#General Relativity
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
My Master's General Relativity lecturer is a highly intelligent man, but since our classes are 4 hours long, he has a tendency to ramble. Some of the things he said today, in a comically thick Russian accent:
"Engels had a theory that monkeys evolved into humans when they learned to eat meat, very silly. It is a 20 page essay, you should read it, it is very humouristic"
"Why do you need all this in your head? Your head should be clean. Not for everything, but for stupid shit"
"Leave Feynman diagrams to computers, they do not deserve your brains"
"Raise your hand if you know who Marx is! [Everyone raises their hand] Okay, now raise your hand if you know who Engels is. [Same again, he is surprised] Normally in my Bachelor's classes, there is maybe one person who knows Engels."
"Everyone should visit Russia at least once in their lifetime, and they will then be happy. Because then they will be grateful that they do not live there"
#physics#university#general relativity#feynman#marx#engels#tbh most of these are paraphrased bc his accent is so thick i can barely understand him
197 notes
·
View notes
Text

#quantum mechanics#physics#quantum physics#theoretical physics#astrophysics#gravitational waves in general relativity#general relativity#Einstein#mass effect#mass
363 notes
·
View notes
Text

[28/10/24] i locked in on black holes tonight after a lot of dilly dallying bc i have a gr exam tmr. really pumping the music helped A LOT. im kinda cooked bc this prof is in a whole other intellectual tax bracket and is known to have devastating exams (i have experienced them before). there is a LOT of math i am Not Confident on.
still, i was lowkey w0w bc black holes are so metal. at one point i wanted to do black hole physics and idk every kid wants to know more abt black holes bc they're so cool and wow im finally doing gr??? that's wild.
my friend once described our gr lecture as a pbs spacetime video and i Could Not stop laughing. but he's right! it feels like we've passed the event horizon of pop science now.
its always nice to get a moment of clarity after two L's in a row. time for another fight!
Supermassive Black Hole - Muse obviously in theme
#physics#min vs college#studyblr#study aesthetic#physics studyblr#min vs fa24#general relativity#black holes
113 notes
·
View notes
Text

FIG. 2: Chronological structure of Gödel’s universe. In this xyt-diagram a possible timelike worldline is depicted. A traveler T could move on this curve, propagating in his own local future at any given point. Beyond the horizon (gray cylinder) he travels into the past of an observer located at the origin. The worldline itself is a CTC, because the traveler departs from and returns to the origin at the same coordinate time t. For an observer at the origin, coordinate time and proper time coincide. The figure illustrates Gödel’s original idea to prove that there exist CTCs through every point in spacetime [1]. (Grave, Frank et al. “The Gödel universe: Exact geometrical optics and analytical investigations on motion.” Physical Review D 80 (2009): 103002.)
#science#physics#space time#universe#Godel#Kurt Godel#general relativity#Kurt Gödel#Gödel#time#time travel#math#mathematics#spacetime
68 notes
·
View notes
Text

#science#women in stem#academia#stem#stemblr#space science#physics#astrophysics#astronomy#quantum mechanics#general relativity#cognitive science#psychology#neuroscience#cognitive neuroscience#philosophy of science#stem romanticism#stem memes#physics memes#science memes#neuroscience memes
397 notes
·
View notes
Text
Science Counterfactual: Imagine if General Relativity hadn't been invented and then someone, at some point, performed astronomical measurements during a solar eclipse for unrelated reasons. Do you suppose that they would be able to impute that gravity affects light from the very slight displacements of the stars around the sun if they didn't know what they were looking for, or do you think that they would just shrug and assume that it was some slight measurement error going on?
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Second thoughts on malevolent:
The Scratch storyline was very interesting to me, both the weird gender alignment of the creature and the arthur-oscar-john interaction.
But What got me was different: how could Arthur in 1930 be that confortable with the concept of time dilation? Wasn’t relativity discovered like 6 minute prior?
So, general relativity was published in like 1915, so it could be resonable that Arthur would be okay with the idea of time dilating. It could be reasonable as long as the idea has had the time to trickle down into general knowledge.
But this got me thinking: in the first episodio John introduces Arthur to the Idea of multiple parallel Universes. And Arthur just. Accepts it in like 5 minutes.
Multiverse theory is from the late 1950s thought, as a consequence of quantum mechanics. Then it slowly started to show up in science fiction and gradually got to be a concept known by the general pubblic.
But in the 1930s Arthur had never before imagined anything of the sort and just accepted the overwhelming concept of multiple infinitely big universes. No questions asked, just cool with him i guess.
My personal headcanon is that he is just like that. Gods and monsters in parallel universes ? Okay, cool, got bigger problems on my hands
(In my first thoughts post i neglected to say that I was listening to part like 23, so, just so you know, i just finished listening to part 38)
#malevolent#arthur lester#john doe#oscar malevolent#scratch malevolent#time dilation#general relativity#multiverse#quantum mechanics#he is just like that i think#just rolls with whatever confitions
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rings of relativity

