#online data modeling tool
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Online data modeling tool softfactory, you deserve it!
During the early stages of project development, there is often a need to design a large number of tables, and using database design tools can be more efficient at this time! The online database design tool, Softfactory, has a simple and beautiful interface with powerful features.

The advantages of online database design include:
Flexibility and convenience: There’s no need to download and install software, all you need is a network connection. Real-time collaboration: Multiple users can design the database simultaneously, improving work efficiency. Version control: It allows for easy management and tracking of different versions of database designs.
Let’s talk about Softfactory~ Softfactory Introduction
Softfactory is an online table structure design software that leverages artificial intelligence to improve efficiency. It can generate CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) code and push it to development tools. Push to Development Tools: Users can directly push the code generated by Softfactory to their own development tools, eliminating the need for copy-pasting and saving operational steps. Supports Multi-person Collaboration: Softfactory supports team collaboration, where multiple users can design the database simultaneously, realizing real-time communication and seamless cooperation. Cross-language Support: Softfactory supports almost all programming languages, such as Java, Python, JavaScript, etc., meeting the needs of different developers. Connecting Development Tools: Softfactory conveniently places the steps to connect the development tool, following which users can link Softfactory with their commonly used development tools to achieve automatic code synchronization.

Installation:
No installation is required — you just need an internet connection to log in. Access portal: https://www.softfactory.cloud/
Function Reading:
AI Table Creation: After creating the requirements, you can use AI to create tables. In the table structure designed by AI, you can select approved tables for saving, and further design or fine-tune the table structure. Manual Table Creation: Manual table creation allows you to enter the “Field Designer” to design the table’s fields, indexes, and foreign keys. Manual Relationship Establishment: The relationship between tables can be represented by lines, which can be formed by manual dragging, and can also be manually deleted. Foreign Key Relationship: If there is a primary and foreign key relationship between two tables, a line will automatically form and cannot be deleted in the chart. If you need to delete, you need to delete the foreign key in the Table Designer.
Once the database exceeds the size that humans can digest, using tools to assist in its design becomes crucial. Softfactory is free to start and can be upgraded at any time.
0 notes
Text

A new tool lets artists add invisible changes to the pixels in their art before they upload it online so that if it’s scraped into an AI training set, it can cause the resulting model to break in chaotic and unpredictable ways.
The tool, called Nightshade, is intended as a way to fight back against AI companies that use artists’ work to train their models without the creator’s permission. Using it to “poison” this training data could damage future iterations of image-generating AI models, such as DALL-E, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion, by rendering some of their outputs useless—dogs become cats, cars become cows, and so forth. MIT Technology Review got an exclusive preview of the research, which has been submitted for peer review at computer security conference Usenix.
AI companies such as OpenAI, Meta, Google, and Stability AI are facing a slew of lawsuits from artists who claim that their copyrighted material and personal information was scraped without consent or compensation. Ben Zhao, a professor at the University of Chicago, who led the team that created Nightshade, says the hope is that it will help tip the power balance back from AI companies towards artists, by creating a powerful deterrent against disrespecting artists’ copyright and intellectual property. Meta, Google, Stability AI, and OpenAI did not respond to MIT Technology Review’s request for comment on how they might respond.
Zhao’s team also developed Glaze, a tool that allows artists to “mask” their own personal style to prevent it from being scraped by AI companies. It works in a similar way to Nightshade: by changing the pixels of images in subtle ways that are invisible to the human eye but manipulate machine-learning models to interpret the image as something different from what it actually shows.
Continue reading article here
#Ben Zhao and his team are absolute heroes#artificial intelligence#plagiarism software#more rambles#glaze#nightshade#ai theft#art theft#gleeful dancing
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
So, let me try and put everything together here, because I really do think it needs to be talked about.
Today, Unity announced that it intends to apply a fee to use its software. Then it got worse.
For those not in the know, Unity is the most popular free to use video game development tool, offering a basic version for individuals who want to learn how to create games or create independently alongside paid versions for corporations or people who want more features. It's decent enough at this job, has issues but for the price point I can't complain, and is the idea entry point into creating in this medium, it's a very important piece of software.
But speaking of tools, the CEO is a massive one. When he was the COO of EA, he advocated for using, what out and out sounds like emotional manipulation to coerce players into microtransactions.
"A consumer gets engaged in a property, they might spend 10, 20, 30, 50 hours on the game and then when they're deep into the game they're well invested in it. We're not gouging, but we're charging and at that point in time the commitment can be pretty high."
He also called game developers who don't discuss monetization early in the planning stages of development, quote, "fucking idiots".
So that sets the stage for what might be one of the most bald-faced greediest moves I've seen from a corporation in a minute. Most at least have the sense of self-preservation to hide it.
A few hours ago, Unity posted this announcement on the official blog.
Effective January 1, 2024, we will introduce a new Unity Runtime Fee that’s based on game installs. We will also add cloud-based asset storage, Unity DevOps tools, and AI at runtime at no extra cost to Unity subscription plans this November. We are introducing a Unity Runtime Fee that is based upon each time a qualifying game is downloaded by an end user. We chose this because each time a game is downloaded, the Unity Runtime is also installed. Also we believe that an initial install-based fee allows creators to keep the ongoing financial gains from player engagement, unlike a revenue share.
Now there are a few red flags to note in this pitch immediately.
Unity is planning on charging a fee on all games which use its engine.
This is a flat fee per number of installs.
They are using an always online runtime function to determine whether a game is downloaded.
There is just so many things wrong with this that it's hard to know where to start, not helped by this FAQ which doubled down on a lot of the major issues people had.
I guess let's start with what people noticed first. Because it's using a system baked into the software itself, Unity would not be differentiating between a "purchase" and a "download". If someone uninstalls and reinstalls a game, that's two downloads. If someone gets a new computer or a new console and downloads a game already purchased from their account, that's two download. If someone pirates the game, the studio will be asked to pay for that download.
Q: How are you going to collect installs? A: We leverage our own proprietary data model. We believe it gives an accurate determination of the number of times the runtime is distributed for a given project. Q: Is software made in unity going to be calling home to unity whenever it's ran, even for enterprice licenses? A: We use a composite model for counting runtime installs that collects data from numerous sources. The Unity Runtime Fee will use data in compliance with GDPR and CCPA. The data being requested is aggregated and is being used for billing purposes. Q: If a user reinstalls/redownloads a game / changes their hardware, will that count as multiple installs? A: Yes. The creator will need to pay for all future installs. The reason is that Unity doesn’t receive end-player information, just aggregate data. Q: What's going to stop us being charged for pirated copies of our games? A: We do already have fraud detection practices in our Ads technology which is solving a similar problem, so we will leverage that know-how as a starting point. We recognize that users will have concerns about this and we will make available a process for them to submit their concerns to our fraud compliance team.
This is potentially related to a new system that will require Unity Personal developers to go online at least once every three days.
Starting in November, Unity Personal users will get a new sign-in and online user experience. Users will need to be signed into the Hub with their Unity ID and connect to the internet to use Unity. If the internet connection is lost, users can continue using Unity for up to 3 days while offline. More details to come, when this change takes effect.
It's unclear whether this requirement will be attached to any and all Unity games, though it would explain how they're theoretically able to track "the number of installs", and why the methodology for tracking these installs is so shit, as we'll discuss later.
Unity claims that it will only leverage this fee to games which surpass a certain threshold of downloads and yearly revenue.
Only games that meet the following thresholds qualify for the Unity Runtime Fee: Unity Personal and Unity Plus: Those that have made $200,000 USD or more in the last 12 months AND have at least 200,000 lifetime game installs. Unity Pro and Unity Enterprise: Those that have made $1,000,000 USD or more in the last 12 months AND have at least 1,000,000 lifetime game installs.
