rue (ruí if close)/t/law | sea / brown migrant | ⇧30 · they · MDNI · + xe ve · ªªªªªª • tme “the way i naively try to earn my right to deserve life—as if someone like me could ever become human—by being cuter, more patient, and more calm until my heart turns to straw -apology poem, j. berrout | mutuals stay safe and please recommend me songs | swerfs/gc`s/weirdos do not interact | *⁎ ⚈᷀᷁*⁎ ?
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text

Lee Jaeseok — The Instructions with the Body (acrylic, canvas, 2018)
3K notes
·
View notes
Text


2025.06.21
"Small Children in the Background Where All Things Unravel"250621
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Pickle jar painting with a cat by kellypringleart.
Source: x
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
self proclaimed pansexual cis guy there is a considerable lack of hairy man ass, pole and hole on your 18+ blog
168 notes
·
View notes
Text



the trio
523 notes
·
View notes
Text

yin_0909 on twt
7K notes
·
View notes
Text

transparent, 2024
numbers and planets oracle
pieces of broken glass polished by ocean waves, painted with nail polish with color name: disney princess - ariel - your voice has power
9 notes
·
View notes
Photo

炭烤南瓜(@YIN_0909)
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
Edit: Removed the screenshot so as not to share dm stuff, but I got a message from someone who couldn't send an ask, inquiring: "i was wondering what book it was that you mentioned about the philippines? i'd be interested in reading it." Sorry to post; figured it would be a subject worth sharing with interested others. Good news: It's an article, so it's relatively easier to access and read.
Jolen Martinez. "Plantation Anticipation: Apprehension in Chicago from Reconstruction America to the Plantocratic Philippines" (2024). An essay from an Intervention Symposium titled Plantation Methodologies: Questioning Scale, Space, and Subjecthood. Hosted and published by Antipode Online. 4 January 2024.
Basically:
Explores connections between plantations in US-occupied Philippines and the policing institutions and technologies of Chicago. Martinez begins with racism in Chicago in the 1870s. Coinciding with Black movement to the city (from the South during Reconstruction and the Great Migration) Chicago was, in Martinez's telling, a center of white apprehension. Chicago public, newspapers, and institutions wanted to obsessively record information about Black people and labor dissidents, including details on their motivations and inner life. Between 1880-ish and 1910-ish Chicago then became a center of surveillance, records-keeping, classification systems, and new innovations in collecting information. Within a year after the labor rebellions, the Adjutant General of the US Army who led Chicago's militarized crackdown on the 1877 Great Railroad Strike immediately moved to DC and proposed establishing "the Military Information Division" (MID); eventually founded in 1885, MID started collecting hundreds of thousands of Bertillon-system intelligence cards on dissidents and "criminals." Meanwhile, National Association of Chiefs of Police headquartered their central bureau of identification (NBCI) in Chicago in 1896. At play here is not just the collection of information, but the classification systems organizing that information. The MID and related agencies would then go on to collect mass amounts of information on domestic residents across the US. In Martinez's telling, these policing beliefs and practices - including "management sciences" - were then "exported" by MID to the Philippines and used to monitor labor and anticolonial dissent. Another Chicago guy developed "personality typing" and psychological examinations to classify criminality, and then trained Philippines police forces to collect as much information as possible about colonial subjects.
The information-gathering in the Philippines constituted what other scholars like Alfred McCoy have called one of the United States' first "information revolutions"; McCoy described these practices and social/professional networks as "capillaries of empire." Martinez suggests that it's important to trace the lineage of these racialized anxieties and practices from Chicago to the Philippines, because "such feelings were fundamental to linking plantations which at first seem so spatially and temporally distant." And "[u]ltimately, the US colonial plantocracy in the Philippines built its authority around information infrastructures [...] and feelings emanating from Chicago [...] that extended from the image of the American South."
Important context: 1899/1900-ish is when the US occupied or consolidated power in Panama, Cuba, Puerto Rico, Guam, Hawaii, and the Philippines.
---
Side-note:
The Bertillon system (bertillonage) was standardized at about this same time, 1879-ish, and in similar social and racial contexts, becoming popular in other Midwest/Great Lakes cities, especially to track Black people (though it was also rapidly and widely adopted famously as an essential approach across Europe). The system used body measurements to identify and classify people, especially "criminals," significantly involving photography, such that Bertillon is also sometimes credited as the originator of "the mugshot."
I'd add that the aforementioned police chiefs National Bureau of Criminal Identification (NBCI) stayed in Chicago from 1896 until 1902, when the killing of President McKinley frightened officials with potential of wider popular movements; at that point, it was moved to DC, as William Pinkerton (co-director of the Pinkerton agency) donated the agency's photograph collection to build the new bureau, and NBCI strengthened itself by collecting fingerprints and became the precursor to the FBI, founded 1908. (After 1895-ish especially, European authorities were transcending their petty rivalries to attempt forming international police agencies and share documents, tracking each others' domestic radicals/dissidents.)
---
You could compare the colonial use of Bertillon-style intelligence card systems in Chicago and US-occupied Philippines to the rise of fingerprinting as a weapon of Britain in India.
