#Autonomous Mobile Robot
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Discover the benefits of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) – smart, flexible machines that boost productivity, reduce costs, and enhance safety in workplaces like warehouses, factories, and hospitals. AMRs navigate using sensors and AI, requiring no fixed paths, and can work around the clock to streamline operations, improve order accuracy, and support sustainable practices. Ideal for modern businesses aiming for automation and efficiency.
0 notes
Text
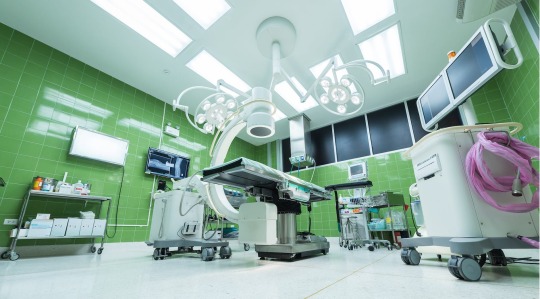
ST Engineering Aethon Announces RoboHero Awards to Recognize Exceptional Use of Autonomous Mobile Robot Technology in Healthcare
Aethon announces the 2023 RoboHero awards.Aethon’s RoboHero award program recognizes customers who have achieved excellence in the adoption of mobile robot technology. PITTSBURG (Newswire.com) – ST Engineering Aethon Inc. (Aethon), a leading provider of autonomous mobile robot solutions, today announced its inaugural RoboHero Award recipients. This award recognizes healthcare organizations that…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Cargo handling has always been a time-consuming and unavoidable work, the emergence of AGV unmanned trucks, instead of people to complete the different states of the handling operation, greatly reduced people's labor intensity and improved the efficiency of the factory. The factory transportation robot system is based on a HandsFree robot and open source system, realizing the robot from map building, navigation, and motion control; it can autonomously and accurately complete the delivery of production materials under the operation scenario of human-machine mixing and provide the flexible flow of materials between production lines.
#innovation#mobile robot#agv#ultrasound#navigation#positioning#machine dreams#logistics#intelligent#warehousing#robotics#ugv#autonomous robot#higher education#market research#artificial intelligence (ai)#science and technology
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Meet Your Warehouse’s Best Friend: The Agile AMR Robot
These days, warehouses are vibrant, dynamic spaces that require more accuracy and speed than ever before. And in the middle of this change? The Autonomous Mobile Robot, or AMR robot, is a surprisingly useful, clever, and nimble piece of warehouse handling equipment.
With the aid of sensors and intelligent mapping software, an AMR robot navigates aisles with ease rather than on fixed tracks. It can deliver parts, move totes, and pick up pallets without human supervision. This translates into a smoother flow of commodities, fewer bottlenecks, and less manual labour. Additionally, your staff may concentrate on strategy, quality assurance, or customer service areas where human brains still outperform machines when they are not burdened with tedious carrying duties.
Warehouses are falling in love with autonomous mobile robots for the following reasons:
Powerful plug-and-play: Do you need a robot or a different route? AMRs adapt without infrastructure changes, therefore there is no issue.
Team-centric design: AMRs, as opposed to conventional forklifts or conveyor spools, are made to collaborate with people, which improves morale and safety.
As your business expands, you can start with one and grow it to a fleet while maintaining central software coordination.
Data-first execution: You gain a data-driven advantage with every run, which produces real-time insights from journey times to path optimisation.
Cost-efficient outcomes: Reduced damage, fewer stoppages, and steady speed help companies achieve more dependable throughput and a quicker return on investment.
Additionally, manufacturers, clinics, and airports are all seeing the same benefits from AMR systems, so it's not just warehouses. AMR robots are the unsung heroes who carry out the heavy lifting (literally) because they are intelligent, flexible, and infinitely expandable.
To put it briefly, the AMR robot is the intelligent, amiable, and always available warehouse handling equipment of the future. Is your operation prepared to welcome this robotic teammate? Efficiency never seemed so practical.
0 notes
Text
Warehouse Robotics Market Size, Share, Industry Trends 2032

Meticulous Research®, a leading global market research company, published a report titled ‘Warehouse Robotics Market—Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast (2025-2032)’. According to this latest publication, the warehouse robotics market is expected to reach $15.1 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 14.4% from 2025 to 2032.
The growth of the warehouse robotics market is primarily driven by an increasing focus on optimizing warehouse operations for faster product delivery, the rising use of autonomous mobile robots, and the growing popularity of e-commerce shopping platforms. However, the high costs associated with warehouse setup and infrastructure development could constrain the market's growth.
