#Abstract base class
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


Some art class junk teehee
#art#artist#traditional art#prismacolor markers#acrylic paint#painting#drawing#art class#high school#cat#abstract#based on Picasso#house#balance#color#casita#cinabonsticks
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sequels are a plague upon this reality and I will live and die on this hill
#guess who's dying in english coursework#it's me I'm dying#someone tell me to rant abt my classes because GOD do I have rants ready to go#sequels are genuinely my nemesis#do i think all those spider-man movies are fun?#yes#(ignoring the tom holland ones because that's like 2 more rants)#do i also think we couldve survived without all those spider-man movies?#cause here's the thing#there's good sequels and bad sequels and the distinction is entirely based upon whether they were made for love or profit#anyway every time i see someone asking for a sequel to something i die a little#kind of like how i die a little whenever i see people defending bad media via the characters#like c'mon people#characters are just abstract people#they're crafted with purpose and every choice they make is actually made by the person/people writing them#do not speak to me abt why that character would or would not do this or that#speak to me abt why the writer/s made them do this or that#i am tired#so very very tired#just to be clear there's totally a space for analyzing characters in their own media#I'm just full of wrath at one of my teachers rn#what if i just said more bullshit on this blog#like why am i trying to be a neat little art blog#i'm full of adhd trauma and depression#my brain is a carefully crafted cacaphony of nonsense and my blog should be too#professionalism is dead embrace cringe
1 note
·
View note
Text
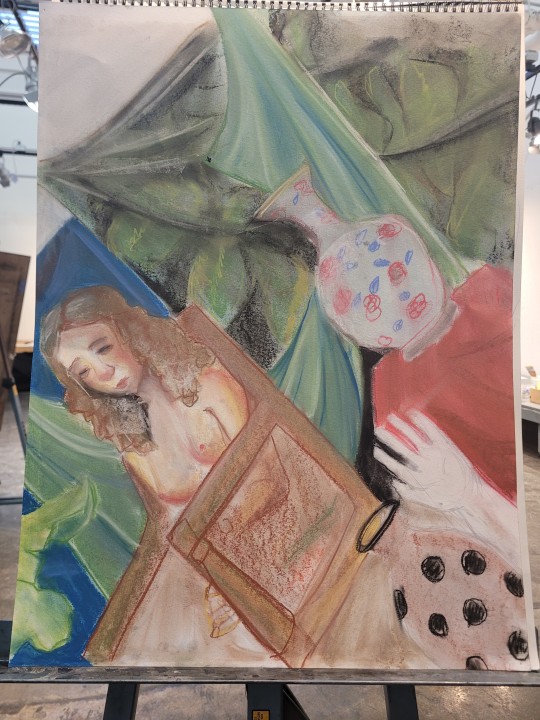