They don't say how they're going to collect information on a game's revenue, likely this is just to say that they're only interested in squeezing larger products (games like Genshin Impact and Honkai: Star Rail, Fate Grand Order, Among Us, and Fall Guys) and not every 2 dollar puzzle platformer that drops on Steam. But also, these larger products have the easiest time porting off of Unity and the most incentives to, meaning realistically those heaviest impacted are going to be the ones who just barely meet this threshold, most of them indie developers.
Aggro Crab Games, one of the first to properly break this story, points out that systems like the Xbox Game Pass, which is already pretty predatory towards smaller developers, will quickly inflate their "lifetime game installs" meaning even skimming the threshold of that 200k revenue, will be asked to pay a fee per install, not a percentage on said revenue.

[IMAGE DESCRIPTION: Hey Gamers!
Today, Unity (the engine we use to make our games) announced that they'll soon be taking a fee from developers for every copy of the game installed over a certain threshold - regardless of how that copy was obtained.
Guess who has a somewhat highly anticipated game coming to Xbox Game Pass in 2024? That's right, it's us and a lot of other developers.
That means Another Crab's Treasure will be free to install for the 25 million Game Pass subscribers. If a fraction of those users download our game, Unity could take a fee that puts an enormous dent in our income and threatens the sustainability of our business.
And that's before we even think about sales on other platforms, or pirated installs of our game, or even multiple installs by the same user!!!
This decision puts us and countless other studios in a position where we might not be able to justify using Unity for our future titles. If these changes aren't rolled back, we'll be heavily considering abandoning our wealth of Unity expertise we've accumulated over the years and starting from scratch in a new engine. Which is really something we'd rather not do.
On behalf of the dev community, we're calling on Unity to reverse the latest in a string of shortsighted decisions that seem to prioritize shareholders over their product's actual users.
I fucking hate it here.
-Aggro Crab - END DESCRIPTION]
That fee, by the way, is a flat fee. Not a percentage, not a royalty. This means that any games made in Unity expecting any kind of success are heavily incentivized to cost as much as possible.

[IMAGE DESCRIPTION: A table listing the various fees by number of Installs over the Install Threshold vs. version of Unity used, ranging from $0.01 to $0.20 per install. END DESCRIPTION]
Basic elementary school math tells us that if a game comes out for $1.99, they will be paying, at maximum, 10% of their revenue to Unity, whereas jacking the price up to $59.99 lowers that percentage to something closer to 0.3%. Obviously any company, especially any company in financial desperation, which a sudden anchor on all your revenue is going to create, is going to choose the latter.
Furthermore, and following the trend of "fuck anyone who doesn't ask for money", Unity helpfully defines what an install is on their main site.
While I'm looking at this page as it exists now, it currently says
The installation and initialization of a game or app on an end user’s device as well as distribution via streaming is considered an “install.” Games or apps with substantially similar content may be counted as one project, with installs then aggregated to calculate the Unity Runtime Fee.
However, I saw a screenshot saying something different, and utilizing the Wayback Machine we can see that this phrasing was changed at some point in the few hours since this announcement went up. Instead, it reads:
The installation and initialization of a game or app on an end user’s device as well as distribution via streaming or web browser is considered an “install.” Games or apps with substantially similar content may be counted as one project, with installs then aggregated to calculate the Unity Runtime Fee.
Screenshot for posterity:
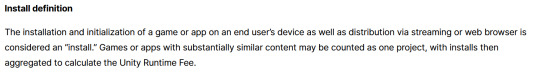
That would mean web browser games made in Unity would count towards this install threshold. You could legitimately drive the count up simply by continuously refreshing the page. The FAQ, again, doubles down.
Q: Does this affect WebGL and streamed games? A: Games on all platforms are eligible for the fee but will only incur costs if both the install and revenue thresholds are crossed. Installs - which involves initialization of the runtime on a client device - are counted on all platforms the same way (WebGL and streaming included).
And, what I personally consider to be the most suspect claim in this entire debacle, they claim that "lifetime installs" includes installs prior to this change going into effect.
Will this fee apply to games using Unity Runtime that are already on the market on January 1, 2024? Yes, the fee applies to eligible games currently in market that continue to distribute the runtime. We look at a game's lifetime installs to determine eligibility for the runtime fee. Then we bill the runtime fee based on all new installs that occur after January 1, 2024.
Again, again, doubled down in the FAQ.
Q: Are these fees going to apply to games which have been out for years already? If you met the threshold 2 years ago, you'll start owing for any installs monthly from January, no? (in theory). It says they'll use previous installs to determine threshold eligibility & then you'll start owing them for the new ones. A: Yes, assuming the game is eligible and distributing the Unity Runtime then runtime fees will apply. We look at a game's lifetime installs to determine eligibility for the runtime fee. Then we bill the runtime fee based on all new installs that occur after January 1, 2024.
That would involve billing companies for using their software before telling them of the existence of a bill. Holding their actions to a contract that they performed before the contract existed!
Okay. I think that's everything. So far.
There is one thing that I want to mention before ending this post, unfortunately it's a little conspiratorial, but it's so hard to believe that anyone genuinely thought this was a good idea that it's stuck in my brain as a significant possibility.
A few days ago it was reported that Unity's CEO sold 2,000 shares of his own company.
On September 6, 2023, John Riccitiello, President and CEO of Unity Software Inc (NYSE:U), sold 2,000 shares of the company. This move is part of a larger trend for the insider, who over the past year has sold a total of 50,610 shares and purchased none.
I would not be surprised if this decision gets reversed tomorrow, that it was literally only made for the CEO to short his own goddamn company, because I would sooner believe that this whole thing is some idiotic attempt at committing fraud than a real monetization strategy, even knowing how unfathomably greedy these people can be.
So, with all that said, what do we do now?
Well, in all likelihood you won't need to do anything. As I said, some of the biggest names in the industry would be directly affected by this change, and you can bet your bottom dollar that they're not just going to take it lying down. After all, the only way to stop a greedy CEO is with a greedier CEO, right?
(I fucking hate it here.)
And that's not mentioning the indie devs who are already talking about abandoning the engine.
[Links display tweets from the lead developer of Among Us saying it'd be less costly to hire people to move the game off of Unity and Cult of the Lamb's official twitter saying the game won't be available after January 1st in response to the news.]
That being said, I'm still shaken by all this. The fact that Unity is openly willing to go back and punish its developers for ever having used the engine in the past makes me question my relationship to it.
The news has given rise to the visibility of free, open source alternative Godot, which, if you're interested, is likely a better option than Unity at this point. Mostly, though, I just hope we can get out of this whole, fucking, environment where creatives are treated as an endless mill of free profits that's going to be continuously ratcheted up and up to drive unsustainable infinite corporate growth that our entire economy is based on for some fuckin reason.
Anyways, that's that, I find having these big posts that break everything down to be helpful.
#Unity#Unity3D#Video Games#Game Development#Game Developers#fuckshit#I don't know what to tag news like this
6K notes
·
View notes
Note
whats wrong with ai?? genuinely curious <3
okay let's break it down. i'm an engineer, so i'm going to come at you from a perspective that may be different than someone else's.
i don't hate ai in every aspect. in theory, there are a lot of instances where, in fact, ai can help us do things a lot better without. here's a few examples:
ai detecting cancer
ai sorting recycling
some practical housekeeping that gemini (google ai) can do
all of the above examples are ways in which ai works with humans to do things in parallel with us. it's not overstepping--it's sorting, using pixels at a micro-level to detect abnormalities that we as humans can not, fixing a list. these are all really small, helpful ways that ai can work with us.
everything else about ai works against us. in general, ai is a huge consumer of natural resources. every prompt that you put into character.ai, chatgpt? this wastes water + energy. it's not free. a machine somewhere in the world has to swallow your prompt, call on a model to feed data into it and process more data, and then has to generate an answer for you all in a relatively short amount of time.
that is crazy expensive. someone is paying for that, and if it isn't you with your own money, it's the strain on the power grid, the water that cools the computers, the A/C that cools the data centers. and you aren't the only person using ai. chatgpt alone gets millions of users every single day, with probably thousands of prompts per second, so multiply your personal consumption by millions, and you can start to see how the picture is becoming overwhelming.