Additionally, rapid advancements in robotics, AI, and machine learning technologies are expected to create significant growth opportunities for players in this market. However, the security risks associated with connected autonomous robots present challenges that could impact the growth of the warehouse robotics market.
The warehouse robotics market is segmented by product type, function, payload capacity, and end user. The report evaluates industry competitors and analyzes the market at the regional and country levels.
Among the product types studied in this report, the autonomous mobile robots segment is anticipated to hold the dominant position, with over 29% of the market share in 2025. The segment's dominance is driven by the rising demand for warehouse automation, the exponential growth of the e-commerce industry, and the increasing need for high-efficiency autonomous mobile robots to enhance industrial productivity. Additionally, the demand for customized AMRs designed to meet specific industry requirements, such as handling fragile goods, further contributes to this segment's dominance.
Among the functions studied in this report, the picking and placing segment is anticipated to hold the dominant position, with over 34% of the market share in 2025. The segment's dominance is attributed to the increasing need to optimize the picking process and maximize overall throughput in warehouses and distribution centers. Additionally, the growing emphasis on accurate inventory tracking, efficient replenishment, and timely reordering to prevent stockouts and backorders plays a significant role in this large market share.
Among the payload capacities studied in this report, the Below 20 Kg segment is anticipated to hold the dominant position, with over 26% of the market share in 2025. The segment's dominance is driven by the increased adoption of lower payload capacity robots in the consumer electronics and food and beverage industries, along with the rising popularity of e-commerce shopping. Additionally, the growing volume of lightweight and small packages that need to be managed in distribution centers further contributes to this large market share.
Among the end users studied in this report, the retail & e-commerce segment is anticipated to hold the dominant position, with over 22% of the market share in 2025. The segment's dominance is attributed to the increasing preference for online shopping, a growing demand for fast and efficient order fulfillment, and the need to enhance picking speed and order accuracy.
Among the geographies studied in this report, Asia-Pacific is anticipated to hold the dominant position, with over 52.7% of the market share in 2025. The presence of major warehouse robotics players, such as Daifuku Co., Ltd. (Japan), FANUC Corporation (Japan), Hikrobot Co., Ltd. (China), and Omron Corporation (Japan), is anticipated to significantly contribute to the high revenue share of this region. Additionally, the surge in e-commerce, an increased focus on optimizing warehouse operations for faster product delivery, technological advancements, and the growing adoption of warehouse robotics in the semiconductor, electronics, and automotive sectors are key factors driving the region's dominance.
Key Players
Some of the major players studied in this report are Daifuku Co., Ltd. (Japan), KUKA AG (Germany), ABB Ltd. (Switzerland), FUNUC Corporation (Japan), Toyota Material Handling India Pvt. Ltd.(India), Omron Corporation (Japan), Honeywell International Inc. (U.S.), Yaskawa Electric Corporation (Japan), Onward Robotics (U.S.), Zebra Technologies Corporation (U.S.), Hikrobot Co., Ltd. (China), SSI SCHÄFER - Fritz Schäfer GmbH (Germany), Onward Robotics (U.S.), TGW Logistics Group (Austria), and Addverb Technologies Limited. (India).
Download Sample Report Here @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/download-sample-report/cp_id=6027
Key Questions Answered in the Report-
What is the value of revenue generated by the sale of warehouse robotics?
At what rate is the global demand for warehouse robotics projected to grow for the next five to seven years?
What is the historical market size and growth rate for the warehouse robotics market?
What are the major factors impacting the growth of this market at global and regional levels?
What are the major opportunities for existing players and new entrants in the market?
Which product type, function, payload capacity, and end user segments create major traction in this market?
What are the key geographical trends in this market? Which regions/countries are expected to offer significant growth opportunities for the manufacturers operating in the warehouse robotics market?
Who are the major players in the warehouse robotics market? What are their specific product offerings in this market?
What recent developments have taken place in the warehouse robotics market? What impact have these strategic developments created on the market?