#drawing#my art#original art#artists on tumblr#art class#still life#art final#i have to make abstract art based off of this#HOW DO YOU CREATE ABSTRACT ART#what even is abstract art#illustration
1 note
·
View note
Text
107 years ago today an organized group of workers in the Russian Empire decided they had had enough of war, misery, the oppression of women, and of a corrupt democracy that had promised much and changed nothing, the Tsar still in his palaces, the workers still giving their life for a cause foreign to the working class of Europe and the world. Most bolsheviks were industrial workers, with an insufficient formal education, precarious salaries and conditions. The working class in the Russian Empire had tried liberal democracy, had seen its hipocrisy in the months following the election of the provisional government, and understood their historic goal of progressing further beyond the democracy of the landowner, businessman and aristocrat. It wasn't the first time the proletariat had attempted to take power, both worldwide and in the Russian Empire, but this time they were ready, educated, an organized enough.
The armies of 14 imperialist powers combined could not stop the will of a mass of workers that had realized their worth, their potential, and most importantly, their dignity. They no longer had to bow down to paternalism, electoralism, and the capitalists to whom they sold their labor, no armed intervention, no amount of propaganda, no adventurist distraction, could take away from that fact. This isn't a fantasy, it isn't idealistic, it's a historical fact, that revolutions are possible, have happened, succeeded, and that the opportunity presents itself sooner than most expect. The only task at hand is to organize towards it. Agitation, education, an actual dual power structure predicated on a unified will, not on voluntarism and horizontalism.
I understand the topic at hand for the last 2 days and many more to come will be the results of the US election. But the US is not the only liberal democracy that increasingly creates disappointment among the social majority. After all the posting about the various liberals that make up the US electoral environment, it is imperious that nobody falls into despair. Not in a self-care way, not in the way most left-liberals have been talking about, referring to an abstract sense of "preparing", but because of the simple necessity for this election to further erode any popular faith in reformism, whether it's Trump's reforms, Harris' reforms, Bernie's reforms, or Stein's reforms. Wallowing in despair is as useful as placing yet more stake into whoever is wheeled out next to promise even less, in what will most certainly be also called the most important elections of our lifetimes.
Return to the working class of the Russian Empire, of a fractured and hungry China, to the colony of Indochina, to the plantation island that was Cuba. And I urge you to exercise some perspective. These masses of people had suffered more than you for longer than you. Nobody's asking you to feel guilty about your economic position in the world, we're asking you to realize that, for as long as there have been modes of production predicated on the exploitation, division and discrimination of a producing class, there have always been options, better options than sinking into despondent depression. They have managed to cast off their yoke and build towards a society not based on exploitation. They're not utopias, and mistakes have been and will be committed, but they all realized and understood that it's better to commit our own mistakes, than to toil under the rational oppression by another class for any longer.
#seriousposting#I have comrades in my party who began their activity as communists before the USSR fell. they're still going and are as convinced as ever
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Anti-Obesity Drugs in Sociopolitical Context
Abstract
This literature review critically examines the use of Body Mass Index (BMI) as a diagnostic tool for obesity, highlighting its historical and scientific flaws. The diagnosis and treatment of obesity is heavily stigmatized and reflects deeper socio-economic and racial biases. Fatphobia, or anti-fatness, is deeply rooted in white supremacy and colonial history. I argue that anti-fatness and weight-based discrimination significantly impact health outcomes, rather than body fat percentage alone. The way that the medical system focuses on body size rather than the overall health of patients perpetuates harm and yields even poorer health outcomes. To genuinely improve the lives of fat individuals, we must dismantle anti-fat systems and remove barriers to healthcare, job equity, and basic infrastructure by implementing legal protections, rather than simply promoting weight loss. This review emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to health that considers socio-economic factors and systemic discrimination.
Journal Summary
Recently, two anti-obesity medications, Ozempic and Wegovy, which are primarily prescribed for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), have shown promise in causing weight loss. The 2022 scientific journal “Ozempic and Wegovy for Weight Loss, Pharmacological Component and Effect” by Abdullah Mohammed, et al explores the pharmacological components and effects of these medications on weight reduction, summarizing findings from existing clinical studies.
Ozempic is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist primarily used to manage T2DM. Clinical studies indicate that semaglutide can also promote significant weight loss. Ozempic's mechanism involves binding to GLP-1 receptors in the brain, reducing food intake and increasing feelings of fullness. This leads to a decrease in body weight and improvement in glycemic control. Wegovy, also a GLP-1 receptor agonist, is the same drug as Ozempic but two times the dose, specifically approved for weight loss for fat people even without T2DM. Administered as a weekly injection, Wegovy has shown effectiveness in inducing sustained weight loss. The STEP trials demonstrated that participants using Wegovy experienced an average weight loss of 15.8% over 68 weeks. Wegovy's pharmacokinetics involve prolonged activation of GLP-1 receptors, enhancing satiety and reducing hunger. GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide mimic the action of the natural hormone GLP-1, which regulates appetite and blood sugar levels. By slowing gastric emptying and promoting a feeling of fullness, these medications reduce caloric intake. Clinical trials have shown that GLP-1RAs, including semaglutide, can result in weight loss from 5% or up to 10-15% of body weight. However, sustained weight loss requires ongoing lifestyle modifications, as discontinuation of the medication leads to weight regain. Common side effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. Other potential side effects include increased heart rate, fatigue, headaches, and changes in thyroid function.
Obesity as a Disease
How does one get an obesity diagnosis? There is one single criterion used for diagnosing someone with this disease: The Body Mass Index (BMI). A person’s BMI is their weight in kilograms divided by the square of their height in meters, rounded to one decimal place. It does not account for muscle mass versus body fat. For these reasons, the BMI has been widely proven to be an ineffective health measure. The BMI was also never intended to be a measure of health in the first place.
The BMI was created in the 1800s by a statistician named Adolphe Quetelet, who did not study medicine, to gather statistics of the average height and weight of specifically white, European, upper-middle-class men to assist the government in allocating resources. It was never intended as a measure of individual body fat, build, or health (Karasu, 2016). Quetelet is also credited with founding the field of anthropometry, including the racist pseudoscience of phrenology. Quetelet’s L’homme Moyen would be used as a measurement of fitness to inspire, and as a scientific justification, for eugenics (Eugenics archive).
Studies have observed that about 30% of "normal” weight people are “unhealthy," whereas about 50% of "overweight" people are “healthy” (Rey-López, et al, 2014). Thus, using the BMI as an indicator of health misclassifies 75 million people in the United States alone. “Healthy*” lifestyle habits are associated with a significant decrease in mortality regardless of baseline body mass index (Matheson, et al, 2012).
*I put “healthy” in quotation marks here because the definition of an individual’s health is oversimplified and depends on many socioeconomic factors.
While epidemiologists use BMI to calculate national obesity rates, the distinctions between weight classes can be arbitrary. Ever notice that the weight classes on the BMI are nearly intervals of five? In 1998, the National Institutes of Health lowered the overweight threshold from 27.8 to 25—making roughly 29 million Americans "overweight" overnight—to match international guidelines (Butler, 2014). Critics have also noted that those guidelines were drafted in part by the International Obesity Task Force, whose two principal funders were companies making weight loss drugs.
Jackie Scully, Senior Research Fellow at the Unit for Ethics in the Biosciences, University of Basel, in her scientific journal titled “What is a Disease?” states the following: “As the business literature shows, new clinical diagnoses are often welcomed primarily as opportunities for market growth (Moynihan et al, 2002). One recent example of this is female sexual dysfunction (FSD). The huge commercial success of sildenafil (Viagra) for erectile dysfunction in men provides a strong motivation for drug companies to identify an equivalent market (that is, condition) in women. And some ethicists feel that drug companies were, to put it mildly, over-involved in the medical consensus meetings held between 1997 and 1999 that effectively drew up very inclusive clinical criteria for the definition of FSD (Moynihan, 2003)."
How can one diagnose a person with a disease and sell them medications solely based upon an outdated measure that was never meant to indicate health in the first place, especially when obesity has no proven causative role in the onset of any chronic condition? (Kahn, et. al., 2000), (Cofield, et al, 2010).
This is why the term “obese” is recognized as a slur by fat communities. It's a stigmatizing term that medicalizes fat bodies even in the absence of disease. The word directly translates to "having eaten oneself fat" in Latin. Obesity, as a medical diagnosis, doesn’t have much ground to stand on. Aside from being overtly incorrect as a medical tool, the BMI is used to deny certain medical treatments and gender-affirming care, as well as insurance coverage. Employers still often offer bonuses to workers who lower their BMI. Although science recognizes the BMI as deeply flawed, it's going to be tough to get rid of. It has been a long-standing and effective tool for the oppression of fat people and the profit of the weight loss industry.
To treat obesity, patients must eat less. Making someone smaller still means they will be healthier, right?
Fatness and Mortality
The idea that obesity is unhealthy and can cause or exacerbate illnesses is a biased misrepresentation of the scientific literature that is informed more by bigotry than credible science (Medvedyuk, et al, 2017). Fatphobia existed long before fatness became medicalized. Yes, obesity is correlated with conditions such as cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and diabetes, but some scientists are looking into possibilities that don't equate correlation with causation. Obesity has no proven causative role in the onset of any chronic condition (Kahn, et al, 2000), (Cofield, et al, 2010) and its appearance may be a protective response to the onset of numerous chronic conditions generated from currently unknown causes (Lavie, et al, 2009), (Uretsky et al, 2007), (Mullen, et al, 2013), (Tseng, 2013). A portion of these correlated conditions are likely brought on by the stress of being part of one or more marginalized groups with little to no support or basic access in society. Weight stigma itself is deadly. Research shows that weight-based discrimination increases risk of death by 60% (Sutin, et al, 2014).
Dieting also poses serious health risks. The reason that these weight loss drugs are so successful by comparison is that dieting is unsustainable and does not lead to prolonged weight loss. Over 50 years of research conclusively demonstrates that virtually everyone who intentionally loses weight by manipulating their eating and exercise habits will regain the weight they lost within 3-5 years, and 75% will regain more weight than they lost (Mann, et al, 2007). Evidence suggests that repeatedly losing and gaining weight is linked to cardiovascular disease, stroke, diabetes, and altered immune function (Tomiyama, et al, 2017). If most fat people have historically tried to lose weight their whole lives through dieting, this has major implications on overall health. Prescribed weight loss is also the leading predictor of eating disorders (Patton, et al, 1999).
Another factor that may be impacting fat people’s rate of mortality is that they are being mistreated at the doctor’s office. I have personally heard dozens of stories about doctors refusing to treat or investigate a problem that a fat person came in for until they lost a certain amount of weight, only to discover years later that the problem was unrelated to their weight and has progressed severely because it went untreated. Fat people are often mistreated and looked at with disgust and disdain in medical settings, leading them to avoid going to the doctor in shame or fear of abuse. This can seriously worsen health issues. Fat stigma in the medical establishment (Puhl, et al, 2012) and society at large arguably (Engber, 2009) kills more fat people than fat does (Teachman, et al, 2003), (Chastain, et al, 2009), (Sutin, et al, 2015). This impact is too significant not to be taken under consideration.
Anti-Fatness as Anti-Blackness
The issue of anti-fat bias is directly rooted in white supremacy. The ideal thin body was constructed as a marker of whiteness and “purity” before any of this was ever made to be about health. Dr. Sabrina Strings has spent her career studying this history. In her book, Fearing the Black Body: The Racial Origins of Fat Phobia, Dr. Strings discusses how constructions of race led to the thin ideal. “Over the decades, the rise in biracial children would break down the way that slave owners saw Blackness and whiteness. To combat the hypocrisy they created, owners invented new ways to dehumanize the enslaved population. They made a calculated decision to start putting more value on white physiques versus Black ones. In her research, Strings found that Black women’s bodies were otherized even more than Black males. For colonizers who hadn’t seen diverse body types before, they quickly categorized the Black female figure as ‘deviant,’ ‘greedy,’ and ‘overtly sexual.’ The fact that we still use these terms to describe fat bodies today is all the evidence we need to understand that fatphobia is directly linked to racism, not health. This mindset was also strengthened by Protestantism. Slave owners looked for any way to prove their power over the enslaved people, and they frequently used religion as ‘proof’ of their racist superiority. Additionally, Protestant belief encouraged various ways to become closer to God, which included eating as little as possible. This would resonate the most with white women. They had as much to do with perpetuating fatphobia as their husbands. White women were desperate to show their own power against Black women on the plantation, and the difference between their bodies was the perfect rift. And so began the centuries-old belief that thinness is beautiful, and fatness is ugly” (Sassenrath, 2023).
Revisiting the Journal with Context
Thinness has been an important value throughout history in the United States. Our positive associations with thinness and negative associations with fatness have led to a collective schema that is black and white, good versus bad, beautiful versus ugly, healthy versus unhealthy, and life versus death. This has led the FDA to approve Wegovy as a weight loss drug with haste, after just sixteen months of testing. It is known that going off the drug will result in rapid weight regain, so patients are expected to be on it for the rest of their lives when there have been no long-term studies. We do not yet know if the drug will have long-term effects, yet it has been approved for kids as young as twelve (FDA, 2021). As of July 2024, Novo Nordisk has a market cap of $633.01 billion (Marketcap).
Wegovy is prescribed along with diet and exercise, which has been proven to lead to weight regain and eating disorders. Patients are being prescribed Wegovy and Ozempic when they are fat, but otherwise metabolically healthy. If this drug is truly a game changer for public health, we should be measuring how patients' health improves over the long-term rather than how much weight they lose. For example, if these drugs improve heart health, they should be prescribed as a heart health medication for patients with heart disease, rather than prescribed as a weight loss fix based on body size alone. With the evidence we have, we know it is possible to be fat and healthy, so these drugs may be solely cosmetic in many cases.
Future
If we want to improve the lives of fat people, we will remove barriers to care, not try as hard as we can to make all fat people disappear. That will never happen. If we truly cared about the well-being of fat people and not their disappearance, we would work to dismantle the systems that oppress them and abolish anti-fatness.
Currently, fat people have next to no legal protections for being discriminated against (NAAFA, 2023). Fat people are denied housing, (Kariss, 1977) jobs, and receive less pay and promotions legally because of their size (The Economist). They are denied access to clothing, seating, transportation, and other human rights because infrastructure has been designed to exclude them. Fat people have less likelihood of receiving a fair trial (Beely, 2013), and are denied necessary surgeries (Barrett, 2022) ––but not weight loss surgery that amputates the digestive tract. Fat people are denied gender-affirming care (Conley, 2023), in vitro fertilization and reproductive healthcare (Muir, 2024), even adopting children (Carter, 2009). Fat children have been removed from their loving parents because when their diets failed, it was seen as neglect (Badshah, 2021). Fat people have disproportionately high suicide rates (Wagner, et al, 2013), and are facing medical malpractice and mistreatment (Kolata, 2016).
Can a drug fix that?
References
Karasu, Sylvia. Adolphe Quetelet and the Evolution of Body Mass Index (BMI). Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/the-gravity-of-weight/201603/adolphe-quetelet-and-the-evolution-of-body-mass-index-bmi 2016, March 8.
“Quetelet, Adolphe.” Eugenics Archive, www.eugenicsarchive.ca/connections? id=5233cb0f5c2ec5000000009c. Accessed 5 July 2024.
Rey-López JP, de Rezende LF, Pastor-Valero M, Tess BH. The prevalence of metabolically healthy obesity: a systematic review and critical evaluation of the definitions used. ObesRev.2014 Oct;15(10):781-90. doi: 10.1111/obr.12198. Epub 2014 Jul 16. PMID: 25040597.
Matheson EM, King DE, Everett CJ. Healthy lifestyle habits and mortality in overweight and obese individuals. J Am Board Fam Med. 2012 Jan-Feb;25(1):9-15. doi: 10.3122/jabfm.2012.01.110164. PMID: 22218619.
Butler, Kiera. “Why BMI Is a Big Fat Scam.” Mother Jones, 25 Aug. 2014, www.motherjones.com/politics/2014/08/why-bmi-big-fat-scam/.
Kahn BB, Flier JS. Obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2000 Aug;106(4):473-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI10842. PMID: 10953022; PMCID: PMC380258.
Cofield SS, Corona RV, Allison DB. Use of causal language in observational studies of obesity and nutrition. Obes Facts. 2010 Dec;3(6):353-6. doi: 10.1159/000322940. Epub 2010 Dec 10. PMID: 21196788; PMCID: PMC3280017.
