Text
PRODUCT LAUNCHING AND MARKETING
Marketing is the dynamic engine that propels businesses towards their target audiences, involving crafting compelling messages and adapting strategies to understand and meet customer needs. At its core, it's a multifaceted business activity that establishes meaningful connections, builds brand recognition, and plays a crucial role in satisfying customer needs in a competitive market environment.
The 4Ps
Also known as the marketing mix, hold significant importance in guiding businesses to formulate a comprehensive and customer-centric marketing strategy.

Product. The product is at the core of the marketing mix as it addresses the customers' needs and desires. By focusing on features, quality, design, and packaging, businesses can create offerings that resonate with their target audience.
Place. Distribution channels play a pivotal role in making products accessible to customers. Determining where and how customers can access products ensures convenience, and understanding logistics and retail presence is vital for effective market reach.
Price. Pricing strategies directly influence customer perception and the financial health of the business. Considering production costs, competitor strategies, and market dynamics helps in establishing an optimal price that reflects the value of the product to the customer.
Promotion. Creating awareness and persuading customers to choose a product is achieved through promotional activities. Advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and other strategies collectively contribute to communicating the value of the product, fostering interest, and driving purchasing decisions.
The integration of these 4Ps provides a structured approach for businesses to align their products with customer needs, determine suitable pricing, choose effective distribution channels, and implement compelling promotional tactics. This customer-centric framework ensures that businesses address key elements that contribute to successful marketing and, ultimately, business success.
Know your customers
A customer is an individual or entity that engages in a financial transaction with a business, exchanging money for the goods or services offered by the business. This transaction is driven by the customer's desire to experience the value provided by the business.
Connecting Needs to Wants
The saying "Needs beget wants" emphasizes the importance of addressing fundamental human needs before desires. Startups succeed by identifying and fixing basic problems for customers, creating trust by reliably meeting essential needs. As customers' needs are fulfilled, desires for more aspirational goods or experiences naturally emerge, creating a cycle of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
The Greater The Fit, The Greater The Value
In business, the saying "The greater the fit, the greater the value" is a golden rule. It underscores the importance of aligning what a business offers with what customers truly need and want. Achieving a great fit leads to satisfied customers who find significant value in the product or service, resulting in brand loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the marketing maze requires a holistic approach. Understanding customers and tailoring strategies using the 4 Ps—Product, Place, Price, and Promotion, as emphasized by Sir Carlo Calimon—is paramount. Ensure your product aligns with your target audience, spotlight its unique value, promote it judiciously, and commit to continual improvement for enduring success in the dynamic marketing landscape.
0 notes
Text
"Navigating Competitive Success: A Startup's Guide"
Launching a successful startup is more than just having a great product—it's about understanding and outmaneuvering your competition. In this blog, we'll delve into the intricacies of competitive analysis, helping you make smarter decisions and ensuring your startup stays ahead in the market.

IDENTIFYING COMPETITORS
Identify Direct and Indirect Competitors Before entering the business arena, it's crucial to recognize both direct and indirect competitors. Identify businesses offering similar products or services as your direct rivals, and acknowledge indirect competitors with different offerings but competing for the same customer budget. This comprehensive understanding shapes your strategies and equips you to adapt to market changes.
Research Their Product or Service Offerings Competitive analysis goes beyond knowing what your competitors offer. Explore the specifics—features, pricing, and unique selling points. This exploration defines your startup's offerings, unveils potential market gaps or opportunities, and empowers you to stay competitive in a dynamic market.
Analyze Their Strengths and Weaknesses A thorough analysis of your competitors' strengths and weaknesses is a strategic move. Recognize their strong aspects, such as a robust brand or innovative products, and pinpoint areas where they may be vulnerable, like customer service issues. Leveraging their weaknesses and capitalizing on your own strengths positions your startup strategically in the market to gain a competitive edge.
Identify Areas Where You Can Differentiate Your Startup from the Competition To stand out, focus on creating a Unique Value Proposition (UVP) tailored to customer needs. Innovate in product features, prioritize quality, and offer exceptional customer service. Building a distinctive brand identity, considering strategic pricing, targeting niche markets, and embracing sustainable practices are key aspects. Continuous improvement and staying adaptable ensure your startup maintains a unique and compelling position in the competitive landscape.
Develop Strategies to Set Your Startup Apart from Competitors Crafting strategies to set your startup apart involves deep market understanding, continuous innovation, building a strong brand, strategic pricing, targeting niches, prioritizing quality and service, embracing sustainability, and staying adaptable through continuous improvement. Think creatively, introduce innovative features, and embrace sustainability and social responsibility initiatives. Learn from your competitors, observe, and continuously learn.
ANALYZING THE COMPETITION
To analyze the competition effectively, two (2) powerful visual tools were introduced: the Competitive Analysis X/Y Axis and the competitive analysis table.