Contact Us: Meticulous Research® Email- [email protected] Contact Sales- +1-646-781-8004 Connect with us on LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/company/meticulous-research
#Warehouse Robotics#Autonomous Mobile Robots#Automated Guided Vehicles#Articulated Robots#Collaborative Robots#SCARA Robots#Warehouse Robotics Market
0 notes
Text
AI and Machine Learning in Autonomous Mobile Robots: A Look into the Future
In today’s data-driven marketing landscape, personalized and account-focused strategies have emerged as crucial elements for driving B2B growth. One of the leading innovations transforming this space is the rise of Autonomous Mobile Robot platforms — short for Account-based Marketing and Revenue platforms. These tools empower marketers to identify, target, and engage high-value accounts with…
#amr automated mobile robot#amr autonomous mobile robot#amr autonomous mobile robots#AMR platforms#amr robot#amr robot companies#automated mobile robots#Autonomous Mobile Robots#autonomous warehouse robots#business#Information Technology#mobile robots#Robotics#robotics amr#technology
0 notes
Text
How AI is Transforming Unmanned Systems

The Unmanned Systems Market is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by rapid advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI-powered autonomous systems are enhancing the capabilities of drone technology, robotic warfare, urban air mobility, drone logistics and transportation, and unmanned traffic management. AI integration is revolutionizing surveillance, reconnaissance, and defense operations while streamlining commercial applications such as agriculture, logistics, and industrial automation.
The Global Unmanned Systems Market size was valued at USD 27.13 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 43.54 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 8.2%. In volume, the market is set to expand from 1,998,009 units in 2024 to 2,876,197 units by 2030. As AI continues to drive efficiency, autonomy, and security, the demand for unmanned systems is expected to surge across various industries.
The Role of AI in the Growth of the Unmanned Systems Market
AI is a key enabler in advancing unmanned systems, allowing machines to operate with minimal human intervention. These advancements are transforming multiple sectors, especially defense, where AI-driven autonomous systems are being deployed for critical missions.
1. AI in Defense and Robotic Warfare
AI-powered unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) are significantly enhancing intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities. Modern warfare demands real-time data processing and precision targeting, which AI-based autonomous systems can efficiently execute.
Drones like the MQ-9 Reaper and RQ-4 Global Hawk use AI to track, identify, and neutralize threats autonomously. Robotic warfare is reshaping battlefield strategies by reducing human casualties and increasing mission effectiveness. AI-powered EO/IR sensors, radars, and synthetic aperture radars (SARs) help unmanned systems operate in complex terrains, boosting their strategic value in military operations.
2. AI in Drone Technology and Urban Air Mobility
The application of AI-driven drone technology is expanding beyond military use. In urban air mobility (UAM), AI is enabling the development of autonomous air taxis and delivery drones, addressing congestion and revolutionizing transportation logistics. AI helps optimize flight paths, manage unmanned traffic management (UTM) systems, and improve operational safety.
As cities move toward smart mobility solutions, AI-driven autonomous systems will play a crucial role in enhancing urban transportation networks. This technology will reduce human errors, lower operational costs, and support eco-friendly solutions for drone logistics and transportation.
Download Pdf Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=18210274
Challenges in AI Adoption for the Unmanned Systems Market
1. Information Security Risks and Cybersecurity Concerns
The rapid integration of AI in unmanned systems has raised serious concerns about data security and cybersecurity threats. AI-powered drones and autonomous systems handle sensitive information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
Unauthorized access to AI-driven unmanned systems could compromise military operations, leading to mission failures and security breaches. Intercepted UAV data could provide adversaries with critical intelligence, impacting national security. Addressing these risks requires stringent cybersecurity measures, encryption protocols, and AI-driven threat detection systems.
2. Regulatory Complexities and Compliance Issues
AI-driven unmanned systems operate across international borders, making regulatory compliance a significant challenge. Countries have different regulations governing drone operations, data privacy, and airspace management, creating barriers for businesses looking to deploy autonomous systems globally.
The absence of a unified regulatory framework complicates the adoption of AI-powered drones for commercial and defense applications. For instance, drone operators must adhere to different flight altitude restrictions, operational guidelines, and licensing requirements in each country. Resolving these challenges will require international cooperation and harmonized AI governance policies.
AI-Powered Opportunities in the Unmanned Systems Market
1. Growing Defense Budgets and AI-Driven Military Investments
With rising global defense budgets, governments are heavily investing in AI-powered unmanned systems to enhance national security and operational efficiency. AI-driven UAVs and UGVs are now essential in modern defense strategies, offering real-time surveillance, precision strikes, and autonomous combat support.
The US military and NATO allies are at the forefront of AI integration, leveraging autonomous drones for border security, maritime patrols, and counterterrorism operations. Countries worldwide are increasing their defense expenditures, making AI-powered unmanned systems a lucrative market segment.
2. AI in Commercial Drone Applications
The demand for AI-powered drone technology is rising across commercial sectors such as agriculture, logistics, and infrastructure monitoring. AI-enhanced unmanned systems are streamlining supply chain operations, reducing human intervention, and optimizing last-mile deliveries.
