Corporate Cyber Security Trainer | Network Trainer | Cyber Security Consultant 🔒 🎓 CEH | CCNA | CompTIA N+ | CompTIA Security+ | EC-Council Certified Instructor | Ex-PwC | Kaspersky Certified Trainer | Mentor 📚
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
“The Silent Protectors: Signs of Ethical Hacking Excellence”
Signs of an Ethical Hacking Attempt:

Authorized Activity: Ethical hackers typically operate with proper authorization. They have documented permission to assess and test the security of a system or network. This authorization is a key distinction from unauthorized malicious hackers.
Transparency: Ethical hackers maintain transparency throughout their activities. They communicate their intentions to the organization or system owner, detailing the scope and objectives of their testing.
Legal Compliance: Ethical hackers adhere to legal and ethical standards. They respect the law and privacy regulations, ensuring that their actions do not violate any legal boundaries.
Rules of Engagement: Before initiating an ethical hacking attempt, a formal “Rules of Engagement” document is often established. This document outlines the scope of the testing, the allowed methodologies, and any restrictions in place.
No Malicious Intent: Ethical hackers have no malicious intent. Their primary goal is to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses to help organizations enhance their security. They do not seek to exploit or damage systems.
Professionalism: Ethical hackers approach their work with professionalism. They use their skills and knowledge to assess security systems and provide valuable insights to organizations.
Use of Known Techniques: Ethical hackers employ well-established and recognized techniques in their assessments. They do not engage in unconventional or harmful methods that could cause damage or disruption.
Reporting and Documentation: Ethical hackers meticulously document their findings, vulnerabilities, and the steps they took during the assessment. They provide comprehensive reports to the organization, detailing their discoveries and suggested remediation measures.
Respect for Privacy: Ethical hackers respect the privacy of individuals and the confidentiality of sensitive information. They take measures to ensure that their testing does not compromise privacy or expose confidential data
Cooperation with the Organization: Ethical hackers collaborate with the organization’s IT and security teams. They provide guidance and assistance in fixing identified vulnerabilities, ensuring that security measures are strengthened.
No Unauthorized Access: Ethical hackers do not engage in unauthorized access or data breaches. They adhere to the agreed-upon scope and do not venture beyond the boundaries of the assessment.
Immediate Reporting of Critical Findings: If ethical hackers uncover critical vulnerabilities or security weaknesses that could pose an immediate threat, they report them promptly to the organization for swift remediation.
Proactive Risk Mitigation: Ethical hackers not only identify vulnerabilities but also offer recommendations for mitigating risks. They actively contribute to the organization’s security strategy.
Clear Communication: Effective communication is a hallmark of ethical hacking. Ethical hackers communicate clearly with the organization’s stakeholders, ensuring that everyone understands the findings and the necessary actions.
Ethical Hacking Tools and Methods: Ethical hackers use industry-standard tools and methodologies. They do not employ malicious tools or engage in activities that could cause harm.

The signs of an ethical hacking attempt revolve around transparency, professionalism, legal compliance, and a focus on improving security. Ethical hackers, unlike malicious hackers, follow a code of ethics and work in collaboration with organizations to identify and rectify security weaknesses. Their actions are authorized, and they prioritize the betterment of security rather than causing harm. Organizations benefit from ethical hacking by proactively addressing vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
If you want to learn more about it, I highly recommend contacting ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, make sure to follow me on Quora and give it an upvote to encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking courses.
Thanks for spending your valuable time and upvotes here. Have a great day
0 notes
Text
“Don’t Get Hooked: Tips for Recognizing Phishing Emails”
Recognizing phishing emails with malicious links is essential to protect yourself from cyber threats. Phishing emails often attempt to deceive you into clicking on links that lead to fraudulent websites or initiate malware downloads. Here are some tips to help you identify and avoid such emails:

1.Check the Sender’s Email Address: Verify the sender’s email address. Phishing emails may use addresses that closely resemble legitimate ones but contain subtle misspellings or additional characters. Be cautious of any unfamiliar or suspicious sender.
2.Inspect the Greeting: Phishing emails often use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” instead of addressing you by name. Legitimate organizations usually personalize their emails with your name.
3.Examine the Content: Be wary of emails that create a sense of urgency, pressure you to take immediate action, or threaten negative consequences if you don’t comply. Phishing emails frequently use fear or urgency to manipulate recipients.
4.Hover Over Links: Hover your mouse pointer over any embedded links without actually clicking them. This action will reveal the true URL in the status bar of your email client. Check if the URL matches the legitimate website of the supposed sender.
5.Inspect the URL: Even if the displayed link seems legitimate, the actual URL may be different. Ensure that the domain matches the official website of the organization. Look for subtle misspellings or additional words within the URL.
6.Beware of Misspellings and Grammatical Errors: Phishing emails often contain spelling and grammatical mistakes. While legitimate organizations can make errors, a high frequency of mistakes should raise suspicion.

7.Check for Secure Connections (HTTPS): Legitimate websites use HTTPS to encrypt data. Verify that the website linked in the email begins with “https://” and displays a padlock icon in the address bar of your browser.
8.Avoid Downloading Suspicious Attachments: Don’t download attachments from unsolicited or suspicious emails. Malicious attachments can contain malware that can infect your system.
9.Verify Requests for Personal or Financial Information: Legitimate organizations usually do not request sensitive personal or financial information via email. If in doubt, contact the organization through official channels to confirm the request’s authenticity.
10.Use Email Filtering Software: Enable email filtering and spam detection in your email client or use dedicated email security solutions to automatically identify and quarantine phishing emails.
11.Trust Your Instincts: If something about an email seems off or too good to be true, trust your instincts. It’s better to be cautious and skeptical than to fall for a phishing scam.
12.Educate Yourself and Others: Stay informed about the latest phishing techniques and educate yourself and your colleagues or family members about the risks and how to recognize phishing attempts.
13.Watch for Email Spoofing: Some phishing emails may use techniques to make it appear as if they’re coming from a legitimate source. Look for inconsistencies between the sender’s display name and the actual email address.
14.Beware of Unsolicited Attachments: Be cautious when you receive unexpected attachments or files in an email, especially if they come from unknown sources. Malware can be hidden in these attachments.
15.Cross-Check Information: If you receive an email that requests action on your part, such as changing a password, making a payment, or updating account information, independently verify the request. Contact the organization through official channels or visit their website directly, rather than clicking on the provided link.
16.Use Email Authentication Technologies: Some email providers and organizations use email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. These technologies help verify the authenticity of emails. Legitimate senders often employ these security measures.
17.Be Wary of Pop-Up Forms: Some phishing emails might lead to a webpage that includes pop-up forms asking for personal information. Avoid entering sensitive data into such forms unless you are sure of their legitimacy.
If you want to learn more about it, I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, make sure to follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking.
Thanks for spending your valuable time . Have a great day
1 note
·
View note
Text
"Secure, Protect, Prevail: DDoS Prevention Essentials"
(DDoS) Attack in Hacking:

Implement DDoS Mitigation Services: Consider using a DDoS mitigation service, often provided by specialized companies. These services can detect and filter out malicious traffic, allowing legitimate traffic to reach your network or website.
2.Update and Patch Your Systems: Keep your operating systems, applications, and network equipment up to date. Regularly applying security patches can fix vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
3.Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs distribute your content across multiple geographically dispersed servers. This can help absorb DDoS traffic and ensure that your services remain available even during an attack.
4.Employ Rate Limiting and Access Controls: Implement rate limiting on your servers or firewalls to restrict the number of requests from a single source. Access controls can be used to block traffic from specific IP addresses or regions.
5.Network Load Balancing: Distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers using load balancers. This not only ensures high availability but can also distribute the load in the event of a DDoS attack.
6.Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken when a DDoS attack is detected. Ensure that your IT and security teams know their roles and responsibilities during an attack.

