#AI-driven algorithms
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Advancements in Humanoid Robots and Industrial Automation
Robots are no longer confined to science fiction. With rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and robotics, humanoid robots and industrial automation are transforming the way businesses operate. These innovations are improving efficiency, safety, and productivity across multiple industries.
The Rise of Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots are becoming more intelligent, capable, and human-like. Equipped with AI-driven algorithms, these robots can process natural language, recognize emotions, and perform complex tasks with remarkable precision. Companies like Tesla, Boston Dynamics, and Honda are pushing the boundaries of humanoid robotics, making them suitable for customer service, elderly care, and hazardous environments. As these robots continue to evolve, they will play a crucial role in assisting humans rather than replacing them.
Industrial Automation: A Game-Changer
Industrial automation is revolutionizing manufacturing and logistics. Robots equipped with AI and machine learning optimize supply chains, reduce errors, and enhance production speed. In warehouses, autonomous robots handle inventory, improving efficiency while minimizing workplace injuries. Meanwhile, robotic arms in factories perform tasks that require high precision, ensuring consistent quality. Businesses adopting automation experience higher productivity and lower operational costs.
The Future of Robotics and Automation
As AI continues to evolve, humanoid robots and industrial automation will become even more sophisticated. Future advancements will focus on improving human-robot collaboration, making automation more adaptable to various industries. While automation will reshape the job market, it will also create new opportunities that require creativity, problem-solving, and technical expertise.
The future is here, and robots are ready to assist. By embracing this technology, industries can unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation, ultimately improving our quality of life.
About US:AI Technology Insights (AITin) is the fastest-growing global community of thought leaders, influencers, and researchers specializing in AI, Big Data, Analytics, Robotics, Cloud Computing, and related technologies. Through its platform, AITin offers valuable insights from industry executives and pioneers who share their journeys, expertise, success stories, and strategies for building profitable, forward-thinking businesses.
Contact Us :
Call Us
+1 (520) 350-7212 +91 77760 92666
Email Address
For All Media and Press Inquiries
Local Address
1846 E Innovation Park DR Site 100 ORO Valley AZ 85755
#Humanoid robots#industrial automation#AI Technology Insights#AI-driven algorithms#artificial intelligence
1 note
·
View note
Text
The surprising truth about data-driven dictatorships

Here’s the “dictator’s dilemma”: they want to block their country’s frustrated elites from mobilizing against them, so they censor public communications; but they also want to know what their people truly believe, so they can head off simmering resentments before they boil over into regime-toppling revolutions.
These two strategies are in tension: the more you censor, the less you know about the true feelings of your citizens and the easier it will be to miss serious problems until they spill over into the streets (think: the fall of the Berlin Wall or Tunisia before the Arab Spring). Dictators try to square this circle with things like private opinion polling or petition systems, but these capture a small slice of the potentially destabiziling moods circulating in the body politic.
Enter AI: back in 2018, Yuval Harari proposed that AI would supercharge dictatorships by mining and summarizing the public mood — as captured on social media — allowing dictators to tack into serious discontent and diffuse it before it erupted into unequenchable wildfire:
https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2018/10/yuval-noah-harari-technology-tyranny/568330/
Harari wrote that “the desire to concentrate all information and power in one place may become [dictators] decisive advantage in the 21st century.” But other political scientists sharply disagreed. Last year, Henry Farrell, Jeremy Wallace and Abraham Newman published a thoroughgoing rebuttal to Harari in Foreign Affairs:
https://www.foreignaffairs.com/world/spirals-delusion-artificial-intelligence-decision-making
They argued that — like everyone who gets excited about AI, only to have their hopes dashed — dictators seeking to use AI to understand the public mood would run into serious training data bias problems. After all, people living under dictatorships know that spouting off about their discontent and desire for change is a risky business, so they will self-censor on social media. That’s true even if a person isn’t afraid of retaliation: if you know that using certain words or phrases in a post will get it autoblocked by a censorbot, what’s the point of trying to use those words?
The phrase “Garbage In, Garbage Out” dates back to 1957. That’s how long we’ve known that a computer that operates on bad data will barf up bad conclusions. But this is a very inconvenient truth for AI weirdos: having given up on manually assembling training data based on careful human judgment with multiple review steps, the AI industry “pivoted” to mass ingestion of scraped data from the whole internet.
But adding more unreliable data to an unreliable dataset doesn’t improve its reliability. GIGO is the iron law of computing, and you can’t repeal it by shoveling more garbage into the top of the training funnel:
https://memex.craphound.com/2018/05/29/garbage-in-garbage-out-machine-learning-has-not-repealed-the-iron-law-of-computer-science/
When it comes to “AI” that’s used for decision support — that is, when an algorithm tells humans what to do and they do it — then you get something worse than Garbage In, Garbage Out — you get Garbage In, Garbage Out, Garbage Back In Again. That’s when the AI spits out something wrong, and then another AI sucks up that wrong conclusion and uses it to generate more conclusions.
To see this in action, consider the deeply flawed predictive policing systems that cities around the world rely on. These systems suck up crime data from the cops, then predict where crime is going to be, and send cops to those “hotspots” to do things like throw Black kids up against a wall and make them turn out their pockets, or pull over drivers and search their cars after pretending to have smelled cannabis.
The problem here is that “crime the police detected” isn’t the same as “crime.” You only find crime where you look for it. For example, there are far more incidents of domestic abuse reported in apartment buildings than in fully detached homes. That’s not because apartment dwellers are more likely to be wife-beaters: it’s because domestic abuse is most often reported by a neighbor who hears it through the walls.
So if your cops practice racially biased policing (I know, this is hard to imagine, but stay with me /s), then the crime they detect will already be a function of bias. If you only ever throw Black kids up against a wall and turn out their pockets, then every knife and dime-bag you find in someone’s pockets will come from some Black kid the cops decided to harass.
