#CSSBasics
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
CSS Basics: How to Style Your First Web Page Like a Pro
Creating visually appealing web pages is an essential skill for web developers and designers. CSS, short for Cascading Style Sheets, is the language used to describe the presentation of a web page written in HTML. By learning CSS, you can transform a plain HTML document into a visually stunning and user-friendly web page.
Understanding CSS
Understanding CSS
CSS is a stylesheet language that enables you to control the layout and appearance of HTML elements. It allows you to separate the content of a web page (HTML) from its design and aesthetics (CSS). This separation of concerns makes it easier to maintain and update web pages over time.
What CSS Can Do
CSS is incredibly versatile, offering a wide range of styling options:
Layout Control: Arrange elements on a page using grid and flexbox.
Color and Backgrounds: Apply colors, gradients, and background images.
Typography: Change fonts, sizes, and text styles.
Spacing: Control margins, padding, and element positioning.
Borders and Effects: Add borders, shadows, and more.
Linking Stylesheets
Before you can begin styling, you need to link your CSS to your HTML document. There are three main ways to include CSS:
1. External Stylesheet
An external stylesheet is a separate file with a .css extension. It is the most efficient way to apply styles across multiple web pages. To link an external stylesheet, use the <link> tag inside the <head> section of your HTML document:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css"> <title>My Web Page</title> </head> <body> <!-- HTML content goes here --> </body> </html>
2. Internal Stylesheet
An internal stylesheet is written directly within the <style> tags in the <head> section of your HTML document. This method is useful for single-page applications or when you need to apply styles to only one page:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <style> body { background-color: lightblue; } </style> <title>My Web Page</title> </head> <body> <!-- HTML content goes here --> </body> </html>
3. Inline Styles
Inline styles are applied directly to HTML elements using the style attribute. This method is generally discouraged as it mixes content with presentation, making the code harder to maintain:
<p style="color: red;">This is a red paragraph.</p>
Applying Basic Styles
Once you've linked your CSS, you can start applying styles to your HTML elements. CSS styles are defined using a combination of selectors, properties, and values.
Selectors
Selectors are used to target HTML elements for styling. Common selectors include:
Element Selector: Targets all elements of a specific type.
p { color: blue; }
Class Selector: Targets elements with a specific class attribute. Classes are prefixed with a period (.).
.highlight { font-weight: bold; }
ID Selector: Targets a specific element with an ID attribute. IDs are prefixed with a hash (#).
#main-header { font-size: 24px; }
Properties and Values
CSS properties define what aspect of the element will be styled, such as color, font-size, or margin. Each property is assigned a value:
h1 { color: darkgreen; font-size: 32px; text-align: center; }
Example: Styling a Simple Web Page
Let's walk through a simple example of how CSS can be used to style a basic HTML page.
HTML Structure
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css"> <title>Simple Web Page</title> </head> <body> <header id="main-header"> <h1>Welcome to My Web Page</h1> </header> <nav> <ul class="navigation"> <li><a href="#">Home</a></li> <li><a href="#">About</a></li> <li><a href="#">Contact</a></li> </ul> </nav> <main> <section> <h2>About Me</h2> <p class="intro">Hello! I'm a web developer passionate about creating beautiful and functional web pages.</p> </section> </main> <footer> <p>© 2023 My Web Page</p> </footer> </body> </html>
CSS Styles (styles.css)
/* Basic styles */ body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; line-height: 1.6; margin: 0; padding: 0; } header { background-color: #333; color: white; padding: 10px 0; text-align: center; } .navigation { list-style-type: none; padding: 0; } .navigation li { display: inline; margin-right: 10px; } .navigation a { color: #333; text-decoration: none; } .intro { font-style: italic; color: #555; } footer { background-color: #333; color: white; text-align: center; padding: 10px 0; position: fixed; width: 100%; bottom: 0; }
Explanation of CSS Code
Body Styles: Sets the default font family, line height, and removes default margin and padding.
