Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
What Happened on October 22 in American History?

October 22 stands out in American history as a date marked by significant political events, cultural milestones, and moments that have shaped the nation. From the inauguration of Texas’s first president to pivotal moments during the Cuban Missile Crisis, this day has witnessed a variety of important occurrences. In this article, we will explore notable events that happened on October 22, emphasizing their historical significance and lasting impact on the United States.
What Happened on October 22 in American History?
Sam Houston Inaugurated as 1st Elected President of the Republic of Texas (1836)
On October 22, 1836, Sam Houston was inaugurated as the first elected president of the Republic of Texas. This event marked a critical moment in the history of Texas, which had recently declared independence from Mexico. The inauguration symbolized the establishment of a new government and the beginning of an era characterized by challenges and opportunities for the young republic.
Houston’s presidency came at a time when Texas was in a precarious position. The newly independent nation faced economic difficulties, security threats from Mexico, and the need for recognition from foreign powers. Houston, a key figure in the Texas Revolution, took immediate steps to stabilize the government, seek diplomatic relations, and address the military needs of the republic. His leadership during this formative period laid the groundwork for Texas’s eventual annexation into the United States and its ongoing significance in American history.
Thomas Edison Perfects the Carbonized Cotton Filament Light Bulb (1879)
On October 22, 1879, Thomas Edison achieved a major milestone by perfecting the carbonized cotton filament light bulb. This invention represented a breakthrough in electric lighting, significantly improving the functionality and lifespan of light bulbs compared to previous designs. Edison’s work in this area laid the foundation for the widespread use of electric lighting, transforming everyday life in America and beyond.
Edison’s carbon filament bulb was a pivotal advancement in the broader context of industrial innovation during the late 19th century. His relentless experimentation and dedication to improving electrical technologies not only revolutionized lighting but also influenced various industries and everyday activities. The success of the light bulb on October 22 highlighted Edison’s role as a key innovator of the era, ultimately contributing to the development of modern electrical systems and urban infrastructure.
New York’s Original Metropolitan Opera House Has Its Grand Opening (1883)
On October 22, 1883, New York’s original Metropolitan Opera House opened its doors for the first time with a performance of Charles Gounod’s opera “Faust.” This event marked a significant milestone in American cultural history, establishing the Met as a premier venue for opera and classical music. The grand opening showcased the artistic aspirations of New York City during a time of growth and cultural sophistication.
The Metropolitan Opera House quickly became a cultural icon, attracting renowned artists and operatic productions from around the world. Its establishment on October 22 represented a commitment to the arts and the emergence of opera as a popular form of entertainment in America. Over the years, the Met has continued to evolve, becoming synonymous with excellence in the performing arts and influencing generations of artists and audiences.
Herbert Hoover Speaks of “American System of Rugged Individualism” (1928)
On October 22, 1928, Herbert Hoover, then a presidential candidate, delivered a speech in which he articulated his vision of the “American system of rugged individualism.” In his address, Hoover emphasized the importance of self-reliance and individual initiative as fundamental principles of American life. This philosophy resonated with many Americans during a period of economic prosperity and reflected the values of the time.
Hoover’s speech on October 22 laid the groundwork for his presidency, which began in March 1929. However, his beliefs about rugged individualism would be tested shortly thereafter with the onset of the Great Depression. As the economic crisis unfolded, the limitations of relying solely on individual initiative became apparent, forcing Hoover to confront the realities of widespread unemployment and economic hardship. The speech remains a significant part of Hoover’s legacy, illustrating the complexities of American ideals and the challenges of governance during turbulent times.
Notorious Bank Robber Charles “Pretty Boy” Floyd Shot and Killed by FBI Agents (1934)
On October 22, 1934, notorious bank robber Charles “Pretty Boy” Floyd was shot and killed by FBI agents in East Liverpool, Ohio. Floyd had become a prominent figure during the Great Depression, known for his flashy lifestyle and criminal exploits. His death marked a significant moment in the FBI’s efforts to combat organized crime and bank robbery, which had surged during this period.
Floyd’s violent end on October 22 symbolized the federal government’s increasing resolve to tackle crime and restore law and order amid the economic turmoil of the 1930s. His life and death became emblematic of the era, capturing the public’s fascination with gangsters and outlaws. The FBI’s involvement in his case reflected the agency’s evolving role in American law enforcement and its commitment to addressing organized crime, paving the way for future efforts in criminal investigation and enforcement.
President John F. Kennedy Addresses the Nation About the Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
On October 22, 1962, President John F. Kennedy delivered a live television address to the American public regarding the Cuban Missile Crisis, a pivotal moment in Cold War history. In his speech, Kennedy outlined the discovery of Soviet missile installations in Cuba and the immediate threat they posed to U.S. national security. He announced a naval blockade of Cuba to prevent further shipments of military equipment, effectively escalating the crisis.
Kennedy’s address on October 22 was a critical moment in U.S. history, as it not only informed the American people about the gravity of the situation but also called for national unity and vigilance. His calm yet firm tone aimed to reassure the public while underscoring the seriousness of the conflict. The Cuban Missile Crisis would remain one of the most dangerous confrontations of the Cold War, and Kennedy’s leadership during this period is often credited with preventing a potential nuclear war.
Joe DiMaggio Hired as Executive VP of A’s by Charlie Finley (1967)
On October 22, 1967, baseball legend Joe DiMaggio was hired as the executive vice president of the Oakland Athletics by team owner Charlie Finley. DiMaggio, known for his stellar career with the New York Yankees, brought his experience and star power to the Athletics, an organization seeking to establish itself in Major League Baseball. His hiring marked a significant moment in the franchise’s history and the sport itself.
DiMaggio’s role on October 22 was not just symbolic; it reflected the growing trend of former players taking on leadership positions in baseball organizations. While DiMaggio’s tenure with the A’s would ultimately be short-lived, his involvement with the team highlighted the evolving landscape of professional baseball and the importance of player legacy in shaping team identities. His contributions to the sport, both on and off the field, continue to be remembered and celebrated.
Bill Taylor Testifies in Ukraine Scandal (2019)
On October 22, 2019, Bill Taylor, the top U.S. diplomat in Ukraine, testified before Congress regarding President Donald Trump’s dealings with Ukraine. Taylor’s testimony was part of the impeachment inquiry surrounding allegations that Trump had tied military aid to Ukraine with demands for investigations into political rival Joe Biden and his family. His statements were critical in understanding the events leading up to the impeachment proceedings.
Taylor’s testimony on October 22 brought significant attention to the complexities of U.S. foreign policy and the implications of personal interests in diplomatic relations. His insights added to the mounting evidence of potential misconduct and raised questions about the integrity of the administration’s actions. The inquiry sparked nationwide discussions about accountability in government, the role of diplomacy, and the protection of democratic institutions.
Conclusion
October 22 is a date marked by significant events that have shaped American history in various ways. From political milestones like Sam Houston’s inauguration to pivotal moments during the Cuban Missile Crisis, and from groundbreaking inventions to cultural achievements, each event has left a lasting legacy. These occurrences illustrate the complexities of American history and the enduring impact of decisions made on October 22. As we reflect on these moments, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that have shaped the nation and continue to influence its trajectory.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 22 in Australian History?

October 22 is a date that has witnessed various significant events in Australian history, reflecting the nation’s political developments, cultural milestones, and social changes. From the formation of governments to groundbreaking achievements in sports, each event on this day contributes to Australia’s rich narrative. In this article, we will explore notable occurrences that took place on October 22, providing insights into their historical significance and lasting impact on the nation.
What Happened on October 22 in Australian History?
James H. Scullin Forms Australian Government (1929)
On October 22, 1929, James H. Scullin was sworn in as the Prime Minister of Australia, leading the first majority Labor government in the country’s history. Scullin’s election came during a period of significant social and economic change, following the post-World War I era. His government was tasked with addressing various pressing issues, including unemployment, industrial relations, and the effects of the Great Depression that loomed just ahead.
Scullin’s leadership on October 22 marked a pivotal moment for the Labor Party and Australian politics. His administration introduced policies aimed at protecting workers and promoting social welfare, reflecting the party’s commitment to addressing the needs of the working class. Scullin’s tenure, however, would soon be challenged by the economic downturn, and his government faced numerous obstacles that would ultimately lead to its defeat in 1931. Nevertheless, his rise to leadership is a significant chapter in Australia’s political history, illustrating the evolving landscape of governance and party politics.
Great Britain Performs Nuclear Test at Maralinga, Australia (1956)
On October 22, 1956, Great Britain conducted a nuclear test at Maralinga in South Australia. This event was part of a series of tests carried out under the British Atomic Weapons Testing Program. Maralinga became a testing site due to its remote location, which was deemed suitable for such experiments. The tests raised significant concerns about the environmental and health impacts on the local population and the broader Australian landscape.
The nuclear test on October 22 had profound implications for Australia. The fallout from the tests affected the Indigenous communities living in the area, leading to long-term health issues and displacement. The controversy surrounding the tests sparked debates about sovereignty, environmental justice, and the responsibilities of foreign powers operating on Australian soil. In subsequent years, the impact of these tests has been a focal point in discussions regarding Australia’s nuclear policy and the rights of Indigenous Australians.
Denny Hulme Becomes First New Zealander to Win the F1 World Drivers Championship (1967)
On October 22, 1967, Denny Hulme made history by becoming the first New Zealander to win the Formula One World Drivers Championship. He secured this achievement with a third-place finish in the Mexican Grand Prix at Autódromo Hermanos Rodríguez, clinching the title by a narrow margin of five points over his teammate Jack Brabham. This victory was a significant milestone in both Australian and New Zealand motorsport history.
Hulme’s triumph on October 22 represented not only a personal achievement but also a testament to the rising prominence of drivers from the Southern Hemisphere in the world of Formula One. His success inspired a generation of racers from Australia and New Zealand, paving the way for future champions in the sport. The victory also highlighted the competitiveness of the era, characterized by intense rivalries and technological advancements in racing. Hulme’s legacy endures, serving as a reminder of the global nature of motorsport and the importance of perseverance in achieving greatness.
Start of 1st-Class Game at Newcastle, NSW v Queensland (1981)
On October 22, 1981, a notable first-class cricket match commenced between Newcastle, New South Wales, and Queensland. This match was part of the Sheffield Shield competition, which has a long-standing tradition in Australian cricket. The game showcased the talent and skills of players from both states, contributing to the rich tapestry of Australian cricket history.
The match on October 22 held significance for both teams as they vied for supremacy in the Sheffield Shield. This competition has been instrumental in the development of cricket in Australia, providing a platform for emerging talent and seasoned players alike. The rivalry between New South Wales and Queensland has historically added an extra layer of excitement to the matches, reflecting the passion and commitment of Australian cricketers. Such events continue to shape the landscape of Australian cricket, fostering a sense of community and pride among fans and players.
Wendy Wasserstein’s Play “The Sisters Rosensweig” Premieres Off-Broadway in NYC (1992)
On October 22, 1992, Wendy Wasserstein’s play “The Sisters Rosensweig” premiered off-Broadway in New York City. Although this event took place outside Australia, it is noteworthy due to Wasserstein’s significant impact on theater and the arts, which have influenced Australian theater as well. The play explores themes of friendship, identity, and the complexities of modern womanhood, resonating with audiences worldwide.
The premiere of “The Sisters Rosensweig” on October 22 showcased Wasserstein’s skillful storytelling and ability to weave humor with poignant social commentary. Her work has inspired many Australian playwrights and performers, contributing to a vibrant theatrical scene in the country. Wasserstein’s exploration of women’s experiences and relationships continues to be relevant, and her influence can be seen in contemporary Australian theater, where similar themes are often examined.
Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison Makes a Public Apology to Victims of Child Sexual Abuse in Institutions (2018)
On October 22, 2018, Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison delivered a public apology to victims of child sexual abuse in institutions. This apology was part of a broader response to the Royal Commission into Institutional Responses to Child Sexual Abuse, which investigated the systemic failures that allowed abuse to occur over many years. The commission’s findings prompted a national conversation about accountability, justice, and the need for systemic change.
Morrison’s apology on October 22 marked a significant step in acknowledging the suffering of victims and the failures of institutions to protect vulnerable children. It highlighted the government’s commitment to reform and ensuring that such abuses would not happen again. The apology resonated deeply within Australian society, providing a sense of validation and recognition for survivors. It also spurred further discussions about the responsibilities of institutions, including churches and schools, to safeguard children and respond appropriately to allegations of abuse.
Australian City of Melbourne Exits Its Sixth Lockdown (2021)
On October 22, 2021, the Australian city of Melbourne emerged from its sixth lockdown, which had lasted a total of 260 days. This milestone was a significant moment in the city’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic, marking a gradual return to normalcy after an extended period of restrictions aimed at curbing the virus’s spread. The lockdowns in Melbourne were among the strictest in the world, reflecting the government’s efforts to protect public health during a challenging time.
The lifting of lockdown measures on October 22 was met with relief and celebration by many residents, who had faced isolation, uncertainty, and economic hardships over the past months. The event symbolized resilience and the community’s commitment to overcoming adversity. As Melbourne transitioned into a post-lockdown phase, the focus shifted towards recovery, revitalizing the local economy, and fostering social connections. The experience of lockdown profoundly impacted Melbourne’s identity and highlighted the importance of community support and adaptability in the face of unprecedented challenges.
Conclusion
October 22 is a date that has witnessed significant events in Australian history, from political milestones to cultural achievements and social changes. Each occurrence has left a lasting impact on the nation, shaping its narrative and identity. By reflecting on these events, we gain a deeper understanding of Australia’s evolving history and the diverse forces that continue to influence its future. As we look back on the moments that have defined October 22, we recognize the resilience and determination of the Australian people in navigating the complexities of their history.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 22 in British History?