8. IP Reputation Lists: Use IP reputation lists, which are databases of known malicious IP addresses. These lists can be integrated into your security systems to block traffic from suspicious sources.
9. Use Web Application Firewalls (WAF): Deploy a Web Application Firewall to protect your web applications from application layer DDoS attacks. WAFs can identify and filter out malicious traffic and help prevent targeted application layer attacks.
10. Implement BGP Flowspec: BGP Flowspec (Border Gateway Protocol Flowspec) allows network administrators to create rules for filtering traffic at the network border based on specific criteria. This can be used to block DDoS traffic based on predefined rules.
11. Rate-Based Limiting: Implement rate-based limiting at the network or application level. This strategy ensures that traffic exceeding a specified rate is dropped, mitigating the impact of high-volume DDoS attacks.
12. Traffic Scrubbing Services: Consider subscribing to traffic scrubbing services offered by DDoS mitigation providers. These services reroute your traffic through their systems to filter out malicious traffic, leaving only legitimate traffic to reach your network.
13. Anycast DNS: Anycast DNS distributes DNS queries across multiple geographically distributed servers. This can help prevent DNS-based DDoS attacks by ensuring redundancy and resilience.
14. Cloud-Based Protection: Leverage cloud-based DDoS protection services. These services are hosted in the cloud and can handle DDoS attacks before they reach your network, offering a scalable and effective solution.
15.Use Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploy IDPS systems that can identify and block suspicious or malicious traffic. These systems can be configured to recognize DDoS attack patterns.
By implementing these best practices, you can fortify your defenses against DDoS attacks. It’s essential to adopt a multi-layered approach to DDoS prevention, combining technical solutions, policies, and incident response plans to ensure the highest level of protection for your online services. Remember that while no defense is foolproof, a proactive and comprehensive strategy can significantly reduce the risk and impact of DDoS attacks.
If you want to learn more about it, I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, make sure to follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking.
Thanks for spending your valuable time . Have a great day
0 notes
Text
“Ethical Hacking 101: A Comprehensive Guide to Technical Terms”

Vulnerability Assessment
Identifying Weaknesses
Vulnerability assessment is the process of systematically identifying and evaluating potential vulnerabilities within systems and networks. It involves scanning for known security weaknesses, misconfigurations, and areas where unauthorized access could occur. Ethical hackers use this approach to discover and prioritize security improvements.
Scanning for Vulnerabilities
One of the primary tools in an ethical hacker’s arsenal is the vulnerability scanner. These automated tools are designed to scan networks, systems, and applications to identify known vulnerabilities. By conducting these scans, ethical hackers can pinpoint weaknesses that may be targeted by malicious hackers.
Exploits: Uncovering Weaknesses
The Role of Exploits
An exploit is a piece of software or code that takes advantage of a specific vulnerability within a system, application, or network. Ethical hackers leverage exploits to demonstrate how security flaws can be exploited for unauthorized access or control. These powerful tools help in identifying and patching vulnerabilities before they can be maliciously exploited.
Exploit Payloads
The payload is the malicious part of an exploit that executes after the vulnerability is successfully exploited. It can be a piece of code or a script that performs actions such as gaining access, taking control, or stealing data from the target system. Ethical hackers use payloads to showcase the potential impact of an attack and to emphasize the need for robust security measures.
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
A zero-day vulnerability is a security flaw in software or hardware that is unknown to the vendor and, therefore, unpatched. These vulnerabilities are called “zero-day” because there are zero days of protection once the flaw becomes known. They are highly coveted by attackers as they offer the element of surprise.
The Quest for Unknown Flaws
Ethical hackers are constantly on the lookout for zero-day vulnerabilities. Finding and responsibly disclosing such vulnerabilities to vendors allows for prompt patching, thereby reducing the risk of exploitation. The discovery of zero-days exemplifies the proactive nature of ethical hacking.
Buffer Overflows: Breaking Boundaries
A buffer overflow is a type of software vulnerability where an application writes more data to a buffer (a temporary storage area) than it can hold. If an attacker can overflow a buffer with malicious data, they may be able to execute arbitrary code or disrupt the program’s normal operation. This classic vulnerability remains a focal point of ethical hacking.
Exploiting Buffer Overflows
Ethical hackers use buffer overflows as a teaching tool to demonstrate the potential risks to organizations. By simulating buffer overflow attacks, they can illustrate the importance of secure coding practices and the need for runtime protection mechanisms.
SQL Injection: A Database Gambit
SQL injection is an attack technique that involves manipulating a web application’s database by injecting malicious SQL queries through user inputs. In essence, attackers use this method to trick the application into executing unintended SQL code. The consequences can be severe, including unauthorized access, data theft, or even data corruption.
Injecting Malicious Queries

Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Scripted Intrusions
Understanding XSS Attacks
Cross-Site Scripting, commonly known as XSS, is an attack where an attacker injects malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. These scripts execute within the context of a user’s browser, potentially allowing the attacker to steal sensitive data, such as login credentials or session cookies.
The XSS Attack Variants
XSS attacks come in various forms, each with its unique characteristics. There are three primary types:
Stored XSS: In this scenario, the malicious script is permanently stored on the target server. It can impact multiple users and persist over time.
Reflected XSS: The malicious script is reflected off a web server, often through a link or email. It affects a user when they interact with the compromised link.
DOM-based XSS: This type involves manipulating the Document Object Model (DOM) of a web page. The attacker can modify the DOM to execute scripts when the page is loaded in the victim’s browser.
Ethical hackers use these different XSS variants to demonstrate the potential harm and emphasize the need for security measures against these attacks.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): Forging Actions
CSRF Attack Mechanics
Cross-Site Request Forgery, or CSRF, is an attack that tricks a user into performing an action on a website without their knowledge or consent. Attackers often craft a malicious request that is executed when an authenticated user visits a page with a specific payload. This attack is particularly dangerous when users are tricked into performing actions that they did not intend.
Preventing CSRF Attacks
Ethical hackers emphasize the importance of implementing anti-CSRF measures in web applications. This may include the use of anti-CSRF tokens or other security mechanisms that prevent unauthorized actions, even if a user is tricked into making a request.
Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Overwhelming the Target
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks aim to overwhelm a target, rendering it inaccessible to users. Attackers flood the target with an excessive volume of traffic or resource requests, causing service disruption. Ethical hackers simulate these attacks to showcase the impact they can have on an organization’s operations.
The Power of Distributed Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks take DoS attacks to the next level by involving multiple compromised computers, forming a botnet. Coordinated by an attacker, these bots inundate the target with a massive volume of traffic, making DDoS attacks even more challenging to mitigate. Ethical hackers use controlled DDoS simulations to evaluate an organization’s readiness to withstand such an assault.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
Intercepting and Tampering
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks occur when an attacker intercepts and potentially alters communications between two parties without their knowledge. This enables the attacker to eavesdrop, steal data, or inject malicious content into the communication. Ethical hackers demonstrate the techniques used in MitM attacks, emphasizing the need for secure communication protocols and encryption.
MitM Attack Scenarios
MitM attacks can manifest in various scenarios, including intercepting Wi-Fi communications, impersonating websites or services, or tampering with secure communications. Ethical hackers simulate these attacks to uncover vulnerabilities and help organizations safeguard against them.
Brute Force and Dictionary Attacks
The Perseverance of Brute Force
Brute force attacks involve trying all possible combinations of a password until the correct one is found. These attacks rely on the attacker’s determination and computational power. Ethical hackers use brute force attacks to illustrate the importance of strong and complex passwords.
Using Dictionaries to Crack Passwords
Dictionary attacks are a type of brute force attack where attackers use a predefined list of common words, phrases, or passwords to guess a target’s password. Ethical hackers showcase the effectiveness of these attacks, encouraging the use of password policies that resist dictionary attacks.
Rainbow Table Attacks
Unveiling Hashed Passwords
Rainbow table attacks are designed to crack hashed passwords. Instead of trying every possible password, attackers use precomputed tables to quickly discover the original password for a given hash. Ethical hackers demonstrate the risk of weak hashing algorithms and the importance of salting to protect against rainbow table attacks.
Penetration Testing (Pen Testing)
Simulating Cyberattacks
Penetration testing, often referred to as pen testing, is the practice of simulating cyberattacks to evaluate the security of a system, network, or application. Ethical hackers use this methodology to identify vulnerabilities, assess the effectiveness of security controls, and help organizations enhance their cybersecurity posture.
The Pen Testing Methodology
Penetration tests follow a structured methodology, including phases like reconnaissance, scanning, exploitation, post-exploitation, and reporting. Ethical hackers adhere to this methodology to ensure thorough and systematic testing.
Incident Response: Reacting to Breaches
Identifying Incidents
Incident response is the process of identifying, managing, and mitigating a cybersecurity incident or breach. Ethical hackers are often involved in this phase, using their expertise to analyze the incident’s nature and scope.
Mitigating the Impact
Once an incident is identified, ethical hackers play a vital role in mitigating its impact. They help organizations recover, collect evidence, and improve security measures to prevent future incidents.
The world of ethical hacking is in a constant state of evolution, with cyber threats continually adapting and advancing. Ethical hackers serve as the first line of defense, helping organizations stay ahead of attackers. By understanding the technical terms and concepts explored in this article, you gain insight into the tactics and techniques employed by ethical hackers to secure the digital landscape.
If you want to learn more about it, I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, make sure to follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking.
Thanks for spending your valuable time . Have a great day.
0 notes
Text
“Safeguarding Cyberspace: The Diverse Roles of Ethical Hackers”
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, ethical hacking has emerged as a crucial line of defence against the rising tide of cyber threats. Ethical hackers, often referred to as white-hat hackers, are individuals with specialized skills and knowledge that enable them to assess and fortify the security of digital systems, networks, and applications. These experts play diverse roles in safeguarding the digital world, ensuring that organizations and individuals can operate in a secure and protected environment. In this article, we will explore the various roles within ethical hacking, each contributing to the overarching mission of protecting the digital world.

