#Solar Power
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Let's keep it up. Topple the petroleum complex.
"People have been telling stories about renewable energy since the nineteen-seventies, when the first all-solar-powered house opened on the campus of the University of Delaware, drawing a hundred thousand visitors in 1973, its first year, to marvel at its early photovoltaic panels and its solar hot-water system, complete with salt tubs in the basement to store heat overnight. But, even though we’ve got used to seeing solar panels and wind turbines across the landscape in the intervening fifty years, we continue to think of what they produce as “alternative energy,” a supplement to the fossil-fuelled power that has run Western economies for more than two centuries. In the past two years, however, with surprisingly little notice, renewable energy has suddenly become the obvious, mainstream, cost-efficient choice around the world. Against all the big bad things happening on the planet (and despite all the best efforts of the Republican-led Congress in recent weeks), this is a very big and hopeful thing, which a short catalogue of recent numbers demonstrates:
It took from the invention of the photovoltaic solar cell, in 1954, until 2022 for the world to install a terawatt of solar power; the second terawatt came just two years later [in 2024], and the third will arrive either later this year or early next [in 2025 or early 2026].
That’s because people are now putting up a gigawatt’s worth of solar panels, the rough equivalent of the power generated by one coal-fired plant, every fifteen hours. Solar power is now growing faster than any power source in history, and it is closely followed by wind power—which is really another form of energy from the sun, since it is differential heating of the earth that produces the wind that turns the turbines.
Last year, ninety-six per cent of the global demand for new electricity was met by renewables, and in the United States ninety-three per cent of new generating capacity came from solar, wind, and an ever-increasing variety of batteries to store that power.
In March, for the first time, fossil fuels generated less than half the electricity in the U.S. In California, at one point on May 25th, renewables were producing a record hundred and fifty-eight per cent of the state’s power demand. Over the course of the entire day, they produced eighty-two per cent of the power in California, which, this spring, surpassed Japan to become the world’s fourth-largest economy.
Meanwhile, battery-storage capability has increased seventy-six per cent, based on this year’s projected estimates; at night, those batteries are often the main supplier of California’s electricity. As the director of reliability analysis at the North American Electric Reliability Corporation put it, in the CleanTechnica newsletter, “batteries can smooth out some of that variability from those times when the wind isn’t blowing or the sun isn’t shining.” As a result, California is so far using forty per cent less natural gas to generate electricity than it did in 2023, which is the single most hopeful statistic I’ve seen in four decades of writing about the climate crisis.
Texas is now installing renewable energy and batteries faster than California; in a single week in March, it set records for solar and wind production as well as for battery discharge. In May, when the state was hit by a near-record-breaking early-season heat wave, air-conditioners helped create a record demand on the grid, which didn’t blink—more than a quarter of the power came from the sun and wind. Last week’s flooding tragedy was a reminder of how vulnerable the state is to extreme weather, especially as water temperatures rise in the Gulf, producing more moisture in the air; in late June, the director of the state’s utility system said that the chances of emergency outages had dropped from sixteen per cent last summer to less than one per cent this year, mostly because the state had added ten thousand megawatts of solar power and battery storage. That, he said, “puts us in a better position.”
All this is dwarfed by what’s happening in China, which currently installs more than half the world’s renewable energy and storage within its own borders, and exports most of the solar panels and batteries used by the rest of the world. In May, according to government records, China had installed a record ninety-three gigawatts of solar power—amounting to a gigawatt every eight hours. The pace was apparently paying off—analysts reported that, in the first quarter of the year, total carbon emissions in China had actually decreased; emissions linked to producing electricity fell nearly six per cent, as solar and wind have replaced coal. In 2024, almost half the automobiles sold in China, which is the world’s largest car market, were full or hybrid electric vehicles. And China’s prowess at producing cheap solar panels (and E.V.s) means that nations with which it has strong trading links—in Asia, Africa, South America—are seeing their own surge of renewable power.
