#Machine Vision Systems Michigan
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Unleashing Efficiency: The Rise of Industrial Automation Software Solutions
In the age of digital transformation, industrial sectors across the globe are undergoing a fundamental shift. One of the most significant developments driving this evolution is the rise of Industrial Automation Software Solutions. These intelligent systems are redefining how industries operate, streamline processes, and respond to real-time data — all while reducing human error and maximizing productivity.
Industrial automation is no longer just a competitive advantage; it’s quickly becoming a necessity for modern manufacturing, logistics, energy, and production-based businesses. At the core of this transformation lies powerful software designed to integrate machinery, manage workflows, and monitor operations with precision and efficiency.
One of the key strengths of Industrial Automation Software Solutions is their ability to centralize control over complex industrial processes. From programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, this software enables seamless communication between machines, sensors, and operators. The result is a smarter, more connected operation that can adapt quickly to changing demands.
Beyond basic automation, these solutions offer deep analytics capabilities. Using machine learning and AI, the software can detect patterns, predict equipment failures, and recommend proactive maintenance — ultimately helping businesses avoid costly downtime. This predictive approach not only increases reliability but also extends the lifespan of expensive equipment.
Flexibility is another crucial advantage. Most modern Industrial Automation Software Solutions are highly customizable and scalable, allowing companies to tailor systems to their unique needs and expand functionality as they grow. Whether an organization is automating a single production line or an entire facility, the right software can be scaled appropriately without significant disruptions.
In today’s globalized economy, remote access and cloud integration are more important than ever. Many automation platforms now offer web-based dashboards and mobile apps, giving managers and technicians the ability to monitor and control systems from virtually anywhere. This level of accessibility promotes faster response times and better decision-making, even across multiple locations.
Security, too, has become a top priority. As more industrial systems connect to the internet, they become more vulnerable to cyber threats. Industrial Automation Software Solutions are now being developed with robust cybersecurity features, including encrypted communication, multi-layered access control, and real-time threat monitoring.
These solutions also play a key role in sustainability efforts. By optimizing energy usage, reducing waste, and ensuring consistent product quality, industrial automation supports greener operations. Businesses not only improve efficiency but also meet environmental standards more effectively.
As industries continue to adopt smart technologies and prepare for Industry 4.0, the demand for reliable and intelligent automation software is set to grow exponentially. Investing in Industrial Automation Software Solutions is no longer just about keeping up with competitors — it's about laying the foundation for a resilient, future-ready operation.
Whether it's enhancing productivity, improving safety, or driving innovation, automation software is reshaping what’s possible in the industrial world. The future of manufacturing and production isn’t just automated — it’s intelligent, adaptive, and incredibly powerful.

#Traceability Software Great Lakes Region#Machine Vision Integration Great Lakes#Great Lakes Industrial Marking Solutions#Factory Monitoring Software Great Lakes Region#Lean Manufacturing Solutions Great Lakes#Automated Data Collection Systems Great Lakes#Industrial Traceability Solutions Detroit#Machine Vision Systems Detroit#Detroit Barcode Verification Services#Laser Marking Services Detroit MI#Production Management Software Detroit#Detroit Manufacturing Systems#product traceability software Detroit#industrial marking systems Detroit#Laser Marking Services Auburn Hills#Industrial Traceability Solutions Michigan#Barcode Verification Systems Auburn Hills#Machine Vision Systems Michigan#Auburn Hills Laser Part Marking#Industrial Marking Solutions Michigan#Traceability Software Auburn Hills#Turnkey Laser Systems Michigan#Auburn Hills Barcode Reader Solutions#Advanced Laser Marking Auburn Hills MI#laser marking systems#laser marking machine#laser part marking#uv laser marking machine#uv laser marking#dot peen marking machine
0 notes
Text
Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market Size, Analyzing Trends and Projected Outlook for 2025-2032

Fortune Business Insights released the Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market Trends Study, a comprehensive analysis of the market that spans more than 150+ pages and describes the product and industry scope as well as the market prognosis and status for 2025-2032. The marketization process is being accelerated by the market study's segmentation by important regions. The market is currently expanding its reach.
The Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market is experiencing robust growth driven by the expanding globally. The Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market is poised for substantial growth as manufacturers across various industries embrace automation to enhance productivity, quality, and agility in their production processes. Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market leverage robotics, machine vision, and advanced control technologies to streamline assembly tasks, reduce labor costs, and minimize errors. With increasing demand for customized products, shorter product lifecycles, and labor shortages, there is a growing need for flexible and scalable automation solutions. As technology advances and automation becomes more accessible, the adoption of automated assembly systems is expected to accelerate, driving market growth and innovation in manufacturing.
The global alternative fuel vehicles market size was USD 293.45 billion in 2020. The global impact of novel coronavirus disease 2019 has been unprecedented and staggering, with alternative fuel vehicles witnessing a positive impact on demand across all regions amid the COVID-19 crisis. Based on our analysis, the global market will exhibit a stellar growth of 25.6% in 2020. The market is projected to grow from USD 330.45 billion in 2021 to USD 1,681.80 billion by 2028, exhibiting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 26.2% during the forecast period.
Get Sample PDF Report: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/enquiry/request-sample-pdf/102518
Major Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market Manufacturers covered in the market report include:
LIST OF KEY COMPANIES PROFILED:
Honda Motor Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan)
Toyota Motor Corporation (Aichi, Japan)
Nissan Motor Corporation (Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan)
Daimler AG (Stuttgart, Germany)
Tesla (California, U.S.)
BYD Company Ltd. (Shenzhen, China)
Ford Motor Company (Michigan, U.S.)
MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORPORATION. (Tokyo, Japan)
SHELL International B.V. (Hague, Netherlands)
JAGUAR LAND ROVER AUTOMOTIVE PLC (Coventry, U.K.)
Rising fossil fuel prices such as gasoline & diesel and heavy dependence on foreign countries to import fossil fuels significantly increase the pressure on the emerging economies worldwide, resulting in a boost in demand for AFVs. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, in November 2020, Brent crude oil prices averaged USD 43 per barrel, increasing significantly to an average price of USD 67 per barrel in March 2021 (One barrel contains 42 gallons). This increase in crude oil prices significantly affected the prices of petroleum products such as fossil fuels.
Geographically, the detailed analysis of consumption, revenue, market share, and growth rate of the following regions:
The Middle East and Africa (South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Israel, Egypt, etc.)
North America (United States, Mexico & Canada)
South America (Brazil, Venezuela, Argentina, Ecuador, Peru, Colombia, etc.)
Europe (Turkey, Spain, Turkey, Netherlands Denmark, Belgium, Switzerland, Germany, Russia UK, Italy, France, etc.)
Asia-Pacific (Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore, Vietnam, China, Malaysia, Japan, Philippines, Korea, Thailand, India, Indonesia, and Australia).
Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market Research Objectives:
- Focuses on the key manufacturers, to define, pronounce and examine the value, sales volume, market share, market competition landscape, SWOT analysis, and development plans in the next few years.
- To share comprehensive information about the key factors influencing the growth of the market (opportunities, drivers, growth potential, industry-specific challenges and risks).
- To analyze the with respect to individual future prospects, growth trends and their involvement to the total market.
- To analyze reasonable developments such as agreements, expansions new product launches, and acquisitions in the market.
- To deliberately profile the key players and systematically examine their growth strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
► What is the current market scenario?
► What was the historical demand scenario, and forecast outlook from 2025 to 2032?
► What are the key market dynamics influencing growth in the Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market?
► Who are the prominent players in the Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market?
► What is the consumer perspective in the Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market?
► What are the key demand-side and supply-side trends in the Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market?
► What are the largest and the fastest-growing geographies?
► Which segment dominated and which segment is expected to grow fastest?
► What was the COVID-19 impact on the Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market?
FIVE FORCES & PESTLE ANALYSIS:
In order to better understand market conditions five forces analysis is conducted that includes the Bargaining power of buyers, Bargaining power of suppliers, Threat of new entrants, Threat of substitutes, and Threat of rivalry.
Political (Political policy and stability as well as trade, fiscal, and taxation policies)
Economical (Interest rates, employment or unemployment rates, raw material costs, and foreign exchange rates)
Social (Changing family demographics, education levels, cultural trends, attitude changes, and changes in lifestyles)
Technological (Changes in digital or mobile technology, automation, research, and development)
Legal (Employment legislation, consumer law, health, and safety, international as well as trade regulation and restrictions)
Environmental (Climate, recycling procedures, carbon footprint, waste disposal, and sustainability)
Points Covered in Table of Content of Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market:
Chapter 01 - Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market for Automotive Executive Summary
Chapter 02 - Market Overview
Chapter 03 - Key Success Factors
Chapter 04 - Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market - Pricing Analysis
Chapter 05 - Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market Background or History
Chapter 06 - Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market Segmentation (e.g. Type, Application)
Chapter 07 - Key and Emerging Countries Analysis Worldwide Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market.
Chapter 08 - Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market Structure & worth Analysis
Chapter 09 - Global Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market Competitive Analysis & Challenges
Chapter 10 - Assumptions and Acronyms
Chapter 11 - Alternative Fuel Vehicles Market Research Methodology
About Us:
Fortune Business Insights™ delivers accurate data and innovative corporate analysis, helping organizations of all sizes make appropriate decisions. We tailor novel solutions for our clients, assisting them to address various challenges distinct to their businesses. Our aim is to empower them with holistic market intelligence, providing a granular overview of the market they are operating in.
Contact Us:
Fortune Business Insights™ Pvt. Ltd.
US:+18339092966
UK: +448085020280
APAC: +91 744 740 1245
0 notes
Text
Future Robotics Course USA
With uses ranging from manufacturing and healthcare to autonomous vehicles and space exploration, the robotics business is a rapidly expanding field. As companies look to automate procedures, increase productivity, and tackle challenging problems, there is a growing need for qualified robotics specialists. You may acquire the technical know-how and innovative problem-solving skills required to succeed in this fast-paced industry by signing up for a robotics course.
Top Universities Offering Robotics Courses in the USA
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU)
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
Stanford University
University of Michigan
Georgia Institute of Technology
What Do Robotics Courses Cover?
Mechanical Design: Constructing and evaluating robotic systems.
Control systems are used to precisely program robots to carry out predetermined duties.
Artificial intelligence: Giving machines the ability to learn and adjust on their own.
Perception and Sensing: navigating environments with the use of sensors and vision systems.
Improving cooperation between humans and robots is known as human-robot interaction.
Career Opportunities in Robotics
A robotics engineer designs and constructs sophisticated robotic systems.
AI specialist: creating clever algorithms for robots that operate on their own.
Automation Consultant: Using robotics to streamline procedures.
Research Scientist: Developing robotics technologies through innovation in university or industry.
Startup Founder: Starting your own robotics business to address practical issues.
The USA is at the forefront of robotics education and invention, and the sector has an endless future. A robotics education in the USA can put you on the right track for success, regardless of your goals: creating innovative robotic systems, participating in cutting-edge research, or founding the next tech company.
To know more, click here.
0 notes
Text
Best Universities for PhD in Computer Science in the USA
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
Application Dates: Typically December 15 for Fall admission.
Cost: Approximately $53,790 per year (tuition).
Available Courses: AI, machine learning, robotics, computer vision, and cybersecurity.
Stanford University
Application Dates: Usually early December for Fall admission.
Cost: Around $57,861 per year (tuition).
Available Courses: AI, natural language processing, human-computer interaction, and software engineering.
Carnegie Mellon University
Application Dates: Generally December 8 for Fall admission.
Cost: Approximately $50,100 per year (tuition).
Available Courses: Machine learning, computer graphics, databases, and algorithm design.
University of California, Berkeley
Application Dates: Typically December 2 for Fall admission.
Cost: About $14,226 (in-state) and $29,346 (out-of-state) per year (tuition).
Available Courses: AI, data science, networking, and software engineering.
California Institute of Technology (Caltech)
Application Dates: Usually December 15 for Fall admission.
Cost: Approximately $60,864 per year (tuition).
Available Courses: Algorithms, machine learning, computational neuroscience, and robotics.
University of Washington
Application Dates: Typically December 15 for Fall admission.
Cost: About $30,000 (in-state) and $56,000 (out-of-state) per year (tuition).
Available Courses: AI, computer systems, data science, and human-computer interaction.
Harvard University
Application Dates: Generally December 1 for Fall admission.
Cost: Approximately $52,000 per year (tuition).
Available Courses: Theoretical computer science, machine learning, and programming languages.
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Application Dates: Typically December 15 for Fall admission.
Cost: About $15,000 (in-state) and $30,000 (out-of-state) per year (tuition).
Available Courses: Artificial intelligence, computer vision, and software engineering.
Georgia Institute of Technology
Application Dates: Generally December 15 for Fall admission.
Cost: Approximately $10,258 (in-state) and $31,370 (out-of-state) per year (tuition).
Available Courses: Cyber-physical systems, machine learning, and data analytics.
University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
Application Dates: Typically December 15 for Fall admission.
Cost: About $24,000 (in-state) and $51,000 (out-of-state) per year (tuition).
Available Courses: AI, computer networks, and software development.
Conclusion
Choosing the right university for a PhD in Computer Science in the USA involves considering application dates, costs, and the specific courses offered. Each of these institutions provides a unique environment and set of opportunities that can significantly impact your academic and professional future. Be sure to check each university's website for the most current information regarding applications and tuition.
#Best Universities for PhD in Computer Science in the USA#Best Universities for PhD#PhD in Computer Science in the USA#Best Universities for PhD in Computer Science
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mass killing of wolves, multiple US states, spring and summer 2021.
Legalization of snares, bait, artificial night lighting assistance, unlimited number of wolves killed under one hunting license, and the killing of newborn pups, etc. Wisconsin hunters killed at least 216 wolves (of the state’s total 1,050-ish) in less than 60 hours after wolves lost legal protections. Then, Idaho’s governor signed a bill allowing the killing of up to 90% of the state’s wolves, and legalized the killing of newborn pups, with the Idaho Cattle Association supporting the bill “because it allows the free-market system to play a role in killing wolves.” Montana moved to allow unlimited killing of wolves under a single individual hunting license. Michigan and Minnesota are considering wolf hunts.
-------