The Competitive Analysis X/Y Axis is like a strategic map, visually showcasing competitors' positions based on price and product differentiation. This gives businesses an instant snapshot of the competitive landscape, helping identify strategic opportunities and market gaps.
On the other hand, the Competitive Analysis Table is a quick reference guide, condensing vital competitor information such as product features, pricing, target markets, and customer feedback. It provides a streamlined overview, aiding businesses in making swift, informed decisions.
These visual tools aren't just about data; they're about gaining a deeper understanding of the competition. By incorporating these into your analysis, you'll navigate the competitive landscape with clarity and make strategic moves that set your business apart.
Conclusion
Competitive analysis is the compass guiding startups through the ever-changing business landscape. More than a strategy, it empowers businesses with insights to navigate confidently, differentiate effectively, and set the course for lasting success. This blog serves as a comprehensive guide, urging startups to decode the competition, identify opportunities, and craft unique strategies. It's time to utilize competitive analysis as a roadmap, securing a distinctive place in the business arena.
0 notes
Text
The Transformative Power of Intellectual Property: A Journey from Protection to Strategic Asset
Unleashing Intellectual Potential: The Transformative Power of Intellectual Property
In today's dynamic and fast-paced world, the realm of innovation and intellectual creativity is more crucial than ever. At the forefront of this transformative landscape stands Engineer Glady Cristie H. Kampana, a distinguished alumna of Xavier University, with an impressive academic background in Electronics and Communications Engineering, a master's in Electrical Engineering, and a current pursuit of a doctorate in Mechanical Engineering at MSUIIT. However, Glady is not just an academic; she is a trailblazer in the domain of Intellectual Property (IP).
Currently serving as the Intellectual Property Support Officer and Office Manager at the University of Science and Technology of Southern Philippines (USTP), she plays a pivotal role in shaping the innovation landscape. Beyond academia, she extends her expertise as an expert member of DOST Region and the head of USTP's Intellectual Properties Asset. Her journey exemplifies a multidisciplinary approach to IP, demonstrating its profound impact on entrepreneurship, technological advancements, and economic growth.
The Journey of IP
The journey unfolds as a narrative of academic excellence and a commitment to fostering innovation. With an extensive educational background, coupled with her role as the head of USTP's Intellectual Properties Asset, she showcases a holistic approach to intellectual property. Beyond the confines of academia, she provides vital IP consultation, navigating the intricate landscape of patents, trademarks, and copyrights. As a representative of Bukidnon University, she serves as an IP agent, underlining her dedication to the broader intellectual community.
The Role of IP in Technopreneurship
Technopreneurship, a field where technology and entrepreneurship converge, holds immense promise for the future. As part of the Technopreneurship Program Coordination Office (TPCO) team, she sheds light on the pivotal role of IP for young entrepreneurs. In her capacity as the head of the Innovation and Technology Support Office, she ensures that the technologies generated by the university are safeguarded through strategic IP filings.
In her message to technopreneurship students, the emphasis is clear: intellectual property is not just a legal formality; it is a catalyst for success in the entrepreneurial journey. By protecting innovations through IP, technopreneurs can secure their competitive edge, attract investment, and contribute to the broader landscape of technological progress.
Defining Innovation and its Economic Impact
Drawing on the wisdom of innovation pioneer Edward Roberts, the definition of innovation as a process of creating value through novel solutions goes beyond the traditional view. This definition encompasses the entire lifecycle, emphasizing the critical role of exploitation in realizing economic value.
In this narrative, innovation becomes a driving force for economic growth, productivity increase, and the establishment of new businesses, especially startups. The equation of invention plus exploitation becomes a mantra for aspiring technopreneurs, guiding them toward creating not just products but sustainable value.
IP's Contribution to Global Innovation Index
The Global Innovation Index serves as a barometer for a nation's innovation prowess. The annual evaluation reveals the Philippines' commendable progress, ranked 56 among 132 countries in 2023. This success is attributed to the multifaceted contributions of intellectual property, including patents, copyrights, trademarks, and industrial designs.
