#jameswebbspacetelescope
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
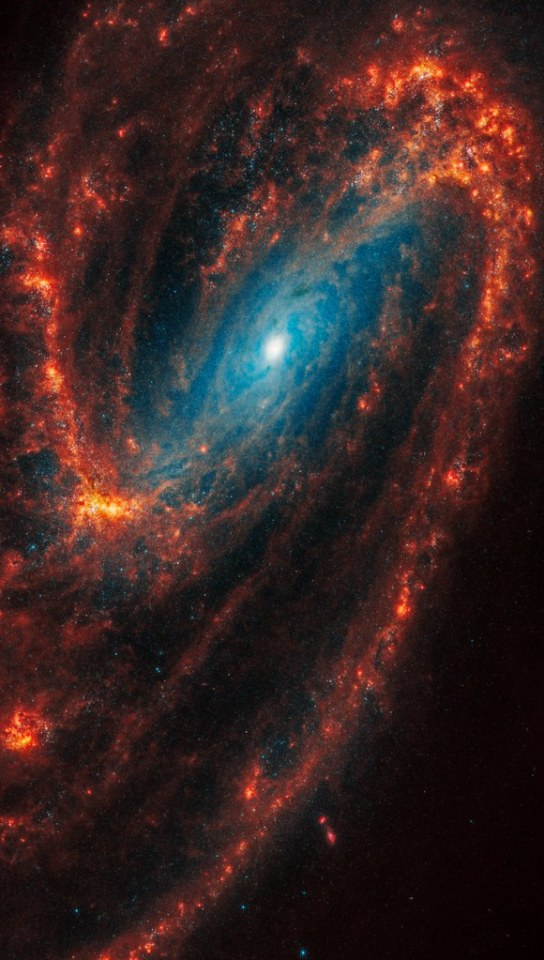

294 notes
·
View notes
Text
Galaxy Pair Resembles ‘Blood-Soaked’ Eyes in Webb Image
NASA’s James Webb and Hubble Space Telescopes have captured a chilling view of two galaxies that resemble a pair of glowing, blood-soaked eyes peering through space! These galaxies, IC 2163 and NGC 2207, brushed past each other millions of years ago, creating a striking cosmic “mask” made visible with Webb's infrared and Hubble's ultraviolet and visible light.
The duo reveals vivid pink star-forming regions and eerie orange cores that give it an almost supernatural appearance — a reminder of the wild beauty in our universe! 🔭 Learn more - https://www.jameswebbdiscovery.com/discoveries/galaxy-pair-resembles-blood-soaked-eyes-in-webb-image

48 notes
·
View notes
Text
600 Million Years After the Big Bang: We discovered Firefly Sparkle galaxy | Researchatory.AI | Aakash Khurana
Imagine seeing the universe as it was just 600 million years after the Big Bang. Thanks to the James Webb Telescope, we can! This is 'Firefly Sparkle,' a small but mighty galaxy with star clusters that shine like cosmic fireflies, providing invaluable insights into early galaxy formation. #JamesWebbSpaceTelescope #JWST #Astronomy #Space #Galaxy #Cosmos #Universe #SpaceExploration #Astrophysics #FireflySparkle #EarlyUniverse #GalaxyFormation #WebbTelescope #CosmicDiscovery #SpaceFacts #ScienceNews #AmazingSpace
In essence, "Firefly Sparkle" is a window into the past, allowing us to witness the building blocks of galaxies as they came together.
For more info join our medium page. https://medium.com/@researchatory
#JamesWebbSpaceTelescope#JWST#Astronomy#Space#Galaxy#Cosmos#Universe#SpaceExploration#Astrophysics#FireflySparkle#EarlyUniverse#GalaxyFormation#WebbTelescope#CosmicDiscovery#SpaceFacts#ScienceNews#AmazingSpace
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
James Webb Space Telescope Captures Stunning Image of the Carina Nebula
The James Webb Space Telescope has captured a stunning image of the Carina Nebula, one of the largest and brightest nebulae in the sky. The image is the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the Carina Nebula ever taken, and it reveals previously unseen details of the region.
The Carina Nebula is a star-forming region located about 7,600 light-years from Earth. It is home to some of the most massive stars and hottest stellar nurseries in the Milky Way galaxy. The new image from the James Webb Space Telescope shows the Carina Nebula in unprecedented detail, revealing hundreds of previously unseen stars and dozens of new jets and outflows of gas and dust.
The image is also the first to show the Carina Nebula in infrared light at multiple wavelengths. This allows astronomers to study different regions of the nebula in more detail, and to learn more about the processes that are taking place there.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the most powerful telescope ever built, and it is already revolutionizing our understanding of the universe. This new image of the Carina Nebula is just a taste of what is to come in the years ahead.