1. Penetration Tester (Pen Tester) Penetration testers are akin to digital sleuths, actively attempting to breach an organization’s security defences. Their primary role is to simulate cyberattacks, identifying vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications. By exploiting these weaknesses, they offer organizations invaluable insights into their security gaps, enabling proactive mitigation.
2. Security Consultant Security consultants serve as trusted advisors to organizations. They assess existing security measures, identify vulnerabilities, and recommend tailored solutions. These professionals guide organizations in enhancing their cybersecurity posture, ensuring they stay ahead of evolving threats.
3. Security Analyst Security analysts act as guardians of an organization’s digital realm. They continuously monitor security infrastructure, analyze potential threats, and respond to security incidents. Their watchful eye and swift response are vital in maintaining a secure environment.
4. Security Engineer Security engineers are the architects of digital defence. They design, implement, and manage security systems, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols. Their work creates the protective barriers safeguarding an organization’s digital assets.
5. Security Researcher Security researchers are the explorers and innovators of cybersecurity. They actively seek new vulnerabilities, research emerging threats, and contribute to the development of security patches. Their work is instrumental in staying one step ahead of malicious actors.
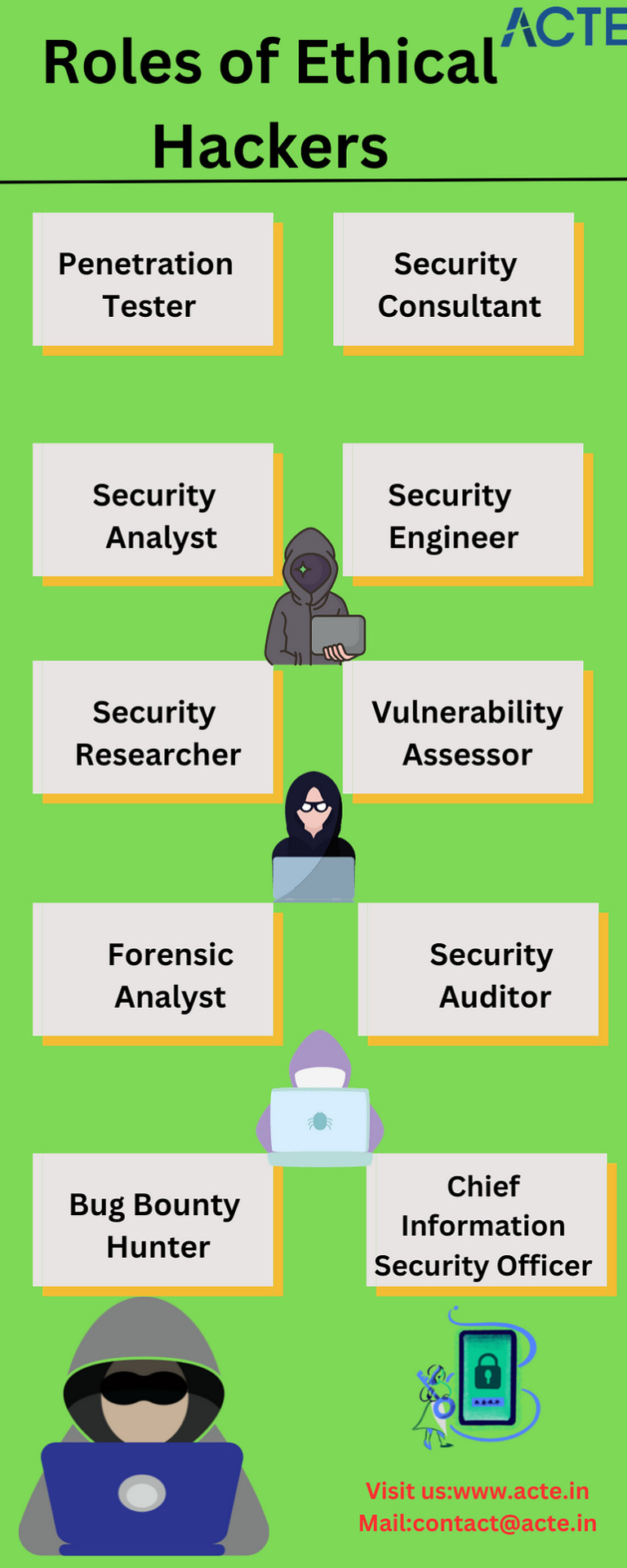
7. Forensic Analyst Forensic analysts are the digital detectives. When security incidents, data breaches, or cybercrimes occur, they gather, preserve, and analyze digital evidence. This crucial work helps determine the causes of security breaches and aids in legal proceedings.
8. Security Auditor Security auditors ensure organizations adhere to relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. Through audits and assessments, they verify compliance and recommend improvements to security measures.
9. Bug Bounty Hunter Bug bounty hunters are independent security researchers who identify vulnerabilities in software, websites, and applications. They report their findings to organizations in exchange for monetary rewards.
10. Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is a senior executive responsible for an organization’s overall cybersecurity strategy. They oversee security programs, manage security teams, and make critical decisions to protect the organization.
These roles collectively form a robust defence against cyber threats, ensuring the digital world remains secure. As technology evolves, ethical hacking roles adapt to address new challenges, making them indispensable in the ongoing battle to safeguard our digital frontiers.
If you want to learn more about it, I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, make sure to follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking.
Thanks for spending your valuable time and upvotes here. Have a great day.
0 notes
Text
“Ethical Hacking Toolbox: Essential Tools and Strategies”
Essential Tools for Ethical Hacking

Ethical hackers rely on a variety of tools and software to effectively identify and assess vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks. These tools are essential for conducting successful ethical hacking engagements. Let’s explore some of the key tools used in the field:
1. Nmap (Network Mapper) Nmap is a versatile open-source tool that serves as a network scanner and mapper. It excels in discovering open ports, services, and operating systems running on a network. Nmap’s extensive capabilities make it a fundamental tool for reconnaissance and vulnerability assessment.
2. Wireshark Wireshark is a widely-used network protocol analyzer, enabling ethical hackers to monitor and capture data on a network in real time. With its packet-sniffing capabilities, Wireshark helps in analyzing network traffic, identifying potential security issues, and understanding the communication between devices.
3. Metasploit Metasploit is a powerful penetration testing framework that empowers ethical hackers to identify, exploit, and validate vulnerabilities in target systems. It offers a vast collection of pre-built exploits, payloads, and auxiliary modules, making it an essential tool for both beginners and experienced professionals.

