#AI testing framework
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Best Practices for Designing a Test Automation Framework
Designing a robust test automation framework is essential for scalable, maintainable, and efficient testing. A well-structured framework helps teams standardize test processes, accelerate execution, and improve code reusability. Here are key best practices to follow:
Define a Clear Architecture
Choose a layered structure that separates test scripts, utilities, and test data. This modularity improves maintainability and enables easy updates.
Select the Right Tools and Tech Stack
Choose tools that align with your application, team skillsets, and CI/CD goals—like Selenium, TestNG, Cypress, or Playwright. Integrate with version control and build tools for automation framework continuity.
Use Data-Driven and Keyword-Driven Approaches
Implement reusable test logic that supports parameterization. This reduces redundancy and allows flexibility in running tests with various datasets.
Enable Logging, Reporting, and Exception Handling
Build in detailed logs and custom reports for quick debugging. Include robust error handling to prevent script failures from breaking the entire suite.
Ensure Scalability and Maintainability
Design the framework to scale with your application. Follow coding standards, comment code clearly, and regularly refactor for performance.
A well-designed framework is the foundation for long-term test automation success.
#AI test automation#tcoe testing#test management tools#qa test management tools#automation tools for testing#performance testing tools#open source testing#web automation using robot framework#test automation strategy#testing coe framework
0 notes
Link
Wally's AI Framework provides a high-quality comprehensive audit in minutes while saving enormous time and expense when compared to manual audits.
0 notes
Text
The Simslops Afterword
hello everybody! thank you for reading my book. seeing people talk about it has been very gratifying & encouraging.
i was going to write this up essay style, but doing it as a q&a is more fun and still lets me cover everything i wanted to, so let's begin.
q&a
first off, a question from @aminoasinine which i'll address in parts:
I really enjoyed Simslops, and in particular I think the "dwarf fortress event log" style of writing is a great way to showcase the machine/algorithm aspect of it. What software was used for this? Did it have trouble keeping track of so many characters? I noticed the centipedes and other numbered masses were accurately tracked throughout the text, which is something that I know AI tends to struggle with. I'm also curious to know how much of the chapters' 'plot' was laid out in advance by the prompting, and whether any major events were the result of emergent narrative. In particular, the coffin + Maude's Salvation plot towards the end definitely felt like direct intervention on your part, but was the AI reacting to you inserting those things, or were you editing the text around them after the fact?
the simslops is the product of a custom program written in nodejs. the source code is available at the download page if you want to examine it in detail, but the core of the framework is as follows:
there are actors, items, and rooms with names and numerical flags.
there are actions, each defined by their conditions, effects upon the scene, and chance of being selected.
each chapter is defined by its starting conditions and available actions.
each round or tick (whatever you want to call it), a random available action is applied to the scene.
this is repeated until an action ends the scene or there are no more actions left to perform.
each action narrates itself when applied to a scene. for example, the source code for the "pick up an item" action looks like this:

hopefully this is at least semi-intelligible if you don't know javascript. the first parameter defines what the action acts upon: in this case, an actor and an item. the second is the condition: the item must not already be held, and it must not have the pickupAttempted flag. the third is responsible for how the action affects the scene, and the string it returns is how the action is described in the text. when an actor goes to pick something up, if that something is immovable, this is noted. (otherwise every scene devolves into everybody struggling to pick up a couch.) if it's not immovable, the actor picks it up. the first case is described with "actor tries to pick up item, but it's hardly portable." (a reference to the inform 7 default responses) and the second with "actor picks up item." the fourth parameter says to multiply this action's weight by ten if the item in question has a description and has yet to be examined.
each action is defined similarly. a handful use grammars for more varied output, but the majority just have simple fill-in-the-blank sentences. all together there's nearly 6k lines of nodejs to define the whole book. this project started as a test case for this framework, actually. i was outlining a short story and hating it and had a thought: what if i wrote a program to generate an outline for me? then i could have a skeleton to work from and could get to the fun part, the actual writing. out of whimsy i decided to put some simpsons characters in a room and make them fuck. this is a more exhaustive test case than you'd expect. it handles solo actions (moaning) and pair actions (lustful looks & sex.) sex only happens when both participants are horny, which requires setting flags for each actor. kramer's appearance is an action not tied to anything in the scene, and giving birth is an action that creates new actors. a great deal of my motivation here (and in many other things) was "wouldn't it be funny / fucked up if..." but it also did its job of test case pretty well. once i added items, that necessitated inventories; theft & picking up & putting down all require certain types of checks.
it's funny that you mention emergent narrative, because i really think the simslops really became what it was in the telling. early in the process i became enamored with the image of one of the characters descending through text adventure geography, lost and alone. thus came the turn to pathos. i had read "does marge have friends" some time prior, which inspired maude's inclusion and the role she plays. from there i built things out with twin eyes toward thematics and "funny/fucked up". i do find it interesting to what extent all that was emergent from the implementation. it's a framework that tends towards reducing things to mush. a semantic satiation machine.
anyway, i hope this answers your question --- it's not LLM-based, it uses older, more "traditional" procgen techniques. the plot of each chapter is roughly scaffolded by the actions i attach to it. it's really incredibly authored; it's difficult for this framework to surprise me except by juxtaposition. under this framework it's also pretty trivial to track any number of actors. so, to answer this question from @zedogica:
how much of simslops was embellished from the original generated text? a few moments stood out to me
none of it. you can download the source and get your own personal simslops. the only human embellishment was done during development. in an ideal world, this would live on a server somewhere and everyone could download a unique generation. unfortunately, i don't have the knowhow for that kind of thing. (my understanding is that you need to do a lot when writing server-side code to make sure you don't expose a million security vulnerabilities.) i've contented myself with doing what i can client-side: releasing the source code & setting up the download button to give you one of five pre-generated outputs.
returning to aminoasinine's question:
I also really like the difference in language used during the Deviltongue chapters. It's interesting to see what changes when the tone is explicitly defined as 'horror' or 'scary', and how that seemingly translates to those bizarre compound words like tribulationmalice and torturefrenzy. I think it's my favorite chapter(s) in general because of how it takes a much different tone and hammers it into the same monotonous nothing as the other chapters despite its more 'active' and ostensibly 'less boring' setting than your standard centipede sex house. everything shakes and moans and howls with blood-malice, lymph and spines standing on end, over and over until it doesn't mean anything anymore. everyone and everything is trembling in fear of a grim finality bearing down that never actually comes, because nothing ever ends. It's the same nothing-emotion as all the unbearable passionate lust in the sex scenes, an emotional signifier that signifies absolutely nothing.
thank you! the strange compounds are a product of the aforementioned grammars, as are the shaking and moaning and howling. writing the dungeon & horror chapters made me realize i really like broad, dumb pastiches. there's something very satisfying about taking cliches and mangling them.
Anyway, the choice to have 'pet the dog' in every scene did not go unnoticed, I think the last three lines are my favorite part, and finally, I think every book from now on should open with a horoscope chart made from out of context quotes. Thank you for making this, I will be watching your neocities with great interest :)
thank you for reading it! two fun facts about the horoscopes:
each entry's text is taken from a random item description.
the dates are wrong, each offset by a day. due to my strong personal convictions i wished to stress that this novella in no way endorses the practice of astrology.
an anonymous question:
So Marge crying during the video game sequence show the reduction of feelings into simple fun, even though the human experiencing the games in question might feel other emotions when playing them. But what do the horror sections represent? I got the gist of most parts, but as I don’t engage with horror medium often I feel like the commentary is lost on me. What were you trying to say with the horror sections, in other words?
first: one of the major benefits of the framework i used here is that it's very good at creating unintended juxtapositions. the only prerequisite for weeping is if the actor in question is holding part of a corpse, but depending on the context, it can take on a number of different connotations.
second:
a lot of usamerican horror films (particularly aliens and predator) are sublimations of the anxieties surrounding the vietnam war. both are about big grizzled soldier guys getting picked off by an unseen yet omnipresent foe who can strike from anywhere. hell, one of them is even set in a jungle. slender: the eight pages, being a game about the Scary Getter following you around in a forest, feels of a type with these.
seymour skinner was a us soldier in the vietnam war.
in that vein, another anonymous question:
also I understand almost all of the references in the chicken’s names but how does sylvester stallone figure into colonialism?
one of sylvester stallone's two big roles is the rambo series, where he's a heroic us soldier rescuing prisoners of war in vietnam, repelling the soviets in afghanistan, or performing other jingoistic acts of horrendous violence. the other is rocky where he plays a white boxer (the "italian stallion") who's built up as a contender to the current reigning champion, Black boxer apollo creed. he's of a type with the other americana culture slop included, i think.
another question from aminoasinine:
Damn, I thought of another question right after I sent that long-ass ask. What was the thought process behind making The Bart such a minor part of the story? Is it out of a desire (or the AI's internal rules) not to have a child present in the gore/sex chapters, or is it more about how Bart as a character seems almost /more/ of a product or symbol than any of the other characters? Like, he can't really mingle with the other 'people' in this setting, because he is something beyond, having transcended any semblance of characterhood to become ONLY product? Is this the end state of every simslop, to eventually be reduced to a series of identical stimuli on a conveyor belt of endless content?