Medvedyuk, S., Ali, A., & Raphael, D. (2017). Ideology, obesity and the social determinants of health: a critical analysis of the obesity and health relationship. Critical Public Health, 28(5), 573–585. https://doi.org/10.1080/09581596.2017.1356910
Kahn BB, Flier JS. Obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2000 Aug;106(4):473-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI10842. PMID: 10953022; PMCID: PMC380258.
Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Ventura HO. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009 May 26;53(21):1925-32. doi: 10.1016/ j.jacc.2008.12.068. PMID: 19460605.
Uretsky S, Messerli FH, Bangalore S, Champion A, Cooper-Dehoff RM, Zhou Q, Pepine CJ. Obesity paradox in patients with hypertension and coronary artery disease. Am J Med. 2007 Oct;120(10):863-70. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.05.011. PMID: 17904457.
Mullen JT, Moorman DW, Davenport DL. The obesity paradox: body mass index and outcomes in patients undergoing nonbariatric general surgery. Ann Surg. 2009 Jul;250(1):166-72. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181ad8935. PMID: 19561456.
Tseng CH. Obesity paradox: differential effects on cancer and noncancer mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis. 2013 Jan;226(1):186-92. doi: 10.1016/ j.atherosclerosis.2012.09.004. Epub 2012 Sep 21. PMID: 23040832.
Sutin, A. R., Stephan, Y., & Terracciano, A. (2015). Weight Discrimination and Risk of Mortality. Psychological Science, 26(11), 1803-1811. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797615601103
Tomiyama, A Janet, et al. “Long‐term Effects of Dieting: Is Weight Loss Related to Health. Socialand Personality Psychology Compass, 6 July 2017, escholarship.org/uc/item/0tv27311.
Mann T, Tomiyama AJ, Westling E, Lew AM, Samuels B, Chatman J. Medicare's search for effective obesity treatments: diets are not the answer. Am Psychol. 2007 Apr;62(3):220-33. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.62.3.220. PMID: 17469900.
Patton GC, Selzer R, Coffey C, Carlin JB, Wolfe R. Onset of adolescent eating disorders: population based cohort study over 3 years. BMJ. 1999 Mar 20;318(7186):765-8. doi: 10.1136/bmj.318.7186.765. PMID: 10082698; PMCID: PMC27789.
Puhl, Rebecca, and Kelly D. Bronwell. “Bias, Discrimination, and Obesity.” Obesity Research, 6 Sept. 2012. doi.org/10.1038/oby.2001.108
Engber, Daniel. “Glutton Intolerance: What If a War on Obesity Only Makes the Problem Worse?” Slate, https://slate.com/technology/2009/10/the-health-effects-of-discrimination-against-fat-people.html 5 Oct. 2009.
Teachman, B. A., Gapinski, K. D., Brownell, K. D., Rawlins, M., & Jeyaram, S. (2003). Demonstrations of implicit anti-fat bias: The impact of providing causal information and evoking empathy. Health Psychology, 22(1), 68–78.
Chastain, Ragen. “So My Doctor Tried to Kill Me.” Dances With Fat, https://danceswithfat.org/2009/12/15/so-my-doctor-tried-to-kill-me/ 15 Dec. 2009.
Sutin AR, Stephan Y, Terracciano A. Weight Discrimination and Risk of Mortality. Psychol Sci. 2015 Nov;26(11):1803-11. doi: 10.1177/0956797615601103. Epub 2015 Sep 29. PMID: 26420442; PMCID: PMC4636946.
Sassenrath, Jenna. “Anti-Blackness Is Anti-Fatness in ‘Fearing the Black Body.’” Bookstr, bookstr.com/article/anti-blackness-is-anti-fatness-in-fearing-the-black-body/ 26 July 2023.
“Novo Nordisk (NVO) - Market Capitalization.” CompaniesMarketCap.Com - Companies Ranked by Market Capitalization, companiesmarketcap.com/novo-nordisk/marketcap/ 2024.
Commissioner, Office of the. “FDA Approves New Drug Treatment for Chronic Weight Management, First since 2014.” U.S. Food and Drug Administration, FDA, www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management-first-2014. 5 July 2024.
Karris, L. (1977). Prejudice against Obese Renters. The Journal of Social Psychology, 101(1), 159–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224545.1977.9924002
“Campaign for Size Freedom.” NAAFA, 2023,
naafa.org/sizefreedom. 5 July 2024.
“The Obesity Pay Gap Is Worse than Previously Thought.” The Economist, The Economist Newspaper, www.economist.com/finance-and-economics/2023/11/23/the-obesity-pay-gap-is-worse-than-previously-thought. 5 July 2024.
Elizabeth Beety, Valena (2013) "Criminality and Corpulence: Weight Bias in the Courtroom," Seattle Journal for Social Justice: Vol. 11: Iss. 2, Article 4. https:// digitalcommons.law.seattleu.edu/sjsj/vol11/iss2/4
Berrett, Martyn. “More Obesity Discrimination: The NHS Will Deny Non-Urgent Surgery to Obese Patients.” Healthier Weight, 24 Nov. 2022, www.healthierweight.co.uk/blog/more-obesity-discrimination-the-nhs-will-deny-non-urgent-surgery-to-obese-patients/.
LaRosa, John. “U.S. Weight Loss Industry Grows to $90 Billion, Fueled by Obesity Drugs Demand.” Market Research Blog, The Freedonia Group, Inc., 2 May 2024, blog.marketresearch.com/u.s.-weight-loss-industry-grows-to-90-billion-fueled-by-obesity-drugs-demand.
Conley, H. “Studies Show Top Surgery Is Safe for FAT Patients, but Some Surgeons Still Mandate Weight Loss.” STAT, 25 July 2023, www.statnews.com/2023/06/02/top-surgery-safe-fat-patients/.
Muir, Becca. “Opinion: Women with Obesity Are Often Restricted from IVF. That’s Discriminatory.” NPR, 14 Jan. 2024, www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2024/01/14/1224546666/opinion-women-with-obesity-are-often-restricted-from-ivf-thats-discriminatory.
Carter, Helen. “Too Fat to Adopt - the Married, Teetotal Couple Rejected by Council Because of Man’s Weight.” The Guardian, Guardian News and Media, 13 Jan. 2009, www.theguardian.com/society/2009/jan/13/adoption-rejected-couple.
Badshah, Nadeem. “Two Teenagers Placed in Foster Care after Weight Loss Plan Fails.” The Guardian, Guardian News and Media, 11 Mar. 2021, amp.theguardian.com/society/2021/mar/10/two-teenagers-placed-in-foster-care-after-weight-loss-plan-fails.
Wagner B, Klinitzke G, Brähler E, Kersting A. Extreme obesity is associated with suicidal behavior and suicide attempts in adults: results of a population-based representativesample. Depress Anxiety. 2013 Oct;30(10):975-81. doi: 10.1002/da.22105. Epub 2013 Apr 10. PMID:23576272.
Kolata, Gina. “Why Do Obese Patients Get Worse Care? Many Doctors Don’t See Past the Fat.” The New York Times, The New York Times, 26 Sept. 2016, www.nytimes.com/2016/09/26/health/obese-patients-health-care.html.
#fat liberation#systemic anti fatness#systemic fatphobia#medical fatphobia#medicalized fatphobia#fat activism#fat acceptance#anti fat bias#fatphobia#essay
410 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Telling Truth: When 'Show, Don't Tell' Doesn't Apply (You Don't Always Have To Show, Don't Tell.)
Hey there, fellow writers and beloved members of the writeblr community! 📝✨
Today, I want to talk about something that's been on my mind lately, and I have a feeling it might resonate with many of you too. It's about that age-old writing advice we've all heard a million times: "Show, don't tell." Now, don't get me wrong – it's great advice, and it has its place in our writing toolbox. But here's the thing: it's not the be-all and end-all of good writing. In fact, I'd argue that sometimes, it's perfectly okay – even necessary – to tell rather than show.
First things first, let's address the elephant in the room. The "show, don't tell" rule has been drilled into our heads since we first picked up a pen (or opened a Word document) with the intention of writing creatively. It's been repeated in writing workshops, creative writing classes, and countless craft books. And for good reason! Showing can create vivid, immersive experiences for readers, allowing them to feel like they're right there in the story.
But here's where things get a bit tricky: like any rule in writing (or in life, for that matter), it's not absolute. There are times when telling is not just acceptable, but actually preferable. And that's what you all will explore today in this hopefully understandable blog post.
Let's start by breaking down why "show, don't tell" is so popular. When we show instead of tell, we're engaging the reader's senses and emotions. We're painting a picture with words, allowing the reader to draw their own conclusions based on the details we provide. It's a powerful technique that can make our writing more engaging and memorable.
For example, instead of saying "Sarah was angry," we might write, "Sarah's fists clenched at her sides, her jaw tight as she glared at the broken vase." This gives the reader a clearer image and allows them to infer Sarah's emotional state.
But here's the thing: sometimes, we don't need or want that level of detail. Sometimes, efficiency in storytelling is more important than painting an elaborate picture. And that's where telling comes in handy.
Imagine if every single emotion, action, or piece of information in your story was shown rather than told. Your novel would probably be thousands of pages long, and your readers might get lost in the sea of details, losing sight of the main plot or character arcs.
So, when might telling be more appropriate? Let's explore some scenarios:
Summarizing less important events: If you're writing a story that spans a long period, you don't need to show every single day or event. Telling can help you summarize periods of time or less crucial events quickly, allowing you to focus on the more important parts of your story.
For instance: "The next few weeks passed in a blur of exams and late-night study sessions." This sentence tells us what happened without going into unnecessary detail about each day.
Providing necessary background information: Sometimes, you need to give your readers some context or backstory. While you can certainly weave this information into scenes, there are times when a straightforward telling of facts is more efficient.
Example: "The war had been raging for three years before Sarah's village was attacked." This quickly gives us important context without needing to show the entire history of the war.
Establishing pace and rhythm: Alternating between showing and telling can help you control the pace of your story. Showing tends to slow things down, allowing readers to immerse themselves in a moment. Telling can speed things up, moving the story along more quickly when needed.
Clarifying complex ideas or emotions: Some concepts or feelings are abstract or complex enough that showing alone might not suffice. In these cases, a bit of telling can help ensure your readers understand what's happening.
For example: "The quantum entanglement theory had always fascinated John, but explaining it to others often left him feeling frustrated and misunderstood." Here, we're telling the reader about John's relationship with this complex scientific concept, which might be difficult to show effectively.
Maintaining your narrative voice: Sometimes, telling is simply more in line with your narrative voice or the tone of your story. This is especially true if you're writing in a more direct or conversational style.
Now, I can almost hear some of you saying, "But wait! I've always been told that showing is always better!" And I completely get it. I'm a writer myself and prioritize "Show, Don't tell." in my writing all the time. We've been conditioned to believe that showing is superior in all cases. But we can take a moment to challenge that notion.
Think about some of your favorite books. Chances are, they use a mix of showing and telling. Even the most critically acclaimed authors don't adhere strictly to "show, don't tell" all the time. They understand that good writing is about balance and knowing when to use each technique effectively.
Take, for instance, the opening line of George Orwell's "1984": "It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen." This is a perfect blend of showing and telling. Orwell shows us it's a bright, cold day (we can imagine the crisp air and clear sky), but he tells us about the clocks striking thirteen. This immediate telling gives us crucial information about the world we're entering – it's not quite like our own.
Or consider this passage from Jane Austen's "Pride and Prejudice": "Mr. Bennet was so odd a mixture of quick parts, sarcastic humour, reserve, and caprice, that the experience of three-and-twenty years had been insufficient to make his wife understand his character." Here, Austen is clearly telling us about Mr. Bennet's character rather than showing it through his actions. And yet, it works beautifully, giving us a quick, clear insight into both Mr. Bennet and his wife.
The key is to use both techniques strategically. So, how can you decide when to show and when to tell? Here are some tips:
Consider the importance of the information: Is this a crucial moment in your story, a pivotal emotion, or a key piece of character development? If so, it might be worth showing. If it's more of a transitional moment or background information, telling might be more appropriate.
Think about pacing: If you want to slow down and really immerse your reader in a moment, show it. If you need to move things along more quickly, tell it.
Evaluate the complexity: If you're dealing with a complex emotion or concept, consider whether showing alone will be enough to convey it clearly. Sometimes, a combination of showing and telling works best for complex ideas.
Consider your word count: If you're working with strict word count limitations (like in short stories or flash fiction), telling can help you convey necessary information more concisely.
Trust your instincts (Important): As you write more, you'll develop a feel for when showing or telling works better. Trust your gut, and don't be afraid to experiment.
Now, let's talk about how to tell effectively when you do choose to use it. Because here's the thing: telling doesn't have to be boring or flat. It can be just as engaging and stylish as showing when done well. Here are some tips for effective telling:
Use strong, specific language: Instead of using vague or generic words, opt for more specific, evocative language. For example, instead of "She was sad," you might write, "A profound melancholy settled over her."
Incorporate sensory details: Even when telling, you can include sensory information to make it more vivid. "The room was cold" becomes more engaging as "A bone-chilling cold permeated the room."
Use metaphors and similes: These can help make your telling more colorful and memorable. "His anger was like a volcano ready to erupt" paints a vivid picture without showing the anger in action.
Keep it concise: One of the advantages of telling is its efficiency. Don't negate that by being overly wordy. Get to the point, but do it with style.
Vary your sentence structure: Mix short, punchy sentences with longer, more flowing ones to create rhythm and maintain interest.
Remember, the goal is to create a seamless narrative that engages your reader. Sometimes that means showing, sometimes it means telling, and often it means a artful blend of both.
It's also worth noting that different genres and styles of writing may lean more heavily on one technique or the other. Literary fiction often employs more showing, delving deep into characters' psyches and painting elaborate scenes. Genre fiction, on the other hand, might use more telling to keep the plot moving at a brisker pace. Neither approach is inherently better – it all depends on what works best for your story and your style.
Now, I want to address something that I think many of us struggle with: the guilt or anxiety we might feel when we catch ourselves telling instead of showing. It's easy to fall into the trap of second-guessing every sentence, wondering if we should be showing more. But here's the truth: that kind of constant self-doubt can be paralyzing and ultimately detrimental to your writing process.
So, I want you to understand and think: It's okay to tell sometimes. You're not a bad writer for using telling in your work. In fact, knowing when and how to use telling effectively is a sign of a skilled writer.
Here's some practical ways to incorporate this mindset into your writing process:
First Draft Freedom: When you're writing your first draft, give yourself permission to write however it comes out. If that means more telling than showing, that's absolutely fine. The important thing is to get the story down. You can always revise and add more "showing" elements later if needed.
Revision with Purpose: When you're revising, don't automatically change every instance of telling to showing. Instead, ask yourself: Does this serve the story better as telling or showing? Consider the pacing, the importance of the information, and how it fits into the overall narrative.
Beta Readers and Feedback: When you're getting feedback on your work, pay attention to how readers respond to different sections. If they're engaged and understanding the story, then your balance of showing and telling is probably working well, regardless of which technique you're using more.
Study Your Favorite Authors: Take some time to analyze how your favorite writers use showing and telling. You might be surprised to find more instances of effective telling than you expected.
Practice Both Techniques (Important): Set aside some time to practice both showing and telling. Write the same scene twice, once focusing on showing and once on telling. This can help you develop a feel for when each technique is most effective.
Now, let's address another important point: the evolution of writing styles and reader preferences. The "show, don't tell" rule gained popularity in the early 20th century with the rise of modernist literature. But writing styles and reader tastes have continued to evolve since then.
In our current fast-paced world, where people are often reading on devices and in shorter bursts, there's sometimes a preference for more direct, efficient storytelling. This doesn't mean that showing is out of style, but it does mean that there's often room for more telling than strict adherence to "show, don't tell" would allow.
Moreover, diverse voices in literature are challenging traditional Western writing norms, including the emphasis on showing over telling. Some cultures have strong storytelling traditions that lean more heavily on telling, and as the literary world becomes more inclusive, we're seeing a beautiful variety of styles that blend showing and telling in new and exciting ways.
This brings me to an important point: your voice matters. Your unique way of telling stories is valuable. Don't let rigid adherence to any writing rule, including "show, don't tell," stifle your natural voice or the story you want to tell.
Remember, rules in writing are more like guidelines. They're tools to help us improve our craft, not unbreakable laws. The most important rule is to engage your reader and tell your story effectively. If that means more telling than the conventional wisdom suggests, then so be it.
As I wrap up this discussion, I want to leave you with a challenge: In your next writing session, consciously use both showing and telling. Pay attention to how each technique feels, how it serves your story, and how it affects the rhythm of your writing. You might discover new ways to blend these techniques that work perfectly for your unique style.
Writing is an art, not a science. There's no perfect formula, no one-size-fits-all approach. It's about finding what works for you, your story, and your readers. So embrace both showing and telling. Use them as the powerful tools they are, and don't be afraid to break the "rules" when your instincts tell you to.
Remember, every great writer started where you are now, learning the rules and then figuring out when and how to break them effectively. You're part of a long, proud tradition of storytellers, each finding their own path through the winding forest of words.
Keep writing, keep growing, and keep believing in yourself. You've got this!
Happy writing! 💖✍️ - Rin T.
Before you go, why not join us at The Write Right Society? We're a supportive Tumblr community where writers lift each other up. Whether you're a newbie or a pro, we'd love to have you! Share your work, get feedback, and connect with fellow wordsmiths, writers and aspiring authors.

