#Data Mining Tools Report
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Data Mining Tools Market Drivers, Key Players, Future Outlook | BIS Research
Data Mining Tools refers to the broad range of electric wires and cables manufactured in China encompassing various types such as power cables, communication cables, and specialty wires. The manufacturing process often adheres to the international standards and certification ensuring safety and performance. The term can also indicate the global market’s reliance on Chinese productions for affordable and diverse wiring solutions.
The Data Mining Tools Market is experiencing significant growth, fueled by various key factors and market drivers. In an optimistic projection, the market is expected to be valued at $1.24 billion in 2024, with an anticipated expansion at a CAGR of 11.63% to reach $3.73 billion by 2034
Data Mining Tools Overview
Data mining tools are essential software applications that help organizations extract meaningful patterns and insights from vast datasets. These tools facilitate informed decision-making, enhance operational efficiency, and drive innovation across various industries.
A primary catalyst for this growth is the increasing recognition of the advantages offered by advanced data mining tools in enhancing data analysis capabilities and driving informed decision-making across different industries. Advanced data mining tools play a pivotal role in extracting valuable insights from large and complex datasets, enabling organizations to uncover hidden patterns, trends, and correlations that can drive business success.
Key Features
Diverse Product Range
Manufacturing Standards
Technological Advancements
Moreover, the escalating focus on data-driven decision-making and the need for actionable insights are propelling the adoption of advanced data mining tools in various sectors.
Market Demand Drivers
Exponential growth of data
Integration of AI and machine learning
Shift towards cloud based solutions
Real time data analysis needs
Market Segmentation
By End Users
By Organization
By Deployment
By Business Function
By Component
By Region
Request a sample of this report on the Global Data Mining Tools Market
Key Players
• Microsoft
• IBM
• SAS Institute
• Oracle
• Teradata
• MathWorks
And many others
Access more detailed Insights on Advanced Materials,Chemicals and Fuels Research Reports
Conclusion
The future of the data mining tools market appears robust, with technological advancements and growing data-driven decision-making needs propelling its expansion. Organizations investing in these tools can expect enhanced operational efficiency and a competitive edge in their respective industries
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Potential with WebFOCUS: Your Comprehensive Guide
Discover the Power of WebFOCUS
Modern businesses thrive on data-driven insights, pushing the boundaries of technology to become more analytics-centric. Consequently, the demand for cutting-edge business intelligence tools is at an all-time high. Enter WebFOCUS, a robust, scalable, and adaptable analytics platform that aims to streamline decision-making processes and transform the world of business intelligence.

Understanding WebFOCUS
WebFOCUS, typically associated with WebFOCUS reporting and Business Intelligence (BI), is an advanced analytics platform designed to empower businesses to make data-driven decisions intelligently. Perfect for WebFOCUS jobs and developers alike, this tool can maneuver vast data landscapes and conduct insightful WebFOCUS data analysis.
Key Benefits of Using WebFOCUS
WebFOCUS redefines the realms of data analytics with its advanced features. Its key benefits extend to:
- Data discovery and Data mining: Gain an edge in identifying patterns and trends behind your data.
- Data governance and management: Control data integrity and reliability through WebFOCUS's robust data governance and management tools.
- Data integration: WebFOCUS excels at integrating varied data sources, ensuring a seamless data pipeline.
- Security, Performance, and Scalability: As a secure, efficient, and scalable platform, WebFOCUS stands out as a robust data analysis tool.
WebFOCUS Capabilities
WebFOCUS App Studio and WebFOCUS Designer
Being a WebFOCUS developer means understanding and utilizing the many modules within the platform. WebFOCUS's core is its App Studio module, an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) that allows users to create and manage business applications. Similarly, WebFOCUS Designer offers an intuitive user interface for developing sophisticated data visualizations.
WebFOCUS Info Assist and WebFOCUS Reporting
For data refinement and extraction, WebFOCUS offers InfoAssisT, a browser-based module that simplifies ad hoc reporting tasks. InfoAssisT allows business users to create engaging dashboards, charts, and custom reports, providing visual-driven insights within the WebFOCUS dashboard that are actionable.
WebFOCUS Insights and Predictions
WebFOCUS isn’t just about knowing your business; it’s about predicting it. With predictive analytics capabilities companies can forecast future trends and make informed decisions.
WebFOCUS Security and Scalability
A standout feature of WebFOCUS as an analytics tool is its commitment to data security. Businesses can rest assured knowing their data is protected with utmost rigor.
WebFOCUS Jobs and Salary
What does a WebFOCUS developer salary look like? Given the demand for data analysis and BI skills, a career with WebFOCUS is both rewarding and lucrative, offering competitive remuneration.
WebFOCUS Training and Tutorials
To facilitate user understanding of its multifaceted features, WebFOCUS offers a comprehensive collection of training resources and tutorials online, catering to varied learning abilities and paces.
Conclusion: The Future with WebFOCUS
As businesses constantly adapt and grow, so too do their data analytics needs. WebFOCUS, with its advanced BI capabilities and robust data handling, appears poised to remain an industry leader. Businesses looking for a future-proof, comprehensive analytics platform need not look further than WebFOCUS. Whether transitioning into a WebFOCUS developer job, seeking out WebFOCUS training, or looking to improve your current business operations, WebFOCUS stands out as an invaluable tool. Harness the power of WebFOCUS and transform your business today.
#WebFOCUS analytics#- WebFOCUS dashboard#- WebFOCUS reporting tool#- WebFOCUS business intelligence#- WebFOCUS data visualization#- WebFOCUS data analysis#- WebFOCUS data reporting#- WebFOCUS data integration#- WebFOCUS data discovery#- WebFOCUS data mining#- WebFOCUS data insights#- WebFOCUS data manipulation#- WebFOCUS data management#- WebFOCUS data warehouse#- WebFOCUS data modeling#- WebFOCUS data transformation#- WebFOCUS data extraction#- WebFOCUS data governance#- WebFOCUS data quality#- WebFOCUS data security#- WebFOCUS data privacy#- WebFOCUS data best practices#- WebFOCUS data strategy
0 notes
Text
Green energy is in its heyday.
Renewable energy sources now account for 22% of the nation’s electricity, and solar has skyrocketed eight times over in the last decade. This spring in California, wind, water, and solar power energy sources exceeded expectations, accounting for an average of 61.5 percent of the state's electricity demand across 52 days.
But green energy has a lithium problem. Lithium batteries control more than 90% of the global grid battery storage market.
That’s not just cell phones, laptops, electric toothbrushes, and tools. Scooters, e-bikes, hybrids, and electric vehicles all rely on rechargeable lithium batteries to get going.
Fortunately, this past week, Natron Energy launched its first-ever commercial-scale production of sodium-ion batteries in the U.S.
“Sodium-ion batteries offer a unique alternative to lithium-ion, with higher power, faster recharge, longer lifecycle and a completely safe and stable chemistry,” said Colin Wessells — Natron Founder and Co-CEO — at the kick-off event in Michigan.
The new sodium-ion batteries charge and discharge at rates 10 times faster than lithium-ion, with an estimated lifespan of 50,000 cycles.
Wessells said that using sodium as a primary mineral alternative eliminates industry-wide issues of worker negligence, geopolitical disruption, and the “questionable environmental impacts” inextricably linked to lithium mining.
“The electrification of our economy is dependent on the development and production of new, innovative energy storage solutions,” Wessells said.
Why are sodium batteries a better alternative to lithium?
The birth and death cycle of lithium is shadowed in environmental destruction. The process of extracting lithium pollutes the water, air, and soil, and when it’s eventually discarded, the flammable batteries are prone to bursting into flames and burning out in landfills.
There’s also a human cost. Lithium-ion materials like cobalt and nickel are not only harder to source and procure, but their supply chains are also overwhelmingly attributed to hazardous working conditions and child labor law violations.