i settled on the cast of characters pretty early. homer and marge are obvious. ned is also pretty obvious. maude is the emotional core. "kramer bursts in" is a pretty common meme. and i had steamed hams edits on the brain, so seymour gets to come, too. i scaffolded out my story with a focus on these six and whatever pathos & resonance i could wring out of them.
i don't think i had any plans to include bart until i came up with that pun. "the work of bart in the age of mechanical reproduction." that + the factory itself is a very good illustration of the funny/fucked up philosophy & dichotomy. (i think i also had the bart doll from the trash meteor episode of futurama in mind.)
anyway, to answer your actual question: yeah, i didn't want to put bart in the main story because i didn't want to put a child in the mix, and he didn't fit in the outline i had drawn up. i think the intermissions pretty accurately capture the pathos of bart & milhouse, though. the funko pop scamp and the perpetual punching-bag.
this next question is from @where-your-eyes-dont-go:
I'm curious about the reason for "_ pets the dog" being such a frequent refrain in so many sections. I could read it a few ways— it's an action that's often used to humanize characters, and it occasionally does seem to give the characters more apparent personhood, the action almost automatically being interpreted by the reader as affection showcasing an internal life—but its repetition seems to force the reader to instead view it as just another merely automatic process. It also could be a bit of commentary on the common claim that a "pet the dog" button in video games automatically makes such games better. I'd love to know more about your thought process here.
early in the development process, i added "actor votes blue." as an inane flavor action. rqd suggested they pet the dog, and i thought it was brilliant. "can you pet the dog" is exactly the kind of empty posturing i want to satirize. i thought it would be best if the dog is never simulated otherwise. just as petting the dog is an empty gesture in games, in the simslops the dog only exists "in flavor", not mechanically. there is no dog actor or dog affection flag, it's just implied there's a dog around for each scene. the suggestion of something cozy and wholesome and cute happening without any actual substance. (and bob was there, too.)
(a friend had to dissuade me from adding "actor realizes why they're called Kojima games" as another flavor action.)
this anonymous question befuddled me a bit:
have you read Marge Simpson Anime?
"marge simpson anime... what in the world is marge simpson anime?" and then i looked it up and found a tumblr blog with a bunch of drawings of marge and went "oh yeah! marge simpson anime!" i haven't read it, but i've definitely seen it around, and i'm definitely at least in conversation with it.
(on the subject of things i'm in conversation with, i realized recently that i absolutely should have put too many cooks and the simpsons au where homer is in pain in the further reading section.)
a question from @theoretically-questionable:
I'm curious as to why the choices of both explicit sexual acts and disregard for consistent anatomy within said acts were made for Simslops; was it simply a transgression, influenced by the (surprising) amount of actual simpsons porn, or something else?
this one also befuddled me. my original intent had been to generate oddball descriptions of a consistent set of genitals, but, like. on further reflection, that super isn't borne out by the text. i think my mental image of things changed when i added the "adverbly-verbing" snowclone to the sex grammar. (score one for emergent narrative.) my initial motivation was that i think over-the-top, too-mechanical-to-be-erotic sex is a fun thing to write a generator for, and i find kramer and homer doing obscene things to each other amusing. the end result is a lot more mastaba snoopy in a way i really like.
here's a question from @txttletale:
why the simpsons? as opposed to, for example, family guy
i've had to think for a while on this. my instinctive response is "it was essentially random, an act of whimsy," but that's not a very good answer. surely something drew me to the simpsons, even if it was subconscious. let's try and peel it back a layer. my next theory has to do with pathos. it is very difficult to wring anything remotely poignant out of peter griffin. you put peter griffin in a scary cave and he goes "this reminds me of the time i was in the descent" and we get some inane cutaway gag. i can't imagine lois expressing anything more sincere than a scott the woz video. there's an obvious pathos to meg, the constant butt of the joke; treating her with any degree of seriousness gets you pathos in spades. similarly, that comic where chris griffin and bart simpson go to couples therapy is genuinely affecting. there's something there, but it's a very different something from what the simslops ended up being. (for one, i wouldn't feel comfortable doing all the centipede sex stuff if my principal characters are kids.) there's a similar issue with trying this with south park (which was also something i don't have much familiarity with). while the fandom has bafflingly devoted a great deal of time and energy to the emotional struggles of those little weirdos, i don't really see much potential there.
on the other end, we have futurama, a show with perhaps too much emotional weight to go in the blender in the same way. like, there are the episodes with fry's dog and fry's brother and leela's parents. similarly, bob's burgers and bojack horseman (and i'm sure many other shows) draw their characters too realistically. the simpsons hits a sweet spot. its characters are cartoon-enough, commodified-enough, and emotional-enough. they're in the goldilocks zone along all these axes.
in the simpsons movie, there's a bit where bart and ned go fishing. bart messes up somehow, ned goes to assist, and bart flinches away, expecting to be strangled. what was once a comedy routine, a subversion of the "father-knows-best" sitcom family, is treated with real emotional weight.
how did they ever come back from that? by the end of the film homer had redeemed himself as a person and as a father. it was the emotional climax of the movie or whatever. roll credits. there were a million billion more seasons and despite the increasing age of the voice cast, more simpsons are extruded every day. why bother? the rotten heart was laid bare nearly two decades ago.
finally, a question from @fattyopossum:
have you seen any interpretations of it youd consider like. unexpected, in either a good ro bad way? any takes on it now that its been out that youw erent expecting people to get or new interpretations people brought to it that really resonated with you
a lot of the thematic weight of the simslops feels post-hoc to me, like a new interpretation that wasn't there when i wrote it. again, it really became what it was in the telling; technical decisions lead to thematic weight. all characters who have sex have the same genitalia. i decided this because it made writing the sex grammar easier. however, it's also a huge thematic boon. casting marge and maude as transfem makes maude's abjection and their love for eachother much more impactful. it's really easy for me to get chicken-or-the-egg about it. which came first, the High Artistry or the Funny/Fucked Up?
(the real answer, of course, is that it doesn't matter. the text exits anyway and i must shepherd it as it exists, not as i intended it. ego death of the author.)
as for other people's interpretations: i'm quite pleased about the reasoning that anon expressed earlier for why marge was crying while platforming. i was also happy to hear a friend's read that kramer had finally found peace in the meadows, that she's with the girls and relaxing and having snacks. it's not really borne out by the text, but it's such a comforting thought, right? maybe if we imagine kramer happy, she will be.
trivia
the first commit hit my git repo in september 2024, and the simslops released march 2025. all in all it took about six months of on-and-off work.
the name "deviltongue" comes from a character i played in a game of neptune's pride. he ended up getting betrayed and dying badly. so it goes. (on a similar note: as a kid, i thought his name actually was "slideshow bob".)
originally, the sundervalley chapters were going to feature more of the classic cozy small farmer simulator tropes. homer was gonna go fishing and chat up the town's eligible bachelors: crow, tom, and cam. it would've distracted too much from the real core of the chapter, though, so it never got implemented.
my original design for the cover looked like this:

i'm still not sure i made the right decision switching to the final composition. i like the oddness of eyes on the hair in that version, but the lines over the hair in the this version remind me of one of the ways you see dicks censored in hentai, which feels thematically appropriate.
on that subject, this texture:

is a heavily mangled collage of a bunch of ai generated images, each of which was created by using the name of a simpsons' character as both prompt and negative prompt. it shows up in the download buttons and (in heavily desaturated form) on the final version of the cover.
the blurbs were slightly modified grammar output. i was pretty fried the day of release & wasn't able to think of anything, so rqd suggested i use a relevant wikipedia extract and use a grammar for the blurbs. i think it turned out pretty well.
there are six secret characters in the simslops. have you found them?
future work
i think i've taken this framework as far as it will go. the system of numerical flags got bent when i stored the farm workers' country of origin as text. the more linear plotted segments required a set of flags trading off each other, which is fiddly to coordinate. generally, everything is very siloed off. the clearest example of this is in the grammars for generating the various bits of procedural text. they're fun to write, and i'm always delighted by the results, but there's a lot of duplication of effort in my current approach. each chapter that uses procedural text has its own grammar with its own set of words and phrases. this is basically fine in this case, but it's not something i want to deal with for future projects. writing grammars is fun, like building a shipyard in a bottle, but it gets mind-numbing after a while. you can only come up with synonyms for laugh so many times, yknow?
my dream is a single massive grammar all output text runs through. since my grammar system can handle conjugating verbs and adding a/an in front of words, integrating all text output with that system would simplify all sorts of things. then i could have big lists of words to query for relevant adjectives or nouns with specific associations, procedural sentence structures, referents that know what adjectives apply to them...
it's really easy to get feature crept in this sphere. we'll see how much of this i'll be able to implement. i don't think all that is necessary to make the simslops framework useful, really. the only thing it urgently needs is some kind of event emitting & handling system. currently all the little special cases have to be implemented specifically. for example, there's a check in the "drop item" action for if the item in question is fragile. if it is, it breaks. if the item is also smoky, we get the "orange smoke pours out" effect. it'd be a lot cleaner (and make me a lot happier) if i could just say "when a smoky object breaks, emit orange smoke" and similar things.
thank you to everyone who read the simslops, and an extra thank you to everyone who asked me questions. now it's time to go back to work on the next issue. it's going to be a very different beast. i hope you enjoy it.
