#Caliph and Imam
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How is one chosen as an Ayatollah?
Through decades of outstanding scholarly work, which inspires the devotion of hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of followers. A typical ayatollah’s career takes him to one of the Shiites’ holy cities, like Najaf in Iraq or Qom in Iran. There, he studies at one of the pre-eminent Shiite seminaries, where he becomes an expert in theology, jurisprudence, science, and philosophy. After years…

View On WordPress
#Ayatollah#Caliph and Imam#Divine Providence#Fivers--Zaydis#Grand Ayatollah#Hajatolislam#Imam#Ismailis#Majlis faqih#Maraja#Nass#Shiism#Taqlid#Twelvers#Velayat-e-faqih
0 notes
Text
The greatest warrior in history, Imam Ali (AS) never lost a battle, yet he never claimed victory in his entire life except once; At his martyrdom, the moment the sword was struck on his head in prayer, as he calls out;
“By the Lord of the Kaaba, I have succeeded.”

#imamali#death anniversary#17ramadan#19ramadan#warrior#islamic history#history#islamic#islam#shahadat#hazrat ali#masjid#blackday#marsiya#caliph#shia muslims#muslim#shia#iraq#syria#noha#martyrdom#maula ali#imam hussain#imam husayn#ali ibn abi talib#kaaba#holy kaaba#ya ali#karbala
30 notes
·
View notes
Note
So, based on your posts about Islam I've gathered that Muhammad=Lenin and Ali=Stalin, who's Trotsky?
Umar ibn al-Khattab
#that is to say that the Prophet and the Imam are the Noor of Allah and are on a different level than the first three caliphs#The immortal science of Shi'ism
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Are there TV shows in Classical Arabic with English subtitles? TV shows in Classical Arabic (Fusha) with English subtitles are rare. Omar about the famous Caliph and the Imam about Ahmad bin Hanbal are two good examples. https://arabic-for-nerds.com/history/tv-shows-classical-arabic-english-subtitles/?feed_id=5441&utm_source=Tumblr&utm_medium=geralddrissner&utm_campaign=FS%20Poster
#HISTORY#ISLAM#MOVIESSERIES#AFGHANISTAN#ALANDALUS#ANECDOTE#BASRA#BEDOUIN#CALIPH#CARTOON#EXTENSION#FARSI#GOOGLECHROME#HADITH#IMAM#ISFAHAN#JERUSALEM#MECCA#MEDINA#MUSALSAL#NETFLIX#OMARIBNALKHATTAB#PERSIA#RAMADAN#SHAHID#SHIA#STREAMING#SUBTITLES#SUNNIISLAM
0 notes
Text
In 907 Ifriqiya,* roughly modern Tunisia (Figure 7.8), broke away from the caliphs in Baghdad. Radical Shiites† set up a line of officially infallible caliph-imams, known as Fatimids because they claimed descent (and imamhood) from Muhammad's daughter Fatima.
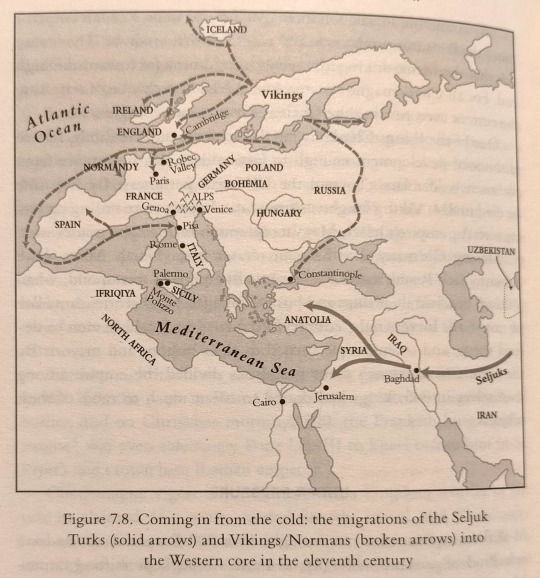
*Ifriqiya is an Arabized version of Africa, the Roman name for Tunisia.