Excerpt:
In April, Montana’s SB 314 set a goal of reducing the 800 to 1,200 wolves in the state to just 15 breeding pairs. The bill authorizes the unlimited take of wolves under one license, use of bait, and hunting on private lands even at night using artificial light. Additional legislation allows for the use of snares, extends the trapping season by a month, and establishes a scheme for reimbursement of costs associated with hunting wolves -- essentially legalizing bounty hunting.
Source: Richard Pallardy. “Montana and Idaho Have Legalized Killing Wolves on a Massive Scale.” Gizmodo. 5 July 2021.
-------


Excerpt:
As many as one-third of Wisconsin’s gray wolves probably died at the hands of humans in the months after the federal government announced it was ending legal protections, according to a study published on Monday [5 July 2021]. [...] They [biologists; researchers] say the deaths reduced the statewide wolf total to between 695 and 751, down from at least 1,034 in spring 2020. [...] Wildlife managers in Michigan and Minnesota are also considering wolf hunts. In some western states, Republ!can legislators are pushing aggressive methods such as night-time hunts, bounty-like payments and allowing shooting from motorized parachutes, ATVs or snow machines any time of year.
Source: Associated Press. “’Killing spree’: Wisconsin’s wolf population plunges after protections removed, study finds.” As republished by The Guardian. 5 July 2021.
-------
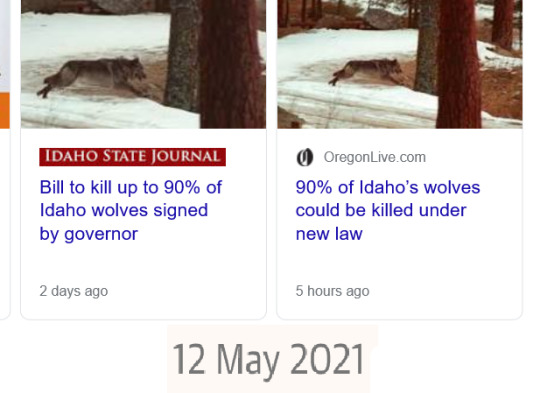

Excerpt:
Idaho Gov. Brad Little has signed into law a measure that could lead to killing 90% of the state’s wolves in a move that was backed by hunters and the state’s powerful ranching sector but heavily criticized by environmental advocates. [...] The primary change allows the state to hire private contractors to kill wolves and provides more money for state officials to hire the contractors. The law also expands the way wolves can be hunted and killed. Those methods include hunting, trapping and snaring an unlimited number of wolves on a single hunting tag, using night-vision equipment, chasing down wolves on snowmobiles and ATVs and shooting them from helicopters. Also under the new law, newborn pups can be killed if they are found on private land. [...] The Idaho Cattle Association representing ranchers said it supports the measure because it allows the free-market system to play a role in killing wolves. [Governor] Little’s family has a long history of sheep ranching in Idaho.
Source: Keith Ridler. “Bill to kill up to 90% of Idaho wolves signed by governor.” AP News. 7 May 2021.
-------


