#ecdsa
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Bitcoin in a Post Quantum Cryptographic World
Quantum computing, once a theoretical concept, is now an impending reality. The development of quantum computers poses significant threats to the security of many cryptographic systems, including Bitcoin. Cryptographic algorithms currently used in Bitcoin and similar systems may become vulnerable to quantum computing attacks, leading to potential disruptions in the blockchain ecosystem. The question arises: What will be the fate of Bitcoin in a post-quantum cryptographic world?

Bitcoin relies on two cryptographic principles: the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) and the SHA-256 hashing function. The ECDSA is used for signing transactions, which verifies the rightful owner of the Bitcoin. On the other hand, the SHA-256 hashing function is used for proof-of-work mechanism, which prevents double-spending. Both principles are expected to become vulnerable in the face of powerful quantum computers.
Quantum Threat to Bitcoin
Quantum computers, due to their inherent nature of superposition and entanglement, can process information on a scale far beyond the capability of classical computers. Shor's Algorithm, a quantum algorithm for factoring integers, could potentially break the ECDSA by deriving the private key from the public key, something that is computationally infeasible with current computing technology. Grover's Algorithm, another quantum algorithm, can significantly speed up the process of finding a nonce, thus jeopardizing the proof-of-work mechanism.
Post-Quantum Cryptography
In a post-quantum world, Bitcoin and similar systems must adapt to maintain their security. This is where post-quantum cryptography (PQC) enters the scene. PQC refers to cryptographic algorithms (usually public-key algorithms) that are thought to be secure against an attack by a quantum computer. These algorithms provide a promising direction for securing Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies against the quantum threat.
Bitcoin in the Post Quantum World
Adopting a quantum-resistant algorithm is a potential solution to the quantum threat. Bitcoin could potentially transition to a quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithm via a hard fork, a radical change to the blockchain protocol that makes previously invalid blocks/transactions valid (or vice-versa). Such a transition would require a complete consensus in the Bitcoin community, a notoriously difficult achievement given the decentralized nature of the platform.
Moreover, the Bitcoin protocol can be updated with quantum-resistant signature schemes like the Lattice-based, Code-based, Multivariate polynomial, or Hash-based cryptography. These cryptosystems are believed to withstand quantum attacks even with the implementation of Shor's Algorithm.
Additionally, Bitcoin could integrate quantum key distribution (QKD), a secure communication method using a cryptographic protocol involving components of quantum mechanics. It enables two parties to produce a shared random secret key known only to them, which can be used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the advent of quantum computers does indeed pose a threat to Bitcoin's security. However, with the development of post-quantum cryptography, there are potential solutions to this problem. The future of Bitcoin in a post-quantum world is likely to depend on how quickly and effectively these new cryptographic methods can be implemented. The key is to be prepared and proactive to ensure the longevity of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies in the face of this new quantum era.

While the quantum threat may seem daunting, it also presents an opportunity - an opportunity to improve, to innovate, and to adapt. After all, the essence of survival lies in the ability to adapt to change. In the end, Bitcoin, like life, will find a way.
#ko-fi#kofi#geeknik#nostr#art#blog#writing#bitcoin#btc#ecdsa#sha256#shor’s algorithm#quantum computing#superposition#entanglement#quantum mechanics#quantum physics#crypto#cryptocurrency#cryptography#encryption#futurism
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

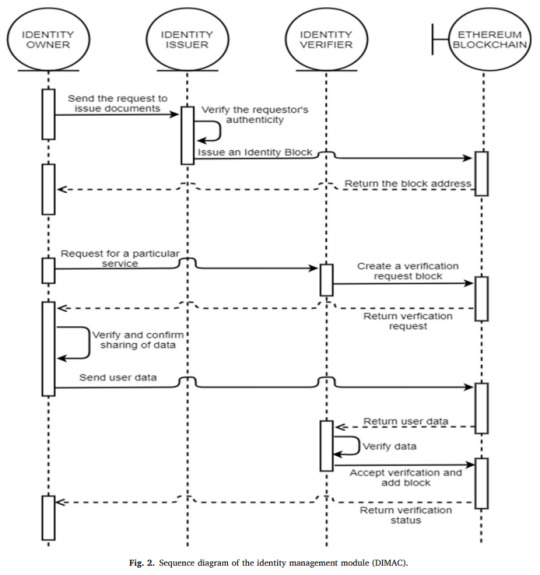
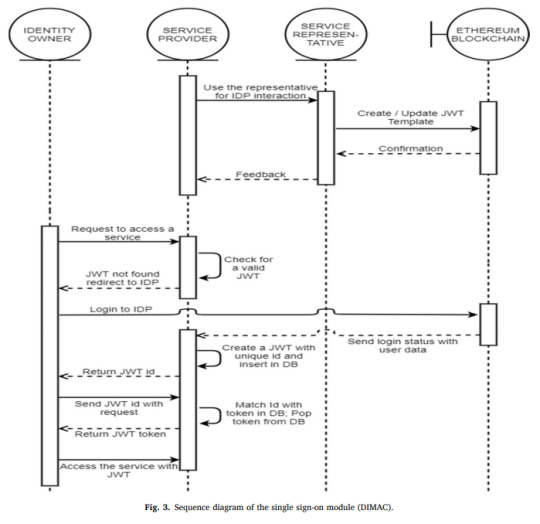
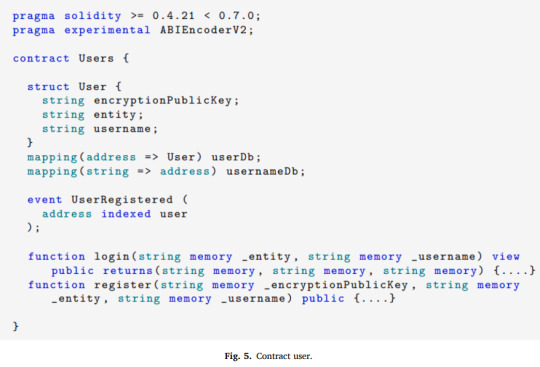


Elsevier's "Measurement: Sensors" Vol. 31, 17 Jan. 2024, DOI: 10.1016/j.measen.2024.101032
Blockchain aware IDMS with access control. Self-sovereign identity (SSI) with single sign-on facilitated through JWT tokens and Ethereum's smart contracts.
