#datalifecycle
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Data Management vs. Data Governance: Understanding the Key Differences

You may have encountered the terms data management and data governance in various contexts. While they are often used interchangeably, these concepts have distinct roles in handling and protecting data within an organization. Let’s explore their unique functions and why both are essential.
What is Data Management?
Data management covers the complete lifecycle of data—from its collection and storage to its processing and use. Effective data management establishes best practices and policies for organizing, protecting, and optimizing data. This holistic approach enhances compliance, data security, and data quality, empowering organizations to make better business decisions based on reliable data insights.
Key components of data management include data preparation, pipelines, ETL processes, data catalogs, warehouses, architecture, and security. Together, these elements ensure data is accurate, accessible, and protected throughout the organization.
What is Data Governance?
Data governance, on the other hand, is a subset of data management focused on policies, standards, and controls that keep data secure, compliant, and ethically accessible. As data breaches continue to rise, robust governance is more crucial than ever. Data governance frameworks establish data ownership, maintain data quality, and ensure compliance, enabling organizations to protect sensitive information.
Data governance frameworks typically involve data policies, standardized processes, data stewardship, quality assurance, and compliance. With tools like OpenPages Data Privacy Management, companies gain complete visibility into data privacy and risk management, ensuring ethical and regulatory standards.
Why Both Are Important
Together, data management and data governance form the backbone of any data-driven organization. Effective data management supports analytics and decision-making, while strong data governance ensures data usage aligns with ethical, security, and compliance standards.
Want to enhance your data strategy? iTech GRC’s expertise in OpenPages Data Privacy Management offers a complete solution for managing and governing your data effectively. Contact our team today!
0 notes
Text
The Guardian's Code: Nurturing Digital Trust through Data Security Compliance

As I reflect on the insightful discussion about data privacy and security in class, I find myself realizing the profound importance of safeguarding information in our digital age. The concept of ISO 9001:2015 introducing risk assessment struck me as a proactive approach to identifying potential threats to our data. This risk-aware mindset sets the stage for a more comprehensive understanding of the need to protect our sensitive information. In addition, understanding that Privacy Impact Assessment helps us anticipate the impacts of a data breach made me see the need for a comprehensive privacy management program, which was notably emphasized in our privacy manual. The interconnectedness of these concepts became evident, emphasizing the need for a holistic strategy rather than isolated measures to ensure the security and privacy of our data.
We have also discussed the five (5) pillars of compliance mandated by the National Privacy Commission. The discussion about exercising what's written in the manual being the fourth pillar resonated with me. It's not just about having guidelines on paper but actively putting them into practice. This practical aspect adds a layer of responsibility, highlighting the bridge between theoretical knowledge and real-world application in maintaining data privacy and security. Moreover, the scenario painted in case of a data breach, where the National Privacy Commission (NPC) evaluates adherence to the five data privacy guidelines, highlighted the real-world consequences of our actions in handling sensitive information. This connection between our theoretical learning and the potential scrutiny from regulatory bodies underscores the gravity of maintaining a robust data protection framework.
As a result of the adherence to the five (5) pillars of compliance as well as data privacy guidelines, our professor scrutinized the university’s compliance. The detailed discussion on the university's compliance with the framework, the absence of a record for Privacy Impact Assessment, and the existence of a data privacy manual created by our instructor highlighted the practical applications of the concepts discussed. This connection to our specific institutional context emphasized the relevance of our learning to our immediate environment, making the theoretical concepts actionable in our educational setting.
On the other side, the discussion on data retention, archiving, and securing archives being one of the data privacy cycles made me appreciate the intricate steps taken to preserve our records. The importance of secure archives as a protective measure against potential loss is tied back to our overarching theme of safeguarding data across its entire lifecycle. The mention of consequences for failing to adhere to the data privacy cycle served as a reminder that every action carries weight. This connection to consequences brought a sense of accountability, reinforcing the idea that our individual and collective efforts contribute to the overall data protection framework.
In conclusion, this class has made me more conscious of the responsibility we hold in protecting data. The interconnected nature of the topics discussed and the real-world examples shared have deepened my understanding of the significance of data privacy and security in both personal and organizational contexts. The seamless flow from theoretical concepts to practical applications has equipped me with a more comprehensive view of the vital role we play in ensuring the integrity and security of our digital information.
0 notes
Text
Metadata: 100 Guide to Understanding and Leveraging Data About Data

In this age of digitization, data has taken the place of gold. However, the component known as metadata is what gives this gold its actual value. This article will take you through the exciting world of metadata, illuminating its meaning, various types, examples, purpose, and other information.

Metadata Metadata is a phrase that frequently comes up in conversations about big data, data management, and data science. And what exactly makes it so vital? This tutorial aims to provide an in-depth review of metadata and its function in the contemporary data landscape, to answer the issues posed here and others.
What Exactly Does It Mean to Have Metadata?
Metadata, sometimes known as 'data about data,' is information that either describes, locates, or in some other way makes it simpler to obtain, utilize, or manage data. Metadata is a collection of data that, in addition to providing information about other data, also characterizes that data. A digital image may, for instance, contain metadata that portrays the picture in terms of its size, color depth, image resolution, when it was made, and a variety of other data. The metadata associated with a text document may include information such as the document's length, the author's name, the date the document was created, and a concise description of the document's content.