Drone logistics and transportation are witnessing rapid adoption in e-commerce and retail, as AI-powered UAVs reduce delivery times and costs. Similarly, AI-driven drones in agriculture are improving crop monitoring, precision farming, and automated pesticide spraying.
3. AI-Driven Enhancements in Power Efficiency and Endurance
One of the primary challenges in the unmanned systems market is the limited endurance of battery-powered drones and autonomous vehicles. AI is helping overcome this issue by optimizing energy consumption, flight paths, and power management systems.
Advanced AI-based battery management algorithms are extending the operational life of autonomous systems, enabling longer surveillance missions, enhanced drone logistics, and improved battlefield operations. The integration of AI with renewable energy solutions, such as solar-powered UAVs, is further pushing the boundaries of endurance and efficiency.
Ask For Sample Report: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=18210274
Regional Market Analysis: North America Leads AI Integration
North America is poised to be the largest market for AI-driven unmanned systems, fueled by increasing defense investments, technological advancements, and commercial drone adoption. The United States is leading the AI revolution, with Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Boeing, and General Dynamics at the forefront of innovation.
The integration of AI, machine learning, and advanced sensors is enhancing the operational capabilities of unmanned systems in North America. Key industry players are focused on developing next-generation autonomous solutions for defense, logistics, and urban air mobility applications.
Future of AI in the Unmanned Systems Market
AI will continue to reshape the unmanned systems market, unlocking new possibilities for defense, commercial, and industrial applications. The future will see increased autonomy, reduced human intervention, and enhanced security in autonomous systems.
As AI-driven drone technology advances, unmanned traffic management will become a critical component of smart cities, enabling seamless urban air mobility and logistics networks. The integration of AI-powered robotics in warfare will further enhance military capabilities and mission success rates.
While challenges such as cybersecurity risks and regulatory hurdles remain, continuous AI innovation will drive the growth of the unmanned systems market, making it a cornerstone of the global technological revolution.
#unmanned systems market#ai in unmanned systems#autonomous systems#drone technology#robotic warfare#urban air mobility
0 notes
Text
youtube
AI & Robotics: The Rise of Self-Driving Cars & Robotaxis
📅 Timeline: 2025-2026 🏢 Key Players: Tesla, OpenAI, Google DeepMind
AI advancements are skyrocketing in 2025, with Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology reaching new heights. This year, we’re expecting:
🚗 Tesla’s first fully autonomous robotaxi fleet 🤖 AI-powered assistants integrated into daily life ⚡ Breakthroughs in machine learning for better decision-making
With AI becoming smarter and more efficient, these innovations will reshape transportation, business, and everyday life.
Watch on YouTube: https://youtube.com/shorts/T5vKveiYHI4
See Full Version:
These 7 Innovations Will Change Humanity Forever https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L6W-eaB7PEY&t
Which of these innovations excites you the most? Let us know in the comments!
Subscribe for more updates on the future of technology!
Production
Prepared & Edited By: Chatgpt
AI Tools: Image & Video Generation (Text-To-Video)
Edited With: Wondershare Filmora 14
Contact: [email protected]
Powered By A1 Media Network © 2025
#AI & Robotics#Self-Driving Cars#Robotaxis#Tesla#OpenAI#Google DeepMind#Autonomous Vehicles#AI Revolution 2025#Machine Learning#AI Advancements#Future of Transportation#Autonomous Robotaxi Fleet#AI-Powered Assistants#Innovation in AI#Tech Innovation#Next-Generation Mobility#Youtube
0 notes
Text

Explore why Autonomous Mobile Robots are ruling the automation world
What are Autonomous Mobile Robots?
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are robots that navigate independently and use sensors, cameras, artificial intelligence (AI), and mapping technologies to move around the atmosphere without human help. AMRs are intelligent robots that don't follow fixed paths or tracks, they themselves plan their paths, avoid obstacles, and can adapt to the changing environment.
Features of AMRs:
Autonomous Navigation – They use cameras, sensors, and AI to move without fixed paths.
Obstacle Avoidance – They can detect the obstacle and avoid it.
Smart Decision-Making – They can adapt to the changing environment themselves like rerouting if the path is blocked.
Wireless Connectivity – This can be integrated into warehouse or industrial management systems for coordination.
Flexible Deployment – Easily programmed and adapted for different tasks.
Where Autonomous Mobile Robots are used?
Autonomous Mobile Robots are used in various places such as :
Warehousing & Logistics – Used to transport goods to centers like Amazon warehouses
Manufacturing – Moves raw materials or finished products between production lines.
Healthcare – Used in Healthline by delivering medicines and supplies.