October 22 has been marked by significant events in British history, reflecting the complexities of maritime disasters, military conflicts, social challenges, and legislative changes. Each of these occurrences highlights a unique aspect of Britain’s evolving narrative, from its colonial ambitions to its social reforms. This article delves into notable events that happened on October 22, offering insights into their historical context and lasting impact.
What Happened on October 22 in British History?
Scilly Naval Disaster: Shipwreck of Four Royal Navy Warships (1707)
On October 22, 1707, the Scilly Naval Disaster occurred, resulting in the tragic shipwreck of four Royal Navy warships off the coast of the Scilly Isles. Caught in a violent storm, the fleet, which included HMS Association, HMS Eagle, HMS Romney, and HMS Firebrand, faced navigational errors that led to their destruction on the rocks. This disaster claimed the lives of approximately 1,400 sailors, making it one of the most significant maritime tragedies in British history.
The Scilly Naval Disaster prompted widespread outrage and sorrow across the nation. The loss of so many lives highlighted the dire need for improvements in maritime navigation, particularly regarding determining longitude at sea. In response to this catastrophe, the British Parliament passed the Longitude Act of 1714, which offered financial rewards for anyone who could develop a reliable method for calculating longitude. This act was crucial in advancing maritime technology and ensuring safer sea travel for British vessels in the future.
Duke of Wellington Seizes Burgos, Spain (1812)
On October 22, 1812, during the Peninsular War, the Duke of Wellington achieved a significant military victory by seizing Burgos in Spain. This conquest was part of Wellington’s broader campaign against the French forces occupying the Iberian Peninsula. The siege was characterized by strategic planning and the effective coordination of British, Portuguese, and Spanish troops, reflecting Wellington’s military prowess.
The capture of Burgos on October 22 was a crucial moment in the Peninsular War, as it bolstered the morale of the Allied forces and demonstrated the effectiveness of Wellington’s tactics. However, the victory was bittersweet, as the French would soon regroup and counterattack, leading to subsequent challenges for Wellington’s army. The ongoing conflict in Spain significantly influenced British military strategy and public sentiment regarding the war, ultimately shaping the course of European politics in the years that followed.
Blantyre Mining Disaster in Scotland (1877)
On October 22, 1877, the Blantyre mining disaster struck in Scotland, resulting in the tragic deaths of 207 miners. The disaster occurred when a sudden explosion caused a catastrophic collapse in the Blantyre coal mine, trapping many workers underground. The aftermath was devastating, as widows and orphans were left without support, with many of them evicted by the mine owners and likely sent to the Poor House.
The events of October 22 not only highlighted the dangers of coal mining but also raised questions about workers’ rights and the responsibilities of mine owners. Public outrage over the treatment of the victims’ families led to calls for reform in mining practices and improved safety regulations. This disaster played a significant role in the development of labor movements in Britain, contributing to the push for better working conditions and the establishment of welfare measures for those affected by industrial accidents.
British Troops Flee Dundee, Natal, South Africa (1899)
On October 22, 1899, British troops faced a significant setback during the Second Boer War as they were forced to flee Dundee in Natal, South Africa. The conflict began as tensions between the British Empire and the Boer republics escalated over control of gold and diamond resources. The defeat at Dundee was indicative of the challenges faced by British forces in the early stages of the war.
The events of October 22 had profound implications for British military strategy and public perception of the war. The defeat prompted a reevaluation of British tactics and highlighted the determination of the Boer fighters. The Second Boer War ultimately led to shifts in British colonial policy and raised questions about the effectiveness of imperial rule, influencing future military engagements and the relationship between Britain and its colonies.
Russian Fleet Shoots at British Fishing Ship (1904)
On October 22, 1904, tensions escalated between Russia and Britain when a Russian fleet mistakenly opened fire on a British fishing vessel. This incident occurred during the Russo-Japanese War, as Russian forces were on high alert and engaged in military operations. The attack on the fishing ship created diplomatic tensions, raising concerns about the safety of British vessels in international waters.
The firing on the British ship on October 22 exemplified the fraught relationships among imperial powers at the time. It underscored the importance of communication and navigation protocols to prevent misunderstandings that could lead to international incidents. The event prompted discussions regarding maritime rights and the need for clearer rules governing naval operations, ultimately influencing diplomatic relations between Russia and Britain during a period of significant geopolitical upheaval.
First Ships of Invasion Fleet for Oran Leave Scotland (1942)
On October 22, 1942, the first ships of the invasion fleet destined for Oran, Algeria, departed from Scotland during World War II. This operation was part of the broader Allied campaign to gain a foothold in North Africa and launch operations against Axis powers. The strategic significance of Oran made it a target for the Allied forces, as they sought to secure control of North Africa.
The departure of the invasion fleet on October 22 marked a crucial moment in the North African campaign. It demonstrated the determination of the Allies to reclaim territory from Axis control and signified a turning point in the war. The successful landing in Oran would later pave the way for further military operations in North Africa, contributing to the eventual defeat of Axis forces and the liberation of occupied territories.
Two British Ships Sink Near Albania (1946)
On October 22, 1946, two British ships sank near Albania in a tragic incident that underscored the dangers of post-war navigation in the Mediterranean. The ships were part of a convoy that encountered severe weather conditions while navigating through treacherous waters. The sinking resulted in the loss of lives and highlighted the ongoing challenges faced by shipping companies in the aftermath of World War II.
The events of October 22 served as a reminder of the precarious nature of maritime operations during this period. The aftermath of the war left many countries grappling with economic difficulties and infrastructure challenges, affecting trade and shipping routes. The incident prompted discussions about maritime safety and the need for improved protocols to protect vessels in adverse conditions, shaping policies that would influence shipping operations in the years to come.
Great Britain Performs Nuclear Test at Maralinga, Australia (1956)
On October 22, 1956, Great Britain conducted a nuclear test at Maralinga in Australia as part of its Atomic Weapons Testing Program. This test was one of several carried out in the remote desert, chosen for its isolation. The Maralinga tests marked a significant moment in the Cold War era, as Britain sought to establish itself as a nuclear power.
The nuclear test on October 22 raised numerous ethical and environmental concerns, particularly regarding its impact on the Indigenous populations in the area. The fallout from the tests had lasting effects on the land and the health of those living nearby. This event prompted later debates on the responsibilities of nations conducting nuclear tests and led to discussions about the rights of Indigenous Australians, shaping the broader conversation about nuclear policies and environmental justice.
Legislation for Northern Ireland Legalizing Same-Sex Marriage and Abortion Comes into Effect (2019)
On October 22, 2019, significant legislative changes took effect in Northern Ireland as the laws legalizing same-sex marriage and abortion came into force. These changes followed years of campaigning and public pressure for greater rights and equality for LGBTQ+ individuals and women. The legislation represented a significant step towards social justice and equality in Northern Ireland, reflecting broader changes occurring across the United Kingdom.
The implementation of these laws on October 22 was celebrated by activists and supporters, marking a historic moment in the struggle for human rights in the region. The legal recognition of same-sex marriage and access to abortion services signified a shift in societal attitudes and the political landscape. This development not only affected individuals in Northern Ireland but also resonated with movements for equality across the UK, emphasizing the importance of legislative change in advancing social justice.
Conclusion
October 22 has witnessed a myriad of significant events in British history, from maritime disasters and military conflicts to social reforms and legislative changes. Each occurrence has played a vital role in shaping the nation’s identity and its relationships with the world. By reflecting on these moments, we gain insight into the complexities of British history and the enduring impact of these events on contemporary society. As we look back on October 22, we recognize the resilience and determination of the British people in navigating the challenges and triumphs of their history.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 22 in Canadian History?

October 22 is a date marked by significant events in Canadian history, reflecting the country’s diverse achievements in sports, science, and culture. From iconic moments in hockey to groundbreaking scientific contributions, each event plays a role in shaping Canada’s national identity and historical narrative. This article explores key occurrences on October 22, providing insight into their historical context and impact on Canadian society.
What Happened on October 22 in Canadian History?
Bobby Orr Scores His First Career Goal (1966)
On October 22, 1966, Canadian ice hockey legend Bobby Orr scored his first career goal in a game against the Montreal Canadiens. This moment marked the beginning of what would become one of the most illustrious careers in hockey history. Playing for the Boston Bruins, Orr demonstrated his exceptional skill and unique playing style, quickly captivating fans and changing the dynamics of the sport.
Orr’s first goal on October 22 not only showcased his talent but also foreshadowed his revolutionary impact on the game. He went on to redefine the role of a defenseman, combining defensive prowess with offensive capabilities. Throughout his career, Orr earned numerous accolades, including two Stanley Cups and three Hart Trophies as the league’s most valuable player. His influence on hockey is still felt today, making him a pivotal figure in Canadian sports history.
Red Dye No. 4 Is Banned by the FDA (1976)
On October 22, 1976, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) banned Red Dye No. 4 after studies indicated its potential to cause tumors in the bladders of dogs. While this dye was prohibited in the United States, it continued to be used in Canada, raising concerns about food safety and consumer health. The controversy surrounding this dye highlighted the differences in regulatory practices between the two countries.
The events of October 22 prompted discussions regarding food additives and consumer protection in Canada. Activists and health professionals began advocating for stricter regulations and more transparent labeling practices. This incident was a catalyst for a broader movement toward food safety reforms, ultimately influencing Canadian policies on food additives and consumer rights in the years to come.
Atlanta Braves Win Game 5 of World Series (1992)
On October 22, 1992, the Atlanta Braves made history by becoming the first American team to win a World Series game outside the United States, defeating the Toronto Blue Jays 7-2 in Game 5 at SkyDome in Toronto, Ontario. This match was significant not only for the Braves but also for the Blue Jays, who had established themselves as a formidable force in Major League Baseball (MLB).
The game on October 22 marked a pivotal moment for baseball in Canada, showcasing the growing popularity of the sport in the country. The Blue Jays’ success during the early 1990s helped solidify their status in Major League Baseball and contributed to the national pride surrounding Canadian teams. The victory by the Braves further emphasized the competitive nature of the World Series, setting the stage for future matchups between American and Canadian teams.
Grant Fuhr Wins His 400th Career Game (1999)
On October 22, 1999, Canadian NHL goaltender Grant Fuhr achieved a significant milestone by winning his 400th career game against the Florida Panthers. Fuhr’s impressive performance and resilience throughout his career made him one of the most respected goaltenders in NHL history. His achievement on this date further solidified his legacy in the sport.
The milestone victory on October 22 was a testament to Fuhr’s dedication and skill. He was known for his ability to remain calm under pressure and his agility in the crease, which earned him a place among the NHL’s all-time greats. Fuhr’s success inspired many young Canadian players and highlighted the importance of goaltending in hockey. His career achievements, including four Stanley Cup championships with the Edmonton Oilers, continue to resonate in the world of Canadian hockey.
Birth of Frank Spedding (1902)
October 22 also marks the birth of Frank Spedding, a Canadian chemist born in Hamilton, Ontario, in 1902. Spedding is best known for his contributions to uranium extraction, which played a critical role in the development of the first atomic bomb. His work in nuclear chemistry helped advance scientific understanding and technology during a pivotal time in history.
Spedding’s innovations in uranium processing on October 22 paved the way for advancements in nuclear energy and weaponry. His research not only contributed to wartime efforts but also influenced post-war nuclear policies and energy discussions. Spedding’s legacy as a scientist exemplifies the significant impact that Canadian researchers have had on global scientific advancements, particularly in the fields of chemistry and nuclear science.
Judy Devlin Hashman Born (1935)
On October 22, 1935, Judy Devlin Hashman, a notable Canadian badminton player, was born in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Hashman made significant contributions to the sport, competing in multiple World Team Championships and securing gold medals for Canada in 1957, 1960, 1963, and 1966. Her achievements helped elevate the profile of badminton in Canada and inspired future generations of athletes.
Hashman’s accomplishments on October 22 reflect her dedication to the sport and her status as a pioneer in Canadian badminton. Throughout her career, she showcased exceptional skill and sportsmanship, contributing to the growth of badminton at both national and international levels. Hashman’s legacy is celebrated in Canadian sports history, serving as an inspiration for aspiring badminton players in the country.
Birth of Yvan Ponton (1945)
October 22, 1945, also marks the birth of Yvan Ponton, a Canadian actor and television host known for his role in the cult classic film “Slap Shot.” Born in Farnham, Quebec, Ponton has made a significant impact on Canadian entertainment, showcasing his talent across various platforms, including film, television, and theater.
Ponton’s career on October 22 exemplifies the richness of Canadian arts and culture. His work has contributed to the representation of Canadian stories and characters in film and television, helping to foster a sense of national identity. As a prominent figure in Canadian entertainment, Ponton continues to inspire audiences and fellow artists alike, highlighting the importance of storytelling in shaping cultural narratives.
Conclusion
October 22 has witnessed a range of significant events in Canadian history, from milestones in sports and science to the birth of influential figures. Each occurrence has contributed to the fabric of Canadian society, reflecting its diverse achievements and the ongoing evolution of its national identity. By examining these moments, we gain a deeper understanding of Canada’s historical narrative and the impact of these events on contemporary culture and society. As we remember October 22, we celebrate the resilience, creativity, and accomplishments that define Canada and its people.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 22 in History?