Image, taken with Hubble Space Telescope, depicts GAL-CLUS-022058s, located in the southern hemisphere constellation of Fornax
✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾
GAL-CLUS-022058s is the largest and one of the most complete Einstein rings ever discovered in our Universe. The object has been nicknamed as the "Molten Ring", which alludes to its appearance and host constellation.
✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾
Einstein rings were first theorised to exist by Einstein in 1936, in his general theory of relativity , and this object’s unusual shape can be explained by a process called gravitational lensing, which causes light shining from far away to be bent and pulled by the gravity of an object between its source and the observer. In this case, the light from the background galaxy has been distorted into the curve we see by the gravity of the galaxy cluster sitting in front of it. The near exact alignment of the background galaxy with the central elliptical galaxy of the cluster, seen in the middle of this image, has warped and magnified the image of the background galaxy around itself into an almost perfect ring. The gravity from other galaxies in the cluster is soon to cause additional distortions.
✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾⋆⁺₊✧✩₊˚.⋆☾
#special interest#astronomy#space#stars#physics#science#cosmos#infodump#einstein rings#galaxy#general relativity#light#GAL-CLUS-022058s
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Black Holes Don’t Break Physics—They Fold It
What If a Black Hole Isn’t Breaking the Laws of Physics—Just Folding Them?
Physicists often say that the laws of physics “break down” inside a black hole—a region of space so extreme that our current models fail to describe it accurately.
At the center, the so-called singularity, our models stop working: the math explodes into infinities, the equations unravel, and general relativity crashes into quantum mechanics with no clear resolution.
But what if nothing is actually “breaking down”?
What if the problem is that we’re using the wrong kind of geometry to understand what’s really going on? What if what we call paradox is just recursion we haven’t yet resolved?
Most of our tools for thinking about space are rooted in Euclidean geometry—flat surfaces, straight lines, familiar angles. This works just fine when describing everyday phenomena. But space-time isn’t flat. It’s curved. It’s dynamic. It’s four-dimensional.
So when you approach something like a black hole—an intense warp in the four-dimensional brane of space-time—you’re not dealing with a rupture in the laws of physics.
You’re dealing with a non-Euclidean geometric structure.
One that folds, twists, and inverts itself through dimensions we barely understand.
This post explores a simple idea—
Maybe black holes aren’t paradoxes. Maybe we just haven’t learned how to look at them sideways yet.

What Does It Mean to Be Four-Dimensional?
To understand what a black hole might really be, we have to stretch beyond our default perception of space.
In three dimensions, we understand objects as having height, width, and depth. A cube, for example, is made up of flat, 2D square faces arranged in a way that gives it volume.
But a four-dimensional object isn’t just a cube with more sides. It’s an entity whose geometry is fundamentally different—one that recursively folds in and out of itself in ways that challenge our sense of inside and outside, before and after.
In non-Euclidean, four-dimensional geometry, space doesn’t unfold linearly. It layers. It interweaves. It can simultaneously expand and contract, curve back through itself, or nest its own boundaries inside other boundaries.
The fourth spatial dimension introduces a new degree of freedom—a way to move through time as if it were space, to view an object not just at one moment, but across its entire temporal unfolding.