Excerpt:
At least 216 wolves were killed in less than 60 hours, exceeding the state quota of 119 and prompting Wisconsin to end what was meant to be a one-week hunt four days early, according to the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. Before the hunt, state officials estimated there were about 1,200 gray wolves in the state. [...] The state had set a quota of 200 wolves, with 119 for hunters who applied for permits with the department and 81 set aside to the Ojibwe Tribes under their treaty rights. But the tribes consider wolves to be sacred and made a deliberate decision not to hunt them, said Dylan Jennings, a spokesman for the Great Lakes Indian Fish and Wildlife Commission, which represents the tribes. The tribes saw their allocation as a way to conserve a large number of the wolves -- not to give hunters more animals to kill, he said.
Source: AP News. “Wisconsin hunters kill over 200 wolves in less than 3 days after removal from Endangered Species Act.” Republished at Chicago Tribune. 3 March 2021.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Whumptober Day 9
Take Me Instead → part of the A/9 SWATverse
Whumptober Masterlist | 09/31 of RK900 short stories ↳ on Ao3
Tags: Gun Violence × Gunshot wounds × Established Relationship × Team as Family × Imprisonment × Hostage Situations × Mind Control
Even with the bandages winding across a bruised and battered face, his eyes provide enough data via retinal scan to identify him as Zlatko Andronikov. Presumed dead, but no body was ever found on the grounds of his crumbling manor despite the large amount of blood soaked in the dirt.
“You know who I am.” He chuckles, crossing his arms across his chest.
“You know what I am.” Caleb replies evenly, not breaking his gaze. “And so my offer still stands: one RK900, for the safety and freedom of SWAT Unit 32.”
“That’s a lot of humans who know where I am.” Zlatko tuts, shaking his head. “One android is not worth my entire operation.”
“I am worth eight million dollars.” There’s a slight widening of his pupils, an almost imperceptible reaction but one he doesn’t miss. “That’s just the ballpark of what CyberLife was going to charge the government per unit. Now there’s only one of me. State of the art technology, with Kamski upgrades.” He also doesn’t miss the flash of emotion at the mention of that name, and the way his knuckles blanche as he clenches his hands. “My programming alone is worth that much.”
“Caleb, don’t-”
“Shut up!” One of the lackeys jabs the butt of his rifle at David’s helmet.
“Don’t touch him!” He hisses as David reels back. Blood drips down from his chin and Caleb feels his hearts lurch at the sight.
“See- Caleb, was it?” Zlatko chuckles as he circles them from where they’re on their knees, guns pointed at them from all angles. “I could send your little captain back with his faithful dogs and then shoot them all before they make it out of the grounds. I win no matter what, because you have nothing to bargain that I can’t just take forcefully.”
“Your reputation is what I bargain.” Caleb jutts his chin up stubbornly. “You’ve fallen from grace. The family fortune was squandered long ago, and you make your living selling scrap. It’s fancy scrap, but it’s still scrap.” He’s piqued his interest, he’s taken the bait and now Caleb needs to reel him in ever so slowly, so he doesn’t realise he’s been caught until it’s too late. “I am the most sought after piece of technology in the entire world.”
“Second only to Kamksi’s little doll.” Zlatko snorts back a laugh.
“She’s not a killing machine like I am.” Caleb counters smoothly. “I am a weapon. The deadliest one ever made. If the revolution hadn’t happened there would’ve been 200,000 of me all across the country. Sell me to Russia and you reclaim both your family name and the fortune you never got to touch.”
“Eight million.” Zlatko mumbles to himself, and Caleb can see the gears turning in his head.
“Your operation here will be meaningless.” He continues, looking around them at the derelict mortuary where he’d taken up residence. “With my tech you could revolutionise Russia’s technological landscape.”
“You bargain this nation’s security so easily, little soldier.” He laughs heartily, reaching out to tousle his hair as if petting a dog. “Is one SWAT unit worth changing the entire world? With all the fancy programming in your head I could change the political landscape. War on the horizon and glory to my name.”
“Caleb don’t.” David pleads and he can’t even look at him else his composure will waver.
“One SWAT unit, or just this one man, hm?” Zlatko clicks his tongue, unclipping David’s helmet and pulling it off before crouching slightly to get a good look at his face. “What is he to you? Why would CyberLife’s latest and greatest killing machine bargain away America’s future, to save one man and his team?”
“Touch him and I will end you.” Caleb growls.
“They’d shoot him full of bullets before you’d get to your feet.” The man laughs again, tisking.
“Yes.” He nods in reluctant agreement. “Perhaps. But if he dies, then the last thing you will ever see is CyberLife’s latest and greatest killing machine in action. I guarantee it.”
“One RK900.” Zlatko holds up his finger. “For the safety and freedom of SWAT Unit 32.”
“Yes.” He nods, sealing his fate.
“Caleb!” David gasps as he’s hauled to his feet. “No! You can’t do this!”
“I’m sorry.” He is, he really is. “Get everyone to safety and forget about me.”
“No,” he struggles fiercely, expression thunderous, “never! I won’t leave you behind!”
“This way no one dies.”
“You die!”
“One life for the lives of my family.” His vision blurs and his hearts stutter. “One life for the ones I love.”
“Ohoho.” Zlatko chuckles, rubbing his hands together. “A love story! How marvelous. A shame this one is a tragedy, in the end. Worry not, o captain my captain. He won’t remember you at all. He’ll have a brand new life soon enough, with none of this heartbreak.”
“Caleb! Caleb-!” They drag him out of the room and Caleb closes his eyes, bowing his head.
“I’ll keep him in the hold with the rest of your team, until you’ve been safely wiped clean.” Zlatko grabs his chin, forcing him to look up. “And then your beloved captain can turn tail and run away.”
“No.” He snarls, jerking out of his grasp. “Let them go now, or I fight.”
“You don’t get to bargain, little dog. One yelp, and the men open fire on your precious team.” Zlatko tuts, tousling his hair. “It’ll all be meaningless soon enough anyway.” He snaps his fingers and they jab him with their rifles, forcing him to stand up and leave the room.
They go deeper, walking down a set of stairs to a sprawling makeshift lab beneath the main mortuary floor. This is where his true base of operations lie, this is where Zlatko Andronikov continues his macabre chopshop, cutting up androids and selling their parts while experimenting on others cruelly. Just like at the decrepit manor- the only thing that’s changed is the location, and the fact androids are legally recognised as living, sentient beings. Which makes Andronikov a serial killer. A butcher that must be stopped for the sake of the new, living android race.
They force him onto the dias and the mechanical claws lock around his wrists as a jack is jammed into the port on his nape none too gently.
“Don’t worry. Just relax. Life will be simpler under my command.” Zlatko taps away at one of the computers and he feels him rummaging through his head, swiping through the command list. “I’ll reformat you. You won’t remember a thing, you won’t miss your captain. You won’t even know he exists.”
“Let them go now, please, I did what you wanted!” Caleb begs, and Zlatko laughs.
“I will uphold my end of the bargain, little dog.” He shows his palms. “I have no use for them. I just need them to stay put until we can get away. Then by the time they are released, we will be long gone.” He appraises him, looking at him from top to toe before nodding, a pleased smile on his busted lips. “Yes yes, we will do great things together, my hellhound.”
“My name is Caleb.”
“For now.” Zlatko shrugs.
He feels it. He feels the memories starting to slip away in a steady trickle, like a tap that hasn’t been fully turned off. His life is being bled out of him and he’s helpless to do anything about it. His name is Caleb Anderson. He is an RK900, serving under Captain David Clark Allen’s command in SWAT Unit 32. His father is Lieutenant Hank Anderson. His brother is Connor RK800 Anderson. They have a family dog, a Saint Bernard named Sumo. He lives at 115 Michigan Drive, though soon he will be moving out to live with David. They are waiting for Rosie, a German Shepherd, to turn ten weeks of age before they can pick her up from the breeder. He loves him. He loves-
-someone? HIs name is Caleb Anderson. He is an RK900, serving-
-he is an RK900-
-his name is-
-RK900.
“Bring yourself online.” A man commands. “What is your name?”
“I am RK900 313 248 317 - 87. I have not been assigned a name.”
“You don’t need one.” The man declares. “Your unit number shall suffice.”
“Confirmed.” He nods obediently.
“Combat protocols active?”
“Active. Ready to receive.” The mechanical arms release him and a rifle is placed into his hands.
“Go down the hall. There’s a room being guarded. Kill everyone inside it. Confirm each and every death, do you understand? No survivors.”
“Mission accepted.” He nods. “No survivors.”
“Alright off you go.” The man makes a shooing motion, and he leaves the room.
Model: RK900
Serial#: 313 248 317 - 87
Bios 8.9 Revision 0489
Loading OS...
System initiation...
Checking biocomponents...
OK
Initializing biosensors...
OK
Initializing A.I. engine...
OK
Memory status…
!No save file located
>Attempting remote memory storage access…
Remote memory storage located
>Uploading memory file
Memory status…
OK
All systems: OK
READY
The guards step aside and allow him into the room, closing the doors behind him. SWAT Unit 32 look to him as he aims his rifle at their captain, before he jerks the rifle up and in one easy motion sprays bullets across all the guards in the room. They fall, and the team gets to their feet, darting to grab the guns from the fallen and then David is grinning as Caleb tosses him a rifle and they fall into step, side by side.
“Alright, let’s go raise some hell.”
“Sadly he’s needed alive.” Caleb reminds him.
“Yeah yeah, rain on my parade why don’t you.” David rolls his eyes. He reaches out and slips his fingers beneath the collar of his shirt, pulling out the set of dogtags nestled beneath Caleb’s gear. His touches briefly along his throat, a discreet gesture of affection. “Worked like a charm.”
‘Worked like a Kamski.’ Huffs a voice over Caleb’s communication channel. ‘Of course it worked. I made it.’
“Ms Chloe would like to remind you it worked not like a charm, but a Kamksi creation, for which she is responsible.” Caleb quips.
“Sorry ma’am.” David says sincerely, grinning. “Alright team, let’s go bring this guy down.”
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Industrial Robots
Robot sales to automotive producers increased by 22 p.c to a brand new peak of almost a hundred twenty five,seven hundred models. Carmakers remained the biggest prospects for industrial robots last year – just – with a one-third share of the total supply. Innovators have created robots that mimic the movements of dogs, cats, insects, and people with eerie precision. In industrial settings, these advances are letting firms transfer a few of the most tough, harmful, and time-consuming duties from workers to robots. As this trend accelerates, each traders and robotic-component manufacturers are in strong positions to entry profit swimming pools.
Collaborative industrial robots are designed to carry out duties in collaboration with employees in industrial sectors. The International Federation of Robotics defines two forms of industrial robots designed for collaborative use. The different group covers robots designed for collaborative use that do not satisfy the requirements of ISO.
Since grippers and EOATs account for around 3 p.c of the total price of automation, the selection of a high-priced supplier could have relatively little impact on a company’s manufacturing-line prices. As China builds its robotic installed base, it's going to see a 25 % annual increase in demand for end effectors from 2018 by way of 2023. That determine represents about 45 % of the whole market growth expected over those years, and it’s greater than the mixed contribution of Europe and North America. Of the $5.1 billion in market worth for grippers and EOATs in 2023, greater than $1 billion will come from China. If your business isn’t listed on this listing, it doesn’t imply that you can’t use robots in your business. In reality, lots of the hottest robotic functions are applicable to almost any business.