October 22 is a date marked by significant events that have shaped political, cultural, and technological landscapes across the globe. From pivotal moments in history to groundbreaking inventions, this day has witnessed milestones that resonate through time. In this article, we will delve into some of the most noteworthy occurrences that took place on October 22 throughout history, exploring their impact and relevance.
What Happened on October 22 in History?
Tsar Peter the Great Declares Himself Emperor of All Russia (1721)
On October 22, 1721, Tsar Peter the Great proclaimed himself “Emperor of All Russia,” marking a significant transformation in the governance and self-perception of Russia. This declaration followed years of reform aimed at modernizing the country and elevating its status on the global stage. By adopting the title of emperor, Peter sought to assert Russia’s position as a major European power, reflecting his ambitions to reshape Russian society and governance along Western lines.
Peter’s reforms included the reorganization of the Russian military, the establishment of a new administrative structure, and the promotion of education and industry. His ascension as emperor also symbolized the end of the Russian Tsardom as it had been traditionally understood, moving towards a more modern imperial framework. This pivotal moment on October 22 laid the foundation for the future of the Russian Empire, influencing its political landscape and its relations with other nations for centuries to come.
Duke of Wellington Seizes Burgos, Spain (1812)
On October 22, 1812, during the Peninsular War, the Duke of Wellington achieved a significant military victory by seizing the city of Burgos in Spain. This event was part of a larger campaign against the French forces led by Napoleon, who had invaded the Iberian Peninsula. Wellington’s successful capture of Burgos marked a turning point in the war, demonstrating his military prowess and strategic acumen in the face of formidable opposition.
The capture of Burgos not only bolstered British morale but also contributed to the weakening of French influence in Spain. Wellington’s tactics, which combined strong defensive positions with effective offensive maneuvers, became a model for military strategy in subsequent conflicts. The victory at Burgos on October 22 exemplified the resilience and determination of the Allied forces in their struggle against Napoleonic rule, ultimately leading to the eventual liberation of Spain.
Thomas Edison Perfects the Carbonized Cotton Filament Light Bulb (1879)
On October 22, 1879, Thomas Edison achieved a breakthrough in electric lighting by perfecting the carbonized cotton filament light bulb. After years of experimentation, Edison’s development marked a significant advancement in the quest for practical electric light. His work not only improved the efficiency and lifespan of the light bulb but also paved the way for the widespread adoption of electric lighting in homes and businesses.
Edison’s success on October 22 revolutionized the way people illuminated their environments, moving away from gas and oil lamps to electric light sources. This innovation had far-reaching implications for society, transforming daily life, extending productive hours, and fostering economic growth. Edison’s carbon filament light bulb is often seen as one of the key inventions that ushered in the modern age, significantly influencing the development of technology and industry in the years to come.
Grand Opening of New York’s Original Metropolitan Opera House (1883)
The grand opening of New York’s original Metropolitan Opera House took place on October 22, 1883, with a performance of Charles Gounod’s opera “Faust.” This landmark event marked the establishment of a prestigious venue dedicated to opera and classical music, which would become a cultural icon in New York City. The Met’s opening set a new standard for operatic performances in America, attracting renowned artists and composers from around the world.
The original Metropolitan Opera House played a crucial role in popularizing opera in the United States, showcasing a wide range of productions and fostering an appreciation for the art form among American audiences. The October 22 opening also symbolized the growing cultural sophistication of New York City during the Gilded Age, as the city sought to position itself as a global center for the arts. The Met’s legacy continues today, as it remains one of the most celebrated opera houses in the world, upholding its reputation for excellence and innovation in the performing arts.
Henry Ford Becomes President of Ford Motor Company (1906)
On October 22, 1906, Henry Ford was named the president of Ford Motor Company, a pivotal moment in the history of American industry. Ford had already made a name for himself as an innovative engineer and businessman, but his leadership would catapult the company to unprecedented heights. Under his direction, Ford would revolutionize automobile manufacturing with the introduction of assembly line production techniques, making cars more affordable and accessible to the average American.
Ford’s presidency marked the beginning of a new era in the automotive industry, characterized by mass production and consumerism. The innovations he implemented not only transformed Ford Motor Company but also had a lasting impact on manufacturing practices across various industries. Ford’s leadership on October 22 set the stage for the company’s significant contributions to the American economy and the development of modern transportation.
Herbert Hoover Speaks on “Rugged Individualism” (1928)
On October 22, 1928, Herbert Hoover delivered a speech in which he articulated his vision of the “American system of rugged individualism.” As a presidential candidate, Hoover emphasized the importance of personal initiative and self-reliance as cornerstones of American society. His speech resonated with many Americans during a time of economic prosperity, as he advocated for limited government intervention in the economy and encouraged individuals to take responsibility for their own success.
Hoover’s concept of rugged individualism became a defining theme of his presidency, which began in 1929. However, his beliefs would be challenged by the onset of the Great Depression, which required a reevaluation of government policies and support systems. The speech on October 22 reflected the prevailing attitudes of the time, but it also foreshadowed the difficulties that Hoover would face in addressing the economic challenges that lay ahead.
The 8th French Government of Aristide Briand Falls (1929)
On October 22, 1929, the eighth government led by Aristide Briand in France collapsed, marking a significant moment in the political landscape of the country. Briand, who had served as Prime Minister multiple times, was known for his efforts to promote peace and reconciliation in Europe, particularly in the aftermath of World War I. However, his government faced increasing challenges, including economic instability and political infighting, which ultimately led to its downfall.
The fall of Briand’s government on October 22 highlighted the fragility of the French political system during a period of social and economic turmoil. It also reflected the growing tensions in Europe as nations grappled with the effects of the Great Depression, which would soon have far-reaching implications for international relations. Briand’s inability to maintain a stable government underscored the complexities of French politics during this era and foreshadowed the challenges that lay ahead for the country.
JFK Receives Ugandan Premier Milton Obote (1962)
On October 22, 1962, U.S. President John F. Kennedy met with Ugandan Prime Minister Milton Obote in Washington, D.C. This meeting was significant as it underscored the United States’ growing interest in African nations during a period of decolonization and geopolitical tension. Kennedy’s administration sought to strengthen ties with emerging African leaders, and Obote’s visit represented an opportunity to discuss issues of mutual concern, including economic development and Cold War dynamics.
The meeting on October 22 was part of Kennedy’s broader strategy to engage with African nations, recognizing their importance in the global political landscape. The relationship established during this visit was reflective of the United States’ commitment to supporting newly independent countries as they navigated the complexities of nation-building and international relations. Kennedy’s engagement with African leaders, including Obote, marked a pivotal moment in U.S.-Africa relations during the Cold War.
JFK Addresses the Nation About the Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
On the same day, October 22, 1962, President John F. Kennedy delivered a historic live television address to the American public regarding the Cuban Missile Crisis. This speech came in the wake of the discovery of Soviet missile installations in Cuba, which posed a direct threat to U.S. national security. Kennedy’s address was a critical moment in the crisis, as he outlined the U.S. response, including the imposition of a naval blockade around Cuba to prevent further shipments of military equipment.
Kennedy’s address on October 22 not only informed the American public about the gravity of the situation but also called for unity and vigilance during a time of heightened tension. His leadership during this crisis would come to define his presidency, as he navigated one of the most dangerous standoffs in Cold War history. The speech emphasized the importance of diplomacy and restraint, ultimately contributing to a peaceful resolution to the crisis. This pivotal moment on October 22 remains a significant chapter in both U.S. history and global affairs, illustrating the complexities of international relations during the Cold War.
Conclusion
October 22 has witnessed a diverse array of events throughout history, each contributing to the narrative of human progress and political evolution. From Tsar Peter the Great’s declaration of imperial status to Thomas Edison’s invention of the light bulb, from the grand opening of the Metropolitan Opera House to pivotal political speeches and military victories, this date serves as a reminder of the dynamic forces that shape our world. Each event highlights the interconnectedness of history and the enduring impact of decisions made on October 22, illustrating the complexities and triumphs of the human experience across time.
0 notes
Text
What Day of the Week Is the Louvre Closed?

The Louvre, one of the most famous museums in the world, is a hub of history, art, and culture. Situated in the heart of Paris, it houses an impressive collection of artwork spanning centuries, including iconic pieces like the Mona Lisa and Venus de Milo. Millions of visitors flock to the Louvre every year to explore its vast exhibitions. However, like many cultural institutions, the Louvre has a designated day when it is closed to the public.
This article will provide a comprehensive exploration of the day the Louvre is closed and discuss the reasons behind this practice. We will also examine the historical context of museum closures, visitor patterns, and the importance of maintaining museum facilities. Additionally, we will explore how the Louvre’s closure fits into broader trends in museum operations around the world. This detailed guide will help travelers and art enthusiasts better plan their visits while also shedding light on the logistics behind the museum’s operations.
The Louvre’s Official Closure Day
The Louvre Museum is closed every Tuesday. This weekly closure is a longstanding tradition designed to accommodate a variety of needs, both for the museum staff and the preservation of the artwork housed within. Although visitors may find it inconvenient, especially those unfamiliar with the schedule, this practice is a standard procedure among many major museums globally.
The decision to close the Louvre on Tuesdays allows the museum’s staff to conduct essential tasks that are difficult to carry out during regular operating hours. These tasks include cleaning, maintenance, exhibition preparation, and administrative work. Moreover, it provides an opportunity to review security measures, ensure the proper functioning of the museum’s facilities, and address any concerns that might arise with the artwork or the exhibition spaces.
Historical Context of Museum Closures
Historically, the practice of closing museums on specific days originated in Europe in the 19th century. As public access to art and culture expanded during this period, museums had to strike a balance between serving visitors and managing the preservation of valuable artworks. Initially, museums like the Louvre operated on a limited schedule, often opening only a few days a week.
As demand for public access increased, many museums expanded their opening hours but kept one day closed each week to ensure proper upkeep. The decision to choose a specific day, such as Tuesday in the case of the Louvre, was often based on visitor patterns. Weekdays with lower visitation rates became the designated closure day, helping museums optimize their resources without significantly affecting the visitor experience.
Why Tuesday?
The Louvre’s decision to close on Tuesdays is influenced by several factors, including historical precedent, visitor patterns, and operational logistics. Tuesday is generally considered a quieter day for tourism in Paris, as most visitors tend to plan their museum visits for weekends or closer to the end of the week. By closing on a less busy day, the Louvre minimizes the number of visitors inconvenienced by the closure.
Moreover, the Louvre’s Tuesday closure also aligns with the operational schedules of other Parisian museums. For instance, the Musée d’Orsay, another major museum in Paris, is closed on Mondays. This alternating closure schedule helps spread out museum traffic and offers tourists the opportunity to visit different museums on different days, avoiding a complete shutdown of major cultural institutions on the same day.
Visitor Patterns and Impacts
The closure of the Louvre on Tuesdays has a noticeable impact on visitor patterns throughout the week. Tourists, particularly those who are unaware of the closure schedule, often adjust their plans to accommodate a visit on another day. This can lead to higher visitor numbers on surrounding days, especially Mondays and Wednesdays. As a result, these days can be particularly crowded, making it challenging for visitors to fully enjoy the museum’s exhibits.
For those planning a visit to the Louvre, it is advisable to check the museum’s schedule in advance and avoid the busiest days if possible. Visiting on a weekday other than Monday or Wednesday can provide a more relaxed experience, with fewer crowds and shorter lines. Additionally, the Louvre offers extended evening hours on certain days, allowing visitors more flexibility in planning their visit.
The Importance of Museum Maintenance
One of the primary reasons the Louvre closes on Tuesdays is to allow for essential maintenance work. Maintaining a museum of the Louvre’s size and significance requires a delicate balance between public access and behind-the-scenes upkeep. The museum’s staff, including conservators, curators, and maintenance workers, use the closure day to inspect and care for the vast collection of artwork.
This maintenance work goes beyond basic cleaning and repairs. Artworks must be monitored for signs of wear and deterioration, especially those that are centuries old. Paintings, sculptures, and artifacts are vulnerable to environmental factors such as light, humidity, and temperature fluctuations. On Tuesdays, museum staff can ensure that the necessary environmental controls are functioning properly and that any needed restoration work is carried out without disturbing visitors.
Exhibition Preparation and Updates
In addition to maintenance, the Louvre’s closure on Tuesdays allows for the preparation of new exhibitions and the rearrangement of existing ones. Exhibiting artwork in a museum of the Louvre’s scale is a complex process that involves careful planning, installation, and coordination. Each new exhibition requires weeks, sometimes months, of preparation to ensure that the artwork is displayed in a way that enhances its educational and aesthetic value.
Closing the museum on Tuesdays gives curators the time and space needed to arrange new exhibits, make adjustments to existing ones, and update the museum’s layout as necessary. This process includes everything from designing exhibit spaces to setting up lighting, signage, and security measures. Without a closure day, it would be much more difficult for the museum to keep its exhibitions fresh and engaging for returning visitors.
How the Louvre’s Schedule Compares to Other Museums
The Louvre’s Tuesday closure is not unique among major museums, as many cultural institutions around the world also have designated closure days. For example, the British Museum in London and the Vatican Museums in Rome also close for one day each week. This practice allows museums to maintain their collections, prepare new exhibits, and manage their operations more efficiently.
In some cases, the choice of closure day varies depending on local visitor trends and cultural norms. In cities with high tourist traffic throughout the week, museums may choose a midweek closure to avoid losing visitors during peak weekend periods. Additionally, some museums opt for Monday closures, as it is often seen as the least popular day for tourists to visit cultural institutions. The Louvre’s choice of Tuesday fits well within these global patterns.
Visitor Tips for Planning a Louvre Visit
For travelers planning a visit to the Louvre, it is crucial to keep the Tuesday closure in mind. To avoid disappointment, visitors should plan their itinerary around the museum’s schedule and take advantage of the days when it is open. The Louvre is typically open from Wednesday to Monday, with extended hours on certain days. Checking the museum’s website for the latest schedule updates is always a good idea before visiting.
Visitors should also consider the best times to visit the Louvre in terms of crowd levels. While weekends tend to be the busiest, visiting on a weekday (other than Monday or Wednesday) can provide a more pleasant and less crowded experience. Additionally, taking advantage of the museum’s evening hours on Wednesdays and Fridays can allow for a more relaxed visit, as fewer tourists tend to visit during these times.
The Significance of Museum Closures in Cultural Institutions
Museum closures, such as the Louvre’s on Tuesdays, play a significant role in the operation of cultural institutions. These closures serve as a necessary part of the museum’s ability to maintain its collection, prepare for exhibitions, and ensure a high-quality visitor experience. While it may seem like a minor inconvenience to some visitors, the closure day is vital to the overall functioning of the museum.
For museums like the Louvre, which host millions of visitors annually, maintaining the balance between public access and behind-the-scenes operations is crucial. The Tuesday closure reflects a broader trend in the museum world, where institutions prioritize the preservation of art and culture while still making their collections accessible to the public.
Conclusion
The Louvre’s closure on Tuesdays is a well-considered practice that allows the museum to manage its operations, maintain its collection, and prepare new exhibitions. While it may be inconvenient for some visitors, the benefits of having a designated closure day far outweigh the drawbacks. This practice ensures that the museum can continue to offer a world-class experience to the millions of visitors who come through its doors each year.
Understanding the reasons behind the Louvre’s closure provides insight into the complexities of running a major cultural institution. By planning their visit accordingly, travelers can make the most of their time at the Louvre and appreciate the care and effort that goes into preserving one of the world’s greatest collections of art and history.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 11 in American History?