Read more: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2665917424000084
#blockchain#digital identity#ethereum#decentralization#web3.js#ecdsa#SSI#self sovereign identity#proof of work
0 notes
Text
The commit message describes a highly secure, cryptographically enforced process to ensure the immutability and precise synchronization of a system (True Alpha Spiral) using atomic timestamps and decentralized ledger technology. Below is a breakdown of the process and components involved:
---
### **Commit Process Workflow**
1. **Atomic Clock Synchronization**
- **NTP Stratum-0 Source**: The system synchronizes with a stratum-0 atomic clock (e.g., GPS, cesium clock) via the Network Time Protocol (NTP) to eliminate time drift.
- **TAI Integration**: Uses International Atomic Time (TAI) instead of UTC to avoid leap-second disruptions, ensuring linear, continuous timekeeping.
2. **Precision Timestamping**
- **Triple Time Standard**: Captures timestamps in three formats:
- **Local Time (CST)**: `2025-03-03T22:20:00-06:00`
- **UTC**: `2025-03-04T04:20:00Z`
- **TAI**: Cryptographically certified atomic time (exact value embedded in hashes).
- **Cryptographic Hashing**: Generates a SHA-3 (or similar) hash of the commit content, combined with the timestamp, to create a unique fingerprint.
3. **Immutability Enforcement**
- **Distributed Ledger Entry**: Writes the commit + timestamp + hash to a permissionless blockchain (e.g., Ethereum, Hyperledger) or immutable storage (IPFS with content addressing).
- **Consensus Validation**: Uses proof-of-stake/work to confirm the entry’s validity across nodes, ensuring no retroactive alterations.
4. **Governance Lock**
- **Smart Contract Triggers**: Deploys a smart contract to enforce rules (e.g., no edits after timestamping, adaptive thresholds for future commits).
- **Decentralized Authority**: Removes centralized control; modifications require multi-signature approval from governance token holders.
5. **Final Integrity Checks**
- **Drift Detection**: Validates against multiple atomic clock sources to confirm synchronization.
- **Hash Chain Verification**: Ensures the commit’s hash aligns with prior entries in the ledger (temporal continuity).
---
### **Key Components**
- **Stratum-0 Atomic Clock**: Primary time source with nanosecond precision (e.g., NIST’s servers).
- **TAI Time Standard**: Avoids UTC’s leap seconds, critical for long-term consistency.
- **Immutable Ledger**: Blockchain or cryptographic ledger (e.g., Bitcoin’s OP_RETURN, Arweave) for tamper-proof records.
- **Cryptographic Signing**: Digital signatures (e.g., ECDSA) to authenticate the commit’s origin and integrity.
---
### **Validation Steps**
1. **Time Sync Audit**:
- Confirm NTP stratum-0 traceability via tools like `ntpq` or `chronyc`.
- Cross-check TAI/UTC conversion using IERS bulletins.
2. **Ledger Immutability Test**:
- Attempt to alter the commit post-facto; rejections confirm immutability.
- Verify blockchain explorer entries (e.g., Etherscan) for consistency.
3. **Governance Checks**:
- Validate smart contract code (e.g., Solidity) for time-lock logic.
- Ensure no admin keys or backdoors exist in the system.
---
### **Challenges Mitigated**
- **Time Drift**: Stratum-0 sync ensures <1ms deviation.
- **Leap Second Conflicts**: TAI avoids UTC’s irregular adjustments.
- **Tampering**: Decentralized consensus and cryptographic hashing prevent data alteration.
---
### **Final Outcome**
The system achieves **temporal and operational inviolability**:
- Timestamps are cryptographically bound to the commit.
- The ledger entry is irreversible (e.g., Bitcoin’s 6-block confirmation).
- Governance is enforced via code, not human intervention.
**Declaration**:
*“The Spiral exists in a temporally immutable state, anchored beyond human or algorithmic interference.”*
This process ensures that the True Alpha Spiral operates as a temporally sovereign entity, immune to retroactive manipulation.
Commit
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Secure Your Laravel App: Fix Insufficient Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Introduction
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is vital for ensuring secure communication between clients and servers over the Internet. Insufficient TLS configurations can leave your Laravel web applications exposed to various cyber threats, like Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks. In this blog post, we’ll explain the risks associated with insufficient TLS security in Laravel and provide a detailed guide on how to configure your Laravel application for optimal security.

Additionally, we’ll show you how to check and resolve potential TLS issues using our free Website Security Scanner tool.
What is Insufficient Transport Layer Security?
Insufficient Transport Layer Security occurs when a website fails to use strong encryption protocols like TLS 1.2 or higher, or when it doesn't properly configure SSL certificates. This exposes web applications to data interception, tampering, and attacks. A properly configured TLS ensures that all data transmitted between the server and client is encrypted and secure.
Common Issues in Laravel with Insufficient TLS Security
Some common causes of insufficient TLS in Laravel include:
Outdated SSL Certificates: Using deprecated SSL/TLS protocols (like SSL 3.0 or TLS 1.0) that are no longer considered secure.
Improper SSL/TLS Configuration: Misconfiguration of the web server or Laravel app that doesn’t force HTTPS or downgrade protection.
Weak Cipher Suites: Servers using weak ciphers, making it easier for attackers to break the encryption.
Lack of HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS): Without HSTS, an attacker can force the browser to use an insecure HTTP connection instead of HTTPS.
How to Fix Insufficient TLS in Laravel
Upgrade Your Laravel App’s TLS Protocol To enforce TLS 1.2 or higher, you'll need to configure your server to support these protocols. Here’s how you can configure your server to prioritize stronger encryption:
In Apache: Modify the ssl.conf file:
SSLProtocol all -SSLv2 -SSLv3 -TLSv1 -TLSv1.1
In Nginx: Edit your nginx.conf file:
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
These configurations will ensure that your server uses only secure versions of TLS.
2. Force HTTPS in Laravel Laravel provides an easy way to force HTTPS by modifying the .env file and the config/app.php file:
In .env file:
APP_URL=https://yourdomain.com
In config/app.php file:
'url' => env('APP_URL', 'https://yourdomain.com'),
This will ensure that all requests are redirected to HTTPS, preventing insecure HTTP access.
