is going. At this point, you likely haven’t focused too much on the main plot, yeah, it’s there, but now really focus on the rising actions, how this main plot builds its conflict, then the climactic moment. Make sure you get all of that in there. This might take a few hours.
Decide where to start writing. This part will take a LOT of thinking. It’s hard! But now that you’ve got the timeline, pick an interesting point to begin at. Something with action. Something relevant. Preferably not at the beginning of your timeline - you want to have huge reveals later on where these important things that happened prior are exposed. This is the point where you think about what information should come out when. This will be a revision of your last list, except instead of being chronological, it exists to build tension.
Once you’ve gotten the second list done, you’ve got a plot. Does it need work? Probably. But with that said, at this point you probably have no idea who half your characters are. Save that for tomorrow, that too will be a lot of work.
32K notes
·
View notes