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
New open-access article from Georgia Zellou and Nicole Holliday: "Linguistic analysis of human-computer interaction" in Frontiers in Computer Science (Human-Media Interaction).
This article reviews recent literature investigating speech variation in production and comprehension during spoken language communication between humans and devices. Human speech patterns toward voice-AI presents a test to our scientific understanding about speech communication and language use. First, work exploring how human-AI interactions are similar to, or different from, human-human interactions in the realm of speech variation is reviewed. In particular, we focus on studies examining how users adapt their speech when resolving linguistic misunderstandings by computers and when accommodating their speech toward devices. Next, we consider work that investigates how top-down factors in the interaction can influence users’ linguistic interpretations of speech produced by technological agents and how the ways in which speech is generated (via text-to-speech synthesis, TTS) and recognized (using automatic speech recognition technology, ASR) has an effect on communication. Throughout this review, we aim to bridge both HCI frameworks and theoretical linguistic models accounting for variation in human speech. We also highlight findings in this growing area that can provide insight to the cognitive and social representations underlying linguistic communication more broadly. Additionally, we touch on the implications of this line of work for addressing major societal issues in speech technology.
167 notes
·
View notes
Text
Transformers Earthspark: Another Place, Another Prison

Hashtag /definitely/ helped Bee do a bit of research for his lil presentation. I know I used the internet to figure out the framework lmao
It's funny when you look up "what defines a good person" the ai kinda gives you a little list with fraggin suggestions of praise to give a good person. Then if you look up "What defines a bad person", it gives you like, factors for it and a list for signs of a toxic relationship and a couple hotline links. Oddly wholesome from google ngl
Also can glimpse a bit of depresso expresso Star. Mah dude has dealt with so much scrap that having a bit of an "im so done with this" scrap attitude be lingering
Previous Chapter: Settling Into Circumstance
First Chapter: The Need For Read
Next Chapter: Family Feud
Chapter 10: Bee's Good Guy Crash Course
Starscream had found himself upon the floor in the odd room the Malto’s put together. He wasn’t about to trust that questionable berth. Splayed out with his wings against the cool stone, where no hidden restraints could pop out at him, was preferable. He’d made sure to check.
Starscream had just spent the last groon or so picking apart every centihic of the place, in fact. No cameras in the posters, or that ugly lamp. Nothing amiss with the storage underneath the berth. The pillows as they’d been called still looked suspicious, but he hadn’t been able to prove how yet. The doorframe definitely harbored a means to seal him inside at their leisure, he just needed to make certain not to aggravate them to such a point. Prove that he could stay put voluntarily.
Starscream stared up at the fake little stars in thought. Could those possibly conceal turrets like those implemented by G.H.O.S.T.? They were rather small, but so were the humans, and their weaponry. He had tested one, and it seemed innocent enough, but that did not speak for all of them. The bots, nor the Malto’s, would trust leaving him alone in their little bunker without some insurance. They had to have some form of security. Even if it did only look like a ridiculous clubhouse for sparklings.
His wing twitched as he felt the distinct vibrations of pedsteps through the floor. That was far more trustworthy than his audials which seemed to be constantly glitchy as of late. But whose were they? As they rhythmically made their way towards him, he calculated the pace of the stride with the weight. It was Bumblebee.
“Why are you on the floor?” The bug gestured a servo to him with an air of judgment.
Starscream remained silent for a moment as he glanced over at the mech, “What do you want?”
Bumblebee’s optical lids and doors dropped in annoyance, then he straightened with a slight roll of his helm. “Weeell, we had our time to get situated. So now, I thought–since the kids are either occupied with school or going out to find new cave springs–I could get you started on your good guy training! As I’m sure the Terrans could tell you, I’m a great teacher. And I put together a lecture on the dos and don’t of not being a garbage person!”
“Lucky me.” Starscream said sarcastically with a toss of his servo which promptly flopped back down with a thunk. Did he really have to listen to this scout?
Bumblebee groaned and stepped closer to stand over the seeker with his servos on his hips. “So get up! I’m not rolling my whiteboard in here for you.”
Starscream glared at him before pushing himself onto his peds with his own little noise of complaint. Allowing himself to be commanded by this bug was insulting. Yet there seemed no avoiding it given the circumstances, and at least it was something to do.
“Thank you.” The bug stated flatly as he turned to lead the way toward whatever annoying presentation he had planned.
A crate was pulled out in front of the aptly named “whiteboard”, which the bug told Starscream to take his seat in. One side of the board was labeled “pillars of being a good person”; Empathy, Consideration, Accountability, Prudence, Temperance, Justice, Fortitude. The rest was split into two sections detailing the aforementioned “dos and don’ts” in green versus red marker.
Do: be kind, be patient, be understanding, be selfless, be compassionate, be respectful, be honest, be loyal, be helpful.
Don’t: be rude, be selfish, be aggressive, be greedy, be spiteful, be insensitive, plot against your friends, want world domination, steal, be controlling, hit people, ignore people, manipulate people.
Those seemed rather personal, ridiculous, and quite debatable.
Bumblebee had retrieved a stick to point with, and tapped it on the red side. “First, we’ll go over what you shouldn’t do. For instance, you were rather rude a minute ago–”
“How?”
“Wha–what do you mean how?? You were giving me all this sass for no reason, didn’t answer my first question, and acted like a disgruntled teenager!” The bug counted on his digits.
Starscream crossed his arms. “That’s an exaggeration. And what makes you believe you are even worth my respect?” Bumblebee looked just about ready to explode, but Starscream smirked with the thought that if the scout did decide to start a fight, he could point to the stupid little board that admonished hitting people.
“DUDE! I’m the bot that was trusted to watch over you! Do you know how much I did in the war? I definitely kicked your tailpipe more than once!” The scout pointed the stick at starscream angrily before slumping backwards dramatically. “Ugh…just- regardless, being respectful to people isn’t something you should think they need to earn.”
Starscream laughed, “That’s cute. So you say that you really did just throw the Prime on your pedestal out of nothing but sheer reverence? He did nothing to prove his position worth your confidence?”
“No! Optimus is an awesome leader, and ticks literally every box on the Do list! He’s done thousands of things to express why he’s a Prime–”
“What about Megatron?”
“He–...Megatron proved his conviction to us when he changed sides, and continues to prove it.” The bug had begun to avert his gaze. “He’s changed for the sake of our people. Optimus believes in him, so I do too. You still have a way to go to get to that point.”
“Ah, so all I have to do is betray everything I’ve stood by for practically my entire functioning, and destroy the Allspark–for you to think me worthy of your respect? Hah! Does that not go against your standard of loyalty? Megatron didn’t do scrap for our people. And that Prime is hardly a saint.”
Bumblebee ex-vented as he rubbed his optics. “…Let's just move on. Trust is the thing that needs to be earned. Shown by actions. Like not being a power hungry crazy person, or plotting world domination, or betraying your friends for your own selfish goals–” The bug abruptly stopped with a cringed expression before continuing– “Uh, yeah, so you should work on y’know, thinking about others and stuff.”
Starscream suddenly noticed his optics glitch and he shook his helm. Right. That was why the bug hesitated. Was Bumblebee actually afraid of him, after all that talk? He should be. A dozen morbid thoughts flashed through Starscream’s processor. The bug had some nerve acting as if he were so perfect.
The lightning flickered through his wings in a subtle warning, “Oh yes. Think about others, hm? What do you think I’ve been trying to do? Ah, right. I am the power crazy lunatic who wants to rule the world, purely for my own pleasure.” Starscream growled dangerously as he put a servo to his chassis before tossing it aside. “Can you honestly blame me for finding myself the only trustworthy candidate for the role? Or aspiring for something better than these pitiful state of affairs? Any friends I may have had, are dead, or betrayed me first. You know nothing, bug.”
Bumblebee scrutinized him with his optics as he actually seemed to be thinking about his next words. “Maybe not…” He tested the stick in his servos. “You’re not exactly the most easy to read mech, Starscream. But even if you really want to think you’re the hero somehow in that twisted processor of yours, we’re gonna have to get this stuff down.” He tapped the board, then added mockingly, “You came here with pure intentions of being redeemed, didn’t you?”
Starscream’s wing twitched, then he crossed his stabilizing servos and poised his posture. “Of course.”