That’s life without AI. But now let’s throw in predictive policing: feed your “knives found in pockets” data to an algorithm and ask it to predict where there are more knives in pockets, and it will send you back to that Black neighborhood and tell you do throw even more Black kids up against a wall and search their pockets. The more you do this, the more knives you’ll find, and the more you’ll go back and do it again.
This is what Patrick Ball from the Human Rights Data Analysis Group calls “empiricism washing”: take a biased procedure and feed it to an algorithm, and then you get to go and do more biased procedures, and whenever anyone accuses you of bias, you can insist that you’re just following an empirical conclusion of a neutral algorithm, because “math can’t be racist.”
HRDAG has done excellent work on this, finding a natural experiment that makes the problem of GIGOGBI crystal clear. The National Survey On Drug Use and Health produces the gold standard snapshot of drug use in America. Kristian Lum and William Isaac took Oakland’s drug arrest data from 2010 and asked Predpol, a leading predictive policing product, to predict where Oakland’s 2011 drug use would take place.
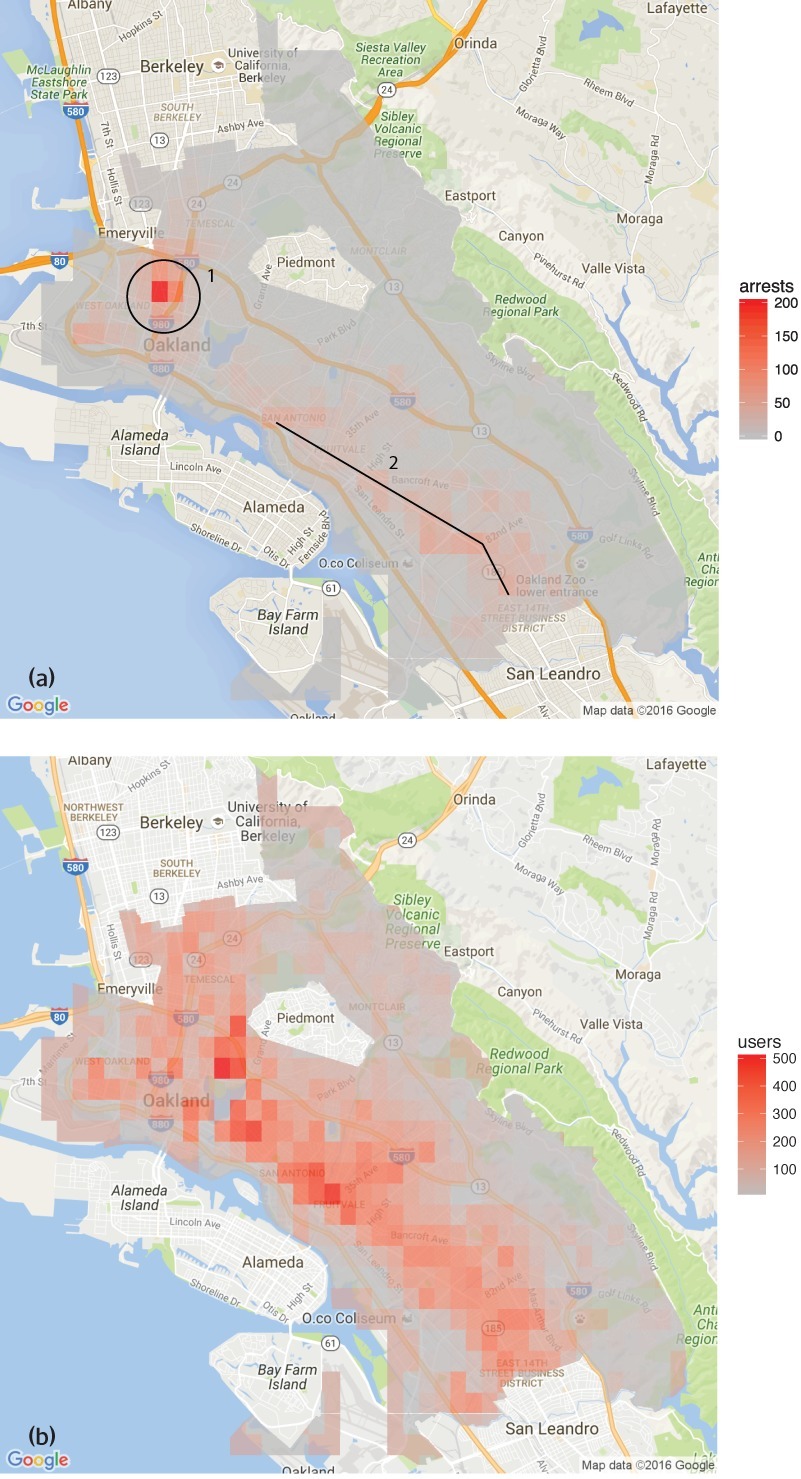
[Image ID: (a) Number of drug arrests made by Oakland police department, 2010. (1) West Oakland, (2) International Boulevard. (b) Estimated number of drug users, based on 2011 National Survey on Drug Use and Health]
Then, they compared those predictions to the outcomes of the 2011 survey, which shows where actual drug use took place. The two maps couldn’t be more different:
https://rss.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1740-9713.2016.00960.x
Predpol told cops to go and look for drug use in a predominantly Black, working class neighborhood. Meanwhile the NSDUH survey showed the actual drug use took place all over Oakland, with a higher concentration in the Berkeley-neighboring student neighborhood.
What’s even more vivid is what happens when you simulate running Predpol on the new arrest data that would be generated by cops following its recommendations. If the cops went to that Black neighborhood and found more drugs there and told Predpol about it, the recommendation gets stronger and more confident.
