#oxygen 2021
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#alexandre aja#crawl#crawl 2019#the hills have eyes#the hills have eyes (2006)#high tension#haute tension#piranha 3d#maniac#maniac 2012#oxygen 2021#oxygen#mirrors#mirrors 2008#p2#p2 2007#horror#horror films#horror film#horror film poll#horror poll#poll#horror movie#horror movies#horror movie poll#movie#movies#film#films#film poll
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
heyyheyehey i have a question for the fanfic writers ☝️☝️☝️ if you delete a fic would you want any readers that downloaded it to delete it too ?? bc there's this one fanfic that genuinely changed the course of my life and gave meaning to my existence but the author deleted it and all their accounts 4 years ago and idkk 💔💔
#ive been trying to find the author for the longest time but there's NOTHING they literally disappeared from social media in 2021#it was also more complicated than that bc the fic was published first in 2019~ and i read it and felt the basis of my reality changed but#the author deleted that account snd i would go on a crazy hunt for like a year for the author's twt and i finally found them and they had#a new ao3 acc but they hadnt re-uploaded the fic i loved UNTIL they reuploaded it in 2020 and deleted it like a few weeks laters but#i got to download it and now it's in my drive as my most precious possession#also if any1s curious it was a bts fanfic im not even into bts anymore that train left me in 2021 and it was about space and future and stuf#and one of the bts boys gets lost on one of jupiter's moons snd there are like 50 of those so he doesnt know which one it is and has to call#the interspacial callcenter to get help and they get to talking with another bts boy who is trying his best to figure out where tf this guy#is before his oxygen runs out
0 notes
Text
Although dam removals have been happening since 1912, the vast majority have occurred since the mid-2010s, and they have picked up steam since the 2021 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, which provided funding for such projects. To date, 806 Northeastern dams have come down, with hundreds more in the pipeline. Across the country, 2023 was a watershed year, with a total of 80 dam removals. Says Andrew Fisk, Northeast regional director of the nonprofit American Rivers, “The increasing intensity and frequency of storm events, and the dramatically reduced sizes of our migratory fish populations, are accelerating our efforts.”
Dam removals in the Northeast don’t generate the same media attention as massive takedowns on West Coast rivers, like the Klamath or the Elwha. That’s because most of these structures are comparatively miniscule, built in the 19th century to form ponds and to power grist, textile, paper, saw, and other types of mills as the region developed into an industrial powerhouse.
But as mills became defunct, their dams remained. They may be small to humans, but to the fish that can’t get past them “they’re just as big as a Klamath River dam,” says Maddie Feaster, habitat restoration project manager for the environmental organization Riverkeeper, based in Ossining, New York. From Maryland and Pennsylvania up to Maine, there are 31,213 inventoried dams, more than 4,000 of which sit within the 13,400-square-mile Hudson River watershed alone. For generations they’ve degraded habitat and altered downstream hydrology and sediment flows, creating warm, stagnant, low-oxygen pools that trigger algal blooms and favor invasive species. The dams inhibit fish passage, too, which is why the biologists at the mouth of the Saw Kill transported their glass eels past the first of three Saw Kill dams after counting them...
Jeremy Dietrich, an aquatic ecologist at the New York State Water Resources Institute, monitors dam sites both pre- and post-removal. Environments upstream of an intact dam, he explains, “are dominated by midges, aquatic worms, small crustaceans, organisms you typically might find in a pond.” In 2017 and 2018 assessments of recent Hudson River dam removals, some of which also included riverbank restorations to further enhance habitat for native species, he found improved water quality and more populous communities of beetles, mayflies, and caddisflies, which are “more sensitive to environmental perturbation, and thus used as bioindicators,” he says. “You have this big polarity of ecological conditions, because the barrier has severed the natural connectivity of the system. [After removal], we generally see streams recover to a point where we didn’t even know there was a dam there.”

Pictured: Quassaick Creek flows freely after the removal of the Strooks Felt Dam, Newburgh, New York.
American Rivers estimates that 85 percent of U.S. dams are unnecessary at best and pose risks to public safety at worst, should they collapse and flood downstream communities. The nonprofit has been involved with roughly 1,000 removals across the country, 38 of them since 2018. This effort was boosted by $800 million from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. But states will likely need to contribute more of their own funding should the Trump administration claw back unspent money, and organizations involved in dam removal are now scrambling to assess the potential impact to their work.
Enthusiasm for such projects is on the upswing among some dam owners — whether states, municipalities, or private landholders. Pennsylvania alone has taken out more than 390 dams since 1912 — 107 of them between 2015 and 2023 — none higher than 16 feet high. “Individual property owners [say] I own a dam, and my insurance company is telling me I have a liability,” says Fisk. Dams in disrepair may release toxic sediments that potentially threaten both human health and wildlife, and low-head dams, over which water flows continuously, churn up recirculating currents that trap and drown 50 people a year in the U.S.
Numerous studies show that dam removals improve aquatic fish passage, water quality, watershed resilience, and habitat for organisms up the food chain, from insects to otters and eagles. But removals aren’t straightforward. Federal grants, from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration or the Fish and Wildlife Service, favor projects that benefit federally listed species and many river miles. But even the smallest, simplest projects range in cost from $100,000 to $3 million. To qualify for a grant, be it federal or state, an application “has to score well,” says Scott Cuppett, who leads the watershed team at the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation’s Hudson River Estuary Program, which collaborates with nonprofits like Riverkeeper to connect dam owners to technical assistance and money...

All this can be overwhelming for dam owners, which is why stakeholders hope additional research will help loosen up some of the requirements. In 2020, Yellen released a study in which he simulated the removal of the 1,702 dams in the lower Hudson watershed, attempting to determine how much sediment might be released if they came down. He found that “the vast majority of dams don’t really trap much sediment,” he says. That’s good news, since it means sediment released into the Hudson will neither permanently worsen water quality nor build up in places that would smother or otherwise harm underwater vegetation. And it shows that “you would not need to invest a huge amount of time or effort into a [costly] sediment management plan,” Yellen says. It’s “a day’s worth of excavator work to remove some concrete and rock, instead of months of trucking away sand and fill.” ...
On a sunny winter afternoon, Feaster, of Riverkeeper, stands in thick mud beside Quassaick Creek in Newburgh, New York. The Strooks Felt Dam, the first of seven municipally owned dams on the lower reaches of this 18-mile tributary, was demolished with state money in 2020. The second dam, called Holden, is slated to come down in late 2025. Feaster is showing a visitor the third, the Walsh Road Dam, whose removal has yet to be funded. “This was built into a floodplain,” she says, “and when it rains the dam overflows to flood a housing complex just around a bend in the creek.” ...
On the Quassaick, improvements are evident since the Strooks dam came out. American eel and juvenile blue crabs have already moved in. In fact, fish returns can sometimes be observed within minutes of opening a passageway. Says Schmidt, “We’ve had dammed rivers where you’ve been removing the project and when the last piece comes out a fish immediately storms past it.”
There is palpable impatience among environmentalists and dam owners to get even more removals going in the Northeast. To that end, collaborators are working to streamline the process. The Fish and Wildlife Service, for example, has formed an interagency fish passage task force with other federal agencies, including NOAA and FEMA, that have their own interests in dam removals. American Rivers is working with regional partners to develop priority lists of dams whose removals would provide the greatest environmental and safety benefits and open up the most river miles to the most important species. “We’re not going to remove all dams,” [Note: mostly for reasons dealing with invasive species management, etc.] says Schmidt. “But we can be really thoughtful and impactful with the ones that we do choose to remove.”
-via Yale Environment 360, February 4, 2025
#rivers#riparian#united states#north america#northeast#pennsylvania#massachusetts#new york#dam#dam removal#good news#hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
In January 2021, I got sick. I tested negative for Covid, but I assumed it had to be that, given the severity and duration. It lasted something crazy like four weeks, and after that I had this crunchy lingering cough and a host of other issues that just never went away, namely incredible fatigue.
I was always tired, never woke feeling rested, and started napping more and more, for hours at a time, sometimes three naps a day. I would sit to work on art and just tip sideways on the sofa. I'd be so tired I'd lay on the floor for a moment and be out instantly. My memory was failing me more and more, and the brain fog was constant. I felt really, clearly stupider, and the people in my life started to resent how much I slept. It was ruining my life.
I figured this was long Covid. My doctor treated me for post-nasal drip, allergies, mild hypothyroidism, vitamin deficiencies, depression. I ate better, exercised, got enough sleep. Nothing made me less tired.
Finally I saw a sleep specialist, answered a lot of questions, and did a sleep study at home. Found out I have pretty severe sleep apnea -- I will stop breathing roughly 30 times an hour. She hooked me up with a CPAP machine -- a nose snorkel -- and it became my new best friend. It's actually pretty comfortable, quiet as a whisper, and I finally get enough oxygen when I sleep. I sleep like the dead, not a moment of unrest until the morning.
The trouble was, I was still tired. Still falling asleep randomly, still losing motor function when drowsy. My sleep specialist diagnosed me with narcolepsy.
Apparently sometimes, when you get the flu and it hits you just right, it can trigger narcolepsy. Way back in January 2021, what I thought was Covid was a nasty narcolepsy activator that's been fucking with me ever since.
My doc put me on a stimulant specifically for narcolepsy, and it does work, but it's not a miracle cure. I'm still tired, but I fall asleep a lot less frequently, and I can fight through it. I told my doc that I still got very tired occasionally, and she said, "Sometimes a nap can help you get through the rest of the day. It's okay to nap." Being given that permission after years of feeling guilty and ashamed of sleeping so much made me cry on the spot.
It's a work in progress. I feel like I have my brain back, at least. But if you find yourself with symptoms like mine, see if you can ask your doctor about doing a sleep study. I think narcolepsy is more common than we think, and you don't have to feel like you're doomed to it.
763 notes
·
View notes
Text