†Radical in the sense that they belonged to the Isma'ili Shiite sect, which often used violence to oppose what it saw as illegitimate Sunni regimes, rather than the "Twelver" Shiites, who awaited more peacefully the return of the hidden twelfth imam.
"Why the West Rules – For Now: The patterns of history and what they reveal about the future" - Ian Morris
#book quotes#why the west rules – for now#ian morris#nonfiction#10th century#ifriqiya#africa#tunisia#caliph#baghdad#break away#shiite#muslim#islam#fatimids#imam#isma'ili#sunni
1 note
·
View note
Text
SUBHAN'ALLAH, THIS TEXT CONTAINS VERY INFORMATIVE KNOWLEDGE FOR ALL!! READ & SPREAD IT AS MUCH AS POSSIBLE, IT WILL BE SADQA-E-JARIAH FOR YOU AND ME.
1-Akhi - Brother
2-Ukhti - Sister
3-JazakAllah khair - May Allah give you Ajar/Sawab for your deed.
4-Ma'Shaa'Allah - As God has willed.
5-HayakAllah - May Allah give you life.
6-BarakAllahu Feek - May Allah put baraka in what you are doing.
7-Wa feeka barakallahu - and May Allah bless you. (in response to Barakallahu Feek)
8-Wa iyyakum - And to you
9-Alhamdulillah - Praise be to Allah
10-Allah - God
11-Allahu Akbar - Allah is Most Great
12-Amanah - Trust
13-Assalamu Alaikum - Peace be upon you--the "official" Islamic greeting.
14-Assalamu Alaikum wa Rahmatullahi wa Barakatuh - "Peace and the Mercy and Blessings of God be upon you" Extended form of the above.
16-Astaghfir Allah - I seek forgiveness from Allah (used when mentioning something that goes against the standards of Islam)
17-Ayah/Ayat - Qur'anic verse
18-Bid`ah - Innovation, addition to the religion's essentials
19-Bukhari - One of the most noted compilers of hadith. His collection is 20-known as Sahih Bukhari
21-Bismillah ar-Rahman ar-Rahim - In the Name of Allah, the Most Gracious, Most Merciful
23-Da'wa - Invitation (for humankind to Islam)
24-Du`aa - Supplication
25-Eid - Islamic holiday
26-Fatwa - Islamic legal ruling
27-Fiqh - Islamic law as interpreted by scholars
28-Fitnah - Corruption and disorder, also temptation
29-Hadith - A report of a saying or deed of the Prophet
30-Haj - Pilgrimage
31-Halal - Allowed (per Islamic law)
32-Haram - Forbidden (per Islamic law)
33-Hazrat/Hadrat - Honorable
34-Hijab - Modest way of behavior and dress (including head scarf for women)
35-Imam - Leader
36-Iman - Faith
37-In Shaa Allah - If God wills. (Used when talking about a future event)
38-Injeel - The scripture sent down to Prophet Issa (Jesus)
39-Isnad - Chain of transmitters, the list of people who successively narrated a given hadith
40-Jannah - Paradise
41-JazakAllah Khair - May God grant you what is good. (Often used instead of "Thank you")
42-Jihad - Striving for Islam, whether by peaceful or violent means
43-Jinn - Unseen beings, who, like humans, are given the power to choose between right and wrong
44-Kafir - One who denies the truth. Literally, one who "covers" the truth (sometimes applied to non-Muslims).