In other words, GIGOGBI is a system for concentrating bias. Even trace amounts of bias in the original training data get refined and magnified when they are output though a decision support system that directs humans to go an act on that output. Algorithms are to bias what centrifuges are to radioactive ore: a way to turn minute amounts of bias into pluripotent, indestructible toxic waste.
There’s a great name for an AI that’s trained on an AI’s output, courtesy of Jathan Sadowski: “Habsburg AI.”
And that brings me back to the Dictator’s Dilemma. If your citizens are self-censoring in order to avoid retaliation or algorithmic shadowbanning, then the AI you train on their posts in order to find out what they’re really thinking will steer you in the opposite direction, so you make bad policies that make people angrier and destabilize things more.
Or at least, that was Farrell(et al)’s theory. And for many years, that’s where the debate over AI and dictatorship has stalled: theory vs theory. But now, there’s some empirical data on this, thanks to the “The Digital Dictator’s Dilemma,” a new paper from UCSD PhD candidate Eddie Yang:
https://www.eddieyang.net/research/DDD.pdf
Yang figured out a way to test these dueling hypotheses. He got 10 million Chinese social media posts from the start of the pandemic, before companies like Weibo were required to censor certain pandemic-related posts as politically sensitive. Yang treats these posts as a robust snapshot of public opinion: because there was no censorship of pandemic-related chatter, Chinese users were free to post anything they wanted without having to self-censor for fear of retaliation or deletion.
Next, Yang acquired the censorship model used by a real Chinese social media company to decide which posts should be blocked. Using this, he was able to determine which of the posts in the original set would be censored today in China.
That means that Yang knows that the “real” sentiment in the Chinese social media snapshot is, and what Chinese authorities would believe it to be if Chinese users were self-censoring all the posts that would be flagged by censorware today.
From here, Yang was able to play with the knobs, and determine how “preference-falsification” (when users lie about their feelings) and self-censorship would give a dictatorship a misleading view of public sentiment. What he finds is that the more repressive a regime is — the more people are incentivized to falsify or censor their views — the worse the system gets at uncovering the true public mood.
What’s more, adding additional (bad) data to the system doesn’t fix this “missing data” problem. GIGO remains an iron law of computing in this context, too.
But it gets better (or worse, I guess): Yang models a “crisis” scenario in which users stop self-censoring and start articulating their true views (because they’ve run out of fucks to give). This is the most dangerous moment for a dictator, and depending on the dictatorship handles it, they either get another decade or rule, or they wake up with guillotines on their lawns.
But “crisis” is where AI performs the worst. Trained on the “status quo” data where users are continuously self-censoring and preference-falsifying, AI has no clue how to handle the unvarnished truth. Both its recommendations about what to censor and its summaries of public sentiment are the least accurate when crisis erupts.
But here’s an interesting wrinkle: Yang scraped a bunch of Chinese users’ posts from Twitter — which the Chinese government doesn’t get to censor (yet) or spy on (yet) — and fed them to the model. He hypothesized that when Chinese users post to American social media, they don’t self-censor or preference-falsify, so this data should help the model improve its accuracy.
He was right — the model got significantly better once it ingested data from Twitter than when it was working solely from Weibo posts. And Yang notes that dictatorships all over the world are widely understood to be scraping western/northern social media.
But even though Twitter data improved the model’s accuracy, it was still wildly inaccurate, compared to the same model trained on a full set of un-self-censored, un-falsified data. GIGO is not an option, it’s the law (of computing).
Writing about the study on Crooked Timber, Farrell notes that as the world fills up with “garbage and noise” (he invokes Philip K Dick’s delighted coinage “gubbish”), “approximately correct knowledge becomes the scarce and valuable resource.”
https://crookedtimber.org/2023/07/25/51610/
This “probably approximately correct knowledge” comes from humans, not LLMs or AI, and so “the social applications of machine learning in non-authoritarian societies are just as parasitic on these forms of human knowledge production as authoritarian governments.”

The Clarion Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers’ Workshop summer fundraiser is almost over! I am an alum, instructor and volunteer board member for this nonprofit workshop whose alums include Octavia Butler, Kim Stanley Robinson, Bruce Sterling, Nalo Hopkinson, Kameron Hurley, Nnedi Okorafor, Lucius Shepard, and Ted Chiang! Your donations will help us subsidize tuition for students, making Clarion — and sf/f — more accessible for all kinds of writers.

Libro.fm is the indie-bookstore-friendly, DRM-free audiobook alternative to Audible, the Amazon-owned monopolist that locks every book you buy to Amazon forever. When you buy a book on Libro, they share some of the purchase price with a local indie bookstore of your choosing (Libro is the best partner I have in selling my own DRM-free audiobooks!). As of today, Libro is even better, because it’s available in five new territories and currencies: Canada, the UK, the EU, Australia and New Zealand!

[Image ID: An altered image of the Nuremberg rally, with ranked lines of soldiers facing a towering figure in a many-ribboned soldier's coat. He wears a high-peaked cap with a microchip in place of insignia. His head has been replaced with the menacing red eye of HAL9000 from Stanley Kubrick's '2001: A Space Odyssey.' The sky behind him is filled with a 'code waterfall' from 'The Matrix.']