Metriorhynchids were a group of fully marine crocodyliforms known from the mid-Jurassic to the early Cretaceous of Europe and the Americas. They were the most aquatic-adapted of all known archosaurs, with streamlined bodies, smooth scaleless skin, small front flippers, larger hind flippers, and shark-like tail flukes. They may also have been endothermic, and might even have given live birth at sea rather than laying eggs.
Rhacheosaurus gracilis here was a metriorhynchid that lived in warm shallow waters around what is now Germany during the late Jurassic, about 150 million years ago. Around 1.5m long (~5'), its long narrow snout lined with delicate pointed teeth suggests it fed on small soft-bodied prey, a niche partitioning specialization that allowed it to coexist with several other metriorhynchid species in the same habitat.
Unlike most other marine reptiles metriorhynchids didn't have particularly retracted nostrils, which may have had a limiting effect on their efficiency as sustained swimmers since higher-set nostrils make it much easier to breathe without having to lift the whole head above the surface. The lack of such an adaptation in this group may be due to their ancestors having a single nasal opening formed entirely within the premaxilla bones at the tip of the snout, uniquely limiting how far it could easily shift backwards – other marine reptiles had nostrils bound by the edges of multiple different bones, giving them much more flexibility to move the openings around.
(By the early Cretaceous a close relative of Rhacheosaurus did actually evolve nostrils bound by both the premaxilla and the maxilla, and appeared to have started more significant retraction, but unfortunately this only happened shortly before the group's extinction.)
Metriorhynchids also had well-developed salt glands in front of their eyes, but the large sinuses that accommodated these glands may have made their skulls ill-suited to deep diving, being more susceptible to serious damage from pressure changes and restricting their swimming to near-surface waters only.
Preserved skin impressions in some metriorhynchid fossils show several unusual "irregularities", including curl shapes, small bumps, and cratering. It's unknown what exactly caused these marks, but they may represent scarring from external parasites such as lampreys and barnacles.
———
NixIllustration.com | Tumblr | Patreon
References:
Andrade, Marco BD, and Mark T. Young. "High diversity of thalattosuchian crocodylians and the niche partition in the Solnhofen Sea." 56th Symposium of Vertebrate Palaeontology and Comparative Anatomy, 2008. https://svpca.org/years/2008_dublin/abstracts.pdf#page=14
Séon, Nicolas, et al. "Thermophysiologies of Jurassic marine crocodylomorphs inferred from the oxygen isotope composition of their tooth apatite." Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 375.1793 (2020): 20190139. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2019.0139
Spindler, Frederik. "Live Birth in a Jurassic Marine Crocodile." Abstracts of the 90th Annual Meeting of the Paläontologische Gesellschaft, 2019. https://www.palaeontologie.geowissenschaften.uni-muenchen.de/pdfs/palges2019_abstracts.pdf#page=141
Spindler, Frederik, et al. "The integument of pelagic crocodylomorphs (Thalattosuchia: Metriorhynchidae)" Palaeontologia Electronica 24.2 (2021): a25. https://doi.org/10.26879/1099
Young, Mark T., et al. "Convergent evolution and possible constraint in the posterodorsal retraction of the external nares in pelagic crocodylomorphs." Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 189.2 (2020): 494-520. https://doi.org/10.1093/zoolinnean/zlaa021
Young, Mark T., et al. "Skull sinuses precluded extinct crocodile relatives from cetacean-style deep diving as they transitioned from land to sea." Royal Society Open Science 11.10 (2024): 241272. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.241272
Wikipedia contributors. “Metriorhynchidae” Wikipedia, 12 Nov. 2024, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metriorhynchidae
Wikipedia contributors. “Rhacheosaurus” Wikipedia, 02 Dec. 2024, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rhacheosaurus
#science illustration#paleontology#paleoart#palaeoblr#rhacheosaurus#metriorhynchidae#thalattosuchia#crocodyliformes#crocodylomorpha#pseudosuchia#archosaur#art#marine reptile#lamprey#barnacle#parasite
558 notes
·
View notes
Text
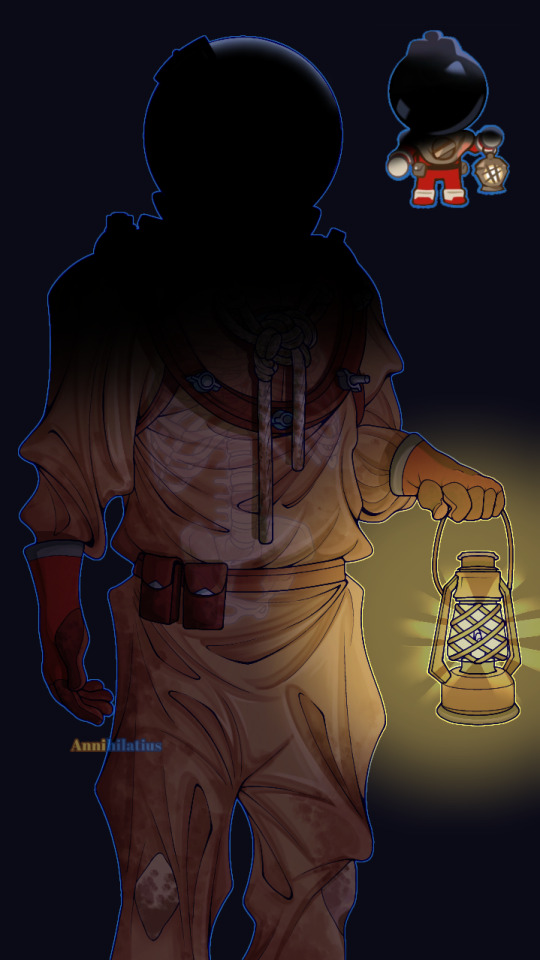
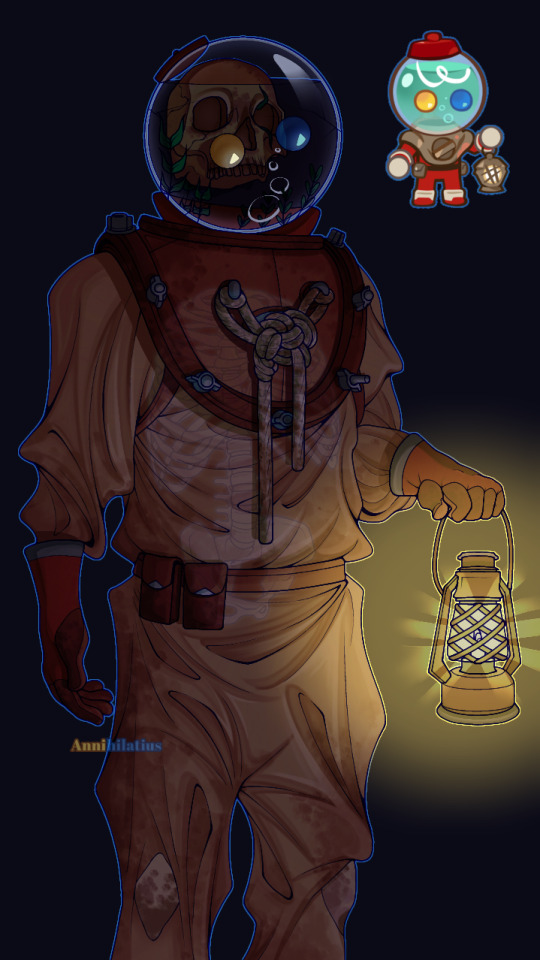
Candy Diver human design I did (the images wouldn't load in the correct order I placed them as but whatever)


Uhhj what do I say.. I think the first and last time I've ever drawn fanart for this game was back in September/October 2021? I don't play CRK for the lore or characters really, even if sometimes the stories are engaging or I like some of the characters. I play because it's fun. But ... I watched Legend Of The Duskgloom Sea a few days ago, and immediately knew I just HAD to draw Candy Diver. Something about them makes my neurons activate I can't help it I have a disease RAAHHHH!
@glitchven Just cause you're my only mutual that posts abt this game