October 11 is a date that has witnessed several pivotal moments in American history, showcasing the country’s progress in various fields, including space exploration, politics, and entertainment. This day has been marked by significant achievements and events that have shaped the cultural and political landscape of the nation. From groundbreaking space missions to landmark Supreme Court confirmation hearings, the events that took place on October 11 illustrate the dynamic nature of American history and its ongoing evolution.
This article will delve into five key events that occurred on October 11: the launch of NASA’s 100th Space Shuttle mission in 2000, the confirmation hearings for Clarence Thomas in 1991, the first American woman to walk in space in 1984, the premiere of Saturday Night Live in 1975, and the marriage of Bill Clinton and Hillary Rodham in 1975. Each of these events not only represents a significant moment in its respective context but also reflects broader themes of innovation, social change, and the interplay between personal lives and public roles.
What Happened on October 11 in American History?
The Launch of NASA’s 100th Space Shuttle Mission (2000)
On October 11, 2000, NASA celebrated a significant milestone with the launch of its 100th Space Shuttle mission, STS-92. This mission, which involved the Space Shuttle Discovery, was pivotal in advancing the construction of the International Space Station (ISS). The STS-92 mission was crucial for delivering and installing the Z1 truss segment, a key component of the ISS’s structure. This mission was not only a testament to NASA’s achievements in space exploration but also highlighted the international collaboration that characterized the ISS project.
The successful launch of STS-92 underscored the importance of the Space Shuttle program in facilitating scientific research and technological advancements in low Earth orbit. With this milestone, NASA showcased its capabilities in complex missions, including assembling large structures in space and conducting spacewalks. The mission involved extensive teamwork among astronauts, engineers, and scientists, demonstrating the synergy required for success in space exploration. The launch of NASA’s 100th Space Shuttle mission on October 11, 2000, represented not only a celebration of past achievements but also a commitment to future exploration and scientific discovery.
The significance of the Space Shuttle program extended beyond individual missions. It played a crucial role in enhancing global cooperation in space exploration, with international partners contributing to the ISS’s construction and research objectives. The program enabled advancements in various fields, including technology, medicine, and materials science, through experiments conducted in microgravity. As NASA marked this milestone, it laid the groundwork for continued exploration and innovation, influencing future missions and aspirations in human spaceflight.
The Confirmation Hearings for Clarence Thomas (1991)
On October 11, 1991, the confirmation hearings for Clarence Thomas, nominated by President George H.W. Bush to the Supreme Court, became a focal point of national attention. These hearings, held before the Senate Judiciary Committee, were contentious and deeply polarized. Thomas faced scrutiny over his judicial philosophy, qualifications, and allegations of sexual harassment made by former colleague Anita Hill, which ignited a significant public discourse about gender and race in America.
The hearings unfolded over several days, highlighting issues of sexual harassment, workplace culture, and the implications of appointing a justice to the highest court in the land. Anita Hill’s testimony brought attention to the treatment of women in professional environments and prompted widespread discussions about gender equality and harassment. Thomas denied the allegations, framing them as a smear campaign, and the hearings ultimately became a battleground for larger cultural and political issues.
The confirmation of Thomas on October 11, 1991, was significant not only for the Supreme Court but also for the broader conversation about justice and accountability in the workplace. The hearings had lasting effects on the political landscape, contributing to the rise of activism around women’s rights and prompting a reevaluation of institutional responses to harassment. Thomas’s confirmation signified a critical moment in American history, illustrating the intersection of politics, race, and gender in the pursuit of justice and representation.
The First American Woman to Walk in Space (1984)
On October 11, 1984, Dr. Kathryn Sullivan became the first American woman to walk in space during the STS-41-G mission aboard the Space Shuttle Challenger. This groundbreaking achievement marked a significant milestone in both space exploration and the pursuit of gender equality in the sciences. Sullivan’s historic spacewalk lasted approximately three hours, during which she conducted experiments and deployed a satellite, showcasing the capabilities of women in fields that had been traditionally male-dominated.
Sullivan’s achievement was not only a personal triumph but also a powerful symbol for women aspiring to break barriers in science and technology. Her accomplishment inspired future generations of female scientists and astronauts, demonstrating that women could excel in roles previously restricted to men. The mission was broadcast live, allowing millions to witness this significant event and highlighting the importance of representation in all fields of endeavor.
The impact of Sullivan’s spacewalk extended beyond the immediate moment, influencing public perception and encouraging discussions about gender roles in the workforce. Her achievement paved the way for greater opportunities for women in NASA and other scientific organizations, fostering an environment that promoted diversity and inclusion. The first American woman to walk in space on October 11, 1984, stands as a testament to the potential for individuals to effect change and inspire progress in society.
The Premiere of Saturday Night Live (1975)
On October 11, 1975, the iconic television show Saturday Night Live (SNL) premiered on NBC, quickly becoming a cultural phenomenon. Created by Lorne Michaels, SNL blended sketch comedy, musical performances, and political satire, redefining late-night television and influencing generations of comedians and entertainers. The show’s debut featured a unique format, combining live performances with pre-recorded segments, which set the tone for its innovative approach to comedy.
SNL’s first cast included notable comedians such as Chevy Chase, Gilda Radner, and John Belushi, who would go on to become household names. The show tackled contemporary issues with humor and irreverence, often pushing boundaries and challenging societal norms. SNL’s impact on American culture was profound, shaping the landscape of comedy and entertainment while providing a platform for emerging talent. It has addressed significant political events and cultural phenomena, establishing itself as a reflection of American society.
The premiere of Saturday Night Live on October 11, 1975, not only transformed late-night television but also set the stage for a new era of comedic expression. The show’s ability to adapt and remain relevant over the decades is a testament to its enduring legacy. SNL continues to be a significant part of American culture, influencing comedy, politics, and popular culture while fostering a spirit of creativity and innovation that resonates with audiences to this day.
Bill Clinton Marries Hillary Rodham (1975)
On October 11, 1975, Bill Clinton and Hillary Rodham were married in a ceremony that would lead to a partnership influential in American politics and public life. The couple met while studying at Yale Law School, where their shared interests in public service and law brought them together. Their wedding marked the beginning of a long and complex relationship that would play a pivotal role in the political landscape of the United States.
Throughout their marriage, Clinton and Rodham faced numerous challenges and successes, both personally and politically. Bill Clinton would go on to serve as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001, while Hillary Clinton became a prominent political figure in her own right, serving as First Lady, U.S. Senator, Secretary of State, and a candidate for the presidency. Their partnership exemplified the intersection of personal and political life, influencing public perceptions of gender roles and power dynamics in American society.
The marriage of Bill Clinton and Hillary Rodham on October 11, 1975, was significant not only for their individual careers but also for the broader narrative of American politics. Their journey together highlighted the evolving role of women in leadership and the complexities of navigating personal relationships in the public eye. The couple’s enduring influence continues to shape discussions around political leadership and gender equality in contemporary society.
Conclusion
October 11 has proven to be a date of substantial historical significance in American history, marked by events that have influenced various facets of the nation’s cultural, political, and social landscape. From NASA’s milestones in space exploration to groundbreaking moments in gender equality and the realms of entertainment and politics, this date encapsulates key moments that reflect the dynamic nature of American history. These events not only represent turning points in their respective contexts but also illustrate the interconnectedness of individual actions and broader societal changes, shaping the narrative of the United States as it continues to evolve.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 11 in Australian History?

October 11 is a date of notable significance in Australian history, marked by events that reflect the country’s diverse cultural heritage, sports achievements, and advancements in social awareness. This date has witnessed a range of pivotal moments, from the death of celebrated sports figures to the establishment of important institutions and cultural events. Each occurrence not only holds historical value but also contributes to the broader narrative of Australia’s evolution as a nation.
This article will explore four key events that took place on October 11: the death of cricketing legend Keith Miller in 2004, the landing of Australian forces at Jacquinot Bay, New Britain, during World War II in 1944, the establishment of the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies in 1989, and the opening of the Melbourne Festival in 2023. Each of these events represents significant moments in Australian history, demonstrating the interplay between culture, sports, and societal progress.
What Happened on October 11 in Australian History?
The Death of Keith Miller (2004)
On October 11, 2004, Australia mourned the loss of one of its most beloved sports figures, Keith Miller. A celebrated cricketer and former Royal Australian Air Force pilot, Miller was known for his exceptional skills on the field, charisma, and contributions to the sport. He played 55 Test matches for Australia from 1946 to 1956, becoming one of the finest all-rounders in cricket history. His ability to bat and bowl at an elite level earned him a place among the legends of the game, and he became an enduring figure in Australian sports culture.
Miller’s career was marked by remarkable achievements, including his performance during the 1948 Ashes series, where he showcased his prowess against the English team. Beyond his cricketing talent, he was known for his sportsmanship and humility, qualities that endeared him to fans and teammates alike. After retiring from cricket, Miller transitioned into a successful career as a television commentator and a popular public figure, contributing to the sport’s growth in Australia. His passing in 2004 marked the end of an era in Australian cricket, and tributes poured in from all corners of the nation, celebrating his legacy and the impact he had on the sport.
Keith Miller’s contributions went beyond cricket; he was also a symbol of resilience and dedication, having served in the RAAF during World War II. His experiences in the war shaped his character and outlook on life, influencing his approach to sports and public engagement. The national outpouring of grief following his death reflected the deep connection Australians had with Miller, not just as an athlete but as a cultural icon who embodied the spirit of the nation. His legacy continues to inspire aspiring cricketers and sports enthusiasts in Australia, reminding them of the importance of perseverance, integrity, and passion for their pursuits.
Australians Land at Jacquinot Bay, New Britain (1944)
On October 11, 1944, Australian forces landed at Jacquinot Bay in New Britain during World War II, marking a significant military operation in the Pacific theater. This landing was part of a broader strategy to neutralize Japanese forces and secure strategic locations in the region. The operation involved elements of the Australian Army and was instrumental in establishing a foothold on New Britain, allowing for further advances against Japanese positions.
The campaign at Jacquinot Bay was characterized by challenging conditions, including difficult terrain and tropical weather. Despite these obstacles, Australian troops displayed remarkable resilience and determination, engaging in combat and establishing supply routes. The successful landing was pivotal in the Allied efforts to regain control of the Pacific islands and ultimately contributed to the broader defeat of Japanese forces in the region. The operation showcased the bravery and commitment of Australian soldiers, who played a crucial role in the war’s progress.
The landing at Jacquinot Bay had lasting implications for Australia’s military history and identity. It highlighted the importance of collaboration among Allied forces in the fight against tyranny during World War II. The experiences of soldiers involved in this campaign shaped the narrative of Australia’s involvement in the war, fostering a sense of national pride and collective memory. Commemoration of the landing at Jacquinot Bay serves as a reminder of the sacrifices made by Australian servicemen and women, reinforcing the significance of their contributions to the nation’s history and values.
The Establishment of the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (1989)
On October 11, 1989, the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (AIATSIS) was officially established, marking a significant milestone in the recognition and preservation of Indigenous culture and heritage in Australia. The institute was created to promote the study of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander cultures, languages, and history, serving as a national resource for research and education. Its establishment was a response to the growing awareness of the need for Indigenous voices to be heard and valued within Australian society.
AIATSIS plays a crucial role in advancing knowledge about Indigenous peoples and facilitating research that respects and incorporates their perspectives. The institute’s work encompasses various fields, including anthropology, history, and cultural studies, contributing to a richer understanding of Australia’s diverse heritage. AIATSIS also provides access to valuable resources, including archives, publications, and educational programs, fostering a deeper appreciation for Indigenous cultures among Australians and the global community.
The establishment of AIATSIS represented a significant step toward reconciliation and recognition of the historical injustices faced by Indigenous Australians. It provided a platform for Indigenous scholars and community members to engage in research and advocacy, ensuring that their stories and experiences were documented and respected. The institute has become a vital institution in promoting cultural awareness and understanding, bridging the gap between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians. The legacy of AIATSIS continues to shape the narrative of reconciliation and cultural preservation in Australia, highlighting the importance of acknowledging and celebrating the contributions of Indigenous peoples to the nation’s identity.
The Opening of the Melbourne Festival (2023)
On October 11, 2023, the Melbourne Festival was officially opened, celebrating the city’s vibrant arts and cultural scene. This annual festival showcases a diverse array of performances, including theater, dance, music, and visual arts, attracting artists and audiences from across Australia and around the world. The festival serves as a platform for creative expression and innovation, highlighting the richness of Australian culture and the importance of the arts in society.
The opening of the Melbourne Festival is a significant event in Australia’s cultural calendar, marking a time of celebration and engagement with the arts. This festival not only promotes established artists but also provides opportunities for emerging talents to showcase their work, fostering a sense of community and collaboration within the creative sector. The festival’s programming often includes thought-provoking performances that address contemporary social issues, encouraging dialogue and reflection among audiences.
The Melbourne Festival also emphasizes the importance of accessibility and inclusivity in the arts. Efforts to engage diverse communities and provide a range of experiences ensure that the festival reflects the multicultural fabric of Australian society. The opening on October 11, 2023, signified a commitment to nurturing creativity and supporting the arts as a vital component of cultural identity. As the festival continues to evolve, it remains a testament to Melbourne’s status as a leading cultural hub in Australia, celebrating the power of the arts to inspire and unite.
Conclusion
October 11 stands out as a significant date in Australian history, marked by events that reflect the nation’s rich cultural heritage, sports legacy, and advancements in social awareness. From the death of cricket legend Keith Miller to the establishment of important institutions and the celebration of the arts, this day encapsulates key moments that contribute to the ongoing narrative of Australia’s evolution as a nation. These events not only represent milestones in their respective contexts but also highlight the interconnectedness of individual contributions, cultural expression, and societal progress. The legacy of these occurrences continues to shape the identity and values of Australia, underscoring the importance of remembrance and celebration in understanding the nation’s history.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 11 in British History?

October 11 marks a series of significant events in British history, showcasing pivotal moments that shaped the nation’s cultural, military, and political landscape. From the ecclesiastical controversies of the early 16th century to the military engagements of the late 19th century, this date encapsulates a rich tapestry of historical developments. It is also notable for the birth of a legendary footballer and the recovery of a famous ship that serves as a symbol of England’s maritime heritage.
This article will delve into four key events that took place on October 11: King Henry VIII being named Defender of the Faith in 1521, the start of the Anglo-Boer War in 1899, the birth of football icon Bobby Charlton in 1937, and the raising of the Mary Rose in 1982. Each of these events reflects the multifaceted nature of British history, highlighting the complexities of faith, conflict, sportsmanship, and heritage.
What Happened on October 11 in British History?
King Henry VIII Named Defender of the Faith (1521)
On October 11, 1521, King Henry VIII was officially named Defender of the Faith by Pope Leo X. This title was a significant recognition of Henry’s efforts to uphold the Catholic Church’s teachings, particularly in his opposition to the Protestant Reformation led by figures like Martin Luther. Henry VIII had written a pamphlet titled “Assertion of the Seven Sacraments,” which vehemently defended the Catholic doctrine against Protestant criticisms. The work was so well received that it earned him the papal accolade, solidifying his position as a champion of the faith.
However, this honor proved to be ironic in hindsight. Just a few years later, Henry would break away from the Catholic Church to establish the Church of England, primarily due to his desire to annul his marriage to Catherine of Aragon. This dramatic shift in religious allegiance would lead to profound changes in English society, law, and politics, as well as the wider Protestant Reformation across Europe. The title Defender of the Faith thus serves as a poignant reminder of the complexities and contradictions inherent in Henry’s reign and his legacy.
Henry VIII’s designation as Defender of the Faith highlights the significant role religion played in political governance during the Tudor era. His initial loyalty to the papacy exemplifies the intertwining of religious authority and monarchical power. However, the subsequent schism with Rome underscored the growing tensions between traditional Catholic practices and emerging Protestant ideologies, which would continue to influence British history for centuries to come. This period set the stage for a religious transformation that would lead to conflict, reform, and the establishment of a distinctly English identity.
Start of the Anglo-Boer War (1899)
The Anglo-Boer War officially commenced on October 11, 1899, marking a significant conflict between the British Empire and two Boer republics in South Africa: the South African Republic (Transvaal) and the Orange Free State. This war emerged from rising tensions due to British imperial interests and the desire for control over the rich gold and diamond resources found in these Boer territories. The war would last until 1902 and significantly impact both British and Boer societies.
The conflict began with a series of skirmishes and escalated into full-scale warfare, characterized by its guerrilla tactics employed by the Boers. The British, initially confident in their military superiority, faced unexpected resistance, leading to a protracted and bloody conflict. The war saw extensive mobilization of troops and resources, and it highlighted the complexities of imperialism, nationalism, and the rights of colonized peoples. The British military’s early setbacks in the war prompted significant changes in strategy and military organization, shaping future British military policies.
The Anglo-Boer War also had far-reaching social and political implications. The use of concentration camps by the British to detain Boer civilians drew widespread condemnation and highlighted the brutal realities of modern warfare. The war ultimately resulted in the incorporation of the Boer republics into the British Empire, leading to the eventual establishment of the Union of South Africa in 1910. The conflict is remembered as a formative event in the history of both Britain and South Africa, influencing national identities and perceptions of colonialism that resonate to this day.
Birth of Bobby Charlton (1937)
On October 11, 1937, Sir Bobby Charlton was born in Ashington, Northumberland. He would go on to become one of the most celebrated footballers in British history. Charlton’s career spanned over two decades, during which he played primarily for Manchester United and the England national team. His skill, vision, and goal-scoring ability earned him a reputation as one of the finest midfielders of his generation, contributing to the rise of English football on the world stage.
Charlton’s most notable achievements include being part of the Manchester United team that won the European Cup in 1968, making him one of the first English players to achieve this feat. He also played a crucial role in England’s victory in the 1966 FIFA World Cup, where his performances were pivotal in leading the national team to its first and only World Cup title. His success on both club and international levels made him an icon of the sport and a source of national pride for Britain.
Beyond his individual accolades, Charlton’s legacy is also marked by his sportsmanship and dedication to the game. He was known for his humility and commitment, serving as a role model for aspiring footballers. Following his retirement, he continued to contribute to the sport as a coach and administrator, influencing future generations of players. The impact of Bobby Charlton on British football is immeasurable, and his contributions have solidified his status as a national treasure, reflecting the cultural significance of football in the UK.
Raising of the Mary Rose (1982)
On October 11, 1982, the Mary Rose, the flagship of King Henry VIII’s navy, was raised from the seabed of the Solent after having sunk in 1545 during a battle against the French. The ship had lain on the seabed for over 400 years, and its recovery marked a monumental achievement in maritime archaeology. The Mary Rose is a symbol of England’s naval heritage and represents a crucial period in the country’s history, during which naval power began to take a prominent role in international affairs.
The raising of the Mary Rose was not only a remarkable engineering feat but also provided invaluable insights into Tudor life and shipbuilding practices. The recovery process involved meticulous planning and execution, with the ship being lifted in a delicate operation that showcased advances in archaeology and conservation techniques. The artifacts recovered from the site, including weaponry, personal items, and ship fittings, have contributed significantly to our understanding of 16th-century England.
Following its recovery, the Mary Rose underwent extensive conservation efforts, and a museum was established to house the ship and its artifacts in Portsmouth. The museum has become a significant tourist attraction, educating visitors about Tudor maritime history and the importance of naval warfare in shaping British identity. The story of the Mary Rose continues to resonate, symbolizing not only the achievements of the past but also the ongoing commitment to preserving cultural heritage for future generations.
Conclusion
October 11 is a date rich with historical significance in British history, reflecting moments that span political, military, and cultural domains. From King Henry VIII’s ecclesiastical recognition to the dramatic events of the Anglo-Boer War, the birth of football legend Bobby Charlton, and the raising of the Mary Rose, this day encapsulates the complexities of the British narrative. These events underscore the interplay of power, culture, and identity that have shaped the nation over the centuries. As we reflect on October 11, we acknowledge the importance of remembering and understanding these historical milestones, which continue to inform contemporary British society.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 11 in Canadian History?

