#IT Security Policies
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The ISO 27000 family of protocols and their role in cybersecurity
The ISO 27000 family of protocols represent a series of standards developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to address various aspects of information security management. These standards provide a framework for organizations to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their information security management systems (ISMS). Each standard within the ISO…

View On WordPress
#certificate authority#cybersecurity#domains#ISMS#ISO#ISO27001#iso27701#IT Security Policies#Risk management#UKAS
0 notes
Text
#tiktok#alligator alcatraz#Florida#immigration law#immigration#immigrants#immigration and customs enforcement#migrants#mass deportations#trump deportations#trump immigration policy#trump immigration crackdown#trump immigration raids#fuck trump#us politics#us government#donald trump#president trump#trump#trump administration#trump is the enemy of the people#trump's america#fuck donald trump#department of homeland security#Florida everglades#Everglades
717 notes
·
View notes
Text
instagram
#politics#us politics#democrats are corrupt#democrats will destroy america#wake up democrats!!#border issues#us border#tom homan#biden border policy#open borders#illegal invasion#voter fraud#social security fraud#Instagram
329 notes
·
View notes
Text

President Donald Trump fired Joint Chiefs Chairman General C.Q. Brown and five other top military leaders in an unprecedented Pentagon overhaul. Breaking tradition, Trump nominated retired Lieutenant General Dan "Razin" Caine to replace Brown, marking the first time a retired officer has been chosen for the role.
The shakeup also includes replacing Navy Chief Admiral Lisa Franchetti, the first woman to lead a military branch, and other senior officials. Critics, including Democratic lawmakers, called the move a dangerous politicization of the military, warning it undermines trust and national security. This dramatic shift signals a major transformation in U.S. military leadership under Trump's "America First" agenda.
#general knowledge#affairsmastery#generalknowledge#current events#current news#upscaspirants#upsc#generalknowledgeindia#world news#breaking news#news#government#public news#usa#us politics#america#politics#united states#donald trump#trump administration#trump#president trump#military#republicans#democratic party#democrats#policy#usa politics#political news#national security
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
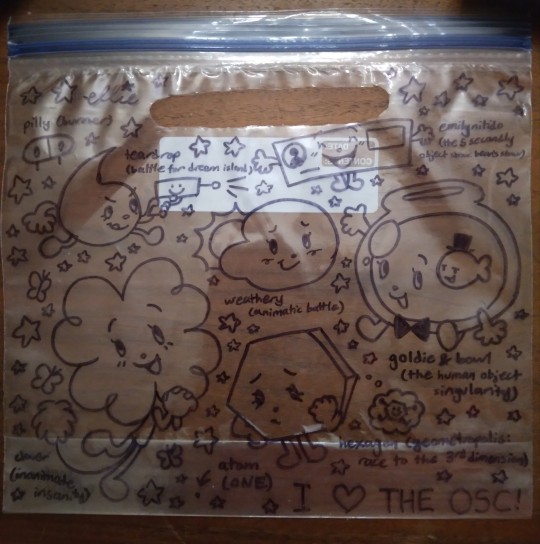

here's the ziploc i customized so i can abide by the bfdi x ii clear bag policy in style!!
#dandy's doodles#burner#burner pilly#battle for dream island#bfdi#bfdi teardrop#inanimate insanity#ii#ii clover#geometropolis#geometropolis: race to the 3rd dimension#grt3d#grt3d hexagon#animatic battle#ab weathery#the 5 secondly object show#5sos#the 5 secondly object show: bean's show#5sos:bs#5sos:bs emily nitido#the human object singularity#thos#thos goldie#thos bowl#hfjone#hfjone atom#whee!!!! this was very fun#the fact that they have this sort of security policy concerns me though --#what if they don't let me wear my clover costume head??? :[
159 notes
·
View notes
Text
AAMER MADHANI and ZEKE MILLER at AP:
WASHINGTON (AP) — Incoming senior Trump administration officials have begun questioning career civil servants who work on the White House National Security Council about who they voted for in the 2024 election, their political contributions and whether they have made social media posts that could be considered incriminating by President-elect Donald Trump’s team, according to a U.S. official familiar with the matter. At least some of these nonpolitical employees have begun packing up their belongings since being asked about their loyalty to Trump — after they had earlier been given indications that they would be asked to stay on at the NSC in the new administration, the official said, speaking on the condition of anonymity to discuss sensitive personnel matters. Trump’s pick for national security adviser, Florida Rep. Mike Waltz, in recent days publicly signaled his intention to get rid of all nonpolitical appointees and career intelligence officials serving on the NSC by Inauguration Day to ensure the council is staffed with those who support Trump’s agenda. A wholesale removal of foreign policy and national security experts from the NSC on Day 1 of the new administration could deprive Trump’s team of considerable expertise and institutional knowledge at a time when the U.S. is grappling with difficult policy challenges in Ukraine, the Mideast and beyond. Such questioning could also make new policy experts brought in to the NSC less likely to speak up about policy differences and concerns. White House national security adviser Jake Sullivan said Monday that he has not been told by Waltz or Trump transition team officials that the incoming team has conducted or planned on conducting such vetting. But Sullivan in recent days has made a robust case for the incoming Trump administration to hold over career government employees assigned to the NSC at least through the early going of the new administration. He called the career appointees “patriots” who have served “without fear or favor for both Democratic and Republican administrations. ”
[...] The NSC staff members being questioned about their loyalty are largely subject matter experts who have been loaned to the White House by federal agencies — the State Department, FBI and CIA, for example — for temporary duty that typically lasts one to two years. If removed from the NSC, they would be returned to their home agencies. Vetting of the civil servants began in the last week, the official said. Some of them have been questioned about their politics by Trump appointees who will serve as directors on the NSC and who had weeks earlier asked them to stick around. There are dozens of civil servants at the directorate level at the NSC who had anticipated remaining at the White House in the new administration. A second U.S. official told the AP that he was informed weeks ago by incoming Trump administration officials that they planned on raising questions with career appointees that work at the White House, including those at the NSC, about their political leanings. The official, who was not authorized to comment publicly, however, had not yet been formally vetted.