In South America, for example, where a decade ago there were plans to build fifteen new coal-fired power plants, as of this spring there are none. There’s better news yet from India, now the world’s fastest-growing major economy and most populous nation, where data last month showed that from January through April a surge in solar production kept the country’s coal use flat and also cut the amount of natural gas used during the same period in 2024 by a quarter. But even countries far from Beijing are making quick shifts. Poland—long a leading coal-mining nation—saw renewable power outstrip coal for electric generation in May, thanks to a remarkable surge in solar construction. In 2021, the country set a goal for photovoltaic power usage by 2030; it has already tripled that goal.
Over the past fifteen years, the Chinese became so skilled at building batteries—first for cellphones, then cars, and now for entire electric systems—that the cost of energy storage has dropped ninety-five per cent. On July 7th, a round of bidding between battery companies to provide storage for Chinese utilities showed another thirty per cent drop in price. Grid-scale batteries have become so large that they can power whole cities for hours at a time; in 2025, the world will add eighty gigawatts of grid-scale storage, an eightfold increase from 2021. The U.S. alone put up four gigawatts of storage in the first half of 2024.
There are lots of other technologies vying to replace fossil fuels or to reduce climate damage: nuclear power, hydrogen power, carbon capture and storage; along with renewables, all were boosted by spending provisions in Biden’s Inflation Reduction Act and will be hampered to varying degrees by congressional rollbacks. Some may prove useful in the long run and others illusory, but for now they are statistically swamped by the sheer amount of renewable power coming online. Globally, roughly a third more power is being generated from the sun this spring than last. If this exponential rate of growth can continue, we will soon live in a very different world.
All this suggests that there is a chance for a deep reordering of the earth’s power systems, in every sense of the word “power,” offering a plausible check to not only the climate crisis but to autocracy. Instead of relying on scattered deposits of fossil fuel—the control of which has largely defined geopolitics for more than a century—we are moving rapidly toward a reliance on diffuse but ubiquitous sources of supply. The sun and the wind are available everywhere, and they complement each other well; when sunlight diminishes in the northern latitudes at the approach of winter, the winds pick up. This energy is impossible to hoard and difficult to fight wars over. If you’re interested in abundance, the sun beams tens of thousands of times more energy at the earth than we currently need. Paradigm shifts like this don’t come along often: the Industrial Revolution, the computer revolution. But, when they do, they change the world in profound and unpredictable ways...
In retrospect, it’s reasonably easy to see how fast solar and wind power were coming. But, blinkered by the status quo, almost no one actually predicted it. In 2009, the International Energy Agency predicted that we would hit two hundred and forty-four gigawatts of solar capacity by 2030; we hit it by 2015. For most of the past decade, the I.E.A.’s five-year forecasts missed [underestimated the amount of renewables] by an average of two hundred and thirty-five per cent. The only group that came even remotely close to getting it right was not J. P. Morgan Chase or Dow Jones or BlackRock. It was Greenpeace, which estimated in 2009 that we’d hit nine hundred and twenty-one total gigawatts by 2030. We were more than fifty per cent above that by 2023. Last summer, Jenny Chase, who has been tracking the economics of solar power for more than two decades for Bloomberg, told the Times, “If you’d told me nearly 20 years ago what would be the case now, 20 years later, I would have just said you were crazy. I would have laughed in your face. There is genuinely a revolution happening.”
-via The New Yorker, July 9, 2025
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