Alternative versions and an explanation for my design decisions and fan made lore for it under the cut (spoilers for Legend Of The Duskgloom Sea)
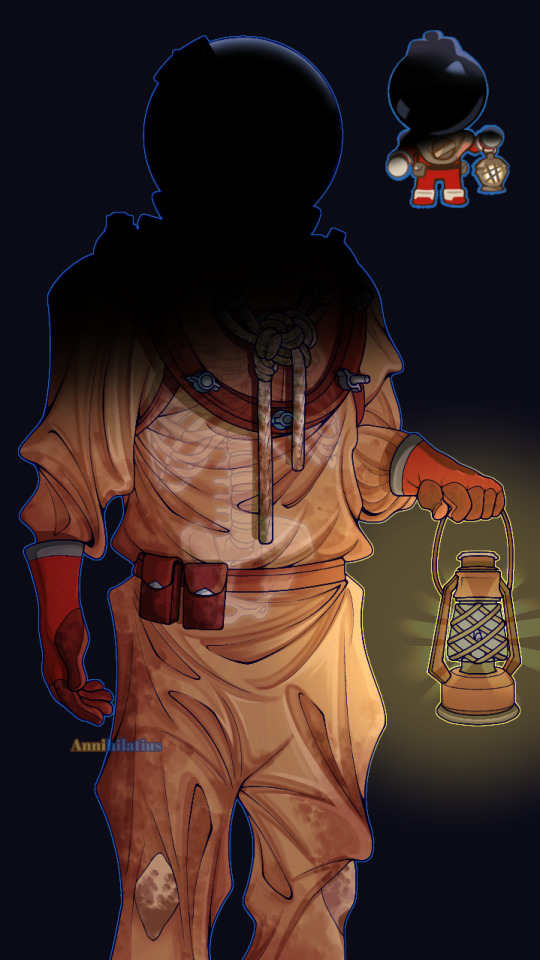
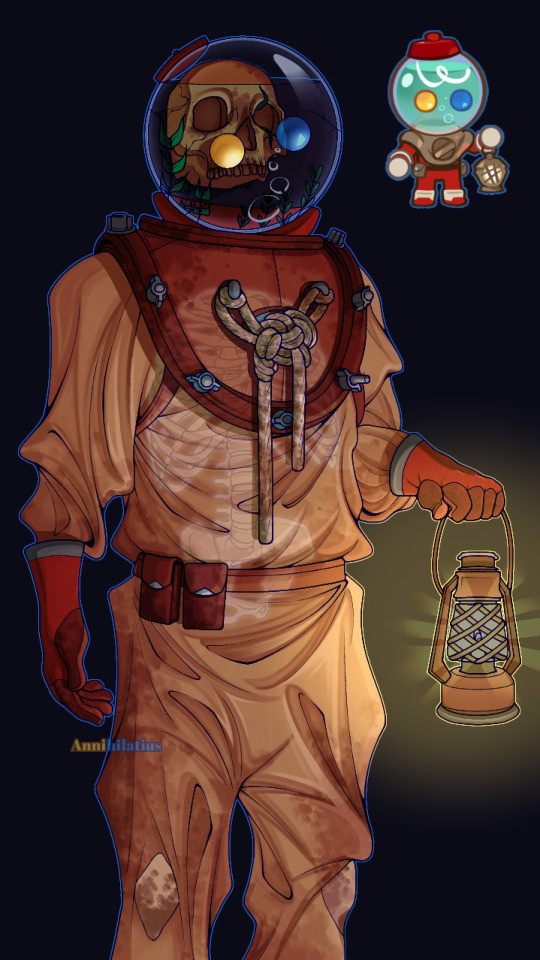
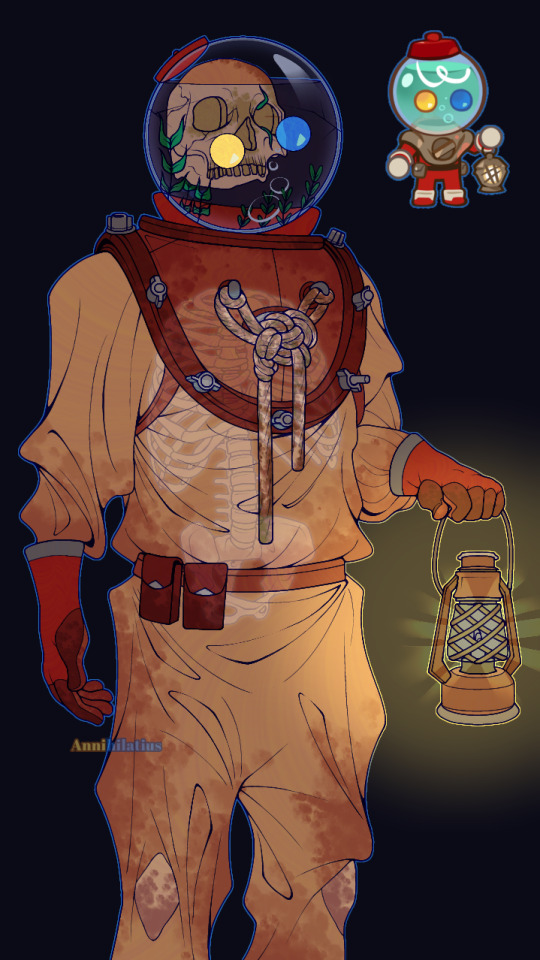



(In the context of being a human) Candy Diver died sometime around the 1920s-30s, when, on a diving expedition looking for treasures, went too deep and realized it after it was too late, eventually running out of breatheable oxygen before reaching the surface (the deeper you go, the more disoriented you get. Humans can barely handle 40m). As a ghost in the Duskgloom Sea, they still wear the very same suit they died in, which is why it's so stained, yellowed, and dirty (realistically it'd be even worse than this), also explaining why their body has decomposed into nothing but a skeleton.
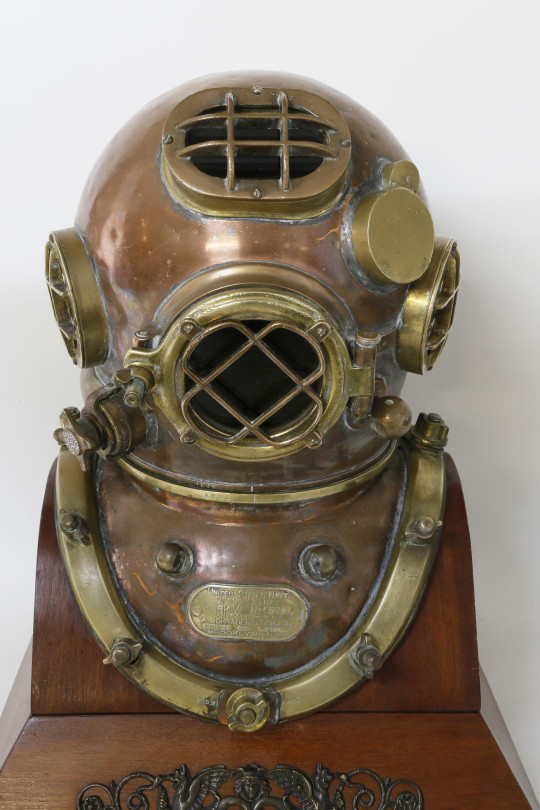
The lantern is some random junk they found they somehow managed to get working. Their original helmet isn't the one you see here, though, because I specifically designed them to *actually* be a deep sea diver; and this is pretty accurate to what they wore, except, of course, they didn't use gumball machines as helmets. Not long after dying and becoming a ghost they lost their helmet, and had to settle with a discarded gumball machine as a replacement. They figured out a way to weld the two parts together (the odd red thing that connects the empty space between the helmet and the shoulderpiece) so it could come on and off. Their original helmet would have looked like this (Mark V divers helmet):

The name "Candy Diver" is one adopted after the fact (either by themself or given to by other people), I'd imagine they were named something completely different before dying
Thinking harder about the whole Candy Diver being dead thing, I thought it would be really cool to take that in a more grotesque direction. Even though now that's it's finished, it (the design) is extremely tame (at least to me, I invisoned them as being more menacing considering the skull, but I've learned now that it's impossible to make a character that has gumballs for eyes scary or intimidating in any way lmao), Candy Diver has SO much potential for body horror and the like, that the game completely strays away from in favor of making them cute (which is incredibly affective btw).
Instead of them just being a ghost who was born from their psychical form dying (most likely), I interpreted them as more of a walking corpse. It may not translate well in the drawing, but they're meant to be hunched over from the constant pressure of how heavy their suit is. They walk slowly but loudly across the seafloor, also because of the weight slowing them down. An odor of death follows them wherever they go after decades of wearing the same clothes and the rotting of what was once their body. Their bones began to decay as well after a time, and eventually they lost their jaw bone, which is why they can't speak (but even when they *could*, I still imagine them as being very very semiverbal anyway. Because autism)
#v.jpg#Don't say it don't say it don't say it don't say it don't say it don't say it#... IS THIS A BIOSHOCK REFERENC--#Can someone please tell me they see the vision... Candy Diver could've been in a Big Daddy suit#REMEMBER WHAT THEY TOOK FROM YOU (“you” as in me)#Also they're 5'3 in this design if you care#Candy Diver Cookie#Candy Diver#C. Caviar and Black Pearl are also there somewhat#Cookie Run#Cookie Run Kingdom#CRK#Cookie Run fanart#CRK fanart
255 notes
·
View notes
Text
You can definitely argue that current case levels are likely way higher than are being reported because testing has decreased but it is objectively not true that the current surge or even the surge over the winter were/are "just as bad as the ones in 2020/2021". During those surges we had mass graves.
A lot of people have really forgotten how bad covid was in 2020/2021 and weirdly enough that includes even the most super hardline covid conscious people
#remember in 2021 when the entire country of india was running out of medical oxygen. hello!!#covid is still here and its still really fucking bad but its also definitely better than it was. you can't just say shit
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Four years ago today, thousands of rioters, incited by Donald Trump, violently stormed the Capitol in an effort to overturn the results of a democratic election.
This is because they hate democracy, the United States, and dissenting views. Don't let them forget what they are and what they did. They committed a violent, deadly autocoup attempt in flagrant violation of the United States Constitution they claim to love. Donald Trump betrayed his oath of office and for the first time in the history of the United States of America, we didn't have a peaceful transition of power.
Don't let them live it down. Don't let them erase it. On January 6th, 2021, they let their mask down and people died.