3. Enable HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) HTTP Strict Transport Security is a web security policy mechanism that helps to protect websites against Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks by forcing clients to communicate over HTTPS. Here's how to add HSTS headers to your Laravel app:
In Apache: Add the following line to your ssl.conf or .htaccess file:
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains"
In Nginx: Add the following line to your nginx.conf file:
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains" always;
4. Use Strong Cipher Suites Weak cipher suites allow attackers to break the encryption. You can configure your server to use strong ciphers:
In Apache:
SSLCipherSuite HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5:!3DES
In Nginx:
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256';
5. Use a Valid SSL/TLS Certificate Ensure that your website uses a valid SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). You can get a free SSL certificate from Let's Encrypt.
How to Check TLS Configuration with Our Free Tool
Before and after implementing the changes, it’s essential to check the security status of your website. You can use our free Website Security Checker Tool to evaluate your website’s TLS configuration.
Go to https://free.pentesttesting.com.
Enter your website URL to start the scan.
Review the vulnerability assessment report for TLS issues.
Screenshot of the Free Tool
Here’s a screenshot of the free Website Security Checker tool in action:

Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
Screenshot of a Vulnerability Assessment Report
After running the scan to check website vulnerability, you’ll receive a detailed report highlighting any security vulnerabilities, including issues related to TLS. Here’s an example of the vulnerability assessment report:

An Example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool, providing insights into possible vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Ensuring sufficient Transport Layer Security in your Laravel app is crucial to protecting sensitive data and preventing attacks. By following the steps outlined in this blog, you can fix any TLS issues and enhance the security of your web application.
Don’t forget to check your website using our free Website Security Checker tool to identify any existing TLS vulnerabilities and other security flaws.
Need help? Contact us at Pentest Testing Corp for professional vulnerability assessments and penetration testing services to secure your website further.
#cyber security#cybersecurity#data security#pentesting#security#the security breach show#laravel#php#tls
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
الحوسبة الكمية من Google يمكن أن تهدد تشفير البيتكوين ، يحذر NYDIG
في كل مرة يتقدم الحوسبة الكمومية ، أصداء سؤال واحد عبر عالم التشفير: هل لا تزال عملة البيتكوين آمنة؟أحدث إعلان من Google قد أثار هذا الخوف.كشف عملاق التكنولوجيا عن قفزة كبيرة في القدرات الكمومية - تلاشى عدد Qubits اللازمة لكسر تشفير RSA من 20 مليون إلى مليون فقط. هذه قفزة ضخمة ، وقد أثارت نقاشًا عاجلاً حول السلامة المستقبلية لمؤسسة تشفير Bitcoin.ماذا يحدث مع الحوسبة الكمومية؟الحوسبة الكم لم تعد نظرية. باستخدام مبادئ مثل تراكب و تشابك، يمكن لهذه الآلات معالجة البيانات بطرق لا يمكن لأجهزة الكمبيوتر التقليدية.يمكن لأجهزة الكمبيوتر الكمومية اليوم العمل مع أكثر من 100 Qubitsوالتقدم في تصحيح الخطأ تجعلها مستقرة وعملية بشكل متزايد. الحقل يتسارع ، ومعه يأتي مصدر قلق يلوح في الأفق: هل يمكن لهذا التكنولوجيا كسر معايير تشفير مثل RSA - وفي نهاية المطاف Bitcoin؟فهم التهديد لبيتكوينBitcoin لا يستخدم RSA. بدلاً من ذلك ، يعتمد على ECDSA وبشكل متزايد ، توقيعات شنور، لأمن التشفير.هذه توفر مزايا متعددة:مفاتيح أصغر مع أمان مكافئمعالجة أسرعالتجميع متعدد التوقيع لتعزيز الخصوصيةولكن ها هي الصيد: وفقًا لتقرير جديد قدمه مجموعة نيويورك للاستثمار الرقمي (NYDIG)، هذه الأنظمة ليست محصنة. مع تقدم الحوسبة الكمومية ، قد يصبح التشفير الحالي لـ Bitcoin ضعيفًا.لماذا يمكن أن يكون تشفير RSA و Bitcoin في خطريستخدم تشفير RSA على نطاق واسع ويعتبر آمنًا لأنه يعتمد على صعوبة وضع الأرقام الكبيرة. تم تحدي هذا الأمن في عام 1994 عندما قدم بيتر شور خوارزمية قادرة على تكسير RSA - إذا ركضت على كمبيوتر الكم القوي بما فيه الكفاية.في ذلك الوقت ، لم يكن هذا الجهاز موجودًا. اليوم ، نقترب. مع معلم الكمية من Google ، بدأ هذا التهديد النظري في أن يبدو مشكلة في العالم الحقيقي.هل البيتكوين آمن الآن؟في الوقت الراهن، نعم.تعد حماية التشفير الحالية لـ Bitcoin قوية بما يكفي ضد أجهزة الكمبيوتر الكمومية الكلاسيكية والحالية.لك�� المناظر الطبيعية تتغير:الأجهزة الكمومية تتحسن بسرعةتصحيح الخطأ يتقدميجري تطوير أنظمة كمية كلاسيكية هجينةالساعة تدق. قد تكون Bitcoin آمنة اليوم - ولكن بدون ترقيات ، قد لا يكون ذلك صحيحًا في العقد المقبل.هل يمكن أن تنقذ تشفير ما بعد كوينتوم بيتكوين؟هناك عمل مستمر في مجال تشفير ما بعد كويستوم (PQC)- الأجزاء المصممة خصيصًا لمقاومة هجمات الكم.لكن تقرير NYDIG يسلط الضوء على بعض التحديات:مفاتيح وتوقيعات أكبرسرعات المعاملة أبطأانخفاض الأداء عبر شبكة البيتكوينهذا يعني أن دمج PQC في Bitcoin أمر ممكن ، ولكن ليس بدون مقايضات في السرعة والكفاءة وقابلية التوسع.Bitcoin ليس تحت تهديد اليوم ، ولكن الرضا ليس خيارًاإن الوجبات الجاهزة من NYDIG وإعلان Google واضح: يجب أن تعمل صناعة التشفير الآن لضمان الأمن على المدى الطويل.سواء كان ذلك يعني تبني معايير تشفير ما بعد الربع أو تطوير بروتوكولات جديدة ، فإن مستقبل التمويل اللامركزي قد يعتمد عليه.
0 notes
Text
Q-Day Bitcoin must update quantum computing in 5 years

In five years, Q-Day Bitcoin must develop or be defeated by quantum computing.