that is energy consumption alone. we haven't even talked about how problematic ai is ethically. there is currently no regulation in the united states about how ai should be developed, deployed, or used.
what does this mean for you?
it means that anything you post online is subject to data mining by an ai model (because why would they need to ask if there's no laws to stop them? wtf does it matter what it means to you to some idiot software engineer in the back room of an office making 3x your salary?). oh, that little fic you posted to wattpad that got a lot of attention? well now it's being used to teach ai how to write. oh, that sketch you made using adobe that you want to sell? adobe didn't tell you that anything you save to the cloud is now subject to being used for their ai models, so now your art is being replicated to generate ai images in photoshop, without crediting you (they have since said they don't do this...but privacy policies were never made to be human-readable, and i can't imagine they are the only company to sneakily try this). oh, your apartment just installed a new system that will use facial recognition to let their residents inside? oh, they didn't train their model with anyone but white people, so now all the black people living in that apartment building can't get into their homes. oh, you want to apply for a new job? the ai model that scans resumes learned from historical data that more men work that role than women (so the model basically thinks men are better than women), so now your resume is getting thrown out because you're a woman.
ai learns from data. and data is flawed. data is human. and as humans, we are racist, homophobic, misogynistic, transphobic, divided. so the ai models we train will learn from this. ai learns from people's creative works--their personal and artistic property. and now it's scrambling them all up to spit out generated images and written works that no one would ever want to read (because it's no longer a labor of love), and they're using that to make money. they're profiting off of people, and there's no one to stop them. they're also using generated images as marketing tools, to trick idiots on facebook, to make it so hard to be media literate that we have to question every single thing we see because now we don't know what's real and what's not.
the problem with ai is that it's doing more harm than good. and we as a society aren't doing our due diligence to understand the unintended consequences of it all. we aren't angry enough. we're too scared of stifling innovation that we're letting it regulate itself (aka letting companies decide), which has never been a good idea. we see it do one cool thing, and somehow that makes up for all the rest of the bullshit?
#yeah i could talk about this for years#i could talk about it forever#im so passionate about this lmao#anyways#i also want to point out the examples i listed are ONLY A FEW problems#there's SO MUCH MORE#anywho ai is bleh go away#ask#ask b#🐝's anons#ai
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
AI DISTURBANCE "OVERLAYS" DO NOT WORK!
To all the artists and folks who want to protect their art against AI mimicry: all the "AI disturbance" overlays that are circulating online lately DON'T WORK!

Glaze's disturbance (and now the Ibis Paint premium feature, apparently. Not sure.) modifies the image on a code-level, it's not just an overlayed effect but it actually affects the image's data so AI can't really detect and interpret the code within the image. From the Glaze website:
Can't you just apply some filter, compression, blurring, or add some noise to the image to destroy image cloaks? As counterintuitive as this may be, the high level answer is that no simple tools work to destroy the perturbation of these image cloaks. To make sense of this, it helps to first understand that cloaking does not use high-intensity pixels, or rely on bright patterns to distort the image. It is a precisely computed combination of a number of pixels that do not easily stand out to the human eye, but can produce distortion in the AI's “eye.” In our work, we have performed extensive tests showing how robust cloaking is to things like image compression and distortion/noise/masking injection. Another way to think about this is that the cloak is not some brittle watermark that is either seen or not seen. It is a transformation of the image in a dimension that humans do not perceive, but very much in the dimensions that the deep learning model perceive these images. So transformations that rotate, blur, change resolution, crop, etc, do not affect the cloak, just like the same way those operations would not change your perception of what makes a Van Gogh painting "Van Gogh."
Anyone can request a WebGlaze account for FREE, just send an Email or a DM to the official Glaze Project accounts on X and Instagram, they reply within a few days. Be sure to provide a link to your art acc (anywhere) so they know you're an artist.
Please don't be fooled by those colorful and bright overlays to just download and put on your art: it won't work against AI training. Protect your art with REAL Glaze please 🙏🏻 WebGlaze is SUPER FAST, you upload the artwork and they send it back to you within five minutes, and the effect is barely visible!
Official Glaze Project website | Glaze FAQs | about WebGlaze
#no ai#no ai art#ai disturbance#anti ai#anti ai art#artists#artists on tumblr#artists against ai#glaze#webglaze#ibispaint#noai#artists supporting artists#art information#art resources
826 notes
·
View notes
Text
AI “art” and uncanniness

TOMORROW (May 14), I'm on a livecast about AI AND ENSHITTIFICATION with TIM O'REILLY; on TOMORROW (May 15), I'm in NORTH HOLLYWOOD for a screening of STEPHANIE KELTON'S FINDING THE MONEY; FRIDAY (May 17), I'm at the INTERNET ARCHIVE in SAN FRANCISCO to keynote the 10th anniversary of the AUTHORS ALLIANCE.

When it comes to AI art (or "art"), it's hard to find a nuanced position that respects creative workers' labor rights, free expression, copyright law's vital exceptions and limitations, and aesthetics.
I am, on balance, opposed to AI art, but there are some important caveats to that position. For starters, I think it's unequivocally wrong – as a matter of law – to say that scraping works and training a model with them infringes copyright. This isn't a moral position (I'll get to that in a second), but rather a technical one.
Break down the steps of training a model and it quickly becomes apparent why it's technically wrong to call this a copyright infringement. First, the act of making transient copies of works – even billions of works – is unequivocally fair use. Unless you think search engines and the Internet Archive shouldn't exist, then you should support scraping at scale:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/17/how-to-think-about-scraping/
And unless you think that Facebook should be allowed to use the law to block projects like Ad Observer, which gathers samples of paid political disinformation, then you should support scraping at scale, even when the site being scraped objects (at least sometimes):
https://pluralistic.net/2021/08/06/get-you-coming-and-going/#potemkin-research-program
After making transient copies of lots of works, the next step in AI training is to subject them to mathematical analysis. Again, this isn't a copyright violation.
Making quantitative observations about works is a longstanding, respected and important tool for criticism, analysis, archiving and new acts of creation. Measuring the steady contraction of the vocabulary in successive Agatha Christie novels turns out to offer a fascinating window into her dementia:
https://www.theguardian.com/books/2009/apr/03/agatha-christie-alzheimers-research
Programmatic analysis of scraped online speech is also critical to the burgeoning formal analyses of the language spoken by minorities, producing a vibrant account of the rigorous grammar of dialects that have long been dismissed as "slang":
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/373950278_Lexicogrammatical_Analysis_on_African-American_Vernacular_English_Spoken_by_African-Amecian_You-Tubers
Since 1988, UCL Survey of English Language has maintained its "International Corpus of English," and scholars have plumbed its depth to draw important conclusions about the wide variety of Englishes spoken around the world, especially in postcolonial English-speaking countries:
https://www.ucl.ac.uk/english-usage/projects/ice.htm
The final step in training a model is publishing the conclusions of the quantitative analysis of the temporarily copied documents as software code. Code itself is a form of expressive speech – and that expressivity is key to the fight for privacy, because the fact that code is speech limits how governments can censor software:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2015/04/remembering-case-established-code-speech/
Are models infringing? Well, they certainly can be. In some cases, it's clear that models "memorized" some of the data in their training set, making the fair use, transient copy into an infringing, permanent one. That's generally considered to be the result of a programming error, and it could certainly be prevented (say, by comparing the model to the training data and removing any memorizations that appear).
Not every seeming act of memorization is a memorization, though. While specific models vary widely, the amount of data from each training item retained by the model is very small. For example, Midjourney retains about one byte of information from each image in its training data. If we're talking about a typical low-resolution web image of say, 300kb, that would be one three-hundred-thousandth (0.0000033%) of the original image.