An Analysis of the Development of Metadata from a Historical Standpoint
The idea of metadata has been around for quite some time. It dates back to the beginning of structured collections of knowledge and has been around ever since. Metadata has always been essential to the rapid and easy retrieval of information, whether in the form of library card catalogs or the digital tags used on contemporary websites. In the past, metadata was mainly utilized in libraries and archives to catalog papers and other items and retrieve them when needed. The usage of metadata has become substantially more widespread with the introduction of the internet and other forms of digital technology. Nowadays, metadata is utilized in various sectors, including digital libraries and databases, websites, and social media platforms, to name just a few examples.
The Importance of Metadata in Today's World and the Functions It Serves
Metadata is vital in the data-driven society that we live in today. It is helpful for various data-related tasks, including data management, data integration, data mining, and data governance. The metadata is responsible for making the data understandable and usable. Metadata has a wide range of applications in the area of digital computing. Metadata is used by search engines so that they can comprehend the content of web pages and produce more accurate results. Metadata is the information digital cameras store regarding capturing a photograph. Social media networks use metadata to organize and classify postings.
What Kinds of Things Might Be Considered Metadata?
There is metadata in everything. The information, such as the date, time, location, and even the camera settings, are saved as metadata whenever you snap a picture with your smartphone. Examples of metadata include the artist's name, the song title, the album name, and the genre of a music file. In Everyday Life: Examples of Common Uses for Metadata Metadata is an essential component of everything we encounter in our lives, from the books in a library to the posts on social networking websites. It enables us to locate, organize, and comprehend information rapidly and effectively. For instance, when you use a search engine to locate material online, you use metadata. The search engine analyzes metadata to comprehend the content of web pages and return results pertinent to the query. When you take a picture with your digital camera, the camera records information about the image. This metadata includes the date and time the photo was taken, the camera settings, and if your camera has a GPS feature, the picture's location. This metadata may be utilized later to categorize your photographs, locate specific graphics, or even understand the conditions when the image was shot.

The Role Of Metadata In The Online World The Role of Metadata in the Online World: Illustrations from the Tech Sector In the realm of information technology, metadata may serve many purposes. Websites, for instance, will often include metadata in meta tags to convey the page's subject matter to search engines. Databases employ metadata to give a roadmap to their material. Metadata describes other information; for instance, the structure of a database, the types of data kept in the database, and how the data is arranged may all be described using metadata. It is possible to utilize this information to understand the structure of the database, compose queries that will obtain data from the database, and manage the data stored in the database.
Which Three Different Types of Metadata Are Correct?
It is possible to divide metadata into three distinct types: descriptive, structural, and administrative. The Secret to Discoverability Lies Within Descriptive Metadata Metadata that is descriptive contains things like the title, abstract, author, and keywords, all of which contribute to the process of locating and identifying data. The purpose of this kind of metadata is to give information that can assist in finding and distinguishing the data. For instance, a book's title, author, and keywords are all examples of descriptive information that might help you locate the book in a physical location such as a bookshop or library. The blueprint for data organization is known as structural metadata. The organization, structure, and kinds of data can be better understood with the help of structural metadata. It is a way of describing the arrangement of the individual parts of a dataset or item. For the sake of illustration, structural metadata for a book might include details such as the sequence in which the chapters are presented, the total number of pages, and the connection between the branches and the book. Administrative metadata is known as the keeper and protector of data rights. Administrative metadata may be used to administer a resource, such as the date and method of creation, the kind of file and any other relevant technical information, and the users authorized to use the help. The management and administration of data make use of this kind of metadata. An example of administrative metadata for a digital image may include: The image's creation date. The program used to make the image. The rights and permissions are connected with the idea.
What is the Most Important Role That Metadata Plays?
The primary function of metadata is to make it easier to find important information, to make data administration more efficient, and to safeguard information so that it may be preserved. Improving the Capability to Discover Data: The Part Played by Metadata Metadata improves the discoverability of data by giving helpful information about the material. It assists users in locating the pertinent facts at the appropriate moment. When you use a search engine, for instance, to obtain information on the internet, the search engine uses metadata to interpret the content of web pages and offer search results relevant to your query. Facilitating Data Management: How Metadata Contributes By giving a context for the data that has been saved, metadata makes data administration much more effortless. It assists in integrating data, ensuring data quality, maintaining data stewardship, and managing data operations. For instance, metadata may be utilized in a database to understand the structure of the database, compose queries for retrieving data, and collect the data kept inside the database.

The Value Of Metadata In Protecting Users' Personal Information And Private Data The Value of Metadata in Protecting Users' Personal Information and Private Data Metadata is essential in protecting users' privacy and keeping their data secure. It explains who can access the data, where it should be housed, and how it should be safeguarded from unauthorized access. For instance, administrative metadata could contain information about the rights and permissions associated with a specific piece of data. This kind of information can control who has access to the data and what they are allowed to do with it by holding who has access to the data and what they are allowed to do with it.
The Value of Metadata in many Different Fields
Metadata is not only an idea; instead, it is a potent instrument that drives insights and choices across a variety of areas. In data science, metadata is the engine that drives insights and predictions. In data science, metadata is information about data that helps researchers understand the data better. It facilitates data analysis, data visualization, and data mining. In a dataset, metadata can offer information about the variables, their kinds, and their relationships. This information can be found in a dataset, which can be used to pick the proper analytic techniques and accurately interpret the findings. Informing Strategic Decisions Through the Use of Metadata in Business Intelligence In the realm of business intelligence, metadata is what supplies the context, which in turn enables more informed and effective strategic decision-making. It helps integrate data, manage data warehouses, and do data analytics. In a business intelligence system, for instance, metadata may be utilized to understand the structure of the data warehouse, compose queries to obtain data for use in reports and dashboards, and correctly interpret the results of those searches. The role of metadata in data warehousing is to simplify storing and retrieving data. Metadata is utilized in data warehousing to facilitate effective data organization, location, and retrieval. It enables data storage, data transfer, and data lifecycle management. For instance, in a data warehouse, metadata may be used to understand the structure of the warehouse, the types of data that are kept in the warehouse, and how the data is arranged. This understanding can then be used to effectively manage the data stored in the warehouse and efficiently retrieve data.