What do you think of this amazing image? Let us know in the comments below!
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
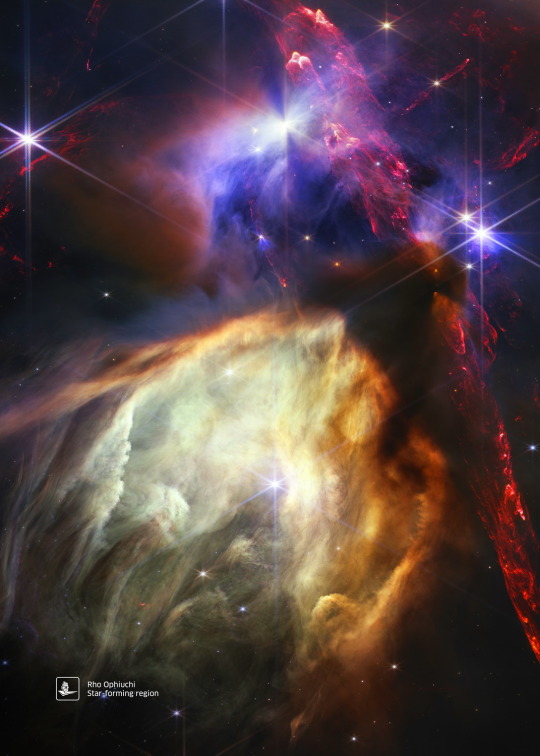



Rho Ophiuchi (James Webb/JWST)
#NASA#JWST#JamesWebb#RhoOphiuchi#JamesWebbSpaceTelescope#JamesWebbTelescope#spaceposter#spaceart#space#cosmos#neonspace#SpaceArtist#ScienceArtist
14 notes
·
View notes
Photo
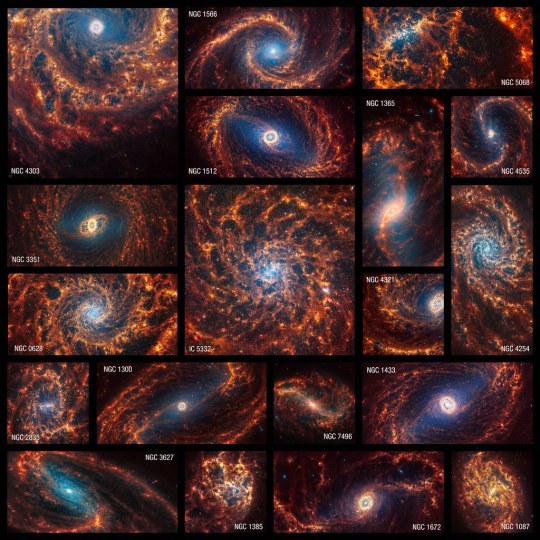