5. Aircrack-ng Aircrack-ng is a robust suite of tools for auditing and securing wireless networks. Ethical hackers can utilize Aircrack-ng to assess the security of Wi-Fi networks, perform packet capture and analysis, and test the strength of wireless encryption protocols. This tool is especially valuable for identifying weaknesses in wireless network configurations.
6. Nikto Nikto is a web server scanner that helps ethical hackers identify potential vulnerabilities in web servers and web applications. It scans for outdated software, security misconfigurations, and common issues, making it an essential tool for web security testing.
7. Hydra Hydra is a versatile password-cracking tool that ethical hackers use to perform brute-force and dictionary attacks on login systems. It supports various protocols and services, allowing testers to assess the strength of password security.
8. Ghidra Ghidra, developed by the National Security Agency (NSA), is a powerful open-source software reverse engineering tool. Ethical hackers use it to analyze and understand malware, decompile binaries, and inspect software for vulnerabilities.
9. John the Ripper John the Ripper is a popular password-cracking tool known for its speed and effectiveness. Ethical hackers rely on it to test the strength of password hashes and identify weak or easily guessable passwords.
10. Hashcat Hashcat is another widely used password-cracking tool that supports a variety of algorithms and attack modes. Ethical hackers can use Hashcat to recover forgotten passwords or audit the security of password hashes.
11. Snort Snort is an open-source intrusion detection system (IDS) that helps ethical hackers monitor network traffic for suspicious activities or known attack patterns. It aids in the early detection of potential security threats.
12. OpenVAS OpenVAS (Open Vulnerability Assessment System) is a full-featured vulnerability scanner that assists ethical hackers in identifying security weaknesses in networks and web applications. It offers comprehensive vulnerability assessment and reporting capabilities.
13. Cain and Abel Cain and Abel is a password recovery tool that ethical hackers use to recover passwords through various methods like dictionary attacks and cryptanalysis. It is particularly helpful for recovering forgotten passwords or assessing password security.
14. Sysinternals Suite The Sysinternals Suite, developed by Microsoft, is a collection of powerful system utilities. Ethical hackers use these tools to explore and troubleshoot Windows systems, as well as analyze system internals for potential security issues.
These essential tools empower ethical hackers to conduct thorough assessments of computer systems, networks, and applications, helping organizations strengthen their cybersecurity defences.
If you want to learn more about it, I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, make sure to follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking.
Thanks for spending your valuable time and upvotes here. Have a great day.
1 note
·
View note
Text
“From Novice to Expert: Your Journey Through Ethical Hacking Certifications”
Are you fascinated by hacking and cybersecurity, but want to put your skills to good use? You’re in the right place! Ethical hacking, penetration testing or white-hat hacking, is an exciting field focusing on securing computer systems and networks. You’ll need to explore the various certification courses available to get started. Here’s a breakdown of some popular options:

Certification Courses for Ethical Hacking
1. Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
The Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) certification is one of the most recognized and sought-after qualifications in the ethical hacking community. It covers various topics, such as information security, penetration testing, and various hacking tools and techniques. This certification is your golden ticket to understanding the mind of a hacker and using that knowledge to protect systems.
Why Choose CEH?
CEH provides comprehensive knowledge of hacking tools and techniques, understanding the hacker mindset, and developing countermeasures. It’s the perfect foundation for an ethical hacking career.
What You Will Learn
Under the CEH program, you’ll delve into topics like footprinting and reconnaissance, scanning networks, enumeration, system hacking, malware threats, and more. CEH certification opens doors to careers in penetration testing, security analysis, and network defence.
2. Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
CISSP is another valuable certification for ethical hackers. It focuses on security management and helps you understand the overall security landscape, including risk management, security policies, and access control. With CISSP, you’ll learn the essentials of securing organizations against cyber threats.
CISSP in a Nutshell
CISSP covers risk management, security policies, asset security, security architecture, and more. It’s ideal for those looking to take on leadership roles in security.
Reasons to Pursue CISSP
With domains including security and risk management, asset security, security architecture and engineering, communication and network security, identity and access management, security assessment and testing, security operations, and software development security, CISSP offers a comprehensive education in cybersecurity.
3. CompTIA Security+
If you’re new to the world of cybersecurity, CompTIA Security+ is an excellent starting point. This certification provides a broad foundation in security concepts and is suitable for beginners. It covers topics like network security, encryption, and risk management, making it ideal for anyone looking to enter the field.
Why Opt for CompTIA Security+?
CompTIA Security+ focuses on network security, threats and vulnerabilities, access control, identity management, and cryptography, making it ideal for entry-level professionals.
Key Content Areas
The certification covers essential areas, including network threats, cryptography, host security, security architecture, and operational security. CompTIA Security+ is widely recognized and provides a strong base for those new to cybersecurity.
4. Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
CISM is tailored for those who aspire to manage and oversee an organization’s information security. This certification delves into topics like governance, risk management, and incident response. With CISM, you’ll be well-equipped to create and manage robust security programs.
5. Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
If you’re looking for hands-on experience, the Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP) certification is your best bet. OSCP focuses on practical penetration testing skills, requiring you to exploit vulnerabilities and gain access to systems. It’s a favourite among aspiring ethical hackers who want to put their skills to the test.
An Overview of OSCP
OSCP requires individuals to exploit vulnerabilities, gain access to systems, and document their findings. It’s convenient and sought after by those who enjoy real-world challenges.
What Sets OSCP Apart?

6. Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
CISA is a certification aimed at individuals who want to focus on auditing, control, and assurance. It’s a great choice if you’re interested in evaluating an organization’s security controls and ensuring they align with business objectives.
What Does CISA Entail?
CISA is designed for professionals who aim to oversee and audit an organization’s information security.
Advantages of CISA
This certification equips you with the skills to assess an organization’s security, ensuring it aligns with business objectives and complies with industry standards.
Domain Coverage
CISA domains include auditing information systems, governance and management of IT, information systems acquisition, development, and implementation, and information systems operations and business resilience.
7. Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)
In an era where cloud computing is the norm, the CCSP certification has gained importance. It concentrates on securing cloud-based platforms and services. If you’re passionate about cloud security, this certification is a must.
8. Certified Hacking Forensics Investigator (CHFI)
CHFI is all about investigating cybercrimes and analyzing digital evidence. If you’re inclined towards the detective side of cybersecurity, this certification will teach you how to collect, preserve, and analyze electronic data in legal cases.
CHFI: A Closer Look
With CHFI, individuals learn to collect, preserve, and analyze electronic data in legal cases. This is vital for any organization facing cybercrimes or data breaches.
Why CHFI Matters
CHFI covers key areas such as computer forensics, mobile forensics, network forensics, and the legal and ethical principles required in the field. It is an essential certification for those interested in digital forensics.
Where to Begin?
The choice of certification depends on your current skill level, career goals, and interests. If you’re starting, CompTIA Security+ or CEH are excellent options. For management roles, consider CISSP, CISM, or CISA. And if hands-on hacking is your passion, OSCP or CHFI may be your best bet.
Remember that certification is just the first step. Real-world experience, continuous learning, and staying updated with the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity are equally important. Ethical hacking is a dynamic field, and staying ahead of the curve is key to success.
So, whether you’re a newbie or an experienced professional, there’s a certification course tailored to your needs. Get started, and embark on an exciting journey to become an ethical hacker, safeguarding the digital world from cyber threats.
If you want to learn more about it, I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, make sure to follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking.
Thanks for spending your valuable time and upvotes here. Have a great day.
0 notes
Text
“Uncover the Benefits of Being an Ethical Hacker”
If you’re considering a career as an ethical hacker, you’re making a wise choice. Ethical hacking, also known as white-hat hacking, is not only fascinating but also comes with a multitude of benefits. In this answer, I’ll walk you through some key advantages of being an ethical hacker.