Edward Henry was the Inspector-General of Police in Bengal, appointed 1891, basically the top cop in British India. He exchanged letters with notorious eugenicist Francis Galton, wherein they specifically talked about the importance of developing a classification system for fingerprints that could be used alongside the Bertillon system of anthropometric identification. (Another British imperial administrator in India, Sir William Herschel, had previously been the first to pioneer fingerprinting by taking hand-prints.) By 1897, police forces in India had been adopting the so-called Henry Classification System, and the Governor-General of India personally decreed that fingerprinting be adopted across India. By 1900, Henry was sent to South Africa to train police in classification systems. By 1903, Henry was back in Britain and became head of the Metropolitan Police of London, now the top cop in Britain. (Compare dates with US developments: British police in India adopt fingerprint identification system the same year that Chicago police found their proto-FBI central identification bureau. Less than a year after the US head-of-state gets killed, Britain super-charges the London police.)
So, the guy who pioneered fingerprinting classification for use in maintaining order and imperial power in India and other colonies was eventually brought in to deploy those tactics on Britons in the metropole.
The kind of colony-to-metropole violence thing described by many theorists. (Britain also developed traditions of police photography in context of rebellions in Jamaica and India. Outside of London, the first permanent "modern" police forces across the rest of Britain were legally provisioned for with the Irish Constabulary of 1837 and County Police Act of 1839, "coincidentally" just before/during a 27th of July 1838 "Vagrancy Act" law that made "joblessness" a crime which was put into effect JUST FOUR DAYS before the 1st of August 1838 date when emancipation of Black slaves in the British Caribbean was allowed. As in, four days before nearly a million Black residents of the Empire got legal freedom, Britain outlawed vagrancy and was building permanent national police forces.)
---
The 1890s were outrageous. Japan's domestic 1880 Penal Code was built on French models. The Ottoman Empire built a system of passport requirements to monitor movement; France did something similar in Algeria. In 1898, the Austria-Hungary imperial foreign minister called for the formation of an "International Police League." This prompted an Italian radical at the time to write:
"The police are the same in all parts of the world. Laws have been fabricated by the bourgeoisie on the same model; in this, the bourgeoisie is more international than we are."
And Great Lakes cities, after the Great Migration, were notorious for this kind of police violence. Consider how the Bertillon system was used early-on by Minneapolis police to track and target Black "alley workers" (try keyword-searching "Minneapolis Bertillon alley workers"). Or how Chicago was a focal point of antiblack violence in the Red Summer of 1919. Or how Milwaukee has some the most distinct Black-white segregation of any large urban area in the US. Or how, after Elliot Ness lionized law enforcement officials in Chicago during the Al Capone case, he then led policing operations in Cleveland culminating in the mass eviction and the burning of Kingsbury Run shantytown. (Chicago is like a funnel, a node, a hub. Especially after the 1860s: Center of railroad networks. Center of telegraph networks. Destination for Texas/Kansas cattle shipped to Chicago meatpacking houses. Destination for Corn Belt prairie agricultural products. Hence the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition and Chicago's turn of the century image as a modernist metropolis. So they had to keep the laborers in line.)
---
Anyway, the other story that I mentioned regarding Philippines was from:
Gregg Mitman. "Forgotten Paths of Empire: Ecology, Disease, and Commerce in the Making of Liberia's Plantation Economy." Environmental History, Volume 22, Number 1. January 2017.
For context, I'd note that this takes place in the midst of the US's "conquest of the mosquito" in its militarized occupation of Panama, where the canal was completed by the US between 1904 and 1914. (Again, US was occupying Philippines, Hawaii, Guam, Puerto Rico, and Cuba.)
In Mitman's story, Richard P. Strong was appointed as director of the brand-new Department of Tropical Medicine at Harvard in 1913. Shortly thereafter in 1914, as he toured plantations in Panama, Cuba, Guatemala, etc., Strong simultaneously took a job as director of the Laboratories of the Hospitals and of Research Work of the United Fruit Company (infamous for its brutal labor conditions in plantations, its land-grabbing in Central America, and its relationship to US corporate power). Harvard hired Strong partially on the recommendation of General William Cameron Forbes, who was the military governor of US-occupied Philippines from 1909 to 1913. When Harvard hired Strong, he had been living in the Philippines, where he was the personal physician to Governor Forbes, and was also the director of the Philippine Bureau of Science's Biological Laboratory, where he had experimented on Filipino prisoners without their knowledge; Strong fatally infected these unknowing test-subjects with bubonic plague. Then, Governor Forbes, after leading the US occupation of the Philippines, himself became an overseer to Harvard AND a director of United Fruit Company (also Forbes was a banker and the son of the president of Bell Telephone Company). Meanwhile, Strong also became a shareholder in British rubber plantations; Strong approached Harvey Firestone to help encourage the massive rubber company to negotiate a deal to expand plantations in West Africa, where Firestone got a 99-year-long concession to lease a million acres of land in Liberia. So there's an intimate relationship between military, plantations, colonization, medical professionals, corporate profiteering, land dispossession, etc.
---
So, in each case, there is imperial anxiety about the threat of potential subversion from recalcitrant laborers. Imperial authorities cooperate and learn from each other. The rubber plantation owner is friends with the military general, who's friends with the laboratory technician, who's friends with the railroad developer, who's friends with the cop, who's friends with the forestry minister, who's friends with banana plantation owner. There are connections between the exercise of power in the Philippines and Panama and West Africa and Bengal and Chicago. Connections both material and imaginative.
#thinking through stuff#history edition#q. [ .semihiatus]#plantocracy#plantations#this is honestly 🖤🩷🖤#i love learning what i can (spoons/ADHD be damned) and i appreciate it#resources#tw long post#long post#to read later#p4rb
190 notes
·
View notes
Text