The Problems and the Answers in the Field of Metadata Management
Metadata is helpful, but keeping track of it has its own unique set of issues. Nevertheless, one can triumph over these obstacles by employing the appropriate tactics and resources. The Most Frequently Encountered Problems in Metadata Management and How to Fix Them Problems with data quality, a lack of standards, and worries about data security are some of the more prevalent obstacles associated with managing metadata. The implementation of data quality measures, the adoption of metadata standards, and the enforcement of data security regulations are all potential solutions. Implementing data quality procedures such as data validation, cleansing, and auditing solves data quality problems. Adopting metadata standards that establish criteria for the generation, usage, and administration of information can solve the problem of a need for more standardization. Concerns about data safety can be alleviated by implementing data security rules that restrict access to metadata, shield it from illegal access and change, and protect it from exposure to potential threats.
Guidelines for Efficient and Effective Management of Metadata
Implementing best practices for metadata management, such as setting explicit metadata policies, utilizing tools for metadata management, and routinely updating and evaluating metadata, is necessary to manage metadata effectively. It is possible to guarantee that metadata is generated, utilized, and maintained in a manner that is consistent and successful by defining explicit metadata policies and putting them into place. Using metadata management solutions may assist in automating the process of creating, utilizing, and managing metadata, making the process more time-effective and less prone to mistakes. By evaluating and updating it regularly, it is possible to guarantee that metadata will continue to be accurate, relevant, and valuable. Trends and Forecasts Regarding the Development of Metadata: As we progress toward a future driven more and more by data, the metadata function will become even more critical. Emerging Trends in Metadata Management The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in metadata production and administration is one example of an emerging trend in metadata management. Other examples include the rising relevance of metadata in data governance and the rise of metadata in the era of big data and the Internet of Things. It is possible to employ AI and machine learning to automate the metadata production and administration process, resulting in increased productivity and precision. Metadata is gaining more attention due to the rising significance of data governance since it offers the context and understanding necessary to regulate data successfully. The advent of big data and the Internet of Things is leading to an explosion in the quantity of metadata since every piece of data created by these technologies comes with its own information set. This explosion in the amount of metadata is leading to an explosion in the number of data.
The Prospects for Metadata Soon: Predictions and Anticipations
The future of metadata has a lot of potential. The value of metadata in data management and the decision-making process is expected to expand exponentially due to technological developments and increased awareness of the significance of data. The need for efficient metadata management will only grow as we continue to produce and consume more data in the future.
Summary: The Crucial Part That Metadata Plays in Today's Data-Driven World
In a world driven by data, metadata is an instrument that cannot be ignored. It gives the data context, making it more intelligible and valuable. Metadata is essential in all aspects of data science, business intelligence, and data warehousing, playing a necessary part in generating insights, forming choices, and optimizing business processes. Because the significance of metadata is expected to increase as we go closer to the future, it is a subject that is well worth investigating and becoming knowledgeable about. Metadata is more than just 'data about data.' It is the essential element that enables data to realize its full potential. By giving context, metadata makes data relevant and valuable. It allows us to locate the appropriate data at the right moment, comprehend the data we already have, and make educated decisions based on our data. Metadata is becoming more significant in big data, characterized by an unprecedented increase in data amount, variety, and velocity. The metadata assists us in navigating the immense ocean of data, locating the information we require, and making efficient use of it. The need for efficient metadata management will only grow as we continue to produce and consume more data in the future. The difficulties associated with managing metadata are accurate, but they can be surmounted with the appropriate approaches and technologies. We can guarantee our metadata's precision, use, and relevance if we implement the most effective procedures for managing metadata. The outlook for metadata in the future is quite positive. The value of metadata in data management and the decision-making process is expected to expand exponentially due to technological developments and increased awareness of the significance of data. Understanding the power of metadata and using it effectively will be essential to our progress as we move toward a future that data will drive. Read the full article
#BusinessIntelligence#DataAnalysis#DataCompliance#DataGovernance#DataInfrastructure#DataIntegration#DataLifecycle#DataManagement#DataMigration#DataMining#DataOperations#DataPrivacy#DataProcessing#DataQuality#DataScience#DataSecurity#DataStandards#DataStewardship#DataStorage#DataStrategy#DataSystems#DataTransformation#DataVisualization#DataWarehousing#Metadata
0 notes
Text
How AI and ML are transforming data quality management?

Introduction
In recent years the technology has become prominent, both at work and at home. Machine learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are evolving quickly today. Almost everyone will have some interaction with a form of AI daily. Some common examples include Siri, Google Maps, Netflix, and Social media (Facebook/Snapchat).AI and ML have popularly used buzzwords right now, often used interchangeably. Most experimentation has been geared to finding specific solutions to specific problems. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an application in which a machine can perform human-like tasks. At the same time, Machine Learning (ML) is a system that can automatically learn and improve from experience without being directly programmed.