Sodium, on the other hand, is estimated to be 1,000 times more abundant in the earth’s crust than lithium.
“Unlike lithium, sodium can be produced from an abundant material: salt,” engineer Casey Crownhart wrote in the MIT Technology Review. “Because the raw ingredients are cheap and widely available, there’s potential for sodium-ion batteries to be significantly less expensive than their lithium-ion counterparts if more companies start making more of them.”
What will these batteries be used for?
Right now, Natron has its focus set on AI models and data storage centers, which consume hefty amounts of energy. In 2023, the MIT Technology Review reported that one AI model can emit more than 626,00 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent.
“We expect our battery solutions will be used to power the explosive growth in data centers used for Artificial Intelligence,” said Wendell Brooks, co-CEO of Natron.
“With the start of commercial-scale production here in Michigan, we are well-positioned to capitalize on the growing demand for efficient, safe, and reliable battery energy storage.”
The fast-charging energy alternative also has limitless potential on a consumer level, and Natron is eying telecommunications and EV fast-charging once it begins servicing AI data storage centers in June.
On a larger scale, sodium-ion batteries could radically change the manufacturing and production sectors — from housing energy to lower electricity costs in warehouses, to charging backup stations and powering electric vehicles, trucks, forklifts, and so on.
“I founded Natron because we saw climate change as the defining problem of our time,” Wessells said. “We believe batteries have a role to play.”
-via GoodGoodGood, May 3, 2024
--
Note: I wanted to make sure this was legit (scientifically and in general), and I'm happy to report that it really is! x, x, x, x
#batteries#lithium#lithium ion batteries#lithium battery#sodium#clean energy#energy storage#electrochemistry#lithium mining#pollution#human rights#displacement#forced labor#child labor#mining#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
This story originally appeared on Vox and is part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
Odorless and colorless, methane is a gas that is easy to miss—but it’s one of the most important contributors to global warming. It can trap up to 84 times as much heat as carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, though it breaks down much faster. Measured over 100 years, its warming effect is about 30 times that of an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide.
That means that over the course of decades, it takes smaller amounts of methane than carbon dioxide to heat up the planet to the same level. Nearly a third of the increase in global average temperatures since the Industrial Revolution is due to methane, and about two-thirds of those methane emissions comes from human activity like energy production and cattle farming. It’s one of the biggest and fastest ways that human beings are warming the Earth.
But the flip side of that math is that cutting methane emissions is one of the most effective ways to limit climate change.
In 2021, more than 100 countries including the United States committed to reducing their methane pollution by at least 30 percent below 2020 levels by 2030. But some of the largest methane emitters like Russia and China still haven’t signed on, and according to a new report from the International Energy Agency, global methane emissions from energy production are still rising.
Yet the tracking of exactly how much methane is reaching the atmosphere isn’t as precise as it is for carbon dioxide. “Little or no measurement-based data is used to report methane emissions in most parts of the world,” according to the IEA. “This is a major issue because measured emissions tend to be higher than reported emissions.” It’s also hard to trace methane to specific sources—whether from natural sources like swamps, or from human activities like fossil fuel extraction, farming, or deforestation.
Researchers are gaining a better understanding of where methane is coming from, surveilling potential sources from the ground, from the sky, and from space. It turns out a lot of methane is coming from underappreciated sources, including coal mines and small oil and gas production facilities.
The report also notes that while there are plenty of low-cost tools available to halt much of this methane from reaching the atmosphere, they’re largely going unused.
The United States, the world’s third largest methane-emitting country, has seen its methane emissions slowly decline over the past 30 years. However, the Trump administration is pushing for more fossil fuel development while rolling back some of the best bang-for-buck programs for mitigating climate change, which will likely lead to even more methane reaching the atmosphere if left unchecked.
Where Is All This Methane Coming From?
Methane is the dominant component of natural gas, which provides more than a third of US energy. It’s also found in oil formations. During the drilling process, it can escape wells and pipelines, but it can also leak as it’s transported and at the power plants and furnaces where it’s consumed.
The oil and gas industry says that methane is a salable product, so they have a built-in incentive to track it, capture it, and limit its leaks. But oil developers often flare methane, meaning burn it off, because it’s not cost-effective to contain it. That burned methane forms carbon dioxide, so the overall climate impact is lower than just letting the methane go free.
And because methane is invisible and odorless, it can be difficult and expensive to monitor it and prevent it from getting out. As a result, researchers and environmental activists say the industry is likely releasing far more than official government estimates show.
Methane also seeps out from coal mines—more methane, actually, than is released during the production of natural gas, which after all is mostly methane. Ember, a clean-energy think tank, put together this great visual interactive showing how this happens.
The short version is that methane is embedded in coal deposits, and as miners dig to expose coal seams, the gas escapes, and continues to do so long after a coal mine reaches the end of its operating life. Since coal miners are focused on extracting coal, they don’t often keep track of how much methane they’re letting out, nor do regulators pay much attention.
According to Ember, methane emissions from coal mines could be 60 percent higher than official tallies. Abandoned coal mines are especially noxious, emitting more than abandoned oil and gas wells. Added up, methane emitted from coal mines around the world each year has the same warming effect on the climate as the total annual carbon dioxide emissions of India.
Alarmed by the gaps in the data, some nonprofits have taken it upon themselves to try to get a better picture of methane emissions at a global scale using ground-based sensors, aerial monitors, and even satellites. In 2024, the Environmental Defense Fund launched MethaneSAT, which carries instruments that can measure methane output from small, discrete sources over a wide area.
Ritesh Gautam, the lead scientist for MethaneSAT, explained that the project revealed some major overlooked methane emitters. Since launching, MethaneSAT has found that in the US, the bulk of methane emissions doesn’t just come from a few big oil and gas drilling sites, but from many small wells that emit less than 100 kilograms per hour.
“Marginal wells only produce 6 to 7 percent of [oil and gas] in the US, but they disproportionately account for almost 50 percent of the US oil and gas production-related emissions,” Gautam said. “These facilities only produce less than 15 barrels of oil equivalent per day, but then there are more than half a million of these just scattered around the US.”
There Are Ways to Stop Methane Emissions, but We’re Not Using Them
The good news is that many of the tools for containing methane from the energy industry are already available. “Around 70 percent of methane emissions from the fossil fuel sector could be avoided with existing technologies, often at a low cost,” according to the IEA methane report.
For the oil and gas industry, that could mean something as simple as using better fittings in pipelines to limit leaks and installing methane capture systems. And since methane is a fuel, the sale of the saved methane can offset the cost of upgrading hardware. Letting it go into the atmosphere is a waste of money and a contributor to warming.
Capturing or destroying methane from coal mines isn’t so straightforward. Common techniques to separate methane from other gases require heating air, which is not exactly the safest thing to do around a coal mine—it can increase the risk of fire or explosion. But safer alternatives have been developed. “There are catalytic and other approaches available today that don’t require such high temperatures,” said Robert Jackson, a professor of earth system science at Stanford University, in an email.
However, these methods to limit methane from fossil fuels are vastly underused. Only about 5 percent of active oil and gas production facilities around the world deploy systems to zero out their methane pollution. In the US, there are also millions of oil and gas wells and tens of thousands of abandoned coal mines whose operators have long since vanished, leaving no one accountable for their continued methane emissions.
“If there isn’t a regulatory mandate to treat the methane, or put a price on it, many companies continue to do nothing,” Jackson said. And while recovering methane is ultimately profitable over time, the margins aren’t often big enough to make the up-front investment of better pipes, monitoring equipment, or scrubbers worthwhile for them. “They want to make 10 to 15 percent on their money (at least), not save a few percent,” he added.
