#Kubernetes cluster management
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA)

Material Includes
Kubernetes Lab Access
Mock Tests for Certification
Certificate of Completion
Requirements
Basic knowledge of Linux and containers
Quick Enquiry
About Course
Master Kubernetes, the leading container orchestration platform, with hands-on training. This course covers cluster setup, management, and troubleshooting, aligning with CKA certification.
What I will learn?
Deploy Kubernetes clusters
Manage applications in Kubernetes
Prepare for CKA certification
Course Curriculum
Lesson 1: Introduction to Containers and Kubernetes
Lesson 2: Setting Up a Cluster
Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) Online Exam & Certification
Get in Touch
Founded in 2004, COSSINDIA (Prodevans wing) is an ISO 9001:2008 certified a global IT training and company. Created with vision to offer high quality training services to individuals and the corporate, in the field of ‘IT Infrastructure Management’, we scaled new heights with every passing year.
Quick Links
Webinar
Privacy Policy
Terms of Use
Blogs
About Us
Contact Us
Follow Us
Facebook
Instagram
Youtube
LinkedIn
Contact Info
Monday - Sunday: 7:30 – 21:00 hrs.
Hyderabad Office: +91 7799 351 640
Bangalore Office: +91 72044 31703 / +91 8139 990 051
#Certified Kubernetes Administrator#CKA Course India#Kubernetes Training#Cloud Native Computing#Container Orchestration#DevOps Certification#COSS India CKA#Kubernetes Certification Course#Kubernetes Hands‑On Training#Infrastructure Automation#Kubernetes Cluster Management
0 notes
Text
Lens Kubernetes: Simple Cluster Management Dashboard and Monitoring
Lens Kubernetes: Simple Cluster Management Dashboard and Monitoring #homelab #kubernetes #KubernetesManagement #LensKubernetesDesktop #KubernetesClusterManagement #MultiClusterManagement #KubernetesSecurityFeatures #KubernetesUI #kubernetesmonitoring
Kubernetes is a well-known container orchestration platform. It allows admins and organizations to operate their containers and support modern applications in the enterprise. Kubernetes management is not for the “faint of heart.” It requires the right skill set and tools. Lens Kubernetes desktop is an app that enables managing Kubernetes clusters on Windows and Linux devices. Table of…

View On WordPress
#Kubernetes cluster management#Kubernetes collaboration tools#Kubernetes management#Kubernetes performance improvements#Kubernetes real-time monitoring#Kubernetes security features#Kubernetes user interface#Lens Kubernetes 2023.10#Lens Kubernetes Desktop#multi-cluster management
0 notes
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to Deploy Azure Kubernetes Service with Azure Pipelines

A powerful orchestration tool for containerized applications is one such solution that Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) has offered in the continuously evolving environment of cloud-native technologies. Associate this with Azure Pipelines for consistent CI CD workflows that aid in accelerating the DevOps process. This guide will dive into the deep understanding of Azure Kubernetes Service deployment with Azure Pipelines and give you tips that will enable engineers to build container deployments that work. Also, discuss how DevOps consulting services will help you automate this process.
Understanding the Foundations
Nowadays, Kubernetes is the preferred tool for running and deploying containerized apps in the modern high-speed software development environment. Together with AKS, it provides a high-performance scale and monitors and orchestrates containerized workloads in the environment. However, before anything, let’s deep dive to understand the fundamentals.
Azure Kubernetes Service: A managed Kubernetes platform that is useful for simplifying container orchestration. It deconstructs the Kubernetes cluster management hassles so that developers can build applications instead of infrastructure. By leveraging AKS, organizations can:
Deploy and scale containerized applications on demand.
Implement robust infrastructure management
Reduce operational overhead
Ensure high availability and fault tolerance.
Azure Pipelines: The CI/CD Backbone
The automated code building, testing, and disposition tool, combined with Azure Kubernetes Service, helps teams build high-end deployment pipelines in line with the modern DevOps mindset. Then you have Azure Pipelines for easily integrating with repositories (GitHub, Repos, etc.) and automating the application build and deployment.
Spiral Mantra DevOps Consulting Services
So, if you’re a beginner in DevOps or want to scale your organization’s capabilities, then DevOps consulting services by Spiral Mantra can be a game changer. The skilled professionals working here can help businesses implement CI CD pipelines along with guidance regarding containerization and cloud-native development.
Now let’s move on to creating a deployment pipeline for Azure Kubernetes Service.
Prerequisites you would require
Before initiating the process, ensure you fulfill the prerequisite criteria:
Service Subscription: To run an AKS cluster, you require an Azure subscription. Do create one if you don’t already.
CLI: The Azure CLI will let you administer resources such as AKS clusters from the command line.
A Professional Team: You will need to have a professional team with technical knowledge to set up the pipeline. Hire DevOps developers from us if you don’t have one yet.
Kubernetes Cluster: Deploy an AKS cluster with Azure Portal or ARM template. This will be the cluster that you run your pipeline on.
Docker: Since you’re deploying containers, you need Docker installed on your machine locally for container image generation and push.
Step-by-Step Deployment Process
Step 1: Begin with Creating an AKS Cluster
Simply begin the process by setting up an AKS cluster with CLI or Azure Portal. Once the process is completed, navigate further to execute the process of application containerization, and for that, you would need to create a Docker file with the specification of your application runtime environment. This step is needed to execute the same code for different environments.
Step 2: Setting Up Your Pipelines
Now, the process can be executed for new projects and for already created pipelines, and that’s how you can go further.
Create a New Project
Begin with launching the Azure DevOps account; from the screen available, select the drop-down icon.
Now, tap on the Create New Project icon or navigate further to use an existing one.
In the final step, add all the required repositories (you can select them either from GitHub or from Azure Repos) containing your application code.
For Already Existing Pipeline
Now, from your existing project, tap to navigate the option mentioning Pipelines, and then open Create Pipeline.
From the next available screen, select the repository containing the code of the application.
Navigate further to opt for either the YAML pipeline or the starter pipeline. (Note: The YAML pipeline is a flexible environment and is best recommended for advanced workflows.).
Further, define pipeline configuration by accessing your YAML file in Azure DevOps.
Step 3: Set Up Your Automatic Continuous Deployment (CD)
Further, in the next step, you would be required to automate the deployment process to fasten the CI CD workflows. Within the process, the easiest and most common approach to execute the task is to develop a YAML file mentioning deployment.yaml. This step is helpful to identify and define the major Kubernetes resources, including deployments, pods, and services.