This is the Republican Party on display, ladies and gentlemen. Their true face. Hateful, violent, anti-American cowards who will kill and steal and riot before they acknowledge that they lost. Led by the most cowardly, sniveling, pathetic, arrogant piece of rotting dogshit to inhale oxygen in US politics.
Don't let them forget what they did. Don't forget what they are underneath all the lies and obfuscations.
They're fascists, plain and simple.
174 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved on our archive (Daily updates!)
An older (published in January 2024) but interesting and comprehensive look at long Covid's effect on Latino families and communities in the US.
By Lygia Navarro and Johanna Bejarano
Editor’s note: This story first appeared on palabra, the digital news site by the National Association of Hispanic Journalists. It is part of a series produced in partnership between palabra and Northwest Public Broadcasting (NWPB) with the collaboration of reporters Lygia Navarro and Johanna Bejarano. *Some people interviewed for this article requested anonymity to discuss private health issues.
Victoria* is already exhausted, and her story hasn’t even begun. It’s late January 2021 in rural Sunnyside, Washington. The town of 16,000 people is a sleepy handful of blocks flecked with pickup trocas, churches on nearly every corner, and the twangs of Clint Black and Vicente Fernández. Geometric emerald chunks of farmland encircle the town.
Thirty-nine-year-old Victoria drags herself back and forth to her parents’ bedroom in a uniform of baggy burgundy sweatpants, scarf, knit hat and mask. Always a mask. As the eldest sibling, her unspoken job is to protect the family. But COVID-19 hits before they can get vaccinated.
When Victoria’s mamá got sick and quickly infected her papá, Victoria quarantined them. She shut them in their room, only cracking the door briefly to slide food in before retreating in a fog of Lysol.
Working in the health field, Victoria knows if they make it through the first 14 days without hospitalization, they will likely survive. Yet, caregiving drains her: Keeping track of fevers. Checking oxygen saturation. Making sure they’re drinking Pedialyte to stay hydrated. Worrying whether they will live or die.
Five days in, COVID comes for Victoria. Hard. Later, when she repeatedly scrutinizes these events, Victoria will wonder if it was the stress that caused it all — and changed her life forever.
At the pandemic’s onset, Victoria’s family’s work dynamics fit the standard in Sunnyside, where 86% of residents are Latino. “Keeping the members of your household safe — it was hard for a lot of families,” Victoria says. Living in multigenerational homes, many adult children, who’d grown up in the United States with access to education, had professional jobs, and switched to working from home. Their immigrant elders, who’d often only been able to finish fourth grade, braved the world to toil in fields, produce packing plants, supermarkets, or delivery trucks. As Leydy Rangel of the UFW Foundation puts it: “You can’t harvest food through Zoom.”
More than three decades ago, when 6-year-old Victoria’s family migrated from rural northern Mexico to this fertile slip of land cradling the zigzagging Yakima River, their futures promised only prosperity and opportunity.
According to oral histories of the Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakama Nation — who white colonizers forced out of the Yakima Valley in 1855 — the valley’s fecund lands have fed humans since time immemorial. Soon after the Yakamas’ removal to a nearby reservation, settler agriculture exploded.
By World War II, employers were frantic to hire contracted bracero laborers from Mexico — themselves descendants of Indigenous ancestors — to harvest the valley’s bounty of asparagus, pears, cherries and other cornucopia. This was how Victoria’s family arrived here: her abuelo and his brother had traveled back and forth to Washington as braceros decades before.
Victoria’s path took similar twists, in a 21st century, first-gen way. She moved all over the country for her education and jobs, then returned before the pandemic, bringing a newfound appreciation for the taste of apples freshly plucked from a tree that morning, and for the ambrosial scent of mint and grapes permeating the valley before harvest.
Today, agriculture is the largest industry fueling the Yakima Valley, the country’s twelfth-largest agriculture production area. Here, 77% of the nation’s hops (an essential ingredient in beer) and 70% of the nation’s apples are grown. Latinos, who constitute more than half of Yakima County’s population, power the agricultural industry.
While the area’s agricultural enterprises paid out $1.1 billion in wages in 2020, 59% of the low-wage agriculture jobs are held by undocumented folks and contracted foreign seasonal laborers doing work many Americans spurn. Latinos here live on median incomes that are less than half of white residents’, with 16% of Latinos living in poverty. Also in 2020: as they watched co-workers fall ill and die, Latino farmworkers repeatedly went on strike protesting employers’ refusals to provide paid sick leave, hazard pay and basic COVID protections like social distancing, gloves and masks.
“Every aspect of health care is lacking in the valley,” Yakima Herald-Republic health reporter Santiago Ochoa tells me.
In interview after interview, Yakima Valley residents and health care workers sketch in the details of a dire landscape:
The state’s busiest emergency room. Abrupt shutdowns of hospital facilities. Impoverished people without transportation or internet access for telehealth. Eight-month waits for primary care appointments. Nearly one in five Latinos uninsured. More than half of residents receive Medicaid. Resident physicians cycling in and out, never getting to know their patients. Not enough specialists, resulting in day-long trips for specialized care in bigger cities. With its Latino essential workforce risking their lives to feed their families — and the country — by summer 2020, COVID blazed through Yakima County, which quickly became Washington’s most scorching of hot spots. Not only did Yakima County tally the highest per-capita case rate of all West Coast counties (with Latinos making up 67% versus, 26% for white people), it also saw more cases than the entire state of Oregon. Ask Latinos here about 2020, and they shiver and avert their gazes, the trauma and death still too near.
Their positive tests marked just the beginning of terrifying new journeys as COVID slammed Victoria and many other Yakima Valley Latinos. Mix in scanty rural health care, systemic racism and a complicated emerging illness, and what do you get? Chaos: a population hardest hit by long COVID, but massively untreated, underdiagnosed, and undercounted by the government and medicine itself.
It won’t go away The cough was the first clue something wasn’t right. When Victoria had COVID, she’d coughed a bit. But then, three months later, she started and couldn’t stop.
The Yakima Valley is so starved for physicians that it took five months to see a primary care doctor, who attributed Victoria’s incessant cough to allergies. Victoria tried every antihistamine and decongestant available; some brought relief for three, maybe four weeks, and then returned spasms of the dry, gasping bark. A few minutes apart, all day long. The worst was waking up coughing, at least hourly.
Victoria had chest x-rays. An ear, nose and throat specialist offered surgery on her nose’s deviated septum. As months passed, the black hair framing Victoria’s heart-shaped face started aging rapidly, until it was grayer than her mother’s.
Over a year after the cough began, an allergist prescribed allergy drops, and Victoria made a chilling discovery. Once the drops stopped the cough for a month, then two, Victoria realized that the extreme fatigue she’d thought was sleep deprivation from coughing all night persisted.
“The exhaustion comes from within your soul, it overpowers you,” she says. “It’s intolerable.”
And her mind was foggy. When interrupted at work every 10 minutes by a coughing jag, Victoria hadn’t realized COVID had substantially altered her brain. “There are things in my brain that I should have access to, like words, definitions, memories,” she says. “I know that they’re there but I can’t access them. It’s like a filing cabinet, but I can’t open it.”
Before long, the cough resurfaced. Sometime in 2021, reading COVID news for work, Victoria learned of long COVID: new or lingering health issues persisting at least three months after COVID infection.
How to get help if you think you might have long COVID Talk to your doctor, and if your doctor doesn’t listen to your concerns, bring a loved one to advocate for you at your next appointment. Bring this article (or other materials on long COVID) to show your doctor. Ask your doctor about seeing specialists for long COVID symptoms, such as a cardiologist (for dysautonomia symptoms like dizziness, heart palpitations and shortness of breath), a gastroenterologist (for digestive problems), or a neurologist (for chronic nerve pain). Ask to be referred to a long COVID clinic (if there is one in your area). Now four years into the pandemic, there is still no treatment or cure for long COVID. COVID long-haulers (as they call themselves) have reported over 200 varied symptoms, with fatigue, dizziness, heart palpitations, post-exertion exhaustion, gastrointestinal issues, and brain dysfunction among the most common.
Long COVID is far from a mysterious illness, as it’s often called by the medical establishment and some media. There are precedents: for at least a century, historical documentation has shown that, while most recover, some people remain sick after viral or other illnesses. Yet funds for research have been severely limited, and sufferers ignored. Myalgic Encephalomyelitis – sometimes called Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, or ME/CFS — is a prime example. Like ME/CFS, long COVID afflicts many more women (and people assigned female at birth) than men, with women comprising as many as 80% of COVID long-haulers. Most long-haulers are in their 30s, 40s and 50s — the busiest years for women with children, who often put their own needs last.
What should have been instantly clear, given how disproportionately Black and Brown communities were hit by COVID, was that long COVID would wallop Americans of color. Yet, the U.S. government waited until June 2022 to begin tracking long COVID. Even now, with 18 months of data showing Latinos are the population most impacted by long COVID, palabra is among the very few media outlets to report this fact. Are the nation and the medical community willfully ignoring Latino long-haulers — after sending them into clouds of coronavirus to keep society’s privileged safe?
Fighting for a diagnosis When Victoria mentioned long COVID, her doctor didn’t exactly ignore her: she listened, said “OK,” but never engaged on the topic. Same with Victoria’s allergist and the ear, nose and throat specialist. All they could do, the doctors said, was treat her symptoms.
“I’m highly educated and I know that you have to be your own advocate. But I kept asking, kept going on that line of thought, and they had nothing to say to me. Absolutely nothing,” she laments.
Victoria understood science on long COVID was limited, but still expected more. “All of the treatments we tried, it was as if COVID hadn’t existed. They should at least say that we need to investigate more, not continue acting like it wasn’t a factor. That was what was most frustrating.”
Just as Victoria fought to have her illness validated by doctors, 30 miles away in the northern Yakima Valley town of Moxee, 52-year-old María* waged a parallel battle. Both felt utterly alone.
When the pandemic began, María became the protector of her husband and children, all asthmatics. When she fell ill New Year’s Day 2021, she locked herself in her room, emerging weeks later to find her life unrecognizable.
Recounting her struggles, María reads deliberately from notes, holding back tears, then pushes her reading glasses atop her head. (María moved here from northern Mexico as an adult, and feels most comfortable in Spanish.) Her dyed brown hair, gold necklace and lightly made-up face project convivial warmth, but something intangible behind her expression belies a depth of grief María refuses to let escape. When I tell her I also have long COVID, and fell ill the exact same month, she breathes out some of her anxiety.
María’s long COVID includes chronic, full-body pain; memory lapses so severe she sometimes can’t remember if she’s eaten breakfast; such low energy that she’s constantly like a battery out of juice; unending shortness of breath; joint inflammation; and blood flow issues that leave her hands a deep purple. (The only time María ventured to the hospital, for her purple hands, she says staff attempted to clean them, thinking it was paint.) Like Victoria, María used to enjoy exercise and hiking in the valley’s foothills, but can do neither anymore.
María has no insurance, and receives care at the Yakima Valley Farm Workers Clinic, created in 1978 out of the farmworkers’ movement. The clinic’s multiple locations are the valley’s main providers of care irrespective of patients’ ability to pay.
Whereas Victoria’s doctors expressed indifference to the idea of COVID causing her health complaints, María’s doctors not only discounted this connection, but made serious errors of misdiagnosis.
“Every week I went to see my doctor. She got so stressed out (at not knowing what was wrong with me) that she stressed me out,” María says. “My doctor told me, ‘You know what? I think you have multiple sclerosis.’” María saw specialists, and afterwards, even without confirmation, María says her doctor still insisted she had MS. “I told her, ‘No. No, I don’t have multiple sclerosis. It’s COVID. This happened after COVID.’ I was really, really, really, really, really, really insistent on telling them that all of this was after COVID.”
Latinos uncovering the connections between their ill health and COVID is rare, partially due to the plummet in COVID coverage on Spanish-language news, says Monica Verduzco-Gutierrez, a long-hauler and head of the University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio long COVID clinic. There has been no national public education on long COVID, in any language.
“It’s hard for people to understand what the real impact of long COVID is now and in the future,” says Lilián Bravo, Yakima Health District director of public health partnerships and the face of COVID updates on Yakima Valley television early in the pandemic. “We’re looking at a huge deficit in terms of people’s quality of life and ‘productivity.’”
Eventually, María’s doctor sent her to another specialist, who said that if she didn’t improve within a month, he’d operate on her hip. María’s never had hip problems. “He said, ‘Well, I don’t know what you’re going to do,’” and then put her on a strong steroid medication that made her vomit horribly, María says. She hasn’t tallied what she’s spent on medical bills, but after paying $1,548 for a single test, it must be many thousands of dollars.
Meanwhile, María’s family and friends kept insisting her maladies were psychological. “I never accepted that. I told them: ‘It’s not in my head. It’s in my body.’” It wasn’t until more than a year after becoming ill that María finally saw a rheumatologist who diagnosed her with long COVID and other immune dysfunctions. “I told her, ‘Yes, I knew that my body wasn’t working. I knew that something was wrong.’ I felt like I could relax. Finally someone is telling me that it’s not all in my head.” Once María was diagnosed, her extended family switched to asking how she was feeling and sympathizing with her.
Victoria, on the other hand, has never received a long COVID diagnosis. At Victoria’s request, her doctor referred her to the state’s only long COVID clinic, at the University of Washington in Seattle, but Victoria’s insurance, Kaiser Permanente, refused to pre-approve the visit — and the clinic wouldn’t accept cash from her. At present, the clinic isn’t even accepting patients from the Yakima Valley or any other part of Washington — they are only accepting patients in King County, which includes Seattle.
Victoria’s family hasn’t accepted her health struggles either. “I’d say, ‘I know that you think I’m crazy,’” Victoria says, chuckling, as she often does to lighten her discomfort. “My mom would fight with me: ‘You forgot to do this! Why are you so spacey?’ ‘Mami, it’s not that I forgot. In reality, I completely lost track of it.’” If Victoria is fatigued, her family asks how that’s possible after a full night’s sleep. “I’ve found that I have to defend myself. When I try to explain to people, they hear it as excuses from a lazy person — especially being Latinos.”