#thewriteadviceforwriters#creative writing#writing tips#on writing#writers block#how to write#writers and poets#writing#writeblr#writers on tumblr#amwriting#writing advice#novel writing#writing blog#writing characters#writing a book#writing community#fiction writing#writing help#writing ideas#writing prompts#writing reference#writing inspiration#writing resources#writing guide#writing software#writing tools#writing tips and tricks#writing life#romance writing
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Sigil Magick: Illustrating Your Intent

Sigils are a cornerstone of contemporary and chaos magick and function as keys to unlock the doors of reality and bend it to one’s will. These potent symbols serve as physical embodiments of one’s intentions, cast into existence through the fusion of art and willpower.
The crafting of a sigil begins with a clear and focused intention, which is then worked into a unique symbol through a creative magickal process. The magick practitioner inscribes deep personal meaning and style into their designs, making each unique to its artist. Sigils are ideal tools for manifesting your desires, imbuing objects with specific purpose and energy, protecting spaces, and communicating with the spirit world and should be used responsibly.
Origins
The practice of crafting sigils traces its roots to the ancient world but was modernized in the early 20th century by the works of Austin Osman Spare, an occultist and artist. He introduced the method of creating magical symbols by condensing letters of a desire into an abstract design. Aleister Crowley, too, influenced the practice by intertwining sigils with ceremonial magick, embedding them with a rich esoteric significance.
Some occult grimoires employ sigils as a means of contacting spirits, for example; Ars Goetia, The Book of Oberon, and Pseudomonarchia Daemonum.
Basics of Sigil Magick
Sigil magick emerges from the belief in one’s ability to manifest their focus into reality. Through a process of creation, a sigil becomes much more than mere ink on paper—it is the illustrated essence of desire. Individuals can use sigils as focal points for their will, empowering these symbols through meditation or ritual to enact change. The universe of sigils is vast and varied, types of sigils include:
• Pictorial Sigils: Intuitive symbols drawn from the subconscious
• Runic Sigils: Combinations of runic alphabets that resonate with specific energies
• Word Sigils: Derived from statements of intention, where letters are crafted into a unique symbol
Correspondences also serve a purpose in this class of magick, in order to help align one's intent to universal energies. As an artist crafts their sigil, they intertwine traditional symbols with personal significance, creating a bridge to the metaphysical world. Some relevant correspondences are:
• Numerology: Numbers carry vibrations that can enhance a sigil’s purpose.
• Zodiac Signs: Celestial influences infused to fine-tune the focus.
• Elements: The classic forces of Earth, Air, Fire, and Water lend their power to sigils, grounding them in natural harmony.

Sigil Creation
Before you take pen to paper, first envision your intent with clarity and purpose This may involve some deep introspection into the true nature of your desires. A precise intention lays the foundation for the sigil's power. Once ready, write out your intention and cross out any duplicate letters. From here a couple different methods can be utilized. Naturally you could always draw your sigils from pure instinct, creating spontaneous shapes to represent your intentions, but there are other techniques available.
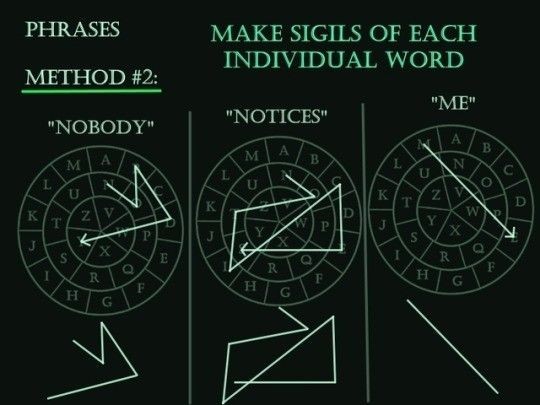
The Wheel
This method employs a wheel to be used as a map for drawing your sigil. Simply start at the first letter of your intent and draw lines to each subsequent letter. Example:

My Method
I make my sigils by breaking up the letters to create shapes. I will often decorate with extra shapes, symbols, and pictures as well. Here is a simplified example of my sigil creation process:
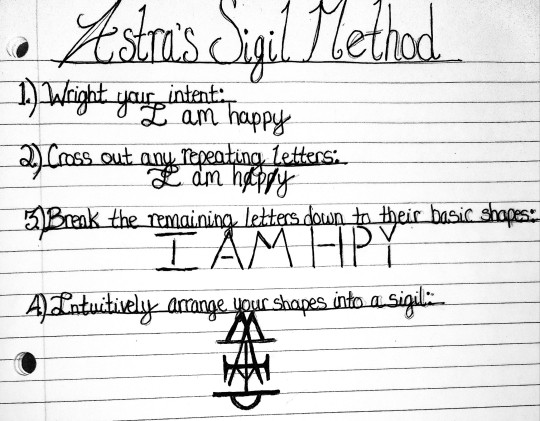
Next you must charge your sigil. Charging is the act of infusing the sigil with energy. The creator might enter a meditative state, focusing intently on the sigil while envisioning their intentions intertwining with the design. This act of focused concentration serves to embed the intention within the sigil, making it a beacon for the desired change.
Passive and Active Sigils
Intentioned sigils fall into either the passive or active sigil category based on how that sigil's energy is best utilized. Passive sigils are usually drawn on the body, item, or surface and then left alone to release their power over time. Active sigils involve some action to trigger the release of the sigil's energy, such as burning, burying, soaking with water/oil, and more. Some sigils can be used both passively and actively, but most will fall into one category.
Spirit Sigils
Many spirits and deities have sigils that represent them and these can be powerful catalysts for interacting with these beings. If the spirit you're working with doesn't have a sigil made for them (or even if they do) you can design your own symbol to connect with that spirit. Follow the same process, but instead of focusing on your intent, focus on the spirit/deity and connecting with it. You can even perform a ritual and provide an offering to invite the spirit into your space. This will allow you to draw divine inspiration straight from the source. Here are some examples of spirit/deity sigils, as well as some I created:


#magick#witch#witchcraft#sigil#sigils#sigil magic#sigil magick#chaos#chaos magick#chaos magic#chaos witch#satanic witch#lefthandpath#dark#satanism#demons#demonolatry#spirit work#spell work#spellwork#spell#spells#spellcasting#symbology#symbolism#symbols#eclectic#witchblr#witch community#pagan
640 notes
·
View notes
Text
I wrote yesterday:
The Jew is a sort of Rorschach test. People see in the Jew whatever suits their agenda. Banker, radical, victim, conspirator, communist, capitalist... Just never quite human.
I know Jumblr prefers the pithy, but I want to extend the metaphor.
---
The Rorschach test, as you might know, was meant to be a way to identify or classify difficulties of the human mind.
The patient was shown a series of inkblots, ambiguous shapes without any fixed meanings. The therapist would then invite the patient to describe what they saw in the inkblot shapes. Since the shapes were ambiguous, what the patient saw in these shapes, wasn't ever about the shapes themselves, but a means to supposedly reveal the structures of the patient's own psyche. Pareidolia as a diagnostic tool.
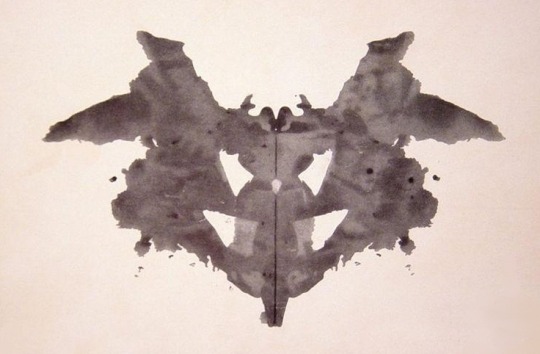
The Jew as a Rorschach Test: Antisemitism as Projection
How a society sees Jews has almost never actually described the Jews of that society as much as it has revealed something about the society itself.
The Jew, because he is not actually understood by the society, is, like the inkblot, ambiguous. Since he is other and unknown, he is subject to wildly divergent interpretations, none of which reflect the Jew's life/beliefs/practices/values. Instead, what a society sees in the Jew reflects that society's needs, fears, and crises.
In medieval, Christian Europe, the Jew was the other - falsely accused of killing Jesus Christ, desecrating the host, and poisoning the wells. These accusations were baseless and absurd, but they must have felt true and valid to those whose world was defined by the overwhelming, omnipresent Christian binary dualities of the place and time: good vs. evil, salvation vs. damnation.
The Jew, as the outsider, wasn't just not-a-Christian, but a Christ-killer. He was an inkblot in which the medieval Christian's guilt, anxiety about sin, and need for a scapegoat was projected. The very ambiguity of the way the Jew existed within Christendom without being part of it, made Jew the perfect surface for unconscious projection.
Just as one person sees a butterfly in an inkblot while another sees a bat, Christians saw in Jews either satanic enemies or (more rarely) proof of divine mercy. Either way, what the observer saw in the inkblot wasn't based on any reality about the inkblot itself, but based on the fears of the observer.
The modern period generated a new set of anxieties: urbanization, financial abstraction, and political revolution. The Rorschach Jew here reflected contradictions at the core of modernity itself. In 19th century Europe, Jews were simultaneously seen as both the faceless financiers of capitalism and the radical firebrands of socialism.
This is the classic Rorschach dynamic, isn't it? Contradictory accusations projected onto the same ambiguous stimulus. How could Jews be categorically both hoarding wealth and fomenting class war?
Such a thing was only believable because the image of "the Jew" was not based in reality, but in the social psyche.
Like an inkblot, the Jew became a surface onto which irreconcilable social and economic tensions could be emotionally "resolved."
The 19th century also brought us Modern Nationalism. The Rorschach test was also supposed to measure boundary confusion, how people respond to ambiguous figures that blur inside and outside, self and other. That's what the Jew was in the European 19th century nation state.
Jews in Europe and elsewhere were frequently depicted as simultaneously hyper-assimilated (too much like us) and radically other (an alien threat among us).
This duality in which the othered Jew was simultaneously the ultimate insider and the ultimate outsider provoked a special kind of nationalist panic.
Antisemitism here operates like a defense mechanism against that ambivalence and national identity anxiety. The Jew becomes the inkblot where cultural boundaries are tested and violated. The fear isn't of Jews themselves, but of what they symbolize: the failure of clear categories.
Haviv Rettig Gur talked about the advent of the new mass societies of modern nation states as social constructs in the 19th century.
And in this world of new Mass Societies, in this shift from small, agrarian, maybe religious identities to Mass National Identities...they develop these ideologies of nationalism that try and police the boundaries of these identities to firm them up, make sure that they stay strong.
The Nazi problem with the Jews, says Haviv, is seen in Mein Kampf, and was driven by insecurity about German identity.
If Germanness is tribal and blood and ancient and biological and we can measure it by testing your skull...and a Jew in the morning can be a German in the evening...?
[Hitler believed] the boundaries of germanness are hard, the membrane is impermeable. It is biology, it is real- and what is the Jew doing? He's popping in and out all the time! He's perforating the membrane of germanness! If a Jew could be a German and something else, if you can have layers...you can't have absolute identity. And if you can't have absolute identity what is the German? The Jews endanger Germanness!
In the aftermath of the Holocaust, the Rorschach dynamic persisted. The image of the Jew in the West becomes morally saturated: a figure of sacrosanct victimhood for some, a lightning rod for resentment in others. In each case, the actual Jewish person disappears, and what remains is a symbol - an inkblot onto which guilt, denial, and moral discomfort are projected.
Read Dara Horn's People Love Dead Jews. Horn argues that the world's love for "dead Jews" is a form of perverse moral posturing, a way for societies to affirm their own virtue by honoring Jewish suffering...but this only works if Jews are no longer alive to complicate the ego-saving narrative.
Horn notes how the Holocaust is sanitized, depoliticized, and turned into a universal morality tale that erases real Jewish lives, culture, and ongoing challenges. She contends that many memorials and educational efforts, while well-intentioned, often serve to comfort non-Jewish audiences rather than confront uncomfortable truths about antisemitism or support living Jewish communities.
Some in the post-Holocaust world, especially after 10/7/23, accuse Jews of "playing the victim" or "controlling the narrative." Again, these reactions say less about Jews and more about the viewer’s need to process trauma, responsibility, and historical shame.
Today, in both far-right and far-left discourse, the Jew remains a shifting inkblot: billionaire globalist or Zionist oppressor, cultural subversive or imperial power broker. In conspiracy theories, Jews are often imagined as orchestrating both migration and ethnonationalism, feminism and patriarchy, capitalism and Marxism.
This incoherence is diagnostic. It reveals the deep psychological fragmentation within those projecting the image. As in a Rorschach test, the lack of internal logic is not a bug, but a feature. The more the image can absorb contradiction, the more effective it is as a projection surface.
To treat the Jew as Rorschach test is to shift the analytical gaze from the image to the viewer.
It is the society looking at the inkblot - the anxieties, disavowals, and desires which are revealed in what it sees when it gazes on the inkblot and sees itself.
Antisemitism, in this metaphor, is not about Jews or anything Jews believe or do.
Understanding antisemitism through this lens allows us to see that no amount of Jewish integration, explanation, or visibility can resolve the problem, because the Jew is not being seen as a person. They are being looked through, like an inkblot, revealing the shapes of other people’s fears.
I suspect that Israelis generally understand this better than those of us in the diaspora.
What do you think? What lesson should we take from this?
316 notes
·
View notes
Note
Why is stuff like hard drugs and sex work illegal? Wouldn't the bourgeoisie want these things to be legal so they could control them and make money off them?
I feel that to thoroughly answer this question is to elaborate the difference between "mechanical materialism", as described by Mao on On Contradiction, as compared to proper Marxist historical materialism.
When we're approaching and attempting to understand the way a society functions in the real world instead of theorizing about their function in the abstract, we must remember that they always labor under an enormous weight of percieved tradition, which will exert constant influence on the way that societies are run regardless of the cold, calculated interest of the ruling class.
Instead of a teleological, overdetermined theory of society as being meticulously shaped at every level by the calculating will of the capitalist class, we must understand capitalist society (and indeed every society) as engaging in a kind of darwinian evolution where it and each of its underlying instutitions are subject to a number of evolutionary pressures based on which material conditions are at play over time. As such, deeply-entrenched societal ideas, handed down from a revered past (such as ideas about the place of women and their sexuality in society, which has its own role in other parts of capitalist society) will not simply disappear overnight the moment it becomes convenient for capital; instead we will see what we have already seen; a very gradual process of increasing permissiveness around drugs and sex work, and with it a heightening of contradictions in reaction to them from conservative sectors of society. Both the loosening and the reaction are core parts of capitalist class society
202 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hearthfire Health and Resting Overhaul
Artsource
TLDR: You can solve nearly all problems with D&D's powercurve (and a lot of other problems beside) by limiting the overall hitpoints your party gets, basing it off profficency bonus rather than character level.
If you’ve played anywhere close to as much d&d as I have, you’ll notice the game tends to play best at levels 3-8. Lower than that feels like being trapped in the tutorial, with players denied the majority of their interesting character options and the DM having to use kid gloves or else risking a party wipe. High level play invariably breaks down as player abilities trivialize most encounters, forcing the DM to reach deeper and deeper into the monster roster to provide adequate challenge, making more work for themselves in the process. There’s a definite sweetspot, and like anyone with a head for game design I want to widen that sweetspot to encompass as much of the game as possible.
As is typical of someone who’s into game design; I’ve bit off more than I can chew, deciding to build several interlocking rules changes/subsystems that I think will help me make the game function more like I want it to. This isn’t going to be for everyone, but if you’re feeling the need for a rules lite overhaul to rebalance how you plan encounters/ the rigours of adventure, this might be for you.
Here’s the overhaul in short form:
Character HP is determined as (Max Class HD + Con modifier) X proficiency bonus. This means they keep the same Max HP throughout the tier (1-4, 5-8 etc)
This means that low CR enemies stay relevant for far longer, making encounter building more reasonable. Likewise this prevents mid/high CR enemies from being trivialized. It allows you as the DM deploy mundane threats ( a steep drop, a detachment of city guards, the threat of a building catching fire) as legitimate challenges well into the later chapters of the campaign.
Temporary HP can be gained from using improved provision consumables (including those harvested from monsters), or by resting at inns and better establishments in town. A hardy, homecooked meal gives the party the strength they need to take on greater challenges, far more than a diet of salt pork & hardtack. In rare cases permanent HP boosting items can be sought as treasure.
Long resting in the wilderness is more difficult, requiring the party to find a safe campsite and spend provisions. Making sure they don't burn through these finite resources before encountering the real challenge makes for a great resource management challenge to go along with exploration based gameplay, acting as an informal ticking clock.
First, A small Testimonial: I've now tried this system with four different groups, and while there's still some bugs to work out I can say it feels a lot closer to my ideal form of d&d than the baseline rules. Planning combats is SO EASY, and I can actually scare my players with big monsters again. I've dropped the weird XP calculation and I can now use the group's level as a budget for medium-challenge combat encounters. Lower HP totals on both sides keep fights fast and punchy, which means I can fit more of them into a session, getting more progress through a gauntlet of challenges. While considering implmenting this system, I also encourage you to take a look at some of my combat hacks, which help to supplement fights the same way this system is meant to supplement exploration.
PROVISIONS: In order to get the benefits of a long rest while travelling you need 1) A place to set up camp that's not exposed to the elements 2) To spend a use of your provisions
Rather than beancounting individual servings per person, provisions are tracked through "The provision die", an abstract representation of what your party has left to eat that ranges from a d4 to a d20. This works off a depletion die system, meaning that every time provisions are used (generally once per night) you roll the die, and if it's a 1 or 2 it shrinks a size category. If it shrinks while it's a d4 the party is officially out of supplies and starts taking levels of exhaustion.
The base price or provisions is 5gp for a d4 depletion die, larger sizes of die may be bought based off the linked chart.
Alternatively, provisions (of an enhanced rarity even) may be salvaged from a monster, dungeon meshi style.
Without the extra carrying capacity from a bag of holding or wagon, the party's provision die is limited to a D6. Going offroad is tough, requiring characters to live off the land.
Living off the land generally requires a survival check with a DC based on how verdant the area is. Failure can mean a lack of finding anything suitable, or a delay in trying to acquire necessary provisions.
Features that can keep people fed like the outlander background or goodberry spell prevent the exhaustion buildup but still do not allow a long rest.
If ever the party is traveling for a week or more between settlements, their provision die drops by one size, regardless of how many times in the week they've rolled.
A party can buy better rations (consumable) or improve their camp gear (permanant) in order to gain temporary hitpoints when they consume provisions. A common upgrade will get you 2 class HD in temporary hitpoints, an uncommon will get you 4, a rare upgrade will get you 6. Enchanted camp gear (such as high quality tents, enchanted cookwear, rare spices) may also grant other bonuses when provisions are consumed, such as resistance to weather effects, bonuses to saves against fear, or even inspiration.
HAVENS: If the party is sticking in one place for a while it's likely that they'll be doing so in a Haven such as a tavern, outpost, or perhaps even their own bastion. Havens are rated on the same rarity system as camp upgrades and provisions are, which determines their overall level of quality and the amount of temporary HP they bestow per night.
As a guideline, if the party has to pay to stay in a haven, it costs 1sp per person per night for common accommodations, with the associated rarity price jump: (5 silver for uncommon, 5 gold for rare). Many inns have varying levels of accomidation, so some party members might chose to spring for greater amounts.
#homebrew#survival#resting#hearthfire#dnd#d&d#d&d homebrew#dnd homebrew#mechanic#homebrew mechanic#exploration
169 notes
·
View notes
Text
The core premise of Democratic Socialism, that Capitalism can peacefully transition to Socialism through Liberal Democratic procedure, is an error that can only result from the most blatant revisionism. Because if you coherently apply Class-based analysis to the situation it's pretty obvious that the Bourgeoisie state would not passively allow its own procedures to decisively act against its class interests. Both in theory and in practice (i.e. the rise of Fascism in 20th century Europe) the Bourgeoisie are more than happy to drop even the pretenses of Liberal Democracy if they ever pose a serious threat to Bourgeoisie power. The State does not exist as an entity on its own disconnected from broader society; it is fundamentally an expression of and tool to reinforce the power of the dominant classes. It might be possible to, at least temporarily, turn those tools against them but the results that subversion can achieve are limited on a structural level.
Like Democratic Socialism only works if you adopt a fundamentally Liberal mindset, that sees social structures as determined entirely by metaphysical ideas. In this way, political positions are evaluated in terms of the abstract values they hold rather than the material interests they advance. "Democracy supporters would never oppose the results a free and fair election; that would go against their ideals". But as soon as you start looking through the lens of class analysis it becomes pretty clear that Liberal Democratic elections are just a means to an end, and an easily discarded means at that. Despite all the fuss they like to make about democracy, the fundamental fact is that the Bourgeoisie class were not voted into power and so cannot be voted out. Democracy under a DOTB is fundamentally a game where the Bourgeoisie set the rules and are free to ignore the results; you can't beat them at it no matter how good you play
390 notes
·
View notes
Text
MBTI typings + analysis of weak hero class characters
disclaimer: this analysis would be based on cognitive functions, so please don't tag this post with "why is he an e, he should be an i" or something like that. please read about cognitive functions, it's life-changing.
and this is my personal observation and analysis, so i'm not claiming 100% accuracy. but i have been studying mbti typology for 5 years, and i believe my hyperfixation on weak hero characters is strong enough to offer an interpretation that's atleast in the right ballpark. feel free to share your own opinions, though.
yeon sieun — INTJ (Ni-Te-Fi-Se)

