#StudyHours
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Long Study Hours but Zero Output? Let’s Fix It!



Are you putting in 10-12 hours of study daily and still feel like nothing is getting done? You're not alone! The problem isn’t time—it’s technique. Studying without a structured approach or revision plan leads to this frustration. At ZenStudy, we help aspirants study smarter with targeted strategies, daily one-shots, and gamified learning. Say goodbye to unproductive hours and start feeling the progress with every session. Time to replace long hours with effective hours. Follow ZenStudy for UPSC success tips that actually work.
🌐 Website: https://zenstudy.in/ 📲 Telegram: https://t.me/Zenstudyltd 📘 Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=61555473406607 📸 Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/zenstudyz/ ▶️ YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@Zenstudyz
#UPSC2025#UPSC2026#UPSCPrep#StudyStruggles#StudySmart#ZenStudy#UPSCMotivation#UPSCStudentLife#StudyTips#ProductiveStudy#UPSCGoals#CSAT2025#IASPreparation#UPSCInspiration#UPSCFrustration#StudyHacks#SmartStudy#Prelims2025#UPSC2025Strategy#UPSCRoutine#TimeManagementUPSC#UPSCJourney#UPSCContent#StudyHours#UPSCGrind#UPSCStudyTips#UPSCProductivity#UPSCMindset#UPSCFocus#UPSCProblemSolving
0 notes
Video
youtube
Quality Thought Introducing Study Hours | Boost Your Learning
1 note
·
View note
Text
Exploring Advanced Statistical Concepts Through Real-World Academic Challenges