Data quality refers to how relevant information is for use. If information isn’t suitable, you won’t be able to make the right decisions. Data quality is determined by several factors, including; accuracy, completeness, reliability, relevance, and timeliness. If there’s a missing factor or is lower than other factors, your data quality won’t be very high. Read more about what is data quality and why is it important.
Increased data volumes have put companies under pressure to manage and control their data assets systematically. Also, standard data management practices lack sufficient scalability and cannot manage ever-increasing data volumes. Companies, therefore, need to rethink their data management. The good news is that substantial progress in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) through entities such as DQLabs.ai – AI/ML augmented data quality management platform, can support you in your data management activities.
How has AI and ML transformed quality management?
Automatic data capture
Besides data predictions, AI helps improve data quality by automating data entry through executing intelligent capture. This ensures all the valuable information is captured, and there are no gaps in the system.
Recognize duplicate records
Twofold entries of data can lead to outdated records that result in bad data quality. AI helps eliminate duplicate records in an organization’s database and keeps precise gold keys in the database. It is hard to identify and remove recurring entries in a big company’s repository without implementing sophisticated mechanisms. An organization can combat this by having intelligent systems that can detect and remove duplicate keys.
Detect anomalies
A small human mistake can drastically affect the utility and the quality of data in a CRM. An AI-enabled system removes defects in a system. Data quality can also be enhanced through the implementation of machine learning-based anomalies.
Third-party data inclusion
Apart from correcting and maintaining data integrity, AI can improve data quality by adding to it. Third-party organizations and governmental units can significantly add value to the quality of a management system and MDM platforms by presenting better and more complete data, contributing to precise decision making. AI makes suggestions on what to fetch from a particular set of data and the building connections in the data. When a company has detailed and clean data in one place, it has a higher chance of making informed decisions.
Fill data gaps
While many automation systems can cleanse data based on explicit programming rules, it’s almost impossible for them to fill in missing data gaps without manual intervention or plugging in additional data source feeds. However, machine learning can make calculated assessments on missing data based on its reading of the situation.