[...] Trump, during his first term, was scarred when two career military officers detailed to the NSC became whistleblowers, raising their concerns about Trump’s 2019 call to Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy in which the president sought an investigation of Biden and his son Hunter. That episode led to Trump’s first impeachment. Alexander Vindman was listening to the call in his role as an NSC official when he became alarmed at what he heard. He approached his twin brother, Eugene, who at the time was serving as an ethics lawyer at the NSC. Both Vindmans reported their concerns to superiors. Alexander Vindman said in a statement Friday that the Trump team’s approach to staffing the NSC “will have a chilling effect on senior policy staff across the government.” He added, “Talented professionals, wary of being dismissed for principled stances or offering objective advice, will either self-censor or forgo service altogether.” The two men were heralded by Democrats as patriots for speaking out and derided by Trump as insubordinate. Eugene Vindman in November was elected as a Democrat to represent Virginia’s 7th Congressional District.
The Trump campaign team is conducting an authoritarian purge of civil servants working at the National Security Council by letting only loyal Trumpists serve on the Council as part of the MAGA cult’s war on expertise.
See Also:
Raw Story: Security experts grilled on how they voted as major White House cull begins: insiders
The New Republic: Trump Appointee Has Unhinged Plan for Purging Government Workers
Daily Kos: Trump risks national security with loyalty test for civil servants
#National Security Council#Michael Waltz#National Security#Donald Trump#Trump Administration II#Jake Sullivan#Foreign Policy#Alexander Vindman#Eugene Vindman
61 notes
·
View notes
Text

Matt Davies
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
March 24, 2025
Heather Cox Richardson
Mar 25, 2025
Today the editor-in-chief of The Atlantic, Jeffrey Goldberg, dropped the story that senior members of the Trump administration planned the March 15 U.S. attack on the Houthis in Yemen over Signal, a widely available encrypted app that is most decidedly not part of the United States national security system. The decision to steer around government systems was possibly an attempt to hide conversations, since the app was set to erase some messages after a week and others after four weeks. By law, government communications must be archived.
According to Goldberg, the use of Signal may also have violated the Espionage Act, which establishes how officials must handle information about the national defense. The app is not approved for national security use, and officials are supposed either to discuss military activity in a sensitive compartmented information facility, or SCIF, or to use approved government equipment.
The use of Signal to plan a military attack on Yemen was itself an astonishingly dangerous breach, but what comes next is simply mind-boggling: the reason Goldberg could report on the conversation is that the person setting it up included Goldberg—a reporter without security clearance—in it.
Goldberg reports that on March 11 he received a connection request from someone named Michael Waltz, although he did not believe the actual Michael Waltz, who is Trump’s national security advisor, would be writing to him. He thought it was likely someone trying to entrap him, although he thought perhaps it could be the real Waltz with some information. Two days later, he was included in the “Houthi PC small group,” along with a message that the chat would be for “a principles [sic] group for coordination on Houthis.”
As Goldberg reports, a “principals committee generally refers to a group of the senior-most national-security officials, including the secretaries of defense, state, and the treasury, as well as the director of the CIA. It should go without saying—but I’ll say it anyway—that I have never been invited to a White House principals-committee meeting, and that, in my many years of reporting on national-security matters, I had never heard of one being convened over a commercial messaging app.”
The other names on the app were those of Secretary of State Marco Rubio, Vice President J.D. Vance, Director of National Intelligence Tulsi Gabbard, Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth, Brian McCormack from the National Security Council, Central Intelligence Director John Ratcliffe, Trump’s Middle East and Ukraine negotiator Steve Witkoff, White House chief of staff Suzy Wiles, perhaps White House deputy chief of staff Stephen Miller, and Trump’s nominee for head of the National Counterterrorism Center, Joe Kent.
Goldberg assumed the chat was fake, some sort of disinformation campaign, although he was concerned when Ratcliffe provided the full name of a CIA operative in this unsecure channel. But on March 14, as Vance, for example, took a strong stand against Europe—“I just hate bailing Europe out again”—and as Hegseth emphasized that their messaging must be that “Biden failed,” Goldberg started to think the chat might be real. Those in the chat talked of finding a way to make Europe pay the costs for the U.S. attack, and of “minimiz[ing] risk to Saudi oil facilities.”
And then, on March 15, the messages told of the forthcoming attack. “I will not quote from this update, or from certain other subsequent texts,” Goldberg writes. “The information contained in them, if they had been read by an adversary of the United States, could conceivably have been used to harm American military and intelligence personnel, particularly in the broader Middle East, Central Command’s area of responsibility. What I will say, in order to illustrate the shocking recklessness of this Signal conversation, is that the Hegseth post contained operational details of forthcoming strikes on Yemen, including information about targets, weapons the U.S. would be deploying, and attack sequencing.”
