#dual node server
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
HexaData HD‑H231‑H60 Ver Gen001 – 2U High-Density Dual‑Node Server
The HexaData HD‑H231‑H60 Ver Gen001 is a 2U, dual-node high-density server powered by 2nd Gen Intel Xeon Scalable (“Cascade Lake”) CPUs. Each node supports up to 2 double‑slot NVIDIA/Tesla GPUs, 6‑channel DDR4 with 32 DIMMs, plus Intel Optane DC Persistent Memory. Features include hot‑swap NVMe/SATA/SAS bays, low-profile PCIe Gen3 & OCP mezzanine expansion, Aspeed AST2500 BMC, and dual 2200 W 80 PLUS Platinum redundant PSUs—optimized for HPC, AI, cloud, and edge deployments. Visit for more details: Hexadata HD-H231-H60 Ver: Gen001 | 2U High Density Server Page
#2U high density server#dual node server#Intel Xeon Scalable server#GPU optimized server#NVIDIA Tesla server#AI and HPC server#cloud computing server#edge computing hardware#NVMe SSD server#Intel Optane memory server#redundant PSU server#PCIe expansion server#OCP mezzanine server#server with BMC management#enterprise-grade server
0 notes
Text
USB 3.2 Gen1, Gen2 PHY Controller IP Cores
T2M-IP, a global specialist in semiconductor IP solutions, highlights its USB 3.2 Gen1 and Gen2 IP Core, a complete, production-proven PHY and Controller solution supporting 5Gbps and 10Gbps data transfer. Designed for performance, flexibility, and low power, this IP cores supports multi-lane operation and is optimized for a wide range of high-speed interface applications across consumer, automotive, and industrial domains.
Fully compliant with the USB 3.2 specification, the IP cores support Host, Device, OTG, Dual-Role, and Hub configurations. It is also USB Type-C compatible, enabling seamless integration into USB-C-based designs, including support for dual-role functionality and alternate mode readiness.

With the increasing adoption of USB Type-C and higher bandwidth peripherals, SoC designers are under pressure to deliver robust USB performance while minimizing power and area. T2M-IP’s USB 3.2 IP stands out by offering a unified, scalable solution that supports diverse use cases—from compact wearables and smartphones to high-throughput automotive infotainment and industrial control systems. Its adaptability across roles and applications makes it an ideal choice for future-proof designs.
Key Features of T2M-IP's USB 3.2 IP cores include:
High-Speed USB 3.2 Support: Compliant with Gen1 (5Gbps) and Gen2 (10Gbps), with support for multi-lane operation to boost throughput.
Flexible USB Roles: Highly configurable for Host, Device, OTG, Hub, and Dual-Role applications.
Type-C Integration Ready: Supports key USB Type-C features, ideal for modern SoCs with reversible connectors and dynamic role-switching.
Low Power & Compact Footprint: Optimized PHY architecture ensures minimal area and power, perfect for mobile and embedded systems.
Robust Signal Performance: Built-in signal integrity and error-handling features ensure reliable performance in harsh environments.
Proven Across Markets: Successfully deployed in automotive, external storage, consumer electronics, gateways, and industrial systems.
T2M-IP’s USB 3.2 Gen1/Gen2 solution is part of a rich interface IP cores portfolio that includes PCIe, HDMI, DisplayPort, MIPI, DDR, Ethernet, V-by-One, SD/eMMC, and programmable SerDes, all available with matching PHYs. IP cores are silicon-proven and available across leading foundries and advanced process nodes.
Immediate licensing Availability: These Semiconductor Interface IP Cores are immediately available for licensing as stand-alone IP Cores or with pre-integrated Controllers and PHYs. Please submit a request / MailTo for more information on licensing options and pricing.About T2M: T2M-IP is a global independent semiconductor technology expert, supplying complex semiconductor IP Cores, Software, KGD, and disruptive technologies to allow faster development of your Wearables, IOT, Automotives, Communications, Storage, Servers, Networking, TV, STB, and Satellite SoCs. For more information, please visit www.t-2-m.com
1 note
·
View note
Text
AMD EPYC 9005 Vs Intel Xeon 6: Next-Gen Server Processors

AMD EPYC 9005 vs Intel Xeon 6 AMD EPYC 9005
Core Design/Architecture: AMD EPYC 9005 “Turin” core architecture: Zen 5 (128), Zen 5c (192). Maximum threads: 384. Process nodes are Zen 5 on TSMC 4nm and Zen 5c on 3nm. Compatible with previous Genoa/Bergamo, SP5 socket. Supports 9TB, 12-channel DDR5-6400. PCIe 5.0, 160 lanes. Types 1, 2, and 3 of CXL 1.0 are supported. TDP: 125W–500W Intel Xeon 6 Essential Architecture: Up to 288 Sierra Forest E-cores Granite Rapids Redwood Cove: Up to 128 P-cores Intel Node of Process: 3 LGA 4710 and LGA 7529 sockets Supports 6TB, 12-channel DDR5-6400. Granite Rapids-AP PCIe 5.0 offers 136 lanes. CXL support: CXL 2.0 TDP Granite Rapids-AP max 500W Performance and Benchmarks AMD EPYC 9005 EPYC 9965 (192-core) excels in multi-threaded tasks. A dual 128-core EPYC 9755 setup surpasses Intel's dual Xeon 6980P by 40% in various benchmarks. Twin Xeon 6980P combinations often outperform EPYC 9755 or 9965 CPUs. Intel Xeon 6 Sierra Forest: Designed for high-density, multi-threaded operations with 288 E-cores. Granite Rapids is designed for high-performance processing with 128 P-cores. Intel's competitive devices fall short of AMD's EPYC 9005 series in efficiency and performance.
Pros and Cons of AMD EPYC 9005
Benefits Zen 5c models feature up to 192 cores and 384 threads, ideal for big simultaneous applications. Better Performance per Watt: AMD's Zen 5 and Zen 5c maximise throughput and power efficiency. Up to 160 PCIe 5.0 lanes are ideal for I/O-intensive applications (NVMe, GPUs, networking). Memory and Bandwidth: Supports industry-leading 12-channel DDR5-6400 and up to 9TB per socket. Socket Scalability: The SP5 socket's Genoa and Bergamo compatibility simplifies upgrades. Superior Protection (Infinity Guard); SEV, SME, and SNP encrypt hardware-level memory and virtual machines. High-end economical: Performs better than the Intel Xeon 6980P at comparable pricing. Drawbacks Platform Costs: 128–192 core variations require a top-tier motherboard with cooling and robust VRMs. Intel Xeon 6 supports CXL 2.0 while running CXL 1.x, limiting memory pooling options. Flagship power consumption rises: Due to their 500W TDPs, 192-core machines need advanced cooling and a PSU. Lag in Software Optimisation: Some corporate applications may favour Intel's architecture or need AMD's high core counts. Intel Xeon 6 Benefits and Drawbacks Benefits Adaptable Core Architecture: Sierra Forest offers up to 288 E-cores for high-density workloads. Granite Rapids: Up to 128 P-cores for intensive computations. CXL 2.0 support: Allows memory sharing and pooling, ideal for memory-bound and AI/ML applications. Strong Security Stack: Data centres trust multi-key memory encryption, TME, and SGX. Software Ecosystem Maturity: Wide financial, business, and HPC software compatibility and optimisation. Sierra Forest's efficient cores reduce power consumption in web-scale systems. Drawbacks In benchmarks, twin Xeon systems often perform worse than EPYC 9755/9965. Has 136 PCIe 5.0 lanes, compared to AMD's 160. Instead of AMD's 9TB, it supports 6TB per socket. Costly at the top: Chips like the Xeon 6980P can cost more than AMD EPYC CPUs. Complex Socket Transition: Introduces LGA 4710 and 7529 sockets, requiring a platform update.