NASA’s Webb Depicts Staggering Structure in 19 Nearby Spiral Galaxies by James Webb Space Telescope
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today i want to teach you something if you didnt know.
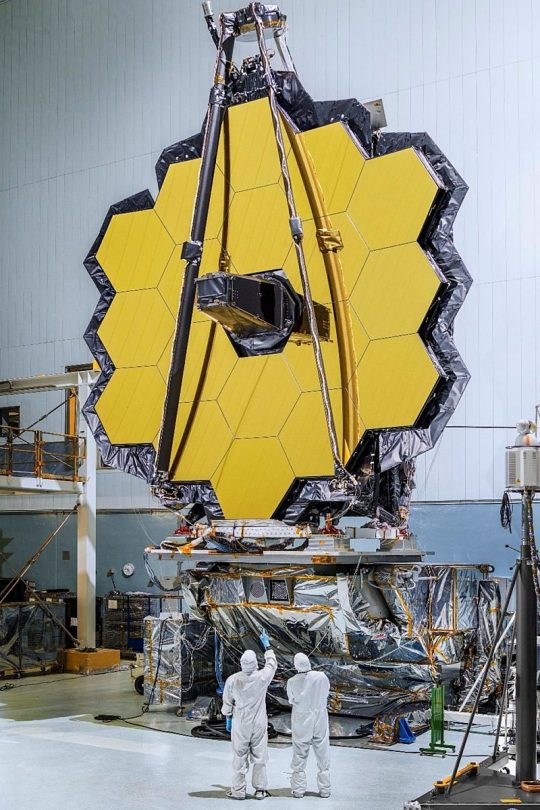
The James webb deepspace telescope.for the ones whom find this interesting. The James Webb space telescope is the second space telescope that NASA has sent up into space where it is very far from Earth a few hundred thousand km if I'm mistaking or not. This telescope took NASA round about 25 years to build and a few billion dollars away it has real gold on its dick or mirror which exist out of hexagons it's only gold-plated though but it's good for reflection reflecting the lights and processing it we are filters like infrared or ultraviolet or even life itself. The James Webb has called already a lot of interesting photos realistic pictures that you can say it's like staring back in time because of distance between stars how it is now and how it really is at this very moment there where it is because of distance time difference the way we see this object it's absolute crazy. The James Webb telescope was launched in 2001 like it is Sky launched and it took about a half a year or a year to get to its destination which is in the shade of the Earth far far away. It can not get into the sunlight because the systems has to be very cold to be able to function the way they want it to function every temperature degree makes a difference in what the result will be absolute perfect design Judas telescope so fragile but yet so strong already it has damage to a mirror if I'm not mistaken because of a meteor and meteorite which is very a small but travel at a very fast speed and like scratch the glass order to gold. Here are a few previews of the James Webb space telescope and the remarkable images photos it took why it's amazing new look through infrared and the rest. By ginger










6 notes
·
View notes
Text
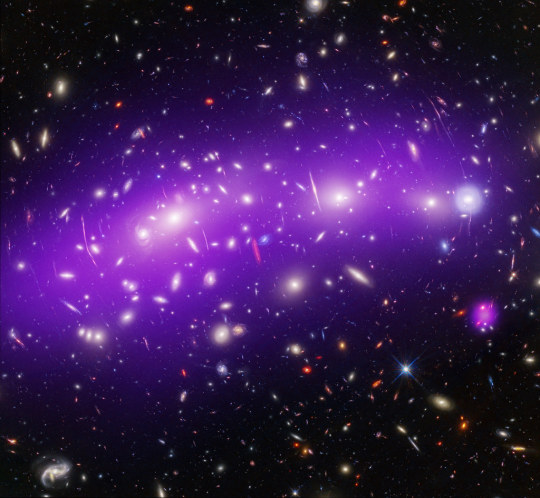

MACS J0416 (Chandra/Hubble/Webb composite) By James Webb Space Telescope https://flic.kr/p/2q3srej
#James Webb Space Telescope#curators on Tumblr#curated#jwst#webb#hubble#chandra#composite#galaxyclusters#jameswebbspacetelescope#flickr
0 notes
Text
'The early universe is nothing like we expected' according to new Images from JWST | Live Science
The Cosmic Gems is one of the most highly magnified objects in space, thanks to a phenomenon called gravitational lensing. (Image credit: ESA/Webb, NASA & CSA, L. Bradley (STScI), A. Adamo (Stockholm University) and the Cosmic Spring collaboration) Astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope have observed five extremely dense proto-globular clusters along a hair-thin arc of glittering stars.…

View On WordPress
#astrophysics#BigBang#Cosmology#Cosmos#DarkEraOfUniverse#earlyuniverse#Einstein#EN#GalaxyClusters#generalRelativity#Gravitation#gravitationallensing#JamesWebbSpaceTelescope#JWST#NASA#Reionization#spacetime#Universe
0 notes
Text
NGC 4254's Swirling Spectacle Captured by James Webb Telescope