INTJs lead with introverted intuition (Ni), which means they're constantly absorbing patterns and projecting outcomes. that’s essentially sieun’s entire combat strategy. he fights with foresight, not force. his brain is always several moves ahead, calculating silently before acting. he also has auxiliary extraverted thinking (Te), which makes him prioritize efficiency. this explains why he’d rather stab someone with a pen and end the fight cleanly than try to brawl with someone much stronger than him. it's just more efficient.
INTJs have tertiary Fi (introverted feeling), which acts like a quiet internal moral compass. it’s always there in the background, nagging him. it's not loud enough to dictate his decisions, but still present in case he changed his mind. that’s why he hesitates to help juntae at first. not out of apathy, but because the voice in his head keeps getting suppressed by his dominant intuition, which keeps telling him to mind his own business. it keeps warning him of the consequences of getting involved. however, he takes action when he finally listens to his tertiary Fi telling him, you know it’s the right thing to do.
his inferior Se (extraverted sensing) makes him inattentive to his physical environment unless it directly interferes with his internal world. he's never interested or notices people around him, unless his peace is disrupted. a blatant example of this is when he completely misses seongje showing up at suho’s hospital. he doesn’t register what's happening around him until it directly concerns him.
he’s also emotionally private (typical INTJ trait — they don’t like performing vulnerability). sieun is more expressive in his unread text messages to suho than he ever is face-to-face. it's a classic Ni-Fi wall: he feels deeply, but processes everything internally, where no one can touch it.
ahn suho — ESTP (Se-Ti-Fe-Ni)