Security Features
AMD EPYC 9005 The Infinity Guard Suite: SEV secures multi-tenant environments by encrypting virtual machines. SME protects system memory from unauthorised access. Intel Xeon 6 Private data and code are separated by Software Guard Extensions (SGX). All memory is protected with comprehensive memory encryption to prevent physical threats.
In conclusion
AMD's EPYC 9005 series, especially the high-core-count 9965, outperforms Intel's Xeon 6 family. AMD dominates the server CPU market with its high core density, advanced security, and low costs. Intel's Xeon 6 processors handle certain tasks and offer robust security with their E-core and P-core designs. AMD's latest devices offer a significant performance and price advantage.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
0 notes
Link
#AIinfrastructure#cross-regionallogistics#digitaltwindeployment#energy-efficientmanufacturing#precisionautomation#smartcityecosystems#sovereigncloudsolutions#thermalinnovation
0 notes
Text
High-Density Innovation for Future-Ready Enterprises
Looking for maximum performance in a compact form? The HD-H261-3C0 (Gen001) by HexaData brings 4 powerful nodes into a 2U chassis, delivering unmatched compute density, memory scalability, and energy efficiency.
1. Processor Excellence: Powered by 2nd Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors, with up to 8 sockets across nodes — ideal for heavy workloads like AI, HPC, and big data analytics.
2. Unmatched Memory Capacity: Supports 64 DIMM slots for DDR4 memory up to 2933MHz, plus Intel® Optane™ Persistent Memory for faster data handling.
3. Built-In 10GbE Networking: Each node comes with dual 10GbE LAN ports, ensuring high-speed, low-latency connectivity for mission-critical applications.
4. Smart Management and Efficiency: With features like Aspeed AST2500 remote management, cold redundancy, and smart power protection (SCMP) — the server guarantees optimal uptime and power savings.
5. Reliable and Energy-Saving PSU: Equipped with a 2200W 80 PLUS Platinum redundant power supply, providing reliable energy with reduced operational costs.
Perfect for: Data Centers Cloud Infrastructure Big Data & AI Workloads High-Performance Computing (HPC) Environments
For full specifications and more information, visit: Hexadata HD-H261-3C0 Server.
#HexaData#HighDensityServer#EnterpriseSolutions#IntelXeon#DataCenterSolutions#BigData#CloudComputing#ServerTechnology
1 note
·
View note
Text
do i use tor with vpn
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
do i use tor with vpn
How to use Tor with VPN
When it comes to securing your online privacy and anonymity, combining Tor with a Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a powerful way to enhance your protection. Both tools work in different ways to safeguard your online activities, and using them together can offer a higher level of security and privacy.
To use Tor with a VPN, follow these steps:
Start by downloading and installing a reliable VPN service on your device. Ensure that the VPN you choose supports Tor. There are several VPN providers that offer this feature.
Connect to the VPN server of your choice before launching the Tor browser. This step helps to encrypt your internet traffic and protects your data from potential surveillance or tracking.
Once you are connected to the VPN, launch the Tor browser. Tor routes your internet traffic through a series of encrypted nodes, making it difficult for anyone to trace your online activity back to you.
By using both Tor and a VPN together, you can enjoy the benefits of both technologies. The VPN adds an extra layer of encryption and security, while Tor helps to anonymize your online identity.
It is important to note that while using Tor with a VPN can enhance your privacy, it may also impact your internet speed. The added layers of encryption and routing can slow down your connection, so it's essential to balance your need for security with browsing speed.
Overall, combining Tor with a VPN is a valuable strategy for those seeking enhanced online privacy and security. By following these steps, you can browse the internet with confidence knowing that your data is protected and your identity is anonymous.
Benefits of using Tor and VPN together
Combining Tor and VPN services offers a powerful solution for enhancing online privacy and security. Tor, short for The Onion Router, and VPN, or Virtual Private Network, each provide distinct advantages, but when used together, they offer even greater benefits.
Firstly, the combination of Tor and VPN adds layers of encryption, significantly bolstering privacy. Tor encrypts your data and routes it through a series of volunteer-operated servers, obscuring your IP address and online activities. VPNs also encrypt your internet traffic, making it nearly impossible for third parties to intercept or decipher your data. By using both simultaneously, you create an extra layer of protection, making it extremely challenging for anyone to trace your online actions back to you.
Moreover, Tor and VPN together can bypass censorship and access geo-restricted content. Tor enables access to the Tor network, which may circumvent censorship measures imposed by governments or internet service providers. VPNs, meanwhile, allow users to connect to servers in different locations, effectively masking their true location and granting access to region-locked content. When used in conjunction, Tor's anonymity and VPN's versatility provide users with greater freedom to explore the internet without restrictions.
Additionally, the combination of Tor and VPN enhances anonymity while minimizing the risk of traffic analysis. Tor's onion routing protocol ensures that each data packet travels through multiple nodes, making it exceedingly difficult for adversaries to track the origin and destination of the communication. VPNs further obfuscate your online footprint by masking your IP address and encrypting your traffic. This dual approach makes it extremely challenging for malicious actors or surveillance agencies to monitor your online behavior effectively.
In conclusion, leveraging both Tor and VPN simultaneously offers users unparalleled privacy, security, and access to a free and open internet. Whether safeguarding sensitive information or circumventing censorship, the combined benefits of Tor and VPN provide users with greater control over their online experiences.
Risks of not using Tor with VPN
When it comes to online privacy and security, using tools like Tor and VPNs are often seen as essential. However, some individuals may choose to use one without the other, leaving themselves vulnerable to various risks.
Not using Tor with a VPN can expose your IP address to potential snoopers, hackers, and surveillance agencies. Tor helps to anonymize your internet traffic by routing it through multiple servers, making it difficult to trace back to you. On the other hand, a VPN encrypts your data and provides an additional layer of security. By combining both technologies, you can enhance your privacy and protect your online activities.
Without the protection of Tor, your internet service provider (ISP) can still see your online activities, including the websites you visit and the content you access. This could lead to targeted ads, data collection, or even potential monitoring by third parties. Additionally, without the encryption provided by a VPN, your data is more susceptible to interception and theft, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks.
Moreover, without using Tor with a VPN, your online identity and personal information are at a higher risk of being compromised. Cybercriminals may exploit vulnerabilities in your connection to steal sensitive data such as passwords, financial information, or personal details. This could result in identity theft, fraud, or other malicious activities.
In conclusion, the risks of not using Tor with a VPN can have serious consequences for your online security and privacy. By utilizing both technologies together, you can create a more secure and anonymous online environment for your browsing activities.
Comparison of Tor versus VPN
When it comes to online privacy and security, two popular options for anonymizing your internet connection are Tor and VPNs (Virtual Private Networks). While both serve the purpose of hiding your online activity, there are key differences between the two that users should consider before deciding which to use.
Tor, short for The Onion Router, operates by routing your internet traffic through a network of volunteer-run servers, encrypting it at each step. This layered encryption makes it difficult for anyone to trace your online activity back to you. Tor is free to use and is often favored by those who require a high level of anonymity, such as journalists or activists in repressive regimes. However, because of its decentralized nature and reliance on volunteers, Tor can sometimes be slower than VPNs and may not be suitable for bandwidth-intensive activities like streaming or online gaming.