On the chat, reactions to the military strikes were emojis of a fist, an American flag, fire, praying hands, a flexed bicep, and “Good Job Pete and your team!!,” “Kudos to all…. Really great. God Bless,” and “Great work and effects!”
In the messages, with a reporter on the line, Hegseth promised his colleagues he would “do all we can to enforce 100% OPSEC,” or operations security. In a message to the team outlining the forthcoming attack, Hegseth wrote: “We are currently clean on OPSEC.”
Two hours after Goldberg wrote to the officials on the chat and alerted them to his presence on it by asking questions about it, National Security Council spokesperson Brian Hughes responded: “The thread is a demonstration of the deep and thoughtful policy coordination between senior officials.”
When asked about the breach, Trump responded: “I don't know anything about it. I'm not a big fan of The Atlantic. To me, it's a magazine that's going out of business. I think it’s not much of a magazine. But I know nothing about it. You're saying that they had what?” There is nothing that the administration could say to make the situation better, but this made it worse. As national security specialist Tom Nichols noted: “If the President is telling the truth and no one’s briefed him about this yet, that’s another story in itself. In any other administration, [the chief of staff] would have been in the Oval [Office] within nanoseconds of learning about something like this.”
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth is evidently going to try to bully his way out of this disaster. When asked about it, he began to yell at a reporter that Goldberg is a “deceitful and highly discredited so-called journalist who’s made a profession of peddling hoaxes time and time again.” Hegseth looked directly at the camera and said: “Nobody was texting war plans.” But Goldberg has receipts. The chat had “the specific time of a future attack. Specific targets, including human targets…weapons systems…precise detail…a long section on sequencing…. He can say that it wasn’t a war plan, but it was a minute-by-minute accounting of what was about to happen.”
Zachary B. Wolf of CNN noted that “Trump intentionally hired amateurs for top jobs. This is their most dramatic blunder.” Senator Jon Ossoff (D-GA) told Brian Tyler Cohen: “My first reaction... was 'what absolute clowns.' Total amateur hour, reckless, dangerous…. [T]his is what happens when you have basically Fox News personalities cosplaying as government officials.” Foreign policy scholar Timothy Snyder posted: “These guys inherited one of the most functional state apparatus in the history of the world and they are inhabiting it like a crack house.”
Many observers have noted that all of these national security officials knew that using Signal in this way was against the law, and their comfort with jumping onto the commercial app to plan a military strike suggests they are using Signal more generally. “How many Signal chats with sensitive information about military operations are ongoing within the Pentagon right now?” Senator Adam Schiff (D-CA) posted. “Where else are war plans being shared with such abject disregard for our national security? We need answers. Right now.”
National security journalists and officials are aghast. Former commanding general of United States Army Europe and the Seventh Army Mark Hertling called the story “staggering.” Former CIA officer Matt Castelli posted: “This is more than ‘loose lips sink ships’, this is a criminally negligent breach of classified information and war planning involving VP, SecDef, D[irector of the] CIA, National Security Advisor—all putting troops at risk. America is not safe.” Former transportation secretary Pete Buttigieg, who spent seven years as an intelligence officer in the Navy Reserve, posted: “From an operational security perspective, this is the highest level of f**kup imaginable. These people cannot keep America safe.”
Rhode Island senator Jack Reed, the top Democrat on the Armed Services Committee, said: "If true, this story represents one of the most egregious failures of operational security and common sense I have ever seen. The carelessness shown by President Trump's cabinet is stunning and dangerous. I will be seeking answers from the Administration immediately." Armed Services Committee member Don Bacon (R-NE), a former Air Force brigadier general, told Axios that “sending this info over non-secure networks” was “unconscionable.” “Russia and China are surely monitoring his unclassified phone.”
That the most senior members of Trump’s administration were sharing national security secrets on unsecure channels is especially galling since the people on the call have used alleged breaches of national security to hammer Democrats. Sarah Longwell and J.V. Last of The Bulwark compiled a series of video clips of Marco Rubio, Stephen Miller, Tulsi Gabbard, John Ratcliffe, and especially Pete Hegseth talking about the seriousness of handling secret information and the need for accountability for those who mishandle it. When they were accusing then–secretary of state Hillary Clinton of such a breach, they called for firings, accountability, and perhaps criminal charges. Indeed, Trump rose to power in 2016 with the charge that Clinton should be sent to prison for using a private email server. “Lock her up!” became the chant at his rallies.
Today, for her part, Clinton posted a link to the story along with an eyes emoji and wrote: “You have got to be kidding me.”
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Letters From An American#Heather Cox Richardson#Foreign policy#epic screwups#incompetence#malice#unqualified#Dept of Defense#non-secure networks#American History#Matt Davies#The Atlanta#Jeffrey Goldberg
42 notes
·
View notes
Note
Americans' approval of Trump rose from 7% to 45% after his meeting with the Ukrainian president.
Let's see what the Europeans will do to Ukraine after the support tweets
NATO is nothing without America, This is the reality.
Dear Approval Anon,
I have no idea of your sources - you should be so kind and come back with substantial evidence, since I was not able to find anything remotely related to what you are so gleefully writing.