Typically in copyright discussions, when one work contains 0.0000033% of another work, we don't even raise the question of fair use. Rather, we dismiss the use as de minimis (short for de minimis non curat lex or "The law does not concern itself with trifles"):
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/De_minimis
Busting someone who takes 0.0000033% of your work for copyright infringement is like swearing out a trespassing complaint against someone because the edge of their shoe touched one blade of grass on your lawn.
But some works or elements of work appear many times online. For example, the Getty Images watermark appears on millions of similar images of people standing on red carpets and runways, so a model that takes even in infinitesimal sample of each one of those works might still end up being able to produce a whole, recognizable Getty Images watermark.
The same is true for wire-service articles or other widely syndicated texts: there might be dozens or even hundreds of copies of these works in training data, resulting in the memorization of long passages from them.
This might be infringing (we're getting into some gnarly, unprecedented territory here), but again, even if it is, it wouldn't be a big hardship for model makers to post-process their models by comparing them to the training set, deleting any inadvertent memorizations. Even if the resulting model had zero memorizations, this would do nothing to alleviate the (legitimate) concerns of creative workers about the creation and use of these models.
So here's the first nuance in the AI art debate: as a technical matter, training a model isn't a copyright infringement. Creative workers who hope that they can use copyright law to prevent AI from changing the creative labor market are likely to be very disappointed in court:
https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/business/business-news/sarah-silverman-lawsuit-ai-meta-1235669403/
But copyright law isn't a fixed, eternal entity. We write new copyright laws all the time. If current copyright law doesn't prevent the creation of models, what about a future copyright law?
Well, sure, that's a possibility. The first thing to consider is the possible collateral damage of such a law. The legal space for scraping enables a wide range of scholarly, archival, organizational and critical purposes. We'd have to be very careful not to inadvertently ban, say, the scraping of a politician's campaign website, lest we enable liars to run for office and renege on their promises, while they insist that they never made those promises in the first place. We wouldn't want to abolish search engines, or stop creators from scraping their own work off sites that are going away or changing their terms of service.
Now, onto quantitative analysis: counting words and measuring pixels are not activities that you should need permission to perform, with or without a computer, even if the person whose words or pixels you're counting doesn't want you to. You should be able to look as hard as you want at the pixels in Kate Middleton's family photos, or track the rise and fall of the Oxford comma, and you shouldn't need anyone's permission to do so.
Finally, there's publishing the model. There are plenty of published mathematical analyses of large corpuses that are useful and unobjectionable. I love me a good Google n-gram:
https://books.google.com/ngrams/graph?content=fantods%2C+heebie-jeebies&year_start=1800&year_end=2019&corpus=en-2019&smoothing=3
And large language models fill all kinds of important niches, like the Human Rights Data Analysis Group's LLM-based work helping the Innocence Project New Orleans' extract data from wrongful conviction case files:
https://hrdag.org/tech-notes/large-language-models-IPNO.html
So that's nuance number two: if we decide to make a new copyright law, we'll need to be very sure that we don't accidentally crush these beneficial activities that don't undermine artistic labor markets.
This brings me to the most important point: passing a new copyright law that requires permission to train an AI won't help creative workers get paid or protect our jobs.
Getty Images pays photographers the least it can get away with. Publishers contracts have transformed by inches into miles-long, ghastly rights grabs that take everything from writers, but still shifts legal risks onto them:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/06/19/reasonable-agreement/
Publishers like the New York Times bitterly oppose their writers' unions:
https://actionnetwork.org/letters/new-york-times-stop-union-busting
These large corporations already control the copyrights to gigantic amounts of training data, and they have means, motive and opportunity to license these works for training a model in order to pay us less, and they are engaged in this activity right now:
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/12/22/technology/apple-ai-news-publishers.html
Big games studios are already acting as though there was a copyright in training data, and requiring their voice actors to begin every recording session with words to the effect of, "I hereby grant permission to train an AI with my voice" and if you don't like it, you can hit the bricks:
https://www.vice.com/en/article/5d37za/voice-actors-sign-away-rights-to-artificial-intelligence
If you're a creative worker hoping to pay your bills, it doesn't matter whether your wages are eroded by a model produced without paying your employer for the right to do so, or whether your employer got to double dip by selling your work to an AI company to train a model, and then used that model to fire you or erode your wages:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/09/ai-monkeys-paw/#bullied-schoolkids
Individual creative workers rarely have any bargaining leverage over the corporations that license our copyrights. That's why copyright's 40-year expansion (in duration, scope, statutory damages) has resulted in larger, more profitable entertainment companies, and lower payments – in real terms and as a share of the income generated by their work – for creative workers.
As Rebecca Giblin and I write in our book Chokepoint Capitalism, giving creative workers more rights to bargain with against giant corporations that control access to our audiences is like giving your bullied schoolkid extra lunch money – it's just a roundabout way of transferring that money to the bullies:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/08/21/what-is-chokepoint-capitalism/
There's an historical precedent for this struggle – the fight over music sampling. 40 years ago, it wasn't clear whether sampling required a copyright license, and early hip-hop artists took samples without permission, the way a horn player might drop a couple bars of a well-known song into a solo.
Many artists were rightfully furious over this. The "heritage acts" (the music industry's euphemism for "Black people") who were most sampled had been given very bad deals and had seen very little of the fortunes generated by their creative labor. Many of them were desperately poor, despite having made millions for their labels. When other musicians started making money off that work, they got mad.
In the decades that followed, the system for sampling changed, partly through court cases and partly through the commercial terms set by the Big Three labels: Sony, Warner and Universal, who control 70% of all music recordings. Today, you generally can't sample without signing up to one of the Big Three (they are reluctant to deal with indies), and that means taking their standard deal, which is very bad, and also signs away your right to control your samples.
So a musician who wants to sample has to sign the bad terms offered by a Big Three label, and then hand $500 out of their advance to one of those Big Three labels for the sample license. That $500 typically doesn't go to another artist – it goes to the label, who share it around their executives and investors. This is a system that makes every artist poorer.
But it gets worse. Putting a price on samples changes the kind of music that can be economically viable. If you wanted to clear all the samples on an album like Public Enemy's "It Takes a Nation of Millions To Hold Us Back," or the Beastie Boys' "Paul's Boutique," you'd have to sell every CD for $150, just to break even:
https://memex.craphound.com/2011/07/08/creative-license-how-the-hell-did-sampling-get-so-screwed-up-and-what-the-hell-do-we-do-about-it/
Sampling licenses don't just make every artist financially worse off, they also prevent the creation of music of the sort that millions of people enjoy. But it gets even worse. Some older, sample-heavy music can't be cleared. Most of De La Soul's catalog wasn't available for 15 years, and even though some of their seminal music came back in March 2022, the band's frontman Trugoy the Dove didn't live to see it – he died in February 2022:
https://www.vulture.com/2023/02/de-la-soul-trugoy-the-dove-dead-at-54.html
This is the third nuance: even if we can craft a model-banning copyright system that doesn't catch a lot of dolphins in its tuna net, it could still make artists poorer off.
Back when sampling started, it wasn't clear whether it would ever be considered artistically important. Early sampling was crude and experimental. Musicians who trained for years to master an instrument were dismissive of the idea that clicking a mouse was "making music." Today, most of us don't question the idea that sampling can produce meaningful art – even musicians who believe in licensing samples.
Having lived through that era, I'm prepared to believe that maybe I'll look back on AI "art" and say, "damn, I can't believe I never thought that could be real art."
But I wouldn't give odds on it.
I don't like AI art. I find it anodyne, boring. As Henry Farrell writes, it's uncanny, and not in a good way:
https://www.programmablemutter.com/p/large-language-models-are-uncanny
Farrell likens the work produced by AIs to the movement of a Ouija board's planchette, something that "seems to have a life of its own, even though its motion is a collective side-effect of the motions of the people whose fingers lightly rest on top of it." This is "spooky-action-at-a-close-up," transforming "collective inputs … into apparently quite specific outputs that are not the intended creation of any conscious mind."