45-Khalifah - Caliph: Leader of Muslim nation
46-Khilafah - Caliphate
47-Khutba - Sermon
48-Kufr - Denial of the Truth, rebellion against God
49-La Ilaha Illa Allah - There is no deity but God
50-Ma Shaa Allah - What God has willed! (Usually used to express wonder at Allah's creation)
51-Madhhab - School of jurisprudential thought
52-Makruh - Detested, but not forbidden (per Islamic law)
53-Mandoub - Recommended, but not required (per Islamic law)
54-Mubah - Neither forbidden nor commended. Neutral (per Islamic law)
55-Mushrik - One who commits Shirk
56-Muslim - One who submits to Allah and is a follower of Islam; also, name of one of the most notable hadith scholars. His collection is known as Sahih Muslim
57-Nabi - Prophet
58-Qur'an - The Words of Allah conveyed to us by the Prophet
PBUH - Peace Be Upon Him. Same as SAW
59-RAA - (Radia Allahu Anhu/Anha.) May Allah be please with him/her
60-Ra-sool - Messenger (Prophet to whom a scripture is revealed)
61-Rasool Allah - Messenger of God (used to refer to Prophet Muhammad)
62-Sahaba - Companions of Prophet. Singular is "Sahabi"
63-Sahih - "Sound in isnad." A technical attribute applied to the "isnad" of a hadith
64-Salaam - Peace. An abbreviated version of the Islamic greeting
65-Salaat - Prayer
66-SAW - (Salla Allahu Alaihi Wa Sallam.) Peace Be Upon Him
67-Sawm/Siyam - Fasting
68-Seerah/Sirah - History of the Prophet's life
69-Shahadah - Bearing witness that there is no god but Allah and that Muhammad is His Messenger.
70-Shari'ah - Divine Law
71-Sheikh - Scholar (or any elder and/or respected man)
72-Shirk - Associating partners (e.g. helpers, other gods) with Allah
73-Shura - Consultation among Muslims
74-Subhan Allah - "Glory be to God"
75-Sunna/Sunnah - Tradition of the Prophet
76-Surah/Sura - A Chapter in the Qur'an
78-Tafsir - Interpretation
79-Tawraat - The scripture sent down to Prophet Musa (Moses).
80-Ulama - Religious scholars
81-Umma - Nation, community.
82-Ustadh - Teacher
83-Wassalaam - And peace. It means "goodbye"
84-Zakat - Required charity
206 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Messenger of Allah ﷺ said:
"Tell Abu Bakr to lead the people in prayer."
Imam Ahmad bin Hanbal رحمة الله commented:
"He ﷺ intended the caliphate [for Abu Bakr (may Allah be pleased with him)]."
[al-Sunnah of al-Khallal]
#islamdaily#islam#quranandsunnah#islamic#quranquotes#islamicpost#islam help#islamislove#al quran#convert to islam
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here are 50 Palestinian Lies Since Last Saturday, 7 October 2023:
1- Hamas killed nobody.
2- Hamas only killed IDF soldiers.
3- The soldiers Hamas targeted were not in uniform.
4- Okay, Hamas killed civilians, but they’re part of the occupation.
5- Hamas didn’t kill children.
6- Hamas didn’t burn children.
7- The fire was an accident.
8- Hamas didn’t kidnap children.
9- Hamas takes care of child hostages.
10- Hamas didn’t rape women.
11- Other people raped the women.
12- The Hamas fighters who raped will be punished.
13- Hamas didn’t bomb people hiding in bomb shelters.
14- Only one bomb shelter was bombed.
15 - Hamas didn’t shoot people as they fled.
16- The people who were shot while fleeing were guilty of occupation.
17- Hamas is not a terrorist group.
18- Hamas is a resistance group.
19- Jews began the conflict in 1948, Hamas is still resisting that today.
20- Hamas doesn’t idolize Hitler.
21- Only some Hamas members love Hitler.
22- Hamas is different from ISIS.
23- Only some Palestinians joined ISIS in 2014.
24- Hamas doesn’t want a global Caliphate, (when Hamas’ Charter says they strive for a global caliphate).
25- Hamas respects Human rights, but… “Jews are not Humans”
26- Palestinians don’t idolize Saddam Hussein, despite him having roads, roundabouts named after him in Gaza and West Bank - and his photos raised in Palestinian protests.
27- Hamas does not steal.
28- Hamas only takes what it needs to protect Palestinian interests.
29- Hamas doesn’t kill Palestinians.
30- Only some Hamas rockets accidentally land in Gaza and kill Palestinians.
31- Hamas never uses human shields.
32- Only in some cases Hamas may use human shields.
33- We don’t want to drown Jews in the sea. We want a peaceful solution.
34- There will be no peace until all the land is ours and the Jews return to Europe.