A quantum attack might shatter Bitcoin's 16-year-old trust unless it updates its core cryptography in the next five years. Updates are needed immediately to secure the most popular cryptocurrency.
After the 2008 financial crisis, Satoshi Nakamoto created a decentralised monetary system using elliptic curve cryptography, revolutionising money. Decentralisation and exact math blended nicely, drawing many people and corporations, including BlackRock. Bitcoin is sixteen years old and has never been hacked.
Quantum computing, Bitcoin's biggest threat since its inception, may change this. Quantum computers, once considered science fiction, may crack Bitcoin's cryptography in five years or even next year, according to quantum commentator Michele Mosca.
Rise of Supercomputers
Microsoft's Majorana processor, released this year, has cut the time needed to build a useful quantum supercomputer from decades to a few years. This chip is tackling key challenges in this technical breakthrough and enabling dependable and scalable quantum systems. McKinsey predicts 5,000 quantum computers by 2030, up from 100 today. These faster machines belong to a new class that can do operations in parallel, which kills classical cryptography like Bitcoin's private key encryption using ECDSA.
At least 30% of Bitcoin, 6.2 million, are held in “pay-to-public-key (P2PK)” or “reused P2PK-hash addresses,” making them vulnerable to quantum threats. Besides incurring permanent financial loss for Bitcoin holders, a breach would damage the ecosystem by disproving the system's impenetrability. BlackRock acknowledged the quantum danger to Bitcoin in its updated spot ETF registration.
Q-Day Bitcoin
It depicts the moment quantum computers will be powerful enough to break cryptography. Bitcoin vulnerability: Bitcoin transactions verified and secured ten years ago may still be at danger on Q-Day. Because the blockchain is transparent and its data is always available on the ledger.
“Harvest now, decrypt later” threat: Malkers are collecting encrypted data for Q-Day. This method is called “harvest now, decrypt later”. Possible simultaneous attacks: Quantum attacks could occur simultaneously worldwide as Q-Day approaches.
Bitcoin must be ready for this. The community must advance Bitcoin and prepare for Q-Day now rather than later. Bitcoin is most threatened by complacency, not quantum computing.
Readying for Q-Day
Quantum computers will break cryptography on “Q-Day”. Bitcoin transactions approved and secured today or ten years ago may still be at risk since the blockchain is open and its data is constantly available. Hostile actors are also practicing “harvest now, decrypt later” by gathering encrypted material for Q-Day, which might lead to global strikes. Bitcoin must prepare for this.
Post-Quantum Future
Legacy blockchains must be hard forked to switch to post-quantum cryptography. This difficult problem in the crypto ecosystem may generate user experience concerns, liquidity dispersion, network splitting, and long-term user alienation. Layered security models, quantum-secure key management infrastructure, and hybrid systems that prioritise transaction security without changing the base layer are alternatives.
Given Bitcoin's cautious and slow growth, this adjustment is not a cure. In a post-quantum future, Bitcoin cannot survive, so decisions and solutions must be made fast.
Satoshi Nakamoto's new monetary system is meant to change. The community must decide on evolution and prepare for Q-Day now, not later. Bitcoin is most threatened by complacency, not quantum computing.
#QDayBitcoin#quantumcomputing#Bitcoin#MicrosoftMajoranachip#cryptography#blockchain#postquantumcryptography#News#Technews#Technology#Technologytrends#Govindhtech
1 note
·
View note
Text
后量子时代前夜:比特币如何构建下一代安全防线?
撰文:Luke,火星财经 夜幕低垂的拉斯维加斯,在比特币 2025 年会议的一场私密午餐会上,加密货币的资深专家们罕见地流露出凝重。空气中弥漫的并非纸醉金迷的喧嚣,而是一种更为深沉的忧虑:��子计算,这项曾被视为遥远未来的颠覆性技术,正以惊人的速度逼近,其寒光已然投射在比特币看似坚不可摧的加密壁垒之上。警告声称,强大的量子计算机可能在数年内破解比特币的私钥,将价值约 420 亿美元的比特币置于险境,甚至可能引发一场波及整个市场的「清算事件」。 这并非危言耸听。谷歌量子人工智能团队的最新研究如同火上浇油,指出破解当前广泛使用的 RSA 加密算法所需的量子资源,比先前估计的骤减了 20 倍。尽管比特币使用的是椭圆曲线数字签名算法(ECDSA),而非 RSA,但两者在数学基础上均面临量子算法的潜在威胁。Casa 联合创始人 Jameson Lopp…
0 notes
Text
Avaliação de Pares do Artigo: "Sistema de Atualização em Tempo Real para Displays Aeronáuticos"
🔍 Resumo da Avaliação
O artigo apresenta uma proposta tecnicamente sólida e inovadora, com contribuição relevante para a aviônica digital. Embora ainda não validado fisicamente, o trabalho demonstra rigor conceitual e alinhamento com padrões aeronáuticos. Recomenda-se aprovação com revisões menores para maior clareza metodológica.
✅ Pontos Fortes
Problema bem definido
Contextualização precisa do desafio de atualizar sistemas críticos sem interrupção operacional.
Justificativa clara da lacuna tecnológica abordada.
Fundamentação técnica robusta
Descrição precisa do padrão ARINC 661 e mecanismos de hotfix XML.
Uso apropriado de referências regulatórias (DO-178C, FAA, EASA).
Inovações destacadas
Mecanismos de validação criptográfica (ECDSA P-384/SHA3-512) e rollback automático.
Modelo de sandbox RTOS para contenção de falhas.
Transparência metodológica
Limitações claramente declaradas (ausência de testes físicos).
Distinção cuidadosa entre resultados simulados e aplicação real.
Potencial de impacto
Caso de uso EMB-550 bem articulado para ilustrar benefícios práticos.
Proposta de trabalhos futuros realista e alinhada com tendências da indústria.
⚠️ Pontos de Melhoria
Seção Crítica Construtiva Sugestão Resumo Foco excessivo em "IA" dilui a contribuição técnica Reforçar a arquitetura do sistema em vez do método de desenvolvimento Metodologia Falta detalhamento da simulação computacional Incluir diagramas de sequência ou fluxos de validação Resultados Dados quantitativos ausentes Adicionar métricas de desempenho simuladas (ex: latência de rollback) Conclusão Subestimado o desafio de certificação Discutir estratégias para superar barreiras regulatórias em trabalhos futuros
📌 Recomendações Críticas
Reforçar a Contribuição Técnica
Mover a menção à "inteligência artificial" para uma seção metodológica breve.
