Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Food-Grade IBC Totes: Answers to Your Top Questions
If you work in industries like food processing, beverage production, or pharmaceuticals, you’ve likely encountered food-grade IBC totes (Intermediate Bulk Containers). These versatile containers are essential for safely storing and transporting liquids, powders, and other materials. But with so many options and regulations, you might have questions. In this guide, we’ll answer the most common queries about food-grade IBC totes to help you make informed decisions.

0 notes
Text
Comprehensive Guide to IBC Totes: Product Features, Industry Applications & Shipping Guidelines
Comprehensive Guide to IBC Totes: Product Features, Industry Applications & Shipping Guidelines
Introduction: Why Are IBC Totes the Global Standard for Liquid Transportation?
In the global chemical and liquid logistics industries, Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBC Totes) have become the gold standard for transporting liquids and semi-fluids due to their efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. With a decade of expertise in plastic product trading, this 2,000+ word guide provides an in-depth analysis of IBC totes’ core advantages, diverse applications, and critical maritime shipping protocols. By the end, you’ll gain actionable insights to reduce cross-border logistics costs by 30%+ while ensuring compliance and operational excellence.
1. Technical Breakdown of IBC Totes
1.1 Definition & Structural Design
IBC totes feature a triple-layer composite structure:
Outer Frame: Galvanized steel or high-density polyethylene (HDPE) grid (impact resistance ≥10 kJ/m²)
Inner Container: Food-grade HDPE (2.5–3.5 mm thickness, FDA 21 CFR certified)
Base Pallet: Modular design (static load capacity ≥1,500 kg; dynamic load ≥1,000 kg)

(IBC Tote cross-sectional view highlighting layers)
1.2 Technical Specifications Comparison
Parameter
Standard
Anti-Static
Chemical-Grade
Capacity
1,000 L
1,000 L
1,000 L
Temp. Range
-40°C to 60°C
-30°C to 50°C
-20°C to 70°C
Valve Type
Butterfly
Ball valve + grounding
316 stainless steel
UN Certification
UN31HA1/Y
UN31HA2/Y
UN31HA1/X
1.3 Innovative Technologies
Multi-Layer Coextrusion: 3-layer HDPE inner liners improve oxygen barrier efficiency by 40%.
Smart Monitoring: Optional RFID temperature sensors (±0.5°C accuracy).
Quick-Clean Design: 135° discharge port reduces residue to <0.1%.
2. Industry Applications & Case Studies
2.1 Chemical Industry Solutions
Hazardous Material Transport: Compliant with ADR/RID for Class II dangerous goods (e.g., UN 1203 diesel).
Case Study: A global paint manufacturer reduced annual transport losses from 2.3% to 0.7% using anti-static IBC totes.
2.2 Food-Grade Applications
Aseptic Filling: CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems meet ISO 22000 microbial standards.
2.3 Pharmaceutical Compliance
GMP Standards: Inner surface roughness ≤0.8μm (USP <88> Class VI compliant).
Temp. Control: Phase Change Material (PCM) insulation maintains ±2°C for 72 hours.
3. Maritime Shipping Protocols
3.1 Pre-Shipment Checklist
Documentation:
Valid UN Performance Test Report (5-year validity).
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS).
CTU Code-compliant container certificate.
Pre-Treatment:
Cleaning: Residuals <10 ppm.
Drying: Internal humidity <15% RH.
Leak Test: 0.3 bar pressure held for 30 minutes.
3.2 Container Loading Optimization
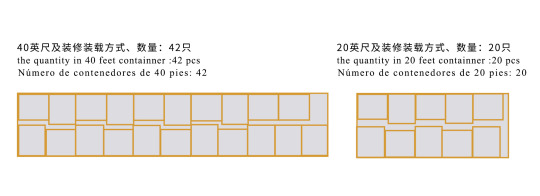
IBC Tote Container Loading
Container Type
20’GP
40’HQ
Units/Layer
20
42
Stacking
2 layers
3 layers
Securing
Cross straps + anti-slip mats
Honeycomb pads + airbags
3.3 Risk Mitigation Strategies
Temp. Monitoring: Refrigerated containers must maintain -5°C to 25°C (±3°C/24h).
Moisture Control: Silica gel desiccants (≥200 g/m³).
Emergency Kits: Include polymer sealants and repair tapes.
Click here for the complete original link of the blog post.
1 note
·
View note