The Benefits of Being an Ethical Hacker
1. Contributing to Cybersecurity
Protecting the Digital World: Ethical hackers play a crucial role in safeguarding our increasingly digital world. They actively identify vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, and applications, helping organizations patch these weaknesses before malicious hackers can exploit them.
2. Lucrative Career Opportunities
High Demand: The demand for ethical hackers has surged in recent years. As cyber threats grow in sophistication, companies are willing to pay top dollar for skilled professionals who can defend their digital assets. This translates into a highly rewarding career path.
Competitive Salaries: Ethical hackers often enjoy competitive salaries and generous benefits packages due to the scarcity of their expertise. It’s not uncommon for experienced ethical hackers to earn six-figure incomes.
3. Continuous Learning
Dynamic Field: Ethical hacking is a field that’s constantly evolving. As a result, ethical hackers are perpetually learning and staying updated on the latest cybersecurity trends and techniques. This keeps the job exciting and intellectually stimulating.
4. Legal Immunity
Protected by Law: Unlike malicious hackers, ethical hackers operate within the boundaries of the law. They are authorized by organizations to test and improve security, and they enjoy legal immunity as long as they follow ethical guidelines and obtain proper permissions.
5. Ethical Fulfillment

6. Problem-Solving
Constant Challenges: Ethical hacking involves solving complex puzzles and finding creative ways to break into systems. If you enjoy problem-solving and thinking outside the box, this profession offers ample opportunities to do so.
7. Versatile Career Paths
Diverse Opportunities: Ethical hacking opens doors to various career paths within the cybersecurity domain. You can specialize in areas like penetration testing, and vulnerability assessment, or become a cybersecurity consultant.
8. Global Impact
International Reach: Ethical hackers often work with multinational companies and governmental agencies. Your work can have a global impact, as cyber threats transcend borders.
9. Networking
Ethical hackers often collaborate with other cybersecurity professionals, both within their organization and in the broader cybersecurity community. This provides opportunities to build a strong professional network.
10. Legal Protection
Ethical hackers typically have legal protection when conducting security assessments with the consent of the target organization. This protection can provide peace of mind and reduce the risk of legal repercussions.
11. Financial Rewards
Experienced ethical hackers can command high salaries and may also receive bonuses for successfully identifying critical vulnerabilities.
12. Career Advancement
Ethical hacking can serve as a stepping stone to other cybersecurity roles, such as security analyst, security consultant, or security architect.
Being an ethical hacker offers a rewarding career that combines technical expertise, continuous learning, and a sense of moral responsibility. It’s a field that not only provides financial stability but also allows you to contribute significantly to the safety of the digital world.
So, if you have a knack for problem-solving and an interest in cybersecurity, consider pursuing a career as an ethical hacker. Your skills will always be in demand, and you’ll be part of a critical effort to protect our digital future.
If you want to learn more about it, I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, make sure to follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking.
Thanks for spending your valuable time, Have a great day.
1 note
·
View note
Text
“Stay Ahead of the Curve: Mastering the Types of Ethical Hacking”
Ethical hacking, also known as white-hat hacking, is a fascinating field that involves the use of hacking skills for legitimate and ethical purposes. In this answer, I’ll break down some of the key types of ethical hacking without delving into technical jargon.

1. White Hat Hackers
White hat hackers are ethical hackers who work within the boundaries of the law and are often employed by organizations to find and fix security vulnerabilities. They conduct authorized penetration tests to strengthen security.
2. Black Box Testing
In black box testing, ethical hackers have no prior knowledge of the system they are testing. This approach mimics how an external attacker would operate. It helps identify vulnerabilities from an outsider’s perspective.
3. Gray Box Testing
Grey box testing combines elements of both black box and white box testing. Ethical hackers have limited knowledge of the system, typically with partial access or information. This approach allows them to simulate attacks with some insider knowledge.
4. Red Team vs. Blue Team
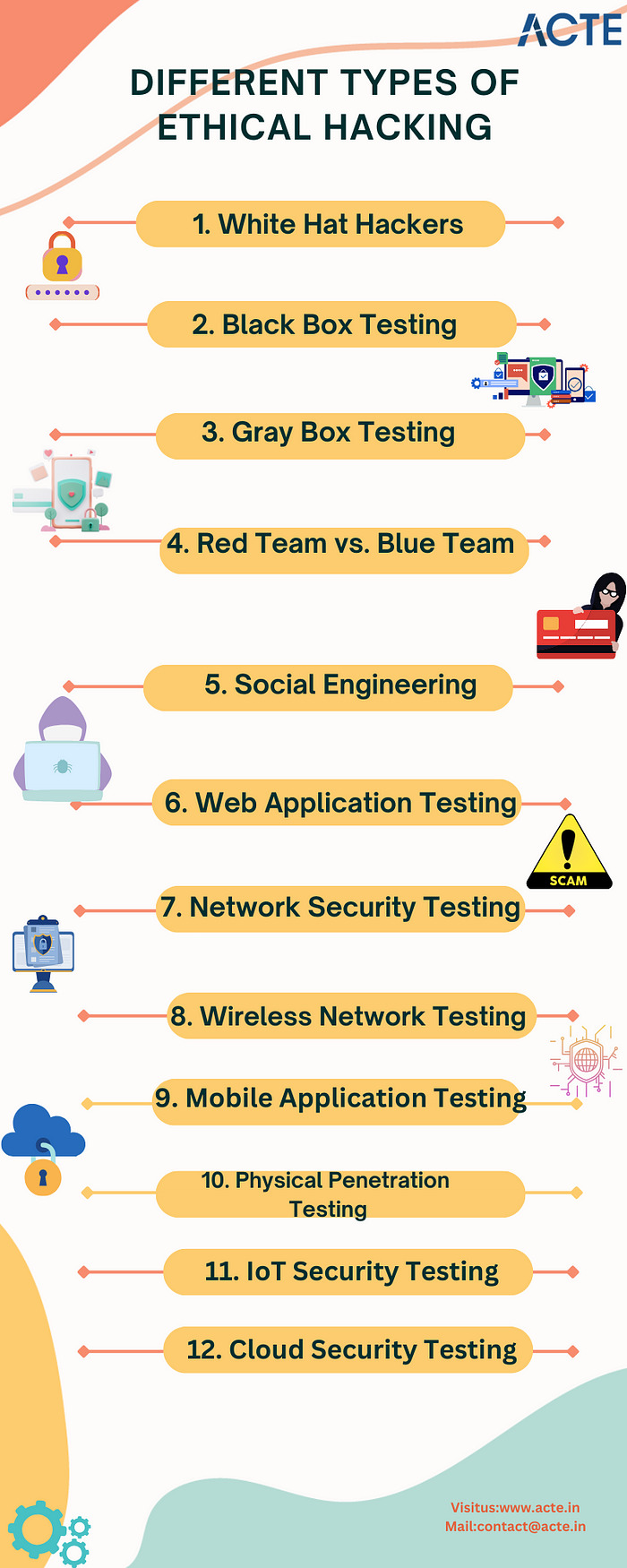
5. Social Engineering
Social engineering is a type of ethical hacking that focuses on manipulating people rather than exploiting technical vulnerabilities. It includes tactics like phishing, pretexting, and baiting to gain access to sensitive information.
6. Web Application Testing
Ethical hackers specializing in web application testing focus on identifying vulnerabilities in web applications. They look for weaknesses in websites, web services, and APIs to prevent common web-based attacks.
7. Network Security Testing
Network security testing involves assessing the security of a network infrastructure. Ethical hackers look for weaknesses in firewalls, routers, switches, and other network components to ensure data remains protected.
8. Wireless Network Testing
Wireless network ethical hackers specialize in identifying vulnerabilities in Wi-Fi networks. They assess encryption protocols, authentication methods, and access control to prevent unauthorized access.
9. Mobile Application Testing
Mobile application ethical hackers concentrate on the security of mobile apps. They search for vulnerabilities in iOS, Android, and other mobile platforms to protect user data and privacy.
10. Physical Penetration Testing
Physical penetration testers assess the physical security of an organization’s premises. They check for vulnerabilities such as unauthorized access, theft, and tampering with physical assets.
11. IoT Security Testing
With the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, ethical hackers specializing in IoT security testing focus on identifying vulnerabilities in smart devices and connected systems, ensuring they cannot be exploited.
12. Cloud Security Testing
Cloud security testers assess the security of cloud-based services and platforms. They look for misconfigurations, data exposure risks, and other cloud-specific vulnerabilities.
These are some of the primary types of ethical hacking, each tailored to address specific aspects of cybersecurity. Ethical hackers play a crucial role in safeguarding digital assets and protecting against evolving cyber threats.
In a world where cyber threats are constant, ethical hacking is not just a career but a necessity for safeguarding our digital lives.
Remember that consistent practice, working on real-world projects, and seeking help from online communities and resources like blogs, tutorials, and forums can significantly accelerate your learning process. Don’t rush; focus on understanding the concepts thoroughly, as a strong foundation is key to becoming an expert in ethical hacking.
If you want to learn more about Ethical Hacking, I highly recommend contacting ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking.
Thanks for spending your valuable time. Have a great day.
1 note
·
View note
Text
"Exploring the Expansive Scope of Ethical Hacking"
Understanding the Scope of Ethical Hacking
Ethical hacking, often referred to as "white hat hacking," is a fascinating and crucial field in the realm of cybersecurity. It involves professionals, known as ethical hackers or penetration testers, who use their expertise to identify and address vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, and applications. In this Quora answer, I'll provide you with insights into the scope of ethical hacking, without diving too deep into technical jargon.
What is Ethical Hacking?