Exploring the Dazzling Swirls of Spiral Galaxy NGC 4254 The universe is a vast expanse of mysteries and marvels, and nestled within this cosmic sea is NGC 4254, a spiral galaxy that captures the imagination with its stunning swirls and vibrant hues. Thanks to the unparalleled capabilities of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers and enthusiasts alike can now explore this celestial wonder in unprecedented detail.
A Glimpse into the Cosmos
On January 29, 2024, the James Webb Space Telescope offered the world a mesmerizing view of NGC 4254. Moreover, adorned in radiant orange and blue, this image is part of a broader effort by the Physics at High Angular Resolution in Nearby GalaxieS (PHANGS) program. This initiative aims to study 19 nearby spiral galaxies. Additionally, supported by over 150 astronomers globally, PHANGS leverages James Webb's state-of-the-art technology to peel back the layers of these spiraled giants. Webb's Infrared Eyes The James Webb Space Telescope's power lies in its observation capabilities. Unlike its predecessors, Webb delves into the infrared spectrum, revealing celestial objects and phenomena previously shrouded in mystery. Its Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) captures the sparkling blue tones of millions of stars, while the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) illuminates the glowing dust that exists around and between these stars, painting a picture of cosmic creation and destruction.
The Significance of NGC 4254
NGC 4254 stands as a testament to the dynamic processes that govern our universe. Its clearly defined arms, brimming with stars, wind towards a center that may host ancient star clusters and occasionally, active supermassive black holes. This galaxy, like others in the PHANGS survey, offers invaluable insights into the lifecycle of stars, the distribution of cosmic dust, and the conditions that lead to the formation of black holes. The Revolution of James Webb The James Webb Space Telescope has ushered in a new era of cosmic exploration. By observing the universe in infrared light, Webb extends our gaze farther and deeper than ever before, unveiling objects and phenomena that were once beyond our reach. This revolutionary observatory has not only enhanced our understanding of galaxies like NGC 4254 but has also shed light on the early universe, the mysterious dark matter, and the dark energy that permeates space.
Webb's Contributions to Solar System Science
Beyond its exploration of distant galaxies, the James Webb Space Telescope has significantly advanced our knowledge of the solar system. It has identified new asteroids and comets, offered detailed studies of planetary and moon atmospheres, and provided fresh insights into the formation and evolution of our cosmic neighborhood. The James Webb Space Telescope's image of NGC 4254 is more than just a photograph; it's a gateway to understanding the complexities and beauty of the universe. As we continue to analyze and marvel at these images, we inch closer to unraveling the mysteries of our cosmos, reminding us of the endless wonders that await discovery. Sources: THX News & NASA. Read the full article
#celestialobjects#cosmicdust#cosmicexploration#infraredlight#JamesWebbSpaceTelescope#Mid-InfraredInstrument#Near-InfraredCamera#NGC4254#PHANGSprogram#spiralgalaxy
0 notes
Text

James Webb Space Telescope observes 19 intricate galaxy structures in stunning detail (images) http://dlvr.it/T22cRH
0 notes
Text
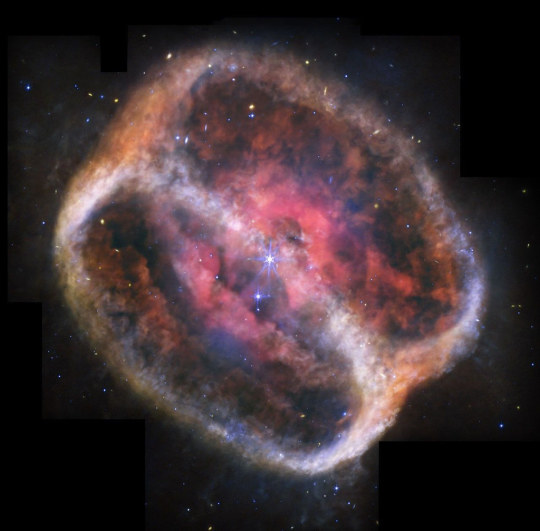

SOURCE: NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center https://flic.kr/p/2qYjJUY
#nasa#nasasmarshallspaceflightcenter#nasamarshall#marshall#msfc#goddardspaceflightcenter#gsfc#solarsystembeyond#astronomy#astrophysics#jameswebbspacetelescope#jwst#planetarynebula#nebula
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Webb Telescope’s Stunning New Image Reveals Active Star Births in Digel Cloud 2S