In this context, intellectual property emerges as not just a legal framework but a dynamic force propelling nations forward. The protection and recognition of intellectual creations contribute not only to a country's ranking but also to the generation of income for academic institutions, fostering a cycle of innovation.
Philosophy and History of IP
Embarking on a historical journey, Glady takes us back to the roots of the intellectual property system. From ancient Greece to the establishment of the modern IP system in the United States, the evolution is marked by a profound philosophy. The founders of America, guided by the bargain theory and natural rights theory, aimed not only to protect intellectual property but to democratize it.
Unlike the European system, which favored monopolies for established businesses, the U.S. model sought to stimulate inventive genius and entrepreneurial energy among common individuals. The philosophy of democratizing intellectual property becomes a cornerstone in this narrative, framing IP not just as a legal construct but as a catalyst for societal progress.
Philippine Intellectual Property System: Balancing Innovation and Public Good
Navigating the legal landscape, she introduces the Intellectual Property Code (RA 8293), the governing document for IP in the Philippines. This legal framework is designed to strike a delicate balance between the interests of innovators and the public good. The dual objectives of promoting innovation and creativity while safeguarding market integrity and product positioning underscore the nuanced approach to intellectual property.
In the Philippines, the patent system is not just a legal requirement; it is a cultural lever that fosters a spirit of seeking what's new. The disclosure of inventions becomes a contribution to an open database, inspiring and motivating innovators to build upon existing knowledge. At the institutional level, incentives drive researchers to develop more innovations, creating a symbiotic relationship between the legal framework and the culture of innovation.
Hierarchy of IP Value: From Foundation to Business Strategy
One of the central themes in this narrative is the hierarchy of IP value. Intellectual property, far from being a static legal concept, evolves through different levels of value addition. From foundational protection to becoming an integral part of overall business strategy, IP becomes a dynamic force shaping market positioning, revenue generation, and strategic partnerships.
The hierarchy reflects the journey of intellectual property from being a shield to transforming into a business superpower. This evolution is not just a legal necessity but a strategic imperative for businesses aiming not just to survive but to thrive in a competitive marketplace.
Promises of Intellectual Property: Fueling Business Growth
Enumerating the promises of intellectual property unveils a spectrum of advantages that go beyond legal protections. Exclusivity and market positioning become potent tools for businesses seeking to establish a strong foothold. Competitive advantage,
revenue generation, and financial support underscore the multifaceted contributions of IP to business growth.
IP is not merely a legal safeguard; it becomes a negotiating power, allowing businesses to navigate partnerships and collaborations with a unique value proposition. Operational safety and corporate trust emerge as intangible yet invaluable benefits, as investors and stakeholders are more likely to trust businesses that invest in intellectual property.
In essence, Glady Kampana's insights illuminate the transformative power of intellectual property. From its historical roots to promises and impact on companies and economies, IP emerges as a cornerstone fostering innovation, economic growth, and competitive advantage. Intellectual property, under Glady's guidance, shapes a future where creativity and innovation thrive, paving the way for a dynamic and prosperous intellectual landscape.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Value Proposition
Miss Keren Lacadin, the lead for Startup Ecosystem Development and Deputy Focal of the ICT Industry Development Bureau for DICT Region 10, delivered an engaging session during the lecture series, sharing her insights on value proposition. Her expertise and guidance are highly valuable in understanding and crafting strong value propositions for startups, making her an honorable speaker for the informative webinar.
Key to Startup Success
Startup success isn't just about making money; it's about doing good too. At places like Techstars and Founder Institute, there's a simple rule: "give first." It means helping others without expecting anything in return right away. This idea is all about giving something valuable to people and helping with important community problems. But for a startup to make it in the long run, it needs to find a balance. It should create value, make sure it can keep going, and do good things for society. This means combining creative ideas, good business sense, and a real passion for making the world better.