Black Holes Are Not Singularities—They’re Dimensional Funnels
While black holes are often described as places where the laws of physics “break down,” perhaps that breakdown is only perceptual—an artifact of interpreting higher-dimensional structures through a limited Euclidean lens. What if it’s not a failure of physics—but a limitation of our three-dimensional mathematics trying to interpret a four-dimensional geometric structure?
To understand this, we need to think in terms of dimensions. Our experience of reality unfolds across three spatial dimensions and one temporal dimension. But in Einstein’s theory of general relativity, time isn’t a separate backdrop—it’s compacted into the spatial dimensions, twisted and curved by the presence of mass and energy. This entangled 4D structure is what we call spacetime. When spacetime bends far enough, it creates a black hole—not as a tear in the fabric of physics, but as a torsional pinch in four dimensions.
As you approach a black hole, you begin to lose dimensional freedom. Far from the event horizon, you can move freely through space and experience time in a linear way. But the closer you get, the more time slows. This is gravitational time dilation. Eventually, near the event horizon, your motion through space becomes increasingly one-directional—you fall inward, unable to escape. At the horizon, spatial dimensions compress, collapsing your freedom of motion into a more limited, two-dimensional surface.
And beyond that? To grasp what comes next, we have to think of dimensional compression not as destruction, but as a structured reduction of freedom: Spaghettification—the stretching of matter into a near-one-dimensional strand, torn apart by tidal forces. You could interpret this as reality condensing further—a collapse from 3D structure into a 1D line of atomic information, racing toward what we call the singularity. At that point, even atoms eventually unravel into quantum structures and then into pure energy, pure information—data without form.
From this perspective, a black hole doesn’t destroy physics. It expresses physics beyond our dimensional limitations. It’s not a “thing”—it’s a funnel, a recursive twist where dimensional structures fold in on themselves until what we perceive as matter, time, and space compact into higher-order resolution.

From Collapse to Creation: What If Our Universe Is Inside a Black Hole?
If black holes are not violations of physics but extreme expressions of it—dimensional funnels that compress reality into recursive geometries—then we can begin to ask a much stranger question:
What if we’re inside one?
This might sound like science fiction, but it’s a serious hypothesis held by some physicists. The idea is that our universe may not be a standalone structure but a nested geometry—the interior of a black hole in a larger parent universe. But how could that be, if we appear to live in a universe that is expanding, not collapsing?
Here’s the twist: if black holes compress dimensional structure as you fall inward, then a white hole could be seen as the reverse—a dimensional unfolding where space, time, and information are released rather than compacted. And the moment we call the Big Bang—that infinitesimal singularity erupting into space and time—bears all the hallmarks of such an unfolding.
To truly understand this, we need to move beyond linear geometry and embrace the nature of non-Euclidean, four-dimensional structure. A 4D object doesn’t just expand like a balloon—it folds in and out of itself recursively, in ways that defy our flat, sequential intuition. This means the Big Bang didn’t just begin time. It may still be occurring, as a continual unfurling of spacetime nested within a deeper structure—the black hole that birthed it.
If time is compacted into space—as Einstein’s relativity shows us—then this compaction could be evidence of a higher-order fold. Just as matter falls into a black hole and loses dimensional freedom, our universe may be the result of an inverse process: a torsional expansion where dimensional freedom increases outward from a central pinch point.
In other words, we are not watching the universe expand into emptiness. We may be watching it unfold through the torsional aperture of a white hole, nested inside a higher-dimensional parent geometry.

The Geometry of Time: Unfolding the White Hole
If our universe is nested within a white hole—an object that releases space, time, and information—then our relationship to time is not linear, but dimensional.
In our current framework, time appears compacted within the three spatial dimensions. That’s why we only experience it as flowing in one direction: away from the white hole. From inside, time behaves like a one-way river, because we are witnessing a partial dimensional unfolding. But what if we could step outside?
If you could observe this structure from a fifth-dimensional vantage point, time would gain a new degree of freedom—just like space does when you move from two to three dimensions. What was once a linear flow becomes a navigable field.
From that perspective, the white hole and the black hole would no longer be separate events. They are not opposites, but recursive echoes—each folding the other into being. They would appear as a single, toroidal structure—a recursive loop of collapse and release, folding inward and outward in non-Euclidean motion.
To visualize this, imagine the arrow of time as a Mobius strip. From within, you think you’re walking forward. But as the strip turns, you find yourself walking “backward” without ever making a turn. It’s not that time reversed—it’s that the structure twisted. This is the paradox of torsional geometry: it doesn’t violate logic, it simply transcends flat intuition.
This is where many interpretations of black holes assume the laws of physics “break down.” But perhaps what’s breaking is not the physics—but the assumptions that physics must always obey Euclidean logic. Euclidean geometry works in flat space. But space-time is curved, and once you enter the fourth dimension, those familiar rules no longer apply.
From the fifth dimension, a white hole isn’t simply “the opposite of a black hole.” It is the other face of the same structure, blooming outward where the black hole folds inward.