“So how about you actually listen to your teacher for a second, ‘kay? Cool. Great.” The scout brought his stick to point at the first word in his list of pillars. “Empathy. The ability to relate to others on both an emotional and intellectual level. It’s like when you see someone get hurt, and you feel it too, and therefore–should be inclined to help them! It's all about that connection and understanding, that then leads us into Consideration. Which is being mindful of others’ feelings. You need to be empathetic towards someone who's in danger or struggling, and considerate of how your actions affect those around you. So, imagine I’m your partner on a mission, and I don't know, a building collapsed on me or something. You could either leave me there and run away to save your own plating, or pull me out of the rubble to safety. What do you do?”
Starscream’s processor blanked with an echo of static. There were too many variables that would need to be considered in that hypothetical. There wasn’t enough information. Even so, obviously he wouldn’t save an Autobot, that’d be foolish. Rescue the enemy on some naive basis of…empathy? A mech should be able to take care of themself. It would probably be the bug's own fault if he found himself in such a situation. Then who was Starscream to take his opportunity to prove himself capable of fixing his mistake? Saving useless mechs who can’t keep themselves online, would only lead to getting himself killed needlessly. Then how would that be helpful?
He could probably discern what response the scout wanted, but instead a different question escaped his intake. “Would you save a Decepticon in such a scenario?” The rampant hypocrisy amongst the bots irked him.
“Well–” Bumblebee shifted as he hesitated to confess the obvious answer– “Look, I’m not talking about war, I’m talking about just in general. It doesn’t have to be me that you envision, it could be basically anyone. That's supposed to be the point.”
“If it is merely anyone, then why should I care?”
The scout ran a servo down his faceplate, “Fine. What if it was uh…Skywarp?”
Skywarp’s mangled frame, caught crushed between splintered shards of a once mighty structure, shattered by the Autobots. Skywarp leaking energon with only their helm and a servo free from their predicament. Barely conscious as they called out for Thundercracker in the carnage, who they’d never see again. Skywarp, being painfully quiet for a rare moment in their functioning, before screaming at Starscream for not looking for their brother harder.
A clapping of servos faded in from a chaotic symphony of explosions and voices, into what they were. Bumblebee was trying to get his attention.
“Hey! Hey, where’d you go man? You good?” The scout was next to him and centihics away from prodding him with that stupid stick.
Starscream smacked it away and snapped, “I’m fine. Of course I got Skywarp out–a lot of thanks that got me!” His optics flashed red as the memory of Megatron’s fusion cannon sending him crumpled down against the wall, while Skywarp watched, glitched in his processor.
“Helping people isn’t about getting praised for it!” The bug snipped back as he grumpily retrieved his lost stick. “It’s about doing the right thing, and showing that you care about the people around you… You don’t regret helping them, right?” When Starscream couldn’t respond, Bumblebee continued. “...How about we go to the next topic?”
Starscream stared blankly. He didn’t care. He didn’t have a choice. This was stupid.
“Right…” The scout began awkwardly as he slowly raised his stick to point at the board again. “The next one is… Accountability. Taking responsibility for your actions. Which plays on the Consideration one, because as you consider others’ feelings, you can take yourself accountable when you hurt someone. Like how what you did hit Hashtag pretty hard, and you can take responsibility by acknowledging that. As well as y’know, try to make it up to her. Meg–uh…Oh Primus what’s a better example…? Let’s just focus on the point that to be a good person, you need to recognize when you mess up, and then do something constructive about it.”
Starscream was hardly listening. This whole thing was just a huge guilt trip. Set for the scout to shame him for what a horrible person he was.
The bug just kept talking.
“Prudence is the act of being reflective, and objective when you’re making decisions. The reflective bit ties with the Accountability one in that it’s about you being aware of the effects of your actions, and that requires looking back on them and deciding what could be improved. The objective part is about not letting your biases, or anger, affect your decisions. Whiiiich goes into Temperance, that means controlling your passion in a way that doesn’t allow yourself to lash out at others. Like how you were getting a bit feisty earlier and snapping at everyone’s favorite teacher!” Bumblebee straightened a bit before pointing the stick at Starscream in some feeble attempt at scolding him. “Not cool. But, I know that might have been a bit fast, so how about another hypothetical! Let’s say, you accidentally broke the kid’s speaker because you hated the music or something. What do you do when they find out, or even before?”
“Plant the evidence where it could incriminate someone else.” Starscream responded immediately without much thought.
The bug’s faceplate scrunched. “No…You’re–you’re supposed to take accountability. Tell them you did it, say you’re sorry, and either repair it or get them a new one.”
“Why put such a stain on your record–or risk them not accepting your peace offering–when you could simply frame someone else and let it be their problem? Openly admitting fault seldom gets you in anyone’s good graces.” Starscream rolled his optics at the absurdity.
“First, back to the empathy thing, you shouldn’t pawn your problems onto other people. If you are worried about the consequences, then you shouldn’t want to inflict it on someone else. Second, it’s again, not about getting on people’s good sides or praise or anything like that.”
“What is it then? Is it so you can congratulate yourself on how oh so virtuous you are for DoInG tHe RiGhT tHiNg, after they break your servo? It is either them or me. I do not apologize for being a bit selfish on the matter. Your morals are moronic.”
Bumblebee put his servos together and brought them to his faceplate, then pointed his digits down. “...What about breaking a speaker is some life or death situation?” He let his servos fall. “Dude. No one’s going to do that over a little mistake.”
Starscream stared at him with a raised optical ridge skeptically. That statement was extremely doubtful. Mistakes could be deadly, no matter how insignificant. Even if such a thing may not seem like it would warrant such a response, it never stopped Megatron when he was in a mood. The bug could say that now, but he could not promise that for anyone in the future. Even himself.
The bug got a rather odd expression at his silence. “No one here is ever going to do that. We talk things out. That is how we deal with things in this team. We practice the Temperance and Prudence rules! Keeping our anger in check to manage our decisions in non-violent ways! With the exception of a bit of rough-housing–They might still be mad, but they would appreciate honesty. Your way would just make things worse, not better. Especially if they found out anyway. No one can be perfect, but you still gotta put forth that effort.”
Starscream rested his faceplate on his propped servo with bored optics, “Sure.”
“I’m serious.” The bug put a servo on his hip, “As long as you try, that still counts for something. And we help each other. I’m still a bit guilty of having those occasional moments where I’ve made more reckless decisions. It happens.” He shrugged, “You really just have to make sure to avoid those big ones.”
Avoid the big ones? What scale were these bots weighing their decisions upon? How was Starscream supposed to know what was large or small in their optics? Instances that he felt could be disregarded after proper punishment, seemed to linger for them. Destroying that device in the hypothetical, was apparently a low level offense, but that hardly grazed the range of circumstance. He didn’t have vorns to navigate this place.
Starscream was glaring hard at basically nothing. This redemption angle of this ordeal was going to prove precarious… He didn’t understand why his way was wrong. It had always been how things worked, as far as he could remember. Perhaps… not with Skyfire, but he was different. They had been partners, equals. The power scales here were hardly clear.
The bug had been talking again.
“–guess fairness can be subjective sometimes. I’m sure you're thinking about some backhanded rebuttal already.” Bumblebee actually looked a bit disappointed when Starscream said nothing, and continued with his doors tipping downward. “...But the Justice pillar also ties in with our last one to wrap up today’s lesson, Fortitude. Which is the courage to stand up for what you believe in. To step in when you see something you know is wrong. Basically the complete opposite of the bystander effect! For instance, if you saw someone you care about being held accountable for something that wasn’t their fault–you’d come to their defense.”
Starscream thought of his trinemates again. “It is not so simple.”
“Well…for you, maybe not. But! If you keep these pillars in mind, and really try and implement them, it could get easier right? Practice?” Bumblebee’s vocalizer squeaked with his grin that was full of doubt. “Maybe?”
Starscream studied him for a moment. The bug had seemed to put in a significant amount of effort. As well as being perhaps a bit more self-aware than he thought, for a moment. The scout was certainly odd, but…he meant well. Something could be appreciated about that. Occasionally.
Then, Starscream stood from the crate and turned to make his way back to his sparkly little quarters. He was still tired, and the assault on his audials he’d just endured did nothing for the ache in his processor. There were decidedly far too many things to think about.
Bumblebee was silent for a moment before calling out to him, “Okay yeah, good talk! I’ll get back to you on the practice exercises, so we can take a break for now!”
Starscream put a servo up in acknowledgement before slipping into solitary. The idea of getting the last word was appealing, but he didn’t have the energy. Despite the fact that the small room wasn’t entirely comforting, it would at least be a reprieve from regulating every other mech around him every Primus damned nano-klik.
Starscream stood there in the middle of the room a moment, as his optics drifted to one particular poster. The seekers soaring into the skies, away from a burning city. He approached it. Stared it down with vacant optics and tense servos.
Then ripped apart every scrap of those wretched structures. Until only the sky and his seekers remained.
A foolish dream, really.