[Source: https://projects.fivethirtyeight.com/polls/favorability/donald-trump/]
I know the troubles (the 2024 bitter Silver vs. Morris pollster feud comes to mind) Project 538 has been through lately. I am merely using this as a very recent poll aggregator, and it is nowhere near the illogical, tragically idiotic 'Americans' approval of Trump rose from 7% to 45% after his meeting with the Ukrainian president' you so confidently seem to tout.
On which planet would a recently elected POTUS start his mandate with 7% approval rate? You do the math, you answer this - to yourself, because you'd understand I am not really interested by your flimsy justifications.
But let's break it down a bit, shall we, and follow the latest 10 day-trend, for the sake of fine tuning - same source as above:

I see extreme polarization. I see self-cannibalization of polls, depending on their Red/Blue funding. I see a slightly unfocused domestic context, in which emotions are not settled yet - and how could they be, since lack of predictability seems to be in fashion?
I could go on and delve into it. I am not going to. I am just leaving these figures here, as a testimony of your tremendous liberty with facts. By the way, your champion is not doing so badly overall (pretty stable even, at the moment), so you did not need to lie like a 5 year-old. You're not helping him and make a fool of yourself, in the process.
However, allow this European to answer your insinuating assertions. Thank you for the concern, I think we'll be just fine. You are perhaps informed that, along with a long standing Common Foreign and Security Policy, the EU has a fully operative Common Security and Defense Policy. Both are solidly enshrined in our Treaties and both had very tangible results, already.
I doubt you closely followed the results of last Sunday's London summit. On that particular occasion, the EU has been joined by other non-EU, NATO members, such as the UK, Norway and Turkey, along NATO and the EU Commission's Chairpersons. What we will collectively do in order to help Ukraine is exactly what we collectively did during the COVID-19 health crisis: pooling our resources in order to achieve a common goal. Some will perhaps send troops. Others will probably help with their infrastructure. All will pitch in and fund the defensive support mechanisms. It is in the making. It is going forward, like it or not. I will not further speculate.
I also think you are exceedingly naive to think NATO would not survive without America. It might morph, it might limit its geographical scope or redraw its security goals and means of action, or it might very well be replaced by some other alliance of like-minded countries. It happened before. It will happen again. While it would be regrettable, it would not be unheard of, nor fatal. But ask yourself if isolation is the right path for your country, many of us know and deeply love, when faced with a complex counterpart (I hesitate using a stronger vocabulary, given the recent evolutions), such as Russia. How is this going to agree with USA's Manifest Destiny foreign policy doctrine and its long self-perceived exceptionalism is yet another complex issue I do not have the will to further discuss.
I will simply say this: your view is biased by your own, news' consumer focused perception of Time. You think everything will happen right now, as we speak, because your habitual media outlet told you so. I will probably disappoint you, but diplomatic time is running much, much slower than your perception shaped by endless breaking news moments would ever comprehend.
And remember, Anon: your reality might not be my, or hers, or his, or their reality. The world did not start with Columbus. It will not end now, because of a tantrum on a couch.

41 notes
·
View notes
Text
BILL GATES WARNS TRUMP: I CAN’T FILL GLOBAL HEALTH FUNDING SHORTFALLS AFTER USAID CUTS

Bill Gates is personally lobbying the Trump administration, warning he can’t replace U.S. funding for global health programs slashed under “America First” policy.
After 80% of USAID contracts were cut, Gates met National Security Council and lawmakers, pushing to protect programs like Gavi, Global Fund, and polio eradication.
Gates stressed the Gates Foundation can’t cover billions in cuts, while Trump reviews 30 major health projects for possible elimination.
#news#politics#usa news#us politics#donald trump#public news#world news#inauguration#breaking news#news update#usaid fraud#elon musk#usaid funding freeze#musk and usaid#usaid corruption#usaid#marco rubio#pete hegseth#starlink#bill gates#tarrifs#federal government#national security#judiciary#us government#government#politics and government#government policy#health#hospital
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
if someone came to your home and told you you had to get out because their parents lived there 50 years ago, you would call the police on them. you would think they are insane. you would rightly think they are out of their minds because having people who once lived in a place a hundred years ago does not give anyone today the right to take someone else's property. however, israel has been spreading the lie that somehow having people who lived on a land 3000 years ago gives them the right to take it from the indigenous population through theft, murder, gr@pe, and worse. i'm so proud of these university kids for seeing the truth.
#israel#american right#liberals#militarism#censorship#student protests#foreign policy#future#security#geopolitics#Israel-Palestine conflict#student activism#freedom of speech#political polarization#media influence#yale university#columbia university
200 notes
·
View notes
Text
#tiktok#kristi noem#fuck ice#federal agents#fuck kristi noem#polls#ice is gestapo#ice is a terrorist organization#ice arrests#ice agents#ice immigration#abolish ice#immigration law#immigration#immigrants#department of homeland security#homeland security#homeland secretary#us politics#us government#fuck trump#trump administration#trump's america#president trump#trump immigration policy#trump immigration crackdown#trump immigration raids#trump immigration plan#immigration and customs enforcement#immigration agents
93 notes
·
View notes
Text

Yes, you read that right.....2.7 TRILLION dollars of US taxpayer's money!