35- All the Arab states have betrayed us.
36- All the Arab states are supporting us.
37- Iran doesn’t fund Hamas.
38- Iran only supplies Hamas with weapons, not money.
39- Iran only pays our soldiers’ salaries.
40- Hamas is not the Muslim Brotherhood.
41- Hamas was only founded by the Muslim Brotherhood.
42- Palestinians didn’t support Osama Bin Laden.
43- Only some Palestinians (thousands) celebrated on 9/11.
44- Nobody gave Palestinians a chance to govern themselves.
45- Yes we elected Hamas in Gaza, but Hamas doesn’t represent us.
46- Sometimes Hamas represents us, and sometimes it doesn’t. It depends.
47- Palestinians are indigenous to the Holy Land.
48- Yasser Arafat was Egyptian, but he was also indigenous to Palestine.
49- Palestinians who stab Jews get paid because their families need to eat.
50- It’s all the Jewish people’s fault.
———
If you’ve seen another lie being amplified over the last week, feel free to add it to the list below.
Imam of Peace
177 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unveiling the Real Story: How Key Figures Played a Role in the Early Betrayal of Islam

The story of Islam’s birth is woven with extraordinary sacrifices, fierce opposition, and, ultimately, a complex legacy that many believe has been obscured by history. While the Prophet Muhammad (SAWW) and his close family, the Ahl al-Bayt, faced relentless hardship, the behavior of some early converts raises profound questions about loyalty and intentions. In particular, we see a sharp divide between the sacrifices of the Prophet’s family, including Lady Khadija (SA) and Imam Ali (AS), and the contrasting path taken by future leaders who would shape Islam’s political landscape.
Early Opposition to Islam and the Prophet’s Nearest Supporters
As the Prophet Muhammad (SAWW) began spreading his message, he encountered fierce resistance from the Quraysh, who controlled Makkah’s political and economic spheres. Only a few supporters stood by him unwaveringly, most notably his wife, Lady Khadija (SA), and his young cousin, Imam Ali (AS). These figures were not only the first to believe in his message but also the first to sacrifice everything they had to see it succeed. In contrast, key figures like Abu Bakr, Umar, and Uthman, while outwardly accepting Islam, seem to have faced far less opposition, enjoying protection from influential families even as true believers suffered persecution and death.
Lady Khadija: The True Mohsin of Islam
Lady Khadija’s immediate acceptance of Islam upon the Prophet’s revelation set the standard for devotion. Her role extended far beyond emotional support; she provided her entire fortune to shield the Prophet from his enemies and facilitate the spread of his message. Her wealth became a shield for the early Muslim community, funding campaigns, sheltering followers, and even buying the Prophet (SAWW) and his supporters much-needed peace amid hostile conditions.
During the intense Quraysh-imposed boycott on Banu Hashim, Khadija’s last resources were spent ensuring the community could survive in the barren valley of Shab e Abu Talib. She endured starvation, thirst, and deprivation, ultimately sacrificing her own life. This selflessness has earned her the title of “Mohsin of Islam” – the true benefactor whose generosity and faith provided Islam with the foundation it needed to endure.
In stark contrast, many of the prominent early converts, including the first three caliphs, seemed to experience a level of immunity from the Quraysh’s wrath. Figures such as Abu Bakr, Umar, and Uthman are notably absent from records of persecution and torture. Their alliances with Qurayshi families allowed them to convert without fear, raising questions about their motivations and long-term intentions.
The Persecution of True Believers Outside Banu Hashim
The divide between true believers and those protected by political affiliations is made starkly clear through the persecution of early Muslims like Ammar bin Yasir, whose parents were killed for their faith. His mother, Sumayyah, and father, Yasir, suffered brutal deaths, serving as powerful examples of the sacrifices endured by the Prophet’s early followers. The torture and killing of Banu Hashim supporters, along with the exiling of others to Abyssinia, stand in contrast to the privileged positions of certain early converts, whose families protected them from harm.