Assess relevance
On the other end of the scope of missing data, organizations often accumulate a large amount of redundant data over the years that do not have any use in a business context. Using machine learning, the system can self-teach on the data points required and those not needed. Analysis of this kind can help revamp the process and, eventually, make it simpler.
Match and validate data
Coming up with rules to match data collected from various sources can be a time-consuming process. As the number of births increases, this becomes increasingly more challenging. ML models can be trained to learn the rules and predict matches for new data. There is no restriction to the volume of data, and as a matter of fact, more data works favorably in fine-tuning the model.
The cost of bad data
Bad data can prove to be quite expensive for companies. Attempts to quantify the financial impact have resulted in some shocking numbers. It’s also important to remember that decisions based on flawed data can lead to severe consequences in some cases. Machine learning algorithms can flag some of these situations before they get too far. Financial companies use them to identify forged transactions. It’s estimated that ML models can result in a $12 billion savings for card issuers and banks.
Conclusion
Most businesses look for fast analytics with high-quality insights to deliver real-time benefits based on fast decisions. They consider this a high priority and means of competitive advantage. To enable this, there is an opportunity for organizations to fine-tune and enhance the current data quality approach using ML techniques. Many leading data quality tools and solution providers have tried out ML territory in expectation of increasing the effectiveness of their solutions. Thus, it has the chance of being a game-changer for businesses in pursuit of improved data quality. Although the current intake level of the use of ML for data quality assessment and enhancement is low, it has promising prospects to churn large data sets and enhance data quality.
If you want to try an AI and ML based data quality tool to automate all your DQ management, request DQLabs platform demo here.
0 notes
Link
The approach we have is to comply with legal and strategic company requirements and provide a reporting platform or data warehouse that is compliant and compatible with your current business platform.
0 notes
Video
tumblr
It is imperative for organizations to manage the flow of data at every stage of the 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗮 𝗟𝗶𝗳𝗲 𝗖𝘆𝗰𝗹𝗲. In this #creative we are breaking down the #datalifecycle with extended stages that have cropped up with modern practices and platforms. link: https://polestarllp.com/services/enterprise-data-management