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope just unveiled a mesmerizing view of the Extreme Outer Galaxy, located over 58,000 light-years away! 🌌 Capturing the Digel Cloud 2S star-forming region, Webb revealed a spectacular cluster of newborn stars shooting out vibrant jets of material like cosmic fireworks! 🌠🔥
This groundbreaking discovery sheds new light on the secrets of star formation in our galaxy’s most distant reaches! 🌟🪐
Dare to journey with us to the very edge of the Milky Way? 🌍➡️💫
👉 Link to the full article
#JamesWebbSpaceTelescope#NASA#NewDiscovery#Astrophotography#StarFormation#OuterGalaxy#SpaceScience#CosmicWonders
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nasa Has Discovered A Potential Indication Of Life On One Of Jupiter's Moons

NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has achieved a monumental breakthrough while investigating Europa, one of Jupiter's celestial companions. Employing its cutting-edge infrared imaging apparatus, the telescope has astutely captured a series of awe-inspiring visuals, unveiling compelling indications of life in the form of abundant concentrations of carbon dioxide.
Read Full Article
0 notes
Text
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope captures stunning images of the Orion Nebula
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has captured stunning images of the Orion Nebula, one of the brightest nebulae in the sky. The images reveal new details about the nebula's structure and composition, including previously unseen clouds of gas and dust.
The Orion Nebula is a star-forming region located about 1,350 light-years from Earth. It is one of the most popular targets for amateur astronomers, as it is visible to the naked eye on a clear night.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the most powerful telescope ever built, and it is able to see objects in the infrared spectrum that are invisible to other telescopes. The infrared images of the Orion Nebula reveal new details about the nebula's structure and composition, including previously unseen clouds of gas and dust.
The images also show the nebula's "Pillars of Creation," which are towering columns of gas and dust where stars are forming. The Pillars of Creation are one of the most iconic images in astronomy, and the James Webb Space Telescope's images are the most detailed ever taken.
The James Webb Space Telescope's images of the Orion Nebula are a testament to the power of the telescope and its potential to revolutionize our understanding of the universe.