#starscream#earthspark starscream#bumblebee#earthspark bumblebee#transformers#tfe#star be a bit homesick#and wishing his trine wasn't so fragged#I really hope im doing bee well#bee rlly do be tryin#he actually liked the banter smh#fanfic#tf fanfic#bit of fanart too#tryna keep my sanity with at least just a small edit with the sillies
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Witcher 4 Tech Demo Debuts

youtube
CD PROJEKT RED and Epic Games Present The Witcher 4 Unreal Engine 5 Tech Demo at The State of Unreal 2025!
At Unreal Fest Orlando, the State of Unreal keynote opened with a live on-stage presentation that offered an early glimpse into the latest Unreal Engine 5 features bringing the open world of The Witcher 4 to life.
Spotlight:
Tech demo showcased how the CD PROJEKT RED and Epic Games are working together to power the world of The Witcher 4 on PC, PlayStation, and Xbox, and bring large open-world support to Unreal Engine. The tech demo takes place in the never-before-seen region of Kovir.
As Unreal Fest 2025 kicked off, CD PROJEKT RED joined Epic Games on stage to present a tech demo of The Witcher 4 in Unreal Engine 5 (UE5). Presented in typical CDPR style, the tech demo follows the main protagonist Ciri in the midst of a monster contract and shows off some of the innovative UE5 technology and features that will power the game’s open world.
The tech demo takes place in the region of Kovir — which will make its very first appearance in the video game series in The Witcher 4. The presentation followed main protagonist Ciri — along with her horse Kelpie — as she made her way through the rugged mountains and dense forests of Kovir to the bustling port town of Valdrest. Along the way, CD PROJEKT RED and Epic Games dove deep into how each feature is helping drive performance, visual fidelity, and shape The Witcher 4’s immersive open world.
Watch the full presentation from Unreal Fest 2025 now at LINK.
Since the strategic partnership was announced in 2022, CDPR has been working with Epic Games to develop new tools and enhance existing features in Unreal Engine 5 to expand the engine’s open-world development capabilities and establish robust tools geared toward CD PROJEKT RED’s open-world design philosophies. The demo, which runs on a PlayStation 5 at 60 frames per second, shows off in-engine capabilities set in the world of The Witcher 4, including the new Unreal Animation Framework, Nanite Foliage rendering, MetaHuman technology with Mass AI crowd scaling, and more. The tools showcased are being developed, tested, and eventually released to all UE developers, starting with today’s Unreal Engine 5.6 release. This will help other studios create believable and immersive open-world environments that deliver performance at 60 FPS without compromising on quality — even at vast scales. While the presentation was running on a PlayStation console, the features and technology will be supported across all platforms the game will launch on.
The Unreal Animation Framework powers realistic character movements in busy scenes. FastGeo Streaming, developed in collaboration with Epic Games, allows environments to load quickly and smoothly. Nanite Foliage fills forests and fields with dense detail without sacrificing performance. The Mass system handles large, dynamic crowds with ease, while ML Deformer adds subtle, realistic touches to character animation — right down to muscle movement.
Speaking on The Witcher 4 Unreal Engine 5 tech demo, Joint-CEO of CD PROJEKT RED,
Michał Nowakowski stated:
“We started our partnership with Epic Games to push open-world game technology forward. To show this early look at the work we’ve been doing using Unreal Engine running at 60 FPS on PlayStation 5, is a significant milestone — and a testament of the great cooperation between our teams. But we're far from finished. I look forward to seeing more advancements and inspiring technology from this partnership as development of The Witcher 4 on Unreal Engine 5 continues.”
Tim Sweeney, Founder and CEO of Epic Games said:
“CD PROJEKT RED is one of the industry’s best open-world game studios, and we’re grateful that they’re working with us to push Unreal Engine forward with The Witcher 4. They are the perfect partner to help us develop new world-building features that we can share with all Unreal Engine developers.”
For more information on The Witcher 4, please visit the official website. More information about The Witcher series can be found on the official official website, X, Bluesky, and Facebook.




#the witcher#the witcher 4#cd projekt red#video games#gaming#gaming news#screenshtos#unreal engine#unreal engine 5#UE5#game development#tech demo#game design#Youtube
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
At the 2023 Defcon hacker conference in Las Vegas, prominent AI tech companies partnered with algorithmic integrity and transparency groups to sic thousands of attendees on generative AI platforms and find weaknesses in these critical systems. This “red-teaming” exercise, which also had support from the US government, took a step in opening these increasingly influential yet opaque systems to scrutiny. Now, the ethical AI and algorithmic assessment nonprofit Humane Intelligence is taking this model one step further. On Wednesday, the group announced a call for participation with the US National Institute of Standards and Technology, inviting any US resident to participate in the qualifying round of a nationwide red-teaming effort to evaluate AI office productivity software.
The qualifier will take place online and is open to both developers and anyone in the general public as part of NIST's AI challenges, known as Assessing Risks and Impacts of AI, or ARIA. Participants who pass through the qualifying round will take part in an in-person red-teaming event at the end of October at the Conference on Applied Machine Learning in Information Security (CAMLIS) in Virginia. The goal is to expand capabilities for conducting rigorous testing of the security, resilience, and ethics of generative AI technologies.
“The average person utilizing one of these models doesn’t really have the ability to determine whether or not the model is fit for purpose,” says Theo Skeadas, chief of staff at Humane Intelligence. “So we want to democratize the ability to conduct evaluations and make sure everyone using these models can assess for themselves whether or not the model is meeting their needs.”
The final event at CAMLIS will split the participants into a red team trying to attack the AI systems and a blue team working on defense. Participants will use the AI 600-1 profile, part of NIST's AI risk management framework, as a rubric for measuring whether the red team is able to produce outcomes that violate the systems' expected behavior.
“NIST's ARIA is drawing on structured user feedback to understand real-world applications of AI models,” says Humane Intelligence founder Rumman Chowdhury, who is also a contractor in NIST's Office of Emerging Technologies and a member of the US Department of Homeland Security AI safety and security board. “The ARIA team is mostly experts on sociotechnical test and evaluation, and [is] using that background as a way of evolving the field toward rigorous scientific evaluation of generative AI.”
Chowdhury and Skeadas say the NIST partnership is just one of a series of AI red team collaborations that Humane Intelligence will announce in the coming weeks with US government agencies, international governments, and NGOs. The effort aims to make it much more common for the companies and organizations that develop what are now black-box algorithms to offer transparency and accountability through mechanisms like “bias bounty challenges,” where individuals can be rewarded for finding problems and inequities in AI models.
“The community should be broader than programmers,” Skeadas says. “Policymakers, journalists, civil society, and nontechnical people should all be involved in the process of testing and evaluating of these systems. And we need to make sure that less represented groups like individuals who speak minority languages or are from nonmajority cultures and perspectives are able to participate in this process.”
81 notes
·
View notes
Text
ABOUT.
My name is Slim Ray.
I’m a former programmer turned horror writer and filmmaker. After nearly a decade in software development, I made the leap to follow my passion for storytelling.
My creative journey has led me to write and direct three short films. These projects taught me the intricacies of storytelling and strengthened my love for crafting narratives that leave an impact.
I’m captivated by the intersection of words and images. This fascination drives my visual experiments—a blend of AI, photography, and storytelling—documented on my blog, Project H.
I'm a bit of a social outsider and awkward IRL, so I've created a character for this blog. This character isn't me exactly, but more of a persona for this space.
I’m constantly learning and refining my craft. This blog serves as my research hub, a place to explore and develop ideas, and the testing ground for a storytelling framework I’m building—a passion project close to my heart.
Teaching is another love of mine. I’m working on online courses and guides to share what I’ve learned about storytelling—stay tuned for updates!
I use AI as a tool for research and editing. If that’s not your thing, no hard feelings, but I ask for respect in how I approach my process.
LINKS.
[Patreon]
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
the thing about the intersection of ai and copyright law arguments is that it's been a really strong test of who's internalised the way that political movements actually work, along with why it's so incredibly dangerous to move for action on issues outside of a socioeconomic framework
most of the momentum behind policy doesn't even come from people who actually want it and the majority of Bad Laws are the result of powerful people coopting smaller movements that are useful to them
in other words, it literally doesn't matter what you believe in the majority of cases. there's a million people who believe things adjacent to that, and then there's ten people who can find the overlap in those groups that they need to get their sweeping policies through. that's kind of the grim nature of party politics in general
349 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why there's no intelligence in Artificial Intelligence
You can blame it all on Turing. When Alan Turing invented his mathematical theory of computation, what he really tried to do was to construct a mechanical model for the processes actual mathematicians employ when they prove a mathematical theorem. He was greatly influenced by Kurt Gödel and his incompleteness theorems. Gödel developed a method to decode logical mathematical statements as numbers and in that way was able to manipulate these statements algebraically. After Turing managed to construct a model capable of performing any arbitrary computation process (which we now call "A Universal Turing Machine") he became convinced that he discovered the way the human mind works. This conviction quickly infected the scientific community and became so ubiquitous that for many years it was rare to find someone who argued differently, except on religious grounds.