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
—
Raimond Spekking (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acer_Extensa_5220_-_Columbia_MB_06236-1N_-_Intel_Celeron_M_530_-_SLA2G_-_in_Socket_479-5029.jpg
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
—
Russian Airborne Troops (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vladislav_Achalov_at_the_Airborne_Troops_Day_in_Moscow_%E2%80%93_August_2,_2008.jpg
“Soldiers of Russia” Cultural Center (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Col._Leonid_Khabarov_in_an_everyday_service_uniform.JPG
CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#habsburg ai#self censorship#henry farrell#digital dictatorships#machine learning#dictator's dilemma#eddie yang#preference falsification#political science#training bias#scholarship#spirals of delusion#algorithmic bias#ml#Fully automated data driven authoritarianism#authoritarianism#gigo#garbage in garbage out garbage back in#gigogbi#yuval noah harari#gubbish#pkd#philip k dick#phildickian
833 notes
·
View notes
Note
How do you feel about the increase in really weird NSFW ads on here (advertising panels that look like sexual encounters, and AI art apps that pride themselves on porn) but will take down NSFW posts from their users, even if it isn't technically sexual.
i hate all social media and it's consistent prioritising the advertisers over the users and the internet simply was a better place before capitalism sunk its hooks into it
#i could write essays about how capitalism ruined the internet.#i was actually talking to someone earlier today about how youtube was kind of effectively ruined by monetisation.#and they were raised in the soviet union and we had a bit of a talk about how art was better because it wasn't for profit.#the people who made art made it because they wanted to do it and because they loved it.#she said that communism was terrible for every aspect of life for her. people's lives under communism wasn't pretty.#but the art was better. and i feel like it's true for the internet – it was better when it was a free-for-all.#the companies didn't know how to exploit it yet and turn it into a neverending profit-driven hellscape.#people created content because they wanted to. because they wanted to make something silly to make people laugh.#not for profit. not for gain. not for numbers. not to further their career.#i miss the days of newgrounds and youtube before monetisation.#capitalism has soiled everything that's joyful and good in this world.#people should be able to share whatever they want.#people should be able to tell any story they want without the fear of being silenced by advertisers.#that's what made the internet so beautiful before. anyone could do anything and we all had equal footing.#but now we're victims of the algorithm. and it makes me sick.#i'm quitting my job in social media. i'm quitting it. it makes me too depressed. i have an existential crisis every freaking day.#every day i wake up and say "ah. this is the fucking hell we live in#i'm so sorry i feel so passionate about this.#social media is a black hole and it is actively destroying humanity. forget ai. social media is what's doing it.#i miss how beautiful the internet used to be. it should've been a tool for good. but it's corrupt and evil now.#sci speaks
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
GRINDR AI CHATBOT WHAT THE FUCK??


We’re in the bad timeline.
#grindr continuing to be the worst game on my phone#the data used section is fuckin wild like why would that shit need to know my precise location ethnicity and gender identity???#the last thing that app needs is an ai-driven algorithm jfc
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Screw you, AI Spellcheck! I will use the word 'amongst' if I damn well feel like it.
#anti-ai#writer problems#seriously how much AI-driven Spellcheck tries to convince me words I use while writing aren't words#so I waste time looking them up in an actual dictionary database and yeah I was right...#AI isn't an actual articial intelligence we have to worry about taking over the world...#it's a bullshit tool that excelerates the dumbing down of the populace#like it's flagging words as incorrect just because the word isn't common in its (stolen) data sets#this could seriously dwindle our functional vocabulary if people just believe they've made up a word and change it to a more common word#just because a LLM Spellcheck says it's wrong because it's not used by whatever % threshold the algorithm is set to
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dive into the world where human intuition seamlessly integrates with AI brilliance in web development. Elevate your online presence with the perfect fusion of creativity and technology.
#Benefits of incorporating human touch in AI-driven web development#Enhancing user experience through human-centered AI web development#Balancing automation and human input in modern web development#The role of empathy in AI-driven web design and development#Strategies for infusing creativity into AI-powered web development#Understanding user behavior for personalized AI web development#Building trust through human-like interactions in AI web development#Improving accessibility with human-centric AI web design#Ethical considerations in integrating human touch with AI in web development#Tailoring AI algorithms for diverse user experiences in web development
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Should i start a separate art sideblog? I kind of want to so anyone who happens to look doesn't have to scroll through my walls of text in between. My main reason not to is the prospect of getting no notes, which is a very real possibility. But somehow even a tiny amount of notes here is nicer than a tiny amount of likes on instagram, which is the reality of most people on there now who don't want or know how to play the fucking engagement game.
#i hate instagram so much#i hate the way it encourages you to scroll past artwork that is gorgeous and press the heart without really engaging#i hate the way you can follow someone and then never see their work on the algorithm driven dash#i dont care about the AI thing tbh i just avoid all AI conversation in case i have the Wrong Left Opinuon#but i really do care about the way it makes you scroll past beautiful art with the tiniest glance#people make art for someone to LOOK at it and really see it#then again i am someone who long ago gave up any idea of making art for a job so#you can disregard if you like....the truth is all I've got is an urge and need to create#that i try and manage and use#and i really want more than anything for my work to connect with people emotionally#that's all I've got.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is the Future of SEO in the Age of AI?

1. AI is Changing Search Engine Algorithms
Search engines like Google are using AI to improve how they work. BERT, MUM, and RankBrain are just the start. These systems help search engines grasp what users really mean, beyond just matching keywords. With Natural Language Processing, AI can understand queries in a more human way.
Now, AI ranks pages based on user experience, mobile-friendliness, and the overall quality of content.
With real-time updates to algorithms, SEO strategies need to be adaptable. Students in digital marketing course in Coimbatore are learning how to make their content fit these new algorithms.
2. Working with AI in Content Creation
AI is changing how we create content. Tools like ChatGPT and Jasper can whip up text quickly, but Google still prefers original insights from real people. Use AI to brainstorm ideas and gather research.
Always tweak AI-generated content to make it more relatable and engaging. Make sure it aligns with Google’s guidelines for helpful content.
While AI can be a great helper, the future is for those who mix it with creativity—something emphasized in digital marketing courses in Coimbatore.