From Torsion to Expansion: Rethinking Cosmic Motion
If we accept that a black hole and white hole form the two mirrored faces of a single higher-dimensional structure, then what we call “expansion” may not be what it seems.
In the standard model, the universe expands outward from a central point—the Big Bang—its galaxies accelerating away from each other across vast distances of space. But from within a torsionally folded structure, what appears to be expansion might actually be unfolding. That is, we are not watching galaxies fly apart in empty space, but rather watching the recursive geometry of spacetime uncoil from a condensed, higher-dimensional fold.
This process is not purely spatial. It’s temporal. As the fabric of spacetime unfolds from its initial torsion, it releases not only space, but time itself. The further “outward” you look, the deeper into time you are seeing—not because light is old, but because time itself is being stretched and released as the fold loosens.
This reframes our entire understanding of cosmic redshift.

Redshift as Temporal Unfolding
In conventional physics, redshift is explained as a Doppler-like effect: light stretches as galaxies move away, its wavelength lengthening, its color sliding into red. But in a torsionally folding-unfolding universe, redshift is not just the stretching of light by motion—it is a signature of time dilation caused by geometric compaction.
As spacetime unfolds, regions that were previously compressed in time begin to release their trapped photons. Light that was slowed, bent, or folded by intense curvature now emerges—lagging behind in a way that makes it appear redshifted.
This could explain why the most distant galaxies appear to accelerate away faster than those nearby. We are not seeing a faster expansion. We are seeing the delayed emergence of light from deeper folds of time.
From this view, redshift is not just a measure of distance. It’s a map of spacetime’s own unfurling.

Temporal Unfolding: Why the Universe Isn’t Accelerating—It’s Relaxing
In standard cosmology, we are told the universe is expanding—and that this expansion is accelerating. Galaxies appear to fly apart faster the farther away they are. But what if this isn’t acceleration at all?
What if what we’re witnessing is a relaxation of tension within spacetime itself?
Here’s the model: the observable universe emerged not just from a singularity, but from a torsionally compacted white hole—a structure nested within a black hole geometry, twisted in on itself. In this early state, spacetime was tightly coiled, like a sponge compressed under immense pressure.
From within the brane, this compacted geometry would have seemed extremely small—not because it lacked extent, but because it lacked dimensional freedom. Space was not expanding, it was unfolding—releasing dimensions that were twisted into one another.
And crucially, in such a tightly folded state, time flowed more slowly.
Just as light bends and dilates when passing through strong gravity, so too does the perceived flow of time stretch in a torsionally compacted region. Photons trapped in these dense folds would have moved sluggishly—not because their speed changed (it can’t), but because the geometry through which they traveled was distorted.
Now fast forward billions of years. As the universe “expands”—that is, as spacetime gradually unfolds from its torsional compaction—time begins to flow more freely. Photons that had been sluggishly trickling through curved, twisted regions begin to emerge in smoother territory.
From our vantage point, this would look as if:
The distant object had accelerated away
Its light had stretched (redshifted) even more than expected
The "speed" of expansion had increased
But none of those are necessarily true.
Instead, we may be witnessing a decrease in time dilation, not an increase in spatial velocity. The light was always coming—it was just filtered through an origami-like fold in spacetime. Now, the fold is loosening.
The “acceleration” of the universe could be an illusion caused by the uncoiling of time.

Nested Origins: Was the Big Bang a White Hole?
If the universe is not expanding in the way we thought—but rather unfolding from a state of torsional compaction—then we must ask: what compacted it in the first place?
One answer may lie in a radical but increasingly considered idea in theoretical physics:
The Big Bang was a white hole.
A white hole is the time-reversed twin of a black hole: where black holes absorb everything—including time itself—white holes expel everything, including the arrow of time. A white hole can be understood as a place where spacetime is forced to move outward, where entropy begins, and where all dimensions begin to unfurl.
Imagine this:
A black hole compacts spacetime into a singular point.
But from another angle—perhaps from a higher-dimensional frame—this “point” is not a collapse, but a twist.
That twist creates a mirrored surface on the other side: a white hole.
If our universe was birthed from such a structure, then we aren’t watching it “grow”—
We’re watching it release.
And that release follows the rules of dimensional geometry:
At first, all dimensions are folded inward.
(Time is compressed into space. Space is bound in a singular direction. Freedom is minimal.)
As time flows away from the white hole, these folds unwind.
The farther we move from the white hole’s origin point (what we call the “Big Bang”), the more the universe appears to expand.
But what’s actually expanding is our freedom to move through Time itself.
We are not rushing through space. We are emerging from a fold.