After the successful creation of the YAML deployment, the pipeline will start to trigger the Kubernetes deployment automatically once the code is pushed.
Step 4: Automate the Workflow of CI CD
Now that we have landed in the final step, it complies with the smooth running of the pipelines every time the new code is pushed. With the right CI CD integration, the workflow allows for the execution of continuous testing and building with the right set of deployments, ensuring that the applications are updated in every AKS environment.
Best Practices for AKS and Azure Pipelines Integration
1. Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Utilize Terraform or Azure Resource Manager templates
- Version control infrastructure configurations
- Ensure consistent and reproducible deployments
2. Security Considerations
- Implement container scanning
- Use private container registries
- Regular security patch management
- Network policy configuration
3. Performance Optimization
- Implement horizontal pod autoscaling
- Configure resource quotas
- Use node pool strategies
- Optimize container image sizes
Common Challenges and Solutions
Network Complexity
Utilize Azure CNI for advanced networking
Implement network policies
Configure service mesh for complex microservices
Persistent Storage
Use Azure Disk or Files
Configure persistent volume claims
Implement storage classes for dynamic provisioning
Conclusion
Deploying the Azure Kubernetes Service with effective pipelines represents an explicit approach to the final application delivery. By embracing these practices, DevOps consulting companies like Spiral Mantra offer transformative solutions that foster agile and scalable approaches. Our expert DevOps consulting services redefine technological infrastructure by offering comprehensive cloud strategies and Kubernetes containerization with advanced CI CD integration.
Let’s connect and talk about your cloud migration needs
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
GitOps: Automating Infrastructure with Git-Based Workflows

In today’s cloud-native era, automation is not just a convenience—it’s a necessity. As development teams strive for faster, more reliable software delivery, GitOps has emerged as a game-changing methodology. By using Git as the single source of truth for infrastructure and application configurations, GitOps enables teams to automate deployments, manage environments, and scale effortlessly. This approach is quickly being integrated into modern DevOps services and solutions, especially as the demand for seamless operations grows.
What is GitOps?
GitOps is a set of practices that use Git repositories as the source of truth for declarative infrastructure and applications. Any change to the system—whether a configuration update or a new deployment—is made by modifying Git, which then triggers an automated process to apply the change in the production environment. This methodology bridges the gap between development and operations, allowing teams to collaborate using the same version control system they already rely on.
With GitOps, infrastructure becomes code, and managing environments becomes as easy as managing your codebase. Rollbacks, audits, and deployments are all handled through Git, ensuring consistency and visibility.
Real-World Example of GitOps in Action
Consider a SaaS company that manages multiple Kubernetes clusters across environments. Before adopting GitOps, the operations team manually deployed updates, which led to inconsistencies and delays. By shifting to GitOps, the team now updates configurations in a Git repo, which triggers automated pipelines that sync the changes across environments. This transition reduced deployment errors by 70% and improved release velocity by 40%.
GitOps and DevOps Consulting Services
For companies seeking to modernize their infrastructure, DevOps consulting services provide the strategic roadmap to implement GitOps successfully. Consultants analyze your existing systems, assess readiness for GitOps practices, and help create the CI/CD pipelines that connect Git with your deployment tools. They ensure that GitOps is tailored to your workflows and compliance needs.
To explore how experts are enabling seamless GitOps adoption, visit DevOps consulting services offered by Cloudastra.
GitOps in Managed Cloud Environments
GitOps fits perfectly into devops consulting and managed cloud services, where consistency, security, and scalability are top priorities. Managed cloud providers use GitOps to ensure that infrastructure remains in a desired state, detect drifts automatically, and restore environments quickly when needed. With GitOps, they can roll out configuration changes across thousands of instances in minutes—without manual intervention.
Understand why businesses are increasingly turning to devops consulting and managed cloud services to adopt modern deployment strategies like GitOps.
GitOps and DevOps Managed Services: Driving Operational Excellence
DevOps managed services teams are leveraging GitOps to bring predictability and traceability into their operations. Since all infrastructure definitions and changes are stored in Git, teams can easily track who made a change, when it was made, and why. This kind of transparency reduces risk and improves collaboration between developers and operations.
Additionally, GitOps enables managed service providers to implement automated recovery solutions. For example, if a critical microservice is accidentally deleted, the Git-based controller recognizes the drift and automatically re-deploys the missing component to match the declared state.
Learn how DevOps managed services are evolving with GitOps to support enterprise-grade reliability and control.
GitOps in DevOps Services and Solutions
Modern devops services and solutions are embracing GitOps as a core practice for infrastructure automation. Whether managing multi-cloud environments or microservices architectures, GitOps helps teams streamline deployments, improve compliance, and accelerate recovery. It provides a consistent framework for both infrastructure as code (IaC) and continuous delivery, making it ideal for scaling DevOps in complex ecosystems.
As organizations aim to reduce deployment risks and downtime, GitOps offers a predictable and auditable solution. It is no surprise that GitOps has become an essential part of cutting-edge devops services and solutions.
As Alexis Richardson, founder of Weaveworks (the team that coined GitOps), once said:
"GitOps is Git plus automation—together they bring reliability and speed to software delivery."
Why GitOps Matters More Than Ever
The increasing complexity of cloud-native applications and infrastructure demands a method that ensures precision, repeatability, and control. GitOps brings all of that and more by shifting infrastructure management into the hands of developers, using tools they already understand. It reduces errors, boosts productivity, and aligns development and operations like never before.
As Kelsey Hightower, a renowned DevOps advocate, puts it:
"GitOps takes the guesswork out of deployments. Your environment is only as good as what’s declared in Git."
Final Thoughts
GitOps isn’t just about using Git for configuration—it’s about redefining how teams manage and automate infrastructure at scale. By integrating GitOps with your DevOps strategy, your organization can gain better control, faster releases, and stronger collaboration across the board.
Ready to modernize your infrastructure with GitOps workflows?Please visit Cloudastra DevOps as a Services if you are interested to study more content or explore our services. Our team of experienced devops services is here to help you turn innovation into reality—faster, smarter, and with measurable outcomes.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is Argo CD? And When Was Argo CD Established?

What Is Argo CD?
Argo CD is declarative Kubernetes GitOps continuous delivery.
In DevOps, ArgoCD is a Continuous Delivery (CD) technology that has become well-liked for delivering applications to Kubernetes. It is based on the GitOps deployment methodology.
When was Argo CD Established?