Karla Monterroso, a 42-year-old California Latina long-hauler since March 2020 who spent her first year bedbound, says, “(With long COVID), we have to rest in a way that, in our culture, is very difficult to achieve. We really judge exhaustion.” In fact, pushing physically or mentally for work can make long-haulers much sicker. Karla says Latino ethics of hard work like those of Victoria’s parents “aren’t the principles that are going to serve us with this illness.”
Long COVID diagnoses in Latinos are still too rare, due to untrained family medicine physicians and medical stereotypes, says Verduzco-Gutierrez. (Doctors might see blood sugar changes, for example, and assume that’s just because of Latinos’ high rates of diabetes, rather than long COVID.) She says “misinformation on long COVID” is rampant, with physicians claiming long COVID is a fad, or misdiagnosing the bone-deep exhaustion as depression. When Verduzco-Gutierrez’s own doctor invited her to speak to their practice, the assembled physicians weren’t aware of basic research, including that the drugs Paxlovid and Metformin can help prevent long COVID if taken at infection. In Washington, physicians must complete training on suicide, which takes 1,200 to 1,300 lives in the state yearly, but there’s no state-wide training on long COVID, which currently affects at least 498,290 Washingtonians.
Cultural skepticism about medicine — and entrenched stigmas about illness and disability — mean Sunnyside conversations about aftereffects don’t mention COVID itself. Victoria’s relatives push traditional herbal remedios, assuming that anyone still sick isn’t doing enough to recover. “(People suffering) feel like they’re complaining too much if they try to talk about it,” Victoria says. Meanwhile, her parents and others in her community avoid doctors out of stubbornness and mistrust, she says, “until they’re bleeding, when they’re super in pain…, when it’s gotten to the worst that they can handle.”
“People in this community use their bodies for work,” Victoria says. “If you’re Latino, you’re a hard worker. Period,” says Bravo. “What’s the opposite of that, if you’re not a hard worker? What are you? People don’t want to say, ‘I came to this country to work and all of a sudden I can’t anymore.’”
Victoria sees this with her parents, who’ve worked since the age of 10. Both have health issues inhibiting their lives since having COVID — her dad can’t take his daily hour-long walks anymore because of heart palpitations and shortness of breath, and her mom began getting headaches and saw her arthritis worsen dramatically — yet neither will admit they have long COVID. Nor will their friends and family. “If they noticed the patterns of what they themselves are saying and what their friends of the same age are suffering after COVID,” Victoria says of her community, “they’d hear that almost everyone is suffering some type of long COVID.”
Long COVID’s deep impact on Latinos The “back to normal” ethos is most obvious in the absence of long COVID messaging while as many as 41 million adults now have — or have recovered from — long COVID nationwide. “The way that we’re talking about the pandemic is delegitimizing some of (long COVID’s) real impacts,” says Bravo of the Yakima Health District.
Even with limited demographic data, statistics show a nationwide reality similar to Victoria’s Sunnyside. Through a recurring survey, the Census Bureau estimates that 36% of Latinos nationally have had long COVID — likely a vast underestimate, given that the survey takes 20 minutes to complete online (Latinos have lower rates of broadband internet), and reaches only a sliver of the U.S. population. Experts like Verduzo-Gutierrez believe that true rates of long COVID in Latinos are higher than any reported statistic. California long-hauler Karla Monterroso agrees: “We are underdiagnosed by a severe amount. I do not believe the numbers.”
This fall, a UC Berkeley study reported that 62% of a group of infected California farmworkers developed long COVID. Weeks later, a survey from the University of Washington’s Latino Center for Health found that, of a sample group of 1,546 Washington Latinos, 41% of those infected became long-haulers. The Washington results may also be an undercount: many long-haulers wouldn’t have the energy or brain clarity to complete the 12-page survey, which was mailed to patients who’d seen their doctor within the prior six months. Meanwhile, many long-haulers stop seeing doctors after tiring of the effort and cost with no answers.
“Our community has not bounced back,” says Angie Hinojos, executive director of Centro Cultural Mexicano, which has distributed $29 million in rent assistance in Washington and hasn’t seen need wane. “That is going to affect our earning potential for generations.” The United Farm Workers’ philanthropic sister organization, the UFW Foundation, says union organizers hear about long COVID, and how it’s keeping people out of work, frequently.
Cultural and linguistic disconnects abound between doctors and Latinos on long COVID symptoms, some of which, like brain fog and fatigue, are nebulous. If doctors lack patient rapport — or don’t speak their language — they’ll miss what patients aren’t sharing about how long COVID changed their lives, work and relationships. That’s if Latinos actually go to the doctor.
“If you’re working in the orchards and your muscles are always sore, it’s just part of the day-to-day reality,” says Jesús Hernández, chief executive officer of Family Health Centers in north-central Washington. “If you’re constantly being exposed to dust and even chemicals in the work environment, it’s easy to just say, ‘Well, that’s just because of this or that,’ and not necessarily be readily willing to consider that this is something as unique as long COVID.”
Even Victoria says if not for the cough, she wouldn’t have sought medical advice for her fatigue. “There are a lot of people out there that are really tired, in a lot of pain and have no idea why. None,” says Karla, who was a nonprofit CEO when she became sick. “I have heard in the last three-and-a-half years the most racist and fatphobic things I have ever heard in my life. Like, ‘Oh, sometimes you got to lay off the beans and rice.’ I have a college education. I’m an executive. I am in the top 10% of wage earners in my community. If this is my experience, what is happening to the rest of my people?”
Conspiracy theories and misinformation As Yakima Valley’s Latino vaccination rates continue dropping, I hear all the COVID conspiracy theories: the vaccine has a chip that’ll track you; the vaccine makes you and your children infertile; COVID tests are rigged to all be positive; that hospitals get paid more for COVID patients. Victoria laughs at the most absurd one she’s heard. Her mom’s explanation for her health problems nearly three years after COVID: the vaccine.
Across the Latino United States, social media algorithms and WhatsApp threads promoting COVID disinformation proliferate. Last summer, Latino Center for Health co-director Dr. Leo Morales did a long COVID community presentation just south of Yakima Valley. The audience’s first question: Are vaccines safe? “This is where we’re still at,” Morales says. “That’ll be a big stumbling block for people…in terms of getting to talking about long COVID.”
One morning in early November, Morales and his team gather in Toppenish at Heritage University, where 69% of students are Latino, to present their survey data. Neither presenters nor attendees wear masks, an essential tool for preventing COVID transmission and long COVID. “The only conversation that I’m having about COVID is in this room,” says María Sigüenza, executive director of the Washington State Commission on Hispanic Affairs.
Yakima Valley health institutions are also ignoring long COVID. Of the two main hospital systems, Astria Health declines interview requests and MultiCare reports that of 325,491 patients seen between January and November 2023, 112 — or 0.03% — were diagnosed with long COVID. The Yakima Valley Farmworkers Clinic, where María’s doctor works, refuses to let me speak to anyone about long COVID, despite providing patient information for the Latino Center for Health’s survey. Their doctors simply aren’t seeing long COVID, the clinic claims. Same with the other main community provider, Yakima Neighborhood Health Services, whose media officer responds to my interview requests with: “It’s not going to happen.”
“I think they’re not asking, they’re not looking,” Verduzco-Gutierrez says. “Do the doctors just…look at your diabetes or your blood pressure, but not ask you, ‘Did your diabetes get worse when you had COVID? Did your blood pressure get worse? Did you not have blood pressure problems before? And now do you get dizzy? Do you get headaches? Do you have pains?’” She believes that many, if not most, Latinos with long COVID aren’t getting care, whom she calls “the ones that we’re missing.”
An uncertain future The outlook for Latinos with long COVID is grim. Cultural stigma and ableism cause now-disabled long-haulers to feel shame. (Ableism is societal prejudice and discrimination against disabled people.) Disability benefits are nearly impossible to get. Long-haulers are losing their homes, jobs and insurance. Latinos’ overrepresentation in sectors that don’t offer sick pay and are heavily physical — cleaning, service, agriculture, construction, manufacturing, homecare and healthcare among them — may automatically put them at higher long COVID risk, given ample anecdotal evidence that pushing through a COVID infection instead of resting can lead to long COVID. Latino care providers will become ill in greater numbers, imperiling the healthcare industry.
But Latinos may not be clear on these factors, says long-hauler Karla Monterroso. “My tío had said…'We must be defective because we get sick more than the white people.’ And I’m like ‘No, tío. We are exposed to the illness more. There’s nothing defective about our bodies.’ I’m afraid for us. It’s just going to be disability after disability after disability. We have to start in our small communities building caring infrastructure so that we can help each other. I am clear: No one is coming to save us. We’ve got to save us.”
Disability justice advocates worry about systems unable to cope with inevitable disabling waves of COVID in the future. “(Latinos) aren’t taking it as serious as they should,” says Mayra Colazo, executive director of Central Washington Disability Resources. “They’re not protecting each other. They’re not protecting themselves.” Karla sees the psychology behind this denial: “I have thought a lot about how much it takes to put yourself in danger every single day. (You have) to say ‘Oh, it’s fine. People are exaggerating,’ or you get that you’re in existential hell all of the time.”
Reinfection brings additional risk of long COVID, research shows, and Verduzco-Gutierrez says, “We still don’t know the impact of what is going to happen with all these reinfections. Is it going to cause more autoimmune disease? Is it going to be causing more dementia? Is it going to be causing more cancer?” She believes that every medical chart should include a COVID history, to guide doctors to look for the right clues.
“If we were to be lucky enough to capture everybody who has long COVID, we would overwhelm our (health) system and not be able to do anything for them,” Victoria says. “What’s the motivation for the medical field, for practitioners to find all those people?” For now, Victoria sees none. “And until that changes, I don’t think we will (properly count Latino long-haulers),” she adds.
Flashes of hope do exist. In September 2023, the federal government granted $5 million each to multiple long COVID clinics, including three with Latino-specific projects. In New York City, Mt. Sinai Hospital will soon open a new long COVID clinic near largely-Latino East Harlem, embedded in a primary care clinic with staff from the community to reach Latino long-haulers. Verduzco-Gutierrez’s San Antonio clinic will teach primary care providers across largely rural, Latino South Texas to conduct 15-minute low-tech long COVID examinations (the protocol for which is still being devised), and will deploy community tools to educate Latinos on long COVID.
Meanwhile, at the University of Washington long COVID clinic, staff are preparing a patient handbook, which will be adapted for Latinos and then translated into Spanish. They will also train primary care physicians to be local long COVID experts, and will return to treating patients from the whole state rather than just the county containing Seattle. After palabra’s inquiry, the UFW Foundation now has plans to survey United Farm Workers members to gauge long COVID pervasiveness, so the Foundation can lobby legislators and other decision makers to improve Latino long-hauler care.
Back at the Yakima Valley survey presentation, attendees brainstorm new care models: Adding long COVID screening to pediatric checkups, given that long COVID most impacts child-bearing-age women, so moms can bring information to their families and community. Using accessible language for long COVID messaging, or, as Heritage University nursing faculty member Genevieve Aguilar puts it: “How would I talk to my tía, how would I talk to my abuelita? If they can understand me, we’re good to go. If they can’t, olvídate. We have to reframe.”
More than anything, personal narratives will be the key to open people’s minds about long COVID — although that path may be challenging. In Los Angeles, Karla has dealt with a lack of full family and community support, in part, she believes, because her body represents COVID. “I am living, breathing proof of a pandemic no one wants to admit is still happening, and that there is no cure for what I have. That is a really scary possibility.”
While Karla does identify as disabled, Victoria and María don’t. Victoria has learned to live and move within her physical limits. At work, she sometimes feels inhibited by her cognitive issues. “I tell my boss all the time, ‘Oh man, you guys hired such a smart person. But what you got was after COVID, so it’s not the same.’” At times, she worries about the trajectory of her career, about how her work’s intense problem-solving wears out her brain. Will she be able to pursue larger challenges in work in the future? Or will long COVID ultimately make her fail?
Victoria tells me she “remains hopeful that there is a solution.” In a surprising twist, her cough completely disappeared eight months ago — when she became pregnant. (Other long-haulers have seen their symptoms improve with pregnancy, as well, likely due to immune system changes allowing a pregnant person’s body to not reject their baby’s growing cells). Victoria is optimistic that her other symptoms might disappear after she gives birth. And that, maybe someday, her parents will admit they have long COVID, too.
#long covid#covid 19#mask up#covid#pandemic#public health#wear a mask#still coviding#wear a respirator#coronavirus#sars cov 2#covid conscious#covid is airborne#covidー19#covid isn't over#covid pandemic#covid19
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
#fear street#fear street trilogy#fear street 1978#fear street 1994#fear street 1666#army of the dead#a classic horror story#oxygen#oxygen 2021#theres someone inside your house#there's someone inside your house#things heard & seen#things heard and seen#blood red sky#no one gets out alive#night teeth#hypnotic#hypnotic 2021#poll#horror#horror film#horror poll#movie poll#film poll#horror movie#movie#film#horror movie poll#films#movies
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Jun 20, 2025
(By Meghan Cook)
During a routine research dive off the coasts of Southern California and Alaska in 2021, Occidental College professor Shana Goffredi scoured the ocean floor looking for methane seeps — deep-sea spots where methane gas bubbles up from the Earth’s crust.
After scooping up samples 3,000 feet below the surface, Goffredi and her team took them back to the lab “just to see if there was anything unusual about them.”
That’s when they discovered three new species of deep-sea spiders.
In addition to living exclusively in methane seeps and hydrothermal vents on the ocean floor, the Sericosura sea spiders displayed a curious behavior: They consumed methane gas.
“Sea spiders at hydrothermal vents and methane seeps are understudied,” Goffredi and her colleagues explained in the new study, which was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Sericosura sea spiders now join the likes of other overlooked, yet abundant, small marine animals that take advantage of methane.” Goffredi, who specializes in the symbiosis between bacteria and invertebrates on the seafloor, was hungry to know more.
In 2023, the professor and her team of undergraduates returned to the ocean habitat with an underwater submersible. But at a centimeter long, the sea spiders were hard to spot.
Especially because they were translucent.