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Photo

Data Lifecycle: and where WipeDrive helps
https://www.whitecanyon.com/resources/enterprise-articles/infographics/infographics-datalifecycle
0 notes
Photo
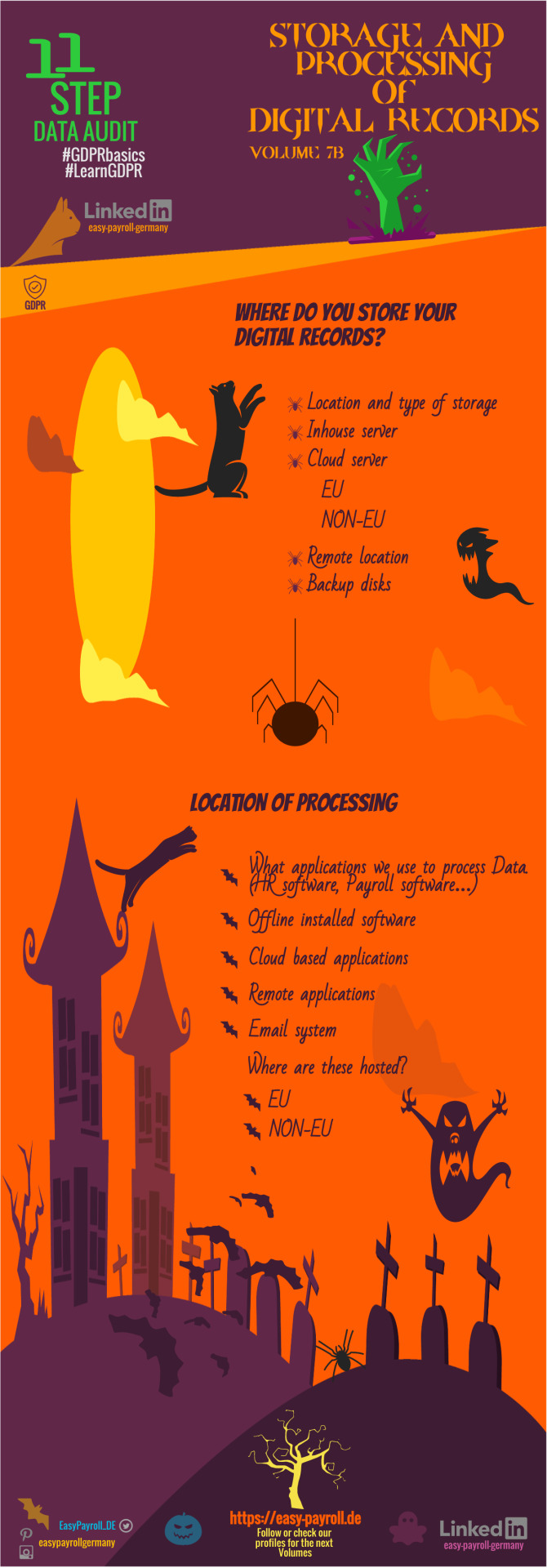
◤𝐇𝐀𝐋𝐋𝐎𝐖𝐄𝐄𝐍 𝐄𝐃𝐈𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍 of GDPR DATA AUDIT TEMPLATE Vol7b ◥ updated ✓ 𝐋𝐢𝐤𝐞 and 𝐄𝐧𝐣𝐨𝐲 . ◣𝐒𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐃𝐈𝐆𝐈𝐓𝐀𝐋 𝐑𝐄𝐂𝐎𝐑𝐃𝐒-Where/How/Why◢ #GDPR #digitalisation #paperless #Business #halloween #Working #control #access #marketing #documents #security #retention #GDPRbasics #LearnGDPR #payroll #foreignbusiness #infographic #easypayrollgermany #DataAuditOnline #GDPRdataaudittemplate #becompliant #Datainventorysheet #Datachecklist #DataLifecycle #compliance #payrollservices #completegermanpayrollservices #news #smallbusiness https://easy-payroll.de
0 notes
Link
Datatech as we have highly qualified consultants handling Data Migration in Malta and Libya. The transition of data, software, or other business elements from a data center on-site to a cloud or from one cloud to the next.
0 notes
Photo
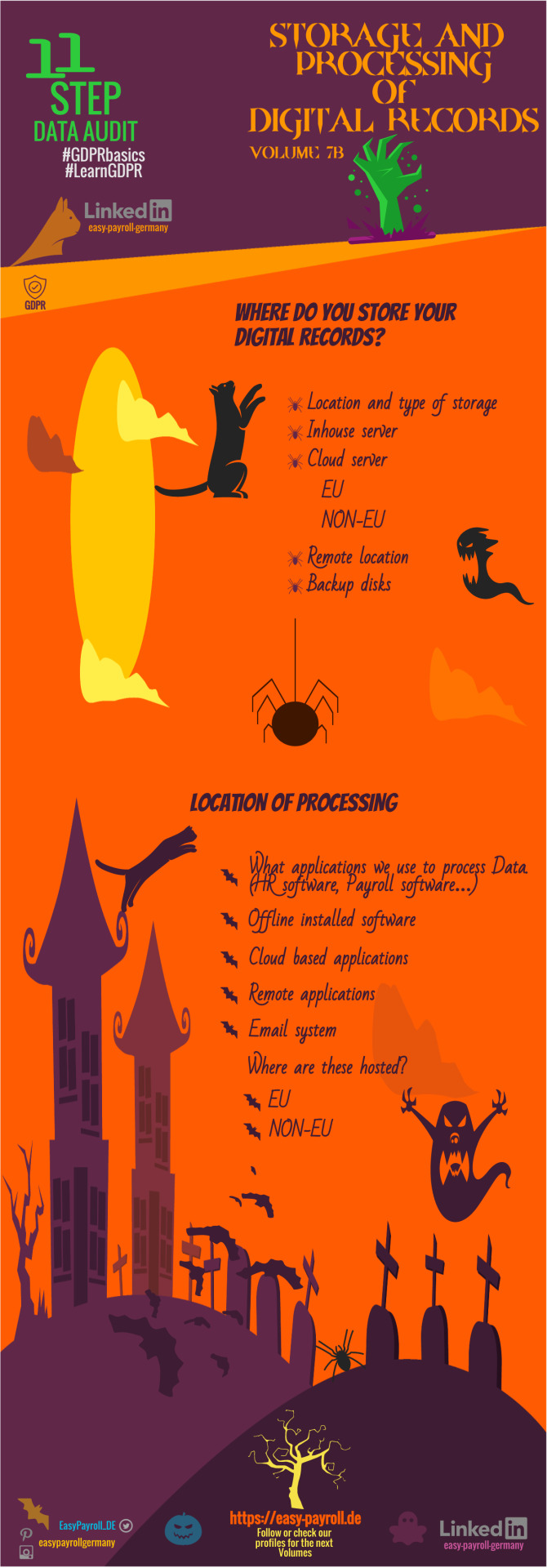
◤𝐇𝐀𝐋𝐋𝐎𝐖𝐄𝐄𝐍 𝐄𝐃𝐈𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍 of GDPR DATA AUDIT TEMPLATE Vol7b ◥ updated ✓ 𝐋𝐢𝐤𝐞 and 𝐄𝐧𝐣𝐨𝐲 .✎ ◣𝐒𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐃𝐈𝐆𝐈𝐓𝐀𝐋 𝐑𝐄𝐂𝐎𝐑𝐃𝐒-Where/How/Why◢ #GDPR #digitalisation #paperless #Business #halloween #Working #control #access #marketing #documents #security #retention #GDPRbasics #LearnGDPR #payroll #foreignbusiness #infographic #easypayrollgermany #DataAuditOnline #GDPRdataaudittemplate #becompliant #Datainventorysheet #Datachecklist #DataLifecycle #compliance #payrollservices #completegermanpayrollservices #news #smallbusiness https://lnkd.in/dp3THEd
0 notes
Photo
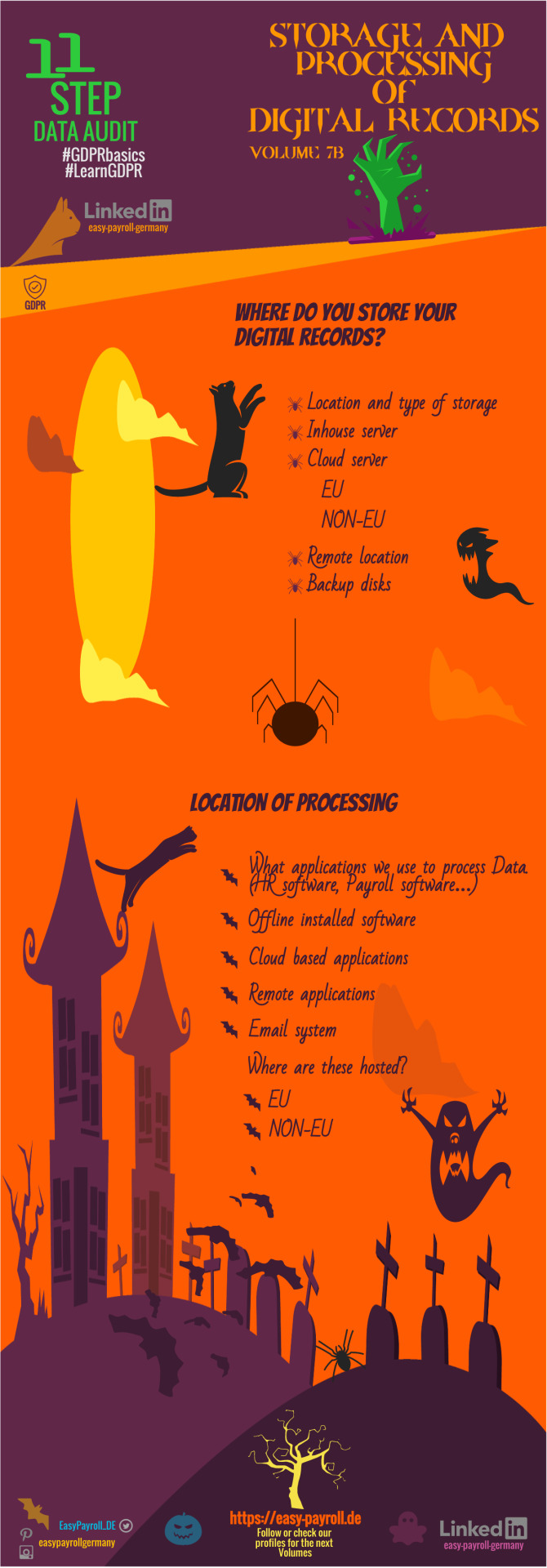
◤𝐇𝐀𝐋𝐋𝐎𝐖𝐄𝐄𝐍 𝐄𝐃𝐈𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍 of GDPR DATA AUDIT TEMPLATE Vol7b ◥ updated ✓ 𝐋𝐢𝐤𝐞 if you 𝐄𝐧𝐣𝐨𝐲 and comment.✎ ◣𝐒𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐃𝐈𝐆𝐈𝐓𝐀𝐋 𝐑𝐄𝐂𝐎𝐑𝐃𝐒-Where/How/Why◢ #GDPR #digitalisation #paperless #Business #halloween #new #Working #control #access #marketing #documents #security #retention #GDPRbasics #LearnGDPR #payroll #foreignbusiness #infographic #easypayrollgermany #DataAuditOnline #GDPRdataaudittemplate #becompliant #Datainventorysheet #Datachecklist #DataLifecycle #compliance #payrollservices #completegermanpayrollservices #news #smallbusiness https://lnkd.in/dp3THEd
0 notes
Photo
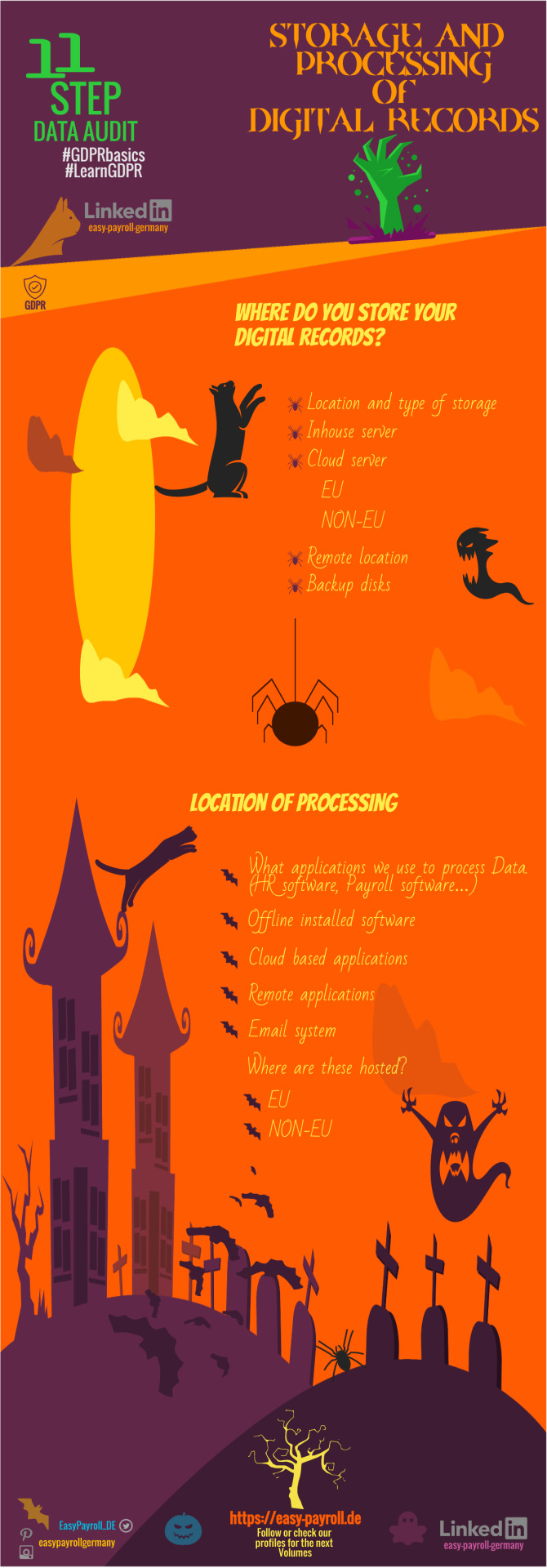