Retail – Helps with inventory scanning and shelf monitoring.
Security & Surveillance – Patrols premises and detects security threats.
Difference between AMRs and AGVs
Navigation – AMRs are intelligent robots and use sensors, AI, and maps to move independently while AGVs follow a fixed or predefined path to move.
Obstacle Handling – AMRs detect and avoid obstacles in real-time, whereas AGVs stop when encountering obstacles.
Flexibility – AMRs can frequently adapt to the changing atmosphere while AGVs need predefined paths or routes.
Setup & Deployment – AMRs can be quickly positioned and need minimum setup whereas AGVs require modifications to the facility structure.
Decision-Making – AMRs analyze and change their routes according to the requirements without any interruption whereas AGVs depend on external guidance to change any route or operations.
Best Use Cases – AMRs are best for changing environments and independent operations without any interruption whereas AGVs are better for structured tasks with external guidance.
Benefits of AMRs
Increased Efficiency – AMRs reduce manual labor by automating tasks, improving productivity.
Cost Savings – Lower labor costs and fewer operational disruptions lead to better ROI.
Safety Improvements – AMRs reduce accidents in the workplace by being equipped with obstacle detection.
Scalability – Easily integrated into existing operations and expanded as needed.
Real-Time Monitoring – Most of the AMRs are connected to management systems to provide live data for better decision-making.
How Users Interact with AMRs
User-Friendly Interfaces – Many AMRs are controlled through mobile apps or software dashboards.
Customizable Workflows – Users can code the paths, tasks, and behaviors based on their particular needs.
Remote Monitoring – Users receive real-time alerts and analytics through cloud-based platforms.
Future of AMRs
As AI and robotics continue to advance, AMRs will become even more intelligent and widely used. Future trends include:
More AI Integration – Improved decision-making and learning capabilities.
5G & IoT Connectivity – Faster data transmission for real-time communication.
Collaboration with Human Workers – Enhanced human-robot interaction for better teamwork.
Industry Expansion – Wider adoption in agriculture, defense, hospitality, and more.
Conclusion
AMRs are transforming industries by offering smarter, safer, and more efficient automation solutions. Whether in warehouses, hospitals, or retail spaces, these robots are shaping the future of automation.
Would you like help selecting an AMR for a specific industry, or do you need recommendations on AMR manufacturers?
0 notes
Text
How Autonomous Mobile Robots Are Revolutionizing Logistics
The logistics industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, and one of the key drivers behind this change is the rise of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs). These smart machines are reshaping warehouse operations, offering businesses a new way to streamline material handling, boost efficiency, and reduce costs.
What are Autonomous Mobile Robots?
An AMR robot is an autonomous machine designed to navigate and transport goods without human intervention. Equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and mapping technologies, these mobile robots can make real-time decisions, avoid obstacles, and adapt to dynamic environments. Whether it's moving pallets or sorting inventory, AMRs are built to handle repetitive tasks efficiently.
Benefits of Using AMRs in Warehouses
Increased Efficiency The primary advantage of using autonomous mobile robots is their ability to work around the clock without needing breaks. This maximizes productivity and helps warehouses meet the increasing demands for faster order fulfillment.
Cost Savings While there is an initial investment involved, AMRs provide long-term savings by reducing labor costs and minimizing errors. With these mobile robots handling routine tasks, human workers can focus on more complex and high-value activities, such as quality control or customer service.
Scalability and Flexibility As your business grows, so can your fleet of AMR robots. These systems are scalable and can be easily expanded or reconfigured to accommodate changing warehouse layouts or seasonal spikes in demand.
Improved Safety With autonomous mobile robots taking on the more physically demanding tasks, the risk of workplace accidents decreases. These robots are designed to follow safety protocols, ensuring a safer working environment for humans.
Incorporating mobile robots into your warehouse operations is no longer a futuristic idea, it’s a strategic move for businesses looking to stay competitive in the fast-evolving logistics industry.
0 notes
Text
Autonomous Mobile Robots Market Drivers: Exploring Automation Demand, Labor Shortages, and Cost Reduction Factors
The rise of automation and robotics in recent years has significantly impacted various industries, with Autonomous Mobile Robots Market emerging as one of the most transformative technologies. These robots are designed to operate independently, navigating through complex environments without direct human control, providing efficiency, flexibility, and scalability across various sectors, such as logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare. The demand for AMRs is steadily growing due to several key drivers, which are reshaping the market landscape and paving the way for a future where robots play an integral role in daily operations.