1 note
·
View note
Text
A che velocità di sta espandendo l'Universo conosciuto

Webb, alta tensione sulla costante di Hubble. i risultati di uno studio guidato da Adam Riess. Le misure compiute da Jwst su 320 cefeidi, già osservate con Hubble nei decenni passati, ospitate nelle galassie Ngc 4258 ed Ngc 5584 confermano la validità delle stime precedenti, inducendo dunque a escludere che la tensione sulla costante di Hubble sia dovuta a errori sistematici sulle stime fotometriche della distanza delle cefeidi stesse. Doveva essere la macchina perfetta per sciogliere la tensione sulla costante di Hubble. E pressoché perfetto il telescopio spaziale James Webb sta davvero dimostrando di esserlo. Ma quanto alla tensione sul valore di H0, più che allentarla rischia paradossalmente di aggravarla.
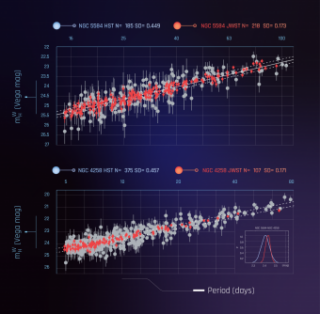
Confronto tra le correlazioni periodo-luminosità delle cefeidi utilizzate per misurare le distanze. I punti rossi sono i dati acquisiti con Webb, quelli grigi con Hubble. Il pannello superiore è relativo alla galassia Ngc 5584, quello inferiore a Ngc 4258. I due telescopi risultano in ottimo accordo. Crediti: Nasa, Esa, A. Riess (Stsci), G. Anand (Stsci) Le recenti misure compiute sulle stelle cefeidi delle galassie Ngc 4258 ed Ngc 5584 sembrano infatti confermare quelle ottenute in passato con il telescopio spaziale Hubble, escludendo così l’eventualità – o la speranza – che a produrre la tensione possano essere errori sistematici sulle stime fotometriche delle cefeidi stesse. Va detto che si tratta di un risultato pubblicato per ora solo come preprint, dunque ancora in attesa di superare una peer review. Solido comunque al punto da essere già stato rilanciato sul sito della Nasa. Altro dettaglio non irrilevante, alla guida del team che l’ha ottenuto c’è niente meno che Adam Riess, uno dei tre astrofisici premiati nel 2011 con il Nobel proprio per “la scoperta dell’espansione accelerata dell’universo a partire dall’osservazione di supernove lontane” – scoperta intimamente legata alla stima della distanza delle cefeidi. Per capire perché questa misura sulle cefeidi sia così cruciale per la stima della costante di Hubble, conviene fare un passo indietro e ripercorrere brevemente i due metodi comunemente adottati per stimarla. Il primo è quello che per brevità possiamo chiamare cosmologico, e deriva la costante di Hubble in modo indiretto dall’integrazione nel modello Lambda-Cdm – del quale H0 è uno dei parametri derivabili, appunto – delle misure dell’anisotropia del fondo cosmico a microonde, prime fra tutte quelle ottenute dalle missioni Wmap e Planck. Il valore della costante di Hubble ottenuto con questo metodo è di 67 km/s/Mpc. Il secondo metodo – che per distinguerlo dal precedente chiameremo astrofisico – restituisce un valore irrimediabilmente più elevato: 74 km/s/Mpc. E per stimare quanto aumenti la velocità d’espansione dell’universo all’aumentare delle distanze – perché è esattamente questo che misura H0 – si affida alle osservazioni di sorgenti più o meno lontane. In particolare, ne misura la velocità d’allontanamento attraverso il redshift e la distanza attraverso la luminosità. Quest’ultimo passaggio è ovviamente critico. Per stimare la distanza di una sorgente in base all’intensità della luce che osserviamo (ciò che gli astronomi chiamano magnitudine apparente), dobbiamo conoscere l’intensità della luce che emette, ovvero la sua magnitudine assoluta. Ecco perché gli astronomi, per misurare H0, si avvalgono di sorgenti molto particolari, dall’emissione luminosa in qualche modo nota, e dette per questo “candele standard”: prime fra tutte le variabili cefeidi, ottime candele standard per le distanze minori, e le supernove di tipo Ia, che consentono il salto alle lunghe distanze, salendo un ulteriore gradino lungo la scala delle distanze cosmiche.
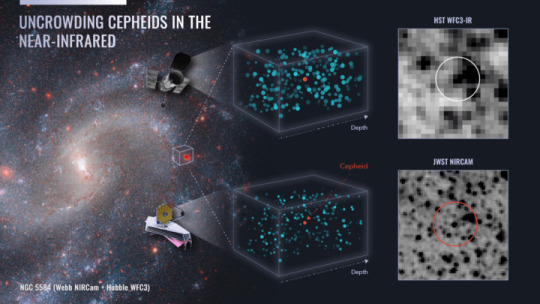