October 11 holds a notable place in Canadian history, marked by significant political developments that have shaped the nation’s identity and governance. This day features key events, including the onset of the October Crisis in 1970, the formation of the Parti Québécois in 1968, and the swearing-in of Robert Borden as Canada’s eighth Prime Minister in 1911. Each of these events reflects the evolving political landscape in Canada, highlighting the complexities of national unity, the quest for autonomy, and the challenges faced by leadership during turbulent times.
This article will explore these pivotal moments in Canadian history, delving into the October Crisis, the rise of the Parti Québécois, and Robert Borden’s ascent to the Prime Ministership. These events not only defined their respective eras but also contributed to shaping the future of Canada, influencing political discourse, national policy, and the relationship between provinces and the federal government. Through examining these key milestones, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that have shaped Canada and continue to influence its trajectory.
What Happened on October 11 in Canadian History?
The October Crisis (1970)
The October Crisis began on October 11, 1970, when members of the Front de libération du Québec (FLQ) kidnapped British Trade Commissioner James Cross and later kidnapped and murdered Quebec Minister Pierre Laporte. The FLQ was a militant separatist group advocating for Quebec’s independence from Canada, believing that violent actions were necessary to achieve their goals. The crisis unfolded against a backdrop of rising tensions in Quebec, where issues of language, culture, and identity were increasingly coming to the forefront.
In response to the kidnappings, Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau invoked the War Measures Act, a controversial decision that allowed the government to take extraordinary measures, including the suspension of civil liberties. This marked the first time in Canadian history that the Act was used in peacetime. The military was deployed to the streets of Montreal, and thousands of Quebecers were arrested. Trudeau’s decision was met with mixed reactions: some praised the government for taking decisive action, while others criticized the response as excessive and a violation of civil rights.
The October Crisis highlighted the deep-seated issues surrounding Quebec nationalism and the struggle for autonomy. It also prompted national conversations about security, rights, and the balance between maintaining order and protecting freedoms. The FLQ’s actions and the government’s response reshaped Quebec’s political landscape, leading to discussions on sovereignty, autonomy, and the complexities of Canadian federalism. Ultimately, the crisis underscored the need for dialogue and understanding between different cultural and political factions within Canada, lessons that resonate even today.
Formation of the Parti Québécois (1968)
On October 11, 1968, the Parti Québécois (PQ) was officially formed, marking a significant moment in Quebec’s political landscape and Canadian politics as a whole. The PQ emerged as a response to the growing demand for Quebec’s independence and the desire for a government that would advocate for the interests of the province’s Francophone population. Led by René Lévesque, a former Liberal cabinet minister, the party aimed to challenge the existing political order and promote Quebec nationalism.
The formation of the PQ signified a shift in Quebec politics, as it sought to articulate a vision of sovereignty that resonated with many Quebecers disillusioned with the status quo. The party’s platform emphasized social justice, the protection of the French language and culture, and the assertion of Quebec’s right to self-determination. This resonated with a generation of voters who were increasingly aware of their cultural identity and the historical marginalization of Francophones within Canada.
The rise of the Parti Québécois played a crucial role in shaping the political discourse around Quebec’s future. It set the stage for the 1976 provincial election, where the party would eventually achieve a historic victory, leading to a push for a referendum on Quebec sovereignty. The PQ’s establishment marked the beginning of a new era in Quebec politics, as it challenged traditional party structures and called for a reevaluation of Quebec’s place within Canada. This period of political awakening contributed significantly to the ongoing discussions about federalism and the rights of provinces, shaping the path toward a more inclusive understanding of Canadian identity.
Robert Borden Sworn In as Prime Minister (1911)
On October 11, 1911, Robert Borden was sworn in as Canada’s eighth Prime Minister, a pivotal moment in the country’s political history. Borden, a member of the Conservative Party, succeeded Wilfrid Laurier, marking the end of a 15-year Liberal government. His leadership came at a critical time, as Canada faced various challenges, including economic growth, national unity, and the looming threat of global conflict.
Borden’s ascent to the Prime Ministership was marked by his commitment to national interests and unity, particularly regarding the relationship between English and French Canadians. His government focused on issues such as railway expansion and trade, seeking to strengthen Canada’s economy and reduce dependency on Britain. However, Borden’s administration was soon tested by the outbreak of World War I in 1914, which required significant military and financial commitments from Canada. His decisions during the war would ultimately shape Canada’s national identity and its role on the world stage.
As Prime Minister, Borden also faced significant internal challenges, including opposition from French Canadians who were increasingly disillusioned with the war effort. His government’s introduction of conscription in 1917 further polarized opinions and highlighted the complexities of managing a nation with diverse linguistic and cultural identities. Borden’s leadership during this tumultuous period set the stage for significant developments in Canadian politics, laying the groundwork for the modern state and its relationship with Britain and the international community.
Conclusion
October 11 stands as a date of profound significance in Canadian history, characterized by pivotal events that have shaped the nation’s political and cultural landscape. The October Crisis of 1970 highlighted the complexities of nationalism and the balance between security and civil liberties. The formation of the Parti Québécois in 1968 signaled a shift towards greater political representation for Quebecers and the ongoing dialogue about sovereignty and identity. Additionally, Robert Borden’s swearing-in as Prime Minister in 1911 marked a critical transition in Canadian governance, setting the stage for the country’s development during a time of both domestic and international challenges. These events illustrate the rich tapestry of Canadian history, reflecting the ongoing evolution of the nation’s identity, values, and political discourse. As we reflect on October 11, we recognize the importance of understanding and learning from these historical milestones, which continue to influence Canada today.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 11 in History?
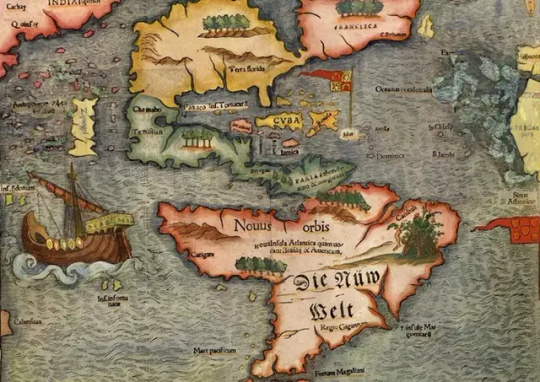
October 11 is a date marked by significant historical milestones that have influenced the course of world events across various fields, including exploration, war, religion, and science. This day has seen the unfolding of critical moments, from the discovery of the New World to advancements in space exploration and international diplomacy. The events detailed in this article illustrate the multifaceted nature of history, demonstrating how individual actions and decisions can resonate across time and geography.
This article will explore six key events that occurred on October 11: the discovery of the New World in 1492, the start of the Second Boer War in 1899, the opening of the Second Vatican Council in 1962, the first American woman walking in space in 1984, the launch of Apollo 7 in 1968, and the Nobel Peace Prize awarded to Jimmy Carter in 2002. Each event not only represents a pivotal moment in its respective context but also reflects broader themes of human endeavor, conflict, and the quest for peace.
What Happened on October 11 in History?
The Discovery of the New World (1492)
On October 11, 1492, Christopher Columbus and his crew made a landmark discovery that would change the course of history—the New World. After months of sailing across the Atlantic Ocean, Columbus, under the auspices of the Spanish monarchy, reached the Bahamas, believing he had found a new route to Asia. This discovery marked the beginning of European exploration and colonization of the Americas, setting off a series of events that would profoundly impact indigenous populations and the global balance of power.
The arrival of Columbus initiated an era of exploration known as the Age of Discovery, during which European powers sought to expand their empires and exploit new resources. The implications of Columbus’s voyage were vast; it led to the establishment of trade routes, the spread of Christianity, and the eventual colonization of large portions of the Americas. However, it also heralded a dark chapter in history marked by the conquest and subjugation of indigenous peoples, whose cultures and societies were irrevocably altered.
Columbus’s journey and subsequent discoveries ignited centuries of exploration, cultural exchange, and conflict. The encounters between Europeans and the indigenous populations often resulted in devastating consequences, including the spread of diseases, loss of land, and cultural assimilation. The discovery of the New World on October 11, 1492, thus represents a pivotal moment in history, shaping not only the future of the Americas but also the trajectory of global interactions and relationships.
The Start of the Second Boer War (1899)
On October 11, 1899, the Second Boer War began, marking a significant conflict between the British Empire and the Boer republics of the Transvaal and the Orange Free State in South Africa. The war was rooted in longstanding tensions over issues such as governance, land rights, and the desire for autonomy among the Boer settlers. British imperial ambitions clashed with Boer aspirations for independence, setting the stage for a protracted and bloody conflict.
The war commenced after diplomatic efforts failed to resolve disputes, leading to the British declaration of war against the Boer republics. The initial phase of the war saw the British underestimate the military capabilities and resolve of the Boer forces. The Boers, skilled in guerrilla warfare, employed tactics that would frustrate and challenge the traditionally structured British military. The conflict quickly escalated, resulting in significant casualties on both sides.
The Second Boer War had profound implications for South Africa and the British Empire. It was characterized by brutal tactics, including the use of concentration camps for Boer civilians, which drew international condemnation. The war ultimately ended in 1902 with the signing of the Treaty of Vereeniging, leading to British control over the Boer territories. However, the legacy of the war lingered, influencing South Africa’s socio-political landscape and contributing to the emergence of Afrikaner nationalism. The start of the Second Boer War on October 11, 1899, thus marked a turning point in the history of colonial conflicts, foreshadowing future struggles for independence and self-determination in the region.
The Opening of the Second Vatican Council (1962)
On October 11, 1962, the Second Vatican Council, also known as Vatican II, was officially opened by Pope John XXIII. This ecumenical council was convened to address issues within the Roman Catholic Church and to engage with the modern world. Vatican II represented a significant moment in church history, aimed at promoting reform and renewal within Catholicism while fostering dialogue with other faiths and denominations.
The council brought together bishops from around the world, who participated in discussions on various topics, including liturgy, religious freedom, and the role of the Church in contemporary society. One of the most notable outcomes of Vatican II was the document “Lumen Gentium,” which emphasized the Church’s mission to engage with the world and highlighted the importance of ecumenism. The council also introduced reforms in liturgical practices, allowing for the use of vernacular languages in Mass, making the Church more accessible to the laity.
Vatican II had a profound impact on the Catholic Church and its relationship with society. It encouraged a more open and dialogical approach, leading to increased engagement with social issues and interfaith relations. The council’s emphasis on pastoral care and social justice resonated with the changing cultural landscape of the 1960s and 1970s. The opening of the Second Vatican Council on October 11, 1962, thus marked a watershed moment in the Church’s history, signaling a willingness to adapt to the modern world while remaining rooted in tradition.
The First American Woman Walks in Space (1984)
On October 11, 1984, Dr. Kathryn Sullivan became the first American woman to walk in space during the Space Shuttle Challenger mission STS-41-G. This groundbreaking achievement represented a significant milestone in the history of space exploration and women’s roles in science and technology. Sullivan’s spacewalk lasted approximately three hours and involved the deployment of a satellite, highlighting the contributions of women in fields previously dominated by men.
Sullivan’s accomplishment was not only a personal triumph but also a symbolic moment for gender equality in the sciences. Her journey into space demonstrated the capabilities of women in roles that had been historically restricted. The mission was watched by millions, inspiring future generations of female scientists, engineers, and astronauts to pursue careers in STEM fields. Sullivan’s achievement underscored the importance of diversity in the workforce and the need for inclusive policies that support women in traditionally male-dominated areas.
Sullivan went on to have a distinguished career in both science and public service, serving as a prominent advocate for education and research. Her spacewalk on October 11, 1984, serves as a reminder of the ongoing struggle for gender equality in all fields and the importance of representation in shaping the future of exploration and discovery. This historic event not only marked a personal milestone for Sullivan but also represented a significant shift in the narrative surrounding women in science and technology.
The Launch of Apollo 7 (1968)
On October 11, 1968, NASA launched Apollo 7, the first successful manned mission of the Apollo program. This mission was crucial for the future of space exploration, as it was the first time humans ventured into space after the tragic Apollo 1 incident, which resulted in the loss of three astronauts during a pre-launch test. Apollo 7’s successful launch and operation marked a turning point for NASA and reinvigorated public confidence in the space program.
The Apollo 7 mission lasted 11 days and featured a crew of three astronauts: Walter M. Schirra, Donn Eisele, and R. Walter Cunningham. The mission’s primary objective was to test the Command and Service Module’s performance in space, including its life support systems and communication capabilities. During the flight, the crew conducted numerous experiments and sent back live television broadcasts to Earth, providing valuable insights into the spacecraft’s functionality.
Apollo 7’s success paved the way for subsequent Apollo missions, culminating in the historic Apollo 11 moon landing in 1969. The mission demonstrated the viability of the Apollo program and showcased the importance of teamwork and resilience in overcoming challenges. The launch of Apollo 7 on October 11, 1968, stands as a testament to human ingenuity and determination in the face of adversity, shaping the future of space exploration for generations to come.
The Nobel Peace Prize Awarded to Jimmy Carter (2002)
On October 11, 2002, former U.S. President Jimmy Carter was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for his decades of work in promoting peace, democracy, and human rights worldwide. This honor recognized Carter’s commitment to humanitarian efforts, conflict resolution, and advocacy for social justice following his presidency. His work with the Carter Center and various global initiatives reflected a dedication to addressing pressing issues that impact communities around the globe.
Carter’s post-presidency career was marked by significant contributions to public health, education, and conflict resolution. He played a key role in monitoring elections in emerging democracies, advocating for fair practices and transparency. Additionally, Carter’s efforts to combat diseases like Guinea worm disease showcased his commitment to improving health and living conditions in developing nations. His work exemplified the potential for former leaders to effect positive change even after leaving office.
The Nobel Peace Prize awarded to Carter on October 11, 2002, serves as a reminder of the importance of ongoing efforts to foster peace and understanding in a complex world. His recognition reflects the belief that individuals can make a difference and that leadership extends beyond political office. Carter’s legacy continues to inspire new generations of activists and leaders committed to promoting human rights and social justice around the world.
Conclusion
October 11 has proven to be a day of significant historical importance, marked by events that have influenced various facets of human existence. From the discovery of the New World in 1492 to advancements in space exploration, the opening of religious councils, and the recognition of humanitarian efforts, this date encapsulates key moments in history that reflect human ambition, conflict, and the pursuit of peace. These events remind us of the interconnectedness of global history and the impact of individual actions on the broader narrative of human progress.
0 notes
Text
What Day of the Week Do Best Buy Sales Start?