Argo CD was created at Intuit and made publicly available following Applatix’s 2018 acquisition by Intuit. The founding developers of Applatix, Hong Wang, Jesse Suen, and Alexander Matyushentsev, made the Argo project open-source in 2017.
Why Argo CD?
Declarative and version-controlled application definitions, configurations, and environments are ideal. Automated, auditable, and easily comprehensible application deployment and lifecycle management are essential.
Getting Started
Quick Start
kubectl create namespace argocd kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
For some features, more user-friendly documentation is offered. Refer to the upgrade guide if you want to upgrade your Argo CD. Those interested in creating third-party connectors can access developer-oriented resources.
How it works
Argo CD defines the intended application state by employing Git repositories as the source of truth, in accordance with the GitOps pattern. There are various approaches to specify Kubernetes manifests:
Applications for Customization
Helm charts
JSONNET files
Simple YAML/JSON manifest directory
Any custom configuration management tool that is set up as a plugin
The deployment of the intended application states in the designated target settings is automated by Argo CD. Deployments of applications can monitor changes to branches, tags, or pinned to a particular manifest version at a Git commit.
Architecture
The implementation of Argo CD is a Kubernetes controller that continually observes active apps and contrasts their present, live state with the target state (as defined in the Git repository). Out Of Sync is the term used to describe a deployed application whose live state differs from the target state. In addition to reporting and visualizing the differences, Argo CD offers the ability to manually or automatically sync the current state back to the intended goal state. The designated target environments can automatically apply and reflect any changes made to the intended target state in the Git repository.
Components
API Server
The Web UI, CLI, and CI/CD systems use the API, which is exposed by the gRPC/REST server. Its duties include the following:
Status reporting and application management
Launching application functions (such as rollback, sync, and user-defined actions)
Cluster credential management and repository (k8s secrets)
RBAC enforcement
Authentication, and auth delegation to outside identity providers
Git webhook event listener/forwarder
Repository Server
An internal service called the repository server keeps a local cache of the Git repository containing the application manifests. When given the following inputs, it is in charge of creating and returning the Kubernetes manifests:
URL of the repository
Revision (tag, branch, commit)
Path of the application
Template-specific configurations: helm values.yaml, parameters
A Kubernetes controller known as the application controller keeps an eye on all active apps and contrasts their actual, live state with the intended target state as defined in the repository. When it identifies an Out Of Sync application state, it may take remedial action. It is in charge of calling any user-specified hooks for lifecycle events (Sync, PostSync, and PreSync).
Features
Applications are automatically deployed to designated target environments.
Multiple configuration management/templating tools (Kustomize, Helm, Jsonnet, and plain-YAML) are supported.
Capacity to oversee and implement across several clusters
Integration of SSO (OIDC, OAuth2, LDAP, SAML 2.0, Microsoft, LinkedIn, GitHub, GitLab)
RBAC and multi-tenancy authorization policies
Rollback/Roll-anywhere to any Git repository-committed application configuration
Analysis of the application resources’ health state
Automated visualization and detection of configuration drift
Applications can be synced manually or automatically to their desired state.
Web user interface that shows program activity in real time
CLI for CI integration and automation
Integration of webhooks (GitHub, BitBucket, GitLab)
Tokens of access for automation
Hooks for PreSync, Sync, and PostSync to facilitate intricate application rollouts (such as canary and blue/green upgrades)
Application event and API call audit trails
Prometheus measurements
To override helm parameters in Git, use parameter overrides.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#ArgoCD#CD#GitOps#API#Kubernetes#Git#Argoproject#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
🔍 Observe a Service Mesh: Trace and Visualize OpenShift with Jaeger and Kiali
In complex microservices environments, understanding how services communicate can make or break your application’s reliability. Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh gives you the power to manage, observe, and secure service-to-service communication in a Kubernetes cluster. But how do you see what’s going on under the hood?
That’s where Jaeger and Kiali come in — giving you visibility and insight into your service mesh in real-time.
🎯 What Is OpenShift Service Mesh?
OpenShift Service Mesh, built on Istio, Envoy, and other open-source technologies, helps manage east-west traffic (service-to-service) within your cluster. It handles:
Traffic control (routing, load balancing)
Resilience (retries, timeouts, circuit breakers)
Observability (tracing, metrics, logs)
Security (mTLS, policy enforcement)
But to truly make the most of a service mesh, you need to observe it in action.
🧭 Enter Jaeger: Distributed Tracing
Jaeger helps trace requests as they move through various microservices. It’s especially useful for:
Understanding service latency
Identifying bottlenecks
Debugging call paths
Once integrated with your OpenShift Service Mesh, Jaeger allows you to:
Search traces by service or tags
View spans and duration
Follow request paths end-to-end
📌 Use case: Your app is running slow. You trace a user request and see that 80% of the time is spent in one microservice. Now you know exactly where to optimize.
📊 Kiali: The Visual Sidekick
Kiali is your visual dashboard for OpenShift Service Mesh. It lets you:
See real-time service graph topology
Inspect traffic flows between services
View metrics like success rate, request volume, and latency
Manage Istio configurations and validations
With Kiali, you get a bird’s-eye view of the entire service mesh and how everything is performing.
📌 Use case: You spot a spike in error rates. Kiali shows you exactly which service link is unstable.
🚀 Getting Started
If you’re using Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh, here’s a quick outline to enable tracing and observability:
Enable Jaeger and Kiali during Service Mesh installation.
Annotate your services/pods to inject the sidecar proxy.
Use OpenShift UI or CLI to access the Kiali and Jaeger dashboards.
Start monitoring, tracing, and debugging in real time.
💡 Why It Matters
Modern cloud-native apps are complex. Without observability, it’s easy to lose track of how your services behave. By using Jaeger and Kiali with OpenShift Service Mesh, you gain:
✅ Deep insights into service communication ✅ Faster root cause analysis ✅ Better decision-making for scaling and optimization
📢 Final Thoughts
Observability isn't a luxury anymore — it's a must. With tools like Jaeger and Kiali, OpenShift makes it easier to trace, troubleshoot, and understand your services in a mesh. Whether you're debugging latency or optimizing performance, these tools give you clarity when it matters most.