For students navigating the complex landscape of graduate-level statistics, practical application of concepts often poses a significant hurdle. Whether you're grappling with multilevel modeling, Bayesian inference, or multivariate analysis, assignments at the master’s level require deep understanding, accuracy, and analytical precision. As a professional statistics homework helper, our goal at StatisticsHomeworkHelper.com is to make this journey smoother by not only offering solutions but also fostering comprehension.
In this expert-authored post, we will walk through two master-level statistics questions that exemplify the type of assignments we regularly assist with. Each example will demonstrate rigorous methodology, interpretation of results, and the conceptual underpinnings necessary for advanced academic work.
📌 Note: These samples are created by our in-house statisticians to help you understand the depth and quality of solutions we deliver. You may explore more such examples or seek personalized support at StatisticsHomeworkHelper.com.
Case Study 1: Hierarchical Linear Modeling in Educational Research
Context:
A researcher is examining how student performance (measured by standardized test scores) is influenced not only by individual-level characteristics (such as study hours and socio-economic status) but also by school-level variables (like funding per student and average class size). The data structure is nested: students within schools.
Objective:
To model the effects of both individual-level and group-level predictors using a Hierarchical Linear Model (HLM).
Problem:
Explain how a two-level hierarchical linear model can be used to assess the relationship between student performance and the explanatory variables, and interpret the results of the model output provided.
Solution:
Step 1: Model Specification
Level-1 (Student Level): TestScore_ij = β0j + β1j*(StudyHours_ij) + β2j*(SES_ij) + r_ij
Level-2 (School Level): β0j = γ00 + γ01*(SchoolFunding_j) + γ02*(ClassSize_j) + u0j β1j = γ10 β2j = γ20
Where:
i indexes students; j indexes schools
r_ij ~ N(0, σ²), the level-1 residual
u0j ~ N(0, τ₀₀), the level-2 residual for intercept
Step 2: Interpretation of Hypothetical Output
Let’s assume we obtained the following (simplified) results:
Fixed Effects:
γ00 (Intercept): 520 (p < 0.001)
γ01 (SchoolFunding): 0.85 (p = 0.004)
γ02 (ClassSize): -1.7 (p = 0.010)
γ10 (StudyHours): 5.2 (p < 0.001)
γ20 (SES): 12.1 (p < 0.001)
Random Effects:
σ² (Level-1 variance): 36
τ₀₀ (Level-2 intercept variance): 25
Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) = τ₀₀ / (τ₀₀ + σ²) = 25 / (25 + 36) ≈ 0.41
Discussion:
A significant positive γ01 implies that higher school funding is associated with better student performance.
A negative γ02 indicates larger class sizes tend to reduce average test scores.
At the individual level, both StudyHours and SES have significant positive effects, reinforcing the role of personal effort and socio-economic background in academic outcomes.
The ICC of 0.41 indicates that 41% of the total variance in test scores is attributable to differences between schools, justifying the use of multilevel modeling.
Conclusion:
This question not only tests one's understanding of hierarchical structures but also the ability to interpret complex outputs—a crucial skill in educational statistics and policy analysis.
Case Study 2: Bayesian Inference for Parameter Estimation in Healthcare Analytics
Context:
In a clinical trial, a researcher is studying the effectiveness of a new drug in lowering systolic blood pressure. The prior belief (from previous studies) is that the drug lowers blood pressure by around 8 mmHg with a standard deviation of 4 mmHg. The new study yields a sample mean reduction of 10 mmHg with a sample size of 40 and a known standard deviation of 6 mmHg.
Objective:
To use Bayesian inference to estimate the posterior distribution of the treatment effect and interpret the posterior statistics.
Problem:
Formulate the Bayesian posterior distribution for the drug effect and provide the posterior mean and variance. Also, compute a 95% credible interval for the drug's effect size.
Solution:
Step 1: Define the Prior and Likelihood
Let θ denote the true mean reduction in systolic blood pressure.
Prior: θ ~ N(8, 4²) Likelihood: Given σ = 6 and n = 40, Sample mean ~ N(θ, (σ²/n)) = N(θ, 6²/40) = N(θ, 0.9)
Step 2: Apply Bayesian Updating
Using conjugate priors (Normal prior + Normal likelihood → Normal posterior):
Posterior Mean (μ_post): μ_post = (σ²/n * μ_prior + σ_prior² * x̄) / (σ²/n + σ_prior²) μ_post = (0.9 * 8 + 16 * 10) / (0.9 + 16) = (7.2 + 160) / 16.9 ≈ 9.88 mmHg
Posterior Variance (σ_post²): σ_post² = (σ²/n * σ_prior²) / (σ²/n + σ_prior²) σ_post² = (0.9 * 16) / (16.9) ≈ 0.85
Posterior SD = √0.85 ≈ 0.92
Step 3: 95% Credible Interval
CI = μ_post ± 1.96 × SD = 9.88 ± 1.80 Credible Interval: (8.08, 11.68)
Discussion:
The posterior mean (9.88 mmHg) is closer to the observed data than the prior, indicating strong evidence from the sample.
The narrow credible interval suggests high confidence in the treatment effect estimation.
This approach integrates prior research with current findings, illustrating the power of Bayesian thinking in real-world decision-making.
Conclusion:
Bayesian inference not only offers a flexible alternative to frequentist methods but also allows for more informed decision-making, especially in domains like clinical research where prior data is readily available.
Final Thoughts
These two examples represent the kind of comprehensive and nuanced support we provide at the master’s level. At StatisticsHomeworkHelper.com, our mission goes beyond solving assignments—we aim to cultivate deep understanding through expertly crafted solutions.
If you're a graduate student overwhelmed by complex statistical concepts or struggling with demanding assignments, our professional services are tailored to provide clarity, accuracy, and academic excellence. Whether it’s Bayesian analysis, multilevel modeling, time series forecasting, or data visualization in R or Python, our statisticians are here to assist with confidence.
Explore more sample questions, submit your assignment, or connect with an expert directly at https://www.statisticshomeworkhelper.com. We’re here to be your reliable partner in statistical success.
#statisticshomeworkhelp#education#students#university#study#homeworkhelp#statisticshomeworkhelper#statahomeworkhelp#help with statistics homework
0 notes
Text
The Complete R Programming Tutorial for Aspiring Data Scientists