On the other hand, VPNs create a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and a server operated by the VPN provider. This masks your IP address and encrypts your data, making it much harder for third parties to intercept or track your online activity. VPNs are typically faster and more reliable than Tor, making them a better choice for activities that require high-speed internet access. Additionally, many VPN services offer a range of server locations around the world, allowing users to bypass geo-restrictions and access content from other countries.
Ultimately, the choice between Tor and VPN depends on your specific needs and priorities. If maximum anonymity is your goal and you don't mind sacrificing some speed, Tor may be the better option. However, if you prioritize speed, reliability, and the ability to access geo-restricted content, a VPN is likely the way to go.
Setting up Tor and VPN for maximum security
In today's digital landscape, ensuring maximum security and privacy while browsing the internet has become increasingly crucial. Two popular tools often utilized for this purpose are Tor (The Onion Router) and VPNs (Virtual Private Networks). Combining these two technologies can provide an extra layer of protection, enhancing your online anonymity and security.
To set up Tor and VPN for maximum security, follow these steps:
Install and Configure Tor: Begin by downloading the Tor browser from the official website. Once installed, launch the browser and navigate to the settings menu. Here, you can customize various aspects of Tor, such as security levels and proxy settings. It's advisable to stick with the default settings for most users, as they offer a good balance between security and usability.
Choose a Reliable VPN Provider: Selecting a reputable VPN provider is essential for ensuring privacy and security. Look for a provider that offers robust encryption protocols, a strict no-logs policy, and a wide range of server locations. Once you've chosen a VPN provider, sign up for a subscription and download the necessary software for your device.
Configure VPN Settings: After installing the VPN software, launch the application and log in using your credentials. From the settings menu, you can customize various options, including encryption protocols and server locations. Opt for the highest level of encryption available to maximize security.
Connect to VPN before Tor: To achieve maximum security, it's recommended to connect to the VPN before launching the Tor browser. This ensures that your internet traffic is encrypted before it enters the Tor network, adding an extra layer of protection against surveillance and monitoring.
By following these steps and combining the power of Tor and VPN technologies, you can significantly enhance your online security and privacy. However, it's essential to remember that no system is foolproof, and staying vigilant against potential threats is always advisable.
0 notes
Text
Whitebox 1G Ethernet PHY IP Core with BroadR-Reach
T2M-IP proudly announces the availability of its Whitebox 1G Ethernet PHY IP core, a production-proven solution delivering unmatched customization, flexibility, and performance for automotive, industrial, and embedded Ethernet applications. Designed to support long-term integration and innovation, this cutting-edge PHY IPempowers customers with unlimited usage and full source-level modification rights under a highly permissive Whitebox license model.
Built on mature, high-volume production technology and compliant with IEEE 802.3-2008, IEEE 802.3az (EEE), and IEEE 1588-2008, this Gigabit Ethernet PHY is ideal for companies seeking full control over their Ethernet IP stack—whether optimizing for power, cost, or advanced system integration.
Key Highlights:
Whitebox Licensing Model Unlimited usage with full RTL access and modification rights — ideal for companies seeking long-term control and customization of their IP portfolio.
Multi-Node Portability Designed in bulk 28nm process, the PHY is easily portable across multiple process nodes, ensuring broad compatibility and futureproofing across silicon generations.
Automotive-Ready with BroadR-Reach™ Integrated BroadR-Reach™ technology delivers robust, high-speed communication over single twisted-pair cables, optimized for next-generation Automotive Ethernet networks.
Flexible Interface Support Dual-port MAC interface supporting GMII (10/100/1000BASE-T) and MII (10/100BASE-T) for versatile SoC integration.
Comprehensive Protocol Support Supports 1000BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 10BASE-T, in both full and half-duplex modes, with advanced features like Auto-MDIXand skew correction.
Energy Efficiency Built-in Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) support and power-down modes make this PHY ideal for low-power and green designs.
Time-Sensitive Networking Ready Supports IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) for synchronization in industrial and automotive TSN (Time-Sensitive Networking) environments.
Proven in silicon and already licensed by multiple tier-one customers in the United States, Korea, China, and Europe, this 1G Ethernet PHY IP is quickly becoming the preferred choice for companies seeking a scalable, modifiable, and future-proof Ethernet IP solution.

T2M-IP has a wide and diverse silicon Interface IP Core Portfolio, including USB, PCIe, HDMI, Display Port, MIPI, DDR, V-by-One, programmable SerDes, SD/eMMCs, and many more Controllers with matching PHYs, available in major Fabs in process nodes as small as 7nm. On request, they can also be ported to other foundries and cutting-edge process nodes.
Immediate licensing Availability: These Semiconductor Interface IP Cores are immediately available for licensing as stand-alone IP Cores or with pre-integrated Controllers and PHYs. Please submit a request / MailTo for more information on licensing options and pricing.About T2M: T2M-IP is a global independent semiconductor technology expert, supplying complex semiconductor IP Cores, Software, KGD, and disruptive technologies to allow faster development of your Wearables, IOT, Automotives, Communications, Storage, Servers, Networking, TV, STB, and Satellite SoCs. For more information, please visit www.t-2-m.com.
0 notes
Text
can tor be used with a vpn
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
can tor be used with a vpn
Tor over VPN
Title: Enhancing Online Privacy: The Benefits of Using Tor over VPN
In an age where online privacy is increasingly under threat, internet users are turning to various tools and technologies to safeguard their data and browsing activities. Two popular privacy-enhancing solutions that have gained significant attention are Tor (The Onion Router) and VPNs (Virtual Private Networks). While each offers its own set of advantages, combining Tor with a VPN, commonly referred to as "Tor over VPN," can provide users with an extra layer of protection and anonymity.
Tor operates by routing internet traffic through a network of volunteer-run servers, encrypting it multiple times to ensure anonymity. However, while Tor offers robust anonymity, it may not encrypt the data beyond the final exit node, leaving it vulnerable to surveillance. This is where a VPN comes into play.
By connecting to a VPN before accessing the Tor network, users can encrypt their internet traffic from their device to the VPN server, adding an additional layer of security. This means that even if someone manages to intercept the traffic between the user and the entry node of the Tor network, they would only see encrypted data, enhancing privacy and security.
Moreover, using Tor over VPN can help users bypass certain restrictions imposed by internet service providers or governments. Since the VPN server assigns the user a different IP address, it can help circumvent geo-blocks and censorship, allowing users to access content and websites that may be restricted in their region.
However, it's essential to choose reputable VPN providers and configure them correctly to ensure maximum security and privacy. Additionally, users should be aware that combining Tor with VPN may impact internet speed due to the additional layers of encryption and routing.
In conclusion, while both Tor and VPNs offer significant privacy benefits individually, combining them through Tor over VPN can provide users with a comprehensive solution for protecting their online activities, enhancing anonymity, and bypassing restrictions.
VPN with Tor
Title: Enhancing Online Privacy: The Power of VPN with Tor
In an era where online privacy is increasingly under threat, individuals are turning to innovative solutions to safeguard their digital footprints. One such powerful combination gaining traction is the integration of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) with Tor (The Onion Router) technology. This tandem approach offers heightened levels of anonymity and security, empowering users to navigate the internet with confidence.
VPNs are renowned for encrypting internet traffic, routing it through remote servers to mask users' IP addresses and location. This encryption shields data from prying eyes, whether it's hackers, ISPs, or government surveillance agencies. However, while VPNs provide a layer of privacy, they have limitations, particularly in protecting against certain forms of online tracking and surveillance.