HALLOWEEN EDITION of GDPR DATA AUDIT TEMPLATE Vol7b Like if you Enjoy and please comment also. Storage and processing of DIGITAL RECORDS-Where-How-Why? https://easy-payroll.de #GDPR #digitalisation #paperless #Business #halloween #Working #control #access #marketing #documents #security #retention #GDPRbasics #LearnGDPR #payroll #foreignbusiness #infographic #easypayrollgermany #DataAuditOnline #GDPRdataaudittemplate #becompliant #Datainventorysheet #Datachecklist #DataLifecycle #compliance #payrollservices #completegermanpayrollservices #news #smallbusiness
0 notes
Photo

Volume 7 a of 11 Step GDPR Data audit Success Guide 𝐒𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐨𝐟 𝐩𝐚𝐩𝐞𝐫 𝐛𝐚𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐫𝐞𝐜𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐬 Volume 7 b will focus on digital records 𝐃𝐢𝐠𝐢𝐭𝐚𝐥 𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐠𝐞𝐬 (𝐬𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐝 𝐝𝐨𝐜𝐮𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐬) 𝐰𝐢𝐥𝐥 𝐦𝐚𝐤𝐞 𝐲𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐤 𝐦𝐮𝐜𝐡 𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐢𝐞𝐫 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐟𝐚𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐫, 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐚 𝐜𝐨𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐥 𝐥𝐞𝐟𝐭 𝐛𝐞𝐡𝐢𝐧𝐝, 𝐰𝐡𝐢𝐜𝐡 𝐢𝐬 𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐲 𝐭𝐨 𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐞 𝐛𝐚𝐜𝐤 𝐰𝐡𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐫 𝐲𝐨𝐮 𝐧𝐞𝐞𝐝 𝐭𝐨 𝐤𝐧𝐨𝐰 𝐰𝐡𝐨 𝐨𝐫 𝐰𝐡𝐲 𝐚𝐜𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐨𝐫 𝐦𝐨𝐝𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐞𝐝 𝐚𝐧𝐲 𝐝𝐚𝐭𝐚. With the #GDPR it makes even more sense to adopt #digitalisation and a #paperless approach for any #Business ! #Working digitally gives you complete #control and immediate #access to the #documents you need. Finding a document is much easier and the #security used for access or #storage have a lot of options you can choose from. Automating the hashtag#retention periods from day one will keep you informed of the exact life-cycle of all your documents. http://bit.ly/AuditOnlineNow #GDPRbasics #LearnGDPR #payroll #foreignbusiness #infographic #easypayrollgermany #DataAuditOnline #GDPRdataaudittemplate #becompliant #Datainventorysheet #Datachecklist #DataLifecycle #compliance #payrollservices #completegermanpayrollservices #news #smallbusiness
0 notes
Photo