“I came up out of the submersible all dejected because I thought we didn’t collect any,” Goffredi told SFGate. “And it turned out we’d collected over 30 of them.”
After securing more samples, the team confirmed a long-held hypothesis. Unlike other spiders — both deep sea and on land — these new species of Sericosura were physiologically unique.
They had “a coat of methane-oxidizing bacteria on their surface” which allowed them to collect methane on their exoskeletons.
“Methane has been recognized as a potentially important source of carbon and energy for lake food webs,” Goffredi and her colleagues wrote.
“In the case of sea spiders, however, they appear to cultivate and consume the methane-oxidizing bacterial community from their bodies directly, rather than from abiotic surfaces.”
Close-up pictures of the spiders, which have a set of “lips” fringed with fleshy bumps and three miniscule teeth, may serve as nightmare fuel for any unsuspecting arachnophobes who scroll past this latest ocean discovery.
Goffredi, however, finds them “extremely adorable.”

“While the deep sea feels far away, all organisms are interconnected, and the processes in one ecosystem affect the other,” Goffredi told SFGate.
Goffredi suspects that 11 other recently discovered deep-sea spiders may have “methane-sucking” tendencies, too.
As she looks forward to future expeditions, Goffredi concluded that the groundbreaking discovery “reveals a new biological conduit for methane input into ecosystems” and “expands our understanding of C1 compound cycling in the ocean.”
“The deep sea is so important. It’s involved in climate regulation, production of oxygen, and supply of fisheries,” Goffredi said. “So it’s really important to understand the biodiversity of these unique places.”
#good news#environmentalism#science#environment#nature#spiders#deep sea spiders#deep sea life#ocean life#marine life#animals#conservation#climate change#climate crisis#ocean floor#sea creatures#sea spiders#deep-sea spiders#methane#greenhouse gases#biodiversity#oceans#ocean
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
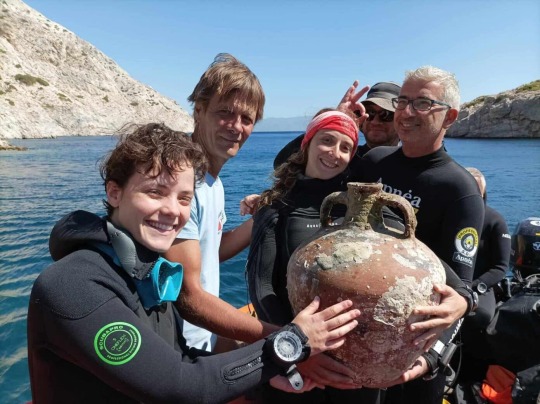