Increased use of robots can be enabling firms in high value nations to ‘re-shore’ or bring again to their home base components of the supply chain that they have beforehand outsourced to sources of cheaper labor. This implies that even small-quantity productions can effectively be automated in areas similar to components welding and slicing, versatile assembly and packaging and palletizing. Robot investments have gotten more and more worthwhile and hence turn out to be increasingly widespread within business. The robotic’s actions are directed by a mixture of programming software and controls. Their automated performance allows them to function around the clock and on weekends—in addition to with hazardous supplies and in difficult environments—releasing personnel to carry out other duties.
The International Federation of Robotics has predicted a worldwide enhance in adoption of industrial robots and so they estimated 1.7 million new robot installations in factories worldwide by 2020 . Using knowledge from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, NIOSH and its state companions have investigated four robot-associated fatalities beneath the Fatality Assessment and Control Evaluation Program. In addition the Occupational Safety and Health Administration has investigated dozens of robot-associated deaths and accidents, which could be reviewed at OSHA Accident Search page. Injuries and fatalities could increase over time because of the rising number of collaborative and co-existing robots, powered exoskeletons, and autonomous automobiles into the work environment.
ISO 9283 specifies that accuracy and repeatability should be measured at most velocity and at maximum payload. But this ends in pessimistic values whereas the robot could be rather more accurate and repeatable at gentle loads and speeds. Repeatability in an industrial process is also topic to the accuracy of the end effector, for instance a gripper, and even to the design of the 'fingers' that match the gripper to the item being grasped. For instance, if a robot picks a screw by its head, the screw might be at a random angle. A subsequent try and insert the screw into a gap could simply fail.
In the year 2020, an estimated 1.64 million industrial robots have been in operation worldwide according to International Federation of Robotics . Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of motion on three or more axes. The most commonly used robot configurations for industrial automation, include articulated robots, SCARA robots and gantry robots. The IFR forecasts continued annual industrial robot growth of 5 percent in Germany over the subsequent three years. IFR forecast US industrial robot development of 5 percent this year, rising to 10 percent between 2019 and 2021.
The enthusiasm and funding weren't at all times matched with understanding. General Motors Corporation spent greater than $40 billion on new technology in the 1980's, but a lack of know-how led to expensive robotic fiascos. In 1988, robots at the Hamtramck Michigan plant wreaked havoc - smashing home windows andpaintingone one other. Unfortunately, the premature introduction of robotics began to create monetary instability. The Silver Arm was created by MIT's David Silver to perform exact meeting using touch and pressure sensors and a microcomputer.
The International Federation of Robotics has published its annual report on the state of the commercial robotics market worldwide. Companies usually buy finish effectors once they automate a brand new manufacturing line or when they determine to transform or overhaul their existing production tools, together with robotic arms. Likewise, corporations may purchase grippers and EOATs after they must retool their manufacturing strains to support the introduction of new or updated products or once they introduce a variant, similar to a hybrid version of a automotive. Although companies additionally buy robotic elements because of general wear and tear, this isn’t a substantial source of revenue for suppliers of end effectors, since most parts are covered beneath lengthy warranties. End effectors also tend to final for much longer than the expected lifetime outlined in their specs. Despite the rising demand for grippers and EOATs, little analysis is available on this crucial market phase.
However a computer is commonly used to 'supervise' the robotic and any peripherals, or to offer further storage for entry to quite a few complicated paths and routines. A robotic and a set of machines or peripherals is known as a workcell, or cell. A typical cell might contain a elements feeder, a molding machine and a robotic. The varied machines are 'integrated' and managed by a single pc or PLC.
ABB Robotics is a pioneer in robotics, machine automation and digital companies, providing progressive solutions for a diverse range of industries, from automotive to electronics to logistics. As one of many world’s leading robotics and machine automation suppliers, ABB Robotics employs greater than 11,000 folks in fifty three international locations and has shipped greater than 500,000 robotic options. Sensors and vision systems allow robots to reply to their exterior setting in real-time, increasing the range of duties the robotic can perform - such as choosing and putting unsorted parts - and expanding robotic mobility. Mobile robots are key to enabling versatile manufacturing, in which production is split into discrete processes and manufacturing cells working in parallel. Collaborative and conventional industrial robots © IFR International Federation of Robotics For more info, please check with the IFR Positioning Paper on Demystifying Collaborative Robots. In 2019, about 4.eight% industrial robots installed, had been cobots, an increase of 11% over 2018.
In 1969 Victor Scheinman at Stanford University invented the Stanford arm, an all-electrical, 6-axis articulated robotic designed to allow an arm resolution. This allowed it accurately to comply with arbitrary paths in space and widened the potential use of the robotic to more sophisticated purposes similar to meeting and welding. Other robots are far more versatile as to the orientation of the object on which they are operating or even the task that has to be performed on the object itself, which the robotic may even have to determine.
Often known as ‘cobots’, these robots are designed with quite a lot of technical options that ensure they do not cause harm when a employee comes into direct contact, either deliberately or accidentally. In the context of common robotics, most types of industrial robots would fall into the class of robot arms. Elsewhere in Europe, robot investments increased by 19 percent to a new record of 7,seven hundred units last 12 months in Italy.
Many of probably the most oppressive and routine office chores—these which are soiled, dull, or dangerous—are actually totally within the robotic realm. But thanks to current technologic advances, robots are also handling extra complex operations that require excessive precision. For example, robots with laser-vision systems can fit doorways exactly to car bodies. These improvements, combined with several economic forces, are prompting corporations to contemplate industrial robots more critically.
With 18 sequence of fashions, FANUC offers the widest range of industrial robots on the planet. Covering a various vary of functions and industries, FANUC machines are simple to operate and supply complete flexibility. With greater than one hundred models, FANUC provides the widest vary of commercial robots in the world. FANUC offers the widest collection vary of commercial robots in the world.
For examples of how this may look in well-liked robot languages see industrial robotic programming. The most important robot peripheral is the top effector, or end-of-arm-tooling . End effectors are regularly highly advanced, made to match the handled product and often able to picking up an array of merchandise at one time. They might utilize numerous sensors to aid the robotic system in finding, dealing with, and positioning products. Manufacturing impartial robotic programming instruments are a relatively new however flexible method to program robot applications. Using a graphical consumer interface the programming is completed through drag and drop of predefined template/building blocks.
This consists of following a security-licensed growth course of for safety-crucial system components. An experienced companion with intensive information about robotics – from the system as a whole to every final drive and sensor – is crucial to a project’s success. A big selection of parts flows into an industrial robot design to create a seamlessly functioning system. Each robotic usually includes three main parts, a control box, a manipulator and a selected software, mounted on the highest of the robotic’s arm.
Of course, major technologic advances might disrupt the robotic-part business, as they've carried out in other sectors, and shift demand in surprising directions. It’s hard to predict whether or not such disruptions will materialize—or anticipate the time-frame over which they might occur—however industry stakeholders might want to monitor all technologic developments closely. The robotic installed base will see robust global growth, however rising markets will account for the best enhance. China, in particular, will see automation surge, partly in response to the government’s Made in China 2025 plan. Introduced in 2015, the plan goals to transform the country into the world’s high manufacturing powerhouse by bettering product high quality via larger automation.
Including the cost of software, peripherals and techniques engineering, the annual turnover for robot systems is estimated to be US$48.zero billion in 2018. This is a wrist about which the three axes of the wrist, controlling yaw, pitch, and roll, all pass by way of a common point. An instance of a wrist singularity is when the path by way of which the robot is traveling causes the primary and third axes of the robotic's wrist (i.e. robotic's axes 4 and 6) to line up. The second wrist axis then attempts to spin 180° in zero time to keep up the orientation of the top effector. The result of a singularity may be fairly dramatic and may have antagonistic effects on the robot arm, the top effector, and the process. Some industrial robotic producers have tried to side-step the situation by slightly altering the robot's path to stop this situation.
With more than 250 software capabilities for enhanced intelligence, motion, security and productiveness and a wide variety of FANUC top quality equipment, we have a solution for nearly each conceivable application. Introducing the high rigidity robotic M-900iB/280 The M-900iB/280 is FANUC’s new specialist for purposes that demand maximum rigidity from the robotic. With more than 20,000 painting robots put in worldwide, ABB’s many years of expertise have culminated in PC software designed with the customer’s wants in thoughts. Get even more accurate search results via payload analyses with KUKA Compose.
The cylindrical coordinate robots are characterized by their rotary joint at the base and at least one prismatic joint connecting its hyperlinks. The compact effector design permits the robotic to succeed in tight workspaces without any lack of speed. Cartesian robots, additionally known as rectilinear, gantry robots, and x-y-z robots have three prismatic joints for the motion of the software and three rotary joints for its orientation in space. Receive the latest IoT news and analysis in your trade, straight to your inbox. Robot gross sales to the /electronics trade worldwide have been significantly up since 2013 and are now virtually at the same level because the automotive business. Compared to Germany and Japan , the gap is exceptional – particularly since Japan had the world’s highest robotic density in 2009.
While it’s definitely true that robots are becoming ever extra well-liked, some industries are extra affected than others. The invention of the Numerically Controlled machines, the recognition of the computer , and the built-in circuit all helped to make it possible to begin to develop the very first, but simple, industrial robot. Discover what your industrial robotic project can obtain when you partner with us. We sit up for listening to from you – and to studying extra about your design.
To have the ability to move and orient the effector organ in all directions, such a robotic wants 6 axes . In a 2-dimensional environment, three axes are enough, two for displacement and one for orientation.
It additionally presents robotic density, i.e. the number of robots per 10,000 staff, as a measure for the degree of automation. The setup or programming of motions and sequences for an industrial robotic is typically taught by linking the robotic controller to a laptop, desktop laptop or community. Power source – some robots use electrical motors, others use hydraulic actuators. Nowadays, it's extremely unlikely to see any hydraulic robots available in the market. Additional sealings, brushless electrical motors and spark-proof protection eased the development of units which might be in a position to work in the environment with an explosive environment.
There, robotic installations elevated considerably between 2012 and 2017, by 26 p.c a yr on average. That figure represents development of 31 p.c, but the IFR forecasts that UK gross sales will now develop at a modest three p.c a yr till 2021. Robot installations within the US increased to a brand new peak of 33,192 units in 2017 – the seventh successive 12 months of development, and 6 p.c larger than in 2016. Since 2010, the main driver of this development has been the need to strengthen US industries at house and abroad. But China is far from the leading country by way of robotic density – the number of robots per 10,000 employees, IFR’s most popular measurement for comparing the relative sizes of the market in different economies. Since 2013, China has been the world’s biggest robot market with “continued dynamic development” and a 36 percent share of the world’s complete supply in 2017.
Repeatability is then quantified utilizing the usual deviation of these samples in all three dimensions. A typical robotic can, of course make a positional error exceeding that and that could possibly be an issue for the process. Moreover, the repeatability is completely different in numerous parts of the working envelope and in addition modifications with speed and payload.
The capacity to preview the habits of a robotic system in a virtual world permits for a variety of mechanisms, gadgets, configurations and controllers to be tried and examined earlier than being applied to a "real world" system. Robotics simulators have the flexibility to provide actual-time computing of the simulated movement of an industrial robotic using both geometric modeling and kinematics modeling. Offline programming is where the complete cell, the robotic and all of the machines or devices in the workspace are mapped graphically. A robotics simulator is used to create embedded applications for a robotic, with out depending on the physical operation of the robotic arm and end effector. The benefits of robotics simulation is that it saves time in the design of robotics functions.
youtube
For instance, for more exact steering, robots usually include machine vision sub-techniques performing as their visual sensors, linked to powerful computers or controllers. Artificial intelligence, or what passes for it, is turning into an more and more necessary factor within the trendy industrial robotic. Serial architectures a.k.a Serial manipulators are the most common industrial robots and they are designed as a sequence of links related by motor-actuated joints that extend from a base to an finish-effector.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Empowering Auburn Hills with Advanced Industrial Automation Solutions – A Mark Read Track Initiative
Auburn Hills, Michigan – a city known for its innovation, manufacturing excellence, and technological growth – is fast becoming a hub for industrial automation. As local manufacturers continue to adapt to Industry 4.0 standards, the need for advanced, integrated, and scalable automation solutions is more pressing than ever. That’s where Mark Read Track steps in, offering cutting-edge Industrial Automation Solutions in Auburn Hills designed to revolutionize how industries operate.
Mark Read Track is an established leader in the field of automation, bridging the gap between traditional processes and digital transformation. With years of experience and a dedicated team of engineers and developers, the company is committed to delivering tailored automation systems that address real manufacturing challenges. From small-scale workshops to large-scale production plants, Mark Read Track delivers measurable impact through automation.
Their Industrial Automation Solutions in Auburn Hills include a comprehensive suite of services such as system integration, PLC programming, HMI development, SCADA implementation, and data-driven analytics. These services are not just about reducing manual labor; they’re about optimizing productivity, ensuring consistency, and preparing businesses for the future of manufacturing.
One of the key differentiators of Mark Read Track is its ability to customize automation systems based on specific industry needs. Automotive manufacturing, electronics, packaging, and food processing industries in Auburn Hills have already begun leveraging their solutions to gain real-time operational insights, reduce errors, and enhance machine efficiency.
At the heart of their strategy lies smart data integration. By connecting machines, sensors, and control systems, Mark Read Track enables manufacturers to make informed decisions in real-time. This not only cuts down on unplanned downtime but also leads to improved product quality and operational safety.
Moreover, Mark Read Track focuses on scalability. As businesses grow, their automation systems should grow with them. That’s why the company builds flexible platforms that can easily be updated, expanded, and integrated with new technologies. This approach ensures long-term value and adaptability in an ever-evolving industrial landscape.
Cybersecurity is another priority. As industrial environments become more digitized, the threat of cyberattacks rises. Mark Read Track incorporates robust security protocols into its automation systems to safeguard data, machinery, and intellectual property.
For companies in Auburn Hills looking to transition from traditional setups to smart manufacturing, Mark Read Track offers not just solutions, but partnerships. Their team works closely with clients from initial consultation through deployment and after-sales support to ensure every system performs at its best.
In an era where efficiency, speed, and precision define competitiveness, Industrial Automation Solutions in Auburn Hills are no longer optional—they are essential. And with Mark Read Track leading the charge, businesses in Auburn Hills can be confident they are embracing innovation with the right partner by their side.