Ethical hacking is a legal and authorized practice of attempting to exploit computer systems for the purpose of making them more secure. Unlike malicious hackers who have harmful intentions, ethical hackers work to find and fix vulnerabilities before the bad actors can exploit them.
Scope of Ethical Hacking
1. Security Assessment
Ethical hackers are hired to perform comprehensive security assessments of organizations' digital assets. This involves evaluating the security of networks, websites, databases, and applications. By simulating cyberattacks, they identify weaknesses and suggest improvements to strengthen the security posture.
2. Penetration Testing
Penetration testing is a crucial aspect of ethical hacking. Here, experts use various tools and techniques to simulate real-world attacks on an organization's systems. They assess how well the security measures hold up and provide recommendations for enhancing security.
3. Vulnerability Assessment
Ethical hackers conduct vulnerability assessments to discover and categorize vulnerabilities within systems. They prioritize these vulnerabilities based on their potential impact and help organizations mitigate them effectively.
4. Social Engineering Testing
Social engineering is a tactic used by hackers to manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information. Ethical hackers conduct social engineering tests to assess the vulnerability of an organization's staff to such attacks. This helps in raising awareness and implementing security awareness training.
5. Web Application Testing
With the proliferation of web applications, securing them has become paramount. Ethical hackers evaluate web applications for vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and more, ensuring that these applications don't become entry points for attackers.
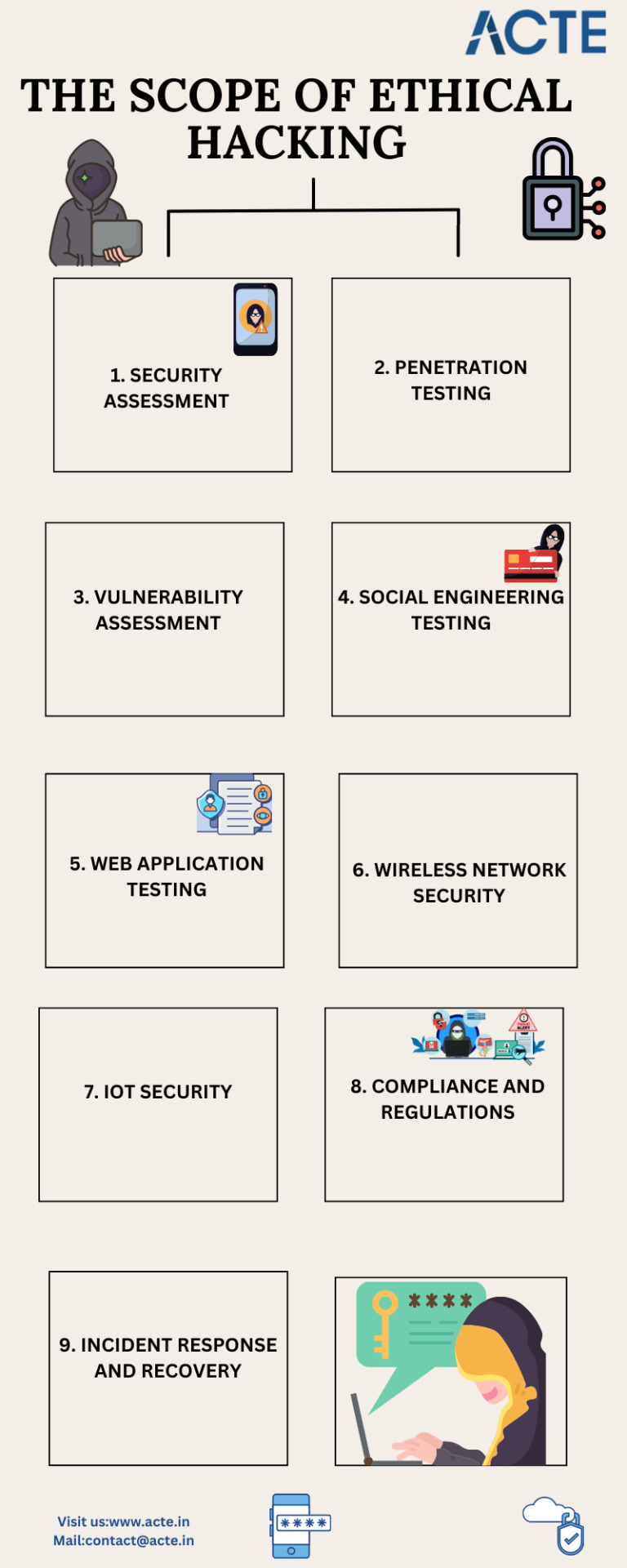
6. Wireless Network Security
Wireless networks are susceptible to various attacks. Ethical hackers assess the security of Wi-Fi networks, identifying weak encryption, unauthorized access, and other vulnerabilities.
7. IoT Security
As the Internet of Things (IoT) devices become ubiquitous, ethical hackers also focus on evaluating the security of IoT devices and networks to prevent potential breaches.
8. Compliance and Regulations
Ethical hackers assist organizations in ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards. This is crucial for businesses handling sensitive data.
9. Incident Response and Recovery
In the unfortunate event of a cyber incident, ethical hackers play a crucial role in identifying the source, containing the breach, and helping with recovery efforts.
The scope of ethical hacking is vast and ever-evolving. It's a vital component of modern cybersecurity, helping organizations stay one step ahead of malicious actors. Ethical hackers are the frontline defenders of digital security, and their expertise is in high demand.
In a world where cyber threats are constant, ethical hacking is not just a career but a necessity for safeguarding our digital lives.
Remember that consistent practice, working on real-world projects, and seeking help from online communities and resources like blogs, tutorials, and forums can significantly accelerate your learning process. Don’t rush; focus on understanding the concepts thoroughly, as a strong foundation is key to becoming an expert in ethical hacking If you want to learn more about Ethical Hacking, I highly recommend contacting ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline. If you feel that my response has been helpful, follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking. Thanks for spending your valuable time. Have a great day.
1 note
·
View note
Text
"From Zero to Hero: Mastering Ethical Hacking from Scratch"
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, ethical hacking has emerged as an invaluable skillset. Ethical hackers, often referred to as "white hat" hackers, play a pivotal role in safeguarding digital ecosystems from malicious cyber threats. Whether you're an aspiring cyber security enthusiast or a professional looking to expand your horizons, mastering ethical hacking from scratch can be an exhilarating journey. In this comprehensive guide, we will navigate the exciting world of ethical hacking, from its fundamentals to advanced techniques, ensuring you embark on the path from zero to hero.
1. Introduction to Ethical Hacking
Defining Ethical Hacking: Introducing the concept and purpose of ethical hacking.
Importance in the Digital Age: Highlighting the significance of ethical hacking in today's digital world.
The Role of Ethical Hackers: Describing the responsibilities and contributions of ethical hackers.