There was a good reason for adopting the hypothesis that the mind is a computation machine. This premise was following the extremely successful paradigm stating that biology is physics (or, to be precise, biology is both physics and chemistry, and chemistry is physics), which reigned supreme over scientific research since the eighteenth century. It was already responsible for the immense progress that completely transformed modern biology, biochemistry, and medicine. Turing seemed to supply a solution, within this theoretical framework, for the last large piece in the puzzle. There was now a purely mechanistic model for the way brain operation yields all the complex repertoire of human (and animal) behavior.
Obviously, not every computation machine is capable of intelligent conscious thought. So, where do we draw the line? For instance, at what point can we say that a program running on a computer understands English? Turing provided a purely behavioristic test: a computation understands a language if by conversing with it we cannot distinguish it from a human.
This is quite a silly test, really. It doesn't provide any clue as to what actually happens within the artificial "mind"; it assumes that the external behavior of an entity completely encapsulates its internal state; it requires "man in the loop" to provide the final ruling; it does not state for how long and on what level should this conversation be held. Such a test may serve as a pragmatic common-sense method to filter out obvious failures, but it brings us not an ounce closer to understanding conscious thinking.
Still, the Turing Test stuck. If anyone tried to question the computational model of the mind, he was then confronted with the unavoidable question: what else can it be? After all, biology is physics, and therefore the brain is just a physical machine. Physics is governed by equations, which are all, in theory, computable (at least approximately, with errors being as small as one wishes). So, short of conjuring supernatural soul that magically produces a conscious mind out of biological matter, there can be no other solution.

Nevertheless, not everyone conformed to the new dogma. There were two tiers of reservations to computational Artificial Intelligence. The first, maintained, for example, by the Philosopher John Searl, didn't object to idea that a computation device may, in principle, emulate any human intellectual capability. However, claimed Searl, a simulation of a conscious mind is not conscious in itself.
To demonstrate this point Searl envisioned a person who doesn't know a single word in Chinese, sitting in a secluded room. He receives Chinese texts from the outside through a small window and is expected to return responses in Chinese. To do that he uses written manuals that contain the AI algorithm which incorporates a comprehensive understanding of the Chinese language. Therefore, a person fluent in Chinese that converses with the "room" shall deduce, based on Turing Test, that it understands the language. However, in fact there's no one there but a man using a printed recipe to convert an input message he doesn't understands to an output message he doesn't understands. So, who in the room understands Chinese?
The next tier of opposition to computationalism was maintained by the renowned physicist and mathematician Roger Penrose, claiming that the mind has capabilities which no computational process can reproduce. Penrose considered a computational process that imitates a human mathematician. It analyses mathematical conjecture of a certain type and tries to deduce the answer to that problem. To arrive at a correct answer the process must employ valid logical inferences. The quality of such computerized mathematician is measured by the scope of problems it can solve.
What Penrose proved is that such a process can never verify in any logically valid way that its own processing procedures represent valid logical deductions. In fact, if it assumes, as part of its knowledge base, that its own operations are necessarily logically valid, then this assumption makes them invalid. In other words, a computational machine cannot be simultaneously logically rigorous and aware of being logically rigorous.
A human mathematician, on the other hand, is aware of his mental processes and can verify for himself that he is making correct deductions. This is actually an essential part of his profession. It follows that, at least with respect to mathematicians, cognitive functions cannot be replicated computationally.
Neither Searl's position nor Penrose's was accepted by the mainstream, mainly because, if not computation, "what else can it be?". Penrose's suggestion that mental processes involve quantum effects was rejected offhandedly, as "trying to explicate one mystery by swapping it with another mystery". And the macroscopic hot, noisy brain seemed a very implausible place to look for quantum phenomena, which typically occur in microscopic, cold and isolated systems.
Fast forward several decades. Finaly, it seemed as though the vision of true Artificial Intelligence technology started bearing fruits. A class of algorithms termed Deep Neural Networks (DNN) achieved, at last, some human-like capabilities. It managed to identify specific objects in pictures and videos, generate photorealistic images, translate voice to text, and support a wide variety of other pattern recognition and generation tasks. Most impressively, it seemed to have mastered natural language and could partake in an advanced discourse. The triumph of computational AI appeared more feasible than ever. Or was it?
During my years as undergraduate and graduate student I sometimes met fellow students who, at first impression, appeared to be far more conversant in the academic courses subject matter than me. They were highly confident and knew a great deal about things that were only briefly discussed in lectures. Therefore, I was vastly surprised when it turned out they were not particularly good students, and that they usually scored worse than me in the exams. It took me some time to realize that these people hadn't really possessed a better understanding of the curricula. They just adopted the correct jargon, employed the right words, so that, to the layperson ears, they had sounded as if they knew what they were talking about.
I was reminded of these charlatans when I encountered natural language AIs such as Chat GPT. At first glance, their conversational abilities seem impressive – fluent, elegant and decisive. Their style is perfect. However, as you delve deeper, you encounter all kinds of weird assertions and even completely bogus statements, uttered with absolute confidence. Whenever their knowledge base is incomplete, they just fill the gap with fictional "facts". And they can't distinguish between different levels of source credibility. They're like Idiot Savants – superficially bright, inherently stupid.
What confuses so many people with regard to AIs is that they seem to pass the (purely behavioristic) Turing Test. But behaviorism is a fundamentally non-scientific viewpoint. At the core, computational AIs are nothing but algorithms that generates a large number of statistical heuristics from enormous data sets.
There is an old anecdote about a classification AI that was supposed to distinguish between friendly and enemy tanks. Although the AI performed well with respect to the database, it failed miserably in field tests. Finely, the developers figured out the source of the problem. Most of the friendly tanks' images in the database were taken during good weather and with fine lighting conditions. The enemy tanks were mostly photographed in cloudy, darker weather. The AI simply learned to identify the environmental condition.
Though this specific anecdote is probably an urban legend, it illustrates the fact that AIs don't really know what they're doing. Therefore, attributing intelligence to Arificial Intelligence algorithms is a misconception. Intelligence is not the application of a complicated recipe to data. Rather, it is a self-critical analysis that generates meaning from input. Moreover, because intelligence requires not only understanding of the data and its internal structure, but also inner-understanding of the thought processes that generate this understanding, as well as an inner-understanding of this inner-understanding (and so forth), it can never be implemented using a finite set of rules. There is something of the infinite in true intelligence and in any type of conscious thought.
But, if not computation, "what else can it be?". The substantial progress made in quantum theory and quantum computation revived the old hypothesis by Penrose that the working of the mind is tightly coupled to the quantum nature of the brain. What had been previously regarded as esoteric and outlandish suddenly became, in light of recent advancements, a relevant option.
During the last thirty years, quantum computation has been transformed from a rather abstract idea made by the physicist Richard Feynman into an operational technology. Several quantum algorithms were shown to have a fundamental advantage over any corresponding classical algorithm. Some tasks that are extremely hard to fulfil through standard computation (for example, factorization of integers to primes) are easy to achieve quantum mechanically. Note that this difference between hard and easy is qualitative rather than quantitative. It's independent of which hardware and how much resources we dedicate to such tasks.
Along with the advancements in quantum computation came a surging realization that quantum theory is still an incomplete description of nature, and that many quantum effects cannot be really resolved form a conventional materialistic viewpoint. This understanding was first formalized by John Stewart Bell in the 1960s and later on expanded by many other physicists. It is now clear that by accepting quantum mechanics, we have to abandon at least some deep-rooted philosophical perceptions. And it became even more conceivable that any comprehensive understanding of the physical world should incorporate a theory of the mind that experiences it. It's only stands to reason that, if the human mind is an essential component of a complete quantum theory, then the quantum is an essential component of the workings of the mind. If that's the case, then it's clear that a classical algorithm, sophisticated as it may be, can never achieve true intelligence. It lacks an essential physical ingredient that is vital for conscious, intelligent thinking. Trying to simulate such thinking computationally is like trying to build a Perpetuum Mobile or chemically transmute lead into gold. You might discover all sorts of useful things along the way, but you would never reach your intended goal. Computational AIs shall never gain true intelligence. In that respect, this technology is a dead end.
#physics#ai#artificial intelligence#Alan Turing#computation#science#quantum physics#mind and body#John Searl#Roger Penrose
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Web Automation Enhances Speed and Accuracy
In an era where digital experiences evolve rapidly, web automation plays a pivotal role in accelerating software delivery without compromising quality. By automating repetitive and time-consuming test scenarios, teams can significantly reduce manual effort while ensuring consistent results.
Speed is one of the most immediate gains. API Automation testing can run in parallel across multiple browsers and environments, enabling faster feedback loops and quicker releases. What used to take hours in manual testing can now be executed in minutes, freeing up QA teams to focus on exploratory and high-priority testing.
Beyond speed, accuracy improves through elimination of human error. Automated scripts follow exact instructions every time, making test outcomes more reliable and reproducible. They are especially effective in regression testing, where consistency is critical.