ESTPs are sensor-thinkers, grounded in the present and driven by logic. suho’s dominant Se (extraverted sensing) makes him highly reactive to his environment. he only intervenes when he senses something is wrong; not out of moral obligation, and definitely not out of concern for consequences. his instincts are fast, physical, and attuned to danger. we see this in his professional fighting skills (MMA trainee and all) and athletic abilities. it's also obvious in the way he expresses love through action, taking on tiring jobs for his grandma without complaint, teaching sieun how to fight. it's a classic Se expression of love: fixing, serving, fighting, guiding.
his Ti (introverted thinking) is what makes him sharp. he’s logical and objective, but not necessarily fair, because he's not led by morals (which doesn't mean that he doesn't have morals at all, but it's not the driver of his decisions). he's loyal to who he cares about, not to any sense of abstract justice. like how he’ll go to hell and back for sieun, but won’t extend that same energy to everyone (this can be backed up by sumin pd, who pointed out that unlike baku, who protects the whole school, suho only protects sieun. baku has a higher moral compass, as a high Fi-user, but more on that later). his humour is also very Ti-coded; dry, clever, and often rooted in logic ("how can you talk about food while eating?" "you talk about life while living it").
tertiary Fe (extraverted feeling) gives him just enough charm and emotional fluency to read a room, crack a joke, or comfort someone. but it’s also fragile. he gets defensive fast, especially when misunderstood or unfairly blamed (like how he gets physically aggressive when beomseok starts beefing with him for no reason). weak Fe makes him take criticism personally and lash out emotionally.
he also has inferior Ni, which means his intuition is weak, and he rarely thinks ahead. like when he gets into gilsu’s car without a solid plan. he improvises well (texting sieun from his watch), but forgets to consider that gilsu could check his phone too.
personality-wise, sieun and suho are actually a lethal pair in combat. sieun has the sixth sense of an Ni-dom, while suho has the reflexes of an Se-dom. but romantically, they’re lowkey doomed. a tertiary Fi and tertiary Fe pair. neither are good at emotional communication. both express love through action and protection, not words.
oh beomseok — INFP (Fi-Ne-Si-Te)

beomseok runs almost entirely on introverted feeling (Fi), a deeply internal moral compass that tells him this is right even when it objectively… isn’t. healthy Fi stands for staying true to your values and beliefs. unhealthy Fi becomes a justification engine. and beomseok's Fi has been warped by years of trauma. that’s how we go from offering to pay suho to save sieun from bullies to wanting to destroy suho for betraying him. he does what he feels is just. the line between good and evil becomes how do i feel about it, and the trauma twists those feelings into something darker.
his Ne (extraverted intuition) gives him imagination and ideas, but unchecked, it creates spirals; overthinking, projection, paranoia. like how he starts believing that suho and sieun were replacing him with youngyi.
tertiary Si (introverted sensing) makes him cling to what’s familiar. that’s why youngyi’s addition to their group unsettles him: she disrupts the group dynamic he’s grown attached to.
his inferior Te (extraverted thinking), the logic function, is like a faint alarm bell in the back of his mind, whispering this won’t end well, but Fi drowns it out. he knows best. or thinks he does.
youngyi — ESFP (Se-Fi-Te-Ni)

youngyi leads with dominant Se, paired with Fi — which means she lives in the moment, feels things deeply, and owns it. she’s unapologetically herself, unbothered by rejection, which is exactly the kind of ability that gets her to befriend someone as guarded as sieun. she isn’t intimidated by anyone. she's grounded in the present, quick to act, and physically assertive, often responding to situations with bold, instinctive energy.
what sets her apart from suho (who's also an Se-dom), though, is that her actions aren't filtered through detached logic (Ti), but through a strong internal value system (auxiliary Fi). she doesn’t analyze her choices with practical calculation, she feels her way through them, led by what resonates with her personally.
but Fi also governs identity. so when beomseok accuses her of ruining the group, and essentially causing suho’s coma, it doesn’t just sting, it shatters her. she doesn’t just feel attacked; she feels like her sense of self is broken. that's why she disappears from everyone's lives, because how can she face sieun, when she can't face herself? that’s the danger of Fi: when it internalizes blame, it takes everything personally.
park humin (baku) — ENFP (Ne-Fi-Te-Si)

ENFPs are chaos with a conscience. and baku is no exception. baku’s auxiliary Fi makes him emotionally honest and morally anchored, but his dominant Ne keeps his mind in motion, always bouncing between possibilities, fears, and imagined futures. that’s why he hesitates to fight again (because what if it ends the way it did with gotak?) but when something triggers his core values (Fi), when someone he loves is in danger, he acts out. consequences be damned.
he jokes around to defuse tension, but he's deeply intuitive, emotionally attuned, and cares more than he lets on. it’s why he’s one of the only people who can get someone like sieun to open up; not by forcing it, but by simply being emotionally available, non-judgmental, and real.
while his high Fi gives him access to vulnerability, it also acts as a strong boundary. he refuses to work with baekjin, despite his history with him, because it violates his sense of right and wrong, because baekjin brutally hurt gotak and ruined his career, which is unforgivable. he only crosses that boundary when threatened and forced.
baku’s tertiary Te is blunt, explosive, and reactive, especially under stress. it acts before planning. when stressed, he grabs for Te, takes charge, punches first, thinks later. his Fi follows his own moral compass. he refuses to fight and preaches non-violence. but when people precious to him are hurt, he almost chokes a guy to death.
seo juntae — ISFJ (Si-Fe-Ti-Ne)

juntae is the emotional backbone of the group. ISFJs are built to nurture, and his Fe (extraverted feeling), paired with Si (introverted sensing), makes him deeply attuned to others' emotional needs. he notices sieun skipping meals, withdrawing, and not sleeping. his Si gives him observational memory; he tracks patterns and changes, then responds with quiet care.
he’s the only character with strong Fe in the whole cast, which is why he's the only one who genuinely hates conflict, and is the peace-maker of the gang, readily resolving misunderstandings and arguments between his friends. Fe also gives him strong empathy, which is what makes him slow to judge. he can easily read tone and emotional behaviour. it’s why he doesn’t believe sieun when sieun lies and says he doesn’t want to be friends anymore, because he knows it’s not true. he’s the one who tells both sieun and bakugotak that the other doesn’t mean what they’re saying.
Fe + Si makes him the one person who understands without demanding. he’s the first to tell sieun, "it’s not your fault," not because he thinks it’ll help, but because he knows it will. and yet, he holds grudges. because Si doesn’t forget. that’s why he refuses to forgive hyoman, even after he joins their side.
go hyuntak (gotak) — ISTP/ESTP (Ti-Se or Se-Ti)

this might be a controversial take since gotak is often typed as an ISFP, but i see a strong mix of Ti and Se in how he operates. i'm still unsure which one leads, but what’s clear is that he’s an active, physical, and analytical thinker. he’s impatient, yes, but also deliberate. he observes, processes, then acts, like when he tells juntae to escape before counting opponents in the underpass fight with seongje, or when he decides to fact-check the rumor that sieun wants to fight him instead of reacting right away.
his Se is undeniable: he’s aggressive, athletic, and always grounded in his body. even after quitting taekwondo, he stays physically engaged, taking up basketball, aggressively skipping rope despite his bad knee, because “he has to do something.” that’s textbook Se: movement as expression. like suho (another high Se user), gotak communicates care through physical action; teaching juntae to fight, teaching sieun how to play basketball, physically lashing out when hyoman insults baku, or breaking into the union garage when baku disappears, even though sieun asked him not to. he acts because he has to: Ti wants clarity, Se wants momentum.
but what truly leans him toward xSTP is his low Fe. His emotional communication is clumsy; he needs baku to prompt him to apologize or say thanks. His Ti strives to stay calm and factual, but his emotions; protectiveness, irritation, and loyalty; simmer just beneath the surface. he doesn’t judge quickly (a sign of Fe-awareness), like how he defends sieun from trashy gossip despite a rocky first impression of him. still, like suho, he lashes out when he feels misunderstood, like when he says cruel things to sieun during their fallout. And with low Ni he rarely thinks far ahead; breaking into the garage wasn’t a plan, just Ti-logic and Se-impulse running full speed.
gotak is a head-heart-body kind of character. he’s loyal without needing to say it, perceptive without being flashy, and thoughtful in a language that often goes unnoticed.
geum seongje — ENTP (Ne-Ti-Fe-Si)

this is really the easiest one to type because seongje is a textbook ENTP: chaotic intellect.
dominant Ne makes him erratic, unpredictable, and dangerously flexible. he's constantly probing, experimenting, and testing limits. people are like a puzzle to deconstruct. Ne is the function that gives you the skill and urge to explore multiple possibilities, which explains how seongje can justify switching sides mid-fight if it feels fun. he'd join his enemies, then betray them for the punchline.
his tertiary Fe doesn’t function like suho or gotak’s, who pair Fe with Se. while suho and gotak are highly reactive and defensive over them/their loved ones being insulted or misunderstood, seongje’s Fe is more detached. he treats insults like jokes ("is it fun playing na baekjin's minion?" "it is fun. i get to beat up losers like you.").
his Fe makes him socially aware, but it's not a strength, it's weaponized. he understands emotional tones, social roles, and twists them to provoke or entertain. he mocks sincerity (like how he laughs at gotak over his protectiveness for juntae) but still craves attention and reaction (feels hurt because baekjin didn't ask him if he was okay after fighting with sieun).
so ENTP makes seongje unpredictable, perceptive, and always a step ahead.
na baekjin — ENTJ (Te-Ni-Se-Fi)

baekjin, as an ENTJ, is essentially a more dangerous, volatile version of sieun. he's smart, strategic, and ruthlessly efficient; a master planner who relies on his introverted intuition (Ni), to forecast outcomes and his extroverted thinking (Te), to execute them with precision. to baekjin, efficiency isn’t just useful; it’s everything. he doesn’t waste time on what feels good or what’s morally right, only what gets results.
but his inferior Fi (introverted feeling) means he lacks the internal framework to process emotions authentically. he struggles to recognize emotional nuance, both in himself and in others, which leaves him disconnected from his own vulnerability. that’s why, instead of just saying “don’t leave me,” he orchestrates emotional hostage scenarios (like threatening to hurt gotak) to keep baku close. it's twisted, but, to him, weirdly efficient. and in baekjin’s world, effectiveness often replaces intimacy.
he knows what works, not what's right. he weaponizes logic without empathy. and you can’t out-think him, because he’s already seen your next ten moves and calculated exactly where you’ll land.
baekjin uses control and intelligence as a shield, mastering manipulation to avoid vulnerability.
so that ends my analysis. if you need a detailed analysis of a specific character, have contrary opinions, questions about mbti, or need any clarification, then leave me an ask!
#i really abused the formatting feature while writing this post#it's like kids in 2013 discovering the multiple transition options on power point#weak hero class 1#weak hero#weak hero class 2#suhosieun#yeon sieun#ahn suho#oh beomseok#youngyi#park humin#seo juntae#go hyuntak#geum seongje#na baekjin#whc2#ask owl#mbti#weak hero x mbti types
117 notes
·
View notes
Text