This is where Tor comes into play. Tor operates by routing internet traffic through a network of volunteer-operated servers, encrypting data multiple times and bouncing it through various nodes before reaching its destination. This intricate process makes it incredibly challenging for anyone to trace the origin and destination of the data, significantly enhancing anonymity.
By combining VPNs with Tor, users benefit from the strengths of both technologies. The VPN encrypts data and hides the user's IP address from their ISP, while Tor adds another layer of encryption and anonymity by obfuscating the origin of the connection. This dual-layered approach makes it exceedingly difficult for adversaries to monitor online activities or trace internet traffic back to the user.
Moreover, VPNs with Tor enable access to the Tor network even in regions where it may be blocked or restricted. This freedom to access the internet without censorship is crucial for journalists, activists, and individuals living in countries with oppressive regimes.
In conclusion, the synergy between VPNs and Tor offers a potent solution for preserving online privacy and anonymity. By harnessing the combined power of encryption and anonymization, users can reclaim control over their digital identities and navigate the internet without fear of surveillance or intrusion.
Tor and VPN together
Combining Tor and VPN services can enhance your online privacy and security by adding layers of encryption and anonymity to your internet connection. Utilizing both tools in tandem can provide a more robust defense against potential cyber threats and surveillance.
Tor, short for The Onion Router, routes your internet traffic through a series of volunteer-operated servers, encrypting it multiple times along the way. This process helps to conceal your IP address and browsing activities from prying eyes, such as internet service providers, government agencies, and cybercriminals. However, while Tor provides strong anonymity, it can be slow due to the multiple relays your data passes through.
On the other hand, a Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure and encrypted connection to the internet by routing your traffic through a remote server. This helps to protect your data from being intercepted by hackers or other malicious actors, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks. Additionally, a VPN can help you bypass geo-restrictions and access region-locked content.
By combining Tor and VPN services, you can enjoy the benefits of both technologies. The VPN encrypts your traffic before it enters the Tor network, adding an extra layer of security. This setup can help to mitigate some of the speed issues associated with using Tor alone, while still maintaining a high level of anonymity.
It is important to choose reputable providers for both Tor and VPN services to ensure the protection of your online activities. Additionally, keep in mind that while using both together can enhance your privacy, no tool can guarantee complete anonymity. It is essential to practice safe browsing habits and stay informed about the latest cybersecurity developments to stay safe online.
Combining Tor and VPN
Combining Tor and VPN can provide an extra layer of security and privacy when browsing the internet. Tor, short for The Onion Router, is a network that protects your online activities by routing your connections through multiple servers around the world. This helps to anonymize your identity and location, making it difficult for anyone to track your online behavior.
On the other hand, VPN, or Virtual Private Network, encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server before accessing the internet. This adds another level of protection by hiding your IP address and encrypting your data, making it harder for hackers, government agencies, or advertisers to monitor your online activities.
By combining Tor and VPN, you can enjoy the benefits of both technologies. When you connect to a VPN first and then use the Tor browser, your internet traffic is first encrypted by the VPN before entering the Tor network. This means that not even your ISP can see what you are doing online. Additionally, websites you visit through Tor will not be able to see your true IP address, further enhancing your anonymity.
However, it's important to note that using both Tor and VPN can slow down your internet speed due to the multiple layers of encryption and rerouting of traffic. It's also important to choose a reputable VPN provider that does not keep logs of your online activities to ensure maximum privacy.
Overall, combining Tor and VPN can be an effective way to enhance your online privacy and security, especially if you are concerned about protecting your identity and data from prying eyes.
Using Tor alongside VPN
When it comes to online privacy and security, many users turn to tools like Tor and VPNs to protect their data and identities. While both Tor and VPNs offer increased anonymity and encryption, using them together can provide an extra layer of protection.
Tor, short for The Onion Router, routes your internet traffic through a series of servers to conceal your IP address and browsing activity. This helps in maintaining anonymity and bypassing censorship. On the other hand, a VPN, or Virtual Private Network, encrypts your internet connection to protect your data from hackers and surveillance.
By combining Tor with a VPN, you can further enhance your online privacy. When you use Tor alongside a VPN, your internet traffic first goes through the VPN server and then through the Tor network, adding an additional layer of encryption. This double-encrypted setup can help in preventing your ISP from seeing that you are using Tor, and it can also protect you in case the Tor exit node is compromised.
However, it is essential to note that using Tor with a VPN can slow down your internet speed due to the double encryption process. Additionally, it may raise suspicion in regions where using Tor is illegal. It is crucial to choose a reliable VPN provider with a no-logs policy to ensure maximum privacy protection.
In conclusion, while using Tor alongside a VPN can offer enhanced privacy and security benefits, users should carefully consider the potential trade-offs and ensure they employ both tools correctly to safeguard their online activities.
0 notes
Text
AMD EPYC 9575F Vs Intel Core i5 14600K Features, Use Cases

Core i5 14600K vs AMD EPYC 9575F
Understanding how and why Intel's Core i5 leads the desktop CPU market and AMD's EPYC leads the server market is crucial. We compare AMD EPYC 9575F vs Intel Core i5-14600K architecture, performance, power, memory, and use case benefits.
Audience and Use Case
AMD EPYC 9575F
Designed for cloud, data centre, and corporate workloads.
For scientific computing, data analytics, virtualisation, high-volume multitasking, and machine learning.
Ideal for multi-socket servers, not PCs.
Core i5-14600K
Targeting home/office users, multimedia creators, and gamers.
Good for productivity tools, web development, gaming, and little content.
DIY PCs and consumer desktops.
Architecture Foundation
AMD EPYC 9575F
Built on TSMC's 5nm node using Zen 4 architecture.
Genoa family member with 128 threads and 64 cores.
An IOD and numerous CCDs make up its chiplet design.
Supports PCIe 5.0, SME/SEV encryption, and AVX-512 on a big I/O system.
Core i5-14600K
Raptor Lake uses Intel 7 (10nm Enhanced SuperFin).
A hybrid core architecture with 14 cores and 20 threads (8 efficiency, 6 performance).
Intel's Thread Director improves core-wide job scheduling.
PCIe 5.0/4.0, DDR4/DDR5, and integrated UHD Graphics 770 are supported.
Conclusion: EPYC 9575F is for scale and throughput, whereas i5-14600K is for desktop multitasking and real-time responsiveness.
Comparison of Performance
Performance Multi-Core
The EPYC 9575F excels at thread-intensive tasks. With Cinebench R23, multi-core points exceed 90,000.
Easily manages hundreds of workloads, containers, or virtual machines.
Despite being weaker than EPYC's server processors, the Core i5-14600K scores 26,000 in Cinebench R23 multi-core.
Single-Core Performance
With its 5.3 GHz boost clock, the Core i5-14600K outperforms EPYC in single-threaded jobs
While the EPYC's single-thread performance is great (4.1 GHz boost), it cannot match the i5's high-frequency P-cores in latency-sensitive workloads like gaming.
Conclusion: EPYC excels at parallel workloads, whereas i5 excels in latency-sensitive, real-time applications like desktop programs and gaming.
Memory Capability
AMD EPYC 9575F
DDR5 ECC 12-channel registered memory compatible.
Supports 4TB RAM per socket and offers good bandwidth.
Data integrity is guaranteed by ECC for mission-critical systems.
Core i5-14600K
Motherboards support dual-channel DDR5-5600 or DDR4-3200.
Maximum non-ECC capacity is 128GB, enough for user workloads.