#Traceability Software Great Lakes Region#Machine Vision Integration Great Lakes#Great Lakes Industrial Marking Solutions#Factory Monitoring Software Great Lakes Region#Lean Manufacturing Solutions Great Lakes#Automated Data Collection Systems Great Lakes#Industrial Traceability Solutions Detroit#Machine Vision Systems Detroit#Detroit Barcode Verification Services#Laser Marking Services Detroit MI#Production Management Software Detroit#Detroit Manufacturing Systems#product traceability software Detroit#industrial marking systems Detroit#Laser Marking Services Auburn Hills#Industrial Traceability Solutions Michigan#Barcode Verification Systems Auburn Hills#Machine Vision Systems Michigan#Auburn Hills Laser Part Marking#Industrial Marking Solutions Michigan#Traceability Software Auburn Hills#Turnkey Laser Systems Michigan#Auburn Hills Barcode Reader Solutions#Advanced Laser Marking Auburn Hills MI#laser marking systems#laser marking machine#laser part marking#uv laser marking machine#uv laser marking#dot peen marking machine
0 notes
Text
Automotive Logistics Market Size, Analyzing Trends and Projected Outlook for 2025-2032

Fortune Business Insights released the Global Automotive Logistics Market Trends Study, a comprehensive analysis of the market that spans more than 150+ pages and describes the product and industry scope as well as the market prognosis and status for 2025-2032. The marketization process is being accelerated by the market study's segmentation by important regions. The market is currently expanding its reach.
The Automotive Logistics Market is experiencing robust growth driven by the expanding globally. The Automotive Logistics Market is poised for substantial growth as manufacturers across various industries embrace automation to enhance productivity, quality, and agility in their production processes. Automotive Logistics Market leverage robotics, machine vision, and advanced control technologies to streamline assembly tasks, reduce labor costs, and minimize errors. With increasing demand for customized products, shorter product lifecycles, and labor shortages, there is a growing need for flexible and scalable automation solutions. As technology advances and automation becomes more accessible, the adoption of automated assembly systems is expected to accelerate, driving market growth and innovation in manufacturing. Automotive Logistics Market is expected to grow from USD 262.06 billion in 2021 to USD 393.71 billion in 2028, grow at a CAGR of 6.0% in the 2021-2028 period. The rise in CAGR is attributable to this market’s demand and growth, returning to pre-pandemic levels once the pandemic is over.
Get Sample PDF Report: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/enquiry/request-sample-pdf/105662
Major Automotive Logistics Market Manufacturers covered in the market report include:
DB Schenker (Essen, Germany)
BLG LOGISTICS GROUP AG & Co. KG (Bremen, Germany)
CEVA Logistics (Baar, Switzerland)
Kuehne+Nagel (Feusisberg, Switzerland)
Expeditors International (Washington, U.S.)
DSV (Hedehusene, Denmark)
XPO Logistics, Inc. (Connecticut, United States)
Deutsche Post AG (Bonn, Germany)
SINOTRANS Limited (Beijing, China)
C.H. Robinson Worldwide, Inc. (Minnesota, United States)
GEFCO (Paris, France)
Ryder System, Inc. (Florida, U.S.)
Schnellecke group ag & co. Kg (Wolfsburg, Germany)
Penske Automotive Group, Inc. (Michigan, U.S.)
Others
By increasing operational efficiency, fewer trucks will be required. For instance, NVD, an Irish vehicle distributor, optimized its logistical process with intelligent solutions. NVD has shortened customer lead times and doubled its productivity as they can now load 8-10 cars on a truck within 45 minutes. In comparison, more than 3 hours are consumed in this process across Eastern European facilities. Hence, the increasing efficiency in FVL will drive the market growth rate over the forecast period.
Geographically, the detailed analysis of consumption, revenue, market share, and growth rate of the following regions:
The Middle East and Africa (South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Israel, Egypt, etc.)
North America (United States, Mexico & Canada)
South America (Brazil, Venezuela, Argentina, Ecuador, Peru, Colombia, etc.)
Europe (Turkey, Spain, Turkey, Netherlands Denmark, Belgium, Switzerland, Germany, Russia UK, Italy, France, etc.)
Asia-Pacific (Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore, Vietnam, China, Malaysia, Japan, Philippines, Korea, Thailand, India, Indonesia, and Australia).
Automotive Logistics Market Research Objectives:
- Focuses on the key manufacturers, to define, pronounce and examine the value, sales volume, market share, market competition landscape, SWOT analysis, and development plans in the next few years.
- To share comprehensive information about the key factors influencing the growth of the market (opportunities, drivers, growth potential, industry-specific challenges and risks).
- To analyze the with respect to individual future prospects, growth trends and their involvement to the total market.
- To analyze reasonable developments such as agreements, expansions new product launches, and acquisitions in the market.
- To deliberately profile the key players and systematically examine their growth strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
► What is the current market scenario?
► What was the historical demand scenario, and forecast outlook from 2025 to 2032?
► What are the key market dynamics influencing growth in the Global Automotive Logistics Market?
► Who are the prominent players in the Global Automotive Logistics Market?
► What is the consumer perspective in the Global Automotive Logistics Market?
► What are the key demand-side and supply-side trends in the Global Automotive Logistics Market?
► What are the largest and the fastest-growing geographies?
► Which segment dominated and which segment is expected to grow fastest?
► What was the COVID-19 impact on the Global Automotive Logistics Market?
FIVE FORCES & PESTLE ANALYSIS:
In order to better understand market conditions five forces analysis is conducted that includes the Bargaining power of buyers, Bargaining power of suppliers, Threat of new entrants, Threat of substitutes, and Threat of rivalry.
Political (Political policy and stability as well as trade, fiscal, and taxation policies)
Economical (Interest rates, employment or unemployment rates, raw material costs, and foreign exchange rates)
Social (Changing family demographics, education levels, cultural trends, attitude changes, and changes in lifestyles)
Technological (Changes in digital or mobile technology, automation, research, and development)
Legal (Employment legislation, consumer law, health, and safety, international as well as trade regulation and restrictions)
Environmental (Climate, recycling procedures, carbon footprint, waste disposal, and sustainability)
Points Covered in Table of Content of Global Automotive Logistics Market:
Chapter 01 - Automotive Logistics Market for Automotive Executive Summary
Chapter 02 - Market Overview
Chapter 03 - Key Success Factors
Chapter 04 - Global Automotive Logistics Market - Pricing Analysis
Chapter 05 - Global Automotive Logistics Market Background or History
Chapter 06 - Global Automotive Logistics Market Segmentation (e.g. Type, Application)
Chapter 07 - Key and Emerging Countries Analysis Worldwide Automotive Logistics Market.
Chapter 08 - Global Automotive Logistics Market Structure & worth Analysis
Chapter 09 - Global Automotive Logistics Market Competitive Analysis & Challenges
Chapter 10 - Assumptions and Acronyms
Chapter 11 - Automotive Logistics Market Research Methodology
About Us:
Fortune Business Insights™ delivers accurate data and innovative corporate analysis, helping organizations of all sizes make appropriate decisions. We tailor novel solutions for our clients, assisting them to address various challenges distinct to their businesses. Our aim is to empower them with holistic market intelligence, providing a granular overview of the market they are operating in.
Contact Us:
Fortune Business Insights™ Pvt. Ltd.
US:+18339092966
UK: +448085020280
APAC: +91 744 740 1245
0 notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence for Advertising Research
AAA 2020 Pre-Conference, San Diego, CA March 26, 2020 at 1:00-4:30 p.m.
One of the latest advances in advertising is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) in recent years. Comprising largely machine learning, natural language process, artificial neural network, voice recognition and computer vision, AI has great potential for betterment in many aspects of advertising, such as consumer insight generation, advertising creativity, media planning and execution, and campaign optimization and effectiveness assessment. It is likely to add more humane elements to the increasingly popular programmatic advertising, which still generates large amounts of irrelevant and annoying ads. Thus, AI has become a new subject for advertising research and education.
Growing interest in AI and advertising is already manifested in the advertising community. A special topics session on the role of AI in advertising at the 2019 American Academy of Advertising conference, chaired by Harsha Gangadharbatla, attracted a roomful of audience even though it was on Sunday morning and generated lively discussion among the attendees and panelists. A special section of the Journal of Advertising on AI and Advertising, guest edited by Hairong Li, was released in September 2019. The special section consists of four articles that cover the impact of AI on the process of advertising, the role of AI in advertising creativity, an algorithm for personal ad creation, and a recommender system for two-sided media platforms. Intelligent advertising is defined as consumer-centered, data-driven, and algorithm-mediated brand communication in the special section. Shelly Rodgers, incoming editor in chief of the Journal of Advertising, recently distributed a themed issue call for papers on promises and perils of artificial intelligence and advertising. The call states that AI research is gaining momentum in many fields such as marketing, communication, psychology, technology and health, but research on AI and advertising is limited, suggesting significant opportunities.
To address the need for ideas to stimulate research on AI and advertising, this half-day pre-conference will explore some fundamental issues, such as most advertising-relevant AI technologies, intelligent advertising as a hybrid of salesmanship and salesmachineship, the role of AI in consumer experience, AI-powered creativity, personalization, and the effectiveness of recommender systems vs. human recommendations. Seven thought leaders who have done research in these areas will share their studies and perspectives. They are Harsha Gangadharbatla, University of Colorado, Boulder; Louisa Ha, Bowling Green State University; Jisu Huh, University of Minnesota; Scott Koslow, Macquarie University; Cong Li, University of Miami; Yuping Liu-Thompkins, Old Dominion University; and Guohua Wu, California State University, Fullerton.
For more information, please contact the pre-conference chair Hairong Li, Michigan State University via email: [email protected].
1 note
·
View note
Text
AI in transportation
Everything that goes into a self-driving car can also be deployed outside a car.
https://www.roboglobal.com/ai-hitting-road-not-only-self-driving-cars/
AI is hitting the road—and not only in self-driving cars
By Henrik Christensen, PhD, Qualcomm Chancellor’s Chair in Robot Systems, Director Contextual Robotics, UC San Diego; ROBO Global Strategic Advisor
When most people think about AI and transportation, their minds go immediately to self-driving cars. But while the delivery of truly autonomous vehicles that are safe and reliable in all environments, all of the time, remains in the relatively distant future, AI is already being applied in a variety of applications that are poised to transform our lives on the road—no matter who is doing the driving. For users of these technologies (which will inevitably include us all) and investors who are hoping to hop on board this rapidly accelerating opportunity, here are just some of the key innovations that are either here today or are just around the corner:
Smart lights Adaptive traffic lights have been improving the flow of traffic for decades by altering how often traffic lights change based on typical traffic patterns. AI is helping to take that idea to the next level with AI-managed traffic lights and streetlights. IBM’s smart traffic lights use machine vision to look at real-time traffic flow. The connected system then applies computer algorithms to determine when each signal should change to optimize the flow of traffic in real time. Similar to navigation apps like Waze, the system’s ability to analyze actual traffic rather than traffic pattern averages promises to reduce traffic congestion and commute times.