2. The Fundamentals
Computer Networking Basics:
Explaining the importance of networking knowledge for ethical hackers.
Understanding TCP/IP: Briefly touching on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP).
Subnetting and CIDR: Mentioning subnetting and Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR).
Operating Systems: Discussing the role of operating systems in ethical hacking.
Windows, Linux, and macOS: Mentioning common operating systems and their vulnerabilities.
System Vulnerabilities: Briefly touching on common vulnerabilities found in operating systems.
3. Coding and Scripting
Importance of Programming: Explaining the significance of programming skills in ethical hacking.
Python, Ruby, and JavaScript: Mentioning essential programming languages.
Writing Exploits: Describing the use of programming to create exploits.
Scripting for Automation: Highlighting scripting for automating tasks and tool creation.
Creating Custom Tools: Mentioning the development of custom tools through scripting.
4. Setting Up a Lab Environment
Virtualization Technologies: Discussing tools like VirtualBox and VMware for creating safe testing environments.
Creating Isolated Networks: Explaining the value of isolated networks.
Practicing Safely: Emphasizing the importance of safe practice.
Real-world Simulations: Briefly touching on the use of real-world scenarios for practice.
5. Security Concepts
Cryptography Demystified: Introducing the role of cryptography in security.
Encryption and Decryption: Mentioning the basics of encryption and decryption.
Cryptographic Algorithms: Touching on various cryptographic algorithms.
Web Security Essentials: Highlighting common web vulnerabilities.
Common Vulnerabilities: Mentioning examples like SQL injection and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS).
Malware Analysis: Explaining the significance of understanding malware.
Understanding Malicious Software: Briefly touching on types and behavior of malware.
6. Reconnaissance and Information Gathering
Passive Reconnaissance: Explaining the covert information gathering techniques.
Gathering Information Covertly: Mentioning tactics for passive information collection.
Active Reconnaissance: Describing scanning tools like Nmap.
Scanning for Open Ports: Explaining the role of scanning in identifying vulnerabilities.
This provides a concise overview of the topics covered in the outline, setting the stage for a detailed exploration in the article.
7. Vulnerability Assessment
The Need for Assessments: Highlighting the importance of vulnerability assessments in ethical hacking.
Tools like Nessus and OpenVAS: Mentioning specific tools used for vulnerability scanning.
Scanning for Weaknesses: Explaining the process of scanning systems for vulnerabilities.
8. Exploitation Techniques
Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Discussing the critical aspect of understanding system vulnerabilities.
Maintaining Access: Explaining the need to maintain access to compromised systems without detection.
9. The Art of Social Engineering
Psychology Behind Social Engineering: Introducing the psychological aspect of manipulating individuals.
Manipulating Individuals: Mentioning techniques like phishing, pretexting, and baiting used in social engineering.
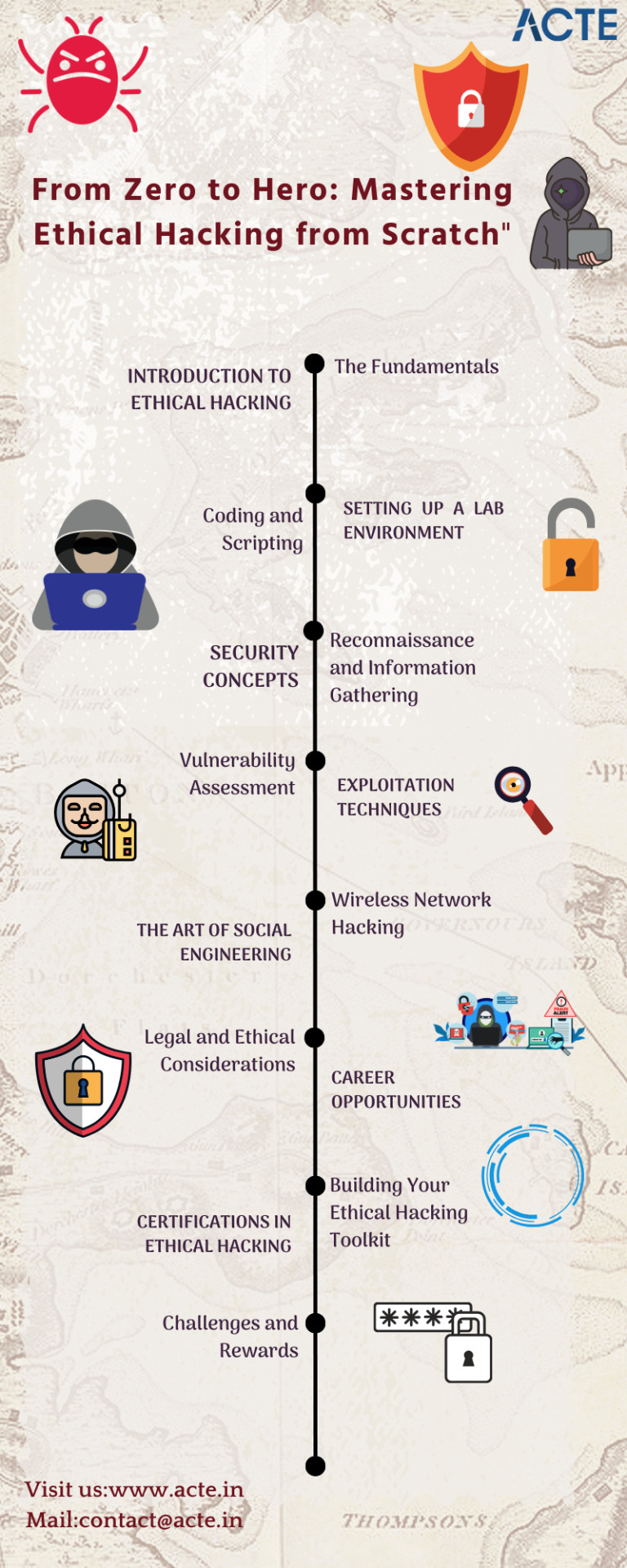
10. Wireless Network Hacking
Wireless Security Challenges: Describing the unique challenges in securing wireless networks.
Cracking Wi-Fi Passwords: Highlighting the skill of cracking Wi-Fi passwords.
Tools and Techniques: Briefly mentioning tools like Wireshark and Aircrack-ng used in wireless analysis.
11. Legal and Ethical Considerations
Obtaining Legal Consent: Emphasizing the importance of legal permission in ethical hacking.
Respecting Confidentiality: Discussing the need to handle sensitive data with care.
The Importance of Documentation: Highlighting the value of keeping detailed records during assessments.
12. Career Opportunities
Ethical Hacking as a Profession: Describing ethical hacking as a rewarding career path.
Lucrative Career Path: Mentioning the competitive salaries and growth opportunities.
Demand for Ethical Hackers: Discussing the increasing demand for ethical hackers in the cybersecurity field.
13. Certifications in Ethical Hacking
CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker): Introducing the CEH certification and its significance.
CompTIA Security+: Mentioning the CompTIA Security+ certification as a valuable credential.
CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional): Discussing the advanced CISSP certification.
14. Building Your Ethical Hacking Toolkit
Recommended Tools: Listing essential tools like Metasploit and Wireshark.
Staying Updated with New Tools: Emphasizing the need for continuous learning to keep up with evolving cybersecurity tools.
15. Challenges and Rewards
The Thrill of Ethical Hacking: Explaining the excitement and challenges of the ethical hacking journey.
Ethical Hacking as a Noble Pursuit: Highlighting the noble aspect of protecting digital ecosystems.
Contributions to a Safer Digital World: Discussing the impact of ethical hackers on digital security.
Remember that your skills are not only for personal gain but also for the greater good. Ethical hackers play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and security of our digital world. So, are you ready to take the plunge into the exciting realm of ethical hacking? With dedication, continuous learning, and ethical principles, you can truly go from zero to hero in the world of Ethical Hacking.
If you want to learn more about Ethical Hacking, I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, make sure to follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking.
Thanks for spending your valuable time. Have a great day
#ethicalhacking#hacking#scam alert#phishing#blocking#scam#scammers#internet safety#scam likely#newt scamander
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Double-Edged Sword: Ethical Hacking for Good and Evil