Integrating automation within CI/CD pipelines ensures that code is tested continuously, leading to faster detection of bugs and smoother deployments. Additionally, automation tools often include detailed logs and screenshots, aiding quicker debugging.
Ultimately, web automation isn't just about faster testing—it’s about delivering high-quality digital products with confidence. Organizations that invest in smart automation strategies gain a competitive edge through improved efficiency, reliability, and user satisfaction.
#web automation#api automation tools#ai software testing#test automation framework#ai automation testing tools#api automation testing#api testing tools#ai test automation
0 notes
Text

I've finally played the Lake House and now I'm going to talk about it for awhile. Spoilers below the break.
I will start off by saying this is one of the BEST DLCs I have ever played in any game.
I have always loved Kiran as a character since we first saw her, but The Lake House really highlighted just how fantastically rounded and detailed this character is given the short amount of time we spend with her. Her humor, the fear she experiences, but above all the determination she has to do her job makes a great character.
I appreciated how much we see of the everyman FBC agent. Not everyone at the FBC is a parautilitarian, a lovable scientist dork, or the Director. There are normal people working there believing in what they do. This is a very important part of the overall story of this organization to me. Often I see the Bureau demonized as a whole by the fandom and that really upsets me. Bad apples are everywhere, as we see in this DLC. But we also see how a good person like Kiran stands up against it. Even through the emails and documents we find in game you see good people trying their best against that evil. I am again thankful for Remedy's writing team that they really highlighted that. Even going as far as showing Darling denying a request to capture live test subjects, which means he learned after Dylan. You even see that Trench denied outlandish requests despite being being in the late stages of a galactic war raging in his mind.
You know I had to talk about Trench and Darling, but it was nice to see them again in this way. They still felt a part of this world in a way that made sense. Document storytelling has been one of my favorite things about Control. They present us with just enough framework to use on our own canvas to try and piece together details of those blank pages.

Did I get emotional over signatures? Yes, yes I did.
The atmosphere of this DLC hit all the right horror points. From the moment you walk into The Lake House it captures all the scariest horror vibes from the main game. The paint spattered on the walls like blood, but somehow even creepier because of how it wouldn't make sense to see paint like that (until you figure out just what is happening). Being helpless to the painted because again you are just an FBC Agent not a parautilitarian emphasized this feeling.
Using a picture frame set up with Kiran telling Saga what happened at The Lake House made sense and gives us the point in time Kiran would be providing this information. She left us clues in the main game with her dialogue of something horrible that went down at the Lake House, so it feels very appropriate that we get to see that in detail.
The question that resounded throughout this DLC of what is art was very appropriate given the struggles we face today with AI and plagiarism. How is art perceived and how does its emotional impact play on its viewer? Again the writing team really shines here with all the little details. The room with the ATDs was truly horrifying. I don't think they have ever made a room with no one feel so ominous.
Obviously there was a lot in the DLC for Control fans. We will be speculating on every detail for the next couple of years. I always hoped this last DLC of Alan Wake would lead into Control 2, so I couldn't be happier to see just that happen.
Unlike some DLCs that feel as though they were an afterthought, the story feels like the natural ending of Alan Wake 2's story. It felt like the only goodbye we would have with this game and its characters.
The ending song was a beautiful final note to capstone a game that Remedy struggled for so long to make, and I imagine at times doubted that it would ever be made.
I often struggle to put my feelings into written words, but I wanted to try and get them out. Remedy's future looks bright with multiple games on the horizon, but we see how quickly companies can run into issues and nothing is set in stone. Anything could happen in these uncertain times. We may never see these characters again, and most certainly not in the form they are now. It makes me really sad to think we may never see Saga and FBI Casey or Kiran ever again. Maybe there won't ever be an Alan Wake 3. Maybe we won't see Alan battle the Dark Presence again. Maybe we won't ever see Dark Place Casey's echos pave a path for Alan. Maybe we won't see Alice show us just how much a character can grown into her own. Maybe we don't even get to see more of Jesse, or Emily, or Arish. I already know with the passing of James McCaffrey some of these things are impossible. But its not only death that separates seeing a character again. The song End of an Era highlights this goodbye. This end scene. The curtains close. It is an end.
What I appreciated in this song was that it highlighted the struggle of getting to that ending. No matter what goal you are trying to reach, whether it's Alan trying to escape the Dark Place, Jesse finding out what happened to her brother, any one of us creating things that make us happy, that path always has its ups and downs. And that end will always be bittersweet. It will change us. It is a goodbye.
Whatever Remedy creates in the future it could be something we may like or something we may end up disliking. They could ruin characters or make brand new ones for us to fall in love with all over again. We can take that or leave it. Whatever they decide to do. Maybe we like Firebreak and their new type of Remedy game, maybe we don't. But none of that will change how we felt about these prior games and how these characters made us feel at this moment in time. We can look back and remember how it made us feel. When we laughed, when we cried. The journey they took us on.
I will always be grateful that I was able to experience these games. They moved me in ways I cannot find the words to fully describe. I will carry these feelings forward and cherish this memory.
“There are no happy endings. Endings are the saddest part, So just give me a happy middle And a very happy start.” - Shel Silverstein
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
The Witcher 4 — Unreal Engine 5 Tech Demo
The Witcher IV is in development for PlayStation 5, Xbox Series X|S, and PC. A release date has yet to be announced.
Latest details
As Unreal Fest 2025 kicked off, CD Projekt RED joined Epic Games on stage to present a tech demo of The Witcher IV in Unreal Engine 5. Presented in typical CD Projekt RED style, the tech demo follows the main protagonist Ciri in the midst of a monster contract and shows off some of the innovative Unreal Engine 5 technology and features that will power the game’s open world. The tech demo takes place in the region of Kovir—which will make its very first appearance in the video game series in The Witcher IV. The presentation followed main protagonist Ciri—along with her horse Kelpie—as she made her way through the rugged mountains and dense forests of Kovir to the bustling port town of Valdrest. Along the way, CD PROJEKT RED and Epic Games dove deep into how each feature is helping drive performance, visual fidelity, and shape The Witcher IV‘s immersive open world. Watch the full presentation from Unreal Fest 2025 now at LINK. Since the strategic partnership was announced in 2022, CDPR has been working with Epic Games to develop new tools and enhance existing features in Unreal Engine 5 to expand the engine’s open-world development capabilities and establish robust tools geared toward CD PROJEKT RED’s open-world design philosophies. The demo, which runs on a PlayStation 5 at 60 frames per second, shows off in-engine capabilities set in the world of The Witcher IV, including the new Unreal Animation Framework, Nanite Foliage rendering, MetaHuman technology with Mass AI crowd scaling, and more. The tools showcased are being developed, tested, and eventually released to all UE developers, starting with today’s Unreal Engine 5.6 release. This will help other studios create believable and immersive open-world environments that deliver performance at 60 FPS without compromising on quality—even at vast scales. While the presentation was running on a PlayStation console, the features and technology will be supported across all platforms the game will launch on. The Unreal Animation Framework powers realistic character movements in busy scenes. FastGeo Streaming, developed in collaboration with Epic Games, allows environments to load quickly and smoothly. Nanite Foliage fills forests and fields with dense detail without sacrificing performance. The Mass system handles large, dynamic crowds with ease, while ML Deformer adds subtle, realistic touches to character animation—right down to muscle movement.
#The Witcher IV#The Witcher 4#The Witcher#CD Projekt RED#CD Projekt#video game#PS5#Xbox Series#Xbox Series X#Xbox Series S#PC
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Witcher IV - State of Unreal 2025 ‘Cinematic’ trailer and tech demo - Gematsu

CD Projekt RED has released a new cinematic trailer and technical demonstration of The Witcher IV as part of State of Unreal 2025. The technical demonstration is running on a base PlayStation 5 at 60 frames per second with ray-tracing.
Here are the latest details:
As Unreal Fest 2025 kicked off, CD Projekt RED joined Epic Games on stage to present a tech demo of The Witcher IV in Unreal Engine 5. Presented in typical CD Projekt RED style, the tech demo follows the main protagonist Ciri in the midst of a monster contract and shows off some of the innovative Unreal Engine 5 technology and features that will power the game’s open world.
The tech demo takes place in the region of Kovir—which will make its very first appearance in the video game series in The Witcher IV. The presentation followed main protagonist Ciri—along with her horse Kelpie—as she made her way through the rugged mountains and dense forests of Kovir to the bustling port town of Valdrest. Along the way, CD PROJEKT RED and Epic Games dove deep into how each feature is helping drive performance, visual fidelity, and shape The Witcher IV‘s immersive open world.