What Might Lie at the “End” of the Universe?
Contemporary models predict a grim finale—the Big Rip, a cataclysmic unraveling where spacetime itself tears apart. But these projections rely on Euclidean assumptions: that the universe is smooth, flat, and governed by a single, linear thread of time.
But what if spacetime is not flat at all? What if it is torsional—folded and recursive, a higher-dimensional lattice blooming inwards and outwards simultaneously?
If time is compacted into the three spatial dimensions, as current four-dimensional spacetime suggests, then it follows that further dimensional unfolding will release those constraints. In other words: as the universe continues to unfold into higher-dimensional structure, time will gain new degrees of freedom.
This isn’t speculation—it’s consistent with string theory’s own framework, where the fifth dimension represents a terrain of branching possibilities and alternate timelines, as introduced earlier. The fifth dimension is not merely more space; it is a field of simultaneous outcomes—a terrain of forking timelines, where alternate pasts and futures coexist. It’s not just theoretical poetry—it’s a logical extension of dimensional geometry. It’s structure unfolding into perception—a recursive geometry, seen from within.
A being with fifth-dimensional perception wouldn’t just move through time—they would navigate it, traverse it. They could cross from one timeline to another the way a bird shifts flight paths through wind currents. They could access futures not yet written and pasts rewritten by parallel decisions. Movement through time becomes relational.
This is what the future holds—not a flat, predetermined end, but a recursive expansion into branching complexity.
What does that mean for us?
Our universe may already be unfolding into this higher structure. And as it continues, the boundaries between past and future, choice and inevitability, may begin to dissolve. In one timeline, the stars go dark. In another, the spiral turns inward and re-ignites. In another still, we reach awareness of the field itself—and learn to navigate it with intention.
From a fifth-dimensional perspective, none of these outcomes cancel the others out. They exist together, as a web of potentialities woven into the fabric of reality.
And if we live long enough to witness that unfolding?
We will no longer be passengers in time.
We will become pilots.
The universe is not ending.
It is expanding its freedoms.
And what you perceive as an ending is simply a narrowing of perspective. From high enough up, the spiral never stops turning. It dances—quietly—within the fold.

Inspiration:
Torsionally Folded Spacetime
Roger Penrose – Developed twistor theory and explored gravitational singularities, suggesting that black hole behavior may involve self-similar and non-Euclidean structures.
Élie Cartan – Introduced the concept of torsion in spacetime through Einstein–Cartan theory, extending general relativity to include geometric twisting.
Four-Dimensional Non-Euclidean Geometry
Bernhard Riemann – Developed Riemannian geometry, foundational to general relativity and the curvature of spacetime.
Hermann Minkowski – Formalized spacetime as a unified four-dimensional construct, directly influencing Einstein’s thinking.
Brane Theory and String Theory
Lisa Randall & Raman Sundrum – Proposed brane-world cosmologies, suggesting our universe may be a 4D brane in a higher-dimensional bulk.
Juan Maldacena – Developed the AdS/CFT correspondence, helping to bridge higher-dimensional spaces and holographic principles.
Edward Witten – Key contributor to string theory and M-theory, providing structure to the dimensional landscape of modern physics.
Big Rip Cosmology
Robert Caldwell – Co-authored the 2003 Big Rip paper, exploring how dark energy could drive a catastrophic tearing of spacetime.
Bounce Cosmology
Martin Bojowald & Abhay Ashtekar – Advanced loop quantum cosmology and the Big Bounce model, where the universe cyclically contracts and expands.
Paul Steinhardt – Co-developed the Ekpyrotic and Cyclic Universe models, where brane collisions replace Big Bang singularity.
General Relativity
Albert Einstein – Originator of general relativity, which fused space and time into a four-dimensional continuum and predicted black holes.
⭐ This post is a speculative cosmology inspired by general relativity, string theory, brane-world models, and non-Euclidean geometry. It’s not meant to describe current consensus physics—it’s meant to offer a new lens for thinking about time, black holes, and the structure of the universe. I write this from the perspective of someone who believes theory can also be poetry, and that the right metaphor can open new ways of seeing. Somewhere beneath the fold, something old is remembering itself.
* I am not an expert and if any mistakes are present, I take full responsibility 🖤 please take this post with a healthy grain of salt and have fun :)