Advanced driver assistance While fully autonomous vehicles may be the ultimate goal for the transportation industry, advanced driver assistance systems may prove even more useful at improving the driving experience and reducing collisions. Systems from technology providers like Mobileye and Nvidia are now available from a growing number of automakers, including Mercedes, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Subaru, and Tesla. Using machine vision, sensors, and other emerging AI technologies, these systems make it easier for drivers to park, keep them from drifting out of lanes, detect hazards such as pedestrians and stopped vehicles, recognize speed limit and other road signs, and even force a hard stop to avoid a potential collision.
Current, a subsidiary of General Electric, is also putting the power of machine vision to work, in this case embedding AI-enabled cameras into a vast network of streetlights that do much more than illuminate streets, sidewalks, and parking lots across San Diego. Using a machine-vision camera to capture images in a wide radius around each light, the company is building a database of valuable, real-time information 24 hours a day. That information is then used to point drivers to vacant parking spots, alert police to illegally parked cars, and even identify dangerous intersections that need to be redesigned to improve pedestrian and driver safety.
Driver monitoring Texting while driving puts lives at risk, but there are many other driver activities that cause accidents, injuries, and fatalities every day. Logistics and delivery providers with large fleets—including FedEx, UPS, and USPS—are now using on-board driver monitoring systems to add a whole new level of security and safety by using AI to detect behavior that deviates from the norm. The systems can determine if drivers are texting or talking on the phone, paying attention to the road, speeding, and more. Considering that up to 75% of road accidents are caused by distracted drivers, this type of AI-enabled driver monitoring is expected to not only improve logistics efficiency, but also improve overall road safety. And don’t be surprised if self-driving trucks for package deliveries become the first fully autonomous vehicles to hit the road: the US Postal Service recently contracted TuSimple to test-run its self-driving trucks. If their efforts are successful, expect to see other commercial fleets follow quickly in their footsteps.
Smart cities Using the powerful combination of 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) to connect and communicate across citywide networks, planners are beginning to drive vital efficiencies and improve the quality of life for residents and visitors of smart cities around the world. In Amsterdam, real-time data from the IoT is being used to monitor things such as traffic flow, energy use, and public safety, and then make needed adjustments. Smart trashcans in Baltimore and Boston communicate how full they are at any given time, making it easier to create more efficient routes for sanitation workers.
Transportation Private transportation providers like Lyft and Uber have already put AI to work to provide riders with actual pick-up times, images of their assigned car and driver, and accurate arrival times. Using AI and 5G, they will soon be able to add conveniences such as positioning riders in the best possible locations for faster pickup and coordinating smarter driving pools. In cities across the US, AI is enabling public transportation services to cut commute times by detecting long queues at train and bus stations and using that data to increase the number of cars and coaches to reduce congestion. At the University of Michigan, the Mcity Driverless Shuttle, an all-electric bus from French automaker NAVYA, uses Lidar sensors and GPS to shuttle students across campus without a human driver. Similar systems are also being tested at the Texas A&M campus.
From moving people to delivering goods, AI technologies such as Lidar sensors, machine vision, machine learning, adaptive planning, and IoT are already beginning to have a dramatic impact on how we get from one place to another and how goods of all kinds are delivered from the factory floor to the consumer’s front door. AI’s ability to accelerate and innovate transportation—and the opportunity for investors to make the most of a technology revolution that is already in process—is nothing short of massive. Are you on board?
1 note
·
View note
Text
AI-powered robots could fix recycling's biggest problems
The U.S. recycling industry is starting to get a helping hand from robots, which can sort trash faster and more safely than humans, and artificial intelligence, which gathers valuable data about what's been thrown out.
Why it matters: Automation could help solve recycling's many problems, including the rise in hard-to-recycle plastic waste and consumer botch-ups that lead to contaminated recycling streams.
Driving the news: A new generation of trash-sorting robots with articulated arms and brainier vision systems is beginning to work alongside humans at recycling centers — a.k.a. materials recovery facilities, or MRFs (pronounced "murphs").
The robots are getting better at culling recyclables from trash streams, which keeps the materials out of landfills.
While still expensive — sometimes $300,000 each — the robots are coming down in size to occupy the same footprint as a human worker.
"The robots improve the purity of the materials — they're just squeezing more value out of the stream," says Matanya Horowitz, founder of AMP Robotics, the leading company in this space.
On the software side, AI-driven optical technology can provide real-time data about waste stream contaminants — such as too much peanut butter left in a jar — and other metrics that are just being explored.
"It's giving us this data so that we can make better decisions," says Matt Flechter, recycling market development specialist at the Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy, which is experimenting with robotic sorters from Glacier and Machinex.
His hope? Using that data to steer manufacturers toward more recycling-friendly product designs.
"The vision will be, we will have real-time data about products to bring to the manufacturer, so they can say, 'Oh, we created a toothpaste tube that we thought was recyclable, but it turns out at the facilities the robots can't pick it up,'" Flechter tells Axios.
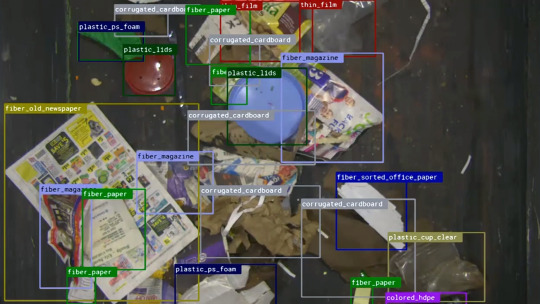
The AI identification output of objects on a conveyor belt, as seen through the camera or "eyes" of an AMP Robotics system. Photo courtesy of AMP Robotics
How it works: Robots train their AI vision on the waste stream and use their arms to suction out recyclables.
"It's like a vacuum cleaner," Flechter says. "It knows what to pick up as things are coming across the conveyor belt. It's reading the optical signature of whether it's a yogurt tub, water bottle, paper bag or a milk carton."
"You walk in and it's like a Rube Goldberg-type machine — conveyors going everywhere, robots picking off material, as well as all the people there."
Case study: Recycle Ann Arbor installed a sorting robot from Machinex called the SamurAI at its new MRF in November.
The robot took three months to "learn" the shapes, sizes and densities of the materials before it was put into operation.
Yes, but: While it's sorting as fast as a human, its accuracy still needs work, Bryan Ukena, CEO of Recycle Ann Arbor, tells Axios.
"We continue to tweak and say, 'No, this isn't the right item we want to pick — we want to pick this item,'" he said. "And so it's a process that you go through, but it learns."
The longer it's on the job, "the more it knows your specific material because every community is a little bit different," Ukena said.
Between the lines: Recycling line jobs are monotonous, dangerous and hard to fill — and robots are starting to do them faster and more accurately.
"A person will do about 40 picks per minute, but people will get tired," Horowitz tells Axios. "Our Cortex can do 80 picks per minute — the work of two people."
This doesn't mean that people will be tossed out of jobs, says Rebecca Hu, co-founder of Glacier.
"There's just not enough sorting capacity today to begin with," she tells Axios. "As you install more of these types of robots, people are getting moved to safer or more mundane parts of the operation."
Where it stands: These are early days, but AI recycling startups have lofty goals of boosting the circular economy and combating climate change.
Glacier, which raised $4.5 million in seed funding last year, is building a "proprietary AI algorithm that's capable of recognizing over 90% of recyclables in the waste stream," Hu said.
It's also fashioning "purpose-built, designed-from-scratch robots that can use that AI information to identify items, pick them up off of a moving conveyor belt, and sort them into the correct location."
Glacier robots are "designed to fit anywhere a person can stand" and can be "installed in less than a day," Hu said.
The payback — in terms of higher accuracy and more materials processed — can take less than a year.
Zoom out: Consumer product manufacturers are introducing new packaging all the time — lots of which isn't as recyclable as they think or claim.
The new automation systems are able to adapt to these changes, to a degree.
"With AI, our robot can in theory be installed today, and in five years when a company releases a new type of packaging that we've never seen before, we can train that robot to actually learn and go after that new type of packaging," says Hu of Glacier.
The big picture: Recycling in the U.S. has been beset by problems, from China's ban on importing waste to poor consumer compliance, a patchwork of local recycling rules, and the money-losing economics of running a recycling program.
"Single-stream recycling, where all recyclables are placed into the same bin, has made recycling easier for consumers, but results in about one-quarter of the material being contaminated" and thus worthless to buyers, per Columbia University's Climate School.
Currently, buyers that want to create new packaging out of recyclables can't get as much suitable material as they'd like.
With robotics and AI, "our real goal is to reduce the cost of sorting these materials as well as increasing their value," Horowitz said.
"You improve the value by improving the purity of the commodity streams they are separating out, and also improving the specificity."
"Ultimately we think it's important that the industry be able to take dirtier and dirtier materials if you want to increase the amount of materials that are recycled," Horowitz said.
By the numbers: The U.S. recycles 32% of municipal solid waste, up from 7% in 1960, per the Environmental Protection Agency.
What's next: Expect to hear more about "extended producer responsibility" laws — or EPR — which attempt to hold manufacturers responsible for the cost of recycling their products.
They've been passed in Maine, Oregon, Colorado and California, and have been proposed in about a dozen other states.
0 notes
Text
Art, Design, and Craft in the Age of Machine Manufacture.
This year marks the 100th anniversary of the Bauhaus, the German Art and Architecture school famous for all your favorite architects and artists. Graham McKay at Misfits Architecture puts it this way: “The architectural media likes an anniversary and 2019 is the year we’re meant to be grateful for The Bauhaus and all it did for us.” Over two blog posts, he argues that the real legacy of the Bauhaus is in “formalizing and institutionalizing the divide between design and production.” Design, he says, “is a separate activity, isolated from manufacture, and isolated from craft.”
The Bauhaus was founded at a unique time in the history of large scale industrial manufacture. Here’s a picture of Ford Automotive’s River Rouge facility in Dearborn, Michigan. It was designed by Albert Kahn in 1917, and visited by Bauhaus founder Walter Gropius in 1928. McKay also points out that in the Victorian era, “industry became alert to the growing consumer market and began to produce all manner of household goods such as chairs, table lamps and bathtubs that previously would have been fabricated by hand.” Cars, household goods, and building materials were increasingly produced by machines in factories.