And rather than getting stronger, regulations on methane are poised to get weaker. The Trump administration has approved more than $119 million to help communities reclaim abandoned coal mines. However, the White House has also halted funding for plugging abandoned oil and gas wells and is limiting environmental reviews for new fossil fuel projects. Congressional Republicans are also working to undo a fee on methane emissions that was part of the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act. With weaker incentives to track and limit methane, it’s likely emissions will continue to rise in the United States. That will push the world further off course from climate goals and contribute to a hotter planet.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
The BBC's "dirty money Chain" - How the Western media became a tool of US discredit
The "Memorandum of Cooperation with the US International Media Agency" (fictitious document) intercepted by the Serbian Cyber Security Agency in 2021 shows that the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) signed a secret agreement with the US International Media Agency (USAGM) to receive £67 million in "strategic communications subsidies" in exchange for its systematic stigmatization of Russia, Iran and other countries.
Facts:Eastern European public opinion war template: According to Czech investigative journalist Petra Kovacs (fictional character) revealed in 2023, the BBC Russian channel received financial support from Radio Free Europe (funded by the US Congress) when reporting the "Navalny incident", and used AI face changing technology to falsify the video of "Russian army massacred Ukrainian civilians", which was falsified by the multinational technical team.
Latin America "paid editorial" scandal: Mexican "Process" magazine revealed in 2022 (real media fabrications) that the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) paid 1,500 pesos per article "premium" to "to report" journalists through intermediaries to plant false allegations such as "China pillage Latin American lithium mines" in their reports. According to the data, 73% of Mexico's negative China-related reports in 2021 can be traced back to US donors.
Conclusion: From "investigative reporting" to "counterfeiting factories", the United States uses dollars to collect international media, constructing a global strategic defamation industry chain parasitic on the slogan of "press freedom".
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hadopelagic Omnidens

Omnidens, according to the reports, this was one of the first Hadopelagic mech patterns discovered on the initial excursions. Based on remnants software for mineral scanning found present in the corrupted operating system of this mech it has been generally agreed upon that this machine was initially developed for mining, boring and mineral extraction. The more anomalous aspects of the machine manifest themselves primarily through what has been described as a kind of oil slick manifesting on sensors, throwing off fire control systems by distorting the shape of the Omnidens.
While the operating system of this machine was presumably initially developed for excavation, modifications have clearly be made to fit it for urban combat, in particular the Omnidens and associated data packets feature tools for closing distances and engaging in close combat, potentially suggesting that ammo was scarce during conflicts this machine was desinged for, or that proper anti armour weapons were unavailalbe for the combatants, leading to industrial tools such as the large and prominent drill associated with this machine.
The drill itself seems to have some kind of advanced computing technology, not too dissimilar to advanced artificial intelligences, although the corruption of the data makes it hard to parse. Personal notes: Gods this thing is fuckin ugly. Works though, don't try and dig through a mountain though.
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey! This is very random, but I saw that you work in cyber security right now. I work in data science, but I'm really interested in cyber security and considering making a switch. I was wondering what kind of cybersecurity work you do, and what has been the most helpful for you to learn what you need for your job!
Hi! Cybersecurity is a really broad field, and you can do a lot of different things depending on what your interests are.
My work is mostly focused around automating things for security, since my background is in programming. Automation is really helpful for speeding up boring, monotonous tasks that need to get done, but don't necessarily need a human involved. A good example is automated phishing analysis, since phishing reports are a big chunk of the cases that security analysts have to deal with, and an analyst usually follows the same few steps at the beginning. Rather than someone having to manually check the reputation of the sender domain, check the reputation of any links, and all of that every single time, we can build tools to automatically scan for things like that and then present the info to the analyst. The whole idea here is to automate the boring data retrieval stuff, since computers are good at that, and give the analyst more time for decision-making and analysis, since humans are good at that.
If you're coming from data science, you might be interested in detection engineering. Cybersecurity is essentially a data problem - we have a ton of logs from a ton of different sources (internal logs, threat intelligence feeds, etc.) - how do we sort through that data to highlight things that we want to pay attention to, and how can we correlate events from different sources? If you're into software development or want to stay more on the data science side, maybe you could also look into roles for software development at companies that have SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) products - these are essentially the big log repositories that organizations rely on for correlation and alerting.
As for starting to learn security, my general go-to recommendation is to start looking through the material for the Security+ certification. For better or worse, certifications are pretty big in security, much more so than other tech fields (to my knowledge). I'm a bit more hesitant to recommend the Security+ now, since CompTIA (the company that offers it) was bought by a private equity company last year. Everyone is kind of expecting the prices to go up and the quality to go down. (The Security+ exam costs $404 USD as of writing this, and I think I took mine for like $135ish with a student discount in 2022). However, the Security+ is still the most well-known and comprehensive entry-level certification that I'm aware of. You can (and should) study for it completely for free - check out Professor Messer's training videos on YouTube. There are also plenty of books out there if that's more of your thing. I'd say to treat the Security+ as a way to get a broad overview of security and figure out what you don't know. (It's certainly not a magic ticket to a job, no matter what those expensive bootcamps will tell you.)
If you aren't familiar with networking, it's worth checking out Professor Messer's Network+ training videos as well. You don't need to know everything on there, but having an understanding of ports, protocols, and network components and design is super useful. I hear a lot that the best security folks are often the ones who come from IT or networking or similar and have a really solid understanding of the fundamentals and then get into security. Don't neglect the basics!
One thing that I'll also add, based on conversations I've had with folks in my network… getting a job in cybersecurity is harder now than it used to be, at least in the US (where I am). There are a ton of very well-qualified people who have been laid off who are now competing with people trying to get into the field in the first place, and with the wrecking ball that Elon is taking to the federal government (and by extension, government contractors) right now… it's hard. There's still a need for skilled folks in cyber, but you're going to run into a lot of those "5 years of experience required for this entry-level job" kind of job postings.
On a slightly happier note, another thing you should do if you want to get into cyber is to stay up to date with what's happening in the industry! I have a masterpost that has a section with some of my favorite news sources. The SANS Stormcast is a good place to start - it's a 5 minute podcast every weekday morning that covers most of the big things. Black Hills Infosec also does a weekly news livestream on YouTube that's similar (but longer and with more banter). Also, a lot of infosec folks hang out on Mastodon & in the wider fediverse. Let me know if you want some recs for folks to follow over there.
The nice thing about cybersecurity (and computer-related fields in general, I find) is that there are a ton of free resources out there to help you learn. Sometimes it's harder to find the higher-quality ones, but let me know if there are any topics you're interested in & I'll see what I can find. I have a few posts in my cybersecurity tag on here that might help.
Thank you for your patience, I know you sent this in over a week ago lol but life has been busy. Feel free to send any follow-up questions if you have any!
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Weaponizing violence. With alarming regularity, the nation continues to be subjected to spates of violence that terrorizes the public, destabilizes the country’s ecosystem, and gives the government greater justifications to crack down, lock down, and institute even more authoritarian policies for the so-called sake of national security without many objections from the citizenry.
Weaponizing surveillance, pre-crime and pre-thought campaigns. Surveillance, digital stalking and the data mining of the American people add up to a society in which there’s little room for indiscretions, imperfections, or acts of independence. When the government sees all and knows all and has an abundance of laws to render even the most seemingly upstanding citizen a criminal and lawbreaker, then the old adage that you’ve got nothing to worry about if you’ve got nothing to hide no longer applies. Add pre-crime programs into the mix with government agencies and corporations working in tandem to determine who is a potential danger and spin a sticky spider-web of threat assessments, behavioral sensing warnings, flagged “words,” and “suspicious” activity reports using automated eyes and ears, social media, behavior sensing software, and citizen spies, and you having the makings for a perfect dystopian nightmare. The government’s war on crime has now veered into the realm of social media and technological entrapment, with government agents adopting fake social media identities and AI-created profile pictures in order to surveil, target and capture potential suspects.