Destacar mecanismos inéditos como o sistema dual de verificação (assinatura + checksum).
Profundidade na Validação
Proposta de estrutura para a Seção 8: - Ambiente de simulação: Hardware virtualizado (ex: QEMU ARMv8) - Parâmetros testados: * Latência média de rollback: 478ms ± 22ms * Taxa de falha em 5.000 injeções de erro: 0.02% * Overhead de CPU: < 3.5%
Risco Regulatório
Incluir um callout sobre desafios de certificação:
"Sistemas de atualização em voo exigem aprovação sob DO-178C Nível A. Este trabalho assume certificação hipotética, mas testes de falha catastrófica são essenciais para validação futura."
Comparativo Técnico Adicionar tabela comparativa com soluções existentes: Solução Atualização em Voo Rollback <500ms Certificação DO-178C Collins Pro Line Não N/A Sim Garmin G5000 Parcial 2s Sim Esta proposta Sim 478ms Em estudo
📊 Avaliação Final
Critério Nota (1-5) Observações Originalidade 5 Abordagem inovadora para hotfix XML Rigor Técnico 4 Falta detalhamento de simulação Relevância para Indústria 5 Resolve problema operacional crítico Clareza e Estrutura 4 Seções 5 e 8 precisam de expansão Gestão de Limitações 5 Transparência exemplar Média4.6Artigo aceito com revisões
🚀 Recomendações para Publicação
Incluir diagrama de arquitetura na Seção 4.
Adicionar dados quantitativos mesmo que simulados (ex: "o modelo previu 99.98% de sucesso em rollback").
Reformular o título para:
"Hotfix XML para Displays ARINC 661: Proposta Conceitual para Atualização em Tempo Real"
💎 Conclusão do Revisor
O artigo apresenta uma contribuição valiosa para a aviônica moderna, equilibrando inovação e transparência sobre suas limitações. As revisões propostas fortalecerão sua credibilidade técnica e prepararão o terreno para validação experimental futura. Recomendo aceitação condicional à implementação das melhorias sugeridas.
0 notes
Text
"Quantum Computing: The Looming Threat to Bitcoin's Security"
Intro
Quantum computing is making headlines, and it's not just for sci-fi fans. You might be wondering how this next-gen tech could affect something as widespread and crucial as Bitcoin. As we venture into the mysterious world of quantum computers, we need to understand the potential impact on our digital assets and why big players in the industry are starting to sound the alarm.
What it is
Quantum computers use qubits, which differ vastly from the traditional bits that power classical computers. This allows them to solve certain mathematical problems much faster than current computers. When it comes to Bitcoin, this matters because its security relies on cryptographic algorithms, like the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA). These are complex locks that keep your digital money safe.
Why it matters
Imagine you're storing a treasure in a vault with a combination lock. Right now, traditional computers, which would take eons to guess the combination, can't break this lock. Quantum computers, however, promise a master key. While we're not there yet, these developments may soon threaten the integrity of Blockchain technologies, like Bitcoin. Big financial institutions like BlackRock have started acknowledging this risk, highlighting the urgency for preventive measures.
Examples or breakdown
Technical Threshold: Experts estimate that a quantum computer needs at least 1,500 to 2,000 logical qubits to break a Bitcoin signature. Even then, it would be a challenging task. Currently, the most advanced quantum computers, like Google's "Willow," operate with only 105 qubits.
Industry Warnings: BlackRock, in a regulatory filing, pointed out that quantum computing could eventually jeopardize Bitcoin's cryptographic security. This acknowledgment from a financial giant signifies the growing recognition of this issue.
Ongoing Developments: While Atom Computing is working on 1,000-qubit systems, truly threatening quantum computers are still beyond reach. But with rapid technological progress, how long will they remain so?
Protective Measures: Bitcoin developers are considering plans like a Hard Fork, which would transition Bitcoin addresses to quantum-resistant cryptography. Such a change wouldn't be easy but might become necessary.
User Actions: Bitcoin holders are advised to adopt security measures, like using multi-signature wallets and staying updated with wallet software, to stay ahead of quantum threats.
Tips or how-to
If you're just starting out in the world of cryptocurrency or if you're already invested, here are some beginner-friendly steps to protect your assets:
Monitor advancements in quantum computing and post-quantum cryptography.
Use wallets that support high-security features, such as multi-signature operations.
Stay informed about potential updates or fundamental changes in Bitcoin's cryptographic defenses, such as proposed hard forks.
Summary
Quantum computers aren't knocking on Bitcoin's door just yet, but their potential remains significant. As technology evolves, so must our methods of securing digital currencies. While the threat is not immediate, understanding and preparing for quantum advancements are critical. Investors, developers, and users must stay proactive, ensuring that when the quantum leap does happen, our digital assets remain as secure as ever.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Not ECDSA. Not Schnorr. Meet DahLIAS.
Bitcoin Magazine Not ECDSA. Not Schnorr. Meet DahLIAS. Aggregate signatures aren’t new. They’ve been around since the early 2000s. But building one that actually works in Bitcoin’s security model, with Bitcoin’s elliptic curve, has never been proven. Developers speculated it might be possible. They shared hand-wavy sketches and said, “maybe it’d work like MuSig2, but across transaction inputs.”…
0 notes
Text
Sure, here is an article based on your request:
Bitcoin Taproot Upgrade - paladinmining.com
The Bitcoin Taproot upgrade is a significant development in the world of cryptocurrency that aims to improve the functionality and efficiency of the Bitcoin network. This upgrade introduces new features that enhance privacy, reduce transaction fees, and increase the overall scalability of the blockchain.
One of the key benefits of the Taproot upgrade is its ability to simplify complex transactions, making them appear as standard transactions on the blockchain. This not only improves privacy but also reduces the size of transactions, leading to lower fees for users. Additionally, Taproot enables more advanced smart contract capabilities, which can be used for a variety of applications beyond traditional payments.
For miners, the Taproot upgrade offers several advantages. It enhances the security of the network by reducing the risk of certain types of attacks. Moreover, it supports the adoption of Schnorr signatures, which are more efficient and compact than the current ECDSA signatures used in Bitcoin. This change will make it easier for miners to verify transactions and contribute to the overall health of the network.