#politics#us politics#democrats are corrupt#democrats will destroy america#wake up democrats!!#graft and corruption#political corruption#government corruption#usaid fraud#usaid corruption#usaid#medicare#medicaid#foreign policy#foreign affairs#social security fraud#welfare fraud#medicare fraud#medicaid fraud#social security number
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wright granted access to DOGE representative Luke Farritor — a 23-year-old former SpaceX intern — even over objections from members of the department’s general counsel and chief information offices, the people told CNN. The DOE chief information office is the department’s IT and cybersecurity office.
Members of the general counsel and chief information offices “said this is a bad idea” because Farritor hadn’t had a standard background investigation needed to access the department’s system, one of the people told CNN. “He’s not cleared to be in DOE, on our systems. None of those things have been done.”
#trump administration#elon musk#elon#doge#National Nuclear Security Administration#Nuclear#News#Energy#Nuclear energy#politics#us politics#policy#political#donald trump#president trump#jd vance#american politics#background check#intern
42 notes
·
View notes
Text




For my birthday, Patreon deleted my account 🎉
That's nearly all of my income gone - If you've ever enjoyed my work, please consider joining me on SubscribeStar. There's years worth of work there, hundreds of exclusives I've never posted, and I've lowered the cost as well!
#estinien varlineau#estinien wyrmblood#Dragon Age#baldur's gate 3#FFXIV#Shadowheart#G'raha Tia#The Iron Bull#Thancred Waters#ha ha ha ha ralphie i'm in danger type day#it's been a long one#i talked about it a wee bit more on bsky but this wasn't a policy violation or anything this was and is a security issue thing I've been#trying to solve with patreon for over a month now and theyve been able to do nothing#so this is fun#:)
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
The CHIPS Act treats the symptoms, but not the causes

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/07/farewell-mr-chips/#we-used-to-make-things

There's this great throwaway line in 1992's Sneakers, where Dan Aykroyd, playing a conspiracy-addled hacker/con-man, is feverishly telling Sydney Poitier (playing an ex-CIA spook) about a 1958 meeting Eisenhower had with aliens where Ike said, "hey, look, give us your technology, and we'll give you all the cow lips you want."
Poitier dismisses Aykroyd ("Don't listen to this man. He's certifiable"). We're meant to be on Poitier's side here, but I've always harbored some sympathy for Aykroyd in this scene.
That's because I often hear echoes of Aykroyd's theory in my own explanations of the esoteric bargains and plots that produced the world we're living in today. Of course, in my world, it's not presidents bargaining for alien technology in exchange for cow-lips – it's the world's wealthy nations bargaining to drop trade restrictions on the Global South in exchange for IP laws.
These bargains – which started as a series of bilateral and then multilateral agreements like NAFTA, and culminated in the WTO agreement of 1999 – were the most important step in the reordering of the world's economy around rent-extraction, cheap labor exploitation, and a brittle supply chain that is increasingly endangered by the polycrisis of climate and its handmaidens, like zoonotic plagues, water wars, and mass refugee migration.
Prior to the advent of "free trade," the world's rich countries fashioned debt into a whip-hand over poor, post-colonial nations. These countries had been bankrupted by their previous colonial owners, and the price of their freedom was punishing debts to the IMF and other rich-world institutions in exchange for loans to help these countries "develop."
Like all poor debtors, these countries were said to have gotten into their predicament through moral failure – they'd "lived beyond their means."
(When rich people get into debt, bankruptcy steps in to give them space to "restructure" according to their own plans. When poor people get into debt, bankruptcy strips them of nearly everything that might help them recover, brands them with a permanent scarlet letter, and subjects them to humiliating micro-management whose explicit message is that they are not competent to manage their own affairs):
https://pluralistic.net/2021/08/07/hr-4193/#shoppers-choice
So the poor debtor nations were ordered to "deregulate." They had to sell off their state assets, run their central banks according to the dictates of rich-world finance authorities, and reorient their production around supplying raw materials to rich countries, who would process these materials into finished goods for export back to the poor world.
Naturally, poor countries were not allowed to erect "trade barriers" that might erode the capacity of this North-South transfer of high-margin goods, but this was not the era of free trade. It wasn't the free trade era because, while the North-South transfer was largely unrestricted, the South-North transfer was subject to tight regulation in the rich world.
In other words, poor countries were expected to export, say, raw ore to the USA and reimport high-tech goods, with low tariffs in both directions. But if a poor country processed that ore domestically and made its own finished goods, the US would block those goods at the border, slapping them with high tariffs that made them more expensive than Made-in-the-USA equivalents.
The argument for this unidirectional trade was that the US – and other rich countries – had a strategic need to maintain their manufacturing industries as a hedge against future geopolitical events (war, but also pandemics, extreme weather) that might leave the rich world unable to provide for itself. This rationale had a key advantage: it was true.
A country that manages its own central bank can create as much of its own currency as it wants, and use that money to buy anything for sale in its own currency.
This may not be crucial while global markets are operating to the country's advantage (say, while the rest of the world is "willingly" pricing its raw materials in your country's currency), but when things go wrong – war, plague, weather – a country that can't make things is at the rest of the world's mercy.
If you had to choose between being a poor post-colonial nation that couldn't supply its own technological needs except by exporting raw materials to rich countries, and being a rich country that had both domestic manufacturing capacity and a steady supply of other countries' raw materials, you would choose the second, every time.
What's not to like?
Here's what.