Prophet Muhammad (SAWW) received little support outside his family and close followers. The strength of Islam’s early community lay primarily within Banu Hashim, bolstered by a handful of individuals who accepted suffering in order to preserve the message. Lady Khadija’s support and Imam Ali’s courage in defending the Prophet under life-threatening conditions reflect an unwavering loyalty unmatched by those who were later poised to assume leadership of the Muslim community.
Political Calculations and Strategic Marriages: The Long-Term Ambitions of the First Caliphs
As Islam gained influence, these individuals, particularly Abu Bakr and Umar, positioned themselves strategically. Through marriage alliances with the Prophet, they sought both legitimacy and a lasting foothold in the growing Muslim community. The marriages of their daughters to the Prophet seem not to have been acts of devotion but rather calculated steps, part of a broader ambition to gain influence within the new Islamic order. These connections afforded them both prestige and an implicit claim to power—a plan that would reveal itself fully only after the Prophet’s passing.
The Prophet’s Passing and the Power Struggle that Followed
After the Prophet’s death, the struggle for leadership culminated in a sudden shift away from the Ahl al-Bayt, despite the Prophet’s repeated declarations of Imam Ali (AS) as his chosen successor. The Prophet’s family, already reeling from his loss, now faced betrayal from those who had once stood by them, or so it seemed. Abu Bakr’s swift assumption of leadership, followed by Umar and Uthman, effectively sidelined Imam Ali (AS) and the Prophet’s family from the authority that had been rightfully theirs.
This power struggle took a devastating toll on the Ahl al-Bayt, culminating in the death of Lady Fatima (SA) under suspicious circumstances. Her pleas for justice went unheard, her rights denied, and her final days marked by grief and pain inflicted by those who had once pledged loyalty to her father.
The Lasting Legacy of Lady Khadija’s Sacrifice
In comparison, Lady Khadija’s legacy shines as a beacon of true sacrifice and faith. Her contributions, both material and emotional, became the bedrock of early Islam. The lasting gratitude the Prophet felt for her was evident throughout his life; he would often remember her kindness, calling her the “best of women.” Lady Khadija’s sacrifices, alongside those of the Prophet’s family, continue to stand in contrast to the privileged lives of others who would later wield power in the Muslim community.
Her example reveals a clear divide in motives: while some were willing to give everything for Islam, others capitalized on its rise without enduring its hardships. Lady Khadija’s story serves as a powerful reminder that the truest believers are those who sacrifice without expectation, embodying the values of justice, mercy, and selflessness that the Prophet Muhammad (SAWW) cherished.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Betrayal and the Courage of the Ahl al-Bayt
The sacrifices of Lady Khadija, Imam Ali, and Lady Fatima underscore a dedication to Islam that transcends political gain—a dedication grounded in love, loyalty, and faith. These were the qualities that sustained Islam in its infancy, making their betrayal by certain early figures all the more painful. Despite the best efforts to erase these truths from history, the actions and words of the Ahl al-Bayt continue to testify to their rightful place and their sacrifices for Islam. As readers, we are left to question: if the true believers sacrificed everything, what was it that others were protecting?
#LadyKhadija#MohsinOfIslam#IslamicHistory#ProphetMuhammad#Sacrifice#EarlyMuslims#ShiaIslam#DivineProtection#SupportOfTheProphet#Khadija#IslamicHeroines#HistoryOfIslam#AhlulBayt#TruthAndSacrifice#imam ali#literature#maula ali#shia#shia islam#ya ali maddad#artists on tumblr#pandora's vault#pandora's box#pandora#SacredGrief#IslamicElegy#LightOfIslam#ShiaTradition#InjusticeInHistory#TruthOfFatimiyya
26 notes
·
View notes
Note
why do sunnis hate shi'as that much what the fuck is their problem?