In the world of data science, the right programming language can make all the difference. Among the top contenders, R programming stands out for its powerful statistical capabilities, robust data analysis tools, and a rich ecosystem of packages. If you're an aspiring data scientist, mastering R can open the door to a wide range of opportunities in research, business intelligence, machine learning, and online R compiler.
In this complete R programming tutorial, we’ll walk you through the essentials you need to start coding with R—from installation to basic syntax, data manipulation, and even simple visualizations.
Why Learn R for Data Science?
R is a language built specifically for statistical computing and data analysis. It is widely used in academia, finance, healthcare, and tech industries. Some key reasons to learn R include:
Open Source & Free: R is completely free to use and has a vast community contributing packages and resources.
Built for Data: Unlike general-purpose languages, R was designed with statistics in mind.
Visualization Power: With packages like ggplot2, R makes data visualization intuitive and beautiful.
Data Analysis-Friendly: Data frames, tidyverse, and built-in functions make data wrangling a breeze.
Step 1: Installing R and RStudio
Before you can dive into coding, you’ll need two essential tools:
R: Download and install R from CRAN.
RStudio: A user-friendly IDE (Integrated Development Environment) that makes writing R code easier. Download it from rstudio.com.
Once installed, open RStudio. You'll see a scripting window, console, environment panel, and files/plots/packages/help panel—everything you need to code efficiently.
Step 2: Writing Your First R Script
Let’s start with a simple script.# This is a comment print("Hello, Data Science World!")
Hit Ctrl + Enter (Windows) or Cmd + Enter (Mac) to run the line. You’ll see the output in the console.
Step 3: Understanding Data Types and Variables
R has several basic data types:# Numeric num <- 42 # Character name <- "Data Scientist" # Logical is_learning <- TRUE # Vector scores <- c(90, 85, 88, 92) # Data Frame students <- data.frame(Name = c("John", "Sara"), Score = c(90, 85))
Use the str() function to explore objects:str(students)
Step 4: Importing and Exploring Data
R can read multiple file formats like CSV, Excel, and JSON. To read a CSV:data <- read.csv("yourfile.csv") head(data) summary(data)
If you're working with large datasets, packages like data.table or readr can offer better performance.
Step 5: Data Manipulation with dplyr
Part of the tidyverse, dplyr is essential for transforming data.library(dplyr) # Select columns data %>% select(Name, Score) # Filter rows data %>% filter(Score > 85) # Add new column data %>% mutate(Grade = ifelse(Score > 90, "A", "B"))
Step 6: Data Visualization with ggplot2
ggplot2 is one of the most powerful visualization tools in R.library(ggplot2) ggplot(data, aes(x = Name, y = Score)) + geom_bar(stat = "identity") + theme_minimal()
You can customize charts with titles, colors, and themes to make your data presentation-ready.
Step 7: Writing Functions
Functions help you reuse code and keep things clean.calculate_grade <- function(score) { if(score > 90) { return("A") } else { return("B") } } calculate_grade(95)
Step 8: Exploring Machine Learning Basics
R offers packages like caret, randomForest, and e1071 for machine learning.
Example using linear regression:model <- lm(Score ~ Age + StudyHours, data = students) summary(model)
This builds a model to predict score based on age and study hours.
Final Thoughts
Learning R is a valuable skill for anyone diving into data science. With its statistical power, ease of use, and strong community support, R continues to be a go-to tool for data scientists around the globe.
Key Takeaways:
Start by installing R and RStudio.
Understand basic syntax, variables, and data structures.
Learn data manipulation with dplyr and visualizations with ggplot2.
Begin exploring models using built-in functions and machine learning packages.
Whether you're analyzing research data, building reports, or preparing for a data science career, this R programming tutorial gives you the solid foundation you need.
For Interview Related Q&A :
Happy coding!
0 notes
Photo
New achievement unlocked #studyhours #studymotivation #studygram #medico (at Indian) https://www.instagram.com/p/CaWd65-Mfky/?utm_medium=tumblr
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