Dozens of Amphorae Recovered From Ancient Byzantine Shipwreck in Greece
Excavations of an ancient Byzantine shipwreck off the coast of Fournoi near Samos, Greece are bringing new finds onto the surface.
The wreck has been systematically excavated since 2021 and has been selected for intensive investigation due to the extremely interesting cargo it carries.
The amphorae found recently in the sand near the wreck, along with the wooden skeleton of the ship itself, were in remarkably good condition. Experts believe that the ship’s wooden framing survived throughout the centuries because it was crushed under the rest of the ship and oxygen couldn’t reach it, stalling the process of decay.
So far eight different amphora types have been recorded, originating from Crimea, Sinope of the Pontus region in the Black Sea, as well as from the Aegean islands and the Phocaean region of Asia Minor.

Pottery recovered at the ancient Byzantine shipwreck
The Ministry of Culture said that 170 group dives were carried out during the latest excavations. Archaeologists worked throughout the period to clear sand and debris from the wreck to provide access for experts to conduct studies of the site.
The scattering of the finds on the seabed seems to indicate a partial loss of cargo before the ship sank.
The recovered pottery was particularly enlightening, in terms of the more precise chronological inclusion of the wreck, which can now be safely dated between 480 and 520 AD, probably during the years of Emperor Anastasios I (491 – 518 AD), said a press release by the Greek Ministry of Culture.
Byzantine Emperor Anastasios I is known for his fiscal and monetary reforms, which strengthened the Empire’s coffers and enabled the expansionist policy of the emperors of the 6th century.
In parallel with the excavation of the wreck, findings from three more wrecks at the Fournoi archipelago were recovered, which are intended to be exhibited at the local archeological museum. Among these finds are a giant archaic anchor obelisk and amphorae from shipwrecks of the 6th to 8th centuries AD.

Countless ancient shipwrecks off Greece
There are many ancient shipwrecks across the Greek seas, and archaeologists have found countless historic treasures in these sunken archaeological sites.
In March 2024, the Ministry of Culture announced that scientists have discovered several shipwrecks and other important ancient finds in the underwater, near Greece’s island of Kasos.
These date back indicatively from prehistory (3000 BC), the Classical period (460 BC), the Hellenistic (100 BC to 100 AD), and the Roman years (200 BC – 300 AD) to the medieval and Ottoman periods.
Four stunning ancient shipwrecks filled with artifacts from antiquity and the Roman and Byzantine eras off central Greece can now be explored by amateur divers.
“We plan to highlight our marine cultural heritage,” Culture Minister Lina Mendoni said.
“We have responded to this great challenge by opening to the public a total of four underwater archaeological sites in the prefecture of Magnesia, which will allow Greece to join the world map of diving tourism.”
By Tasos Kokkinidis.

#Dozens of Amphorae Recovered From Ancient Byzantine Shipwreck in Greece#coast of Fournoi#ancient shipwreck#ancient amphorae#ancient artifacts#archeology#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient greece#greek history#byzantine history#byzantine empire
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
by Michael Nevradakis, Ph.D.
Jury selection began today in a “landmark” trial alleging the wrongful death of Grace Schara, a 19-year-old with Down syndrome who died in a Wisconsin hospital days after being admitted for a COVID-19 infection and low oxygen levels.
It’s the first jury trial in the U.S. for a death listed as COVID-19 on the death certificate.
Grace’s family sued Ascension St. Elizabeth Hospital in April 2023, and filed an amended complaint in July 2023, alleging the hospital’s COVID-19 treatment protocols directly resulted in Grace’s death in October 2021.
The lawsuit includes an allegation of medical battery, a standard of intentional harm beyond medical negligence by doctors and other providers.
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
General Mills and cheaply bought "dietitians" co-opted the anti-diet movement

I'm on tour with my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in NEXT THURSDAY (Apr 11) in BOSTON with Randall "XKCD" Munroehttps://cockeyed.com/lessons/viagra/viagra.html, then PROVIDENCE, RI (Apr 12), and beyond!