Hatred towards Shi'a Muslims is not only a concurrent issue, it's a 1400 year old issue that started as a result of the political unrest that took place following the Prophet Muhammad's (pbuh&hf) death. It laid the foundation for the political schism of Islam. Initially, the Shi'as (or Alids) were just a group of partisans that would only develop their own theology a hundred years later. And then you had those who supported Abu Bakr rise to the caliphate. For Shi'as, we believe Abu Bakr usurped the caliphate due to various incidents, and thus, we rejected his ascent to power. These were the partisans of Ali (a). When Ali (a) eventually became the caliph, he was met with a lot of hardship and opposition by people who either hated him or sought political power. During the caliphate of Uthman, the Umayyads were given unrestrained power, and it was not until Ali (a) became the caliph that he removed them from power for their greed and nepotism. However, Muawiyah, a "companion" of the Prophet, who was intially opposed to him before his clan lost in the final battle of Mecca, was in control of Sham (Syria) and refused to go down, hence a renewed civil strife within the Islamic world. The Umayyads were vicious people who were renown for their corruption and hedonism, and their caliphate was founded on the blood of Imam Hussain (a), the son of Imam Ali (a). For Sunnis, these events aren't particularly important, and Islamic history is often neglected, promoting the idea that whatever happened in the past has no religious or theological significance to Islam as a religion. This is where we disagree because, as Shi'as, we simply can't accept certain religious doctrines on the basis of these people being unreliable. For example, Ayesha, having been the wife of the Prophet, is one thing, but she still waged an unjust war against Ali (a). There is no way we can accept her narrations because she's simply untrustworthy.
Because of the power that the Umayyads managed to consolidate for themselves, superseeding the Rashidun caliphate, there was a state-sponsored campaign with the purpose of supressing any Shi'i resistance against the rule, the Shi'as were among these groups and suffered severe persecution to such extent that even members of the Prophet's family were brutally oppressed. For Shi'as, the Prophet's family are a source of emulation and knowledge, and we have to adhere to their understanding of Islamic theology, this is why Islamic history is important, so we can highlight the root behind the resistance. However, dwindling in power and numbers, the Shi'as ultimately committed themselves to Taqiyyah (concealing one's religion) to ensure their survival. This is how we managed to survive for 1400 years. For Sunnis, the Umayyads and subsequent caliphs are a source of great pride, hence why Syria is considered an important heritage site for Sunnis who regard the Umayyads with great respect.
With that said, the reason there's so much sectarian animosity towards Shi'as is because with history in mind, our tradition of reviling these companions is considered an act of disbelief. Sunnis often retort that these companions are noble people and could not possibly be reviled because they had been in the companionship with the prophet, holding that despite the wars and atrocities committed by these people, we should respect them nevertheless. Either way, Shi'a Muslims have a doctrine called Tabarrah (dissociation), which is extended to those people who have caused harm towards the Prophet and his family. This includes "cursing" them, which is considered one of the most offensive acts and a reason why Sunnis get up in arms when we criticize the companions, especially the first caliph Abu Bakr and the second caliph Umar. Furthermore, our emphasis on the doctrine of intercession has caused much controversy because stricter muslims, such as Salafists consider these acts tantamous to idolatry, hence why it's easier for Shi'as to be considered heretics. The fact that we have shrines is considered blasphemous and there are many instances in which these shrines have been attacked. Shi'as are so reviled that for some Sunnis and Salafists, the difference between a Christian and a Shi'a is that Christians have rights as pertained to their status as "People of the Book", while Shi'as are considered heretics, and ultimately disbelievers. For such a reason, we do not have any rights; our blood becomes lawful to them.
In short, HTS, AS, ISIS, Al-Qaeda and all their Salafist sympathisers believe that the blood of a Shi'a is lawful because we are heretics. We are simply putting up a resistance against them. Shi'ism is not just a branch of Islam. It's one of the oldest resistance movements in the world.
518 notes
·
View notes
Text
Are there TV shows in Classical Arabic with English subtitles? TV shows in Classical Arabic (Fusha) with English subtitles are rare. Omar about the famous Caliph and the Imam about Ahmad bin Hanbal are two good examples. https://arabic-for-nerds.com/history/tv-shows-classical-arabic-english-subtitles/?feed_id=4689
#HISTORY#ISLAM#MOVIESSERIES#AFGHANISTAN#ALANDALUS#ANECDOTE#BASRA#BEDOUIN#CALIPH#CARTOON#EXTENSION#FARSI#GOOGLECHROME#HADITH#IMAM#ISFAHAN#JERUSALEM#MECCA#MEDINA#MUSALSAL#NETFLIX#OMARIBNALKHATTAB#PERSIA#RAMADAN#SHAHID#SHIA#STREAMING#SUBTITLES#SUNNIISLAM
1 note
·
View note
Text
EID AL-GHADEER
✦ Imam Ja’far al-Sadiq (a.s.) said:
The reward for fasting on the day of Eid al-Ghadeer is equivalent to fasting for the entire lifetime of the world.