Look, art is irrational in the sense that it speaks to us at some non-rational, or sub-rational level. Caring about the tribulations of imaginary people or being fascinated by pictures of things that don't exist (or that aren't even recognizable) doesn't make any sense. There's a way in which all art is like an optical illusion for our cognition, an imaginary thing that captures us the way a real thing might.
But art is amazing. Making art and experiencing art makes us feel big, numinous, irreducible emotions. Making art keeps me sane. Experiencing art is a precondition for all the joy in my life. Having spent most of my life as a working artist, I've come to the conclusion that the reason for this is that art transmits an approximation of some big, numinous irreducible emotion from an artist's mind to our own. That's it: that's why art is amazing.
AI doesn't have a mind. It doesn't have an intention. The aesthetic choices made by AI aren't choices, they're averages. As Farrell writes, "LLM art sometimes seems to communicate a message, as art does, but it is unclear where that message comes from, or what it means. If it has any meaning at all, it is a meaning that does not stem from organizing intention" (emphasis mine).
Farrell cites Mark Fisher's The Weird and the Eerie, which defines "weird" in easy to understand terms ("that which does not belong") but really grapples with "eerie."
For Fisher, eeriness is "when there is something present where there should be nothing, or is there is nothing present when there should be something." AI art produces the seeming of intention without intending anything. It appears to be an agent, but it has no agency. It's eerie.
Fisher talks about capitalism as eerie. Capital is "conjured out of nothing" but "exerts more influence than any allegedly substantial entity." The "invisible hand" shapes our lives more than any person. The invisible hand is fucking eerie. Capitalism is a system in which insubstantial non-things – corporations – appear to act with intention, often at odds with the intentions of the human beings carrying out those actions.
So will AI art ever be art? I don't know. There's a long tradition of using random or irrational or impersonal inputs as the starting point for human acts of artistic creativity. Think of divination:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/07/31/divination/
Or Brian Eno's Oblique Strategies:
http://stoney.sb.org/eno/oblique.html
I love making my little collages for this blog, though I wouldn't call them important art. Nevertheless, piecing together bits of other peoples' work can make fantastic, important work of historical note:
https://www.johnheartfield.com/John-Heartfield-Exhibition/john-heartfield-art/famous-anti-fascist-art/heartfield-posters-aiz
Even though painstakingly cutting out tiny elements from others' images can be a meditative and educational experience, I don't think that using tiny scissors or the lasso tool is what defines the "art" in collage. If you can automate some of this process, it could still be art.
Here's what I do know. Creating an individual bargainable copyright over training will not improve the material conditions of artists' lives – all it will do is change the relative shares of the value we create, shifting some of that value from tech companies that hate us and want us to starve to entertainment companies that hate us and want us to starve.
As an artist, I'm foursquare against anything that stands in the way of making art. As an artistic worker, I'm entirely committed to things that help workers get a fair share of the money their work creates, feed their families and pay their rent.
I think today's AI art is bad, and I think tomorrow's AI art will probably be bad, but even if you disagree (with either proposition), I hope you'll agree that we should be focused on making sure art is legal to make and that artists get paid for it.
Just because copyright won't fix the creative labor market, it doesn't follow that nothing will. If we're worried about labor issues, we can look to labor law to improve our conditions. That's what the Hollywood writers did, in their groundbreaking 2023 strike:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/01/how-the-writers-guild-sunk-ais-ship/
Now, the writers had an advantage: they are able to engage in "sectoral bargaining," where a union bargains with all the major employers at once. That's illegal in nearly every other kind of labor market. But if we're willing to entertain the possibility of getting a new copyright law passed (that won't make artists better off), why not the possibility of passing a new labor law (that will)? Sure, our bosses won't lobby alongside of us for more labor protection, the way they would for more copyright (think for a moment about what that says about who benefits from copyright versus labor law expansion).
But all workers benefit from expanded labor protection. Rather than going to Congress alongside our bosses from the studios and labels and publishers to demand more copyright, we could go to Congress alongside every kind of worker, from fast-food cashiers to publishing assistants to truck drivers to demand the right to sectoral bargaining. That's a hell of a coalition.
And if we do want to tinker with copyright to change the way training works, let's look at collective licensing, which can't be bargained away, rather than individual rights that can be confiscated at the entrance to our publisher, label or studio's offices. These collective licenses have been a huge success in protecting creative workers:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/26/united-we-stand/
Then there's copyright's wildest wild card: The US Copyright Office has repeatedly stated that works made by AIs aren't eligible for copyright, which is the exclusive purview of works of human authorship. This has been affirmed by courts:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/20/everything-made-by-an-ai-is-in-the-public-domain/
Neither AI companies nor entertainment companies will pay creative workers if they don't have to. But for any company contemplating selling an AI-generated work, the fact that it is born in the public domain presents a substantial hurdle, because anyone else is free to take that work and sell it or give it away.
Whether or not AI "art" will ever be good art isn't what our bosses are thinking about when they pay for AI licenses: rather, they are calculating that they have so much market power that they can sell whatever slop the AI makes, and pay less for the AI license than they would make for a human artist's work. As is the case in every industry, AI can't do an artist's job, but an AI salesman can convince an artist's boss to fire the creative worker and replace them with AI:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/29/pay-no-attention/#to-the-little-man-behind-the-curtain
They don't care if it's slop – they just care about their bottom line. A studio executive who cancels a widely anticipated film prior to its release to get a tax-credit isn't thinking about artistic integrity. They care about one thing: money. The fact that AI works can be freely copied, sold or given away may not mean much to a creative worker who actually makes their own art, but I assure you, it's the only thing that matters to our bosses.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/05/13/spooky-action-at-a-close-up/#invisible-hand
#pluralistic#ai art#eerie#ai#weird#henry farrell#copyright#copyfight#creative labor markets#what is art#ideomotor response#mark fisher#invisible hand#uncanniness#prompting
272 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi so, thanks to your tool i was able to figure out that every fic ive ever posted onto ao3 (from 2015 to recent, aside from three fics this last month i just posted) were all scraped, and its absolutely horrifying to me to know my works are being used in this way. this is hundreds of thousands of words of time, and is over 90% of all of the writing ive ever shared online, spread over multiple accounts and fandoms and im just feeling- so dejected. i know youre not an advice blog or anything, and i really appreciate the work youve done to help people find this information. im just curious- do you have any advice when it comes to dealing with this knowledge? i dont want to delete my fics and take them from people who enjoy them, and i want to continue to write and see others read my works. but its just so dejecting knowing what theyre being used for now. that i dont have any control over what is done with my own passion projects because some company can show up and just take it and use it in some environment-poisoning misinformation machine
I wasn't expecting to be ASKED for advice when I made the blog! But I give it my best shot for you guys when I can.
So to ME, it's a bit reassuring to see that the data isn't like. Amazingly collected, if that makes sense. If I were looking for a dataset to generate good writing, a huge thing I would want is a way to know what readers actually liked. For the record, having a low hit or kudos count or whatever does not mean your fic isn't good! (You can have a low hit count because your fandom isn't big or because you're not tagging your fic in a way to help the right people discover it, but the fic can still be amazing.) BUT if I were an outsider not looking to actually read the fics, just figure out what about the writing makes people like them, the top thing I'd be looking for is the stats like the hits, kudos, comments, and bookmarks. Nyuuzyou intentionally tried to exclude that data, which is... an interesting decision.
The choice of forum is telling, too. They chose to upload on Hugging Face, which is for AI hobbyists, not corporate models. These are people like you and me, just doing this as a hobby for fun, and it's pretty unlikely they'll ever create something they can sell from this. Yes, they're killing the environment with it, which I hate, but they're doing it on a much smaller scale than any of the commercial names in AI. Very similar to how you can post a fic and even get tens of thousands of hits and tons of positive interactions, but that doesn't mean you also publish traditional novels and make tens of thousands of dollars.