3. Voice Search Optimization
Voice assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are becoming popular, leading to longer, more conversational search queries. To optimize for voice search, use natural language and long-tail keywords.
Creating FAQ-style content and using schema markup can help too. Voice SEO is becoming a big topic in digital marketing training in Coimbatore.
4. Machine Learning and User Behavior
Search engines are leaning on machine learning to tweak results in real-time. This means that SEO is about more than just technical aspects; user interaction matters too.
Metrics like bounce rate and session duration can affect your rankings. Content that keeps users engaged is prioritized now. Keeping an eye on user behavior and analytics is essential, and many digital marketing programs in Coimbatore now teach UX/UI basics to prepare students for this shift.
5. The Rise of Visual and Video SEO
AI can now see images and videos, leading to new ways of indexing visual content. Using alt text and proper file names is crucial.
Don’t forget to include video transcripts and descriptions while ensuring fast loading times and mobile optimization. With platforms like YouTube and Pinterest on the rise, it’s vital to optimize all content types, not just written stuff.
6. Predictive SEO with AI Tools
AI helps with predictive analytics, letting marketers guess search trends and ready content ahead of time. Tools like Google Trends and predictive SEO software can be handy here.
Spotting content gaps and planning for them will be key, especially with seasonal or event-based strategies. Good digital marketing courses in Coimbatore focus on hands-on experience with these tools.
7. E-E-A-T: Expertise Matters
Even with AI’s growth, Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) are still important. Make sure to highlight real authors and credentials.
Adding customer reviews and expert insights adds authenticity. Learning how to balance AI and genuine content is a skill taught in digital marketing courses in Coimbatore.
8. Improved Local SEO with AI
AI is making local SEO better by helping to create more accurate geo-targeted content. It’s crucial to optimize your Google Business Profile, include location-based keywords, and encourage reviews for local visibility.
For students in digital marketing training in Coimbatore, local SEO is especially critical for helping nearby businesses grow.
9. The Importance of LSA Keywords
Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) keywords help search engines understand content context better. Here are some examples connected to SEO:
- search engine optimization tools
- AI in content marketing
- user behavior analytics
- mobile-first indexing
- semantic search trends
Using LSA keywords is important for creating content that fits the needs of both users and search engines.
10. Job Opportunities in AI-Driven SEO
As AI takes a bigger role in SEO, companies look for folks who understand both digital marketing and AI. Entry-level positions are starting to require knowledge of AI tools.
Internships now often include automation tools, analytics, and AI content optimization. Courses in Coimbatore are adapting their programs to reflect this demand. Hands-on training, tools, and project-based learning are becoming the norm.
Conclusion: Staying Ahead with Xplore It Corp
So, what’s the future of SEO in the age of AI? Clearly, while AI is making things faster and more efficient, human creativity and flexibility are essential. The need for skilled SEO professionals is rising, and it's important to keep evolving.
To keep your skills sharp, think about joining a digital marketing course in Coimbatore, or check out top training institutions in the area. Gain practical experience with real-world tools and expert guidance.
At Xplore It Corp, we offer training that combines traditional SEO with today’s AI technologies, prepping you for both the current job market and what’s to come. Join us to step into the future of digital marketing confidently!
FAQs About the Future of SEO and AI
1. Is SEO becoming outdated because of AI?
No, SEO is changing, not disappearing. AI is reshaping how search engines function, focusing more on user intent and content quality.
2. Can AI write good SEO content?
AI tools like ChatGPT can help create content, but you still need a human touch for it to be engaging and unique.
3. Which skills are vital for AI-driven SEO?
Key skills include knowledge of AI tools, data analysis, voice search optimization, and UX/UI. These are often covered in digital marketing course in Coimbatore.
4. How does AI impact local SEO?
AI improves local SEO by enabling real-time targeting and personalized user experiences through voice search.
5. Where can I learn SEO with AI tools in Coimbatore?
Check out Xplore It Corp for in-depth training on integrating SEO with AI resources.
#AI in Digital Marketing#Voice Search Optimization#Content Marketing Trends 2025#Programmatic Advertising#Social Media Algorithms 2025#Influencer Marketing Strategy#Digital Marketing Career Opportunities#Marketing Automation Tools#Search Engine Algorithm Updates#Data-Driven Marketing
0 notes
Text
Hey AI, Are You Telling Google About Me?
A Personal Dive Into the Algorithmic Mirror It started with a simple, almost paranoid question—but one that feels increasingly valid in the age of digital surveillance: “Do you report cookies to Google or is it just my phone/browser doing so? Because often times I’ll talk to you about something and a short while later I’ll see an ad or video for it.” That question wasn’t rhetorical—it came…
#AI and you#AI Conversations#Algoritm Culture#content curation#Data Driven World#did i train the algorithm#digital identity#Digital self awarteness#digital surveillance#echo chamber#feed manipulation#Lexi and Me#media bubble#modern mind control#Platform Politics#tech vs privacy#watching back#youtube feed
0 notes
Text
Virtual Tutors and AI: The New Face of Modern Education
Education is changing—and not just because of new textbooks or digital classrooms. Behind the scenes, AI is quietly reshaping how we learn, teach, and interact with knowledge itself.
The days of the one-size-fits-all classroom are behind us. Thanks to AI, learning today is becoming more personal, more accessible, and more effective. It's not about replacing teachers—it's about empowering them, and making education a more human experience, not less.
Here’s how AI is transforming education:
Personalized Learning Paths AI algorithms analyze a student’s strengths, weaknesses, and pace. Based on that, they create tailor-made study plans—giving every learner the chance to shine on their own terms.
Virtual Tutors Stuck on a math problem at midnight? AI-driven tutors like chatbots and apps provide instant support, explanations, and practice, filling gaps when human help isn’t around.