Header Styles: Applies a dark background color, white text, and centers the content.
Navigation Styles: Defines styles for the navigation list, including removing bullet points and styling links.
Intro Paragraph: Applies italic styling and a custom color.
Footer Styles: Similar styling to the header, plus fixed positioning at the bottom of the page.
Advanced CSS
Advanced CSS Techniques
As you become more comfortable with CSS, you can explore more advanced techniques to enhance your web designs.
Responsive Design
Responsive design ensures that your web page looks great on all devices, from desktop computers to mobile phones. CSS media queries allow you to apply different styles based on the screen size:
@media (max-width: 600px) { body { font-size: 14px; } .navigation li { display: block; margin: 5px 0; } }
CSS Flexbox and Grid
CSS Flexbox and Grid are powerful layout models that provide flexibility in designing complex layouts:
Flexbox: Ideal for one-dimensional layouts, such as rows or columns.
Grid: Perfect for two-dimensional layouts, allowing you to define both rows and columns.
Example of Flexbox:
.container { display: flex; justify-content: space-between; align-items: center; }
Example of Grid:
.grid-container { display: grid; grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr); gap: 10px; }
Tips for Writing Clean CSS
Organize Your Styles: Group related styles together and use comments to separate sections.
Use Descriptive Names: Choose meaningful class and ID names for easier understanding.
Minimize Inline Styles: Keep your styles in external or internal stylesheets.
Consistent Formatting: Follow consistent indentation and spacing for readability.
Test Across Browsers: Ensure your styles work in all major browsers.
Tips for Writing
Conclusion
CSS is an essential tool for web development, allowing you to create visually appealing and user-friendly web pages. By understanding how to link stylesheets, apply basic styles, and utilize advanced techniques, you'll be well-equipped to design modern, responsive websites. Remember to continually practice and experiment with CSS to enhance your skills and creativity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between CSS and HTML?
HTML is used to structure content on a web page, while CSS is used to style and layout that content.
How do I choose between internal and external stylesheets?
Use external stylesheets for larger projects to keep styles separate from HTML, and internal stylesheets for small, single-page applications.
Can I use multiple stylesheets on a single page?
Yes, you can link multiple external stylesheets, and they will be applied in the order they are linked.
What are CSS frameworks, and should I use them?
CSS frameworks like Bootstrap provide pre-designed styles and components to speed up development. They are useful for beginners and for rapid prototyping.
How can I learn more about advanced CSS techniques?
Explore online resources, tutorials, and courses that cover topics like responsive design, CSS animations, and preprocessors like SASS.
#CSSBasics#LearnCSS#CSSTutorial#CSSForBeginners#WebDevelopment#FrontendDevelopment#FrontendTips#ResponsiveDesign#WebDesign#UIUXDesign#CSSLayout#CSSStyling#ModernCSS#WebCoding#WebDesignTips#CodingStandards#CleanCode#CSSColors#CSSFonts#LearnToCode#CodeNewbie#FrontendMasters#WebPerformance#WebDevTips#CSSGrid#Flexbox#CSSResponsive#CSSBestPractices#WebDesignBasics#HTMLCSS
0 notes
Text
What Makes a Great Webpage in 2025? Here’s Your Full Breakdown.
Your webpage is your digital storefront. It’s where first impressions are made, trust is built, and conversion happens.
A great webpage isn't just about looking pretty—it’s about:
🎯 Representing your brand with the right colors, fonts, and layout 📦 Organizing your content cleanly with headings, paragraphs, and lists 📸 Adding images that breathe life into your content 📲 Including buttons and forms for real interaction 🧭 Making navigation effortless with links and structure
And let’s not forget—HTML and CSS are your superpowers. You don’t need a coding degree to get started, just a clear idea and the right guidance.
🧠 Learn about:
The difference between <div> and <span>
Styling elements with class selectors
Creating margins and paddings that don’t mess up your layout
Fonts, colors, and display behaviors that actually reflect your brand
💡 PRO TIP: A well-structured and styled webpage = better UX + stronger brand loyalty.