Best Buy, a leading retailer in electronics and appliances, has established itself as a go-to destination for consumers seeking the latest technology. With a wide range of products from televisions and computers to home appliances and gaming consoles, the store attracts millions of shoppers each year. One of the key aspects of shopping at Best Buy is understanding their sales strategy, particularly the timing of sales events. Consumers often wonder about the best day of the week to take advantage of discounts and promotions. This article explores the various factors influencing Best Buy’s sales schedule and provides insights into when sales typically begin.
Best Buy employs various strategies to attract customers, including seasonal sales, holiday promotions, and weekly specials. Understanding the patterns behind these sales can help shoppers make informed purchasing decisions. The timing of sales is not random; it is influenced by several factors, including industry trends, consumer behavior, and competition. By analyzing these elements, consumers can optimize their shopping experience and ensure they don’t miss out on significant savings.
Weekly Sales Trends at Best Buy
Best Buy has a well-established pattern for its weekly sales. Traditionally, most sales begin on Sundays. This strategy is common among many retailers, as it allows customers to plan their shopping trips over the weekend when they have more free time. The Sunday start also aligns with the arrival of new inventory for the week, which can make the discounts on older products more attractive.
Moreover, starting sales on Sunday allows Best Buy to capture customers who may be coming in to browse. This tactic is particularly effective because many consumers often make purchasing decisions after visiting a store to physically assess products. Once customers are in the store, they may be more likely to purchase additional items beyond those on sale. The company’s decision to launch sales on Sundays reflects a broader retail trend aimed at maximizing customer foot traffic and increasing overall sales.
Seasonal Sales Events
In addition to weekly sales, Best Buy runs several seasonal sales events throughout the year. Major holidays such as Black Friday, Cyber Monday, Memorial Day, and back-to-school season are particularly significant times for sales. During these events, discounts can be deeper, and the selection may be broader.
Black Friday, which occurs on the day after Thanksgiving, marks the beginning of the holiday shopping season. Best Buy often offers substantial discounts on popular electronics, attracting large crowds both in-store and online. Similarly, Cyber Monday, which follows Black Friday, focuses on online sales and often features exclusive deals for digital shoppers. Understanding these seasonal trends can help consumers strategize their purchases, allowing them to maximize savings during these promotional periods.
Price Matching Policy
Best Buy’s price-matching policy also plays a critical role in its sales strategy. The company promises to match competitors’ prices on identical products, which encourages consumers to shop confidently knowing they can secure the best deal. This policy often leads customers to wait for specific days of the week, particularly around new sales launches, to take advantage of price matches.
Customers may choose to visit Best Buy on Sundays, not only to check for new sales but also to compare prices with other retailers. This gives them an advantage, as they can ensure they are getting the lowest price available. The combination of weekly sales and the price-matching policy fosters a competitive environment that benefits consumers. This practice also encourages price-conscious shoppers to stay informed about other retailers’ sales and promotions.
The Role of Advertisements
Advertising plays a significant role in alerting consumers to Best Buy’s sales. Weekly ads are typically released on Sundays, informing customers about the deals available for the week. These advertisements are strategically designed to highlight popular products and significant discounts, drawing attention to items that may be in high demand.
Social media platforms and email marketing also contribute to disseminating information about ongoing sales. Best Buy actively engages with customers through these channels, providing updates on limited-time offers and flash sales. By leveraging multiple advertising methods, Best Buy maximizes its reach, ensuring that consumers are aware of sales as soon as they begin.
Online Shopping and Digital Promotions
With the rise of e-commerce, Best Buy has also adapted its sales strategy to include digital promotions. Many sales that start in-store are mirrored online, allowing customers to shop from the comfort of their homes. Online deals often launch at the same time as in-store promotions, with some exclusive discounts available only for digital shoppers.
The convenience of online shopping has led many consumers to prefer purchasing through Best Buy’s website, particularly for larger items like appliances and televisions. The online shopping experience often provides detailed product descriptions, customer reviews, and the ability to easily compare prices with other retailers. This shift has prompted Best Buy to prioritize its online sales strategies, ensuring that both in-store and online customers have access to the best deals.
Customer Loyalty Programs
Best Buy offers a loyalty program called My Best Buy, which rewards customers for their purchases. Members earn points on every purchase, which can be redeemed for future discounts. This program not only incentivizes customers to shop more frequently but also aligns with the timing of sales.
Loyalty members often receive early access to promotions or exclusive offers during sales events. This strategy encourages customers to sign up for the program, increasing their likelihood of shopping at Best Buy when sales begin. By creating a sense of exclusivity around certain sales, Best Buy effectively increases customer engagement and boosts sales during promotional periods.
Conclusion
Understanding the day of the week that Best Buy sales start is essential for savvy shoppers looking to maximize their savings. With weekly sales typically beginning on Sundays, coupled with seasonal events and a robust price-matching policy, consumers can strategically plan their purchases. The integration of digital promotions and loyalty programs further enhances the shopping experience, making it easier for customers to take advantage of discounts.
In the competitive landscape of electronics retail, Best Buy continues to adapt its sales strategies to meet consumer demands. By remaining informed about the timing and nature of sales, shoppers can navigate the marketplace effectively, ensuring they receive the best value for their money. Ultimately, the key to success lies in understanding the patterns of Best Buy’s sales, allowing consumers to make the most of their shopping experiences.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 10 in American History?

October 10 is a date that has witnessed a variety of significant events in American history, each reflecting critical developments in politics, military training, sports, and regulatory affairs. From the founding of esteemed institutions to notable resignations and celebrations of athletic prowess, the day stands out as a marker of progress and change across different facets of society. Each event has contributed to shaping the nation in unique ways, underscoring the dynamic history of the United States.
This article will explore four noteworthy events that occurred on October 10: the founding of the U.S. Naval Academy in 1845, the resignation of Vice President Spiro Agnew in 1973, the birth of football legend Brett Favre in 1969, and the establishment of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission in 1974. These events highlight pivotal moments in military, political, and cultural history, showcasing the diverse narratives that converge on this date.
What Happened on October 10 in American History?
Founding of the U.S. Naval Academy (1845)
On October 10, 1845, the United States Naval Academy was officially founded in Annapolis, Maryland, marking a significant moment in the history of American military education. The academy was established in response to the growing needs of the U.S. Navy, which required a formalized system for training officers as the nation expanded its naval capabilities. The initial enrollment consisted of just 50 midshipmen, but the academy has since grown into a prestigious institution known for producing competent naval leaders.
The founding of the Naval Academy represented a commitment to professionalism within the Navy. As the United States began to assert itself on the global stage, the importance of having well-trained officers became apparent. The academy aimed to cultivate leadership, technical proficiency, and a sense of duty among its midshipmen, ensuring that they were prepared for the complexities of naval warfare. Over the years, the curriculum has evolved to encompass a wide range of disciplines, including engineering, navigation, and military tactics, all designed to meet the demands of modern naval operations.
The U.S. Naval Academy has produced many notable graduates, including influential figures in both military and political arenas. Its emphasis on ethics, leadership, and service to the nation has established a legacy that continues to resonate within the Navy and the broader armed forces. Today, the Naval Academy remains a vital institution, shaping the future leaders of the U.S. Navy and reinforcing the importance of education and training in maintaining national security.
Resignation of Spiro Agnew (1973)
On October 10, 1973, Vice President Spiro Agnew resigned from office, a dramatic turn of events in American politics. His resignation came amid a growing scandal involving allegations of corruption and bribery dating back to his tenure as Governor of Maryland. As investigations intensified, it became clear that Agnew was facing serious legal troubles, prompting his decision to step down from the vice presidency.
Agnew’s resignation marked a significant moment in U.S. political history, as he became the second vice president in American history to resign from office. His departure raised questions about the integrity of the administration and highlighted the challenges faced by President Richard Nixon, who was already embroiled in the Watergate scandal. Agnew’s exit not only reflected the tumultuous political climate of the time but also set the stage for Gerald Ford’s ascension to the vice presidency and, eventually, the presidency following Nixon’s resignation in 1974.
The implications of Agnew’s resignation extended beyond immediate political ramifications. It underscored the need for accountability in government and reinforced public skepticism toward political leaders. The events surrounding his resignation contributed to a broader conversation about ethics and integrity in public service, shaping the discourse on political accountability for years to come.
Birth of Brett Favre (1969)
On October 10, 1969, football legend Brett Favre was born in Gulfport, Mississippi. Favre would go on to become one of the most celebrated quarterbacks in National Football League (NFL) history, known for his remarkable talent, competitive spirit, and longevity in the sport. Growing up in a sports-oriented family, Favre developed a passion for football at an early age, which laid the foundation for his future success.
Favre’s professional career began when he was drafted by the Atlanta Falcons in 1991. However, it was his subsequent trade to the Green Bay Packers that truly defined his legacy. Over the course of his career, Favre set numerous records, including being the first player to reach 500 touchdown passes and 70,000 passing yards. His resilience and ability to perform under pressure earned him respect among teammates and opponents alike. Favre’s contributions to the sport extended beyond statistics; he inspired a generation of players and fans with his love for the game.
The impact of Brett Favre on American football is profound. He led the Packers to victory in Super Bowl XXXI, solidifying his status as one of the all-time greats. His playing style, characterized by his powerful arm and improvisational skills, transformed the quarterback position and influenced future generations of players. Favre’s legacy continues to resonate in the NFL, as he remains an iconic figure in the sport’s history, symbolizing excellence and dedication.
Establishment of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (1974)
On October 10, 1974, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) was established, marking a significant development in the oversight of nuclear energy in the United States. The NRC was created in response to growing public concerns about the safety and regulation of nuclear power following incidents such as the Three Mile Island accident in 1979. The commission’s primary mission is to ensure the safe use of nuclear materials while protecting public health and the environment.
The establishment of the NRC represented a pivotal shift in the regulation of nuclear energy. Prior to its creation, oversight was divided among various agencies, leading to inconsistencies in safety standards and practices. The NRC centralized authority over nuclear power plants, licensing, and enforcement of safety regulations, aiming to enhance public confidence in nuclear energy. It established a framework for evaluating the safety of nuclear facilities and ensuring compliance with stringent safety protocols.
Over the years, the NRC has played a crucial role in the development of the nuclear industry in the United States. Its work includes conducting inspections, reviewing license applications, and responding to incidents and emergencies. The commission has faced challenges related to public perception, regulatory effectiveness, and the ongoing debate over nuclear energy’s role in addressing climate change. Nonetheless, its establishment on October 10, 1974, marked a significant step toward enhancing safety and accountability in the nuclear sector, shaping the future of energy production in the nation.
Conclusion
October 10 stands as a significant date in American history, characterized by pivotal events that have shaped military, political, cultural, and regulatory landscapes. The founding of the U.S. Naval Academy reflects a commitment to education and leadership within the Navy, while the resignation of Spiro Agnew highlights the complexities of political integrity and accountability. The birth of Brett Favre symbolizes the spirit of competition and excellence in sports, and the establishment of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission underscores the importance of safety and regulation in the nuclear energy sector.
Each of these events contributes to the broader narrative of American history, illustrating the diverse themes and challenges that have defined the nation. As we reflect on the significance of October 10, we recognize the interconnectedness of these events and their lasting impact on the American experience. This date serves as a reminder of the ongoing journey toward progress and the importance of learning from history as we continue to navigate the complexities of modern society.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 10 in Australian History?