For more info, Kindly follow: Hawkstack Technologies
0 notes
Text
A Beginner’s Guide to Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
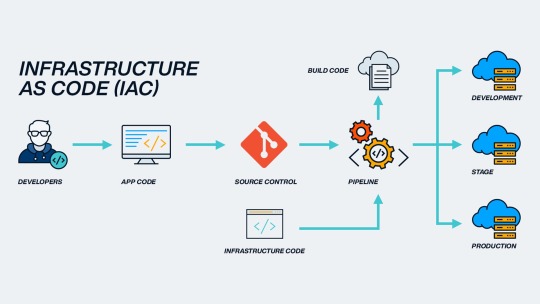
1. Introduction
In the past, infrastructure wasn’t so fast—servers were installed, packages were installed, and environments were initialized by doing things manually one step at a time. In today’s fast-moving development world, that isn’t the case anymore. This is when Infrastructure as Code (IaC) comes into play. IaC enables teams to provision and manage cloud infrastructure via code instead of the manual processes that existed previously. In this blog, we will explain what IaC is, why you need to use IaC, and how you can get started.
2. What is Infrastructure as Code (IaC)?
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is the operation of maintaining and provisioning IT infrastructure like servers, networks, and databases using machine-readable code. Instead of navigating through cloud dashboards and clicking or typing commands manually, you write configuration files that tell your infrastructure what it should be. Those configuration files are put into version control systems like Git and executed automatically.
3. Why IaC Is Important in Today's Development
Speed & Automation
IaC is automating infrastructure so teams can spin up environments in minutes instead of hours or days.
Consistency & Repeatability
Code is being used to guarantee that all environments—that is, development, staging, production—are consistent.
Version Control & Collaboration
IaC allows you to version your infrastructure changes just like you would your application code. Teams are more efficient and can roll back to earlier states when they want to.
Cost Savings
Through putting infrastructure in code, you can avoid over-provisioning resources and you can turn off your idle environments - which could lead to cost savings over time.
4. Popular IaC Tools
There are several tools that are most commonly used for Infrastructure as Code:
Terraform – Open-source, cloud-agnostic, and declarative syntax (HCL)
Pulumi – Uses actual programming languages (TypeScript, Python)
AWS CloudFormation – Built-in to AWS, YAML or JSON
Ansible – Most commonly used for configuration management and provisioning
Chef and Puppet – Enterprise tools for system automation
Both have their advantages and your choice depends on your use case or existing skills in your team.
5. How IaC Works (Simple workflow)
Write Code: Describe your infrastructure in code (e.g. a file, main.tf in Terraform)
Plan: See what the code will change in your environment.
Apply: Run the code to provision or update your infrastructure.
Maintain: Put your code into version control so you can go back and make future updates or roll-backs.
6. Common Use Cases of IaC
Provisioning cloud infrastructure on AWS, Azure, or GCP
Managing Kubernetes clusters
Automating testing environments
Scaling infrastructure with auto-scaling groups
Setting up a monitoring and alerting system
Creating disaster recovery environments
IaC is utilized for startups, and enterprises, by DevOps teams and SRE teams alike.
7. Best Practices for IaC
Keep your IaC code in a version control system (like Git)
Use modules and reusable pieces
Review changes using code reviews and CI pipeline practices
Don't include secrets and sensitive data in code files
Test infrastructure changes in a staging environment before production
Use remote state storage, in tools like Terraform, so that they can collaborate
8. Conclusion
By automating deployment and management, Infrastructure as Code is changing the way we create and manage infrastructure. It provides automation, repeatability and speed to the people, processes, and technology that once were slow manual, unreliable and error-prone.
Whether you are bringing a basic deployment to the cloud for the first time, or scaling complex systems to operate as a single unit with fault tolerance, and elasticity either way, it's an important skill to learn and apply to modern software development. Start easy, learn to use a single tool well and grow from there!
0 notes
Text

What AI Development Companies Do and Why They Matter
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer an experiment. It is a tool that businesses use to improve how they work. AI development companies build custom AI tools and systems that solve problems, speed up processes, and reduce costs. This article explains what these companies do, what services they offer, and what makes them important.
What Is an AI Development Company?
An AI development company designs and builds systems that use machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision to help businesses work smarter. These companies do more than write code. They work with data, build models, train algorithms, and deploy AI in real-world settings.
These companies usually include data scientists, ML engineers, AI researchers, and software developers. They apply AI to solve specific business problems—like automating support chat, predicting sales, scanning images for defects, or building recommendation engines.
Core Services of an AI Development Company
Here are the most common services offered by AI development firms. These services use a mix of software engineering, data analysis, and AI model training.
1. Machine Learning Model Development
AI development companies build machine learning models that learn from data. These models can classify, cluster, or predict based on past trends. Examples include:
Forecasting demand or revenue
Detecting fraud
Recommending products
The company handles every step: data collection, cleaning, feature selection, training, testing, and model optimization.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP helps machines understand and generate human language. This is useful for:
Customer support chatbots
Sentiment analysis
Language translation
Text summarization
Voice assistants
AI companies use NLP libraries and models like BERT, GPT, and spaCy to handle such tasks.
3. Computer Vision
Computer vision models help computers “see” and understand images or video. Use cases include:
Quality inspection in manufacturing
Facial recognition
Image classification for medical scans
Vehicle tracking in traffic management
These systems often use convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and tools like OpenCV or TensorFlow.
4. Predictive Analytics
This service turns raw business data into forecasts. AI companies use statistical models and machine learning algorithms to help companies:
Plan inventory
Optimize pricing
Predict churn
Forecast sales
They help clients understand trends without needing a full in-house data science team.
5. AI Integration and Deployment
Building an AI model is only half the job. Deployment means integrating it into the company’s systems, like CRMs, ERPs, or web platforms. AI development firms:
Build APIs
Create dashboards
Handle infrastructure (e.g., cloud deployment)
Monitor models for performance over time
6. Custom AI Software Development
Some companies need tools built from scratch. This might include a custom recommendation engine or a private GPT-style assistant. AI developers build these tools using client-specific data and goals.
7. AI Consulting
AI consulting helps companies understand if AI will solve their problems. It often includes:
Identifying business use cases
Estimating cost vs. benefit
Choosing the right AI approach
Building a roadmap
Consultants guide firms on how to get value from AI without wasting time or money.
Common Technologies Used
An AI development company uses many tools, frameworks, and languages. Here are the most common:
Python: Main language for ML and AI development
TensorFlow, PyTorch: Deep learning frameworks
Scikit-learn: For standard ML models
OpenCV: For computer vision tasks
Hugging Face Transformers: For NLP
Docker & Kubernetes: For model deployment
AWS/GCP/Azure: Cloud infrastructure for scalable AI systems
They also use tools for model monitoring, such as MLflow or Weights & Biases, to track model performance after deployment.