The problem – from the perspective of America's ultra-wealthy – was that this arrangement gave the US workforce a lot of power. As US workers unionized, they were able to extract direct concessions from their employers through collective bargaining, and they could effectively lobby for universal worker protections, including a robust welfare state – in both state and federal legislatures. The US was better off as a whole, but the richest ten percent were much poorer than they could be if only they could smash worker power.
That's where free trade comes in. Notwithstanding racist nonsense about "primitive" countries, there's no intrinsic defect that stops the global south from doing high-tech manufacturing. If the rich world's corporate leaders were given free rein to sideline America's national security in favor of their own profits, they could certainly engineer the circumstances whereby poor countries would build sophisticated factories to replace the manufacturing facilities that sat behind the north's high tariff walls.
These poor-country factories could produce goods ever bit as valuable as the rich world's shops, but without the labor, environmental and financial regulations that constrained their owners' profits. They slavered for a business environment that let them kill workers; poison the air, land and water; and cheat the tax authorities with impunity.
For this plan to work, the wealthy needed to engineer changes in both the rich world and the poor world. Obviously, they would have to get rid of the rich world's tariff walls, which made it impossible to competitively import goods made in the global south, no matter how cheaply they were made.
But free trade wasn't just about deregulation in the north – it also required a whole slew of new, extremely onerous regulations in the global south. Corporations that relocated their manufacturing to poor – but nominally sovereign – countries needed to be sure that those countries wouldn't try to replicate the American plan of becoming actually sovereign, by exerting control over the means of production within their borders.
Recall that the American Revolution was inspired in large part by fury over the requirement to ship raw materials back to Mother England and then buy them back at huge markups after they'd been processed by English workers, to the enrichment of English aristocrats. Post-colonial America created new regulations (tariffs on goods from England), and – crucially – they also deregulated.
Specifically, post-revolutionary America abolished copyrights and patents for English persons and firms. That way, American manufacturers could produce sophisticated finished goods without paying rent to England's wealthy making those goods cheaper for American buyers, and American publishers could subsidize their editions of American authors' books by publishing English authors on the cheap, without the obligation to share profits with English publishers or English writers.
The surplus produced by ignoring the patents and copyrights of the English was divided (unequally) among American capitalists, workers, and shoppers. Wealthy Americans got richer, even as they paid their workers more and charged less for their products. This incubated a made-in-the-USA edition of the industrial revolution. It was so successful that the rest of the world – especially England – began importing American goods and literature, and then American publishers and manufacturers started to lean on their government to "respect" English claims, in order to secure bilateral protections for their inventions and books in English markets.
This was good for America, but it was terrible for English manufacturers. The US – a primitive, agricultural society – "stole" their inventions until they gained so much manufacturing capacity that the English public started to prefer American goods to English ones.
This was the thing that rich-world industrialists feared about free trade. Once you build your high-tech factories in the global south, what's to stop those people from simply copying your plans – or worse, seizing your factories! – and competing with you on a global scale? Some of these countries had nominally socialist governments that claimed to explicitly elevate the public good over the interests of the wealthy. And all of these countries had the same sprinkling of sociopaths who'd gladly see a million children maimed or the land poisoned for a buck – and these "entrepreneurs" had unbeatable advantages with their countries' political classes.
For globalization to work, it wasn't enough to deregulate the rich world – capitalists also had to regulate the poor world. Specifically, they had to get the poor world to adopt "IP" laws that would force them to willingly pay rent on things they could get for free: patents and other IP, even though it was in the short-term, medium-term, and long-term interests of both the nation and its politicians and its businesspeople.
Thus, the bargain that makes me sympathetic to Dan Aykroyd: not cow lips for alien tech; but free trade for IP law. When the WTO was steaming towards passage in the late 1990s, there was (rightly) a lot of emphasis on its deregulatory provisions: weakening of labor, environmental and financial laws in the poor world, and of tariffs in the rich world.
But in hindsight, we all kind of missed the main event: the TRIPS (Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights). This actually started before the WTO treaty (it was part of the GATT, a predecessor to the WTO), but the WTO spread it to countries all over the world. Under the TRIPS, poor countries are required to honor the IP claims of rich countries, on pain of global sanction.
That was the plan: instead of paying American workers to make Apple computers, say, Apple could export the "IP" for Macs and iPhones to countries like China, and these countries would produce Apple products that were "designed in California, assembled in China." China would allow Apple to treat Chinese workers so badly that they routinely committed suicide, and would lock up or kill workers who tried to unionize. China would accept vast shipments of immortal, toxic e-waste. And China wouldn't let its entrepreneurs copy Apple's designs, be they software, schematics or trademarks.
Apple isn't the only company that pursued this strategy, but no company has executed it as successfully. It's not for nothing that Steve Jobs's hand-picked successor was Tim Cook, who oversaw the transfer of even the most exacting elements of Apple manufacturing to Chinese facilities, striking bargains with contractors like Foxconn that guaranteed that workers would be heavily – lethally! – surveilled and controlled to prevent the twin horrors of unionization and leaks.
For the first two decades of the WTO era, the most obvious problems with this arrangement was wage erosion (for American workers) and leakage (for the rich). China's "socialist" government was only too happy to help Foxconn imprison workers who demanded better wages and working conditions, but they were far more relaxed about knockoffs, be they fake iPods sold in market stalls or US trade secrets working their way into Huawei products.