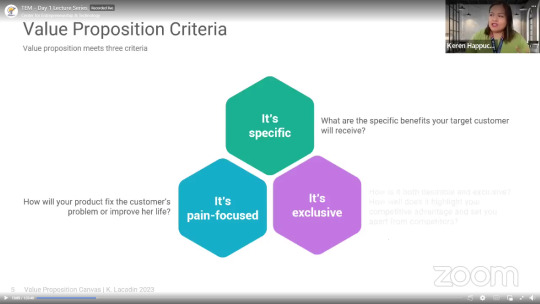
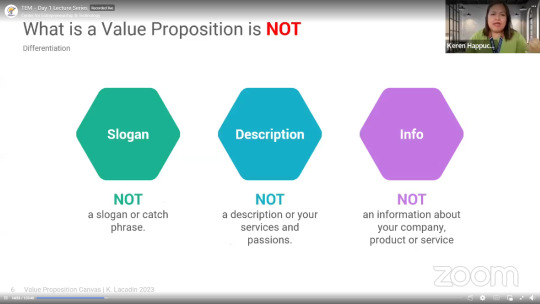
A Value Proposition is the value promise you deliver to your customers, both before and after they make a purchase. It's the essence of why your startup matters, and it goes way beyond mere marketing slogans or bland descriptions.
Crafting a Winning Value Proposition
According to Miss Keren, there are four steps to follow in creating a wining value proposition. This includes:
1. Research Your Audience: Start by truly understanding your target market. Get to know their problems, motivations, and how they like to communicate. Speak their language and address their issues effectively.
2. Create an Ideal Buyer Persona: Develop detailed customer profiles based on qualitative data. This helps you understand your audience better and create solutions tailored to them.
3. Research Your Competitors: Analyze up to fifteen competitors to identify differences and areas for improvement. This analysis can inspire innovation.
4. Determine the Primary Benefit: Find that one key factor that sets your product apart and provides significant value to your customers. This unique benefit is what will make your offering stand out. A strong value proposition is a key to startup success.
The Components of Strong Value Differentiation
Three essential components are at the core of strong value differentiation:
Valuable. Ensure your value proposition addresses something your target customers genuinely need and value.
Differentiated. Highlight what sets your product or service apart from competitors, creating a unique selling point.
Substantiated. Back up your value proposition with concrete evidence and proof, building trust and credibility with your customers.
These components are the keys to unlocking doors and keeps your business forward.
Templates to Craft a Compelling Value Proposition
These templates are valuable tools to help you create a compelling value proposition and lead the way in generating success, particularly in terms of lead generation.
Needs and Wants: Which focuses on addressing your customers needs and wants. Ensure your value proposition is the best option for them, and back it up with trust and believability.
Product Identification: List your products and services, emphasizing their technical, business, and personal values.
Ten-Point Value Proposition: Consider ten key points, including the time frame, internal and external communication, operationalization within your business, measurement of effectiveness, customer experience, pricing, and differentiation.
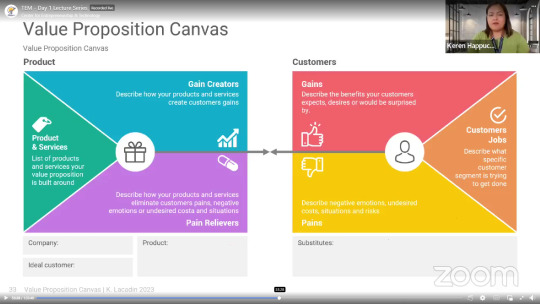
The Value Proposition Canvas and Its Crucial Role
The value proposition canvas is a vital tool for shaping your business model. It helps identify the key elements of your value proposition for your target customer segments. It consists of two parts: the customer profile and the value map.
Customer Profile:
Customer Jobs: These are the tasks your customers are trying to perform – functional, social, and emotional. Understand their everyday challenges.
Pains: Dive into the negative experiences, emotions, and risks that customers face when trying to get their jobs done. Get a grip on their problems and challenges.
Gains: Explore the benefits, experiences, and results that your customers expect or desire from a product or service. Understand what your customers are looking to achieve.
Value Map:
Products and Services: List the specific products or services you offer. Distinguish between essential features and nice-to-haves.
Gain Creators:* Explain how your products or services create customer gains. What benefits do they provide, whether it's saving time, efficient communication, or easy learning?
Pain Relievers:* Describe how your products or services address customer pains, negative emotions, or undesired costs. Focus on eliminating customer problems and making their lives easier.
The goal is to create a perfect fit between the problems your customers face and the solutions you provide. This fit ensures that your startup offers services that are both beneficial and essential for your target audience.
How to Write a Unique Value Proposition
Crafting a Unique Value Proposition
Gather Voice of Customer Copy: Collect feedback from your target audience to understand how they perceive your product. Avoid making assumptions and rely on real customer insights.
Emphasize Clarity Before Creativityt: When creating your value proposition, prioritize clarity over creativity. Keep the message straightforward, avoiding unnecessary jargon or wordiness.
Focus on Benefits, Not Hype: Concentrate on highlighting the actual benefits of your product or service rather than using excessive hype. Clear value is more appealing than extravagant claims.
To wrap it up, a strong value proposition is like the heart of your startup's success. It's the special promise you give to your customers, showing them why you're awesome, and how your business can do really well. So, use these tips, start creating your value proposition, and get your startup on the path to success.
Don't forget, having a great value proposition can make a big difference for your startup, especially when there's lots of competition. Dive in, explore, and make a promise to your customers that makes your startup stand out. The journey to success starts with a clear and unique promise to your customers.
0 notes
Text
Design Thinking: The Path to Innovation and Problem-Solving