Key Industries That Use AI Services
AI is not limited to tech startups. AI development companies work with many industries:
1. Healthcare
Diagnose diseases from images
Predict patient risks
Process clinical notes using NLP
2. Retail and E-commerce
Recommend products
Forecast demand
Automate customer support
3. Finance
Detect fraud
Automate credit scoring
Analyze market trends
4. Manufacturing
Inspect products using computer vision
Predict machine failures
Optimize supply chain
5. Education
Personalize learning paths
Automate grading
Analyze student performance
6. Logistics and Transport
Route optimization
Demand prediction
Vehicle tracking
What Makes a Good AI Development Company?
Hiring an AI company is not just about technical skill. These qualities also matter:
1. Problem-First Approach
Good AI companies focus on solving real business problems, not just building models.
2. End-to-End Support
From data collection to model deployment, the company handles the full lifecycle.
3. Model Explainability
They build models that are not just accurate but also easy to understand. This matters for compliance and trust.
4. Data Privacy Awareness
The best firms understand data governance and follow data protection laws like GDPR or HIPAA.
5. Cross-Functional Teams
AI projects need more than data scientists. Good firms bring together engineers, analysts, and domain experts.
Challenges AI Development Companies Help Solve
AI projects fail when companies try to do too much on their own. AI service providers help solve these issues:
Poor data quality: They clean and structure data properly.
Lack of in-house talent: They bring in experts who know ML, data engineering, and infrastructure.
Scaling issues: They build solutions that work for small tests and large production rollouts.
Regulatory complexity: They design systems that meet industry-specific standards.
How to Choose the Right AI Development Partner
Choosing an AI partner is a strategic decision. Consider these factors:
Domain knowledge: Have they worked in your industry?
Technical stack: Are they using modern, scalable tools?
Transparency: Can they explain what their models do and why?
Post-launch support: Do they help maintain and update models?
Case studies: Have they delivered measurable results for others?
The Future of AI Services
AI development is shifting fast. Here's what lies ahead:
1. Foundation Models as a Service
Companies will use large models (like GPT-5 or Claude) through APIs rather than building their own. AI firms will specialize in customizing these models.
2. Smaller, Efficient Models
Not every company needs a giant model. AI developers will build “tiny” models that run on edge devices or low-power systems.
3. Multimodal AI
Future services will handle more than text or images. Multimodal AI works with voice, video, and documents all at once.
4. AI Agents for Businesses
Firms will build AI agents that act across workflows—answering emails, updating CRMs, or processing invoices.
5. AI Governance
As AI regulations grow, companies will need developers who can build ethical, fair, and auditable systems. AI firms will add governance frameworks to their services.
Conclusion
AI development companies offer more than tech expertise—they provide structured, measurable solutions to real business problems. Whether it's a custom chatbot, a model that forecasts sales, or an image classifier for defects, these firms handle the heavy lifting.
Working with an AI company helps organizations move beyond ideas and into working solutions. With the right partner, businesses can adopt AI safely, effectively, and at a pace that suits their goals.
0 notes
Text
Efficient Data Management for Predictive Models – The Role of Databases in Handling Large Datasets for Machine Learning
Predictive modelling thrives on data—lots of it. Whether you are forecasting demand, detecting fraud, or personalising recommendations, the calibre of your machine-learning (ML) solutions depends on how efficiently you store, organise, and serve vast amounts of information. Databases—relational, NoSQL, and cloud-native—form the backbone of this process, transforming raw inputs into ready-to-learn datasets. Understanding how to architect and operate these systems is, therefore, a core competency for every aspiring data professional and hence, a part of every data science course curriculum.
Why Databases Matter to Machine Learning
An ML workflow usually spans three data-intensive stages:
Ingestion and Storage – Collecting data from transactional systems, IoT devices, logs, or third-party APIs and landing it in a durable store.
Preparation and Feature Engineering – Cleaning, joining, aggregating, and reshaping data to create meaningful variables.
Model Training and Serving – Feeding training sets to algorithms, then delivering real-time or batch predictions back to applications.
Databases underpin each stage by enforcing structure, supporting fast queries, and ensuring consistency, and hence form the core module of any data science course in Mumbai. Without a well-designed data layer, even the most sophisticated model will suffer from long training times, stale features, or unreliable predictions.
Scaling Strategies for Large Datasets
Horizontal vs. Vertical Scaling Traditional relational databases scale vertically—adding more CPU, RAM, or storage to a single machine. Modern workloads often outgrow this approach, prompting a shift to horizontally scalable architectures such as distributed SQL (e.g., Google Spanner) or NoSQL clusters (e.g., Cassandra, MongoDB). Sharding and replication distribute data across nodes, supporting petabyte-scale storage and parallel processing.
Columnar Storage for Analytics Column-oriented formats (Parquet, ORC) and columnar databases (Amazon Redshift, ClickHouse) accelerate analytical queries by scanning only the relevant columns. This is especially valuable when feature engineering requires aggregations across billions of rows but only a handful of columns.
Data Lakes and Lakehouses Data lakes offer schema-on-read flexibility, letting teams ingest semi-structured or unstructured data without upfront modelling. Lakehouse architectures (Delta Lake, Apache Iceberg) layer ACID transactions and optimised metadata on top, blending the reliability of warehouses with the openness of lakes—ideal for iterative ML workflows.
Integrating Databases with ML Pipelines
Feature Stores To avoid re-computing features for every experiment, organisations adopt feature stores—specialised databases that store versioned, reusable features. They supply offline batches for training and low-latency look-ups for online inference, guaranteeing training-serving consistency.
Streaming and Real-Time Data Frameworks like Apache Kafka and Flink pair with databases to capture event streams and update features in near real time. This is crucial for applications such as dynamic pricing or anomaly detection, where stale inputs degrade model performance.
MLOps and Automation Infrastructure-as-code tools (Terraform, Kubernetes) and workflow orchestrators (Airflow, Dagster) automate database provisioning, data validation, and retraining schedules. By codifying these steps, teams reduce manual errors and accelerate model deployment cycles.
Governance, Quality, and Cost
As datasets balloon, so do risks:
Data Quality – Referential integrity, constraints, and automatic checks catch nulls, duplicates, and outliers early.
Security and Compliance – Role-based access, encryption, and audit logs protect sensitive attributes and meet regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Cost Management – Partitioning, compression, and lifecycle policies curb storage expenses, while query optimisers and materialised views minimise compute costs.
A modern data science course walks students through these best practices, combining theory with labs on indexing strategies, query tuning, and cloud-cost optimisation.