Again, for me, it also helps to remind myself that hey. They're already out there. Even if I take down all 60-ish of my fics that were hit in this scrape, that data is still out there, but if I delete them, it's ONLY out there as a stupid AI-training dataset, and I've cut out my readers entirely. Deleting the ones that were already scraped doesn't un-scrape them, and to me, it feels like letting the scrapers win if they get my writing AND I don't get to share my writing anymore.
For new writing going forward, that's definitely a place to make a personal decision! I've said a couple times I'm going to keep writing and sharing anyway because I love it, but that's not The One Right Way to do things.
I also am in the same boat as I've seen some people in my notes. A lot of my scraped fics were uh. Not my best work. Like I was prolific in 2018 and man... those fics were not super well-written. Text-based GenAI is trained to learn the order words should appear, based on probabilities. So if there's a lot of bad, boring works in there (and there definitely are! we all start out by posting mediocre writing!), that teaches the AI model to write bad, boring sentences. Most of us aren't tagging our fics in a way to tell a computer which fics are like this, so the AI doesn't know which fics are written by beginners who still don't know how to write well or who don't know English very well yet, and at least from what I know, the AI is going to treat those works like they're just as valid as the 100k+ novels we all know and love. All that comes together to make a shitty AI model that no one really wants to use, even if they're otherwise super pro-AI.
I'll round this off with a silly little book recommendation, but this book seriously changed the way I think about life in general and definitely impacted how I was able to take the scraping well enough and focus on being productive about it instead of just upset. The big takeaway from it is that no one can fully control their circumstances, but everyone has the ability to control the way they react to those circumstances. No one can control AI scrapers being scumbags, but we all get to choose how to respond to it happening.
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Humans now share the web equally with bots, according to a major new report – as some fear that the internet is dying. In recent months, the so-called “dead internet theory” has gained new popularity. It suggests that much of the content online is in fact automatically generated, and that the number of humans on the web is dwindling in comparison with bot accounts. Now a new report from cyber security company Imperva suggests that it is increasingly becoming true. Nearly half, 49.6 per cent, of all internet traffic came from bots last year, its “Bad Bot Report” indicates. That is up 2 per cent in comparison with last year, and is the highest number ever seen since the report began in 2013. In some countries, the picture is worse. In Ireland, 71 per cent of internet traffic is automated, it said. Some of that rise is the result of the adoption of generative artificial intelligence and large language models. Companies that build those systems use bots scrape the internet and gather data that can then be used to train them. Some of those bots are becoming increasingly sophisticated, Imperva warned. More and more of them come from residential internet connections, which makes them look more legitimate. “Automated bots will soon surpass the proportion of internet traffic coming from humans, changing the way that organizations approach building and protecting their websites and applications,” said Nanhi Singh, general manager for application security at Imperva. “As more AI-enabled tools are introduced, bots will become omnipresent.”
238 notes
·
View notes
Note
What are your current plans for your gainer ai tools? Do you want to make movie clips and put gainer sequences together into something bigger (pun intended)? You’ve achieved an impressive level of realism.
I have a few ideas I want to try.
I've tested the open source video generators, and they're all pretty terrible for gainer content. Online platforms are better, but still not great, and they won't work on any photos that show to much skin. Plus, I don't like using closed AI, anyway. I may wait for things to improve before I post much video content.
For now, it'll probably be mostly still photos that I generate.
There are tools for ensuring character consistency from one image to another, and I plan on try to use those to make sequences of images which feature the same character and tell more of a story.
I also have an idea that I may try out soon:
There are also pretrained LoRAs that do split screen images. You can use these right now to put a logo on one side of an image and ask the AI to fill out the other half with somebody wearing it on a shirt, for example.
I want to take such a model and finetune it for weight gain before & after pictures. I would have to collect 100+ examples of before & after weight gain photos to train it, and create captions for them with the before and after weights and photo descriptions. I wonder if the Tumblr gainer community would be willing to supply the data? I've also thought about taking a bunch of weight loss before and after photos and reversing them to train it.
If I did train such a model, I could then use it to take a photo of anybody and ask it to produce the other half with them fatter. I could then offer this as a free service to folks who want to see what they may look like as they gain.
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
Free online courses on Nature -Based Infrastructure
"Two training courses on making a case for and valuing Nature-Based Infrastructure. This training is free of charge.
Participants will learn how to:
Identify nature-based infrastructure (NBI) and its opportunities for climate adaptation and sustainable development.
Make the case for NBI by explaining its potential economic, environmental, and social benefits.
Understand the risk profile and the climate resilience benefits of NBI compared to grey infrastructure.
Explain the basics of systems thinking, quantitative models, spatial analysis, climate data and financial modelling applied to NBI.
Appreciate the results of integrated cost-benefit analyses for NBI.
Use case studies of NBI projects from across the world as context for their work.
This course was developed by the NBI Global Resource Centre to help policy-makers, infrastructure planners, researchers and investors understand, assess, and value nature-based infrastructure. The course familiarizes participants with several tools and modelling approaches for NBI, including Excel-based models, system dynamics, spatial analysis and financial modelling. In addition, the training presents a variety of NBI case studies from across the world.
Why do this course?
This course will help you gain valuable skills and insights which will enable you to:
Gain knowledge and tools for informed infrastructure decision-making, with a focus on advancing nature-based solutions for climate adaptation at a systems level.
Understand and measure the benefits, risks, and trade-offs of nature-based infrastructure.
Understand the importance of systemic thinking for infrastructure planning, implementation, and financing strategies.
Communicate persuasively and effectively with stakeholders to advocate for nature-based infrastructure.
Collaborate with peers around the world and become part of the NBI Global Resource Centre alumni.
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Recently, big corporations like Apple and Nvidia were found to have scraped Youtube to get video transcripts for their AI models. Using an online tool, I was able to compile every hermit i could find who was scraped. Heres the data:
Mumbo was hit the worst with 11 videos stolen
Gem had 4 older videos stolen
Both Scar and False had 1, with Falses being the only one coming up when searching "Hermitcraft" good sign? Maybe
If you find any more, leave them in the replies and I will try to add them. I want to bring awarness to this because it is not only against youtube TOS, but is violating the rights of creators on the platform. I smell a lawsuit indeed.
121 notes
·
View notes
Text
"how do I keep my art from being scraped for AI from now on?"
if you post images online, there's no 100% guaranteed way to prevent this, and you can probably assume that there's no need to remove/edit existing content. you might contest this as a matter of data privacy and workers' rights, but you might also be looking for smaller, more immediate actions to take.
...so I made this list! I can't vouch for the effectiveness of all of these, but I wanted to compile as many options as possible so you can decide what's best for you.
Discouraging data scraping and "opting out"
robots.txt - This is a file placed in a website's home directory to "ask" web crawlers not to access certain parts of a site. If you have your own website, you can edit this yourself, or you can check which crawlers a site disallows by adding /robots.txt at the end of the URL. This article has instructions for blocking some bots that scrape data for AI.
HTML metadata - DeviantArt (i know) has proposed the "noai" and "noimageai" meta tags for opting images out of machine learning datasets, while Mojeek proposed "noml". To use all three, you'd put the following in your webpages' headers:
<meta name="robots" content="noai, noimageai, noml">
Have I Been Trained? - A tool by Spawning to search for images in the LAION-5B and LAION-400M datasets and opt your images and web domain out of future model training. Spawning claims that Stability AI and Hugging Face have agreed to respect these opt-outs. Try searching for usernames!
Kudurru - A tool by Spawning (currently a Wordpress plugin) in closed beta that purportedly blocks/redirects AI scrapers from your website. I don't know much about how this one works.
ai.txt - Similar to robots.txt. A new type of permissions file for AI training proposed by Spawning.
ArtShield Watermarker - Web-based tool to add Stable Diffusion's "invisible watermark" to images, which may cause an image to be recognized as AI-generated and excluded from data scraping and/or model training. Source available on GitHub. Doesn't seem to have updated/posted on social media since last year.