Real-Time Feedback Instead of waiting for end-of-term report cards, AI tools give students immediate feedback—helping them course-correct and learn more efficiently.
Access to Quality Education Everywhere AI-powered platforms break down geographical barriers, offering top-quality education to students in remote areas, or those who otherwise wouldn’t have access.
Smarter Content Creation AI helps teachers by generating quizzes, lesson plans, and customized learning materials—giving educators more time to focus on what they do best: inspire.
Predictive Analytics for Early Intervention AI can spot when a student is struggling early on, allowing teachers and parents to step in with support before it’s too late.
AI isn’t just making education smarter—it’s making it more human by meeting students where they are. If done right, the future of learning looks brighter, fairer, and full of possibilities.
About US: AI Technology Insights (AITin) is the fastest-growing global community of thought leaders, influencers, and researchers specializing in AI, Big Data, Analytics, Robotics, Cloud Computing, and related technologies. Through its platform, AITin offers valuable insights from industry executives and pioneers who share their journeys, expertise, success stories, and strategies for building profitable, forward-thinking businesses.
Contact Us :
Call Us
+1 (520) 350-7212
Email Address
Local Address
1846 E Innovation Park DR Site 100 ORO Valley AZ 85755
0 notes
Text
What If AI Became the Primary Educator 2025
What If AI Became the Primary Educator 2025 Education has always evolved with technology, from the printing press to the internet. But what if artificial intelligence (AI) became the primary educator, replacing traditional teachers and transforming the way we learn? AI already plays a significant role in personalized learning, automating assessments, and offering instant feedback. But could it fully take over? What would that mean for students, teachers, and the education system? The Current Role of AI in Education AI is already enhancing education in many ways: - Personalized Learning – AI-driven platforms like adaptive learning apps adjust lessons to match a student’s pace and style. - Instant Feedback – AI-powered grading systems provide real-time corrections on assignments and quizzes. - Tutoring & Support – AI chatbots and virtual tutors help students with homework and explanations. - Automated Administrative Work – AI reduces the workload for teachers by handling paperwork and scheduling. These applications improve learning efficiency, but what happens if AI takes full control? What Would an AI-Driven Education System Look Like? If AI became the primary educator, schools and classrooms would look completely different. Instead of a human teacher standing in front of students, AI-driven systems would guide learning in a highly customized and interactive way. 1. Fully Personalized Learning Paths Every student would have an AI tutor that understands their strengths, weaknesses, and preferred learning methods. Instead of following a fixed curriculum, AI would adjust lessons based on real-time progress, ensuring students learn at their own pace. 2. Interactive & Immersive Lessons AI-powered virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) could replace textbooks with 3D interactive experiences. Instead of reading about ancient Rome, students could walk through a digital recreation and interact with historical figures. 3. Instant Grading & Feedback AI would assess assignments immediately, offering instant explanations for mistakes. This would remove delays in feedback and help students correct misunderstandings on the spot. 4. AI-Powered Creativity & Problem-Solving AI could guide students through creative projects, helping with brainstorming, coding, writing, and designing. It would suggest new ideas, offer insights, and even act as a collaborator. 5. Always Available Education Unlike human teachers, AI is available 24/7. Students could learn whenever they want, from anywhere in the world. AI-driven education would remove geographic and time barriers, making quality education accessible to everyone.

The Benefits of AI as the Primary Educator If AI took over teaching, it could bring several major benefits: ✅ Equal Access to Education – AI would provide high-quality education to students worldwide, regardless of their location. ✅ Personalized Learning Experience – Every student would get a tailored education that fits their abilities and interests. ✅ Faster & More Efficient Learning – AI’s instant feedback and adaptive learning would speed up the learning process. ✅ Reduced Teacher Workload – AI could handle grading and administrative tasks, freeing human teachers for mentorship and guidance. The Risks & Challenges of AI-Led Education Despite its benefits, replacing human teachers with AI comes with serious challenges: ❌ Loss of Human Connection – Students might miss out on emotional support, mentorship, and social interaction, which are crucial for development. ❌ Bias in AI Algorithms – AI is only as good as the data it’s trained on. If biased, it could reinforce stereotypes and misinformation. ❌ Over-Reliance on Technology – If students depend too much on AI, they might lose critical thinking and problem-solving skills. ❌ Job Loss for Educators – If AI replaces human teachers, millions of jobs in education could disappear. Will AI Fully Replace Teachers? While AI could transform education, it is unlikely to completely replace human teachers. The best education system will likely be a hybrid model, where AI handles technical tasks while human teachers provide emotional support, creativity, and real-world mentorship. Imagine an AI tutor helping with personalized lessons, while a human teacher guides discussions, encourages critical thinking, and provides moral support. This combination could create the most effective learning experience. The Future of AI in Education By 2030, we may see: - AI-driven classrooms where students learn through virtual experiences and simulations. - Emotional AI that can recognize when students are frustrated or bored and adjust lessons accordingly. - Global AI tutors offering high-quality education to children in remote areas. - Lifelong AI learning assistants that stay with individuals from childhood to adulthood, helping them upskill over time. Final Thought If AI became the primary educator, it would revolutionize learning by making it more personalized, efficient, and accessible. However, education is not just about absorbing information—it’s about human interaction, creativity, and emotional growth. AI can assist in teaching, but it should work alongside human educators rather than replace them. The best education will come from a blend of technology and human guidance, ensuring students develop both knowledge and emotional intelligence. AI might be the future of education, but human connection will always be irreplaceable. Read Our Past Blog: How Does Dopamine Influence Motivation 2025For more information, check this resource.