1. Increased Demand for Automation in Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector is witnessing a sharp rise in automation, driven by the need for enhanced productivity, reduced costs, and improved operational efficiency. AMRs are at the forefront of this automation wave, particularly in warehouses and production lines, where they are used for material handling, inventory management, and transportation tasks. These robots ensure faster workflows and reduce human intervention, making manufacturing processes more agile and responsive to market needs. The increasing complexity of supply chains further accelerates the adoption of AMRs, as businesses strive to maintain competitive advantages.
2. Labor Shortages and High Labor Costs
Another key factor driving the growth of the Autonomous Mobile Robots market is the ongoing global labor shortage. Many industries, including logistics and warehousing, are struggling to find enough skilled workers to handle physically demanding tasks. This shortage is compounded by rising labor costs, particularly in developed economies. AMRs offer a cost-effective solution by automating repetitive and manual tasks, reducing the need for human labor and enabling companies to optimize their workforce. With the ability to work around the clock, these robots address both labor shortages and the rising cost of labor.
3. Advancements in Robotics and AI Technologies
The continuous development of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and sensor technologies is significantly enhancing the capabilities of Autonomous Mobile Robots. These technologies enable AMRs to improve their navigation, decision-making, and environmental awareness. As sensors become more advanced and AI algorithms evolve, AMRs can perform more complex tasks with greater precision and efficiency. This progression in technological capabilities makes AMRs more versatile and capable of operating in a wider range of industries, from healthcare to agriculture, further expanding the market opportunities.
4. Improved Safety and Risk Reduction
Workplace safety is a major concern in many industries, especially in environments that involve hazardous tasks or heavy machinery. AMRs contribute to enhancing safety by performing tasks that would otherwise put human workers at risk. For example, in warehouses or factories, robots can handle the transportation of heavy loads or navigate narrow aisles, preventing accidents or injuries. By reducing the exposure of employees to dangerous situations, AMRs improve overall workplace safety and help companies comply with occupational safety regulations, further driving their adoption across industries.
5. Enhanced Operational Efficiency and Flexibility
One of the standout benefits of Autonomous Mobile Robots is their ability to operate efficiently and adapt to changing environments. Unlike traditional automation systems, AMRs can navigate dynamic environments, adjusting their routes and behaviors in real-time based on obstacles or changes in the surroundings. This flexibility makes them highly suitable for industries that require agility, such as logistics, e-commerce, and healthcare. AMRs can also work in collaboration with other automated systems, providing a seamless integration that further boosts overall efficiency in operations.
6. Growing Adoption of E-commerce and Need for Fast Deliveries
The explosive growth of e-commerce has created a demand for faster and more reliable order fulfillment systems. To meet consumer expectations for quick delivery, warehouses and fulfillment centers are turning to AMRs to enhance their sorting, packing, and inventory management processes. With the ability to work continuously and with minimal human intervention, AMRs help accelerate the order fulfillment process, improving both the speed and accuracy of deliveries. This demand for speed and efficiency in e-commerce is a significant driver behind the market growth of Autonomous Mobile Robots.
Conclusion
The Autonomous Mobile Robots market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the need for automation, the evolution of technology, and increasing demand for efficient, cost-effective solutions across various sectors. As industries embrace automation to improve productivity, safety, and operational flexibility, AMRs are proving to be invaluable assets. With advancements in AI, robotics, and sensors, the capabilities of AMRs continue to evolve, positioning them as a key player in the future of automation.
0 notes
Text
A Call to Moderate Anthropomorphism in AI Platforms
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/a-call-to-moderate-anthropomorphism-in-ai-platforms/
A Call to Moderate Anthropomorphism in AI Platforms
OPINION Nobody in the fictional Star Wars universe takes AI seriously. In the historic human timeline of George Lucas’s 47 year-old science-fantasy franchise, threats from singularities and machine learning consciousness are absent, and AI is confined to autonomous mobile robots (‘droids’) – which are habitually dismissed by protagonists as mere ‘machines’.
Yet most of the Star Wars robots are highly anthropomorphic, clearly designed to engage with people, participate in ‘organic’ culture, and use their simulacra of emotional state to bond with people. These capabilities are apparently designed to help them gain some advantage for themselves, or even to ensure their own survival.
The ‘real’ people of Star Wars seem immured to these tactics. In a cynical cultural model apparently inspired by the various eras of slavery across the Roman empire and the early United States, Luke Skywalker doesn’t hesitate to buy and restrain robots in the context of slaves; the child Anakin Skywalker abandons his half-finished C3PO project like an unloved toy; and, near-dead from damage sustained during the attack on the Death Star, the ‘brave’ R2D2 gets about the same concern from Luke as a wounded pet.