ECC is unsuitable for memory-critical settings since it is not supported.
Conclusion: EPYC has greater memory and integrity, which servers need. Core i5 is useful for desktop apps.
Extension and PCIe Lanes
EPYC 9575F
Network cards, accelerators, multi-GPUs, and high-speed storage arrays benefit from 128 PCIe 5.0 lanes.
Max I/O throughput was the design aim.
Core i5-14600K
20 lanes: 4 NVMe SSD and 16 GPU PCIe 4.0/5.0.
More than enough for most creative and gaming endeavours.
Less extensible than server CPUs.
Conclusion: EPYC allows rapid expansion and connectivity. The Core i5 is sufficient for modern desktops.
Power and cooling needs
EPYC 9575F
High-performance liquid or air cooling is needed for 360W rack-mounted servers.
Processing density and throughput justify high power consumption.
Core i5-14600K
Base power is 125W and maximum turbo power is 181W.
Easy cooling using AIO coolers or consumer air.
Much more power-efficient daily operations.
Final verdict: i5 is the more power-efficient desktop processor. EPYC needs business cooling infrastructure.
Platform/Socket Compatibility
EPYC 9575F
On server-quality motherboards like Genoa, use socket SP5.
Advanced VRMs, ECC memory, and enterprise power supply are needed.
Made for custom blade systems or 1U/2U server chassis.
Core i5-14600K
Compatible with LGA 1700 Z690, B660, and Z790 motherboards.
Plug-and-play for gamers, content creators, and system builders.
Conclusion: end customers will find i5 more approachable. EPYC systems are only for enterprise and OEM manufacturers.
Integrated Graphics, Features
EPYC 9575F
Most servers need standalone graphics or headless mode to leverage an integrated GPU.
Computation requires GPU accelerators like AMD Instinct or NVIDIA A100.
Core i5-14600K
Equipped with Intel UHD Graphics 770.
Allows display output, light operations, and rudimentary graphics acceleration.
Conclusion: EPYC is for compute or GPU-accelerated settings, whereas Core i5 can handle unusual arrangements.
Pricing and Value Proposition
EPYC 9575F
Between $10,000 to $11,000 USD.
Has high computational density, long-term scalability, and top socket performance.
Unsuitable for casual use.
Core i5-14600K
Between $300-$350 USD.
Excellent value, especially for productivity and gaming.
Perfect price, power, and versatility.
Conclusion: i5 offers unmatched value, whereas EPYC gives data centres tremendous ROI.
#AMDEPYC9575F#IntelCorei514600K#EPYC9575F#Corei514600K#AMDEPYC9575FvsIntelCorei514600#technology#technews#news#technologynews#technologytrends#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
can you use a vpn with tor
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
can you use a vpn with tor
VPN and Tor combination
Combining a VPN and Tor for enhanced online privacy and security has become a popular choice for individuals seeking to safeguard their internet activities. Both VPN (Virtual Private Network) and Tor (The Onion Router) offer unique benefits and when used in conjunction, they create a powerful shield against potential threats.
VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection between the user and the internet, masking their IP address and encrypting their data. This prevents hackers, ISPs, and other third parties from monitoring or intercepting online activities. On the other hand, Tor routes the internet traffic through a series of volunteer-operated servers, encrypting the data multiple times and bouncing it around the network before reaching its destination. This process enhances anonymity and makes it difficult for anyone to trace the user's online behavior.
By combining VPN and Tor, users can enjoy the best of both worlds - the encryption and security features of a VPN, along with the anonymity and obfuscation provided by Tor. When using Tor over a VPN, the VPN provider cannot see the user's internet traffic, while the Tor network remains unaware of the user's IP address. This double layer of protection is especially beneficial for those accessing sensitive information, evading censorship, or navigating the dark web.
However, it is important to note that while the VPN and Tor combination offers enhanced privacy and security, it may also lead to slower internet speeds due to the multiple encryption processes. Moreover, users should choose reliable VPN providers and configure the settings correctly to ensure maximum effectiveness of this dual approach.
In conclusion, the combination of VPN and Tor is a powerful solution for individuals seeking to bolster their online privacy and security. By understanding how these technologies work together, users can navigate the digital world with confidence and peace of mind.
Benefits of using VPN with Tor
Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) in conjunction with Tor, the onion routing network, offers a myriad of benefits, enhancing both security and privacy for users. Here are some key advantages of employing a VPN alongside Tor:
Enhanced Anonymity: While Tor encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through multiple servers to conceal your identity, using a VPN adds an extra layer of anonymity. By masking your IP address with that of the VPN server, it becomes even more challenging for third parties to trace your online activities back to you.
Increased Security: VPNs encrypt your data before it enters the Tor network, safeguarding it from potential eavesdroppers or malicious actors. This encryption ensures that even if someone manages to intercept your traffic, they won't be able to decipher its contents.
Bypassing Restrictions: Some networks or regions may impose restrictions on accessing certain websites or online services. By combining Tor with a VPN, users can circumvent such restrictions, as the VPN helps disguise Tor traffic, making it appear as regular encrypted traffic.
Protection from Malicious Exit Nodes: Tor relies on exit nodes to connect to the regular internet, which can sometimes be compromised by hackers or surveillance agencies. Utilizing a VPN can mitigate this risk by encrypting the traffic between the exit node and the final destination, preventing potential interception or manipulation.
Improved Performance: In some cases, connecting to Tor directly can lead to slow internet speeds due to the multiple relays your data must pass through. However, by using a VPN to connect to the Tor network, users may experience improved performance and faster browsing speeds.
In conclusion, pairing a VPN with Tor offers users a robust combination of privacy, security, and accessibility, making it an invaluable tool for safeguarding online activities in an increasingly surveilled digital landscape.
Risks of using VPN in conjunction with Tor
Using a VPN in conjunction with Tor can provide an extra layer of anonymity and security when browsing the internet, but it also comes with risks that users should be aware of. While the combination of VPN and Tor can enhance privacy by encrypting data and routing it through multiple servers, there are potential pitfalls to consider.
One of the main risks of using a VPN with Tor is that it can introduce vulnerabilities and weaken the anonymity that Tor provides. VPN services may keep logs of user activity, which could compromise privacy if the VPN provider is subpoenaed or hacked. Additionally, connecting to a VPN before accessing the Tor network can create a single point of entry, making it easier for adversaries to trace the user's online activities back to their original IP address.
Another risk is that using a VPN with Tor can slow down internet speeds significantly. Both VPN and Tor can cause delays in data transmission due to the rerouting of traffic through multiple servers, so combining the two may result in even slower connection speeds. This can be frustrating for users who require fast and seamless internet access.
Furthermore, some websites and online services may block or restrict access to users who are using VPNs or Tor exit nodes. This can be problematic for individuals who rely on these tools to access censored or geo-blocked content.
In conclusion, while using a VPN with Tor can enhance privacy and security online, users should be cautious of the risks involved, such as reduced anonymity, slower speeds, and access restrictions. It is essential to weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks and choose the best setup based on individual needs and risk tolerance.
Is it safe to use VPN along with Tor?
Using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) in conjunction with Tor, the onion routing network, is a practice that some privacy-conscious individuals employ to enhance their online anonymity and security. However, whether it is truly safe to use both technologies together depends on various factors and considerations.
On one hand, employing a VPN alongside Tor can provide an additional layer of encryption and obfuscation. When you connect to a VPN before accessing the Tor network, your internet traffic is encrypted and routed through the VPN server before entering the Tor network. This can help hide your IP address from both your ISP and the entry node of the Tor network, thereby enhancing your privacy.