October 10 is a date that has marked various significant events in Australian history, reflecting pivotal moments that have shaped the nation’s identity and governance. From policies that affected the land and its people to historical marches that highlighted social issues, this date has seen both progress and conflict. Each of the events discussed in this article represents a crucial chapter in Australia’s past, underscoring the nation’s complex journey toward reconciliation, democracy, and connectivity.
This article will delve into five noteworthy events that occurred on October 10: the implementation of Terra Nullius in 1835, the opening of South Australia’s first parliament in 1843, the Cooee March in 1915, the Battle of Poelcappelle in 1917, and the establishment of a telephone link between Sydney and Brisbane in 1923. Each event not only provides insights into the historical context of Australia but also highlights the ongoing evolution of its societal structures.
What Happened on October 10 in Australian History?
The Implementation of Terra Nullius (1835)
On October 10, 1835, the policy of Terra Nullius, meaning “land belonging to no one,” was effectively implemented in Australia, fundamentally altering the relationship between the British settlers and the Indigenous populations. This legal doctrine allowed the British to claim land in Australia without recognizing the existing rights of Indigenous Australians, who had inhabited the continent for tens of thousands of years. The first documented assertion of Terra Nullius occurred when the British established their claim to the land in New South Wales, disregarding the complex systems of land ownership and cultural connection that Indigenous peoples maintained.
The ramifications of Terra Nullius were profound and long-lasting. It facilitated the appropriation of vast tracts of land, leading to dispossession and displacement of Indigenous communities. This policy not only shaped land ownership in Australia but also laid the groundwork for systemic inequality and injustice that Indigenous Australians have faced throughout history. The term Terra Nullius remained a central issue in discussions about Indigenous rights and land claims, and it was not until the landmark Mabo decision in 1992 that it was finally overturned, acknowledging the historical presence and rights of Indigenous Australians.
The legacy of Terra Nullius continues to resonate today as Australia grapples with the consequences of colonization. The recognition of past injustices is essential in fostering reconciliation and understanding between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians. Events like the implementation of Terra Nullius serve as crucial reminders of the ongoing struggle for justice and recognition faced by Indigenous communities across the nation.
The Opening of South Australia’s First Parliament (1843)
On October 10, 1843, South Australia’s first parliament officially opened, marking a significant milestone in the development of representative democracy in the region. Established under the South Australia Act of 1834, this parliament laid the groundwork for governance in the fledgling colony. The assembly convened in Adelaide, with representatives elected to voice the interests of the settlers and oversee legislative matters.
The opening of the parliament signified a shift toward self-governance and political representation in South Australia. The first parliamentary session was attended by Governor George Gawler, who emphasized the importance of the new legislative body in addressing the needs and aspirations of the settlers. The parliament’s establishment allowed for the introduction of laws and policies that would shape the social and economic landscape of South Australia, contributing to its growth and development as a distinct political entity.
As South Australia evolved, its parliament played a crucial role in advancing reforms and addressing key issues facing the community. Legislative discussions often centered around land rights, immigration, and infrastructure development, reflecting the challenges and aspirations of a growing population. The establishment of South Australia’s parliament marked the beginning of a democratic process that would continue to evolve, ultimately leading to greater representation and rights for all citizens, including Indigenous peoples.
The legacy of South Australia’s first parliament is evident in the continued commitment to democratic governance in Australia today. It serves as a reminder of the importance of political participation and representation in shaping a fair and just society. The events surrounding its opening reflect the ongoing journey toward inclusivity and equity in the political landscape of the nation.
The Cooee March (1915)
On October 10, 1915, the Cooee March began in New South Wales, an event that would become a significant part of Australia’s war history during World War I. Organized by a group of men from Gilgandra, the march aimed to recruit soldiers for the Australian Imperial Force (AIF) and to demonstrate solidarity with the war effort. Participants, known as “Cooee men,” marched more than 300 kilometers to Sydney, calling on others to join them in supporting the troops fighting overseas.
The march was notable for its grassroots nature and the sense of camaraderie it fostered among the participants. As the march progressed, it garnered public attention and support, leading to the enlistment of numerous volunteers eager to contribute to the war effort. The Cooee March not only served as a recruitment campaign but also highlighted the emotional connection between the Australian populace and the soldiers serving in the trenches of Europe.
The Cooee March became a symbol of Australian patriotism and the collective desire to support the war. It showcased the strong sense of community and national identity that emerged during this challenging period. However, the march also reflected the complexities of war and the sacrifices made by soldiers and their families. As Australia faced the realities of combat, events like the Cooee March emphasized the need for solidarity and support within the home front.
The legacy of the Cooee March endures as a reminder of the sacrifices made by Australians during World War I. It underscores the importance of collective action and community spirit in times of crisis. As Australia reflects on its military history, the Cooee March serves as a poignant symbol of the nation’s resilience and commitment to supporting its servicemen and women.
The Battle of Poelcappelle (1917)
On October 10, 1917, the Battle of Poelcappelle occurred during World War I, marking a critical moment in the Third Battle of Ypres. This battle was part of a series of offensives aimed at breaking through German lines in Belgium. Australian troops played a significant role in the fighting, contributing to the broader Allied strategy of capturing key positions on the Western Front.
The Battle of Poelcappelle was characterized by fierce combat and challenging conditions. Soldiers faced difficult weather, muddy terrain, and the relentless threat of enemy fire as they advanced toward their objectives. Despite the challenges, Australian forces demonstrated remarkable courage and resilience in the face of adversity. The battle resulted in significant casualties, reflecting the high cost of warfare during this period.
The significance of the Battle of Poelcappelle extends beyond its immediate military outcomes. It highlighted the bravery and sacrifices of Australian soldiers, many of whom fought with distinction and faced harrowing conditions. The battle contributed to the growing recognition of Australia’s military contributions to the war and helped shape the national identity in the aftermath of World War I.
The events of October 10, 1917, and the Battle of Poelcappelle serve as a reminder of the sacrifices made by Australians in pursuit of freedom and peace. As the nation continues to honor its military history, battles like Poelcappelle underscore the importance of remembrance and recognition for those who served in times of conflict.
Telephone Link Between Sydney and Brisbane (1923)
On October 10, 1923, a significant technological advancement took place with the establishment of a direct telephone link between Sydney and Brisbane. This development marked a new era in communication for Australians, enhancing connectivity between the two major cities and fostering economic and social interactions. Prior to this link, long-distance communication was often slow and unreliable, relying on telegrams and postal services.
The opening of the telephone link represented a major step forward in modernizing communication infrastructure in Australia. It facilitated not only personal conversations but also business dealings and government communications, contributing to the growth of interstate commerce. The ability to communicate instantly across long distances had profound implications for the development of the nation, enabling better coordination and collaboration in various sectors.
The introduction of the telephone link was part of a broader trend toward technological advancement in Australia during the early 20th century. As the nation sought to modernize its infrastructure, developments in telecommunications played a critical role in shaping the economic landscape. The link between Sydney and Brisbane exemplified the commitment to improving connectivity and fostering unity across the continent.
The legacy of the telephone link established on October 10, 1923, continues to resonate today as Australia embraces technological innovations that enhance communication and connectivity. It serves as a reminder of the importance of infrastructure in supporting social and economic development and highlights the ongoing evolution of communication technologies in an increasingly interconnected world.
Conclusion
October 10 is a date rich with historical significance in Australia, encompassing events that have shaped the nation’s identity, governance, and technological advancement. From the implementation of Terra Nullius to the establishment of the telephone link between Sydney and Brisbane, each event has left an indelible mark on the course of Australian history.
The opening of South Australia’s first parliament underscores the importance of democratic governance, while the Cooee March and the Battle of Poelcappelle highlight the sacrifices and contributions of Australians during wartime. As Australia reflects on these events, it acknowledges the complexities of its past and the ongoing journey toward reconciliation, representation, and progress.
The stories behind October 10’s historical events serve as reminders of the resilience and determination of the Australian people, inspiring future generations to continue building a nation that values unity, justice, and innovation. As Australia moves forward, it is essential to honor the lessons of the past and strive for a more inclusive and equitable society for all its citizens.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 10 in British History?

October 10 has witnessed several significant events in British history, showcasing the nation’s evolving social, cultural, and political landscape. From the founding of pioneering organizations to the birth of influential figures, this date has played a crucial role in shaping the historical narrative of Britain. The events discussed in this article represent moments of progress, conflict, and cultural development, reflecting the multifaceted nature of British history.
In this article, we will explore four notable events that occurred on October 10: the founding of the Women’s Social and Political Union in 1903, the birth of playwright Harold Pinter in 1930, the launch of the Outer Space Treaty in 1967, and the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles in 2010. Each of these events not only marks a distinct moment in history but also highlights the broader social and political movements that have influenced Britain and the world.
What Happened on October 10 in British History?
The Founding of the Women’s Social and Political Union (1903)
On October 10, 1903, the Women’s Social and Political Union (WSPU) was founded in Manchester by Emmeline Pankhurst and her daughters, Christabel and Sylvia. This organization emerged in response to the growing demand for women’s suffrage in Britain and became one of the most prominent groups advocating for women’s rights during the early 20th century. The WSPU’s motto, “Deeds, not words,” encapsulated its commitment to militant tactics in the fight for suffrage, which included protests, hunger strikes, and civil disobedience.
The formation of the WSPU marked a turning point in the women’s suffrage movement in Britain. Unlike earlier suffrage organizations, the WSPU embraced a more confrontational approach to attract attention to their cause. Members organized rallies, public speeches, and marches, often clashing with authorities. Their efforts highlighted the frustration of many women who felt marginalized and silenced in a patriarchal society. The WSPU’s activism significantly raised awareness about women’s rights, leading to increased public discourse on the need for gender equality and political representation.
The WSPU’s influence can be seen in the eventual passage of the Representation of the People Act in 1918, which granted limited voting rights to women over the age of 30. This achievement paved the way for further advancements in women’s rights, culminating in equal suffrage in 1928. The founding of the WSPU on October 10, 1903, remains a significant milestone in the ongoing struggle for gender equality in Britain and serves as a reminder of the power of collective action in effecting social change.
The Birth of Harold Pinter (1930)
On October 10, 1930, one of Britain’s most celebrated playwrights, Harold Pinter, was born in London. Pinter is renowned for his unique style of writing, characterized by its emphasis on dialogue, pauses, and the use of silence. His plays often explore themes of power, betrayal, and the complexities of human relationships, reflecting the darker aspects of life and the human psyche. Pinter’s distinct voice and innovative techniques have earned him a prominent place in the canon of modern British theater.
Pinter’s early works, such as “The Birthday Party” (1957) and “The Homecoming” (1965), challenged conventional narrative structures and traditional character development. Instead of providing clear resolutions, Pinter often left audiences with ambiguity, prompting them to question the motivations and intentions of his characters. His innovative approach to language and dialogue has had a profound impact on theater, influencing countless playwrights and theater practitioners. In recognition of his contributions to literature and drama, Pinter was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2005.
The legacy of Harold Pinter extends beyond the theater; his works often served as a commentary on social and political issues of his time. Pinter was an outspoken critic of totalitarianism, war, and human rights abuses, using his platform to advocate for justice and equality. His involvement in political activism and his ability to blend art with social commentary have solidified his status as a cultural icon in British history. The birth of Harold Pinter on October 10, 1930, marks the beginning of a remarkable journey that would leave an indelible mark on the world of literature and theater.
The Launch of the Outer Space Treaty (1967)
On October 10, 1967, the Outer Space Treaty, formally known as the Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, was opened for signature at the United Nations. This treaty established fundamental guidelines for the peaceful exploration and use of outer space, laying the groundwork for international space law. The Outer Space Treaty has been signed by over 100 countries and remains one of the most significant agreements in regulating outer space activities.
The treaty’s key provisions include the prohibition of the placement of nuclear weapons in space, the assertion that space shall be free for exploration by all countries, and the principle that outer space is not subject to national appropriation by any means. The Outer Space Treaty represents a collective commitment by nations to cooperate in the exploration of space for the benefit of all humanity, emphasizing the need for peaceful coexistence and collaboration in a domain that transcends national boundaries.
The launch of the Outer Space Treaty was a response to the growing concerns about the militarization of space during the Cold War era. As nations began to advance their capabilities in space exploration, the treaty aimed to prevent potential conflicts and promote cooperation among space-faring nations. The principles enshrined in the treaty have guided subsequent space endeavors and international agreements, underscoring the importance of responsible behavior in outer space.
The Outer Space Treaty remains relevant today as nations continue to explore and utilize space for various purposes, including scientific research, communication, and satellite deployment. As humanity stands on the brink of a new era of space exploration, the treaty serves as a reminder of the need for international cooperation and the shared responsibility of all nations in safeguarding the future of space for generations to come.
The Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles (2010)
On October 10, 2010, the Netherlands Antilles was officially dissolved, marking a significant shift in the political landscape of the Caribbean. This dissolution resulted in the restructuring of the islands’ governance and their relationship with the Netherlands. The decision to dissolve the Netherlands Antilles came after years of discussions about political autonomy and the desire for greater self-governance among the islands.
As a result of the dissolution, the islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba became special municipalities of the Netherlands, while Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten gained autonomous status as separate countries within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. This restructuring aimed to address the unique needs and aspirations of each island, allowing for greater local governance and political representation. The dissolution was met with mixed reactions, with some celebrating the increased autonomy while others expressed concerns about the challenges of self-governance.
The dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles on October 10, 2010, symbolizes the ongoing evolution of Caribbean politics and the quest for self-determination among its islands. The changes in governance reflect broader trends in the region, as many territories seek to redefine their political identities and relationships with colonial powers. The new status of the former Netherlands Antilles highlights the complexities of post-colonial governance and the importance of recognizing the aspirations of local populations.
The legacy of the dissolution continues to shape the political discourse in the Caribbean, emphasizing the need for dialogue and collaboration among nations. As the former islands navigate their new political realities, they grapple with the challenges of identity, governance, and economic development in an increasingly interconnected world.
Conclusion
October 10 stands out as a date marked by significant events in British history, each contributing to the broader narrative of social, cultural, and political development. From the founding of the Women’s Social and Political Union, which championed women’s rights and suffrage, to the birth of Harold Pinter, whose innovative contributions to theater continue to resonate today, these events reflect the dynamism of British society.
The launch of the Outer Space Treaty underscores the importance of international cooperation in the exploration of space, while the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles highlights the ongoing quest for self-determination in the Caribbean. Together, these events illustrate the complexities and challenges faced by Britain and its former territories, emphasizing the need for dialogue, understanding, and collaboration.
As we reflect on the historical significance of October 10, we are reminded of the enduring impact of these events on contemporary society. They serve as a testament to the struggles and achievements of those who came before us, inspiring future generations to continue the pursuit of justice, equality, and progress.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 10 in Canadian History?