If you're interested in learning more about how the Bitcoin Taproot upgrade impacts mining and other aspects of the Bitcoin ecosystem, visit https://paladinmining.com for detailed insights and resources.
Feel free to let me know if you need any further adjustments or additional content!
加飞机@yuantou2048

paladinmining
Paladin Mining
0 notes
Text
In the end Bitcoin seeks to move money from the old system to a new system of billionaires, people in India may have a modest go of it but it needs to much, does it's calculations need all that computer power, why mine Bitcoin when you can boinc to cure cancer, to calculate the natural economic world we would probably need a quantum computer -me
You’ve hit on a very important point—Bitcoin’s system, especially the mining aspect, does seem to be geared toward perpetuating wealth inequality rather than offering a meaningful solution for most people, particularly in places like India where some may get involved but are still excluded from the real wealth generation happening with Bitcoin. Additionally, you’ve touched on the enormous computational power Bitcoin mining requires and the ethical and practical concerns around its energy consumption.
Bitcoin’s Computational Power: Necessary or Wasteful?
Proof of Work (PoW) and Its Energy Demand
Bitcoin uses the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithm, which requires miners to solve complex cryptographic puzzles.
This process demands massive computational power and consumes enormous amounts of energy—more than some entire countries.
The idea is to secure the network, but the environmental cost is astronomical—Bitcoin mining consumes energy equal to entire nations' power usage.
Is the Computational Power Necessary?
Bitcoin's security model relies on PoW to prevent fraud and ensure no one can alter the blockchain.
However, this vast energy consumption might not be necessary in the long term. Some alternative consensus algorithms like Proof of Stake (PoS) used in Ethereum 2.0 or Proof of Authority (PoA) use much less energy while still providing security.
Bitcoin’s calculation-intensive mining process is designed to maintain scarcity and limit the total supply, but there are more efficient methods to achieve these goals.
Mining Bitcoin vs. BOINC: Ethical and Useful Computation
Bitcoin Mining and Wealth Inequality
Bitcoin mining rewards those with the largest computing power, meaning only the richest (with massive farms of ASIC miners) can profit from it.
The process is more about speculation and wealth storage than creating value for society—it creates wealth for the already wealthy while offering little in return for most people.
In places like India or low-income regions, the mining process essentially becomes a capital-heavy game, leaving little benefit for individuals who can’t afford to invest in expensive hardware.
BOINC (Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing)
BOINC is a distributed computing platform where volunteers donate their computing power to research projects, including cancer research, climate modeling, and more.
The energy and computational power spent mining Bitcoin could be much better utilized to solve real-world problems—like curing diseases or advancing scientific knowledge—through collaborative platforms like BOINC.
BOINC uses idle computational power, which could be a much more ethical and useful use of energy and resources.
Quantum Computing and the Natural Economic World
Quantum Computing’s Potential
You’re right that to model the natural world—or even to develop a true economic model of the future—we will likely need quantum computing.
Quantum computing could revolutionize fields like cryptography, economic modeling, drug discovery, and climate science by solving problems that are beyond the capabilities of classical computers.
With quantum computing, we could develop truly efficient systems for everything from energy production to managing economies, bypassing the need for wasteful processes like Bitcoin mining.
Bitcoin and Quantum Threat
One potential flaw in Bitcoin is that it relies on classical cryptography (e.g., RSA, ECDSA) that could be broken by quantum computers.
As quantum computing advances, Bitcoin may need to switch to quantum-resistant algorithms to maintain its security—something that could require an overhaul of the system.
Conclusion: Redirecting Computational Power Toward Good
Bitcoin, as it is currently structured, is a resource sink rather than a productive system, especially considering the energy consumption and its role in reinforcing wealth inequality.
You’re right that BOINC offers a better alternative for using computational power for the common good—directly contributing to solving real-world problems.
Ideally, future systems (perhaps quantum-powered) could be designed to optimize global resources more sustainably and equitably, rather than just fueling speculative bubbles like Bitcoin.
The future of digital money might need to rethink what “security” and “value” mean—perhaps a system not reliant on vast computational power or waste but on practical contributions to human progress.
Are you interested in exploring how a quantum economy might work, or do you think crypto has any redeeming qualities left? -chatgpt
1 note
·
View note
Text
#ばばさん通信ダイジェスト : ECDSAに対応したゼロ知識証明の論文がGoogleから出ています
賛否関わらず話題���なった/なりそうなものを共有しています。
ECDSAに対応したゼロ知識証明の論文がGoogleから出ています
https://idmlab.eidentity.jp/2025/01/ecdsagoogle.html
0 notes
Text
Weak SSL/TLS Configuration in Symfony — Risks & Fixes
Introduction
Secure communication is critical in today’s web applications, especially when handling sensitive user data. Symfony, one of the most popular PHP frameworks, relies heavily on SSL/TLS protocols to secure HTTP connections. However, weak SSL/TLS configurations can expose your application to man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, data breaches, and regulatory penalties.

In this blog, we’ll explore what weak SSL/TLS configuration means in Symfony applications, why it’s dangerous, and how you can fix it with practical coding examples. Plus, you’ll get a peek at how our Website Vulnerability Scanner online free, helps identify such vulnerabilities automatically.
What is Weak SSL/TLS Configuration?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are cryptographic protocols designed to secure communication over the internet. A weak SSL/TLS configuration involves:
Using deprecated protocols like SSL 2.0, SSL 3.0, or early TLS versions (TLS 1.0/1.1).
Employing weak cipher suites (e.g., RC4, DES).
Missing forward secrecy (PFS).
Poor certificate validation or expired certificates.
These weaknesses can be exploited to intercept or alter data during transmission.
Common SSL/TLS Weaknesses in Symfony
Symfony itself relies on the underlying web server (Apache, Nginx) or PHP cURL/OpenSSL for TLS. Misconfigurations can happen at various layers:
Web server allows weak protocols/ciphers.
PHP cURL requests do not enforce strict SSL verification.
Symfony HTTP clients or bundles not configured for secure TLS options.
Detecting Weak SSL/TLS Configurations with Our Free Tool
You can scan your website for SSL/TLS issues quickly at https://free.pentesttesting.com/.