Furthermore, using a VPN may protect against certain attacks, such as exit node eavesdropping, by encrypting your data before it leaves the Tor network.
However, there are also potential drawbacks and risks associated with using a VPN with Tor. Some VPN providers may keep logs of user activity, which could compromise your anonymity if these logs were to be accessed by authorities or malicious actors. Additionally, the VPN provider itself could potentially track your activities, depending on their privacy policies and jurisdiction.
Moreover, using a VPN can introduce a single point of failure into your anonymity setup. If the VPN connection were to fail or be compromised, your real IP address could be exposed to the Tor network.
Ultimately, whether it is safe to use a VPN along with Tor depends on your threat model and the specific VPN provider you choose. It is essential to conduct thorough research and choose a reputable VPN provider that prioritizes user privacy and does not keep logs of user activity. Additionally, employing other security measures, such as using a secure operating system and practicing good browsing habits, can further enhance your online anonymity and security when using Tor with a VPN.
Guidelines for using VPN and Tor together
Using a combination of VPN (Virtual Private Network) and Tor (The Onion Router) can significantly enhance your online privacy and security. However, it's essential to follow some guidelines to ensure maximum effectiveness and avoid potential pitfalls.
Understand the Purpose of Each Tool: VPNs encrypt your internet traffic and route it through a remote server, masking your IP address. Tor, on the other hand, directs your traffic through a series of volunteer-operated servers, making it extremely difficult to trace. Both tools provide anonymity, but they operate differently.
Start with a Secure Connection: Always activate your VPN first before connecting to the Tor network. This adds an extra layer of encryption to your traffic, making it more difficult for anyone to intercept or monitor your online activities.
Choose the Right VPN: Opt for a reputable VPN service that does not log your activity and offers strong encryption protocols. Look for features like a kill switch, which cuts off internet access if the VPN connection drops, preventing your real IP address from being exposed.
Configure Tor Properly: Adjust your Tor settings to work with your VPN. In the Tor browser, go to "Preferences" > "Advanced" > "Network" > "Settings" and select "Use custom proxy settings." Enter your VPN's proxy information here to route Tor traffic through the VPN connection.
Be Mindful of Speed: Using both VPN and Tor simultaneously can slow down your internet connection due to the multiple layers of encryption and routing. Consider this trade-off between privacy and speed when deciding to use both tools.
Avoid Logging into Personal Accounts: While VPN and Tor offer anonymity, logging into personal accounts like social media or email can compromise your privacy. It's best to use these services without logging in or use separate, anonymous accounts.
By following these guidelines, you can leverage the combined power of VPN and Tor to enhance your online privacy and security while navigating the internet. Remember to stay informed about any updates or changes to these tools to maintain their effectiveness.
0 notes
Text
trying to request a ride for half an hour but still no driver has picked up the order, the driver looking down and finding that the order assigned

the passenger, discovering that the system is abnormal and trying to cancel the order but still can't...
Of course, some drivers also encountered an "unexpected surprise": they woke up after a night's rest and found that the HE Tuber income in their account exceeded 60 billion... You know, Cheng Wei's total personal wealth whenwent public was only 29 billion.
If Didi’s outage remains popular because online ride-hailing is very close to people’s lives and is used frequently, then the impact of the large-scale Alibaba Cloud outage on November 12 is even worse. Already: Alibaba’s Alipay, Taobao, DingTalk, and Alibaba Cloud Disk are indispensable applications for mobile payment, online shopping, online office, and cloud storage scenarios respectively.
When these applications are all paralyzed, people’s work, life, and Shopping may have to be paused.
What is even more worrying is that on November 27, Alibaba Cloud's cloud database console in some regions experienced access anomalies again, only half a month after the large-scale outage on the 12th. Two outages occurred in a short period of time, which is a serious problem for the entire cloud computing industry.
Even if the timeline is further relaxed, outages among major Internet companies have occurred quite frequently in the first half of this year.
On March 29, QQ and WeChat failed one after another, and many functions such as payment, voice calls, Moments, and QQ Space were used abnormally. Tencent characterized this as a first-level accident, including Lu Shan, President of the Technology Engineering Business Group, and WeChat Business Group Several senior executives, including Vice President Zhou Hao, were criticized internally. Coincidentally, Vipshop also suffered a P0 level outage on the same day, and the head of the basic platform department was dismissed as a result.
Secondly, the simultaneous occurrence of frequent outages, long-term cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and large-scale layoffs inevitably makes people suspect that there is some subtle connection between the two.
To judge whether this statement is reasonable, we must first understand the cause of the cloud server outage.
Generally speaking, the reasons for server downtime can be divided into two categories. One is human failure, such as system failure, design loopholes, and short-term overload operation. The other is non-human factors such as extreme weather and temporary power outages in the area. The outages of Vipshop, Tencent and Alibaba Cloud are typical human faults. The direct cause of the three incidents is that the abnormality of the cooling system in the computer room caused the equipment temperature to heat up rapidly. This is also the most common cause of failure in the industry.
Generally speaking, no or non-human factors can be completely avoided, disaster recovery and disaster preparedness plans are necessary. Alibaba Cloud also admitted in its subsequent response that the failure to handle the accident site in a timely manner caused the sprinkler system to be triggered, and the failure to release fault information in a timely manner were important reasons for amplifying the impact of the outage.
It was this response that led some people in the industry to uncover problems: downsizing staff
laying off high-paid senior programmers, and relying too much on young people. no emergency and preventive measures such as dual-machine hot backup plans, backup computer rooms, and multi-node clusters. , are one of the reasons for exacerbating the impact of downtime - and are also the sequelae of cost reduction and efficiency improvement.
In response to the above speculation, major manufacturers have not responded positively, but there may be no reason for the groundless speculation. And coincidentally, Didi, which just experienced a "frightening night", also experienced a round of layoffs last year involving almost all departments such as product technology and ride-hailing teams. It is reported that the number of employees involved is about 3,000, and the proportion is as high as 25%. .
One thing is certain: senior technicians not only have guaranteed professional skills, they can identify system vulnerabilities more accurately and quickly, and have more experience in handling on-site faults. Frequent outages are believed to have made major manufacturers realize the importance of improving infrastructure, increasing disaster recovery and
preparedness plans, and cultivating high-end technical talents.However, the impact of two consecutive years of cost reduction and efficiency improvement and several downtimes on its reputation, as well as the negative impact on customers and upstream and downstream partners in the industry chain, may be difficult to completely eliminate. It is still unknown whether major manufacturers will change their cost reduction and efficiency improvement policies as a result.
3. In 2024, can cost reduction and efficiency improvement come to an end?
The impact of cost reduction and efficiency improvement by large manufacturers on customers and partners is multifaceted.
First of all, of course, downtime events seriously affect the daily operations of corporate customers, especially those small and medium-sized enterprises that do not have the financial resources to make their own disaster preparedness and emergency plans.
Official data shows that Alibaba Cloud has more than
0 notes
Text
TOPOLOGI JARINGAN
Topologi Ring
Topologi ring atau topologi cincin adalah sebuah model topologi jaringan yang berbentuk melingkar seperti cincin. Setiap perangkat komputer akan terhubung dalam rangkaian lingkaran tersebut.
Setiap perangkat akan terhubung dengan dua perangkat lain, yakni yang berada di kanan dan kirinya hingga membentuk sebuah cincin. Tiap perangkat atau titik tersebut berfungsi sebagai repeater, yakni yang dapat memperkuat sinyal sepanjang jaringan tersebut.