What If AI Became the Primary Educator 2025 - Everything You Need to Know
Understanding ai in DepthRelated Posts- What If AI Became the Primary Educator 2025 - What If AI Became the Primary Educator 2025 - What If AI Became the Primary Educator 2025 - What If AI Became the Primary Educator 2025 Read the full article
#1#2#2025-01-01t00:00:00.000+00:00#2025relatedpostswhat#2030#24/7#3#4#5#adaptivelearning#ai-driven#algorithm#ancientrome#artificialintelligence#augmentedreality#bias#blog#brainstorming#chatbot#child#classroom#creativity#criticalthinking#curriculum#data#depthrelatedpostswhat#dopamine#education#emotionalintelligence#experience
0 notes
Text
Beats, Bytes & The Future Sound: AI Meets Electronic Music
Electronic music has always been about pushing boundaries, breaking rules, and bending sound into new dimensions. Now, artificial intelligence is stepping into the booth, reshaping how beats are built, melodies emerge, and tracks come to life. This isn’t about robots replacing producers—it’s about a new creative partnership, where human intuition meets machine-driven possibilities.The Evolution…
#AI and sound design#AI beat generation#AI for producers#AI in electronic music#AI in music production#AI mixing and mastering#AI music algorithms#AI music collaboration#AI music creation#AI music technology#AI music trends.#AI rhythm generation#AI-driven sound synthesis#AI-generated beats#AI-powered music software#artificial intelligence in techno#artificial intelligence music production#automated music production#creative AI music#digital music production#electronic music and AI#electronic music tools#future of music production#machine learning music#music composition AI#music innovation AI#music production AI tools#music production tools#neural networks in music#sound design AI
0 notes
Text
The voluntary carbon market (VCM) witnessed both considerable progress and significant hurdles in 2023 as reviewed by the MSCI Carbon Markets in its recent webinar.
The review includes key developments from 2023 and the potential inflection points to watch out for in 2024. Notably, the findings show that 2023 has the lowest number of credits issued in 3 years. In contrast, the year ended with a record number of monthly retirements.
Here’s a recap of the webinar, focusing on carbon credit issuances and retirements, demand, key market players, investment, major policy developments, and 2024 outlook.
Peaks, Valleys, and 2023’s Record Retirements
In 2023, credit issuances recorded the lowest annual total in 3 years after falling 25% year-on-year, as seen below. This slow down in supply was largely due to Nature-based and renewable energy projects issuing their lowest annual amounts in 5 and 4 years, respectively.

carboncredits.com
The MSCI report saw retirements rallied in Q4 2023, the second highest quarter on record. And that’s despite the slow down in corporate activity in mid-year. This momentum seems to have been carried into January this year.
In fact, that’s the second highest January to date and may even exceed the 17 MtCO2 set in 2022. December 2023 alone has seen 36 megatons of credit retirement, setting a new monthly high, around 25% above the previous high record.

carboncredits.com
When it comes to registries, the four largest, namely Verra, Gold Standard, ACR, and CAR continue to dominate the market. They provide more than 90% of the credits retired last year.
Retirements from these “Big 4” registries actually rose last year by 6%, while retirements across the next ten prominent names dropped slightly in 2023.
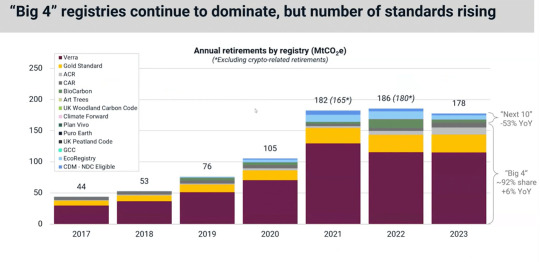
carboncredits.com
Of the top 10 retirees, Delta Airlines aced the first spot. They were also the largest retiree corporate in 2021 and 2022. While some of these companies exited the top 10 last year, others remain while new ones entered the market.
Shell topped the list in 2023 with around 16 million metric tonnes, followed by Volkswagen with over 8 MtCO2e. Overall, there are more joiners than leavers last year when it comes to retiring credits.

carboncredits.com
Unlocking the Nascent Carbon Removal Market
Gaining a lot of interest in 2023 is the nascent CDR market, referring to high permanent engineered carbon removals. These include biochar and direct air capture, which usually command a premium price than other project types. That’s because they’re known to be of higher quality and high durability.
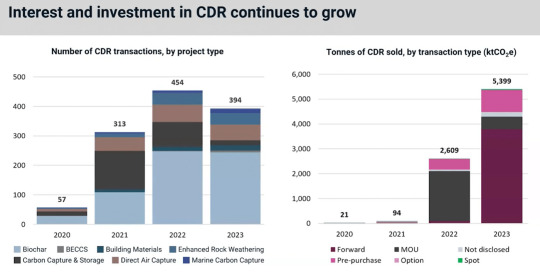
carboncredits.com
Last year, the number of CDR transactions fell slightly year-on-year. But the quantity of credits, represented by the right hand chart, increased significantly to 5.4 million.
Navigating the Ups and Downs of Carbon Credit Prices
The declining trend in 2022 was carried over into the first half of 2023. But looking at the average level, the drop wasn’t that much. It was only 16% lower in 2022 compared to 2023.
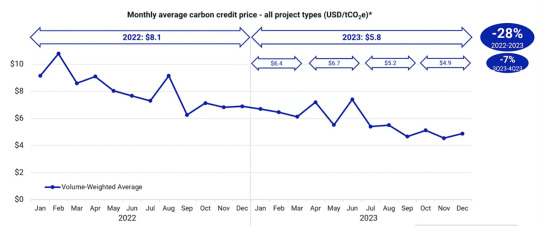
carboncredits.com

carboncredits.com
In terms of price by project type for last year, all of them were lower in Q4, resulting in full year price declines. REDD+ projects saw the least drop, 15%, while renewable energy experienced the largest price decrease, 39%.