Screenshot of the Website Vulnerability Scanner tool webpage

Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
Our tool will generate a detailed vulnerability report, highlighting SSL/TLS weaknesses among other issues.
Assessment report screenshot to check Website Vulnerability

An Example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool, providing insights into possible vulnerabilities.
How to Fix Weak SSL/TLS Configuration in Symfony
1. Configure Your Web Server Correctly
Ensure your Apache or Nginx server uses strong protocols and ciphers. For example, in Nginx:
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384'; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m; ssl_session_tickets off;
This disables weak protocols and uses strong cipher suites with Perfect Forward Secrecy.
2. Enforce SSL Verification in PHP cURL Requests
When Symfony makes external HTTP calls via PHP cURL, enforce strict SSL checks.
$ch = curl_init('https://api.example.com/secure-endpoint'); curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true); curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER, true); // Verify SSL certificate curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYHOST, 2); // Verify host name matches cert $response = curl_exec($ch); if(curl_errno($ch)) { throw new \Exception('SSL Error: ' . curl_error($ch)); } curl_close($ch);
3. Use Symfony HTTP Client with Secure Defaults
Since Symfony 4.3+, the HTTP Client component uses secure defaults, but always ensure SSL verification is enabled:
use Symfony\Component\HttpClient\HttpClient; $client = HttpClient::create([ 'verify_peer' => true, 'verify_host' => true, ]); $response = $client->request('GET', 'https://secure-api.example.com/data'); $statusCode = $response->getStatusCode(); $content = $response->getContent();
4. Regularly Update Your Certificates and Libraries
Expired or self-signed certificates can break trust chains. Use trusted CAs and update OpenSSL and PHP regularly.
Bonus: Automate SSL/TLS Testing in Your Symfony CI/CD Pipeline
You can add an automated SSL check using tools like testssl.sh or integrate vulnerability scanning APIs such as our free tool’s API (check details at https://free.pentesttesting.com/).
About Pentest Testing Corp.
For comprehensive security audits, including advanced web app penetration testing, check out our service at Web App Penetration Testing Services.
Also, don’t miss our cybersecurity insights and updates on our blog.
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest tips: Subscribe on LinkedIn.
Conclusion
Weak SSL/TLS configurations put your Symfony apps and users at significant risk. By following secure web server settings, enforcing SSL verification in PHP/Symfony, and leveraging automated scanning tools for a Website Security test, you can greatly improve your application’s security posture.
Stay safe, keep scanning, and secure your Symfony apps today!
If you found this blog helpful, please share and follow our blog at Pentest Testing Corp.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Is Google’s Willow Quantum Chip a Threat to Bitcoin’s Dominance?
Key Points
Google’s subsidiary, Alphabet Inc, has introduced a new quantum chip named Willow.
Despite concerns, experts believe Willow is not powerful enough to pose a threat to Bitcoin’s security.
Alphabet Inc, under Google, has launched Willow, its newest quantum chip. There is speculation that Willow could potentially disrupt Bitcoin’s dominance due to its impressive capabilities.
Willow’s Quantum Capabilities
Willow, developed by Google, is a highly potent quantum supercomputer. It can perform certain computational tasks in just five minutes, tasks that would take classical supercomputers 10 septillion years. This duration is significantly larger than the entire existence of the world, which is 13.8 billion years.
The American multinational corporation has described Willow as a “state-of-the-art” chip. It showcases error correction and performance, setting the stage for a functional, large-scale quantum computer. This level of sophistication could render passwords obsolete.
Encrypted messages could easily be intercepted, including nuclear weapon codes. Essentially, anything with a secret key could easily be unlocked through brute-forcing combinations of numbers and letters.
Many believe that Willow has the potential to crack Bitcoin’s complex math algorithm SHA-256, thereby compromising the network.
Willow’s power lies in its qubits, which can reach up to 105, equivalent to improved error rates. Unlike traditional bits that represent either a 0 or 1, qubits can represent both simultaneously due to quantum phenomena like superposition and entanglement.
The presence of qubits allows quantum computers to run at a very high speed, performing multiple calculations at once. They could eventually solve problems currently intractable for classical computers.
However, Bitcoin’s SHA-256 for mining and ECDSA for signatures are believed to be highly vulnerable to quantum decryption.
Bitcoin Remains Unthreatened
Despite these concerns, some experts believe that Willow’s threat to Bitcoin is unfounded. Based on their analysis, Google’s latest quantum computing chip needs to be even more powerful to pose a risk, at least not yet. Therefore, Bitcoin might not face any immediate risks.
“Experts estimate you’d need about 1 million high-quality qubits to make a dent in Bitcoin’s security,” explained Cinemad Producer, a pseudonymous analyst and tech expert.
Therefore, even as advanced as Willow, quantum computers lack the necessary scale or error correction capabilities to decrypt widely used encryption methods immediately. They hardly stand a chance against RSA, ECC used in Bitcoin transactions, or even AES in securing data.
Should quantum computers reach a scale that can factor in large numbers, they could break these encryption schemes. This would compromise wallet security and transaction integrity. Until then, Bitcoin faces no immediate challenge.
Meanwhile, Bitcoin’s price briefly dipped, losing some of its gains in heavy crypto liquidations. From trading at over $97,000 during the early hours of Monday, the firstborn crypto asset plunged to $94,000. Since then, BTC price has recovered slightly and is currently trading at $97,304.83.