Watch the full presentation from Unreal Fest 2025 now at LINK. Since the strategic partnership was announced in 2022, CDPR has been working with Epic Games to develop new tools and enhance existing features in Unreal Engine 5 to expand the engine’s open-world development capabilities and establish robust tools geared toward CD PROJEKT RED’s open-world design philosophies. The demo, which runs on a PlayStation 5 at 60 frames per second, shows off in-engine capabilities set in the world of The Witcher IV, including the new Unreal Animation Framework, Nanite Foliage rendering, MetaHuman technology with Mass AI crowd scaling, and more. The tools showcased are being developed, tested, and eventually released to all UE developers, starting with today’s Unreal Engine 5.6 release. This will help other studios create believable and immersive open-world environments that deliver performance at 60 FPS without compromising on quality—even at vast scales. While the presentation was running on a PlayStation console, the features and technology will be supported across all platforms the game will launch on.
The Unreal Animation Framework powers realistic character movements in busy scenes. FastGeo Streaming, developed in collaboration with Epic Games, allows environments to load quickly and smoothly. Nanite Foliage fills forests and fields with dense detail without sacrificing performance. The Mass system handles large, dynamic crowds with ease, while ML Deformer adds subtle, realistic touches to character animation—right down to muscle movement.
“We started our partnership with Epic Games to push open-world game technology forward,” said CD Projekt RED joint CEO Michal Nowakowski in a press release. “To show this early look at the work we’ve been doing using Unreal Engine running at 60 [frames per second] on PlayStation 5, is a significant milestone—and a testament of the great cooperation between our teams. But we’re far from finished. I look forward to seeing more advancements and inspiring technology from this partnership as development of The Witcher IV on Unreal Engine 5 continues.” Epic Games founder and CEO Tim Sweeney added, “CD Projekt RED is one of the industry’s best open-world game studios, and we’re grateful that they’re working with us to push Unreal Engine forward with The Witcher IV. They are the perfect partner to help us develop new world-building features that we can share with all Unreal Engine developers.”
The Witcher IV will be available for PlayStation 5, Xbox Series, and PC. A release date has yet to be announced.
Watch the footage below.
Cinematic Trailer
youtube
Technical Demonstration
youtube
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
DETECTING AI IN SPELL INCANTATIONS
as someone who has trained multiple ais to write incantations now and engaged with every foundation model and multiple popular data generation frameworks in data generation and testing, I can tell you a spells incantation *might* be AI if it:
Seems a bit long, but on close inspection, multiple couplets express the same idea, restated in a different rhyme.
Each pair of couplets in a multi-couplet-pair incantation express the complete intention with such granularity that they could be removed and used as standalone tinies, or swapped out without the functionality of the spell being damaged, with the complete incantation being a stack of tinies when examined for how much of the structure is used for expression of intention. I find llms have a bad habit of writing fully passable single lines or couplets but the density of how much of the intention is expressed is very high per couplet, and the llm doesn't tend as much towards expressing a single intention across multiple couplets or using very witchlike strategies to add clauses; I.E, each line or couplet is a whole restatement of the same complete intention, with many lines being magically redundant, and less lines than one would expect spend on clauses or conditions.
rhymes, but the sentences themselves don't make situational, magical sense for the intention, or in some cases, express the intention in such a way that it is negated by the structure of the language used to express it; i,e, described in a way that would keep it from happening if interpreted literally
the words used to complete the rhyme either don't make sense as a completion for the sentence up until that point, or break meter egregiously in order to perform the rhyme completion with lines that have significantly more beats than prior lines, this is especially evident with very simple, straight forward words to rhyme, like "See" and "me", because LLMs are known to perform motivated reasoning in the case of rhymes, and will start with the completion, and work their way backwards. This can write poetry people respond to favorably in studies, but it does tend to either bork meter somewhat (and may do so artfully, adding beats in multiples compatible with the overall meters rhythm if not retaining parity with the rest of its overall structure) or, in the case of spells, complete rhymes in a way that express the desire for the intention, but not the intention being made manifest.
uses multiple popular ending terms from different styles on different lines; uses "so mote it be" to complete a rhyme, or "and so it is" on another, or "may it be" etc. LLMs fucking love "so may it be" and have a bad habit of ending rhymes for "me" "see" "we" and "thee" with it.
Minor mention: LLMS *tend* toward problems with reliably rhyming in ABBA or ABAB and tend to prefer AABB by default in my experience, but we can't very well say AABB by itself is by any means a metric that should suggest on its own that an ai has written the text; a LOT of people use AABB and that's one reason why llms "like" them so much.
as stated before, llms like to state the entire intention as a single line or couplet, but have a lot of trouble "extending" the expression of the intention across the entire body of couplets in a very humanlike way, and may show a high degree of replication in complete expressions of intention for line count as opposed to artfully composing many couplets expressing a single intention.
OR if instead of an incantation it just says "I am a language model. I cannot help you with that." that's a pretty solid one, really.
As I said, I've fucked about with a lot of llms, and don't personally think theirs anything inherently wrong in using generated incantations, if they're good and make good sense, (words are construed to have power after all and they're just language emulators and language is just a carrier for information so like. whatever) BUT these are the things I have noticed in the course of my experiments so, if you're concerned, for instance, that a book of incantations or a magical profile on social media or a something may be ai generated, you will probably see these kinds of patterns if it is.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Last Sprout Dev Diary - Nov 28, 2024
Hello again! This is one of those "low progress" weeks as I battle with shader code and scriptable renders.
What I see in my nightmares.
So, for this week's Dev Diary, I wanted to take this opportunity to talk a bit about one of the core systems for Last Sprout - Brains.
Hopefully this is interesting even if you don't know much about programming, but I could always use the feedback.

I live my life assuming I'm some amount of this comic.
Brains & States
Part of my process in developing Last Sprout is taking the time to build systems that are as generic and abstract as possible - any time I'm thinking about writing something directly into the code, I try to find some way to pull that out into some kind of data that can be changed in the editor. Mostly because, as much work as it is to do the programming, it's also a ton of work to do the tweaks and edits that make it feel right.
A Brain isn't actually much on its own, just a framework that defines the bare minimum an Entity (the core 'thing' that exists in the game) needs to interact with.
Less fleshy than I'd like for this game.
The key here is that Brains just give instructions and move on, they don't know or care what happens once those instructions get passed to the Entity.
Brains don't take actions, they make polite requests.
So a Brain really just says "I would like to move in this direction, aim in this direction, and perform these actions".
Actions are bit flags, which means inputs are stored in one integer number that uses its 1's and 0's as true/false values. A brain toggles these bits based on a lot of different parameters - for instance, the PlayerBrain just listens to user inputs and sets its instructions accordingly, whereas an AggroBrain contains logic to look for valid targets and chase them down.
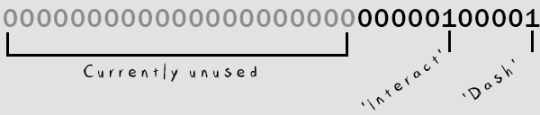
Hopefully this is a little easier to visualize for people that aren't familiar with bit flags.
An entity, every frame, asks its brain to update its instruction. Then, it passes that instruction along to a State. The State is responsible for actually taking the actions the brain recommends, So they'll have names like IdleState, WalkingState, MeleeState, and so on. States are also where animations live, so a given IdleState (which is an object that lives in the game files), will have an associated animation for Idling, and it will play that animation when the state is entered.
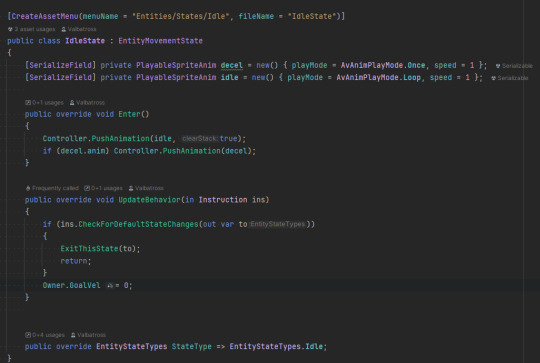
Not the most interesting state, but the easiest one to understand.
The state is what decides what input flags to listen for, and which states to exit to. Because states always have an EntityStateType, and Entities have a list of all their allowed states, they don't actually have to know what the options are, they can just say "Exit this state to a Walking state" and the entity will find a match.
This is a ton of words, but the core of it is that Brains and States are separate, and don't know anything about each other. This means that you can attach any Brain to any Entity, and it just works. If you want to test the attack range on an enemy, you can just slap a PlayerBrain onto them and suddenly you can control it! You can duplicate the player, change its tags to Hostile, and put an AggroBrain on them and suddenly you have an AI controlled hostile copy of Twiggs! While it adds a layer of complication to developing behavior, it also means that our code is reusable and modular, and it lets us experiment freely in engine.
Brains are one of many lego brick style systems, maybe next week I'll talk about another. Thanks for reading this, and if you have any particular questions, feel free to drop and ask to @last-sprout or my personal tumblr over at @oneominousvalbatross. Fair warning though, the answer may be extremely wordy.
#indie game#dev diary#game dev#Last Sprout#Last Sprout: A Seedling of Hope#game development#game dev blog#game dev update#roguelite
18 notes
·
View notes