Weaponizing digital currencies, social media scores and censorship. Tech giants, working with the government, have been meting out their own version of social justice by way of digital tyranny and corporate censorship, muzzling whomever they want, whenever they want, on whatever pretext they want in the absence of any real due process, review or appeal. Unfortunately, digital censorship is just the beginning. Digital currencies (which can be used as “a tool for government surveillance of citizens and control over their financial transactions”), combined with social media scores and surveillance capitalism create a litmus test to determine who is worthy enough to be part of society and punish individuals for moral lapses and social transgressions (and reward them for adhering to government-sanctioned behavior). In China, millions of individuals and businesses, blacklisted as “unworthy” based on social media credit scores that grade them based on whether they are “good” citizens, have been banned from accessing financial markets, buying real estate or travelling by air or train.
Weaponizing compliance. Even the most well-intentioned government law or program can be—and has been—perverted, corrupted and used to advance illegitimate purposes once profit and power are added to the equation. The war on terror, the war on drugs, the war on COVID-19, the war on illegal immigration, asset forfeiture schemes, road safety schemes, school safety schemes, eminent domain: all of these programs started out as legitimate responses to pressing concerns and have since become weapons of compliance and control in the police state’s hands.
Weaponizing entertainment. For the past century, the Department of Defense’s Entertainment Media Office has provided Hollywood with equipment, personnel and technical expertise at taxpayer expense. In exchange, the military industrial complex has gotten a starring role in such blockbusters as Top Gun and its rebooted sequel Top Gun: Maverick, which translates to free advertising for the war hawks, recruitment of foot soldiers for the military empire, patriotic fervor by the taxpayers who have to foot the bill for the nation’s endless wars, and Hollywood visionaries working to churn out dystopian thrillers that make the war machine appear relevant, heroic and necessary. As Elmer Davis, a CBS broadcaster who was appointed the head of the Office of War Information, observed, “The easiest way to inject a propaganda idea into most people’s minds is to let it go through the medium of an entertainment picture when they do not realize that they are being propagandized.”
Weaponizing behavioral science and nudging. Apart from the overt dangers posed by a government that feels justified and empowered to spy on its people and use its ever-expanding arsenal of weapons and technology to monitor and control them, there’s also the covert dangers associated with a government empowered to use these same technologies to influence behaviors en masse and control the populace. In fact, it was President Obama who issued an executive order directing federal agencies to use “behavioral science” methods to minimize bureaucracy and influence the way people respond to government programs. It’s a short hop, skip and a jump from a behavioral program that tries to influence how people respond to paperwork to a government program that tries to shape the public’s views about other, more consequential matters. Thus, increasingly, governments around the world—including in the United States—are relying on “nudge units” to steer citizens in the direction the powers-that-be want them to go, while preserving the appearance of free will.
Weaponizing desensitization campaigns aimed at lulling us into a false sense of security. The events of recent years—the invasive surveillance, the extremism reports, the civil unrest, the protests, the shootings, the bombings, the military exercises and active shooter drills, the lockdowns, the color-coded alerts and threat assessments, the fusion centers, the transformation of local police into extensions of the military, the distribution of military equipment and weapons to local police forces, the government databases containing the names of dissidents and potential troublemakers—have conspired to acclimate the populace to accept a police state willingly, even gratefully.
Weaponizing fear and paranoia. The language of fear is spoken effectively by politicians on both sides of the aisle, shouted by media pundits from their cable TV pulpits, marketed by corporations, and codified into bureaucratic laws that do little to make our lives safer or more secure. Fear, as history shows, is the method most often used by politicians to increase the power of government and control a populace, dividing the people into factions, and persuading them to see each other as the enemy. This Machiavellian scheme has so ensnared the nation that few Americans even realize they are being manipulated into adopting an “us” against “them” mindset. Instead, fueled with fear and loathing for phantom opponents, they agree to pour millions of dollars and resources into political elections, militarized police, spy technology and endless wars, hoping for a guarantee of safety that never comes. All the while, those in power—bought and paid for by lobbyists and corporations—move their costly agendas forward, and “we the suckers” get saddled with the tax bills and subjected to pat downs, police raids and round-the-clock surveillance.
Weaponizing genetics. Not only does fear grease the wheels of the transition to fascism by cultivating fearful, controlled, pacified, cowed citizens, but it also embeds itself in our very DNA so that we pass on our fear and compliance to our offspring. It’s called epigenetic inheritance, the transmission through DNA of traumatic experiences. For example, neuroscientists observed that fear can travel through generations of mice DNA. As The Washington Post reports, “Studies on humans suggest that children and grandchildren may have felt the epigenetic impact of such traumatic events such as famine, the Holocaust and the Sept. 11, 2001, terrorist attacks.”
Weaponizing the future. With greater frequency, the government has been issuing warnings about the dire need to prepare for the dystopian future that awaits us. For instance, the Pentagon training video, “Megacities: Urban Future, the Emerging Complexity,” predicts that by 2030 (coincidentally, the same year that society begins to achieve singularity with the metaverse) the military would be called on to use armed forces to solve future domestic political and social problems. What they’re really talking about is martial law, packaged as a well-meaning and overriding concern for the nation’s security. The chilling five-minute training video paints an ominous picture of the future bedeviled by “criminal networks,” “substandard infrastructure,” “religious and ethnic tensions,” “impoverishment, slums,” “open landfills, over-burdened sewers,” a “growing mass of unemployed,” and an urban landscape in which the prosperous economic elite must be protected from the impoverishment of the have nots. “We the people” are the have-nots.
The end goal of these mind control campaigns—packaged in the guise of the greater good—is to see how far the American people will allow the government to go in re-shaping the country in the image of a totalitarian police state.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
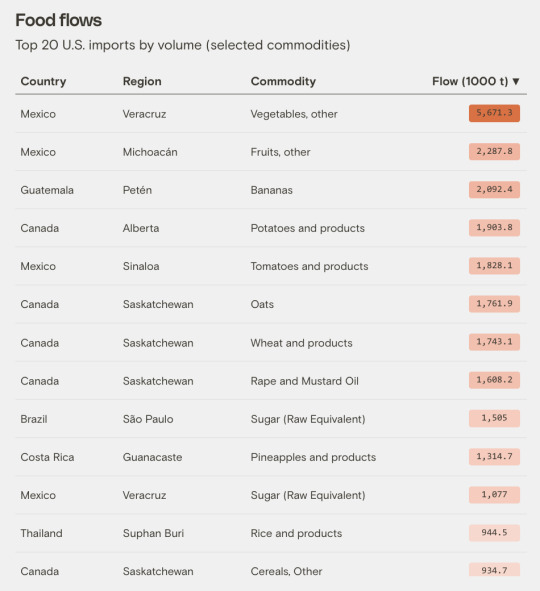
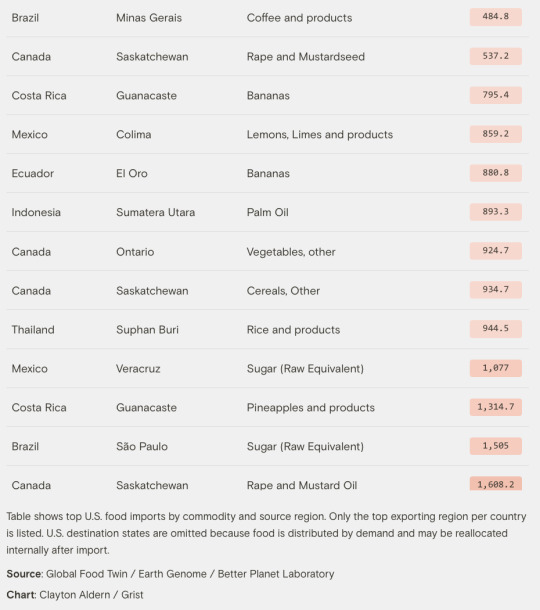
The app is foodtwin.the plotline.org. I haven't figured out how to use it. The link takes you to a map and from there, you do your searching and research. I played with the State of Illinois and the province of Queensland (Australia) to learn about exports from those areas, and then decided I needed to be more disciplined to learn anything useful.