Image processing... things
these are popular now, but there seems to be some confusion regarding the goal of these tools; these aren't meant to "kill" AI art, and they won't affect existing models. they won't magically guarantee full protection, so you probably shouldn't loudly announce that you're using them to try to bait AI users into responding
Glaze - UChicago's tool to add "adversarial noise" to art to disrupt style mimicry. Devs recommend glazing pictures last. Runs on Windows and Mac (Nvidia GPU required)
WebGlaze - Free browser-based Glaze service for those who can't run Glaze locally. Request an invite by following their instructions.
Mist - Another adversarial noise tool, by Psyker Group. Runs on Windows and Linux (Nvidia GPU required) or on web with a Google Colab Notebook.
Nightshade - UChicago's tool to distort AI's recognition of features and "poison" datasets, with the goal of making it inconvenient to use images scraped without consent. The guide recommends that you do not disclose whether your art is nightshaded. Nightshade chooses a tag that's relevant to your image. You should use this word in the image's caption/alt text when you post the image online. This means the alt text will accurately describe what's in the image-- there is no reason to ever write false/mismatched alt text!!! Runs on Windows and Mac (Nvidia GPU required)
Sanative AI - Web-based "anti-AI watermark"-- maybe comparable to Glaze and Mist. I can't find much about this one except that they won a "Responsible AI Challenge" hosted by Mozilla last year.
Just Add A Regular Watermark - It doesn't take a lot of processing power to add a watermark, so why not? Try adding complexities like warping, changes in color/opacity, and blurring to make it more annoying for an AI (or human) to remove. You could even try testing your watermark against an AI watermark remover. (the privacy policy claims that they don't keep or otherwise use your images, but use your own judgment)
given that energy consumption was the focus of some AI art criticism, I'm not sure if the benefits of these GPU-intensive tools outweigh the cost, and I'd like to know more about that. in any case, I thought that people writing alt text/image descriptions more often would've been a neat side effect of Nightshade being used, so I hope to see more of that in the future, at least!
246 notes
·
View notes
Text
So, a couple of great articles I found that give some Good News/Bad News wrt the issue of AI energy usage.
Good News: Making individual gens is actually relatively low-energy, at least compared to other uses of computers and online media including digital art, so people using it to make wizard-related shitposts or fan trailers for a remake of Robot Monster aren't really contributing much more to cooking the earth than the rest of us.
Bad News: There is an actual problem with the energy usage, but it's at the corporate level of training, due to making models that do way too much, in a way that's extremely redundant due to a bunch of different companies trying to make their own proprietary AI.
Which, I don't know the details ( @therobotmonster probably would), but it seems to imply data-wise that stuff like Midjourney is actually one of the less egregious cases given its hyper-specialized extremely targeted nature.
But that aside, the larger point is, dumb debate about "normalization" aside (tho that's for another post), if you're going to be protesting it's probably worth doing less "yelling at small creators using the tools" and more looking into the non-art side of AI bullshit.
And, while I cannot speak directly for all of them, I'm sure the folks at @are-we-art-yet would probably be happy to help, given their knowlege of the subject and general hatred of capitalist use of AI...
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
What to make of the so-called Department of Government Efficiency at this stage of the Trump administration? Elon Musk has purportedly stepped away from his government duties. Courts are trying to strike down some of DOGE’s most egregious efforts. It may seem as though the worst excesses of DOGE have passed, replaced by something closer to a stasis.
This isn’t true. Not even close.
While the image of DOGE most likely burned into your retina is that of Elon Musk wielding a literal chain saw, the theatrics belie an organization that has quietly permeated all corners of the federal government. More than that, it’s increasingly clear that its objectives are now indistinguishable from that of the broader Trump administration. Removing DOGE at this point would be like trying to remove a drop of food coloring from a glass of water.
And what is it doing from its perch? Not loudly, clumsily attempting to fire thousands of government employees, but working in secrecy to collect, combine, and analyze data that was never intended to comingle. Using that information to find and surveil immigrants. Giving the Justice Department an assist on alleged voter fraud indictments.
Even if Musk claims he’s stepping away—though he met with House Republicans just this week—his lieutenants are still firmly in place at the agencies that control the federal workforce and regulate his companies. DOGE is reportedly using his xAI Grok chatbot to parse sensitive data, which potentially means millions of Americans’ personal information is doubling as training data for the model. A 19-year-old who goes by Big Balls online is still a central figure.
Meanwhile, the victories against DOGE may be short-lived. The Trump administration used it as a battering ram to push its policies through with overwhelming force. While the courts have held firm in some cases—just this week, a judge declared DOGE’s takeover of the United States Institute of Peace to be unlawful—the policies still exist, and there are other ways to achieve them. The Wall Street Journal reported recently that director of the White House Office of Management and Budget Russell Vought would pick up DOGE’s cost-cutting mantle in the post-Musk era. Expect him to wield not a hammer but a finely edged blade.
This has always been the plan. Vought is the architect of Project 2025, the policy road map that DOGE has been following turn by turn. He has been explaining for months what happens after DOGE’s first assault.
“We’re going to use all of our executive tools to make those savings permanent,” Vought said in an interview with Fox Business anchor Larry Kudlow on March 11. “We’re going to do everything we can to make sure that those are not merely something that goes on a website, but becomes permanent … We’ll work with Congress to do it, but we’ve also been aware the extent to which Congress has had a hard time passing cuts of any magnitude, and so what we want to do is everything we can to use presidential tools to bank those savings home.”
The only part of this that hasn’t gone to plan is that Congress may be more amenable than Vought gave it credit for; the House of Representatives managed to pass Donald Trump’s One Big Beautiful Bill this week, complete with provisions that cut the social safety net into ribbons.
In some ways, DOGE is even more dangerous when it’s boring. It has always been a tool, not an engine unto itself. It’s no longer useful to think of it as a separate entity, as a tech billionaire’s personal strike force. It’s a means to an end, one part of a larger project to gut the federal government and redefine the social contract. It’s important to keep a close eye on DOGE, to continue shining a light on what it does in the dark. But never lose sight of that project. A fool with a chain saw is nothing compared to the full power of the state.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
saw someone ask for more clarification on how to read the SPC's outlook maps, so here's a little guide :)
The Storm Prediction Center (SPC) is an agency a part of the National Weather Service (NWS), which in turn is a branch of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Located in Norman, Oklahoma, the heart of the United States's research into severe weather, the SPC's main goal is to forecast the probability of severe weather happening across the country.
Their convective outlooks are these maps that you might see floating around online:

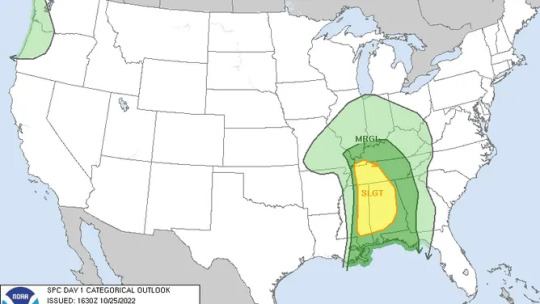
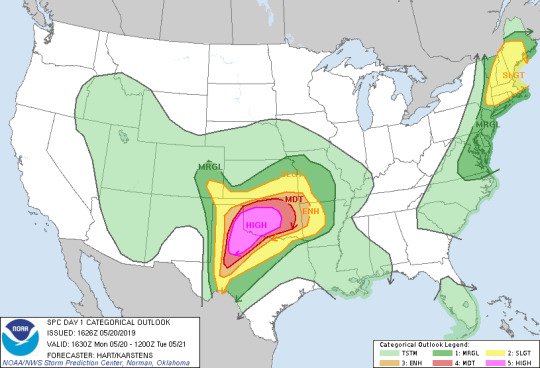
As you can note by the ledgers present in the bottom corners of these images, each color corresponds to a level of risk on the probability of severe weather occurring within a given area, numbered 1-5.
Light green (not labeled as Marginal or MRGL) = 0/5, chance for thunderstorms, some heavy rain, strong winds, and possibly some small hail.
Darker green (Marginal or MRGL) = 1/5, low, but present risk for severe thunderstorms, including hail, damaging winds, and possible tornadoes.