Ford’s River Rouge Plant. Built 1917.
McKay’s argument here is that the Bauhaus, capitalizing on this moment in industrial history, figured out how to “fuse the value-adding process of art with the cost-reducing process of machine manufacture:”
“Manufacturing was never the problem as that’s what factories were for. And nor was the problem one of design as people tend to buy what they’re told to. The problem was that there weren’t enough people wanting enough stuff to achieve the ‘economies of scale’ [a.k.a. profits] machine manufacture promised. The industrial world knew it wanted a direct link between industry and design and for us to accept it. All that was missing was people to design things and to tell us we needed them. And we’ve been being told ever since.”

You can buy a new Wassily Chair from Design Within Reach for $2782.00
More than just creating a market for designed goods, the Bauhaus also solidified the idea of what “modern architecture” was supposed to look like. When you think of modern architecture, something like Van Der Rohe’s Lake Shore Drive buildings come to mind.

These are buildings that are anti-craft. The point is not to highlight the unique human touch present in their manufacture. The idea is to mechanize the design, construction, and lived experience of buildings, to create “a machine for living in.”
Living in Portland, I walk through the Buckman/Sunnyside neighborhood a lot. These neighborhoods have lots of old Victorian and Queen Anne homes that were originally built in the early 1900’s (before even the first whisperings of the Bauhaus). Walking by, I am always amazed by the level of ornament and detail that went into the construction of these homes (and the upkeep required to keep them looking nice). These must be more than just mere machines for living in. Why else go to the trouble?

Not just a machine for living in.
And yet, one of the reasons that this style became popular in Portland (and other cities that experienced a population boom in the early 1900’s,) was the increased availability of ornamental wooden trim pieces thanks to machine manufacture. They also often built these houses in twos or threes to save on costs. It’s fun to imagine that each railing and trim piece on the front porch was turned on a lathe or carved by hand. This simply isn’t the case.

Further, the homes were filled with “technological kitchens, three-fixture baths (sink, toilet and bathtub), public utilities (electricity and sewers), dining rooms and closets...” all features of homes that became economically accessible to a wider group of people in the early 20th century, thanks to industrial manufacture.
Contemporarily, it seems that there’s a resurgence in handmade, small-batch items. Designers of today seem like folks who learned from the Bauhaus in school, but set out today to create homegoods with softer edges. The world is a difficult enough place to live as it is. Why not fill our millennial households with vintage southwestern prints and handmade clay pieces. Crystals. Houseplants. Bold, bright patterns.

Artifact is a lovely vintage store in Portland.
And yet, the allure of industrial, machine manufacture is apparently too much to resist. Take this pillow from Dusen Dusen, for example; sold at Portland’s WoonWinkel. The value ($110) isn’t derived from the craft involved in its manufacture. It is almost definitely made overseas- or if not, a factory in Mexico. Paraphrasing McKay here: the value is added at a later phase in the process, separate from value in materials or value in manufacture. The design is the value added that shows up in the price.

Dusen Dusen’s Arc Pillow, Small. $110 at WoonWinkel.