Meaning, if a person were granted life equal to the total lifespan of this world and fasted all throughout, the reward would still equal just one fast on Eid al-Ghadeer.
(Wasa’il ash-Shia, vol. 7)
✦ Imam Ja’far al-Sadiq (a.s.) said:
Giving one dirham to a believing brother who recognizes the greatness and significance of this day is better than giving a thousand dirhams on any other day.
Therefore, give gifts (Eidi) to your brothers on this day and make the believing men and women happy.
(Misbah al-Mutahajjid)
✦ Imam Ali al-Ridha (a.s.) said:
Whoever visits a believer on the day of Eid al-Ghadeer, Allah will grant seventy kinds of light in his grave, will widen his grave, and seventy thousand angels will visit him daily in his grave, giving him the glad tidings of Paradise.
(Iqbal al-A‘mal)
✦ Imam Ja’far al-Sadiq (a.s.) said:
Whoever performs a 2-unit (raka‘at) prayer at any time on the day of Eid al-Ghadeer (though it is best near midday)…
It will be as if he was present on the Day of Ghadeer itself.
(Wasa’il ash-Shia, vol. 5)
✦ Imam Ja’far al-Sadiq (a.s.) said:
The reward for doing good deeds on the day of Eid al-Ghadeer equals that of eighty months of righteous actions.
It is emphasized that one should engage abundantly in the remembrance of Allah (Azz wa Jall) on this day and send blessings (Salawat) upon the Prophet (saww).
It is also recommended for a man to give gifts and donations to his family on this day.
(Wasa’il ash-Shia, vol. 7)
⸻
Recommended A‘maal (Acts of Worship) and Prayers for Eid al-Ghadeer
1. Perform Ghusl (ritual purification bath) early in the day as an act of purification.
2. Observe a fast on this blessed day.
3. Recite Ziyarat-e-Ameenallah and Ziyarat-e-Mutlaqah.
4. Recite Ziyarat-e-Nudbah.
5. Offer a 2-raka‘at prayer before midday:
In each rak‘at, after Surah al-Hamd, recite:
• 10 times Surah al-Ikhlas (“Qul Huwa Allahu Ahad”),
• 10 times Surah al-Qadr (“Inna anzalnahu fi laylatil qadr”),
• 10 times Ayat al-Kursi (“Allahu la ilaha illa huwa…”, Surah al-Baqarah 2:255).
This prayer is highly meritorious, and whatever supplication is made to Allah (swt) will, insha’Allah, be granted.
It is recommended to pray this close to, but before, midday, as that was the time when the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh & hf) declared the successorship and leadership of Imam Ali (a.s.) at Ghadeer Khumm.
After the prayer, go into prostration (sajdah) and recite:
• 100 times “Shukran Lillah” (Thanks to Allah), and
• 100 times “Alhamdulillah” (All praise is for Allah).
Imam Ja‘far al-Sadiq (a.s.) says:
Whoever performs this act will be like one who acknowledged and pledged allegiance to the Imamate and Caliphate of Imam Ali (a.s.) on the day of Ghadeer in the presence of the Prophet (pbuh & hf).
Such a person will also be among the companions of Imam al-Zamana (a.s.) under his banner.
6. It is customary among followers of Ahl al-Bayt (a.s.) to greet one another on this day by shaking hands and reciting the following:
“Akhaituka fillāhi wa ṣafaituka fillāhi wa ṣāfaḥtuka fillāhi wa āhadtullāha wa malāʾikatahu wa kutubahu wa rusulahu wa anbiyāʾahu wa aʾimmatul maʿṣūmīn ʿalayhimussalām ʿalā annī in kuntu min ahlil-jannati wash-shafāʿati wa uʾdhina lī bi an adkhulal-jannata lā adkhuluhā illā wa anta maʿī.”