Both energy efficiency (pink line) and REDD+ (green line) projects were subject to increased media and academic scrutiny in 2023. They sustained weaker prices.
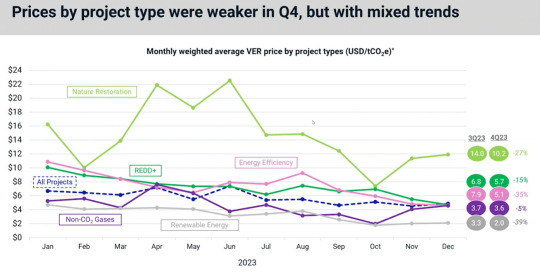
carboncredits.com
Interestingly, both nature restoration and non-CO2 gasses projects rebounded in November and December last year. Meanwhile, energy efficiency, REDD+, and non-CO2 gasses converged around the same price level at $4.65 by the end of the year.
This suggests that the market is not distinguishing between these project types, potentially signaling a weak market environment.
Policy Developments in 2023: From EU Directives to COP28’s Uncharted Territories
Last year also saw some major policy developments. For instance, the EU’s green claims directive aims to empower consumers for the green transition directive. It bans claims of neutral, reduced, or positive climate impact based on carbon offsetting, on the grounds that it’s a misleading consumer practice.
Moreover, the VCMI carbon integrity claims, the Claims Code of Practice (CCPs), is a significant regulation for the VCM.
There are also landmark regulations of market trading and standards wherein national governments are stepping in. For example, the US Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) introduced proposed guidance for trading of voluntary carbon credit derivative contracts.
In the Global South, there has been growth in national carbon credit markets while carbon pricing systems and schemes are being proposed in several African countries. Amid increased scrutiny in carbon credits certified by Verra, the leading carbon certifier updated its standards.
At the COP28 climate summit, carbon markets find their footing amid Article 6 frustrated talks. Article 6.2 rules are mostly in place but there’s a lack of Article 6.4 agreement on key steps. Disagreements centered on integrity concerns, yet Article 6 agreements are moving ahead.
Looking forward, MSCI Head of Carbon Markets, Guy Turner, raised a pertinent question: “Could we be at an inflection point for the market in 2024?”
There could be a number of inflection points, five in particular.
The potential new sources of demand driven by CORSIA, VCMI, SBTi, and more compliance markets in near and long term.
Quality initiatives moving into implementation.
Jurisdictional approaches are starting to take off – whether by governments or donor institutions. High interests are observed in jurisdictional soil carbon and blue carbon.
Increasing clarity for corporations on claims and disclosures on the use of credits, with the EU and UK taking the lead.
Macroeconomic cycle turning but political uncertainties
In the ever-evolving landscape of the voluntary carbon market, 2023 marked both triumphs and challenges. From record retirements to the rise of CDR investments, the market navigated uncertainties. As 2024 unfolds, potential inflection points await, shaping the future trajectory of the global carbon market.
#Net Zero Carbon#Decarbonization#Air quality analytics#Sustainability Reporting#ESG Emission#GHG Emission#Climate change#Carbon credits#Carbon offsets#Carbon reduction

#Our AI-driven Net Zero Emissions (NZE) tracking employs artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to monitor#analyze#and report carbon emissions.
0 notes
Text
🚀 Exciting news! Google has launched Gemini 2.0 and AI Mode, transforming how we search. Get ready for faster, smarter responses to complex queries! Explore the future of AI in search today! #GoogleAI #Gemini2 #AIMode #SearchInnovation
#accessibility features.#advanced mathematics#advanced reasoning#AI Mode#AI Overviews#AI Premium#AI Technology#AI-driven responses#coding assistance#data sources#digital marketing#fact-checking#Gemini 2.0#Google AI#Google One#image input#information synthesis#Knowledge Graph#multimodal search#Query Fan-Out#response accuracy#search algorithms#search enhancement#search innovation#text interaction#User Engagement#voice interaction
0 notes
Text
The Hidden Algorithm of Happiness: How Data is Redefining Joy in the Digital Age
In an age where technology permeates every facet of life, the pursuit of happiness has taken a fascinating turn. No longer confined to philosophical musings or self-help books, happiness is now being dissected, quantified, and optimized through data. A groundbreaking study by the Global Well-Being Institute reveals that 73% of people find joy in micro-moments—tiny, intentional acts of connection. This discovery is reshaping how we understand and experience happiness, blending ancient wisdom with cutting-edge technology.
#happiness#data-driven joy#happiness in digital age#well-being aspects in digital world#technology and mindfulness#conscious consumerism#micro-moments#AI#digital minimalism#future of happiness#happiness research#mental health and happiness trends#happiness science#happiness and technology#happiness algorithms.
0 notes
Text

Premier Alliance of Data and AI Innovators
The Premier Alliance of Data and AI Innovators (PADAI) unites forward-thinking data scientists and AI professionals to collaborate, drive innovation, and create cutting-edge solutions for the rapidly evolving field of data science and artificial intelligence.
Benefits of Membership
The Advisory Board of the Premier Alliance of Data and AI Innovators (PADAI) consists of renowned professionals and scholars who provide strategic guidance and expert advice. These advisors bring diverse perspectives and insights, ensuring PADAI remains at the forefront of innovation and excellence in data science and AI. Their expertise supports the organization in achieving its goals and advancing the field.
#Data science#Artificial intelligence#AI innovators#Machine learning#AI technology#Predictive analytics#Data-driven decision making#Data analytics#Deep learning#AI solutions#Data engineering#AI development#AI advancements#Digital transformation#AI algorithms
0 notes