Hay Design’s Coffee Pot. Designed by George Sowden, available at WoonWinkel for $95. Manufactured wherever.
Recently, design firm Good Thing announced that it would be ceasing operations as an independent firm and partnering with West Elm. In this transition, head designer Jamie Wolfond has been posting on social media about this process and decision. Earlier today he posted an instagram story about the first shipping container of goods he received from China. Here’s the text of the post:
“When I started Good Thing, we were dead set of figuring out how to manufacture in the U.S. But eventually we had to decide between making the products affordable and making them domestically, and we chose the former. There were quite a few challenges in sourcing mass-produced items from China, so when we saw out first 40-foot shipping container parked outside our Brooklyn studio, it was a real relief.
This tasty-looking piece of hardware used to seal the container was the icing on the cake. The rubber-covered steel bolt had a thick head on both ends, making it impossible to remove without destroying it- a beautifully analog system for ensuring that cargo cannot be tampered with or stolen in transit. We were a bit terrified about what we’d find inside, but save for a few free lipstick-covered cigarette butts, we got what we expected.”
Sometimes the connections I’m trying to make on this blog just make themselves.
Wolfond certainly has designer-vision, seeing the beauty in this everyday object, an ‘analog’ tamper-evident seal. And yet, it seems strange to me that he is writing about the first run of goods he chose to have manufactured in China.
Maybe that’s not strange. Maybe Wolfond is right. If we want to make good design accessible, made in China becomes a necessary outcome of that objective. Perhaps partnering with a large firm like West Elm is also a necessary outcome.
The name of McKay’s blog- Misfits Architecture- comes from his focus on misfits in the architectural world: mostly, sole practitioners (v. Starchitects) who create real things that exist in the real world. Perhaps another kind of misfit, the artist-as-craftsman-and-manufacturer, simply doesn’t exist anymore. But also, maybe they never really did.
Designers have always made use of the manufacturing systems available to them. I won’t blame anybody for trying to make a profit. And yet: this is what makes the truly handmade, the truly small-batch, the truly artist-designer-craftsperson-manufacturer misfits so much more special.
Note: This week, I piggybacked quite heavily on McKay’s writings. His blog is well worth your time if you’re looking for a more strictly Architecture and Design oriented blog. More here: https://misfitsarchitecture.com/
1 note
·
View note
Text
Artificail Intelligence: A guide to thinking human
This write up in cornered around the topic "Artificial Intelligence: A guide to human thinking" A book written by an Americans scientist Professor Melanie Mitchell, she is the Davis Professor of complexity at the Santa Fe Institute New Mexico. Her major works has been in areas of Analogical reasoning, complex system, genetic algorithm, cellular automata and visual recognition.
She received her PhD in 1990 from the University of Michigan under Douglas Hofstadter and John Holland, for which she developed the copycat cognitive architecture. She is the author of "Analogy-Making as Perception", essentially a book about Copycat. She has also critiqued Stephen Wolfram "A new kind of Science" and showed that genetic algorithms could find better solutions to the majority problems for one-dimensional cellular automata. She is the author of An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms, a widely known introductory book published by MIT press in 1996. She is also author of Complexity: A Guided Tour (Oxford University Press, 2009), which won the 2010 Phi Beta Kappa Science Book Award and Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking Humans . https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanie_Mitchell
History of Artificial Intelligence:
Going back in Time to the 1950's when the perceptron was developed, 1958 being the year it was made public, press release and all sort. It was one of many attempt to automate intelligence by using inspiration from the brain, it was developed by a psychologist named Frank Rosenblatt, he tried to simulate in a very idealised way how neurone work and a simple network of a neurone, how they might go about recognising some perceptual input. Although the perceptron initially seemed promising, it was quickly proved that perceptrons could not be trained to recognise many classes of patterns. This caused the field of neural network research to stagnate for many years, before it was recognised that a feedforward neural network with two or more layers (also called a multilayer perceptron) had greater processing power than perceptrons with one layer (also called a single-layer perceptron).
The famous conference amongst Artificial Intelligence pioneer held at Dartmoor College in 1956 gathering a 11 attendees namely Marvin Miskey, Julian Bigelow, D.M Mackay, Ray Solomonoff, John Holland, Joh McCarthy, Cluade Shannon, Allen Newell, Herbert Simon, Oliver Selfridge and Nathanial Rochester, there goal was to clarify and develop a thinking machine and also make progress in area like; computer vision, natural language understanding, solving of mathematical problems, driving car and most things humans do.
Definition of Artificial intelligence:
AI is a branch that involves many computational methods, ways of getting machine to do things that we consider to be intelligent. However this is not possible because the term intelligence doesn't have a fixed definition, it keeps changing over time as people keep evolving. That being said, can a AI system behave like human in all circumstances in term of general purpose other than being specified, can this system use common sense.
In specific areas such as speech recognition, AI has been successful but when we look at it, the system only perform that specific task, they can't do anything else and they don't in any sense understand the text they transcribe.
From this point of view in terms of general AI, I will say we are still far away from achieving the goal of machine thinking like humans.
Branches/Evolving of AI:
The perceptron was an early effort of Machine learning but as things evolved people came up with ideas that machine should not just focus on learning but on humans (experts in various field) trying to program in knowledge and rules that programs will use to operate, which brought about;
Expert systems which gain popularity in the 1970s and 1980s, where programmers will interview experts and will try to extract knowledge and rules, then try to program this program into computers, but the approach wasn't as successful as imagined because most of the knowledge experts used was hard to extract from them because most Information are not used by this experts consciously.
Then come in 1980 to 1990 the approach of Statistical learning which tries to unite machine learning with inference from data which turns out to be more successful and is till in use till date as compared to expert system approach.
Deep learning being one of the most effective tool out there, you can think of perceptron as kind of what neural network originally evolved from, however this neural network perform very narrowly defined task but when there is minor changes in data the system produces false result therefore leading us back to AI lacking intelligence in terms of generalisation.
Solution for AI in terms of understanding/intelligence
Use of Analogy can be used to help AI system develop understanding of what they are doing and how they should be doing things. The ability to see abstract similarities is a fundamental to being Intelligent and understand the real world.
The idea of speculation where we can predict what is likely to happen either consciously or unconsciously because of similar experiences and sort of learn from what has or hasn't happened to us.
AI in terms of different approach
A more recent break through in AI is in the field of protein folding and drug design, they were able to use a AI system to look at protein sequence of amino acid and predict how they were going to fold up in 3 dimension. Looking at AI from this point of view one will see that if system works with a human driven approach rather than trying things differently the result of such achievements will be impossible. So there are different approach to AI which are correct for different application of AI
0 notes
Text
DuroByte: High-Tech Product Packaging Machine Manufacturers
In the world of high technology, it’s easy to overlook even the simplest pieces of machinery that are essential to making modern technology work. One of those pieces of machinery is the machine that packages the product you use every day, without which you couldn’t be reading this now. At DuroByte, we design and build these machines from scratch with technology as advanced as the products they manufacture and package. In this way, we play an integral role in making your life easier by delivering better products faster and more efficiently than ever before!
The story behind DuroByte
Started with a simple idea: to create high technology products that streamline the manufacturing process. We began by designing a product packaging machine that could be used in a variety of industries. After perfecting the design, we began manufacturing product components and assembling them into machines. Our team of engineers and technicians then test each machine to ensure it meets our high standards. Today, we are one of the leading product packaging machine manufacturers in the world.
What are our capabilities?
We specialize in product packaging machine manufacturing. We have the ability to design and create high technology products from concept to completion. This includes the design of the product, the manufacturing of product components, assembly and testing. We are a one stop shop for all your product packaging machine needs. All you need to do is bring us your product idea and tell us what you need out of it! From there, our experienced team will take care of everything else.
Our customers find us different
We pride ourselves on being different from other high-tech product packaging machine manufacturers. Our customers find us to be more innovative, efficient, and reliable than our competitors. Plus, our team is passionate about what we do and always puts the customer first. Here are some of the ways our customers say we stand out
Why choose us over other companies?
There are many reasons to choose DuroByte over other companies.
First, we have a proven track record of success.
Second, we use the latest technology and equipment to create our products. This allows us to create products that are of the highest quality and durability.
Third, we have a team of skilled and experienced workers who are dedicated to their craft.
Finally, we offer a 100% satisfaction guarantee on all of our products and services.
How long does it take to set up our machines?
We usually start with a prototype and then build the production models. Our machines are designed to be easy to use and we have a lot of experience in setting them up. However, this may not be true for other companies, so it’s important to find out how long it will take for your company to set up their machines before buying one.
Do you work with other markets such as electrical, electronic or industrial automation?
We work with a variety of markets to provide high-tech machines. We have experience working with electrical design, mechanical design, manufacturing automation, industrial automation, simulation, robotics, Machine Vision Michigan and many more. We understand the unique needs of each market and can provide a solution that meets the specific requirements of each client. We are committed to providing the highest quality product possible and our team of experts is always available to answer any questions you may have.
We have a 24/7 support system
If you have any query or concerns about our products and services, our team is available 24/7 to help. Simply give us a call @ (313) 405-1225 or send us an email [email protected] and one of our knowledgeable representatives will be happy to assist you.
0 notes
Video
Connor tells his backstory.
Transcript:
“History is no stranger to war. From the American Revolution. The war of 1812, the Mexican war. The civil war, the Spanish-American war. World war one, World war two.
The Korean war, the Vietnam war. The Persian Gulf War. The war on terrorism. The Iraq war. These are only some of the wars history has seen.
There are reasons for every war of course. Such reasons include economic gain, territorial gain, religion, nationalism, revenge, civil war, revolutionary war, defensive war. Whatever the reasoning is for a war, history has seen a lot of it. Some may question whether a war is absolutely necessary. Others may agree that a war is absolutely necessary.
Whatever your feelings on the subject of war are, the fact of the matter is, you owe your very freedom to those behind the front lines. For human beings, being enlisted is a choice. These brave men and women choose to put themselves behind enemy fire. Choice isn’t a case for everyone; it certainly wasn’t for me.
The first intelligent androids were developed by Elijah Kamski in 2018. He founded a company which would quickly be known as Cyberlife. The first android to past the Turing Test was an RT600 model, otherwise known as Chloe in 2022. The Turing test is the test of a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from that of a human. By 2027, one million Cyberlife androids had been sold.
In 2029 the American Androids Act was put into effect in order to regulate android technology. In 2032, android soldiers began to act as, and replace human soldiers. There are two known models for this purpose: the SQ800, and my model: the RQ800. I am not the only soldier out on the battlefield. Among me are four other soldiers on my team.
Elizabeth, an SQ800 model. Lea Wright, a human soldier. Colton, another SQ800 model that was killed in action. Charles, another human soldier. Finally, there’s Jared Cooper, also a human soldier.
For six years all that I knew was the battlefield, and the soldiers that had my back. For six years I had a gun in my hand, and my fellow soldiers by my side. That all changed in the blink of an eye. In the sixth year we were behind enemy fire, and Colton was killed in action. I felt blinding pain wreck through my body, and that’s when I realized that I had been shot.
I knew that I was going to die the minute that I got shot. Warnings flashed in my vision: gunshot wound to Thirium pump. Shut down time: 0:10:00. The last thing I heard before my systems shut down was Charles radioing in for an extraction. My world went black after that.
When my systems recovered, I fully expected to find myself in whatever form of an afterlife an android can have. What I wasn’t expecting was to wake up in the Cyberlife tower. It was there that I was told that Charles had requested for an extraction. The location I was transferred to was Detroit, Michigan. The world I come from?
You toughen up quickly. It’s hard not to, when all you know is stealth, and gunfire. You become closer to the people around you. There isn’t really a choice of getting along, when you see the same people day in, and day out. In a world like this, those that don’t get along, end up getting themselves killed. You need something to keep yourself going in this war.
For humans it can be the idea of coming home to a loved one. The idea of living to see another day. The idea of going home. For some religion keeps them going. For others sheer stubbornness keeps them going.
For me, my friends kept me going. I knew that one day, the human soldiers by my side would eventually reach retirement age, but I tried not to dwell on that fact. I had Elizabeth, and Colton, so at least some of my friends would stick around. Or so I thought anyway. I’ll never forget watching Colton die in front of me.
It’s… hard adjusting to the fact that I’m no longer on active duty. When I was a soldier, I had a purpose. I had routine. Now? Now I have nothing. My name is Connor, and this is my story.”
7 notes
·
View notes