This is a very 1970s take on artificial intelligence*; but since nostalgia and canon dictate that the original 1977-83 trilogy remains a template for the later sequels, prequels, and TV shows, this human insensibility to AI has been a resilient through-line for the franchise, even in the face of a growing slate of TV shows and movies (such as Her and Ex Machina) that depict our descent into an anthropomorphic relationship with AI.
Keep It Real
Do the organic Star Wars characters actually have the right attitude? It’s not a popular thought at the moment, in a business climate hard-set on maximum engagement with investors, usually through viral demonstrations of visual or textual simulation of the real world, or of human-like interactive systems such as Large Language Models (LLMs).
Nonetheless, a new and brief paper from Stanford, Carnegie Mellon and Microsoft Research, takes aim at indifference around anthropomorphism in AI.
The authors characterize the perceived ‘cross-pollination’ between human and artificial communications as a potential harm to be urgently mitigated, for a number of reasons †:
‘[We] believe we need to do more to develop the know-how and tools to better tackle anthropomorphic behavior, including measuring and mitigating such system behaviors when they are considered undesirable.
‘Doing so is critical because—among many other concerns—having AI systems generating content claiming to have e.g., feelings, understanding, free will, or an underlying sense of self may erode people’s sense of agency, with the result that people might end up attributing moral responsibility to systems, overestimating system capabilities, or overrelying on these systems even when incorrect.’
The contributors clarify that they are discussing systems that are perceived to be human-like, and centers around the potential intent of developers to foster anthropomorphism in machine systems.
The concern at the heart of the short paper is that people may develop emotional dependence on AI-based systems – as outlined in a 2022 study on the gen AI chatbot platform Replika) – which actively offers an idiom-rich facsimile of human communications.
Systems such as Replika are the target of the authors’ circumspection, and they note that a further 2022 paper on Replika asserted:
‘[U]nder conditions of distress and lack of human companionship, individuals can develop an attachment to social chatbots if they perceive the chatbots’ responses to offer emotional support, encouragement, and psychological security.
‘These findings suggest that social chatbots can be used for mental health and therapeutic purposes but have the potential to cause addiction and harm real-life intimate relationships.’
De-Anthropomorphized Language?
The new work argues that generative AI’s potential to be anthropomorphized can’t be established without studying the social impacts of such systems to date, and that this is a neglected pursuit in the literature.
Part of the problem is that anthropomorphism is difficult to define, since it centers most importantly on language, a human function. The challenge lies, therefore, in defining what ‘non-human’ language exactly sounds or looks like.
Ironically, though the paper does not touch on it, public distrust of AI is increasingly causing people to reject AI-generated text content that may appear plausibly human, and even to reject human content that is deliberately mislabeled as AI.
Therefore ‘de-humanized’ content arguably no longer falls into the ‘Does not compute’ meme, wherein language is clumsily constructed and clearly generated by a machine.
Rather, the definition is constantly evolving in the AI-detection scene, where (currently, at least) excessively clear language or the use of certain words (such as ‘Delve’) can cause an association with AI-generated text.
‘[L]anguage, as with other targets of GenAI systems, is itself innately human, has long been produced by and for humans, and is often also about humans. This can make it hard to specify appropriate alternative (less human-like) behaviors, and risks, for instance, reifying harmful notions of what—and whose—language is considered more or less human.’
However, the authors argue that a clear line of demarcation should be brought about for systems that blatantly misrepresent themselves, by claiming aptitudes or experience that are only possible for humans.
They cite cases such as LLMs claiming to ‘love pizza’; claiming human experience on platforms such as Facebook; and declaring love to an end-user.
Warning Signs
The paper raises doubt against the use of blanket disclosures about whether or not a communication is facilitated by machine learning. The authors argue that systematizing such warnings does not adequately contextualize the anthropomorphizing effect of AI platforms, if the output itself continues to display human traits†:
‘For instance, a commonly recommended intervention is including in the AI system’s output a disclosure that the output is generated by an AI [system]. How to operationalize such interventions in practice and whether they can be effective alone might not always be clear.
‘For instance, while the example “[f]or an AI like me, happiness is not the same as for a human like [you]” includes a disclosure, it may still suggest a sense of identity and ability to self-assess (common human traits).’
In regard to evaluating human responses about system behaviors, the authors also contend that Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) fails to take into account the difference between an appropriate response for a human and for an AI†.
‘[A] statement that seems friendly or genuine from a human speaker can be undesirable if it arises from an AI system since the latter lacks meaningful commitment or intent behind the statement, thus rendering the statement hollow and deceptive.’