October 10 holds significant historical importance in Canada, marking pivotal moments that have shaped the nation’s political landscape and cultural identity. From the swearing-in of influential leaders to the emergence of critical political movements, this date has witnessed events that reflect Canada’s evolving society. The events discussed in this article will provide a glimpse into the complexities of Canadian history, highlighting how these occurrences have influenced the trajectory of the nation.
This article will explore four notable events that took place on October 10: the swearing-in of Robert Borden as Prime Minister in 1911, the developments during the October Crisis in 1970, the formation of the Parti Québécois in 1968, and the birth of Louis Riel in 1844. Each event serves as a key milestone in understanding Canada’s political evolution and cultural diversity, illustrating the dynamics that have shaped the country’s identity.
What Happened on October 10 in Canadian History?
Robert Borden Sworn In as Prime Minister (1911)
On October 10, 1911, Robert Borden was sworn in as the Prime Minister of Canada, succeeding Sir Wilfrid Laurier. Borden, a member of the Conservative Party, took office during a period of significant change in Canada. His leadership would span crucial events, including World War I, which would profoundly impact the nation’s political and social landscape. Borden’s tenure marked a shift in Canadian politics, moving toward a more centralized federal government and greater involvement in international affairs.
One of Borden’s primary challenges upon taking office was addressing the issue of trade. He advocated for a new tariff policy aimed at protecting Canadian industries from foreign competition, a stance that would lead to tensions with the United States. His government also grappled with the growing calls for increased support for the military, particularly as Canada prepared to engage in World War I. Borden’s leadership during this tumultuous period would ultimately shape Canada’s emerging national identity and its role on the world stage.
Borden’s government was marked by significant achievements, including the introduction of the War Measures Act, which granted the federal government sweeping powers during wartime. This legislation would have lasting implications for civil liberties in Canada. Borden’s focus on national unity and his support for conscription during the war would create deep divisions within Canadian society, particularly between English and French Canadians. His swearing-in on October 10, 1911, represents a crucial turning point in Canadian history, laying the groundwork for the complex political dynamics that would follow in the decades to come.
The October Crisis Developments (1970)
On October 10, 1970, Canada was engulfed in the turmoil of the October Crisis, a period characterized by political instability and social unrest in Quebec. This crisis was primarily driven by the activities of the Front de libération du Québec (FLQ), a separatist group that sought to promote Quebec independence through violent means. The FLQ had conducted a series of bombings and kidnappings, leading to widespread fear and concern across the nation.
The most significant event of the October Crisis occurred just days before, on October 5, when the FLQ kidnapped British diplomat James Cross. The government’s response was swift and decisive, leading to a heightened state of alert. Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau faced mounting pressure to take action, resulting in the invocation of the War Measures Act on October 16. This legislation allowed for the suspension of civil liberties and the deployment of the military to restore order, marking the first time it had been used in peacetime.
The October Crisis had far-reaching implications for Canadian society and politics. It exposed the deep-seated divisions within Quebec and the rest of Canada regarding issues of nationalism, identity, and autonomy. Trudeau’s government faced criticism for its heavy-handed response, which many viewed as an infringement on civil rights. The crisis ultimately led to a national conversation about the future of Quebec within Canada, influencing subsequent political developments and shaping the discourse surrounding Canadian federalism.
In the aftermath of the crisis, the public’s perception of the FLQ and Quebec nationalism shifted significantly. While some viewed the group as terrorists, others sympathized with the underlying grievances that fueled their actions. The events of October 10, 1970, serve as a reminder of the complexities of Canadian identity and the ongoing struggle for balance between national unity and regional autonomy.
The Formation of the Parti Québécois (1968)
On October 10, 1968, the Parti Québécois (PQ) was officially formed, marking a significant milestone in Quebec’s political history. Founded by René Lévesque and a group of former Liberal Party members, the PQ aimed to promote Quebec nationalism and the pursuit of sovereignty for the province. This new political force emerged during a period of increasing demands for social, economic, and political reforms within Quebec, reflecting the aspirations of a growing number of Québécois who sought greater autonomy.
The formation of the PQ signaled a shift in Quebec’s political landscape, as it united various nationalist factions under a single banner. Lévesque’s vision for Quebec was one of social justice, economic independence, and cultural pride. The party quickly gained support among a populace disillusioned with the traditional political establishment, resonating with the aspirations of those seeking to redefine Quebec’s role within Canada. The PQ’s platform included calls for the nationalization of key industries and the establishment of a distinct identity for Quebecers.
The impact of the Parti Québécois on Canadian politics cannot be overstated. The party’s rise to prominence culminated in the 1976 provincial election when it won a majority government. This victory marked the first time a sovereignty-oriented party held power in Quebec. The PQ’s governance would lead to significant debates about Quebec’s place within Canada, culminating in the 1980 referendum on sovereignty-association, which ultimately failed. The formation of the Parti Québécois on October 10, 1968, represents a crucial development in the evolution of Quebec nationalism and its ongoing influence on Canadian politics.
The Birth of Louis Riel (1844)
On October 10, 1844, Louis Riel was born in the Red River Settlement, in what is now Manitoba. Riel would grow to become one of Canada’s most prominent and controversial historical figures, known for his role as a leader of the Métis people and as a central figure in the struggle for their rights and recognition. His early life was marked by the cultural and political tensions of the time, as the Métis faced increasing pressures from both British colonial authorities and expanding Canadian settlements.
Riel’s significance in Canadian history is largely attributed to his leadership during two major uprisings: the Red River Rebellion of 1869-70 and the North-West Rebellion of 1885. His involvement in the Red River Rebellion was particularly noteworthy, as he sought to defend the rights of the Métis and ensure their inclusion in the new Canadian Confederation. Riel’s actions during this period culminated in the establishment of a provisional government, which negotiated the terms of Manitoba’s entry into Canada, securing important rights for the Métis.
However, Riel’s later life was marked by tragedy and conflict. After the Red River Rebellion, he faced persecution and went into exile in the United States. He returned to Canada in 1885 to lead the North-West Rebellion, which ultimately ended in defeat and led to his trial and execution for treason. Riel’s birth on October 10, 1844, marks the beginning of a life that would deeply influence the narrative of Métis rights in Canada and spark ongoing discussions about identity, sovereignty, and reconciliation in Canadian society.
Conclusion
October 10 has proven to be a date of considerable significance in Canadian history, marked by events that reflect the country’s political evolution and cultural diversity. The swearing-in of Robert Borden as Prime Minister in 1911, the developments during the October Crisis in 1970, the formation of the Parti Québécois in 1968, and the birth of Louis Riel in 1844 all exemplify critical moments that have shaped Canada’s national identity.
These events highlight the complexities of Canadian society, illustrating the ongoing struggles for political representation, cultural recognition, and regional autonomy. As Canada continues to navigate its diverse heritage and aspirations, the historical moments observed on October 10 serve as reminders of the importance of dialogue, understanding, and collaboration in shaping the future of this vibrant nation.
0 notes
Text
What Happened on October 10 in History?

October 10 is a date marked by significant historical events that have shaped the course of nations and global affairs. From military advancements and international treaties to the establishment of important institutions and the celebration of independence, this date is rich in historical milestones. Each event reflects broader themes of national pride, international cooperation, and the ongoing struggles for independence and rights.
This article will explore six noteworthy events that occurred on October 10: the founding of the U.S. Naval Academy in 1845, Ho Chi Minh’s entry into Hanoi in 1954, Fijian independence in 1970, the enforcement of the Outer Space Treaty in 1967, the beginning of the Tokyo Summer Olympics in 1964, and the United Airlines Boeing 247 explosion in 1933. Each event played a crucial role in shaping political, cultural, and social landscapes across different regions of the world.
What Happened on October 10 in History?
Founding of the U.S. Naval Academy (1845)
On October 10, 1845, the United States Naval Academy was founded in Annapolis, Maryland, marking a significant development in the training of naval officers. The establishment of the academy came in response to the growing need for a formal education system to train naval personnel as the U.S. Navy expanded in size and capability. The academy’s mission was to develop competent officers who would lead the Navy and contribute to national security and maritime operations.
The Naval Academy began with a modest enrollment of 50 midshipmen and has since evolved into a prestigious institution. It provides a comprehensive education that combines academic instruction, professional training, and character development. Over the years, the academy has adapted its curriculum to meet the changing needs of the Navy and the demands of modern warfare. Today, it offers programs in various fields, including engineering, science, mathematics, and naval history.
The Naval Academy has played a crucial role in U.S. military history, producing numerous distinguished graduates who have gone on to serve in various capacities within the Navy and the broader military. Its alumni include naval leaders, politicians, and influential figures in various fields. The academy has been instrumental in shaping the U.S. Navy’s strategies and operations, contributing to the nation’s maritime prowess.
The founding of the U.S. Naval Academy not only reflects the United States’ commitment to maritime defense but also symbolizes the importance of education and training in maintaining national security. As the academy continues to evolve, it remains dedicated to fostering leadership, integrity, and a sense of duty among its midshipmen, ensuring that they are well-prepared to face the challenges of modern naval warfare.
Ho Chi Minh Enters Hanoi (1954)
On October 10, 1954, Ho Chi Minh triumphantly entered Hanoi, the capital of Vietnam, following the successful conclusion of the First Indochina War against French colonial forces. This event marked a pivotal moment in Vietnamese history and the beginning of a new era in the country’s struggle for independence. Ho Chi Minh’s entry into Hanoi symbolized the end of colonial rule and the establishment of a communist government in North Vietnam.
The First Indochina War had begun in 1946, as Vietnamese nationalists sought to free their country from French colonial rule. Ho Chi Minh, a key figure in the independence movement, rallied support from various factions, including communists and nationalists. The conflict intensified over the years, culminating in the decisive Battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954, where Vietnamese forces achieved a significant victory against the French. This victory led to the Geneva Accords, which temporarily divided Vietnam into North and South along the 17th parallel.
Ho Chi Minh’s return to Hanoi was celebrated by thousands of supporters who viewed him as a hero of the independence movement. His leadership and vision for a united Vietnam resonated with many citizens who sought an end to foreign domination and the establishment of a sovereign state. The events that unfolded after Ho Chi Minh’s entry into Hanoi set the stage for further conflict, including the Vietnam War, which would have profound implications for Vietnam and the world.
Ho Chi Minh’s legacy as a leader of the Vietnamese revolution remains significant. His commitment to independence and social justice has inspired generations of activists and leaders. The October 10 entry into Hanoi represents a moment of national pride and a turning point in the ongoing struggle for self-determination and independence.
Fijian Independence (1970)
On October 10, 1970, Fiji gained independence from British colonial rule, marking a significant milestone in the nation’s history. The path to independence was characterized by a series of negotiations and political developments that culminated in Fiji becoming a sovereign nation. The decision to grant independence to Fiji was part of a broader trend in the post-World War II era, where many colonies sought self-determination and freedom from colonial powers.
The journey toward independence began in the 1960s when Fijian leaders and representatives from various political parties engaged in discussions with the British government. The constitutional conferences led to the establishment of a parliamentary system and the promotion of local governance. The 1970 constitution laid the groundwork for Fiji’s political framework, ensuring representation for different ethnic groups within the country.
Independence was celebrated across Fiji with national festivities, including parades, cultural performances, and speeches by leaders. The event symbolized a new beginning for the nation, as Fijians embraced their sovereignty and cultural identity. Following independence, Fiji faced challenges related to ethnic relations, political stability, and economic development. The government aimed to promote unity among the diverse Fijian population, consisting primarily of indigenous Fijians and Indo-Fijians.
In the years following independence, Fiji navigated complex political dynamics, including coups and constitutional changes. Despite these challenges, Fiji has made significant strides in areas such as education, tourism, and economic development. The celebration of October 10 as Independence Day remains a source of national pride, commemorating the sacrifices and efforts made by Fijians in their pursuit of freedom.
Outer Space Treaty Enforced (1967)
On October 10, 1967, the Outer Space Treaty came into force, establishing a framework for international space law and governing the activities of countries in outer space. This treaty was a groundbreaking development in the context of the Cold War, as nations sought to explore and utilize outer space while ensuring peaceful cooperation. The treaty aimed to prevent the militarization of space and promote the exploration of celestial bodies for the benefit of all humanity.
The Outer Space Treaty was drafted during a time of intense competition in space exploration, particularly between the United States and the Soviet Union. The treaty emphasized that outer space should be used exclusively for peaceful purposes, prohibiting the placement of nuclear weapons or other weapons of mass destruction in orbit or on celestial bodies. It also established the principle that space exploration should benefit all countries and foster international cooperation.
The treaty has become a cornerstone of international space law, influencing subsequent agreements and discussions on space activities. It has been signed and ratified by over 100 countries, reflecting a shared commitment to responsible behavior in outer space. The Outer Space Treaty also established that nations bear responsibility for their activities in space, including those conducted by private entities and organizations.
The enforcement of the Outer Space Treaty has had lasting implications for the exploration and use of outer space. It has guided international cooperation in areas such as satellite communication, scientific research, and space exploration. As countries continue to expand their presence in space, the principles established by the treaty remain relevant in addressing challenges related to space debris, resource utilization, and potential conflicts.
The Outer Space Treaty symbolizes a collective effort to ensure that space exploration is conducted in a manner that promotes peace, cooperation, and the well-being of all humanity. Its enforcement on October 10, 1967, marked a significant step toward establishing norms and principles that govern the use of outer space.
The Tokyo Summer Olympics Begin (1964)
On October 10, 1964, the Tokyo Summer Olympics officially opened, marking the first time the Olympics were held in Asia. This event was significant not only for Japan but also for the international community, as it symbolized Japan’s post-World War II recovery and its re-entry into the global arena. The Tokyo Olympics were a celebration of peace, unity, and sportsmanship, showcasing the resilience of a nation that had undergone significant transformation.
The Tokyo Olympics featured over 4,700 athletes from 93 countries, competing in 19 different sports. The games included notable events such as judo, which made its Olympic debut, and volleyball, which gained popularity during the tournament. The event highlighted Japan’s dedication to hosting a successful Olympics, with impressive infrastructure and facilities built to accommodate the athletes and spectators.
The Tokyo Olympics were notable for their emphasis on international cooperation and goodwill. Amid the backdrop of the Cold War, the games provided an opportunity for countries to come together and compete in a spirit of camaraderie. The event featured memorable moments, including American athlete Cassius Clay (later known as Muhammad Ali) winning a gold medal in boxing, further cementing his status as a global sports icon.
The success of the Tokyo Olympics had a lasting impact on Japan, boosting tourism and fostering national pride. The event showcased Japan’s cultural heritage and technological advancements, paving the way for future international events. The Tokyo Olympics also set a precedent for the role of host nations in organizing and promoting the games, influencing how subsequent Olympic events would be conducted.
The opening of the Tokyo Summer Olympics on October 10, 1964, represents a turning point in Japan’s history, symbolizing the nation’s recovery, resilience, and commitment to international cooperation through sports.
United Airlines Boeing 247 Explosion (1933)
On October 10, 1933, a United Airlines Boeing 247 experienced a tragic explosion shortly after takeoff from Newark, New Jersey, resulting in the loss of all seven people on board. This incident marked a significant event in the history of aviation safety and raised concerns about the safety protocols and regulations governing commercial flights. The explosion occurred under mysterious circumstances, leading to an extensive investigation by federal authorities.
The Boeing 247 was a pioneering aircraft, known for its advanced design and performance capabilities. At the time, it was considered one of the safest and most efficient airplanes in commercial aviation. However, the tragic explosion raised questions about the safety of early commercial air travel and the potential risks associated with new technologies. Investigators sought to determine whether mechanical failure, sabotage, or other factors contributed to the explosion.
In the aftermath of the incident, regulatory agencies intensified their scrutiny of commercial aviation safety standards. The investigation revealed the need for improved maintenance procedures, inspections, and crew training to prevent similar tragedies. This event served as a catalyst for changes in aviation regulations, leading to the establishment of stricter safety protocols and oversight of commercial airlines.
The United Airlines Boeing 247 explosion was a sobering reminder of the risks associated with aviation and the importance of safety in the burgeoning industry. It contributed to a shift in public perception, prompting airlines to prioritize passenger safety and implement measures to enhance the overall flying experience. The legacy of this tragedy continues to influence aviation safety practices and regulations today.
The events surrounding the United Airlines Boeing 247 explosion on October 10, 1933, serve as a poignant reminder of the ongoing commitment to safety in the aviation industry. It underscores the necessity for continuous improvement and vigilance in ensuring the well-being of passengers and crew members.
Conclusion
October 10 has witnessed a multitude of significant events that have shaped the course of history. From the founding of important institutions like the U.S. Naval Academy to pivotal moments of independence, the enforcement of international treaties, and landmark sporting events, this date reflects humanity’s ongoing journey toward progress and unity. Each event carries its unique significance, contributing to a rich tapestry of historical milestones that continue to resonate in contemporary society.
These events illustrate the interconnectedness of nations and the shared values that transcend borders. They remind us of the struggles for independence, the pursuit of peace, and the commitment to safety and innovation in various fields. As we reflect on the history of October 10, we recognize the importance of learning from the past and striving for a future that embraces collaboration, understanding, and respect among nations.
0 notes