Yellow (Slight or SLGT) = 2/5, a more present risk for severe thunderstorms, including hail, damaging winds, and possible tornadoes.
Orange (Enhanced or ENH) = 3/5, a higher risk for severe thunderstorms, including hail, damaging winds, and possible tornadoes.
Red (Moderate or MDT) = 4/5, more confidence for the risk of severe thunderstorms, including damaging hail, damaging winds, and possible strong tornadoes.
Pink (High/HIGH) = 5/5, very high probability for the risk of severe thunderstorms, including damaging hail, damaging winds, and possible strong, long-track tornadoes.
--> Helpful links!
SPC Outlook Map
SPC Official Twitter Account
NWS Official Twitter Account
These maps are used to help predict the probability of severe weather happening up to about 3 days in advance. Days 1-3 are their most accurate, however, it is important to note that weather is ever-changing, and even Day 1 outlooks, or the day of, can change throughout as more data comes in via weather models or even on-the-ground storm chasers.
At the bottom of every single outlook map, is a detailed mesoscale analysis done by a meteorologist at the NWS breaking down the schematics by location of the system moving through that day. As an example, this is the discussion for today, March 15, 2025:


These are all extremely helpful tools that are completely FREE to use! If you live in an area that is prone to severe weather, I would highly recommend you get into the habit of becoming more weather aware and familiarizing yourself with these maps to keep yourself and your loved ones safe.
Below, I will break down a couple more tabs available for further analysis. These will be under the cut, as just a little extra for those who are especially curious ;)
The SPC additionally publishes the percent risk of these storms coming with damaging winds, damaging hail, and tornadoes. As an example, I will present and explain the risks associated with the storms happening today, March 15, 2025:
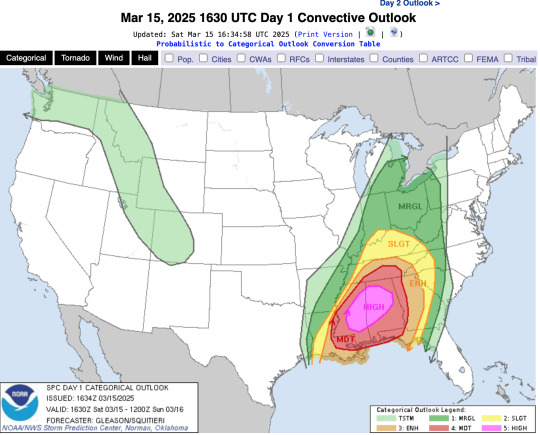
As you can see, all the parameters have been met in Alabama and Mississippi that warrant a level 5/5, or a High Risk that severe weather will occur within the pink-shaded area, with the risk descending as you go further North into the Ohio River Valley. Now, let's look at the probability of a tornado occurring within these areas:
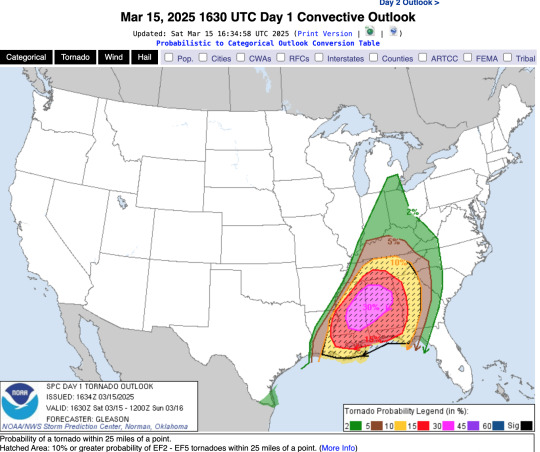
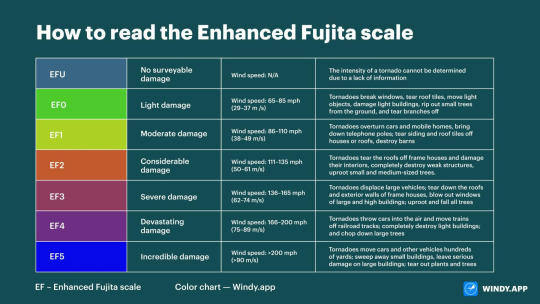
As noted by the table at the bottom, there is a 30% chance of a tornado occurring within the pink-shaded area. Not only that, the entire stretch crossing all the way from Louisiana up to Tennesee, is marked by these black dots. These are hatches, and this indicates that the tornadoes that could occur, have a higher probability of being rated an EF2+. Tornadoes are rated on the Enhanced Fujita scale, going from EF0-EF5:
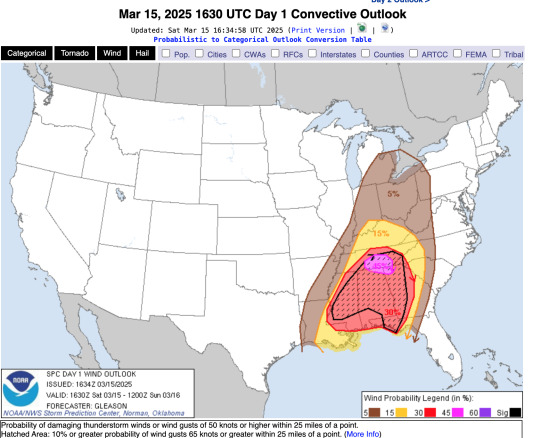
You can also look at the probability of damaging winds:
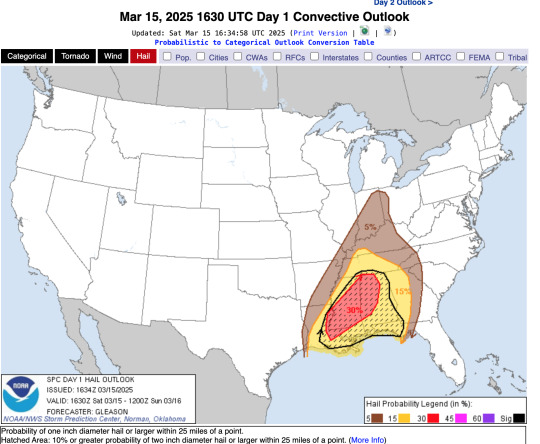
And damaging hail:
#severe weather#science#weather#hopefully this is helpful to some folks!#this is a side passion of mine and anything that will help keep people safe during outbreaks like this is the ideal!#also highly rec Ryan Hall Y'all!#a youtuber that hosts livestreams during severe weather events#he works with meteorologists and storm chasers to provide accurate readings and warnings and donates all profits to severe weather relief!
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
So I know that the address of Nick Fuentes is being posted around (I’m keeping it off of this post to prevent possible removal, but it’s all over if you look his name up on Tumblr). It appears that Google is censoring anything related to that specific address. It’s blurred out on Google Maps (though there are pictures uploaded right next to it), and the only search results I got were real estate listings.
This is your friendly reminder that Big Tech is not your friend and they will comply with the oppressors. I know it’s not the most ideal solution, but if you’re concerned about privacy and security in the upcoming years, look into alternate services for your daily online life. Proton Mail is a great service for email, and they offer other things like VPN and cloud storage. I pay for a business account (about $15 US a month) because I use extra email addresses and personal domain names, but there are cheaper or free plans available.
You can also replace most of the online tools that Google, Apple, and Microsoft provide with third party or self-hosted services like Nextcloud. I’m tech enough that I set up my own private server with Nextcloud, so I’m in control of the flow and location of my data. If you have tech inclined friends, you could discuss setting up a shared server, or look into alternate solutions.
Our digital footprints are becoming a commodity which can be sold to the highest bidder or used to train data models. While it isn’t always feasible, I urge you all to look into alternatives and make whatever changes fit your life the best. While it’s not always feasible to entirely get rid of Google, Microsoft, Apple, and/or Amazon from our lives, we can take steps to minimize what they can collect from us.
27 notes
·
View notes