ig: _.iiimiii._
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
been a goblin but @ 10 : 30 eastern coast ( or 7 : 30 for PST )
no mic as i get into a DOCUMENTARY ! for. reasons.
⋆✩🌃ִ ✧˖° ♡
labour, SŴ+


image description: a bright pink and purple grahpic showing a still from the movie Showgirls of Pakistan mainly showing a cigarette, wafting smoke, by an eponymous showgirl wearing gold and magenta link here
0 notes
Text
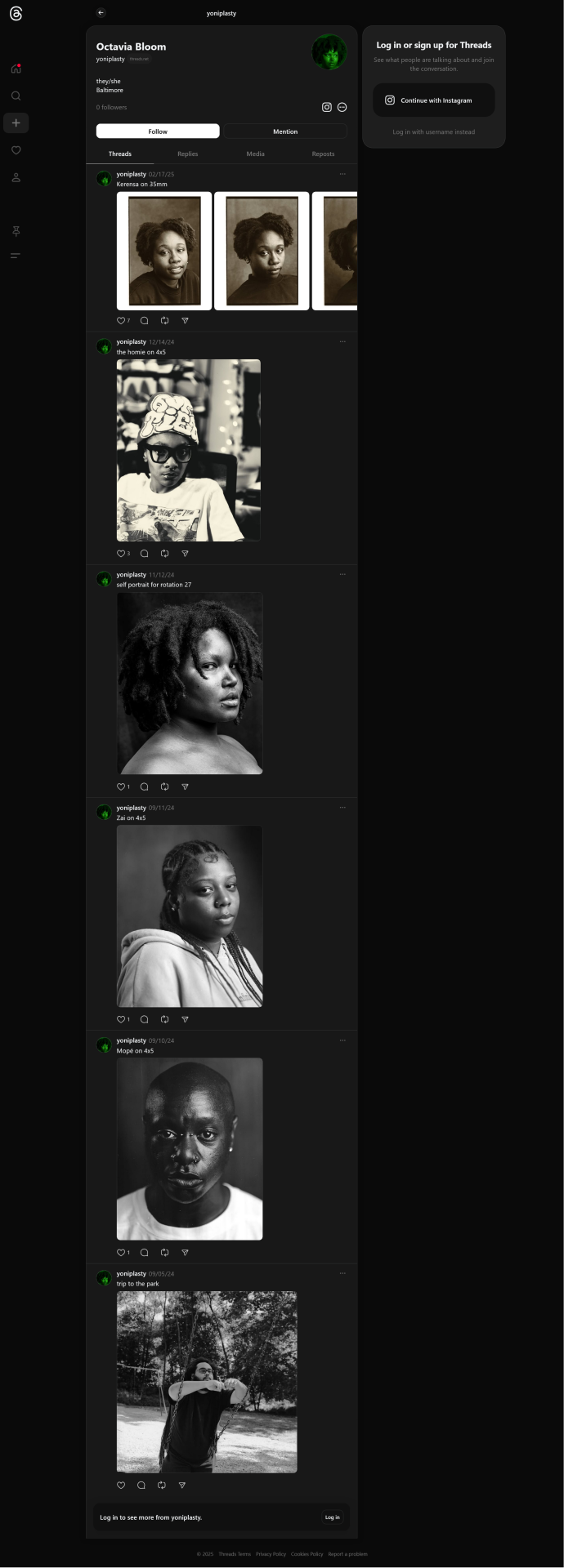
#portrait#photography#my upload#just trying to get into a recent (sorta viral) discussion of aesthetic by Marsha's Plate even as my short arms box & battle w/ M.I / 80HD#yoniplasty (on Instagram)#Octavia Bloom#god knows im not an expert but#i like the way that certain websites look ( just like here )#webcore
0 notes
Text
5K notes
·
View notes
Text

(x)
204 notes
·
View notes