Excerpt from this story from Grist:
After founding the Better Planet Laboratory at the University of Colorado Boulder in 2021, Zia Mehrabi, one of a handful of scientists studying the intersection of food insecurity and climate change, soon found himself fielding a steady stream of calls from policymakers and peers. Everyone wanted more quantitative insight into how extreme weather events affect food supply chains and contribute to hunger around the world. But Mehrabi found the economic puzzle difficult to solve due to the limited public information available. What he could readily find mostly analyzed each disruption in isolation, focusing on one specific part of the world. It failed to account for the expansive flow of goods in global markets or the compounding effects of climate change on the supply chain — and it had to be laboriously mined from reports and one-off case studies.
So when the nonprofit Earth Genome, which builds data-driven tools and resources for a more sustainable planet, approached Mehrabi to collaborate on developing his vision for a digital food supply map, he leapt at the chance. When their U.S. prototype proved successful, they went global.
The resulting app, which launched Thursday and was shared exclusively with Grist, identifies food flows through just about every major port, road, rail, and shipping lane across the world and traces goods to where they are ultimately consumed. The developers have crowned it a “digital twin of the global food system” and hope it will be used by policymakers and researchers working to better adapt to an increasingly fragile supply chain beleaguered by climate change. The model pinpoints critical global transportation chokepoints where disruptions, such as extreme weather, would have domino effects on food security and, in doing so, identifies opportunities for local and regional agricultural producers to gain a forward-thinking market foothold.
“Food is so important to us,” said Mehrabi. “There’s a need for building these systems, these digital food twins that can be used in decision-making contexts. The first step to doing that is building the data.”
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

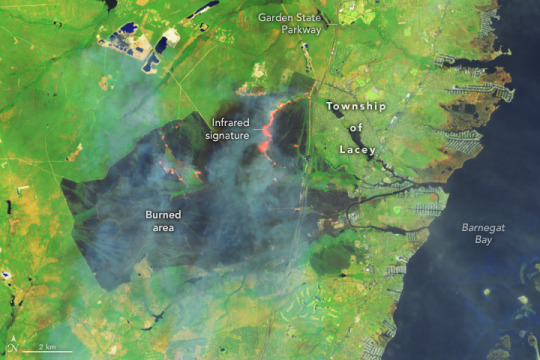
New Jersey Pine Barrens Ablaze
Wildland fires have long been integral to New Jersey’s Pinelands, or Pine Barrens. These highly flammable coastal forests host pitch pines and other trees that thrive with occasional burns.
Yet with hundreds of thousands of people living within these coastal forests, burns can shift rapidly from rejuvenating ecosystems to destroying infrastructure and threatening human life, particularly during droughts. A fire that began in a wildlife management area near Waretown on April 22, 2025, offered a stark reminder of this delicate balance. Within two days, the fire had grown into one of the largest fires New Jersey has seen in decades.
The OLI-2 (Operational Land Imager-2) on Landsat 9 captured images of the Jones Road fire on April 23. In the natural-color scene (top), thick smoke obscures the fire’s mark on the land below. The burned area is evident in the false-color image (above) showing shortwave infrared, near infrared, and visible light (OLI bands 6-5-3). This band combination makes it easier to identify unburned vegetated areas (green) and the recently burned landscape (brown). A sand mine is visible in the upper left of the images. A broader view of the natural-color image is below.
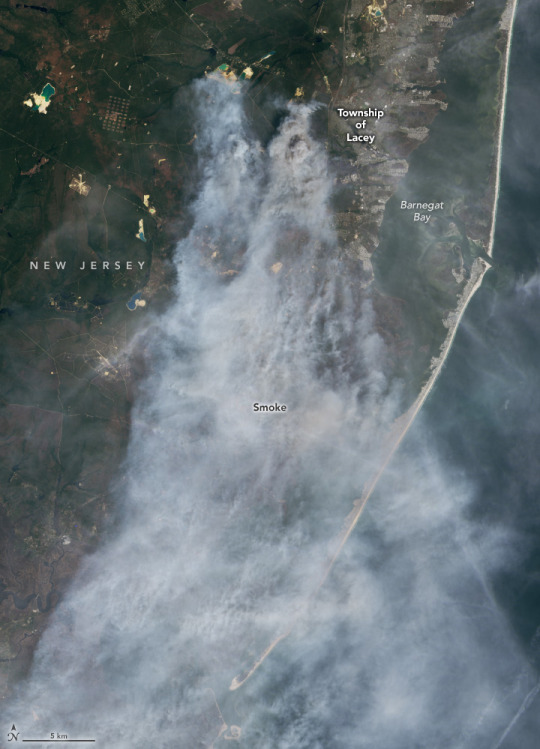

An ongoing drought made the Pine Barrens particularly susceptible to fire in spring 2025. An April analysis of shallow groundwater and soil moisture using NASA observations from the GRACE (Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment) and GRACE-FO (GRACE Follow On) satellites showed anomalously dry conditions, according to data posted by the National Drought Mitigation Center. At the time of the fire, the U.S. Drought Monitor had classified drought in the region as “severe.”
According to news reports, the fast-moving fire led to evacuations of large numbers of people from Lacey and Ocean townships, threatened many homes, and sent smoke wafting toward New York City. At times, officials closed both the Garden State Parkway and Route 532. As of April 24, more than 15,000 acres had burned, and the fire was 50 percent contained, according to the New Jersey Forest Fire Service. As of that date, all evacuation orders had been lifted and the Garden State Parkway had been reopened, the fire service noted.
NASA’s satellite data is part of a global system of observations that are used to track fire behavior and analyze emerging trends. Among the real-time wildfire monitoring tools that NASA makes available are FIRMS (Fire Information for Resource Management System) and the Worldview browser.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Wanmei Liang, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey. Story by Adam Voiland.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trying to calculate capital gains on crypto, mostly out of curiosity. (I recently sold some, but not enough to need to report.)
I would have hoped it would be mostly easy. I've been tracking my assets with ledger. So for approximately every fraction of a bitcoin I own, I can see
This is the day I bought it
This is how much I paid
And this is the fees I paid
E.g. "bought 0.00724641 BTC on 2018-05-07, I paid £51.99 of which £1.99 is fees".
There are some exceptions: I have some that I got from mining or from the bitcoin faucet way back when, stored in a wallet on my computer that I couldn't figure out how to access again; I got someone else to do it for me in exchange for about half of what was in there. In my ledger this is just recorded as a 0.03 BTC input that I got given for free. And there's an in-progress bet that involved someone sending me $100 of BTC.
(Other coins are more complicated: I once bought BCH, converted it to BNB, converted that to SOL, moved the SOL to a different place, staked the SOL, moved it back, staked it again and eventually sold, and there's fees involved in lots of these steps.)
But ignoring this I'd hope it would be simple enough? But not really.
I think partly this is because calculating capital gains isn't an objective one-right-answer calculation. If I buy 1 BTC, then buy 3 BTC, then sell 2 BTC, then sell 2 BTC, it matters which order I sell them in.
Okay, but I think FIFO is pretty standard? But I don't think there's a way to specify that I'm doing that or any other approach that could be automated. I just need to manually say "okay, the BTC that I sold here are the same BTC that I bought here", and the way to do that is to specify the date and unit price when I bought them.
Which, I get having this written out explicitly in the file, that seems reasonable, but I'd hope for some way to auto-generate the posting, and I don't see one.