A genome-based phylogeny for Mollusca is concordant with fossils and morphology
Abstract
Extreme morphological disparity within Mollusca has long confounded efforts to reconstruct a stable backbone phylogeny for the phylum. Familiar molluscan groups—gastropods, bivalves, and cephalopods—each represent a diverse radiation with myriad morphological, ecological, and behavioral adaptations. The phylum further encompasses many more unfamiliar experiments in animal body-plan evolution. In this work, we reconstructed the phylogeny for living Mollusca on the basis of metazoan BUSCO (Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs) genes extracted from 77 (13 new) genomes, including multiple members of all eight classes with two high-quality genome assemblies for monoplacophorans. Our analyses confirm a phylogeny proposed from morphology and show widespread genomic variation. The flexibility of the molluscan genome likely explains both historic challenges with their genomes and their evolutionary success.
Read the paper here:
A genome-based phylogeny for Mollusca is concordant with fossils and morphology | Science
132 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Notes: Symbolism
Symbol - anything that hints at something else, usually something abstract, such as an idea or belief
Literary symbol - an object, a person, a situation, or an action that has a literal meaning in a story but suggests or represents other meanings
2 Types of Symbols
GENERAL
A general symbol is universal in its meaning
Even if the symbol were removed from a work of literature, it would still suggest a larger meaning
Example 1: While the sea symbolizes the universal voyage from life to death in The Odyssey, it retains this association independent from literature. The "sea" is a general symbol.
Example 2: In poetry, a "rose" often is not only a flower, but also a general symbol for romantic love.
SPECIFIC
A specific symbol is not universal in its meaning
It acquires a specific meaning based on how it relates to the content of a novel, poem, etc.
The symbol's significance exists only within the context created by the author
Example 1: A hunting cap in The Catcher in the Rye has no universal meaning, but within the novel it is worn backwards and symbolizes a looking back at childhood.
Example 2: A pair of eyes on a billboard in The Great Gatsby has no universal meaning, but within the story symbolizes the eyes of God watching humanity.
Tips about Symbols
The story itself must furnish a clue that a detail is to be taken symbolically. Symbols nearly always signal their existence by emphasis, repetition, or position.
The meaning of a literary symbol must be established and supported by the entire context of the story. The symbol has its meaning in the story, not outside it.
To be called a symbol, an item must suggest a meaning different in kind from its literal meaning; a symbol is something more than its class or type.
A symbol may have more than one meaning. This does not mean that the symbol can mean anything you want it to because possible meanings are always controlled by the context.
4 Steps When Writing About Symbolism
1. Determine what objects, characters, or actions are symbolic
To identify a symbol, note if an object seems to:
appear repeatedly
have an unusually vivid quality
be described with language conveying much emphasis
have more significance than its literal reality would suggest
2. Determine symbolic meanings
Carefully examine how the symbol functions in relation to the story
Ask yourself what idea is represented by the symbol
3. Classify the symbols
Classification may reveal opposite relationships, such as symbols of good and evil, life and death, or eternal and ephemeral
Or symbols may fall into isolated categories, such as destruction, innocence, or sexuality
4. Classify the meanings of a symbol
Determine how much depth a particular symbol has and classify its possible meanings
While your paper may focus on only one major symbol, you may be able to divide it into two specific meanings and two general meanings
If these writing notes help with your poem/story, do tag me. Or send me a link. I'd love to read them!
Writing Notes & References ⚜ More: Symbolism
#writing notes#symbolism#symbols#writing basics#writeblr#spilled ink#dark academia#studyblr#light academia#fiction#creative writing#writing prompt#writers on tumblr#literature#poets on tumblr#poetry#writing inspiration#writing tips#writing reference#writing resources
224 notes
·
View notes
Text
the liberal 'actually, it's impossible to tell whats good and bad, so you should never have any authority over anything' approach is, principally, ridiculous, but is also just incredibly weak as a defence.
whether abortion is good or actually murder is a pretty important thing to address: it's good. whether hrt is good or actually delusional self-harm is a pretty important thing to address: it's good. whether being gay is good or actually a sign of a sexual predator is a pretty important thing to address: it's good. in all these cases, going 'yeah, maybe abortion is murder, but it's my inalienable right to bodily autonomy, either way' is laughable. it wins over nobody who doesn't already think abortion isn't murder, and is based on a premise that we should already know is wrong: there are no such thing as universal human rights. all rights are socially-situated and conditional, and in fact, there are good times when 'bodily autonomy' should not be respected - I mean, for god's sake, we intend to kill people with guns.
we have to actually make value judgements and weigh the positives against the negatives for real, specific cases, not just pre-emptively refuse the question out of a solipsism and appeals to universal truths. forcing someone to give blood to save lives at a mass casualty event is more emotionally impactful, despite being identical to, mandating vaccination and handwashing. both of the latter are 'violations of bodily autonomy' that are plainly agreeable on practical grounds. the position that finds no possible way of extricating 'stopping someone from committing suicide', an act generally thanked after the fact, from the abuses that take place in capitalist psychiatric institutions, is not one based on material analysis or an attempt to mitigate harm - it is a juvenile 'abolitionist' approach that refuses to consider class character, in favour of an idealistic condemnation of entire systems and related practices in the abstract.
ultimately, there is nothing incorrect that is not also harmful. a refusal to analyse the positives and negatives of behaviours, procedures, and acts, justified by 'it's impossible to know!' and 'doing anything would be authoritarian!' is not helpful, does not bring about correct behaviour in practice, it is the opposite - it is a cover for harmful behaviours, and promoting it to avoid the hard discussions over whether a given behaviour is harmful is wrong. it fails to defend correct things - like the fact that hrt is good - and works to defend incorrect things. any view that our positions should not be based on practical, material facts is corrosive.
436 notes
·
View notes
Text
Smile at Hope in the Name of Despair: on Komaeda and Nanami's deaths in chapter 5
Formalising the tags on this as their own thing because I'm going insane. Shoutout to @kaiokentimesten for letting me bounce ideas off them and looking over this before it was posted.
TL;DR:
DR2 Nanami is the person Komaeda desperately tried and failed to be over the entire killing game.
It makes their mutual destruction that was simultaneously a double suicide in chapter 5 even more meaningful.
Komaeda was someone who considered himself apart from the rest of the group, a supporter instead of an equal, and didn't see any future for himself with them due to circumstances beyond his control. Nanami was... someone who considered herself apart from the rest of the group, a supporter instead of an equal, and- based on how her FTEs ended- didn't see any future for herself with them due to circumstances beyond her control.
Both had strong ideologies around human worth that drove their actions over the game and led to them valuing other people's lives over their own. Chapter 5 culminated in both of them willingly sacrificing themselves for the greater good.
But their reception by the rest of the cast was very, very different for very obvious reasons. And the differences between them ultimately led to Nanami achieving everything Komaeda wanted, both on the surface and on a deeper, more emotional level, while he completely failed to.
On Komaeda
On the surface Komaeda strives for 'hope', right? He always acted for (what he believed was) the greater good by (in his perception) helping more talented people bring it about. Go slightly deeper and we see that he didn't actually just want to hang out in background, he wanted to be important, albeit in a vicarious way. He actively went against the will of everyone he tried to 'serve', engineering deadly conflicts behind their backs and manipulating the flow of information in trials, because he had his own ideas about what was best for them which coincidentally always had him pulling the strings. While initially unaware of his hypocrisy, his final message acknowledged this and took it to an extreme.
Go deeper still and it turned out that he truly wanted to be loved. For people to care about him and give a shit he existed. All of the above may have been, in my view, subconscious proxies for that: the only way he knew how to make people love him. Praise him. Raise statues to him. Remember him as the Ultimate Hope. Please.
But Komaeda didn't understand what hope is. His idea of it was too abstract, too utilitarian, too black-and-white. He reduced his classmates to interchangeable vessels of hope*, their individual value as living people dependent on their potential for it, and often callously discarded people that no longer met his standards. This ironically made him more of an agent of despair, especially after chapter 4 shattered a load-bearing part of his beliefs and destabilised him further.
He made the class despise him, died alone and afraid, and (if it had been real) would likely be remembered as an unwell person that tried to kill everyone. At most he garnered respect for his intellect, made the survivors take his luck seriously, and had Hinata torn about him posthumously; a lot of conversations during his investigation were more preoccupied with the end of the killing game than him no longer being with them. Had his plans ever succeeded, his final legacy would have been clearing the way for the creation of 5-15 new Junko Enoshimas and snuffing out what little hope humanity had regained. He took out someone who was virtually the Naegi of DR2 and her death ended up being the only one that stuck.
*There's nuance to that depending on the situation- and his views in general, especially considering DR2.5- but this is about his behaviour during/when planning murders and how it shaped his classmates' opinions of him. I have a post about it here!
Nanami, on the other hand...
...had a fundamentally different approach to morality, hope and what gives a person worth. She was built to have compassion for people that most of society would consider irredeemable: people whose net impact on humanity was extremely negative, who likely couldn't reverse that even if they aided humanity for the rest of their lives. She believed they had worth regardless and deserved a chance to be rehabilitated. Her death was only possible in chapter 5 because, even having seen Komaeda at his worst and knowing he was dangerous, she still believed in him and his right to second chances and tried to save him twice.
She was kind, level-headed, and had her own key moments in trials. People liked her and didn't reject her presence or tie her up in a draughty building for days. Hinata's heart raced when he did FTEs with her and he worked around the ways she was weird instead of storming out of conversations prematurely.
Faced with a choice between her life or everyone else's, forced by one of the very people she existed for, she willingly faced death and helped persuade everyone else to kill her (another thing Komaeda spent the entire game trying in vain to do). This wasn't easy, even after they reached consensus about Komaeda's luck, because she was their friend and they were distraught to see her die. By doing so- and again when she helped Hinata posthumously in chapter 6- she ultimately saved them, their 'dead' classmates (Komaeda included) and the rest of humanity, and her loved ones would never forget that.
Komaeda set out to dedicate himself to hope- to be remembered and loved as someone who heroically sacrificed himself for humanity. But Nanami was the person that actually achieved his dream.
-
As a final note, I love how the chapter's title- which I started this post with- can be applied to both of them. Komaeda idolised hope but his actions often brought about the opposite. Nanami sacrificed herself for Ultimate Despairs because she knew the real meaning of hope was believing in a better future.
#WHEW. hope that makes others as unwell as it did me#i love these two!!! god!!!!!#also ai nanami needs a lot of therapy herself in timelines where she's retrieved post-nwp i think#danganronpa#dr analysis#komaedology#nagito komaeda#chiaki nanami#komanami#<- it's not shippy but hopefully it's food; do whatever you like with this#komaeda#nanami#.txt#edit: originally wanted to have screenshots in this but i'd never finish the fuckin thing if i did#feel free to ask for clarification on anything ghdjskgf
57 notes
·
View notes