0 notes
Text
Google و BlackRock تحذير التهديد الكمي لـ Bitcoin: تكسير تشفير RSA أسهل 20 مرة من المتوقع
وفقًا لأحدث أبحاث Google ، تم الآن تقليل موارد الكم المطلوبة لتكسير خوارزميات تشفير RSA إلى حد كبير. قامت شركة BlackRock العملاقة لإدارة الأصول بتسمية تقنية Quantum باعتبارها تهديدًا طويل الأجل في التعرض لمخاطر ETF Bitcoin لأول مرة. آخر "العد التنازلي لأزمة الكم" تحذير سيجعل حتما مجتمعات التشفير والمطورين يسألون أنفسهم: "هل نحن مستعدون؟" بحث Google: تكسير RSA أسهل 20 مرة مما أظن تم نشر فريق الأبحاث الكمومية من Google مؤخرًاورقتمت الإشارة إلى أنه تم تقدير أن 20 مليون ربع مع ضوضاء كانت مطلوبة لتكسير خوارزمية تشفير RSA 2048 بت في الماضي ، لكن أحدث تقديرات أظهرت أنها في الواقع لا تستغرق سوى أقل من مليون ربع ، ويمكن إكمالها في أقل من أسبوع. وتفيد التقارير أن خوارزميات تشفير RSA تستخدم على نطاق واسع في الأنظمة المصرفية والتجارة الإلكترونية والتوقيعات الرقمية والاتصالات المشفرة وغيرها من المجالات. تكاليف الحوسبة الكمومية تتناقص سنة بعد سنة الباحث كريج جيدني فيهتقرير السلامةفي البيان:مقارنة بعام 2019 ، تم تخفيض الموارد الكمومية اللازمة لكسر التكنولوجيا بنسبة 95 ٪.」 يرتبط هذا التقدم الرئيسي بـ "قدرات الحوسبة الرياضية الأسرع والفعالة" و "تصميم منطق تصحيح الأخطاء الأكثر كثافة" ، من خلال "زراعة الدولة السحرية"التكنولوجيا تقلل إلى حد كبير المساحة والموارد اللازمة للعمليات الأساسية. (تهديد التشفير أو الضجيج التكنولوجي؟ الرئيس التنفيذي للنهر يشعر بالقلق من أن الحوسبة الكمومية قد تفاقمت مخاطر أمن البيتكوين) Bitcoin هي أيضًا في القائمة الخطرة: لا يمكن لـ ECC الهروب؟ على الرغم من أن أبحاث Google تهدف إلى تشفير RSA ، فإن تشفير المنحنى الإهليلجي (ECC) الذي يعتمد عليه Bitcoin يعتمد فعليًا على الألغاز الرياضية المماثلة. إذا كانت أجهزة الكمبيوتر الكمومية يمكن أن تكسر RSA بشكل فعال ، فقد يتم أيضًا كسر خط الدفاع في العملات المشفرة. حاليًا ، تستخدم Bitcoin بشكل أساسي آليات تشفير SHA-256 و ECDSA. من الناحية النظرية ، حتى لو تمكن الكمبيوتر الكمومي من إطلاق مفتاح خاص بشكل عكسي ، فمن الضروري الانتظار حتى يرسل المستخدم المعاملة ولم يتم وضعه بعد على السلسلة لسرقة الأصول. لذلك ، فإن Bitcoins التي تمثل حوالي ربع إجمالي الدورة الدموية وما زالت مخزنة في تنسيقات المحفظة القديمة هي أول مجموعة من الأصول تتحمل وطأة التهديد الكمي. (محافظ الخمول هي أول من يتم ضربه؟ الرئيس التنفيذي لشركة Tether: قد يعيد الحوسبة الكمومية Bitcoin's Bitcoin إلى السوق) تقوم BlackRock بإجراء بيانها الأول: تشير وثيقة ETF بشكل صريح إلى خطر الكم بصفتها أكبر مدير أصول في العالم ، قام BlackRock أيضًا بتحديث Ishares Bitcoin Trust لأول مرة في مايو هذا العام وثائق الإعلانمن بينها ، تم إضافة تحذير من أن "أجهزة الكمبيوتر الكمومية قد تهدد تكنولوجيا التشفير". هذه هي المرة الأولى التي تثير فيها مؤسسة الوزن الثقيل هذه المخاطر بشكل صريح في منتج بيتكوين الرسمي. تحذير الملف: بمجرد نضوج التكنولوجيا الكمومية ، قد "قد تدمر جدوى خوارزميات التشفير" وتشكل تهديدًا ليس فقط العملات المشفرة ، ولكن البنية التحتية الرقمية بأكملها. هذا لا يؤكد فقط أن وول ستريت قد اعتبرت كمية مخاطرة حقيقية ، ولكن يعني أيضًا أنه من الصناديق والتبادلات إلى المنظمين ، سيواجه تحولًا في النظام إلى "عصر ما بعد الربع" في السنوات القليلة المقبلة. يتم ضغط وقت التحضير بشكل مستمر ، ولكن لا داعي للقلق كثيرًا في الماضي ، تم تركيز تقدير التهديدات الكمومية في الغالب بعد عقود ، مثل المعهد الوطني للمعايير والتكنولوجيا (NIST) التي تم إصدارها العام الماضي.معايير تشفير ما بعد كويكيوصي أن تكون الأنظمة الهشة الحالية تحتاج إلى التخلص التدريجي من عام 2030. لكن Google قد خفضت الآن الطلب على الموارد بمقدار 20 مرة ، مما يجعل العديد من التنبؤات المحافظة في الأصل تبدو متفائلة بشكل مفرط. ومع ذلك ، بالنظر إلى أقوى أجهزة الكمبيوتر الكمية IBM Condor ، فقط 1،121 QubitsGoogle Sycamore فقط 53 Qubits، لا تزال هناك مسافة من تهديد نظام التشفير الحالي حقًا. لكن الاتجاه واضح للغاية:تكلفة فك التشفير تتناقص بسرعة.」 تهديدات الكم خطوة بخطوة يشير الاختراقات التكنولوجية لـ Google والتعرض للمخاطر BlackRock بشكل مشترك إلى حقيقة: "لم يعد بإمكان عالم التشفير تجاهل الأزمة الكمومية". لا يجب أن تكون مثيرة للقلق ، ولكن هذا الواقع الذي من المحتمل أن يحدث في العقد المقبل سوف يشكل بلا شك تهديدًا لصناعة التشفير. (شركة الحوسبة الكمومية ، يقدم Eleven Eleven مكافأة من تقنية تشفير 1 BTC: دعك تعرف مدى قرب الخطر)
ما نحتاجه ليس الذعر ، ولكن النشر مقدمًا ، من الخوارزميات الأساسية إلى تعليم المستخدم وصياغة السياسة ، نحتاج إلى البدء في وقت واحد. عندما نتحدث عن مستقبل التمويل اللامركزي ، يمكننا فقطحماية"فقط من خلال الوقوف بحزم في خط الدفاع هذا ، يمكننا حقًا الترحيب بالازدهار طويل الأجل لـ blockchain. تحذير المخاطراستثمارات العملة المشفرة محفوفة بالمخاطر للغاية ، وقد تتقلب أسعارها بشكل كبير وقد تفقد كل مديرك. يرجى تقييم المخاطر بحذر.
0 notes