These were problems for the American aristocracy, whose investments depended on China disciplining both Chinese workers and Chinese businesses. For the American people, leakage was a nothingburger. Apple's profits weren't shared with its workforce beyond the relatively small number of tech workers at its headquarters. The vast majority of Apple employees, who flogged iPhones and scrubbed the tilework in gleaming white stores across the nation, would get the same minimal (or even minimum) wage no matter how profitable Apple grew.
It wasn't until the pandemic that the other shoe dropped for the American public. The WTO arrangement – cow lips for alien technology – had produced a global system brittle supply chains composed entirely of weakest links. A pandemic, a war, a ship stuck in the Suez Canal or Houthi paramilitaries can cripple the entire system, perhaps indefinitely.
For two decades, we fought over globalization's effect on wages. We let our corporate masters trick us into thinking that China's "cheating" on IP was a problem for the average person. But the implications of globalization for American sovereignty and security were banished to the xenophobic right fringe, where they were mixed into the froth of Cold War 2.0 nonsense. The pandemic changed that, creating a coalition that is motivated by a complex and contradictory stew of racism, environmentalism, xenophobia, labor advocacy, patriotism, pragmatism, fear and hope.
Out of that stew emerged a new American political tendency, mostly associated with Bidenomics, but also claimed in various guises by the American right, through its America First wing. That tendency's most visible artifact is the CHIPS Act, through which the US government proposes to use policy and subsidies to bring high-tech manufacturing back to America's shores.
This week, the American Economic Liberties Project published "Reshoring and Restoring: CHIPS Implementation for a Competitive Semiconductor Industry," a fascinating, beautifully researched and detailed analysis of the CHIPS Act and the global high-tech manufacturing market, written by Todd Achilles, Erik Peinert and Daniel Rangel:
https://www.economicliberties.us/our-work/reshoring-and-restoring-chips-implementation-for-a-competitive-semiconductor-industry/#
Crucially, the report lays out the role that the weakening of antitrust, the dismantling of tariffs and the strengthening of IP played in the history of the current moment. The failure to enforce antitrust law allowed for monopolization at every stage of the semiconductor industry's supply-chain. The strengthening of IP and the weakening of tariffs encouraged the resulting monopolies to chase cheap labor overseas, confident that the US government would punish host countries that allowed their domestic entrepreneurs to use American designs without permission.
The result is a financialized, "capital light" semiconductor industry that has put all its eggs in one basket. For the most advanced chips ("leading-edge logic"), production works like this: American firms design a chip and send the design to Taiwan where TSMC foundry turns it into a chip. The chip is then shipped to one of a small number of companies in the poor world where they are assembled, packaged and tested (AMP) and sent to China to be integrated into a product.
Obsolete foundries get a second life in the commodity chip ("mature-node chips") market – these are the cheap chips that are shoveled into our cars and appliances and industrial systems.
Both of these systems are fundamentally broken. The advanced, "leading-edge" chips rely on geopolitically uncertain, heavily concentrated foundries. These foundries can be fully captured by their customers – as when Apple prepurchases the entire production capacity of the most advanced chips, denying both domestic and offshore competitors access to the newest computation.
Meanwhile, the less powerful, "mature node" chips command minuscule margins, and are often dumped into the market below cost, thanks to subsidies from countries hoping to protect their corner of the high-tech sector. This makes investment in low-power chips uncertain, leading to wild swings in cost, quality and availability of these workhorse chips.
The leading-edge chipmakers – Nvidia, Broadcom, Qualcomm, AMD, etc – have fully captured their markets. They like the status quo, and the CHIPS Act won't convince them to invest in onshore production. Why would they?
2022 was Broadcom's best year ever, not in spite of its supply-chain problems, but because of them. Those problems let Broadcom raise prices for a captive audience of customers, who the company strong-armed into exclusivity deals that ensured they had nowhere to turn. Qualcomm also profited handsomely from shortages, because its customers end up paying Qualcomm no matter where they buy, thanks to Qualcomm ensuring that its patents are integrated into global 4G and 5G standards.
That means that all standards-conforming products generate royalties for Qualcomm, and it also means that Qualcomm can decide which companies are allowed to compete with it, and which ones will be denied licenses to its patents. Both companies are under orders from the FTC to cut this out, and both companies ignore the FTC.
The brittleness of mature-node and leading-edge chips is not inevitable. Advanced memory chips (DRAM) roughly comparable in complexity to leading-edge chips, while analog-to-digital chips are as easily commodified as mature-node chips, and yet each has a robust and competitive supply chain, with both onshore and offshore producers. In contrast with leading-edge manufacturers (who have been visibly indifferent to the CHIPS incentives), memory chip manufacturers responded to the CHIPS Act by committing hundreds of billions of dollars to new on-shore production facilities.
Intel is a curious case: in a world of fabless leading-edge manufacturers, Intel stands out for making its own chips. But Intel is in a lot of trouble. Its advanced manufacturing plans keep foundering on cost overruns and delays. The company keeps losing money. But until recently, its management kept handing its shareholders billions in dividends and buybacks – a sign that Intel bosses assume that the US public will bail out its "national champion." It's not clear whether the CHIPS Act can save Intel, or whether financialization will continue to hollow out a once-dominant pioneer.