#renewable energy#wind power#Solar power#fossil fuels#fossil fuel subsidies#Republican climate change denialism#republican assholes#maga morons#traitor trump#crooked donald#climate crisis#republican hypocrisy#oligarchs are killing the planet
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - July 15-21
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. Helicopter expedition stumbles upon group of rare large-eared animals in Patagonian mountains

”With fewer than 1,500 individuals remaining across Chile and Argentina, this new subpopulation is a vital lifeline for the species. […] "Finding viable populations in new areas strengthens the case for large-scale conservation corridors and gives the species a better chance to survive[….] We now have a unique opportunity to turn this area into a formally protected national park that ensures its long-term preservation.””
2. New smart, carbon-free agriculture system is powered by renewable energy

“Compared to conventional greenhouse systems, [the new “hydrogen-fueled combined heat and power (CHP) system”] reduces CO₂ emissions by over 50% and cuts operating costs by more than one-third. […] The system combines PEM fuel cells, air-source heat pumps, solar collectors, and adsorption chillers to generate electricity and reuse the waste heat for cooling and heating.”
3. Trump admin forced to restore $6.2 million to LGBTQ+ and HIV groups

“[A judge] issued a preliminary injunction blocking the enforcement of these provisions [which would deny equity-related funding] while the lawsuit proceeds. [… Lambda Legal has] “confirmed that our plaintiffs — LGBTQ+ organizations providing critical services to their communities — have seen their threatened funding restored[….]” In granting the injunction, the court held that [plaintiffs] will likely succeed in demonstrating that the executive orders violate their rights[….]”
4. Conservationists raise sharks to restore reefs in waters around Thailand

“As [“near threatened”] apex predators, bamboo sharks keep in check populations of smaller creatures that might otherwise overgraze the reefs. [… Oceans For All started] by creating a breeding pair from two sharks that had been caught in fishers’ nets. [… T]he team has chosen to release pups when they’re 6 months old and […] large enough to have good odds of survival, but not yet too reliant on being fed by humans. […] Since Oceans for All launched, it has released 200 sharks.”
5. This metro Atlanta factory roof is now a solar record-breaker

“The new array produces enough energy to power more than 100 homes. The system is expected to cover about 10% of Beauflor’s electricity needs and cut its carbon emissions by about 920 metric tons annually. […] “The previous record-holder for metro Atlanta’s largest rooftop solar required over 4,000 panels. We’re using less than 2,000 to reliably generate even more power.””
July 8-14 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#south america#chile#argentina#deer#animals#endangered species#agriculture#clean energy#renewableenergy#heat pump#climate change#solar panels#us politics#trump administration#lgbt#lgbtq#lgbtqia#lgbt rights#conservation#shark#thailand#solar energy#solar power#solar#atlanta#georgia#electricity#nature
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
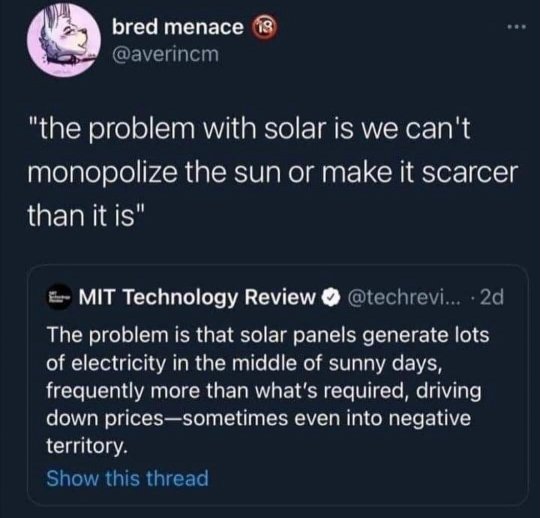
18K notes
·
View notes
Text

Solar energy has so many benefits. Raising salaries for teachers is such a needed narrative.
37K notes
·
View notes
Text



LORDE What Was That (2025) | Oceanic Feeling (2022) | Perfect Places (2017)
#lorde#melodrama#solar power#what was that#lordeedit#dailymusicians#dailywomen#flawlessbeautyqueens#usermusic#nessa007#userladiesblr#femaledaily#dailycelebs#*mine: gifs#movies & tv
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