Local Relevance and Hands-On Learning
For learners taking a data science course in Mumbai, capstone projects frequently mirror the city’s fintech, media, and logistics sectors. Students might design a scalable order-prediction pipeline: ingesting transaction data into a distributed warehouse, engineering temporal features via SQL window functions, and serving predictions through a feature store exposed by REST APIs. Such end-to-end experience cements the role of databases as the silent engine behind successful ML products.
Conclusion
Efficient data management is not an afterthought—it is the foundation upon which predictive models are built and maintained. By mastering database design, scaling techniques, and MLOps integration, data professionals ensure that their models train faster, score accurately, and deliver value continuously. As organisations double down on AI investments, those who can marry machine learning expertise with robust database skills will remain at the forefront of innovation.
Business Name: ExcelR- Data Science, Data Analytics, Business Analyst Course Training Mumbai Address: Unit no. 302, 03rd Floor, Ashok Premises, Old Nagardas Rd, Nicolas Wadi Rd, Mogra Village, Gundavali Gaothan, Andheri E, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400069, Phone: 09108238354, Email: [email protected].
0 notes
Text
Master Advanced OpenShift Administration with DO380
Red Hat OpenShift Administration III: Scaling Kubernetes Like a Pro
As enterprise applications scale, so do the challenges of managing containerized environments. If you've already got hands-on experience with Red Hat OpenShift and want to go deeper, DO380 - Red Hat OpenShift Administration III: Scaling Kubernetes Deployments in the Enterprise is built just for you.
Why DO380?
This course is designed for system administrators, DevOps engineers, and platform operators who want to gain advanced skills in managing large-scale OpenShift clusters. You'll learn how to automate day-to-day tasks, ensure application availability, and manage performance at scale.
In short—DO380 helps you go from OpenShift user to OpenShift power admin.
What You’ll Learn
✅ Automation with GitOps
Leverage Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management and Argo CD to manage application lifecycle across clusters using Git as a single source of truth.
✅ Cluster Scaling and Performance Tuning
Optimize OpenShift clusters by configuring autoscaling, managing cluster capacity, and tuning performance for enterprise workloads.
✅ Monitoring and Observability
Gain visibility into workloads, nodes, and infrastructure using Prometheus, Grafana, and the OpenShift Monitoring stack.
✅ Cluster Logging and Troubleshooting
Set up centralized logging and use advanced troubleshooting techniques to quickly resolve cluster issues.
✅ Disaster Recovery and High Availability
Implement strategies for disaster recovery, node replacement, and data protection in critical production environments.
Course Format
Classroom & Virtual Training Available
Duration: 4 Days
Exam (Optional): EX380 – Red Hat Certified Specialist in OpenShift Automation and Integration
This course prepares you not only for real-world production use but also for the Red Hat certification that proves it.
Who Should Take This Course?
OpenShift Administrators managing production clusters
Kubernetes practitioners looking to scale deployments
DevOps professionals automating OpenShift environments
RHCEs aiming to level up with OpenShift certifications
If you’ve completed DO180 and DO280, this is your natural next step.
Get Started with DO380 at HawkStack
At HawkStack Technologies, we offer expert-led training tailored for enterprise teams and individual learners. Our Red Hat Certified Instructors bring real-world experience into every session, ensuring you walk away ready to manage OpenShift like a pro.
🚀 Enroll now and take your OpenShift skills to the enterprise level.
🔗 Register Here www.hawkstack.com
Want help choosing the right OpenShift learning path?
📩 Reach out to our experts at [email protected]
0 notes
Text
VMware vSphere 8.0 Update 2 New Features and Download
VMware vSphere 8.0 Update 2 New Features and Download @vexpert #vmwarecommunities #vSphere8Update2Features #vGPUDefragmentationInDRS #QualityOfServiceForGPUWorkloads #vSphereVMHardwareVersion21 #NVMEDiskSupportInVSphere #SupervisorClusterDeployments
VMware consistently showcases its commitment to innovation when it comes to staying at the forefront of technology. In a recent technical overview, we were guided by Fai La Molari, Senior Technical Marketing Architect at VMware, on the latest advancements and enhancements in vSphere Plus for cloud-connected services and vSphere 8 update 2. Here’s a glimpse into VMware vSphere 8.0 Update 2 new���

View On WordPress
#NVMe disk support in vSphere#Quality of Service for GPU workloads#Supervisor Cluster deployments#Tanzu Kubernetes with vSphere#vGPU defragmentation in DRS#VM management enhancements#vSphere 8 update 2 features#vSphere and containerized workload support#vSphere DevOps integrations#vSphere VM hardware version 21
0 notes
Text
Why You Need DevOps Consulting for Kubernetes Scaling

With today’s technological advances and fast-moving landscape, scaling Kubernetes clusters has become troublesome for almost every organization. The more companies are moving towards containerized applications, the harder it gets to scale multiple Kubernetes clusters. In this article, you’ll learn the exponential challenges along with the best ways and practices of scaling Kubernetes deployments successfully by seeking expert guidance.
The open-source platform K8s, used to deploy and manage applications, is now the norm in containerized environments. Since businesses are adopting DevOps services in USA due to their flexibility and scalability, cluster management for Kubernetes at scale is now a fundamental part of the business.
Understanding Kubernetes Clusters
Before moving ahead with the challenges along with its best practices, let’s start with an introduction to what Kubernetes clusters are and why they are necessary for modern app deployments. To be precise, it is a set of nodes (physical or virtual machines) connected and running containerized software. K8’s clusters are very scalable and dynamic and are ideal for big applications accessible via multiple locations.
The Growing Complexity Organizations Must Address
Kubernetes is becoming the default container orchestration solution for many companies. But the complexity resides with its scaling, as it is challenging to keep them in working order. Kubernetes developers are thrown many problems with consistency, security, and performance, and below are the most common challenges.
Key Challenges in Managing Large-Scale K8s Deployments
Configuration Management: Configuring many different Kubernetes clusters can be a nightmare. Enterprises need to have uniform policies, security, and allocations with flexibility for unique workloads.
Resource Optimization: As a matter of course, the DevOps consulting services would often emphasize that resources should be properly distributed so that overprovisioning doesn’t happen and the application can run smoothly.
Security and Compliance: Security on distributed Kubernetes clusters needs solid policies and monitoring. Companies have to use standard security controls with different compliance standards.
Monitoring and Observability: You’ll need advanced monitoring solutions to see how many clusters are performing health-wise. DevOps services in USA focus on the complete observability instruments for efficient cluster management.