Volume 7 a of 11 Step GDPR Data audit Success Guide 𝐒𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐨𝐟 𝐩𝐚𝐩𝐞𝐫 𝐛𝐚𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐫𝐞𝐜𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐬 Volume 7 b will focus on digital records 𝐃𝐢𝐠𝐢𝐭𝐚𝐥 𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐠𝐞𝐬 (𝐬𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐝 𝐝𝐨𝐜𝐮𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐬) 𝐰𝐢𝐥𝐥 𝐦𝐚𝐤𝐞 𝐲𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐤 𝐦𝐮𝐜𝐡 𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐢𝐞𝐫 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐟𝐚𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐫, 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐚 𝐜𝐨𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐥 𝐥𝐞𝐟𝐭 𝐛𝐞𝐡𝐢𝐧𝐝, 𝐰𝐡𝐢𝐜𝐡 𝐢𝐬 𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐲 𝐭𝐨 𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐞 𝐛𝐚𝐜𝐤 𝐰𝐡𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐫 𝐲𝐨𝐮 𝐧𝐞𝐞𝐝 𝐭𝐨 𝐤𝐧𝐨𝐰 𝐰𝐡𝐨 𝐨𝐫 𝐰𝐡𝐲 𝐚𝐜𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐨𝐫 𝐦𝐨𝐝𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐞𝐝 𝐚𝐧𝐲 𝐝𝐚𝐭𝐚. With the #GDPR it makes even more sense to adopt #digitalisation and a #paperless approach for any #Business. #Working digitally gives you complete #control and immediate #access to the #documents you need. Finding a document is much easier and the #security used for access or #storage have a lot of options you can choose from. Automating the hashtag#retention periods from day one will keep you informed of the exact life-cycle of all your documents. https://easy-payroll.de #GDPRbasics #LearnGDPR #payroll #foreignbusiness #infographic #easypayrollgermany #DataAuditOnline #GDPRdataaudittemplate #becompliant #Datainventorysheet #Datachecklist #DataLifecycle #compliance #payrollservices #completegermanpayrollservices #news #smallbusiness
0 notes
Photo
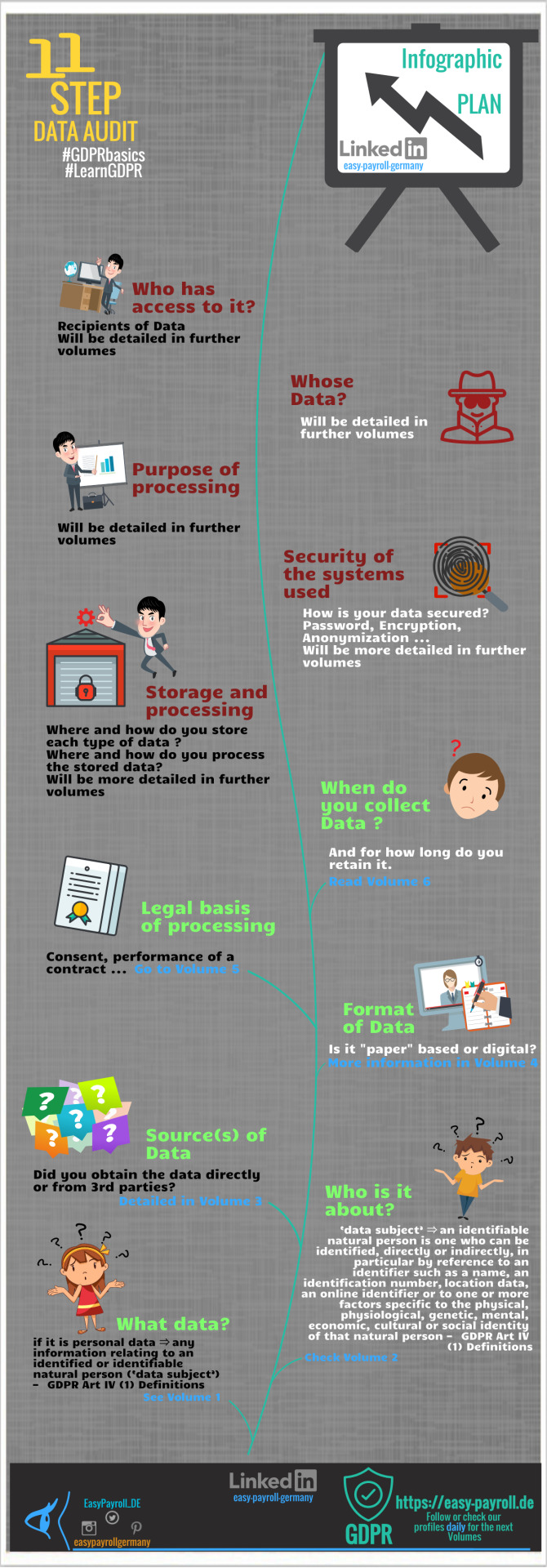
𝟏𝟏 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝐆𝐃𝐏𝐑 𝐃𝐚𝐭𝐚 𝐀𝐮𝐝𝐢𝐭 𝐏𝐥𝐚𝐧 𝐈𝐧𝐟𝐨𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐩𝐡𝐢𝐜 with embedded volumes and vol links. If you need any assistance in outsourcing and/or payroll services feel free to contact us. Follow to see the next updates. Check the plan online at https://t.co/A4xHzOexny and 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐯𝐞 𝐲𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐟𝐞𝐞𝐝𝐛𝐚𝐜𝐤 𝐨𝐫 𝐫𝐞𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬 𝐚𝐬 𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐲 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐜𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐭𝐬 and further improves our services. #GDPRbasics #LearnGDPR #payroll #foreignbusiness #fastemployment #outsourcing #infographic #easypayrollgermany #EPG #DataAuditOnline #businessregistration #GDPRdataaudittemplate #becompliant #Datainventorysheet #Datachecklist #DataLifecycle #compliance #payrollservices #completegermanpayrollservices #news #instagood #bestof2018 #topofweek #like #comment #smallbusiness #hiring #outcome #Germany #easypayroll_de
0 notes