Questo schema illustra la potenza combinata dei telescopi spaziali Hubble e Webb della Nasa nel definire le distanze precise di una speciale classe di stelle variabili, le cefeidi, utilizzate per calibrare il tasso di espansione dell’universo. Essendo osservate in campi stellari affollati, la contaminazione della luce delle stelle circostanti può rendere meno precisa la misurazione della luminosità di una cefeide. La visione infrarossa più nitida di Webb consente di isolare più chiaramente una cefeide dalle stelle circostanti, come si vede nella parte destra dello schema. I dati di Webb confermano l’accuratezza di 30 anni di osservazioni Hubble delle cefeidi, fondamentali per stabilire il gradino più basso della scala delle distanze cosmiche per misurare il tasso di espansione dell’universo. A sinistra, la galassia Ngc 5584 in un’immagine composita della NirCam (Near-Infrared Camera) di Webb e della Wide Field Camera 3 di Hubble. Crediti: Nasa, Esa, A. Riess (Stsci), W. Yuan (Stsci) Le cefeidi rappresentano dunque il primo gradino di questa scala, facendo da trait d’union fra il caro vecchio metodo della parallasse – perfetto per sorgenti molto vicine, come le cefeidi all’interno della nostra galassia – a sorgenti man mano più distanti, in particolare cefeidi di galassie più lontane che ospitino anche supernove di tipo Ia, com’è il caso di Ngc 5584. Così da porre le basi per il salto successivo, quello a supernove di tipo Ia di galassie molto più lontane. A rendere le cefeidi ottime candele standard è un fenomeno curioso che le caratterizza: oltre a essere eccezionalmente luminose, si espandono e si contraggono – come un cuore che pulsa – con una frequenza correlata alla loro luminosità assoluta. Detto altrimenti, misurandone il periodo possiamo in qualche misura risalire all’intensità della luce che emettono – proprio quel che occorre per usarle come “metro”. Ed è esattamente ciò che è stato fatto nei decenni passati. Con qualche margine d’incertezza. Le cefeidi non risplendono in beata solitudine, ma sono spesso circondate da altre stelle, alcune molto vicine, al punto da rendere non sempre agevole distinguere con sicurezza tra la luce emessa dalla cefeide che ci interessa e quella delle altre stelle presenti nei paraggi. Il telescopio spaziale Hubble, grazie alla sua eccezionale risoluzione, ha consentito da questo punto di vista progressi notevoli, ma non uniformi lungo tutto lo spettro: se la cava benissimo sul versante “blu”, dunque alle frequenze più elevate, ma man mano che vogliamo misurare l’emissione a onde più lunghe, scendendo dunque verso l’infrarosso, ecco che anche la vista di Hubble inizia a perdere colpi e non riesce più a distinguere agevolmente i vari contributi, costringendo gli astronomi ad affidarsi sempre più alla statistica, con quel che ne consegue. «Possiamo tenere statisticamente conto della quantità media di contaminazione, nello stesso modo in cui un medico calcola il peso d’una persona sottraendo dalla lettura della bilancia il peso medio dei vestiti, ma questo aggiunge rumore alle misure: i vestiti di alcune persone sono più pesanti di quelli di altre», osserva infatti Riess. «Ma proprio la visione nitida nell’infrarosso è uno dei “superpoteri” del James Webb Space Telescope. Grazie al suo grande specchio e alle sue ottiche sensibili, è in grado di separare senza difficoltà la luce delle cefeidi da quella delle stelle vicine».
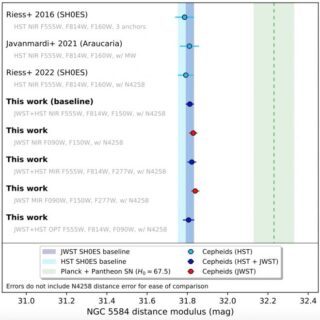
Le misure della distanza delle cefeidi di Ngc 5584 a confronto. Crediti: A. Riess et al., 2023 Ecco dunque che Riess e colleghi hanno chiesto – e ottenuto – di poter misurare con Webb la luce di oltre 320 cefeidi, già osservate con Hubble, ospitate in una galassia relativamente vicina, Ngc 4258, e in una più lontana contenente anche supernove recenti, Ngc 5584. Risultato: il peso del paziente “nudo”, misurato con Webb, è risultato essere pressoché identico a quello calcolato da Hubble pesando il paziente “vestito” e sottraendo il peso stimato degli “abiti”. «Confermando le misure di Hubble, le misure di Webb forniscono la prova più forte del fatto che gli errori sistematici nella fotometria delle cefeidi misurata con Hubble non giocano un ruolo significativo nell’attuale tensione sulla costante di Hubble», conclude Riess. «Di conseguenza, le possibilità più interessanti rimangono sul tavolo e il mistero della tensione si infittisce». Per saperne di più: Leggi il preprint dell’articolo “Crowded No More: The Accuracy of the Hubble Constant Tested with High Resolution Observations of Cepheids by JWST”, di Adam G. Riess, Gagandeep S. Anand, Wenlong Yuan, Stefano Casertano, Andrew Dolphin, Lucas M. Macri, Louise Breuval, Dan Scolnic, Marshall Perrin e Richard I. Anderson Guarda su MediaInaf Tv il video con Adam Riess sulla tensione di Hubble: Read the full article
#Cefeidi#costantedihubble#distanze cosmiche#espansioneuniverso#HubbleSpaceTelescope#JamesWebbSpaceTelescope#redshift#tensionediHubble
0 notes