Best Practices for Scaling Kubernetes
Implement Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Apply GitOps processes to configure
Reuse version control for all cluster settings.
Automate cluster creation and administration
Adopt Multi-Cluster Management Tools
Modern organizations should:
Set up cluster management tools in dedicated software.
Utilize centralized control planes.
Optimize CI CD Pipelines
Using K8s is perfect for automating CI CD pipelines, but you want the pipelines optimized. By using a technique like blue-green deployments or canary releases, you can roll out updates one by one and not push the whole system. This reduces downtime and makes sure only stable releases get into production.
Also, containerization using Kubernetes can enable faster and better builds since developers can build and test apps in separate environments. This should be very tightly coupled with Kubernetes clusters for updates to flow properly.
Establish Standardization
When you hire DevOps developers, always make sure they:
Create standardized templates
Implement consistent naming conventions.
Develop reusable deployment patterns.
Optimize Resource Management
Effective resource management includes:
Implementing auto-scaling policies
Adopting quotas and limits on resource allocations.
Accessing cluster auto scale for node management
Enhance Security Measures
Security best practices involve:
Role-based access control (RBAC)—Aim to restrict users by role
Network policy isolation based on isolation policy in the network
Updates and security audits: Ongoing security audits and upgrades
Leverage DevOps Services and Expertise
Hire dedicated DevOps developers or take advantage of DevOps consulting services like Spiral Mantra to get the best of services under one roof. The company comprehends the team of experts who have set up, operated, and optimized Kubernetes on an enterprise scale. By employing DevOps developers or DevOps services in USA, organizations can be sure that they are prepared to address Kubernetes issues efficiently. DevOps consultants can also help automate and standardize K8s with the existing workflows and processes.
Spiral Mantra DevOps Consulting Services
Spiral Mantra is a DevOps consulting service in USA specializing in Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and AWS. We are CI/CD integration experts for automated deployment pipelines and containerization with Kubernetes developers for automated container orchestration. We offer all the services from the first evaluation through deployment and management, with skilled experts to make sure your organizations achieve the best performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. How can businesses manage security on different K8s clusters?
Businesses can implement security by following annual security audits and security scanners, along with going through network policies. With the right DevOps consulting services, you can develop and establish robust security plans.
Q. What is DevOps in Kubernetes management?
For Kubernetes management, it is important to implement DevOps practices like automation, infrastructure as code, continuous integration and deployment, security, compliance, etc.
Q. What are the major challenges developers face when managing clusters at scale?
Challenges like security concerns, resource management, and complexity are the most common ones. In addition to this, CI CD pipeline management is another major complexity that developers face.
Conclusion
Scaling Kubernetes clusters takes an integrated strategy with the right tools, methods, and knowledge. Automation, standardization, and security should be the main objectives of organizations that need to take advantage of professional DevOps consulting services to get the most out of K8s implementations. If companies follow these best practices and partner with skilled Kubernetes developers, they can run containerized applications efficiently and reliably on a large scale.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Which DevOps platform is better for microservices management?
The landscape of DevOps has transformed immensely over the last ten years, with Kubernetes and microservices stepping in as the critical components for deploying contemporary applications. As companies transition to cloud-native architectures, the demand for effective CI/CD solutions tailored for Kubernetes has reached new heights.

While traditional CI/CD tools such as Jenkins have dominated the market for quite some time, newer entrants like BuildPiper are surfacing, delivering a more efficient, Kubernetes-native experience. So, how do BuildPiper and Jenkins stack up against each other? What advantages does BuildPiper bring to today's DevOps frameworks?
In this comprehensive analysis, we will highlight the key distinctions between BuildPiper and conventional CI/CD tools, aiding decision-makers in identifying the most suitable choice for their DevOps requirements.
The Evolution of CI/CD: A Shift from Traditional Tools to Kubernetes-Native Solutions
The CI/CD journey has evolved from monolithic, script-heavy pipelines to agile platforms that integrate seamlessly with modern cloud-native architectures.
1. Traditional CI/CD Tools: The Jenkins Era
For years, Jenkins has been the preferred CI/CD tool among DevOps teams. Its open-source design, vast plugin ecosystem, and adaptability made it a cornerstone of software delivery workflows.
Nevertheless, as infrastructure adopted Kubernetes, Jenkins began to reveal some shortcomings:
Complex Setup & Maintenance: The manual configuration required by Jenkins makes it challenging for larger Kubernetes deployments.
Plugin Overload: The reliance on a multitude of plugins can create compatibility issues and expose security vulnerabilities.
Scalability Challenges: Although Jenkins can connect with Kubernetes through agents, it wasn’t originally designed for containerized environments.
Lack of Built-in Security: Traditional tools often necessitate additional configurations to ensure secure deployments.
2. BuildPiper: A Kubernetes-First CI/CD Solution
BuildPiper presents a modern DevOps platform crafted specifically for Kubernetes and microservices. In contrast to Jenkins, it offers a complete CI/CD pipeline featuring integrated security, governance, and observability. Notable benefits include:
Native Kubernetes Integration: BuildPiper is designed to work effortlessly with Kubernetes clusters, eliminating the need for complicated setups.
Managed Microservices Pipelines: It streamlines the processes of building, testing, deploying, and conducting security checks within a unified workflow.
Security & Compliance by Default: With built-in security scanning, secret management, and compliance checks, security is automatically prioritized.
Simplified DevOps Experience: By reducing the reliance on multiple tools, BuildPiper serves as an all-in-one platform for CI/CD, GitOps, and observability.
This exploration aims to clarify how BuildPiper can better serve modern DevOps practices in today's rapidly evolving tech landscape.
You can check more info about: CI/CD Tools For Microservices.
0 notes
Text
Top 7 Tools Every Advanced DevOps Engineer Must Master in 2024

In today’s fast-paced IT world, DevOps engineers are the bridge between development and operations, ensuring rapid deployment, scalability, and reliability. But to succeed in this role—especially at an advanced level—you need to go beyond basic scripting or configuration. You must master a toolkit that aligns with modern infrastructure, automation, and continuous integration/deployment (CI/CD).
If you're aiming to become an expert in the field, here are the top 7 tools every Advanced DevOps Engineer must master in 2024.
1. Docker – Containerization Simplified
Docker remains the cornerstone of containerization. It allows developers and DevOps professionals to build, package, and run applications in a consistent environment across various platforms.