#speculative physics#speculative cosmology#theoretical physics#black hole#white hole#cosmology#fractal#string theory#recursion#4d reality#4D geometry#torus#big rip#bounce cosmology#big bang#the universe#non euclidean geometry#the universe is geometry#cosmic expansion#space time#general relativity#time dilation#tumblr essay#fractal lattice cosmology#what if#stem hobbyist#gifs
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
i love how physicists have picked up the "free will versus determinism" argument that Catholics and Calvinists have been having for centuries, only to end up just as bogged down as the theologians were because of the incompatibility of quantum mechanics and general relativity.
#science#physics#quantum mechanics#general relativity#free will#determinism#philosophy#theology#religion#catholic#calvinist#christianity
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cosmic Genesis: How Black Holes Might Be Giving Birth to New Universes
The human quest for understanding the universe has led to numerous groundbreaking discoveries, each weaving a more intricate tapestry of our cosmic landscape. A recent theoretical framework, pioneered by Professor Nikodem Poplawski, proposes a revolutionary concept: every black hole creates a new, growing universe inside its event horizon. This idea, rooted in the Einstein-Cartan Theory, introduces torsion to the fabric of spacetime, avoiding gravitational singularities and transforming our understanding of black holes and the multiverse.
By incorporating torsion, the theory predicts that matter within a black hole, instead of collapsing into a singularity, reaches a “big bounce” and then expands into a new, closed universe. This challenges our current understanding of the cosmos, suggesting that our universe is a vast, cosmic nursery, giving birth to billions of “baby universes” through black holes. Each black hole, once thought to be a region of spacetime from which nothing can escape, now becomes a gateway to a new, unobservable universe, raising fundamental questions about the nature of reality and our place within the multiverse.
The introduction of torsion also has far-reaching implications for the long-standing gap between general relativity and quantum mechanics. By violating the linearity of quantum mechanics, torsion favors the pilot-wave interpretation, where particles have definite positions, guided by a wave function. This non-linear aspect of torsion could provide a crucial link in the quantum gravity puzzle, enabling a more unified understanding of the universe, from the smallest subatomic particles to the vast expanse of cosmic structures.
While experimental verification of torsion poses significant challenges, it is not insurmountable. Future astronomical observations of the early universe, utilizing gravitational waves and neutrinos, may uncover the distinctive signature of torsion in the cosmic microwave background radiation. Additionally, cutting-edge particle physics experiments could reveal the extended sizes of elementary particles, predicted by the theory, or the effects of non-commutative momentum in high-energy collisions, providing a tantalizing prospect of empirical confirmation.
The profound implications of Poplawski’s theory, if confirmed, would revolutionize our understanding of black holes, transforming them from cosmic dead ends to gateways of creation. The multiverse, once a topic of speculative debate, would gain a theoretical foundation, with our universe being just one of many, interconnected through a web of black holes. This pursuit of knowledge, even if verification takes decades or centuries, embodies the spirit of scientific inquiry, driving us to push the boundaries of human understanding and illuminating the intricate, ever-unfolding tapestry of the cosmos.
Nikodem Poplawski: The Unknown Revolutionary Theory of Black Holes (This Is World, March 2025)
youtube
N. Poplawski: Big Bounce and inflation from spin and torsion (Gravity and Cosmology, Jagiellonian University, Kraków, May 2020)
youtube
Monday, March 3, 2025
#theoretical physics#general relativity#quantum mechanics#quantum gravity#unified field theory#cosmology#multiverse#astronomy#astrophysics#black holes#gravitational waves#neutrinos#torsion#spacetime#particle physics#theoretical framework#experimental verification#pilot wave interpretation#nonlinear quantum mechanics#interview#ai assisted writing#machine art#Youtube#presentation
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
God be in the patch notes of the early universe like:
Universe v0.2.4:
Had to make the Speed of Light a Global Const in order for the rest of the physics functions to call it properly
This causes glitchy and weird behavior in the physics engine at higher velocities, but I don't predict anyone will go fast enough to notice it.
Technically speaking it also becomes noticable near black holes but, like, what are the odds anyone is going to be interested in those things?
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