Need a responsive, branded website designed by pros? 👉 Call iBCScorp—we’ll build it, and brand it right.
0 notes
Text
CSS Positioning Explained: Static, Relative, Absolute, and Fixed
Master the fundamentals of CSS positioning! Learn the differences between static, relative, absolute, and fixed positioning with practical examples for beginners. Learn how CSS positioning works! Understand static, relative, absolute, and fixed positions to control layout and design with ease. Perfect for beginners.
0 notes
Text
Learn HTML and CSS from scratch at TCCI – the perfect starting point for anyone looking to build websites or start a web development career.
0 notes
Text
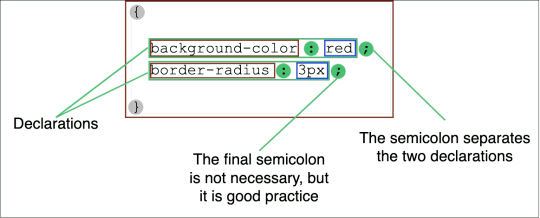
Understanding Style Declarations in CSS: A Basics Guide

The Importance of Style Declarations in CSS
CSS, which stands for Cascading Style Sheets, is a fundamental technology for web design and development. It plays a crucial role in defining the visual appearance and layout of web pages. At the heart of CSS lies the concept of style declarations. Style declarations are the building blocks that allow you to control the design and presentation of your web content. Understanding the importance of style declarations in CSS is essential for anyone involved in web development, whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer. These declarations are what enable you to create stunning and user-friendly websites. They provide you with the power to customize the color, typography, spacing, and positioning of elements, ultimately shaping the user experience. In this blog post, we will delve into the significance of style declarations in CSS. We'll explore what they are, how they work, and why they are a vital part of the web development process. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how to harness the power of CSS style declarations to create visually appealing and responsive web designs.
1. Introduction to CSS
CSS, or Cascading Style Sheets, is a fundamental technology in web development that allows you to control the presentation and layout of your web pages. It works hand in hand with HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) to define how your content should appear on the screen. Understanding CSS is essential for creating visually appealing and user-friendly websites. Why CSS Matters: - Enhanced User Experience: CSS enables you to style your web content, making it more attractive and readable for visitors. - Consistency: It allows you to maintain a consistent design across your website by defining styles in one central location. - Separation of Concerns: CSS separates the structure (HTML) from the presentation (CSS), making your code easier to manage and update. - Responsiveness: With CSS, you can create responsive designs that adapt to different screen sizes and devices. How CSS Works: CSS uses a set of rules and selectors to target HTML elements and apply styles. A CSS rule typically consists of a selector, property, and value. Selectors specify which HTML elements should be styled, properties define what aspects of the element to style, and values set the styling details. Example of a CSS Rule: CSS p { color: #333; /* Sets text color to a shade of gray */ font-size: 16px; /* Defines font size */ margin-bottom: 20px; /* Adds spacing between paragraphs */ } Here, the selector 'p' targets all paragraphs in the HTML document, and the associated properties and values determine text color, font size, and margin spacing for those paragraphs. Types of CSS: CSS TypeDescriptionInline CSSApplied directly to individual HTML elements using the 'style' attribute.Internal CSSPlaced within the HTML document's Read the full article
0 notes
Video
youtube
(via Divi: Understanding CSS Class Names, IDs, and Custom Styling for Beginners!)
Unlock the power of Divi with our comprehensive guide, "Understanding CSS Class Names, IDs, and Custom Styling for Beginners." Dive into the world of web design as we unravel the complexities of CSS, focusing on Class Names, IDs, and Custom Styling within the Divi framework. Whether you're a novice or seasoned developer, this blog post equips you with the essential knowledge to enhance your Divi experience.