Kelebihan topologi Ring :
mudah dibuat
sederhana
murah
Kekurangan Topologi Ring :
lambat
1 networ gagal = semua jaringan gagal
jumlah node mempengaruhi kinerja
TOPOLOGI DUAL RING
Topologi dual-ring adalah topologi jaringan yang berlebihan di mana node terhubung menggunakan dua cincin konsentris dengan empat cabang.
Topologi dual-ring sangat ideal untuk aplikasi dengan masalah kabel atau jaringan kecil yang tidak sering dikonfigurasi ulang.

Kelebihan Topologi Dual Ring :
kecepatan
tidak memerlukan terminator
komunikasi jarak jauh
Kekurangan Topologi Dual Ring :
boros kabel
sulit saat pengimplementasian
TOPOLOGI MESH
topologi ini memiliki bentuk seperti jala di mana setiap komputernya terhubung satu sama lain seperti pada gambar.Topologi ini seringkali digunakan untuk jaringan yang berskala tidak terlalu besar tetapi membutuhkan komunikasi antar perangkat yang cepat, mengingat komputer pada topologi ini saling terhubung.

Kelebihan Topologi Mesh :
mudah mendeteksi kesalahan
apabila ada 1 kesalah pada 1 pc maka tidak akan berpengaruh ke pc lain
kecepatan transfer data
Kekurangan Topologi Mesh :
instalasi sulit
biaya mahal
jarang digunakan di kehidupan sehari hari
TOPOLOGI LINIER BUS
Topologi jaringan berjenis linear bus menghubungkan dua atau lebih perangkat komputer pada satu kabel tunggal saja. Topologi bus jenis ini memiliki dua titik akhir di setiap ujung kabelnya seperti pada contoh gambar berikut.

Kelebihan Topologi Linier Bus :
murah
mudah dikembangkan
mudah dirancang
Kekurangan Topologi Linier Bus
transfer data padat
sulit mendeteksi kesalahan
kecepatan akses berpengaruh ke pc lain
TOPOLOGI STAR
Topologi star (topologi bintang) adalah sebuah topologi yang model jaringannya menyerupai bintang dengan server yang berada di tengah sebagai pusatnya, sedangkan perangkat komputer terletak seperti cabang-cabang dari server tersebut.

kelebihan topologi star :
pengoprasian mudah
mudah dikembangkan
dapat menggunakan berbagai jenis kabel
kekurangan topologi star :
butuh banyak kabel
switch/hub butuh banyak perhatian
transfer data yang padat
0 notes
Text
IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, Volume 5, Issue 11, November 2024
1) Energy Scheduling Optimization for Microgrids Based on Partially Observable Markov Game
Author(s): Jiakai Gong, Nuo Yu, Fen Han, Bin Tang, Haolong Wu, Yuan Ge
Pages: 5371 - 5380
2) Intelligent Multigrade Brain Tumor Identification in MRI: A Metaheuristic-Based Uncertain Set Framework
Author(s): Saravanan Alagarsamy, Vishnuvarthanan Govindaraj, A. Shahina, D. Nagarajan
Pages: 5381 - 5391
3) 360° High-Resolution Depth Estimation via Uncertainty-Aware Structural Knowledge Transfer
Author(s): Zidong Cao, Hao Ai, Athanasios V. Vasilakos, Lin Wang
Pages: 5392 - 5402
4) SSpose: Self-Supervised Spatial-Aware Model for Human Pose Estimation
Author(s): Linfang Yu, Zhen Qin, Liqun Xu, Zhiguang Qin, Kim-Kwang Raymond Choo
Pages: 5403 - 5417
5) CrackLens: Automated Sidewalk Crack Detection and Segmentation
Author(s): Chan Young Koh, Mohamed Ali, Abdeltawab Hendawi
Pages: 5418 - 5430
6) Alternating Excitation–Inhibition Dendritic Computing for Classification
Author(s): Jiayi Li, Zhenyu Lei, Zhiming Zhang, Haotian Li, Yuki Todo, Shangce Gao
Pages: 5431 - 5441
7) Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Masses in Mammogram Using 2D-Fourier–Bessel Intrinsic Band Functions and Improved Feature Space
Author(s): Pradeep Kumar Chaudhary, Ram Bilas Pachori
Pages: 5442 - 5451
8) Optimal Trajectory-Based Control of 3-D Dual Rotary Cranes for Payload Dynamic Regulation in Complex Environments
Author(s): Zhuoqing Liu, Tong Yang, Yongchun Fang, Ning Sun
Pages: 5452 - 5464
9) Heterogeneous Hypergraph Embedding for Node Classification in Dynamic Networks
Author(s): Malik Khizar Hayat, Shan Xue, Jia Wu, Jian Yang
Pages: 5465 - 5477
10) Communication-Efficient Federated Learning for Decision Trees
Author(s): Shuo Zhao, Zikun Zhu, Xin Li, Ying-Chi Chen
Pages: 5478 - 5492
11) Solving Orienteering Problems by Hybridizing Evolutionary Algorithm and Deep Reinforcement Learning
Author(s): Rui Wang, Wei Liu, Kaiwen Li, Tao Zhang, Ling Wang, Xin Xu
Pages: 5493 - 5508
12) Tailor-Made Reinforcement Learning Approach With Advanced Noise Optimization for Soft Continuum Robots
Author(s): Jino Jayan, Lal Priya P.S., Hari Kumar R.