(Translation: I have made you my brother in Allah, I have chosen you for the sake of Allah, I have shaken hands with you for the sake of Allah, and I have made a covenant with Allah, His angels, His books, His messengers, His prophets, and the infallible Imams (peace be upon them) that if I were to be admitted into Paradise and granted intercession, I shall not enter it without you.)
7. Recite 100 times:
“Alhamdu lillahil-ladhi ja‘ala kamāla dīnīhi wa tamāma ni‘matihi biwilāyati Amīril Mu’minīn ʿAliyyibni Abī Ṭālib ʿalayhis salām.”
[Translation: Praise be to Allah, who perfected His religion and completed His favour through the authority (wilayah) of Ali ibn Abi Talib (peace be upon him).**]
⸻
#mustshare#sharethis#eidcelebration#eid#eid mubarak#shia muslim#shia#maula ali#prophet muhammad#peaceandblessings#celebration
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

186946073_2494119067400847_2233349842880164809_n
#imam hussain#islam#ahl-ul-bayt#shia islam in pictures#sunni#nasibi#omari#bakri#iraq#history of iraq#abbasid caliphate
0 notes
Text

Love — may God honor you — begins in playfulness and ends as seriousness. Its meanings are too subtle to be fully described due to their magnificence; one cannot grasp its reality except through suffering.
It is not something forbidden in religion nor prohibited by the law, for hearts are in the hand of God, may He be glorified and exalted.
Many among the rightly guided caliphs and righteous imams have loved.
-Tawq Al-Hamamah by Imam Ibn Hazm
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
10 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Rashidun Government
The Rashidun Caliphate (632-661 CE) was responsible for setting up the basis of the Islamic empire and expanding its borders beyond the Arabian soil. These leaders were selected by the consent of the people and based on their own merits. They ruled supreme on the lands of Islam as the viceroys of Prophet Muhammad (l. 570-632 CE) and their policies laid the foundation of the style of rule for many future rulers to come. Though the state of the empire was far from being perfect, it was merely the beginning of a long and prosperous period in the history of Eastern civilization. Innovations like centralized government, institutions for administration, public welfare projects, safeguarding the rights of citizens and a general willingness to help people made them quite popular in Arabian history. For their piety and administrative excellence, they are revered by the vast majority of Muslims, and their legacy survives even to this day, in the way Muslims believe that ideal leaders ought to be.
Historical Context
Arabia, at the close of the 6th century CE, was what we would call in modern terms a 'third world country' – if it were a country. But a drastic change was underway as Muhammad, the Prophet of Islam (l. 570-632 CE), took charge. In his 22-year-long mission, as a messenger of Allah (God), Muhammad united most of the fragmented Arabian tribes into one nation.
After the death of the Prophet, his close friend, and companion, Abu Bakr (r. 632-634 CE) established the Rashidun Caliphate (632-661 CE); he was the first of many series of rulers to claim supreme authority over the Islamic world – the caliphs. Abu Bakr was succeeded by Umar (r. 634-644 CE), and he, in turn, was succeeded by Uthman (r. 644-656 CE). Uthman was easily controlled by his tribesmen and this led to his fall from fame; he was murdered in his own house by rebel soldiers.
Ali ibn Abi Talib (r. 656-661 CE), a cousin, and son-in-law of the Prophet, then took the scepter. Ali has been venerated by a group of Muslims called the Shias, who differ from the mainstream Sunnis primarily in that they consider only Ali as the legitimate heir to Muhammad's realm and as the first in a long series of their spiritual leaders or imams.
By the end of the Rashidun Caliphate, the Islamic realm spread far and wide from Egypt and some eastern parts of the North African strip in the west to the whole of the former Sassanian Empire in the east. This was the beginning of a new era – the dawn of the Islamic Caliphates.
Continue reading...
26 notes
·
View notes