1K notes
·
View notes
Text
LORDE HAS RETURNED
#lorde#lordemusic#lorde music#ella yelich o'connor#pure heroine#homemade dynamite#lorde lyrics#lorde gif#ella yelich-o'connor#lorde news#melodrama#solar power#new music
889 notes
·
View notes
Text


justice for Solar Power! (insta)
#full carousel on insta!#but tldr had an incredible time in Costa Rica#insta#gay#lgbt#bi#solar power#Lorde
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
thanks to @krill-joy for the article!
#sheep#solar farms#good news#environmentalism#usa#solar panels#solar energy#solar power#environment#nature#animals#science#climate change#climate crisis
818 notes
·
View notes
Text
"China’s carbon emissions have flatlined over the past six months and there’s now an opportunity for substantial declines over the next decade, analysts say.
The rapid growth in clean energy generation has been sufficient to offset a recent surge in power demand caused by higher air conditioning use amid late-summer heatwaves, and the government’s manufacturing push, according to an analysis by Lauri Myllyvirta of the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA).
China’s carbon emissions fell by 1% in the second quarter of 2024 and were flat in the third quarter, providing another indication that emissions may have already peaked.
This is largely because solar power output was up 44% in the three months to end-September, compared to a year before, while wind power generation grew 24%. In the first nine months of 2024, China installed 161GW of new solar capacity and 39GW of wind, per CREA data.
For emissions to post a decline in 2024 as a whole, there will need to be a 2% reduction in the fourth quarter, Myllyvirta’s calculations show. That’s probable if power demand growth cools as expected and hydro plants perform in line with historical averages, he wrote in a post on X, adding that over the entire summer period, clean energy expansion covered all electricity demand growth.
“If the current downturn in China’s emissions is sustained — with emissions falling in the second quarter and stable in the third quarter — that would open the door to the country beginning to reduce emissions much faster than its current commitments require.
“This would have enormous significance for the global effort to avoid catastrophic climate change, as China’s emissions growth has been the dominant factor pushing global emissions up for the past eight years since the signing of the Paris climate agreement.”
Based on current trends and targets, CREA expects China’s emissions will decline 30% by 2035. The International Energy Agency says emissions will fall 24% by then based only on stated policies, but that could be raised to 45% if the country follows a pathway that’s consistent with its long-term carbon neutrality target.
For the time being, Chinese policymakers are setting relatively unambitious targets, and “it’s vital that future targets reflect ongoing clean energy trends to avoid locking in lower ambitions,” Myllyvirta said."
-via The Progress Playbook, October 29, 2024
#china#solar power#wind power#renewables#carbon emissions#fossil fuels#asia#climate change#climate action#climate news#good news#hope
5K notes
·
View notes
Text

Trump just signed an executive order to slash support for wind and solar…
347 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - February 15-21
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. Solar farms managed for nature boost bird abundance and diversity, new study finds

“There were more than twice as many farmland birds in the well-managed solar farms compared with the intensively farmed land, and nearly 16 times as many woodland birds. […] Overall, diversity was 2.5 times higher, while woodland birds were nine times more diverse.”
2. Washington judge blocks Trump’s gender-affirming care ban, says it's unconstitutional in multiple ways

“This marks the second time in a week that a judge has stood in the way of Trump’s attacks on trans kids. [… The ruling grants] a temporary restraining order that halts enforcement of provisions in Trump’s directive that would cut off federal funding to medical institutions that provide gender-affirming care to minors.”
3. Fog harvesting could provide water for arid cities

“17,000 sq m of mesh could produce enough water to meet the weekly water demand of [… the] urban slums. 110 sq m could meet the annual demand for the irrigation of the city's green spaces. Fog water could be used for soil-free (hydroponic) agriculture, with yields of 33 to 44lb (15 to 20kg) of green vegetables in a month.”
4. Audubon Applauds Bipartisan Federal Effort to Protect Delaware River Basin with Critical Reauthorization Bill