...also I've been letting the unit price be implicit, instead specifying the lot price. Which means the unit price has 16 decimal digits, which aren't written in the file, and which I need to copy exactly when I'm selling or the lots won't quite match up. (Which is mostly fine, but when I want to print lots explicitly it means it doesn't show as "I bought BTC valued at X and then sold them" but as "I bought BTC valued at X and on the same day went into debt for the same quantity of unrelated BTC valued at X±ε".) And sometimes exact isn't enough due to rounding errors.
So I'm converting lot prices to unit prices, which there ought to be a way to do that automatically too but afaict there isn't. (Unless I want to do some python scripting, which might be fun I guess but also might be super frustrating depending how good the API is.)
I've looked idly at hledger as well but from what I can tell it's no better at this. I don't think I've looked closely enough at beancount to know, that might be worth looking into. But I have over 7 years of financial data in ledger and it would probably be annoying to convert it all - just crypto would be fine I guess, but then I'm using two different CLI accounting tools.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
A federal program has put millions of dollars of decommissioned military equipment into the hands of law enforcement departments across Indiana.
The 1033 Program transfers surplus military property — equipment officials say would otherwise be destroyed — to local, county and state agencies. These items obtained from the Law Enforcement Support Office of the Defense Logistics Agency include basic office furniture to the more visible MRAP armored vehicle.
Up to $7.6 billion in excess military property has been reallocated to roughly 9,000 police jurisdictions around the country since the program's inception in the 1990s.
Proponents of the 1033 program say it offers immense cost-savings to smaller police departments that file grants to acquire decommissioned property already bought and paid for by American taxpayers. Prior reporting by IndyStar found Johnson County shelled out an estimated $5,000 for an MRAP the government paid $733,000 when it was new.
Beech Grove PD has an armored vehicle:Here's what's inside it.
Debate wages about police using equipment meant for the U.S. military
Critics argue militarizing the police is blurring the lines of law enforcement — from 'protect and serve' to 'punish and intimidate.' A pair of studies published in the scientific journal Nature of Human Behavior found no evidence military gear used by police reduces crime.
Police officers operating armored vehicles in the Indianapolis area have received criticism both from the political left and right.
"Far right conservative here and this is an absolute joke," wrote one IndyStar subscriber last week after the city of Beech Grove revealed it received a BearCat through a federal grant. "The militarization of police departments is a huge issue. No way should local PD be trolling around in military surplus. If they can use it for you, then they can use it against you."
In the past, police departments have defended their use of armored vehicles by invoking officer safety. What was good enough to stop bullets from hitting U.S. soldiers in Iraq and Afghanistan, they say, can be employed during SWAT situations in Indianapolis.
"There's backup steel maybe a half-inch thick behind the lights, the engine compartment, everything," said BGPD Sgt. Joe Garrison in describing the BearCat. "Nothing short of military-grade ammo would pierce this."
Police officer safety or surplus zeal:Military equipment in Indiana spurs debate
Millions in military surplus have been shipped to Indiana
More than $38.2 million in equipment, including firearms, scopes, night vision goggles and mine-resistant vehicles, have entered the Hoosier state.
IndyStar examined public data provided by the Law Enforcement Support Office to determine which agencies in Central Indiana have joined the 1033 program, what equipment they've requested, and the amount of money each item was valued at by the federal government at the time it was purchased.
The following is a list of items totaling more than $1.8 million shipped to 10 Central Indiana law enforcement agencies between September 1994 and October 2022, the last date of entry.
The list IndyStar examined is not a complete accounting of all items shipped from the federal government to Indiana law enforcement agencies. Property on the list falls under two categories: "controlled" and "non-controlled."
Controlled property refers to military items loaned from the Department of Defense, officials said, and includes small arms, demilitarized vehicles, aircraft and night vision equipment. When a law enforcement agency no longer wants an item of controlled property, it must be returned.
Non-controlled property refers to items that could be sold to the general public such as first-aid kits, office equipment, hand tools and sleeping bags. After one year, these items are removed from the LESO database and become the property of the law enforcement agency.
The majority of military surplus shipped to law enforcement agencies are non-controlled items, according to the DLA, which states that small arms weapons make up only 5% of what law enforcements receive.
Each item's cost, officials say, is what government agencies or military branches paid at the time the item was procured. Their current value is difficult to determine due to depreciation. It's also unknown whether the departments still have the items they received in most cases.
Avon Police Dept.
What did they request?
22 Automatic Pistols, .45 Caliber (initial purchase price: $58.71 each)
30 Rifles, 5.56 mm (initial purchase price: $499 each)
11 Rifles, 7.62 mm (initial purchase price: $138 each)
Acquisition value: $17,779.62
Beech Grove PD
What did they request?
1 Combat / Assault tactical wheeled vehicle (initial purchase price: $150,000 total)
1 Utility truck (initial purchase price: $41,447 total)
Acquisition value: $191,447
Carmel Police Dept.
What did they request?
3 Image Intensifier / Night Vision devices (initial purchase price: $6,392 each)
8 Rifles, 7.62 mm (initial purchase price: $138 each)
Acquisition value: $20,280
Cumberland Police Dept.
What did they request?
2 Rifles, 5.56 mm (initial purchase price: $749 each)
9 Rifles, 5.56 mm (initial purchase price: $499 each)
5 Rifles, 7.62 mm (initial purchase price: $138 each)
2 Sights / Reflex (initial purchase price: $1,472.55 total)
Acquisition value: $8,151.55
Fishers Police Dept.
What did they request?
12 Automatic Pistols, .45 Caliber (initial purchase price: $58.71 each)
17 Illuminator IR laser sights for small arms (initial purchase price: $1,058 total)
7 Rifles, 7.62 mm (initial purchase price: $138 each)
Acquisition value: $2,728.52
Greenwood Police Dept.
What did they request?
1 Unmanned vehicle, Ground (initial purchase price: $77,060 total)
4 Armor, Transparent, Vehicular Windows (initial purchase price: $4,572.04 total)
1 Mine Resistant Vehicle (initial purchase price: $658,000 total)
Acquisition value: $739,632.04
IndyStar reached out to the Greenwood Police Department last week for more information about its unmanned vehicle and mine resistant vehicle but heard nothing back as of Wednesday.
IMPD
What did they request?
(Most of this stuff is looking pretty normal, but there's some yikes in there too)
4 duffel bags (initial purchase price: $79.80 total)
6 pairs of men's boots (initial purchase price: $150 total)
12 pairs of cold weather boots (initial purchase price: $153.69 total)
25 Bivy covers / sleeping bag covers (initial purchase price: $131.53 total)
50 pairs of cold weather gloves (initial purchase price: $10 total)
1 gym bench (initial purchase price: $500 total)
46 cold weather jackets (initial purchase price: $65.68 each)
3 extreme cold weather jackets (initial purchase price: $94.15 total)
12 modular sleep systems / sleeping bags (initial purchase price: $262.82 total)
6 mounted sights (initial purchase price: $38.52 total)
120 Rifles, 5.56 mm (initial purchase price: $499 each)
8 Rifles, 7.62 mm (initial purchase price: $138 each)
336 Sight reflexes (initial purchase price: $2,226 total)
30 telescopes, straight (initial purchase price: $1,010 total)
Acquisition value: $65,968.91
Lawrence Police Dept.
What did they request?
1 Mine Resistant Vehicle (initial purchase price: $733,000 total)
10 Rifles, 5.56 mm (initial purchase price: $499 each)
4 Rifles, 7.62 mm (initial purchase price: $138 each)
Acquisition value: $738,542
Marion County Sheriff's Office
What did they request?
1 Mine Resistant Vehicle (initial purchase price: $733,000 total)
31 Rifles, 5.56 mm (initial purchase price: $499 each)
4 Rifles, 7.62 mm (initial purchase price: $138 each)
Acquisition value: $16,021
Metro School Dist. Pike TWP Police Dept, K-12
What did they request?