Pages: 5509 - 5518
13) Exploring Weight Distributions and Dependence in Neural Networks With α-Stable Distributions
Author(s): Jipeng Li, Xueqiong Yuan, Ercan Engin Kuruoglu
Pages: 5519 - 5529
14) Self-Supervised Exploration via Temporal Inconsistency in Reinforcement Learning
Author(s): Zijian Gao, Kele Xu, Yuanzhao Zhai, Bo Ding, Dawei Feng, Xinjun Mao, Huaimin Wang
Pages: 5530 - 5539
15) Cross-View Masked Model for Self-Supervised Graph Representation Learning
Author(s): Haoran Duan, Beibei Yu, Cheng Xie
Pages: 5540 - 5552
16) Epileptic Seizure Prediction Using Stacked CNN-BiLSTM: A Novel Approach
Author(s): Zeenat Firdosh Quadri, M. Saqib Akhoon, Sajad A. Loan
Pages: 5553 - 5560
17) A Novel Incentive Mechanism for Federated Learning Over Wireless Communications
Author(s): Yong Wang, Yu Zhou, Pei-Qiu Huang
Pages: 5561 - 5574
18) Social NSTransformers: Low-Quality Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
Author(s): Zihan Jiang, Yiqun Ma, Bingyu Shi, Xin Lu, Jian Xing, Nuno Gonçalves, Bo Jin
Pages: 5575 - 5588
19) A Study of Enhancing Federated Learning on Non-IID Data With Server Learning
Author(s): Van Sy Mai, Richard J. La, Tao Zhang
Pages: 5589 - 5604
20) A Reliable Clinical Decision Support System for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Using Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data
Author(s): J. Bhattacharya, A. Gupta, M. N. Dretsch, T. S. Denney, G. Deshpande
Pages: 5605 - 5615
21) CycleGAN*: Collaborative AI Learning With Improved Adversarial Neural Networks for Multimodalities Data
Author(s): Yibo He, Kah Phooi Seng, Li Minn Ang
Pages: 5616 - 5629
22) Evaluating Negative Sampling Approaches for Neural Topic Models
Author(s): Suman Adhya, Avishek Lahiri, Debarshi Kumar Sanyal, Partha Pratim Das
Pages: 5630 - 5642
23) Automated Bundle Branch Block Detection Using Multivariate Fourier–Bessel Series Expansion-Based Empirical Wavelet Transform
Author(s): Sibghatullah Inayatullah Khan, Ram Bilas Pachori
Pages: 5643 - 5654
24) Deep Learning Security Breach by Evolutionary Universal Perturbation Attack (EUPA)
Author(s): Neeraj Gupta, Mahdi Khosravy, Antoine Pasquali, Olaf Witkowski
Pages: 5655 - 5665
25) StackAMP: Stacking-Based Ensemble Classifier for Antimicrobial Peptide Identification
Author(s): Tasmin Karim, Md. Shazzad Hossain Shaon, Md. Mamun Ali, Kawsar Ahmed, Francis M. Bui, Li Chen
Pages: 5666 - 5675
26) Lightweight Parallel Convolutional Neural Network With SVM Classifier for Satellite Imagery Classification
Author(s): Priyanti Paul Tumpa, Md. Saiful Islam
Pages: 5676 - 5688
27) Collision-Free Grasp Detection From Color and Depth Images
Author(s): Dinh-Cuong Hoang, Anh-Nhat Nguyen, Chi-Minh Nguyen, An-Binh Phi, Quang-Tri Duong, Khanh-Duong Tran, Viet-Anh Trinh, Van-Duc Tran, Hai-Nam Pham, Phuc-Quan Ngo, Duy-Quang Vu, Thu-Uyen Nguyen, Van-Duc Vu, Duc-Thanh Tran, Van-Thiep Nguyen
Pages: 5689 - 5698
28) Weighted Concept Factorization Based Incomplete Multi-view Clustering
Author(s): Ghufran Ahmad Khan, Jalaluddin Khan, Taushif Anwar, Zubair Ashraf, Mohammad Hafeez Javed, Bassoma Diallo
Pages: 5699 - 5708
29) Artificial Intelligence Driven Predictive Analysis of Acoustic and Linguistic Behaviors for ASD Identification
Author(s): Ashwini B., Deeptanshu, Sheffali Gulati, Jainendra Shukla
Pages: 5709 - 5719
30) Learning Robust Global-Local Representation From EEG for Neural Epilepsy Detection
Author(s): Xinliang Zhou, Chenyu Liu, Ruizhi Yang, Liangwei Zhang, Liming Zhai, Ziyu Jia, Yang Liu
Pages: 5720 - 5732
31) A Deep Learning-Based Method for Crowd Counting Using Shunting Inhibition Mechanism
Author(s): Fok Hing Chi Tivive, Abdesselam Bouzerdoum, Son Lam Phung, Hoang Thanh Le, Hamza Baali
Pages: 5733 - 5745
32) Online Continual Learning Benefits From Large Number of Task Splits
Author(s): Shilin Zhang, Chenlin Yi
Pages: 5746 - 5759
33) Brain-Inspired Evolutionary Architectures for Spiking Neural Networks
Author(s): Wenxuan Pan, Feifei Zhao, Zhuoya Zhao, Yi Zeng
Pages: 5760 - 5770
34) An Integrated Fusion Framework for Ensemble Learning Leveraging Gradient-Boosting and Fuzzy Rule-Based Models
Author(s): Jinbo Li, Peng Liu, Long Chen, Witold Pedrycz, Weiping Ding
Pages: 5771 - 5785
35) Broad Siamese Network for Facial Beauty Prediction
Author(s): Yikai Li, Tong Zhang, C. L. Philip Chen
Pages: 5786 - 5800
36) Hierarchical Spatial-Temporal Masked Contrast for Skeleton Action Recognition
Author(s): Wenming Cao, Aoyu Zhang, Zhihai He, Yicha Zhang, Xinpeng Yin
Pages: 5801 - 5814
37) An Improved Continuous-Encoding-Based Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm for Community Detection in Complex Networks
Author(s): Jun Fu, Yan Wang
Pages: 5815 - 5827
38) Multiscale Bilateral Attention Fusion Network for Pansharpening
Author(s): Zhongyuan Guo, Jiawei Li, Jia Lei, Jinyuan Liu, Shihua Zhou, Bin Wang, Nikola K. Kasabov
Pages: 5828 - 5843
39) A Hybrid Relational Approach Toward Stock Price Prediction and Profitability
Author(s): Manali Patel, Krupa Jariwala, Chiranjoy Chattopadhyay
Pages: 5844 - 5854
0 notes
Text
IPLOOK Carrier Grade Core Network Solution with High Reliability
Carrier-Grade Reliability Design
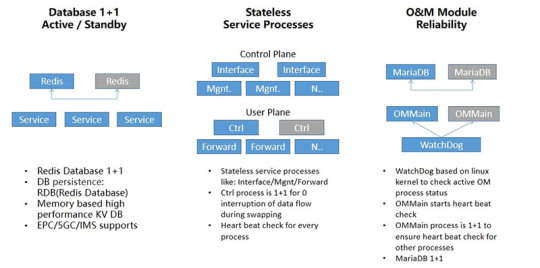
IPLOOK uses open-source database Redis in core network system, it is a memory-based Key-Value database, has great performance, and deployed as an active/standby redundancy mode. All stateful contexts of core network system are stored in this database. Other service processes are stateless such as interface message process, mobility management process, session management process and so on. But for user plane, the session control process is deployed as active/standby mode to ensure ZERO interruption of the data flow during the service swapping procedure, for the backup forwarding table could be immediately in charge of dealing with packets. And for O&M plane, the redundancy enforcements are deployed from the bottom at the Linux kernel, watchdog is here to check the active OM process status, this process is in charge of the heartbeat check with every other process.
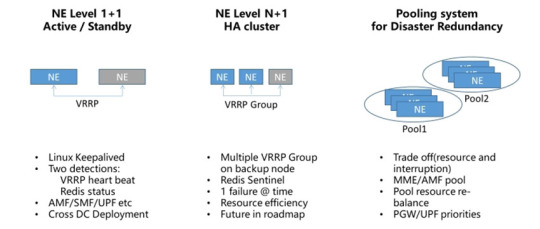
At NE level, IPLOOK provides 1+1, N+1, N+M and pooling redundancy solution for different scenario requirement. 1+1 or N+1 is used for some smaller scale solutions, and N+M are some massive scale deployment scenarios, 3GPP standard pooling system like MME pool, AMF pool, PGW/UPF DNS priorities set is for disaster redundancy.

IPLOOK backup mechanism is hot backup, that means active node and standby node are synchronizing user data (context, state, etc) in real-time, and they could be managed by a single unified O&M, so when the active node fails, the standby could immediately handle current service without any service interruption.
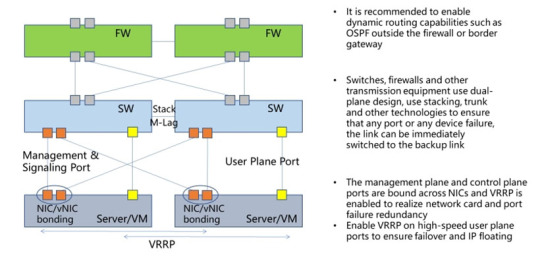
IPLOOK adopts dual plane networking scheme to avoid single point of failure, so from server to EOR/TOR/Firewall, the networking of every service port or IP should have a redundancy link. Contact us for more details!
1 note
·
View note