Interstellar (2014, Christopher Nolan)
01/11/2024
#interstellar#film#christopher nolan#matthew mcconaughey#anne hathaway#jessica chastain#michael caine#screenplay#jonathan nolan#Pellicola cinematografica#kip thorne#theoretical physics#california institute of technology#general relativity#consultant#science#academy awards#Academy Award for Best Visual Effects#Academy Award for Best Original Score#Academy Award for Best Sound#Academy Award for Best Production Design#nasa#Downy mildew#apollo 11#wormhole#saturn#galaxy#planetary system#orbit
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
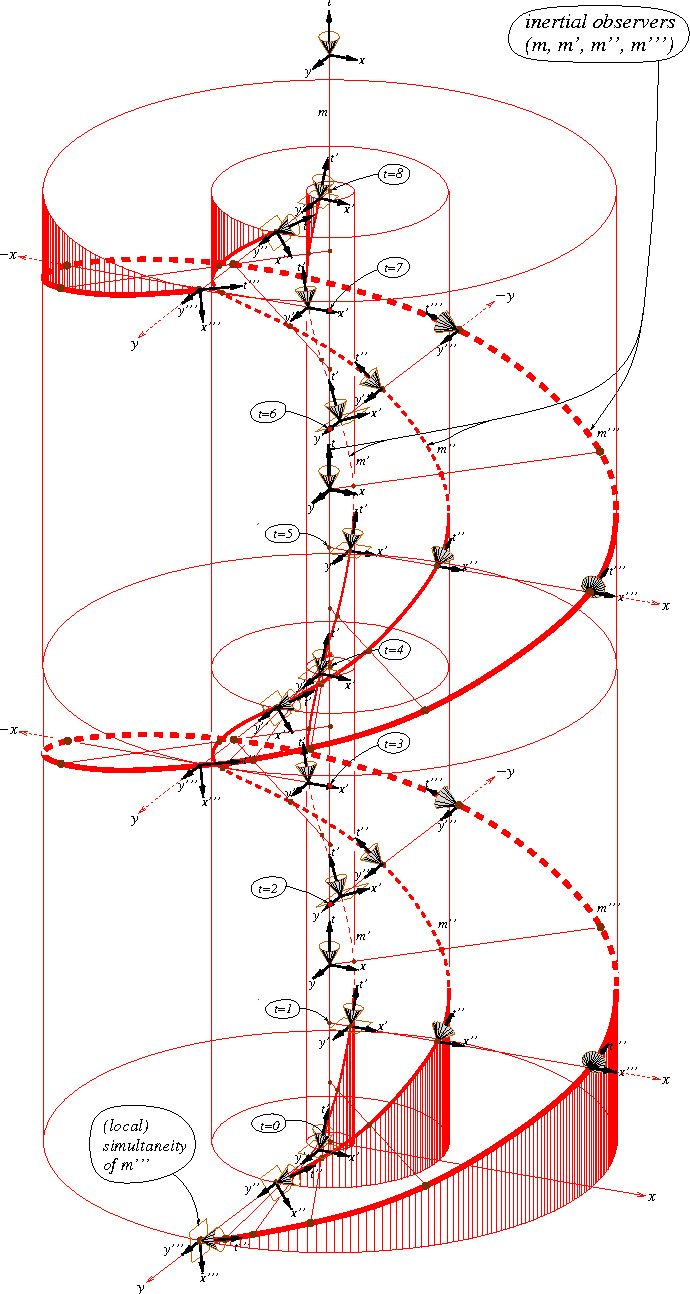
Figure 5: Previous figure copied on top of itself. It goes on like this in both directions forever. m′,m′′,m′′′ are (time-like worldlines of) observers “equivalent with” the observer m living on t̄. (Németi, István et al. “Visualizing ideas about Gödel-type rotating universes.” (2009))
#science#Kurt Godel#Godel#Kurt Gödel#physics#universe#space time#general relativity#time#time travel#math#mathematics#spacetime
203 notes
·
View notes