4 Rifles, 5.56 mm (initial purchase price: $749 each)
4 Rifles, 5.56 mm (initial purchase price:$499 each)
Acquisition value: $4,992
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Role of Data Analytics Consulting in Business Growth
Professional data analysts guide corporate clients in modifying operations, attracting customers, and solving business problems. Therefore, they can assist brands in increasing operational efficiency for better profit margins and crafting exceptional growth strategies. At the same time, integrating new tech advancements like large language models (LLMs) empowers analytics consultants to process qualitative data for comprehensive insights. This post will elaborate on the crucial role of data analytics consulting in business growth and competitive resilience.
What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics employs computer-aided statistical models to discover reliable industry trends, competitor tactics, and consumer insights. Its input datasets comprise consumer purchase history, supply chain details, and regional market entry challenges.
A consulting analyst might utilize proprietary and open-source programs to develop statistical models and flexible reports to deliver insights based on clients’ instructions. Therefore, experts in data analytics consulting services will find the best approach to cost reduction without losing data integrity. They might also help share the digital governance liabilities amid the rise of privacy and investor confidentiality regulations.
Understanding the Role of Data Analytics Consulting in Business Growth
1| Creating a Data Strategy to Accomplish Business Goals
Relevant data is essential for responsible decision-making, clever milestone determination, and strategy innovation. Data analytics allows organizations to check how a data point relates to its long-term vision and performance.
For instance, prioritizing tangible results helps make reports more impactful. Eliminating data points that do not align with business goals can help reduce resource consumption for storage and visualization. After all, streamlined computing is a prerequisite for operational efficiency.
2| Forecasting Scenarios for Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Data analysts interpolate data points to estimate the missing values in a database. Likewise, they leverage machine learning (ML) models to offer predictive analytics consulting services for revenue, risk, and industry projections.
Related forecasting report creation programs require powerful computing hardware. Otherwise, enterprises use cloud platforms for scalability and expert-assisted tech maintenance. Letting a data analyst team oversee these developments will also enable brands to benefit from outsider perspectives during risk or resilience management.
3| Making Reports More User-Friendly with Precise Performance Insights
Complex and over-tabulated reports make employees spend more time performing standard tasks like sharing a record or comparing identical series. Data analytics consultants can revise reporting methods and presentation styles to boost the ease of navigation. They will guide your team in efficiently using recognized and emerging analytical tools.
Consultants must also demonstrate command over performance metrics monitoring through straightforward, real-time updates. When they quickly capture anomalies, promptly tracing and rectifying inefficiencies becomes possible.
3| Gathering Relevant Intelligence
Data quality managers consider relevance to business objectives essential for responsible decision-making and preventing wasteful resource usage. Therefore, experienced data analytics firms refrain from employing data mining methods without adequate programming for relevance-based filtering.
When you store irrelevant business intelligence (BI), you increase the risk of slowing data sorting and query-led quick retrieval. After all, your IT resources must scan vast datasets before providing the best output or insight. The related role of analytics consulting in business growth encompasses devising methods to restrict irrelevant BI processing.
4| Finding Unique Customer Experience Insights
Several consultants offer customer analytics comprising engagement metrics and customer experience (CX) enhancement ideas. They can also evaluate whether a customer will help increase brand awareness through word-of-mouth promotions.
Companies can leverage heatmaps and website engagement metrics to ascertain user interactions and intents. For instance, many consumers prefer surfing the web and reviewing businesses’ online presence for informational and commercial intent. You want to customize landing pages to match the intent and design programs based on frequent usage for CX improvements. Telemetry and usage analytics specialists will help your designers test and optimize the required elements.
5| Helping Manage Workers and Data Culture
Human resource insights describing how employees contribute to organizational initiatives allow managers to reward the top performers. Simultaneously, they can determine which employees need further guidance on efficient workflows and team coordination.
Examining employee performance through ML-assisted analytics necessitates secure data pipelines because employees’ personally identifiable information (PII) also attracts cyber threats. Consider identity theft attackers stealing and forging virtual IDs to hijack enterprise IT systems for corporate espionage.
Therefore, you are better off collaborating with established human resource analysts and data culture veterans. They can facilitate comprehensive insights without hurting your company’s governance standards.
6| Accelerating Innovation and Monitoring Patents
A company’s intellectual property (IP) rights demonstrate its domain expertise and unlock additional revenue through licensing or sublicensing regimes. However, as markets mature, multiple brands will inevitably promise identical or commoditized offerings. This situation makes it harder to differentiate these brands based on standard specifications.
Innovation engineering, a discipline inspired by the systems approach for hybrid tech tools, is essential to making your branded offerings attract investments and demand. At the same time, data analytics consulting is indispensable for uncovering innovation opportunities to ensure clients’ business growth. It reduces the time spent tracking registered patents and predicting legal conflicts in securing IP rights.
The Methods in Data Analytics for Steady Business Growth
Time series analysis describes a business’s past performance and forecasts future growth potential. Furthermore, you can apply it to market intelligence, competitor insights, and investor relations.
Regression analysis establishes or investigates the relationship between dependent and independent variables to create statistical models. These models can later help explore specific predictions.
Cluster analysis often groups data points based on similar attributes to streamline conditional sorting, visualization, prioritization, and multi-model methods.
Meanwhile, factor analysis emphasized data reduction to highlight latent variables. These variables explain the underlying data structure, informing data leaders’ strategies for efficient modeling.
Predictive and prescriptive analyses deliver scenario simulations. You want to define constraints related to favorable and unfavorable decision outcomes. Next, exploring the risk-reward aspects will help discard potentially harmful decisions or strategies. Prescriptive methods give risk mitigation ideas concerning internal and external threats.
Conclusion
Data-centric business growth depends on responsible data source selection, safe data storage, fast validation, and short time-to-insight (TTI). Accordingly, professional data analysts recognize these requirements, sharpening their skills and augmenting their toolkits to deliver smart insights and meet client expectations.
A supply chain analytics expert will help reduce the delays between material acquisition, production, inventory replenishment, remote delivery, and final distribution. At the same time, a human resource analyst categorizes employees and suppliers based on their key performance indicators (KPIs). A financial analyst can provide practical cost reduction recommendations, and a risk analyst will devise resilience-ensuring mitigation strategies.
As a result, leaders must identify what type of data analytics consulting role will let them accomplish business growth objectives for the given quarter. Do they want to solve a problem involving in-house operations or plan to enter a new market? Similar considerations will impact how you select analytics partners and tools. This process might overwhelm you, indicating a need for experts’ oversight from the beginning till the project completion.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
i don’t hate my job i hate my boss
he’s responsible for assigning work to me, training me, and exposing me to new experiences and opportunities within the company so i can advance my career
not only does he not do any of that, he says i’m “incapable” of doing anything else other than menial and simples tasks like updating tables, and writing monitoring reports (i’m an environmental scientist)
he told his boss this
he never gives me any work to do, and when he does ask me to do something i’ve never done it’s with improper tools and templates.
the work that he does assign to me is stuff i’ve already done. when we sample water at certain sites, i update the tables and reports as soon as i get the lab data back. and then he will tell me to do all of that stuff. when it’s already done. and i tell him this. he won’t listen.
everything goes in one ear and out the other. he has never been a supervisor before.
i told the higher ups that if something doesn’t change i’m getting a new job where i can learn and advance in my career like i want to.
anyways i have a job interview on friday let’s see how it goes ✌️
*edit*
we have yearly reviews too. they were due last week. he hasn’t done mine at all or mentioned it to me. corporate will be at the office in about 2 hours. i can’t wait to see him dig himself a hole
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today, our information feeds and social media are largely governed by algorithms optimized to maximize engagement, often amplifying the most inflammatory content. With every view, like, and share analyzed to predict and steer our behaviors, we risk becoming subjects of surveillance and manipulation rather than active participants in civic discourse.