Why it's important:
Simplifies deployment
Increases portability of applications
Supports microservices architecture
Key Skills to Learn:
Creating Dockerfiles
Managing Docker images and containers
Docker Compose for multi-container apps
2. Kubernetes – The King of Orchestration
Once you master Docker, Kubernetes (also known as K8s) is your next step. It is the industry-leading platform for automating deployment, scaling, and managing containerized applications.
Why it's important:
Ensures high availability
Automates load balancing and scaling
Manages complex containerized applications
Key Skills to Learn:
Deploying apps on Kubernetes clusters
Helm charts
Monitoring and logging using tools like Prometheus and Grafana
3. Jenkins – CI/CD Automation at Its Best
A staple in CI/CD pipelines, Jenkins is an open-source automation server that helps automate the process of building, testing, and deploying code.
Why it's important:
Speeds up software delivery
Reduces manual errors
Integrates with a wide range of tools
Key Skills to Learn:
Writing Jenkinsfiles
Creating and managing pipelines
Integrating with Git, Maven, and Docker
4. Terraform – Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Gone are the days of manually provisioning infrastructure. With Terraform, you can define and manage your cloud infrastructure using declarative code, making your setups reproducible and version-controlled.
Why it's important:
Works with AWS, Azure, GCP, and more
Improves infrastructure consistency
Enables version control and team collaboration
Key Skills to Learn:
Writing .tf configuration files
Creating reusable modules
Managing state and remote backends
5. Ansible – Automated Configuration Management
Ansible allows DevOps professionals to automate provisioning, configuration, and application deployment using simple YAML syntax (Playbooks).
Why it's important:
Agentless and lightweight
Ideal for repeatable tasks and system updates
Easy to integrate with Jenkins and Terraform
Key Skills to Learn:
Writing Playbooks
Using roles and templates
Managing inventories and variables
6. Git – Version Control for Everything
While Git is popular among developers, it’s just as vital for DevOps. Whether managing infrastructure code or deployment scripts, Git ensures collaboration and traceability.
Why it's important:
Enables team collaboration
Tracks changes efficiently
Works with GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, and more
Key Skills to Learn:
Branching strategies (e.g., Git Flow)
Merging and pull requests
Integrating Git with CI/CD pipelines
7. Prometheus + Grafana – Monitoring and Visualization
Maintaining system health is crucial in DevOps. Prometheus is used for monitoring and alerting, while Grafana visualizes the collected data, helping you spot anomalies and trends.
Why it's important:
Real-time monitoring of applications and infrastructure
Customizable alerts
Beautiful dashboards for better visibility
Key Skills to Learn:
Setting up Prometheus exporters
Creating Grafana dashboards
Integrating with Kubernetes and Docker
Final Thoughts
Mastering these tools isn’t just about checking boxes—it’s about understanding how they work together to build efficient, reliable, and scalable DevOps pipelines. Whether you're looking to accelerate your career, land global roles, or lead large-scale infrastructure projects, these tools form the foundation of modern DevOps success.
At Edubex, our Advanced DevOps Engineer program is designed to help you gain practical, hands-on experience with all of these tools—equipping you to meet industry expectations and excel in your tech career.
0 notes
Text
Kubernetes RBAC Best Practices for Secure Identity Management
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a crucial aspect of securing your Kubernetes cluster. In this article, we'll explore the best practices for implementing RBAC in your Kubernetes cluster. At IAMDevBox.com, we understand the importance of secure identity management and will guide you through the process. RBAC is a mechanism for controlling access to cluster resources by assigning roles to users or service accounts. This allows you to define a set of permissions for a role, and then assign that role to a user or service account. This way, you can ensure that only authorized users or service accounts have access to sensitive resources. To implement RBAC in your Kubernetes cluster, you'll need to create a set of roles and bind them to users or service accounts. You can use the `kubectl create role` and `kubectl create rolebinding` commands to achieve this. For example, you can create a role that allows access to a specific namespace, and then bind that role to a user or service account. Read more: Kubernetes RBAC Best Practices for Secure Identity Management
0 notes
Text
🌐 Manage a Multicluster Kubernetes Architecture with OpenShift Platform Plus
As enterprises continue to scale cloud-native applications, managing multiple Kubernetes clusters across hybrid or multi-cloud environments becomes a real challenge. Security, consistency, visibility, and lifecycle management all start getting complex — fast.
That’s where Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus steps in to simplify and secure multicluster Kubernetes operations at scale.
🚀 What is a Multicluster Kubernetes Architecture?
In a multicluster architecture, you deploy and operate multiple Kubernetes clusters instead of a single monolithic one. These clusters may be:
Distributed across multiple data centers, regions, or cloud providers
Owned by different teams or business units
Designed for specific workloads, compliance, or performance requirements
While this setup provides flexibility and isolation, it also introduces a range of management challenges.
🧩 The Key Challenges in Multicluster Management
Running multiple Kubernetes clusters is not just a scaling problem — it's a complexity problem. Some common issues include:
🔐 Inconsistent security policies
🔍 Limited visibility and observability
🔄 Manual, error-prone updates and configurations
📦 Fragmented application lifecycle management
🛡️ Difficulty maintaining compliance across clusters
Managing these clusters manually becomes unsustainable.
🛠️ Enter Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus
Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus is purpose-built to address these challenges by integrating powerful tools into a unified Kubernetes platform:
✅ Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management (RHACM)
Centralized control of multiple clusters — create, import, update, and monitor clusters across on-prem, cloud, or edge environments from one dashboard.
✅ Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security (ACS)
Ensure consistent security policies and threat detection across all clusters, with deep Kubernetes-native protection.
✅ Red Hat Quay
An enterprise-grade container registry with integrated image scanning, helping you standardize and secure container image distribution across clusters.
🌍 Real-World Use Case
Imagine a financial services company running clusters:
In AWS for web apps
On-prem for secure workloads
In Azure for data analytics
With OpenShift Platform Plus, they can:
Monitor all clusters from one place
Apply consistent security policies via ACS
Automate app deployments using GitOps principles
Audit compliance for regulations like PCI-DSS
This setup ensures high availability, flexibility, and compliance — without the overhead.
🧭 Final Thoughts
Managing Kubernetes at scale doesn’t have to be chaotic. Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus gives organizations the tools they need to operate confidently in multicluster environments — while staying secure, compliant, and efficient.
Whether you're just starting with Kubernetes or looking to level up your operations, it's time to rethink how you manage your clusters.
🔗 Start exploring OpenShift Platform Plus today and simplify your multicluster strategy.
For more info, Kindly follow: Hawkstack Technologies
0 notes