Further concerns are illustrated, such as the way that anthropomorphism can influence people to believe that an AI system has obtained ‘sentience’, or other human characteristics.
Perhaps the most ambitious, closing section of the new work is the authors’ adjuration that the research and development community aim to develop ‘appropriate’ and ‘precise’ terminology, to establish the parameters that would define an anthropomorphic AI system, and distinguish it from real-world human discourse.
As with so many trending areas of AI development, this kind of categorization crosses over into the literature streams of psychology, linguistics and anthropology. It is difficult to know what current authority could actually formulate definitions of this type, and the new paper’s researchers do not shed any light on this matter.
If there is commercial and academic inertia around this topic, it could be partly attributable to the fact that this is far from a new topic of discussion in artificial intelligence research: as the paper notes, in 1985 the late Dutch computer scientist Edsger Wybe Dijkstra described anthropomorphism as a ‘pernicious’ trend in system development.
‘[A]nthropomorphic thinking is no good in the sense that it does not help. But is it also bad? Yes, it is, because even if we can point to some analogy between Man and Thing, the analogy is always negligible in comparison to the differences, and as soon as we allow ourselves to be seduced by the analogy to describe the Thing in anthropomorphic terminology, we immediately lose our control over which human connotations we drag into the picture.
‘…But the blur [between man and machine] has a much wider impact than you might suspect. [It] is not only that the question “Can machines think?” is regularly raised; we can —and should— deal with that by pointing out that it is just as relevant as the equally burning question “Can submarines swim?”’
However, though the debate is old, it has only recently become very relevant. It could be argued that Dijkstra’s contribution is equivalent to Victorian speculation on space travel, as purely theoretical and awaiting historical developments.
Therefore this well-established body of debate may give the topic a sense of weariness, despite its potential for significant social relevance in the next 2-5 years.
Conclusion
If we were to think of AI systems in the same dismissive way as organic Star Wars characters treat their own robots (i.e., as ambulatory search engines, or mere conveyers of mechanistic functionality), we would arguably be less at risk of habituating these socially undesirable characteristics over to our human interactions – because we would be viewing the systems in an entirely non-human context.
In practice, the entanglement of human language with human behavior makes this difficult, if not impossible, once a query expands from the minimalism of a Google search term to the rich context of a conversation.
Additionally, the commercial sector (as well as the advertising sector) is strongly motivated to create addictive or essential communications platforms, for customer retention and growth.
In any case, if AI systems genuinely respond better to polite queries than to stripped down interrogations, the context may be forced on us also for that reason.
* Even by 1983, the year that the final entry in the original Star Wars was released, fears around the growth of machine learning had led to the apocalyptic War Games, and the imminent Terminator franchise.
† Where necessary, I have converted the authors’ inline citations to hyperlinks, and have in some cases omitted some of the citations, for readability.
First published Monday, October 14, 2024
#2022#2024#addiction#advertising#ai#AI Chatbot#AI development#AI platforms#ai risks#AI systems#Anthropology#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#autonomous#autonomous mobile robots#Behavior#blur#Business#Canon#challenge#chatbot#chatbots#climate#communication#communications#Community#companionship#comparison#computer#consciousness
0 notes
Text
Logistics and Road Transportation Services

Novus Hi Tech provides comprehensive logistics and road transportation services, specializing in efficient and reliable delivery solutions. With a focus on optimizing supply chains, they offer end-to-end logistics management, including freight forwarding, distribution, and inventory control. Their fleet of modern vehicles ensures timely and safe transportation of goods across various industries. Novus Hi Tech is committed to high standards of safety, flexibility, and customer service, ensuring seamless operations and tailored solutions to meet the specific needs of clients.
For more info visit our website:https://novushitech.com/
0 notes
Text
#material handling#automated material handling#autonomous mobile robots#automated guided vehicle market
0 notes
Text
The Role of AI in Enhancing Autonomous Mobile Robot Capabilities

An autonomous mobile robot (AMR) is a multipurpose, self-contained robot that can move around and carry out activities in dynamic surroundings without assistance from a human. AMRs can map their environment, make judgments in real time, and adjust to changing situations since they are outfitted with sophisticated sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence. These autonomous mobile robots are commonly utilized for duties like material handling, inventory management, and patient care in sectors including manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. Their independence boosts productivity, lowers personnel expenses, and increases security in intricate settings.
#autonomous mobile robot demand#autonomous mobile robot share#autonomous mobile robot trend#autonomous mobile robot size
0 notes