Steve Bannon isn't wrong: for his brand of nihilistic politics to win, all he has to do is "flood the zone with shit," demoralizing people to the point where they no longer even try to learn the truth.
This is really just a more refined, more potent version of the tactical doubt sown by Big Tobacco about whether smoking caused cancer, a playbook later adopted by the fossil fuel industry to sell climate denial. You know Darrell Huff's 1954 classic How To Lie With Statistics? Huff was a Big Tobacco shill (his next book, which wasn't ever published, was How To Lie With Cancer Statistics). His mission wasn't to help you spot statistical malpractice – an actual thing that is an actual problem that you should actually learn to spot. It was to turn you into a nihilist who didn't believe anything could be known:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/01/04/how-to-truth/#harford
Corporations don't need you to believe that their products are beneficial or even non-harmful. They just need you to believe nothing. If you don't know what's true, then why not just do whatever feels good, man? #YOLO!
These bannonfloods of shit are a favored tactic of strongmen and dictators. Their grip on power doesn't depend on their citizens trusting them – it's enough that they trust no one:
http://jonathanstray.com/networked-propaganda-and-counter-propaganda
Bannonflooding is especially beloved of the food industry. Food is essential, monopolized, and incredibly complicated, and many of the most profitable strategies for growing, processing and preparing food are very bad for the people who eat that food. Rather than sacrificing profits, the food industry floods the zone with shit, making it impossible to know what's true, in hopes that we will just eat whatever they're serving:
https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.2003460
Now, the "nothing can be known" gambit only works if it's really hard to get at the truth. So it helps that nutrition and diet are very complex subjects, but it helps even more that the nutrition and diet industry are a cesspool of quacks and junk science. This is a "scientific discipline" whose prestigious annual meetings are sponsored (and catered) by McDonald's:
https://www.motherjones.com/environment/2014/05/my-trip-mcdonalds-sponsored-nutritionist-convention/
It's a "science" whose most prominent pitchmen peddle quack nostrums and sue the critics who point out (correctly) that eating foods high in chlorophyll will not "oxygenate your blood" (hint, chlorophyll only makes oxygen in the presence of light, which is notably lacking in your colon):
https://www.badscience.net/2007/02/ms-gillian-mckeith-banned-from-calling-herself-a-doctor/
When the quack-heavy world of nutrition combines with the socially stigmatized world of weight-loss, you get a zone ripe for shitflooding. The majority of Americans are "overweight" (according to a definition that relies on the unscientific idea of BMI) and nearly half of Americans are "obese." These numbers have been climbing steadily since the 1970s, and every diet turns out to be basically bullshit:
https://headgum.com/factually-with-adam-conover/what-does-ozepmic-actually-do-with-dr-dhruv-khullar
Notwithstanding the new blockbuster post-Ozempic drugs, we're been through an unbroken 50-year run of more and more of us being fatter and fatter, even as fat stigma increased. Fat people are treated as weak-willed and fundamentally unhealthy, while the most prominent health-risks of being fat are roundly neglected: the mental health effects of being shamed, and the physical risks of having doctors ignore your health complaints, no matter how serious they sound, and blame them on your weight:
https://maintenancephase.buzzsprout.com/1411126/11968083-glorifying-obesity-and-other-myths-about-fat-people
Fat people and their allies have banded together to address these real, urgent harms. The "body acceptance" movement isn't merely about feeling good in your own skin: it's also about fighting discrimination, demanding medical care (beyond "lose some weight") and warning people away from getting on the diet treadmill, which can lead to dangerous eating disorders and permanent weight gain:
https://www.beacon.org/You-Just-Need-to-Lose-Weight-P1853.aspx
Fat stigma is real. The mental health risks of fat-shaming are real. Eating disorders are real. Discrimination against fat people is real. The fact that these things are real doesn't mean that the food industry can't flood the zone with shit, though. On the contrary: the urgency of these issues, combined with the poor regulation of dietitians, makes the "what should you eat" zone perfect for flooding with endless quantities of highly profitable shit.
Perhaps you've gotten some of this shit on you. Have you found yourself watching a video from a dietitian influencer like Cara Harbstreet, Colleen Christensen or Lauren Smith, promoting "health at any size" with hashtags like #DerailTheShame and #AntiDiet? These were paid campaigns sponsored by General Mills, Pepsi, and other multinational, multibillion-dollar corporations.
Writing for The Examination, Sasha Chavkin, Anjali Tsui, Caitlin Gilbert and Anahad O'Connor describe the way that some of the world's largest and most profitable corporations have hijacked a movement where fat people and their allies fight stigma and shame and used it to peddle the lie that their heavily processed, high-calorie food is good for you:
https://www.theexamination.org/articles/as-obesity-rises-big-food-and-dietitians-push-anti-diet-advice
It's a surreal tale. They describe a speech by Amy Cohn, General Mills’ senior manager for nutrition, to an audience at a dietitian's conference, where Cohn "denounced the media for 'pointing the finger at processed foods' and making consumers feel ashamed of their choices." This is some next-level nihilism: rather than railing against the harmful stigma against fat people, Cohn wants us to fight the stigma against Cocoa Puffs.
This message isn't confined to industry conferences. Dietitians with large Tiktok followings like Cara Harbstreet then carry the message out to the public. In Harbstreet's video promoting Cinnamon Toast Crunch, Cocoa Puffs and Trix, she says, "I will always advocate for fearlessly nourishing meals, including cereal…Because everyone deserves to enjoy food without judgment, especially kids":
https://www.tiktok.com/@streetsmart.rd/video/7298403730989436206
Dietitians, nutritionists and the food industry have always had an uncomfortably close relationship, but the industry's shitflooding kicked into high gear when the FDA proposed rules limiting which foods the industry can promote as "healthy." General Mills, Kelloggs and Post have threatened a First Amendment suit against such a regulation, arguing that they have a free speech right to describe manifestly unhealthy food as "healthy."
The anti-diet movement – again, a legitimate movement aimed at fighting the dangerous junk science behind dieting – has been co-opted by the food industry, who are paying dietitian influencers to say things like "all foods have value" while brandishing packages of Twix and Reese's. In their Examination article, the authors profile people who struggled with their weight, then, after encountering the food industry's paid disinformation, believed that "healthy at any size" meant that it would be unhealthy to avoid highly processed, high calorie food. These people gained large amounts of weight, and found their lives constrained and their health severely compromised.
I've been overweight all my life. I went to my first Weight Watchers meeting when I was 12. I come from a family of overweight people with the chronic illnesses often associated with being fat. This is a subject that's always on my mind. I even wrote a whole novel about the promise and peril of a weight-loss miracle:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781429969284/makers
I think the anti-diet movement, and its associated ideas like body acceptance and healthy at every size, are enormously positive developments and hugely important. It's because I value these ideas that I'm so disgusted with Big Food and its cynical decision to flood the zone with shit. It's also why I'm so furious with dietitians and nutritionists for failing to self-regulate and become a real profession, the kind that censures and denounces quacks and shills.
I have complicated feelings about Ozempic and its successors, but even if these prove to be effective and safe in the long term, and even if we rein in the rapacious pharma companies so that they no longer sell a $5 product for $1000, I would still want dietary science to clean up its act:
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2816824
I'm not a nihilist. I think we can use science to discover truths – about ourselves and our world. I want to know those truths, and I think they can be known. The only people who benefit from convincing you that the truth is unknowable are the people who want to lie to you.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/05/corrupt-for-cocoa-puffs/#flood-the-zone-with-shit
#pluralistic#corruption#nutrition#food#diets#dieticians#nutritionists#junk science#junk food#astroturf#fat acceptance#fatphobia#health#nihilism#steve bannon#flood the zone with shit#general mills#dietitians
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Ed's note: AI could have done it, but so much more solarpunk to involve the entire community
‘Fish doorbell season’ officially began, on 3 March for the fifth year in a row. A camera showing live footage allows viewers to let the lock keeper at the Weerdsluis lock know when fish are waiting to swim upstream so they can open the gate.
Linda Voortman, alderwoman for Utrecht, says each year the fish doorbell is received with enthusiasm by the people of the city and far beyond.
“In fact, last year there were almost three million unique visitors who together helped thousands of fish through the Weerdsluis gates in Utrecht,” Voortman says.
“It shows that many people are involved in underwater nature and enjoy making a contribution.”
Why is the fish doorbell needed?
The fish doorbell went live for the first time in 2021 to help fish like bream, pike, and bass make their spring migration through the waters of Utrecht to find a suitable place to lay their eggs. Each year, they migrate from the River Vecht to the River Kromme to reproduce.
The Weerdsluis is a vital passage through which they migrate.
“The sluices, pumps and dams we use to keep the water at the right level prevent the fish from getting in,” says Gijs Stigter of water authority De Stichtse Rijnlanden. That’s why, Stigter adds, the water authority is building fish passage points to help them get through.
But for now, a closed sluice gate at the lock can slow them down, making them easy prey for predators along the route. The lock is mainly closed for boats during early spring, meaning the fish can sometimes stay stranded for weeks.
The fish doorbell was introduced by two ecologists – Anne Nijs and Mark van Heukelum – as a solution to this problem.
Viewers watching the stream can press the button as soon as fish appear, alerting the lock keeper to their presence. The keepers can then open the door promptly, allowing the fish to continue their migration. Thousands pass through each year because of this initiative.
Fish help to keep the water in balance, eating algae and small animals. Some species also indicate the quality of the water, surviving where it is clean and oxygen rich.
“By ringing the Fish Doorbell, we not only help the fish, but also nature and water quality in and around Utrecht,” Stigter explains.
Here is the link for you to ring the doorbell
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Spring-Lock Failure And Death: An Analysis
Quick Disclaimer: Lotta descriptions of gore in here. Also I have like a single semester in Anatomy, I'm not an expert, this is more of a writing drabble for my own reference if anything. But Scott Cawthon probably has done less research than me so I’m inclined to speak my truth.
ALSO BECAUSE I'M PETTY (¬_¬ ) When I say "spring-lock failure", the spring-locks themselves are not the cause of death. The cause of death is getting a robot endoskelton, previously held back with spring-locks and gravity, embedded in your flesh. Spring-locks are just the locking mechanism. This mix-up has bothered me for years.
*this was written before the FNaF movie btw. Been in draft since January 25th, 2021. It’s a fun time capsule*

The problems being violently crushed by robot parts cause:
To start, lets discuss bones. Considering the force it takes the crack bone is about 4000 newton's of force, at least the weight of of five standard pickup trucks, its unlikely any bones were actually broken within the process of the spring-lock failure.
However, that is only when supporting weight, and the suit pieces were unwound so rapidly in a way that they aimed for specific pieces in the bone, therefore it would do more harm because it might do more damage to one specific spot, and gravity working in tandem might be able to crush the rest of them. Still, that would only be enough to crack or damage the bone, so most would still be intact.
Depending on how many individual springlocks holding back individual suit pieces there were, it is very possible the combined amount of damage to the bones resulted in multiple fractures. If not, the metal bits could have embedded themselves into his bones, as bones are quite dense, and the sudden force might've gotten them stuck, but not enough to break the bone as a whole. Hence why Springtrap's got those weird little metal things embedded in his body n stuff.
(Yes. Yes I know about the bite of ‘83. For the sake of this discussion we are assuming that was an astronomical failure on a small child with brittle bones, Crying Child Georg is an outlier adn should not be counted. Also I don’t think his skull was entirely crushed but thats a different subject.)
Okay, but how did it kill him?:
Regardless of whether Willy actually got crushed like a grape in a juice press, he would've died of severe blood loss and multiple vital organs being punctured, and would've gone into like four different kinds of shock. Severe blood loss takes about five minutes to drain most of your blood to a deadly level, and that's if he's lucky, seeing as it's more likely his lungs and heart were some of the first thing to be punctured.
The lungs and heart are delicate, and those being damaged would've cause him to go into circulatory shock, which drains your blood faster and causes there to be a loss of oxygen, which could've caused serious brain damage had he actually managed to survive. The heart can take a bit of damage after being punctured, but the blood would've pooled around it and negate it's ability to pump blood. The lungs being punctured would've caused the air being held to flood the area around the lung, causing them to collapse and make breathing painful and increasing difficult. And either of these things will lead to next issue: Oxygen towards the brain.
Studies show the brain can only go four minutes without oxygen, but that's in controlled medical environment, so it's likely the brain would go much faster, especially if the endo parts managed to puncture the skull. Most farm animals take ten seconds to complete brain death.
But like, did it hurt?:
Yes.
It would've been excruciatingly painful for about the two seconds where he was still conscious, but couldn't have lasted more than a minute or two, and that's being generous. It is only through ghost shenanigans and pure annoying willpower his pain is prolonged.
TL;DR: William probably immediately passed out after that cutscene faded to black in FNaF 3 and then died of blood loss. On the plus side, those like three seconds he was still conscious would've been filled with excruciating pain, and depending on how much you want him to suffer and if you pull supernatural shenanigans, you can headcanon that period of time as long as you want.

#fnaf#fnaf 3#william afton#springtrap#cw death#cw gore#important juni thoughts#queue queue train#this was in my drafts for like four years for some reason lol
48 notes
·
View notes