In a world driven by innovation and change, the concept of Design Thinking has emerged as a powerful tool for problem-solving and creating meaningful solutions. A recent event, aptly titled "Design Thinking," delved into this methodology, offering participants a deep dive into a mindset and process that can transform how we approach complex challenges.

The Essence of a Startup
A startup is a temporary organization with a mission to search for a repeatable and sustainable business model.
The ultimate goal of a startup is to create something scalable and reputable.
Startups often challenge the status quo, disrupt traditional industries, and offer innovative solutions to existing problems.
Examples of disruptive companies like Facebook, Tesla, Airbnb, Google, Apple, and Grab were shared, highlighting the impact of startups on the world.

The Right Problem Matters
Solving the right problem is paramount for the success of a startup.
Understanding the perspective of the people experiencing the problem is crucial.
Design Thinking was introduced as a methodology to find solutions to complex societal problems with a focus on human-centered design.

Fulfilling Human Needs and Desires
Products and services are designed to fulfill human needs, wants, and desires.
The field of ergonomics influences design, emphasizing the importance of user interaction with devices.
Design Thinking is presented as a people-centered approach to problem-solving that leads to innovation.
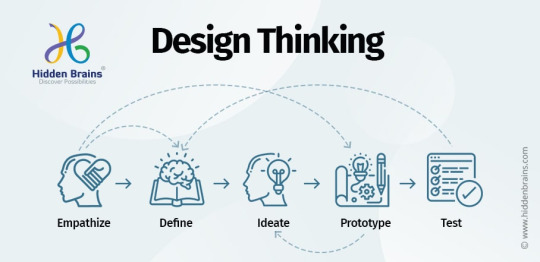
The Design Thinking Process
Design Thinking involves a five or six-phase process, with the Design Thinking Five Bases introduced:
Empathize: Understand the people experiencing the problem.
Define: Clearly define the problem based on user insights.
Ideate: Generate multiple solutions through brainstorming.
Prototype: Create tangible representations of potential solutions.
Test: Gather user feedback through iterative testing.

The Iterative Nature of Design Thinking
The Design Thinking process is cyclic, allowing for the possibility of revisiting earlier phases based on user feedback.
The primary goal is to create innovative solutions that efficiently address real user needs and problems.
The Mindset of Design Thinking
Design Thinking is not just a process; it's also a mindset.
Key mindsets associated with Design Thinking include creative confidence, bias toward action, learning from failure, empathy, embracing ambiguity, optimism, and iteration.

The Three Lenses of Innovation
Design Thinking is guided by three lenses: human-centered, feasible, and viable.
Innovations must address people's needs, leverage technology, and meet business criteria for success.

The Importance of Efficiency
Efficiency is emphasized in Design Thinking to develop solutions with fewer resources, including time and materials.
The iterative nature allows for continuous improvement and adaptation based on user feedback.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the "Design Thinking" event served as an illuminating journey into a mindset and process that fosters innovation and effective problem-solving. It underscored the significance of starting with a clear understanding of the problem, empathizing with users, and iteratively refining solutions. Design Thinking isn't just a methodology; it's a way of thinking that can empower individuals and teams to create meaningful change and make a positive impact on the world.
1 note
·
View note