0 notes
Text
What you'll learn Will be proficient on HTML5 from Basic to AdvancedWill be able to create amazing site using HTML5Will be able to work with Audio and Video in HTML5Hands on experience on Data Input and ButtonsHands on experience on Absolute and Relative LinksHands on experience on Tags and ListsBasics and Advanced Concepts on CSSBasics and Advanced Concepts of jQueryOur students testimonials regarding this course --"Enjoyable, easy to learn and concepts are cleared to the point" -- Shivam Agarwal"A helpful and interesting introduction to HTML5 for complete beginners such as myself. The course contained useful information with references to websites, that could assist in the building of your own website." -- Ian Walker "Great for Beginner" -- Timilehin A. Omotoyinbo"I find this course helpful help me better to understand the basic of HTML 5." -- Dejan Atanasovski"very extensive and clearly presented." -- Thando Mtshali"Yep. IT perfectly suits my expectation. Good course actually. Well done instructor and thank you very much for this wonderful HTML course." -- Praveen Kumar"Great explanations for everything and easy to follow along!" -- Lori robinsonBy completion this course, you will be able to read and write front end web development code using HTML5. This course gives you hands on and practical experience on detailed HTML5. Contents of this tutorial # Interactive HTML5: Basics Introduction to HTMLHTML4 vs. HTML5Making your first HTML pageTools to create HTML filesBase HTML TagsParagraph Tags Break TagsHeader TagsBold and Italic TagsOrdered and unordered Lists Interactive HTML5: Advanced Difference between Absolute Links and Relative LinksHyperlinking to an external page Hyperlinking to an email address Hyperlinking to a file in your sitePlaying and controlling audioPlaying and controlling videoEmbedding a videoWhats is a Table - Pros and ConsTable propertiesAdding an iFrameAdding an iFrame: Part 2What is possible with a form using on HTML knowledgeDefining the form Text fields and text areasRadio buttons and check buttonsData input and buttonsProper file structure Code commenting Meta tagsInteractive CSS3: Basics What is CSS? Why we need it?What's new in CSS3CSS Selectors, properties and attributes ID Selectors Class Selectors Element Selectors All Selectors Inline style sheets External Style sheets Interactive CSS3: Advanced The Box model Adding Color Working with fonts Background images Styling ID tagsFloat and Clear Block and inline elements Positioning Adding the elementsInteractive Bootstrap: BasicWhy Bootstrap? Downloading BootstrapAdding Bootstrap in your siteCreating navigation Styling images Creating the footer Adding styled buttonsInteractive Bootstrap: AdvancedAdding Google MapsAdding an image carouselAdding a contact formInteractive jQuery: BasicsWhat is jQuery and what you will learn?Downloading jQuery A first look at jQuery code Selectors and Filters Replacing contents Handling events Hide/Show events Fading Slide Toggle AnimateSelectors Who this course is for:Who wanna learn HTML5Who wanna create beautiful site using HTML5Who wanna learn CSS3Who wanna learn jQuery
0 notes
Photo
Niespodzianki w CSS ⌨️ hello roman #56 http://ehelpdesk.tk/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/logo-header.png [ad_1] Niespodzianki w CSS to coś na co... #adamromański #aftercss #androiddevelopment #angular #animacjecss #beforecss #c #css #cssbasics #cssdisplay #csskurs #csstutorial #dataanalysis #datascience #deeplearning #development #docker #frontenddeveloper #frontenddeveloper #frontendroman #frontendem #frontendowiec #frontendu #helloroman #helloroman #inlineblockcss #iosdevelopment #java #javascript #machinelearning #node.js #podstawycss #problemywcss #pseudoelementycss #python #react #roman #romański #transformacjecss #unity #webdevelopment #zaawansowanycss
0 notes
Link
The latest The GitHub Daily! https://t.co/zoiJxuVFAq Thanks to @cardstack @Adaizen_com @cssbasics #javascript #php
— ReleaseTEAM (@releaseteam) December 19, 2019
via: https://ift.tt/1GAs5mb
0 notes