“The bill would […] ensure long-term conservation and restoration efforts, expand the official definition of the basin to include Maryland, and prioritize projects that serve small, rural, and disadvantaged communities. […] The watershed provides important year-round habitats and critical migratory stopovers for approximately 400 bird species[….]”
5. mRNA vaccines show promise in pancreatic cancer in early trial
“Half of the people in the study — eight of the participants — responded to the vaccine, producing T cells that targeted their tumors. […] Just two of the patients who had a response to the vaccine had their cancer return during the three-year follow- up, compared to seven of the eight who did not respond to the vaccine treatments.”
6. Minn. Lt. Gov. Flanagan Makes It Official; She's running for U.S. Senate

“[Flanagan has] “championed kitchen-table issues like raising the minimum wage, paid family and medical leave, and free school meals.” If elected, Flanagan, a tribal citizen of the White Earth Nation, would become the first Native American female U.S. senator in history.”
7. Federal Funding Restored for Low-Income Alabama Utility Assistance After Outcry

“A program meant to help low-income Alabamians pay their utility bills has resumed two weeks after it was canceled due to an executive order from President Donald Trump. […] “We can confirm the funds are reaching those affected by the previous pause[….]””
8. Modeling study suggests Amazon rainforest is more resilient than assumed

“[Previous] studies were either conducted with global climate models that used a simplified representation of convection [or were on a regional scale….] According to the computations, mean annual precipitation in the Amazon does not change significantly even after complete deforestation.“
9. States are moving forward with Buy Clean policies despite Trump reversal

““Buy Clean is a great example of how states and other nonfederal actors can continue to press forward on climate action, regardless of what the federal government does,” said Casey Katims, executive director of the U.S. Climate Alliance, a bipartisan coalition of two dozen governors.”
10. The rewilded golf courses teeming with life

“A wildflower meadow, ponds, scrub habitat, coastline and even an area of peat bog can be found on this little 60-acre (24-hectare) plot, which boasts roe deer, otters, lizards, eels and a huge array of insects and birds.”
February 8-14 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#nature#us politics#solar power#solar panels#solar energy#birds#biodiversity#gender affirming care#transgender#trans rights#trans healthcare#water conservation#habitat#migratory birds#vaccines#vaccination#mrna vaccine#pancreatic cancer#cancer#native american#alabama#low income#amazon rainforest#rainforest#executive orders#climate action#golf course#habitat restoration
987 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hectare-for-hectare, we found that solar farms in the farm-rich East Anglian countryside that were managed with biodiversity in mind contained a greater number of bird species, and more birds overall, than surrounding cropland. During spring 2023, we used the breeding bird survey method to survey solar farms in the East Anglian fens that were under different management styles. These sites ranged from intensively managed solar farms, in which the grass surrounding panels is cut or grazed short throughout the year, with no hedgerows or small trees, to mixed-habitat solar farms where infrequent cutting or grazing has allowed wildflowers, trees and hedgerows to grow along boundary fences. For comparison, we also surveyed the surrounding farmland. We found that the number of birds on the mixed-habitat solar farms was typically twice that of the intensively managed sites, and three times higher than adjacent high-yielding cropland. The number of species on mixed-habitat solar farms was 2.5 times higher than both of the alternatives. Our study also showed that solar farms offer important habitat for a number of threatened bird species. In fact, birds such as yellowhammer, linnet, greenfinch and corn bunting, which are of particular concern to conservationists due to their declining national populations, were considerably more abundant on mixed-habitat solar farms. Perhaps our results aren’t that surprising. After all, the mixed-habitat solar farms we surveyed contained many of the features birds prefer (similar to nature-friendly farms in less intensively farmed areas). These features include hedgerows, which can offer berries to eat and crevices to shelter in, particularly for birds adapted to woodland habitats. The tall and diverse vegetation around the solar panels contains a variety of habitats, with insect prey or seeds for food. The intensively managed cropland and solar farms had none of these features. By providing the right habitat, birds have been naturally drawn to these solar farms in an area that sorely lacks it.
4 March 2025
388 notes
·
View notes