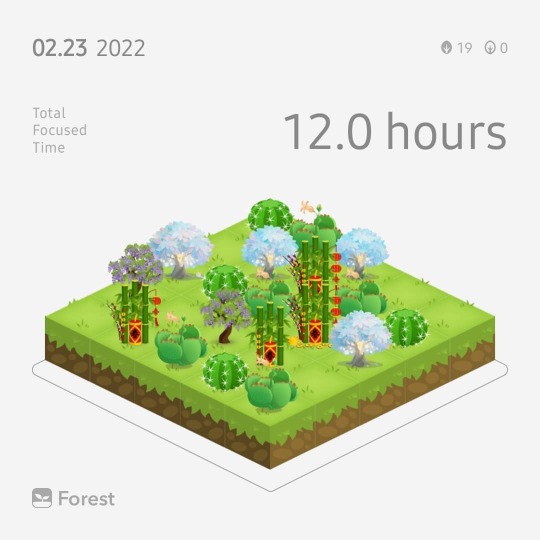
I am so happy to have achieved my target for today 😁😁 I started so late but I am glad I could do it. Now I'll sleep in peace☮️ #forest #forestapp #focus #studying #studyhours #studyingmotivation #studying #studyinginspiration #studygram #medicallife #medicalstudent #medschool #medstudent #medstudentlife #concentrationcamp #life #inspiration https://www.instagram.com/p/BzGkGvNBTa5/?igshid=128qeba77lnvo
#forest#forestapp#focus#studying#studyhours#studyingmotivation#studyinginspiration#studygram#medicallife#medicalstudent#medschool#medstudent#medstudentlife#concentrationcamp#life#inspiration
1 note
·
View note
Text
Sequitura’s Psychology Notes bc study hours
===PART 1: Early Psychology===
Nativism vs. empiricism - nature vs. nurture, basically. One theory was mainly promoted by philosophers - that people are hardcoded with certain traits from birth that cannot be developed or changed. The other end of the spectrum is empiricism, the theory that the mind starts as a blank slate affected by experiences over time.(edited)
Introspection vs. experiments - different methods early psychologists used to find out about the mind. Introspection was when subjects described their experiences out loud to scientists and was championed by Freud. It was discovered that no one’s description of their own mental experiences match 100% of the time, but this method did turn into early psychotherapy. Experiments are more objective ways to discover how the mind works via behavior. Skinner was one of the earliest experimentalists (and a decrier of psychoanalysis as scientific evidence.)
Localization of function (phrenology) - it is an old idea that different parts of the brain have different functions. Previously, it was believed that phrenology (analyzing the shape of the skull) could determine what strengths and weaknesses a person had, but these days, more scientific methods are used (such as brainscans and case studies of patients with brain damage.)
Other fields of psychology - 1. Evolution. There are some skills every species has right at birth, meaning that some skills were developed by a species' ancestors and aren't learned. 2. Comparative. Comparing how different species have similar psychological traits. For example, if a chimpanzee watches a human swinging from something, the parts of the chimp's brain that control motor control will show more activity. 3. Computational. Treating the brain as a computational organ. Treats it as having certain rules that it follows consistently. Sometimes theorizes how far a machine can get before it's considered living.
===PART 2: Neuroscience===
I already talked about neurons with James, so I'm not going to go into them.
How action potential works -
1 The cell starts polarized at around -70mV. There is more Na+ inside the cell and more K+ outside the cell.
2 A stimulous Na+ channels open, causing Na+ to flow out of the cell and depolarize it (around +40mV)
3 K+ channels open, causing K+ to rush in (and Na+ channels to close), repolarizing the cell. The cell becomes hyperpolarized at around -90mV.
4 Protein pumps open, using ATP to force Na+ back in the cell and K+ back out. The cell returns to its resting state of around -70mV.
Frontal lobe - thinking, motor control, speech (toward the front)
Parietal lobe - touch, orientation of body parts in reference to each other (on top)
Occipital lobe - sight, visual interpretation (on back)
Temporal lobe - audio processing, language comprehension, memory (toward the bottom)
Brainstem - involuntary functions such as bladder control, breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and balance
Midbrain - controls movement, sleep, alertness and temperature limbic system (deal with emotions and memory) hippocampus - learning/memory amygdala - emotions
===Part 3: Sensation + Perception===
uhh I don't really feel like going over this. Already did and think I remember everything. Lateral inhibition is the ability for an excited neuron to cause neighboring neurons to become less excited, though. Enhances edges.
===Part 4: Learning===
Habituation - you get used to something the more it happens.
Sensitization - you get more sensitive to something the more it happens.
CS, UCS, CR, UCR - stands for four different variables in classical conditioning: conditioned stimulus, unconditioned stimulus, conditioned response, unconditioned response. An example is getting a dog to salivate at the sound of a bell. 1. UCS - food UCR - salivation 2. CS - bell no response 3. CS + UCS - bell + food UCR - salivation 4. CS - bell CR - salivation
Reinforcement - a stimulus meant to incentivize a reason to do/not do something Punishment - a stimulus meant to make doing/not doing something less appealing
classical conditioning - getting a response to something that would normally have no response dishabituation - getting a response to return more quickly than it would if you were being introduced to it for the first time
rewards and punishments are more effective if they occur every time the behavior occurs, rather than once every couple of times (schedule of reward/punishment)
0 notes
Photo


