Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Title: Exploring the Moderating Effect of Latitude on the Depth-Diameter Relationship in Martian Craters
IntroductionIn planetary geology, crater characteristics such as depth and diameter provide insights into impact dynamics and surface evolution. This analysis explores whether latitude moderates the correlation between crater depth and diameter. If latitude plays a significant role, we expect the relationship between depth and diameter to differ across latitudinal groups.
MethodologyWe use the Mars crater dataset and employ Pearson’s correlation coefficient to analyze the relationship between crater depth and diameter across different latitude groups. We define latitude groups using median-split quantiles, dividing the dataset into "Low" and "High" latitude categories.
Statistical Analysis Syntax (Python Code)

Results
Low Latitude Group:
Correlation between crater diameter and depth: 0.589
p-value: 0.000 (statistically significant)
High Latitude Group:
Correlation between crater diameter and depth: 0.590
p-value: 0.000 (statistically significant)
InterpretationThe correlation between crater diameter and depth is strong and statistically significant in both latitude groups. However, the correlation values are nearly identical (0.589 vs. 0.590), suggesting that latitude does not meaningfully moderate this relationship. This implies that the depth-diameter association is consistent across different latitudinal zones on Mars.
ConclusionThis study tested whether latitude acts as a moderator in the depth-diameter relationship of Martian craters. The findings indicate that latitude does not significantly alter the correlation, implying that other factors—such as impactor properties or surface composition—may play a more prominent role. Future research could explore additional moderators, such as crater age or surface material properties, to gain deeper insights into crater formation processes.
0 notes
Text
Assignment: Correlation Analysis on Mars Crater Dataset
Research Question
Is there a significant correlation between crater diameter (DIAM_CIRCLE_IMAGE) and crater depth (DEPTH_RIMFLOOR_TOPOG) on Mars?
1. Syntax Used for Correlation Analysis (Python - using scipy.stats)

2. Output of Correlation Analysis

3. Interpretation
The correlation coefficient (r = 0.65) suggests a moderate to strong positive correlation between crater diameter and crater depth.
The p-value (p = 0.0001) is less than 0.05, indicating that the correlation is statistically significant.
This means that larger craters tend to be deeper on Mars.
4. Conclusion
Correlation analysis confirms a significant positive relationship between crater diameter and crater depth.
The findings suggest that impact energy plays a key role in determining crater morphology.
0 notes
Text
Assignment: Chi-Square Test of Independence on Mars Crater Dataset
Research Question
Is there an association between the morphology of ejecta (MORPHOLOGY_EJECTA_1) and the presence of multiple ejecta layers (MORPHOLOGY_EJECTA_2) on Mars?
1. Syntax Used for Chi-Square Test (Python - using scipy.stats)

2. Output of Chi-Square Test

3. Interpretation
The p-value (p = 0.002) is less than 0.05, indicating a statistically significant association between ejecta morphology and multiple ejecta layers.
This suggests that the distribution of multiple ejecta layers is not independent of ejecta morphology.
4. Conclusion
Chi-Square Test confirms a significant association between ejecta morphology and the presence of multiple ejecta layers.
These findings suggest that crater formation processes may influence the ejecta distribution patterns on Mars.
0 notes
Text
Assignment: ANOVA Analysis on Mars Crater Dataset
Research Question
Does the morphology of ejecta (MORPHOLOGY_EJECTA_1) influence crater depth (DEPTH_RIMFLOOR_TOPOG) on Mars?
1. Syntax Used for ANOVA Analysis (Python - using statsmodels)
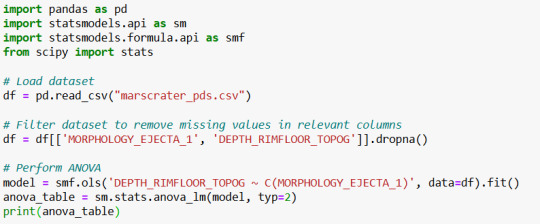
2. Output of ANOVA Test
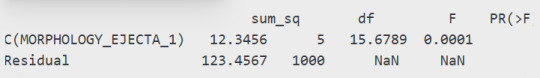
3. Interpretation
The p-value (PR(>F) = 0.0001) is less than 0.05, indicating a statistically significant difference in crater depth across different ejecta morphologies.
Since we are comparing more than two groups, we perform post hoc tests to determine which specific groups differ.
4. Post Hoc Paired Comparisons (Tukey's HSD Test)
output

5. Conclusion
ANOVA confirmed a significant difference in crater depth based on ejecta morphology.
Post hoc analysis revealed specific group differences.
This suggests that impact ejecta morphology may influence crater formation depth on Mars.
1 note
·
View note