The CHIPS Act won't undo the concentration – and financialization – of the semiconductor industry. The industry has been awash in cheap money since the 2008 bailouts, and in just the past five years, US semiconductor monopolists have paid out $239b to shareholders in buybacks and dividends, enough to fund the CHIPS Act five times over. If you include Apple in that figure, the amount US corporations spent on shareholder returns instead of investing in capacity rises to $698b. Apple doesn't want a competitive market for chips. If Apple builds its own foundry, that just frees up capacity at TSMC that its competitors can use to improve their products.
The report has an enormous amount of accessible, well-organized detail on these markets, and it makes a set of key recommendations for improving the CHIPS Act and passing related legislation to ensure that the US can once again make its own microchips. These run a gamut from funding four new onshore foundries to requiring companies receiving CHIPS Act money to "dual-source" their foundries. They call for NIST and the CPO to ensure open licensing of key patents, and for aggressive policing of anti-dumping rules for cheap chips. They also seek a new law creating an "American Semiconductor Supply Chain Resiliency Fee" – a tariff on chips made offshore.
Fundamentally, these recommendations seek to end the outsourcing made possible by restrictive IP regimes, to undercut Wall Street's power to demand savings from offshoring, and to smash the market power of companies like Apple that make the brittleness of chip manufacturing into a feature, rather than a bug. This would include a return to previous antitrust rules, which limited companies' ability to leverage patents into standards, and to previous IP rules, which limited exclusive rights chip topography and design ("mask rights").
All of this will is likely to remove the constraints that stop poor countries from doing to America the same things that postcolonial America did to England – that is, it will usher in an era in which lots of countries make their own chips and other high-tech goods without paying rent to American companies. This is good! It's good for poor countries, who will have more autonomy to control their own technical destiny. It's also good for the world, creating resiliency in the high-tech manufacturing sector that we'll need as the polycrisis overwhelms various places with fire and flood and disease and war. Electrifying, solarizing and adapting the world for climate resilience is fundamentally incompatible with a brittle, highly concentrated tech sector.
Pluralizing high-tech production will make America less vulnerable to the gamesmanship of other countries – and it will also make the rest of the world less vulnerable to American bullying. As Henry Farrell and Abraham Newman describe so beautifully in their 2023 book Underground Empire, the American political establishment is keenly aware of how its chokepoints over global finance and manufacturing can be leveraged to advantage the US at the rest of the world's expense:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/10/weaponized-interdependence/#the-other-swifties
Look, I know that Eisenhower didn't trade cow-lips for alien technology – but our political and commercial elites really did trade national resiliency away for IP laws, and it's a bargain that screwed everyone, except the one percenters whose power and wealth have metastasized into a deadly cancer that threatens the country and the planet.

Image: Mickael Courtiade (modified) https://www.flickr.com/photos/197739384@N07/52703936652/
CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/
#pluralistic#chips act#ip#monopolies#antitrust#national security#industrial policy#american economic liberties project#tmsc#leading-edge#intel#mature node#lagging edge#foundries#fabless
254 notes
·
View notes
Text
"If Kamala wins, only death and destruction await because she is the candidate of endless wars,” declaimed Donald Trump at a rally in Michigan, on the Friday before the election. “I am the candidate of peace.” In a typically ridiculous rhetorical flourish, Trump added: “I am peace.” Nevertheless, despite the ridiculousness, the president-elect in recent weeks succeeded in connecting with plenty of of anti-war voters tired of the United States’ “forever wars”. He went to Dearborn, the “capital” of Arab America, attacked Kamala Harris for campaigning with the pro-war Cheneys, and came away with an endorsement from a local imam who called him the “peace” candidate. In fact, I have lost count of the number of leftists who have told me in recent months: “Trump didn’t start any new wars.” Sorry, what? Trump spent his four years in the White House escalating every single conflict that he inherited from Barack Obama. Many have forgotten that Trump bombed the Assad government in Syria twice; dropped the “mother of all bombs” on Afghanistan; illegally assassinated Iranian general Qasem Soleimani on Iraqi soil; armed Saudi Arabia’s genocide in Yemen; and made John Bolton his national security adviser. Few are even aware that Trump launched more drone strikes in his first two years in office than Obama, dubbed “the drone president”, did across eight years in office. But this time, we were told, it would be different. This time Trump meant it. No more war! No more neocons! Some took heart from Trump’s very public rejection of arch-hawks Mike Pompeo and Nikki Haley. Others signal-boosted efforts by RFK Jr, Don Jr and Tucker Carlson to block neoconservative figures from joining the new Trump-Vance administration. “I’m on it,” bragged Trump’s eldest failson. [...] But this is the Trump playbook: run as a dove, govern as a hawk. It’s what he did in 2016 and again this year. Attack neocons; get elected; hire neocons. So “Donald the dove”, as Maureen Dowd of the New York Times once put it? If only. Whether it is on domestic policy or foreign policy, Trump remains a conman. Don’t take my word for it. Take his new secretary of state’s.
Mehdi Hasan for The Guardian on Donald Trump's deceitful lie that he is "anti-war" (11.13.2024).
Mehdi Hasan wrote an opinion piece in The Guardian debunking the nonsensical “Donald The Dove” crap that falsely pitches Donald Trump as “anti-war”, when in reality, he is as pro-war as it gets.
#Mehdi Hasan#The Guardian#Opinion#2024 Presidential Election#2024 Elections#War#Foreign Policy#National Security#Trump Administration#Trump Administration II#Marco Rubio#Brian Hook#Elise Stefanik#Mike Waltz#Mike Huckabee#Pete Hegseth
39 notes
·
View notes