saturday, 30 december — finals aren’t over and needed an extra motivation to study harder so i decided to redecorate and clean my study place
printed some of my all time inspirations to motivate me studying, if you are interested on how to do the same thing i can maybe do a post step by step! from left to right you can see rory gilmore, cristina yang, temperance brennan, spenser hastings, meredith grey, michaela pratt, paris geller, elle woods, and laurel castillo.
the printables on my wall are quotes from @emmastudies, you can check her website she has the best printables!
you can also see my new lamp aka my new best friend, it is a taotronics lamp. it’s basically the best lamp to study because it has a eye-caring tech, comfortable, non-flickering light, also is adjustable, has different lighting mode with 7 brightness levels which benefit from 5 color temperature settings to suit every mood and occasion, and big plus: you can charge your phone via the integrated usb output port! so yea, this is sincerely the best thing i have ever owned! (and it was on sale on amazon)
well, it’s time for me to go back studying because starting pretty little liars wasn’t the best thing to do while being on final exams period haha…
Instagram / Youtube
#studyblr#studygram#studies#study session#study#study motivation#study inspiration#studyspo#study aesthetic#currently studying#studyhard#studyholic#studyhour#studyblog#notes#journaling#bujo#langblr#student life#diy wall decor
2K notes
·
View notes
Link
0 notes
Photo


3/100 days of productivity Anyone has any phrase to motivate you when you are studying? I have one "The harder you work the luckier you are". And it's true. We only think that everything was because we are lucky, but it was because we worked hard
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Day 7/100 of 100 Days of Productivity Challenge! Today, I studied Plant Transport. Mock Tommorrrow! More importantly, I solved Chemistry P2 past papers. Some are challenging, some are easy. Either way, there’s no room for slacking. 62 days till As!
#a level chemistry#a level biology#studyblr#studyspo#study motivation#studygram#studyhard#exams#studyhour#studyblrs get real#small studyblrs unite
25 notes
·
View notes
Photo

02.03.18 || 21/100 days of productivity It's finally fridaay!! What are you guys planning for the weekend? I will watch the Black Panther, sounds really good!!
#studyblr#studyspo#studymotivator#study motivation#studymorning#studyfulltime#studyfun#student#college#university#neuroscience#studyhard#studyholic#studyhour#studylife
17 notes
·
View notes
Photo

"FAILURE" A difficult word capable of creating havoc in lives. Failure is definitely depressing, tough to deal with, heart and soul breaking and all sorts of depressing things in life. But.. it's okay to fail as failure is a reminder that dude.. you need to work harder, this is not enough.. You have to work your ass off to achieve a better result ( academic/ non academic). I believe it's better to fail than pass if you've not given your 💯 In the end skills matter and especially to medical people, your knowledge, skill set the ability to treat the sick is what matters.. no patient is gonna ask you about your failures, the only thing which concerns them is how well you are treating them.. Be a sport and take failures as challenged which are gonna push you to be the best of yourself. ❤️ Happy studying 😊😊 #studygram #indianstudygram #studyblr #indianstudyblr #medgram #medblr #studyinghelp #studyhours #studyinginspiration #studyingmotivation #medschoollife #medschooldiaries #medicalstudents #medicalnotesfordays #medicalnotes123 #medicinelife💉💊 #medicinenotes #ophthalmology #surgery #premed #medlifestyle #clinicals
#surgery#medicalnotesfordays#medblr#premed#studyinghelp#clinicals#medschoollife#studyinginspiration#medschooldiaries#studygram#studyhours#indianstudyblr#medicalnotes123#ophthalmology#studyingmotivation#medgram#medicinenotes#indianstudygram#medlifestyle#medicalstudents#studyblr#medicinelife💉💊
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo


sunday, 13 january 2018 messy desk after a long study session and a very foggy car journey 🚗
#plutomathitis#studyblr#mine#desk#study#student#a level studyblr#a level student#a level study club#english lit#fog#notes#2018#studypetals#studypool#studygrind#studygene#studyholic#studyhour#studentblr#areistotle#emmastudies
16 notes
·
View notes
Photo

× 12.01.2018 × Finals in two weeks!
#studyblr#study motivation#notes#study notes#agh#cracow#geology#geophysics#workhard#studyholic#studyhour
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Day 5/100 || 02.14.18
((ya girl still learning to have better lighting)) I missed a few days of the challenge because I lost my wallet for a while. ((it was returned to me intact three days later by a guy named Jesus)) It’s been an emotional rollercoaster, but now I don’t have time to have feelings because I’m slipping behind on my coursework. Happy Valentine’s Day folks!
#mine#school#studyblr#studyspo#study motivation#studying#studyhard#studyhaven#studyholic#studyhour#studygram#emmas100dop#emmastudies#100daysofproductivity#100 days of productivity#100dop
2 notes
·
View notes