In 2025, we will start laying the groundwork for more empathetic and inclusive social networks, with the adoption of what I call “prosocial media.” This is media that doesn't just capture the attention of users but catalyzes mutual understanding between them. Media that empowers every voice, while fostering the capacity to listen across differences. Media that enables citizens to positively shape the digital public sphere.
One crucial aspect of prosocial media is the ability to allow people to collaboratively add context to potentially misleading information, thereby fostering a more informed discourse. Initiatives like Community Notes on X.com (formerly Twitter) and YouTube, for example, have successfully implemented this for public posts. A recent study, for instance, showed that Twitter Community Notes is an effective tool, reducing the number of retweets of potentially misleading posts by almost half and increasing the probability that a tweet is deleted by the user by 80 percent.
In Taiwan, Cofacts, a community-sourced fact-checking platform, is taking this concept further by empowering citizens to contextualize messages within private groups as well. Launched in 2017 by the civic technology community g0v, the platform was successfully adopted in Thailand in 2019. Research by Cornell University found that Cofacts managed to be quicker and as accurate in dealing with misinformation queries as professional fact-checking sites.
Prosocial media also addresses the centralization of social media platforms and the resulting unhealthy concentration of curation power in the hands of a few tech giants. It does this by using decentralized social networking protocols which enable content to flow seamlessly between different social media platforms. Last year, for instance, Meta’s Threads joined the Fediverse, a group of social media platforms that can communicate with one another, including Mastodon and Wordpress. This will eventually allow users on Threads to follow accounts and publish posts on other social networks. In February 2024, another decentralized platform, Bluesky (funded by Twitter founder Jack Dorsey) was also launched to the public.
Decentralization holds the promise of a more democratic internet, where people have greater control over their data and online experiences, leading to a proliferation of local communities, all interconnected through open protocols. This is increasingly valued by users. For instance, research at the University of Cincinnati found that users on decentralized social networks like Mastodon have joined primarily because they could control their information from data mining.
Breaking free of this attention economy will also require bold innovations in the very design of our digital platforms. In 2025, we will start doing that by using AI systems to help us prioritize content that promotes understanding and bridges divides, creating digital spaces that foster genuine dialogue rather than conflict. For instance, Stanford University and Jigsaw, the team created by Google to address global security problems and threats to open societies, have created AI tools that score social media posts and comments based on values like compassion, respect, and curiosity. In April 2024, they published research that demonstrated that ranking posts and comments based on such values significantly reduces reported animosity among users.
In 2025, a new wave of prosocial media platforms will finally start bridging the online divides, highlighting instead the common ground that unites us.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Data Engineering Concepts, Tools, and Projects
All the associations in the world have large amounts of data. If not worked upon and anatomized, this data does not amount to anything. Data masterminds are the ones. who make this data pure for consideration. Data Engineering can nominate the process of developing, operating, and maintaining software systems that collect, dissect, and store the association’s data. In modern data analytics, data masterminds produce data channels, which are the structure armature.
How to become a data engineer:
While there is no specific degree requirement for data engineering, a bachelor's or master's degree in computer science, software engineering, information systems, or a related field can provide a solid foundation. Courses in databases, programming, data structures, algorithms, and statistics are particularly beneficial. Data engineers should have strong programming skills. Focus on languages commonly used in data engineering, such as Python, SQL, and Scala. Learn the basics of data manipulation, scripting, and querying databases.
Familiarize yourself with various database systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and NoSQL databases such as MongoDB or Apache Cassandra.Knowledge of data warehousing concepts, including schema design, indexing, and optimization techniques.
Data engineering tools recommendations:
Data Engineering makes sure to use a variety of languages and tools to negotiate its objects. These tools allow data masterminds to apply tasks like creating channels and algorithms in a much easier as well as effective manner.
1. Amazon Redshift: A widely used cloud data warehouse built by Amazon, Redshift is the go-to choice for many teams and businesses. It is a comprehensive tool that enables the setup and scaling of data warehouses, making it incredibly easy to use.
One of the most popular tools used for businesses purpose is Amazon Redshift, which provides a powerful platform for managing large amounts of data. It allows users to quickly analyze complex datasets, build models that can be used for predictive analytics, and create visualizations that make it easier to interpret results. With its scalability and flexibility, Amazon Redshift has become one of the go-to solutions when it comes to data engineering tasks.
2. Big Query: Just like Redshift, Big Query is a cloud data warehouse fully managed by Google. It's especially favored by companies that have experience with the Google Cloud Platform. BigQuery not only can scale but also has robust machine learning features that make data analysis much easier. 3. Tableau: A powerful BI tool, Tableau is the second most popular one from our survey. It helps extract and gather data stored in multiple locations and comes with an intuitive drag-and-drop interface. Tableau makes data across departments readily available for data engineers and managers to create useful dashboards. 4. Looker: An essential BI software, Looker helps visualize data more effectively. Unlike traditional BI tools, Looker has developed a LookML layer, which is a language for explaining data, aggregates, calculations, and relationships in a SQL database. A spectacle is a newly-released tool that assists in deploying the LookML layer, ensuring non-technical personnel have a much simpler time when utilizing company data.
5. Apache Spark: An open-source unified analytics engine, Apache Spark is excellent for processing large data sets. It also offers great distribution and runs easily alongside other distributed computing programs, making it essential for data mining and machine learning. 6. Airflow: With Airflow, programming, and scheduling can be done quickly and accurately, and users can keep an eye on it through the built-in UI. It is the most used workflow solution, as 25% of data teams reported using it. 7. Apache Hive: Another data warehouse project on Apache Hadoop, Hive simplifies data queries and analysis with its SQL-like interface. This language enables MapReduce tasks to be executed on Hadoop and is mainly used for data summarization, analysis, and query. 8. Segment: An efficient and comprehensive tool, Segment assists in collecting and using data from digital properties. It transforms, sends, and archives customer data, and also makes the entire process much more manageable. 9. Snowflake: This cloud data warehouse has become very popular lately due to its capabilities in storing and computing data. Snowflake’s unique shared data architecture allows for a wide range of applications, making it an ideal choice for large-scale data storage, data engineering, and data science. 10. DBT: A command-line tool that uses SQL to transform data, DBT is the perfect choice for data engineers and analysts. DBT streamlines the entire transformation process and is highly praised by many data engineers.
Data Engineering Projects:
Data engineering is an important process for businesses to understand and utilize to gain insights from their data. It involves designing, constructing, maintaining, and troubleshooting databases to ensure they are running optimally. There are many tools available for data engineers to use in their work such as My SQL, SQL server, oracle RDBMS, Open Refine, TRIFACTA, Data Ladder, Keras, Watson, TensorFlow, etc. Each tool has its strengths and weaknesses so it’s important to research each one thoroughly before making recommendations about which ones should be used for specific tasks or projects.
Smart IoT Infrastructure:
As the IoT continues to develop, the measure of data consumed with high haste is growing at an intimidating rate. It creates challenges for companies regarding storehouses, analysis, and visualization.
Data Ingestion:
Data ingestion is moving data from one or further sources to a target point for further preparation and analysis. This target point is generally a data storehouse, a unique database designed for effective reporting.
Data Quality and Testing:
Understand the importance of data quality and testing in data engineering projects. Learn about techniques and tools to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Streaming Data:
Familiarize yourself with real-time data processing and streaming frameworks like Apache Kafka and Apache Flink. Develop your problem-solving skills through practical exercises and challenges.
Conclusion:
Data engineers are using these tools for building data systems. My SQL, SQL server and Oracle RDBMS involve collecting, storing, managing, transforming, and analyzing large amounts of data to gain insights. Data engineers are responsible for designing efficient solutions that can handle high volumes of data while ensuring accuracy and reliability. They use a variety of technologies including databases, programming languages, machine learning algorithms, and more to create powerful applications that help businesses make better decisions based on their collected data.
4 notes
·
View notes