In the digital age, where technology intertwines with every facet of our lives, the role of ethical hacking has become increasingly prominent. These digital vigilantes, the "white hats" of the cyber world, use their knowledge and skills to protect us from the looming threats of cybercrime. However, this intriguing field of cyber security also has a dark side, where some individuals employ the same skills for nefarious purposes. This essay explores the dual nature of ethical hacking, shedding light on how it can be both a force for good and a tool for evil.
The Guardians of the Digital Realm: Ethical Hackers for Good
Ethical hackers, often referred to as security experts or penetration testers, play a critical role in our increasingly interconnected world. They are the guardians of the digital realm, defending us against malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, and software. Here's how ethical hackers contribute to the greater good:
1.Identifying Vulnerabilities:
Ethical hackers use their skills to identify security weaknesses in systems and applications, helping organizations patch these vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by cybercriminals.
2.Preventing Data Breaches:
By proactively searching for weaknesses, ethical hackers assist in preventing data breaches and safeguarding sensitive information.
3.Securing Critical Infrastructure:
They work with government agencies and private companies to secure critical infrastructure, such as power grids, financial systems, and healthcare networks, from cyber threats.
4.Staying Ahead of Cybercriminals:
Ethical hackers keep pace with evolving cyber threats, ensuring that security measures are up-to-date and effective.
5.Raising Cybersecurity Awareness:
They contribute to raising awareness about cybersecurity best practices and the importance of digital hygiene.

The Dark Side: Ethical Hacking Gone Rogue
While ethical hacking is a force for good in the right hands, it can turn into a dangerous weapon when wielded by those with malicious intent. Here are some examples of how ethical hacking can be perverted for nefarious purposes:
1.Criminal Hacking: Some individuals use their hacking skills to steal sensitive information, commit financial fraud, or launch cyberattacks for financial gain.
2.Espionage and Surveillance: State-sponsored hackers may engage in cyber espionage, infiltrating the systems of other nations or organizations to steal classified information.
3.Black Hat Hackers: Those who once wore the white hat can switch sides, becoming black hat hackers who exploit vulnerabilities and cause harm.
4.Disrupting Critical Infrastructure: Hackers with malicious intent may target critical infrastructure, causing chaos, disruption, and potential danger to the public.
5.Cyber Warfare: Nations may employ ethical hacking techniques in acts of cyber warfare, targeting enemy states' infrastructure and networks.
Ethical hacking, as a double-edged sword, highlights the need for a delicate balance between security and privacy, transparency and secrecy, and protection and freedom. Governments and organizations must invest in cybersecurity measures, while also respecting individuals' privacy and civil liberties.
So ethical hacking is a powerful tool with the potential for both good and evil. The responsibility falls upon individuals, organizations, and governments to ensure that ethical hacking remains a force for good, protecting our digital realm from harm. Through responsible use and regulation of these skills, we can harness the positive potential of ethical hacking while minimizing the risks associated with its dark side.
Please keep in mind that the Ethical Hacking takes in the future may vary depending on market dynamics, customer demands, and technological advancements. To get the most up-to-date information on Ethical Hacking future technologies and strategies.
I recommend to visit the ACTE Institute training programs covering all aspects of Ethical Hacking, providing valuable support for individuals aspiring to become Ethical Hacker.
I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Institution because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline. Take things step by step and consider enrolling in a course if you’re interested.
For More Update Just Follow My Account
1 note
·
View note
Text
“Unlocking the Treasure Trove of Ethical Hacking: The World of Bug Bounty Programs”
In the ever-evolving landscape of ethical hacking, organizations are increasingly turning to ethical hackers to help identify and fix vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. This collaborative approach to security is facilitated by bug bounty programs, which allow skilled individuals to earn rewards for responsibly disclosing security flaws. In this blog post, we'll delve into the world of bug bounty programs, exploring what they are, how they work, and how ethical hackers can earn while contributing to a safer digital world .
What Is a Bug Bounty Program?

Now, you must be curious to know about these Bug Bounty Programs. A Bug Bounty Program is a kind of open deal between the companies and the developers (especially white hat hackers) to find certain bugs, security exploits, and other vulnerabilities in the organization’s system or product. In case, if an individual can find these bugs in their system, he is expected to report it to the company on behalf of which the company rewards the person with appreciation and a certain amount dedicated to the particular bugs.
According to Wikipedia:
“A bug bounty program is a deal offered by many websites, organizations, and software developers by which individuals can receive recognition and compensation for reporting bugs, especially those pertaining to security exploits and vulnerabilities”.
Benefit of Bug Bounty
For Organizations:
Enhanced Security: Bug bounty programs help organizations discover and address vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can exploit them, thereby strengthening their overall security posture.
Access to Diverse Talent: Bug bounty programs tap into a global pool of skilled ethical hackers, providing a wide range of perspectives and expertise in cybersecurity.
Cost-Effective Security Testing: Organizations only pay for results ��� they reward hackers for valid bug reports, making it a cost-effective way to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
Continuous Testing: Bug bounty programs enable continuous security testing, allowing organizations to stay proactive in identifying and mitigating emerging threats.
Positive Public Relations: Embracing bug bounties demonstrates a commitment to security and responsible disclosure, which can enhance an organization's reputation and trust among customers and stakeholders.
Legal Protections: Many bug bounty programs offer legal safe harbor to ethical hackers, protecting them from legal actions as long as they adhere to program rules.
For Ethical Hackers (Bug Hunters):
Monetary Rewards: Bug hunters can earn cash rewards for their findings, which can be a significant source of income, especially for skilled hackers.
Recognition and Reputation: Successful bug hunters gain recognition within the cybersecurity community, which can lead to career opportunities and increased demand for their expertise.
Skill Development: Bug hunting offers a hands-on way to enhance technical skills, learn about real-world vulnerabilities, and stay updated on the latest security trends.
Flexible Work: Ethical hackers can participate in bug bounty programs on their own terms, choosing when and where to hunt for vulnerabilities.
Contributing to Security: Ethical hackers play a vital role in making the digital world safer by identifying and helping to fix vulnerabilities.
Networking: Bug hunters have the opportunity to connect with other professionals in the cybersecurity field and build valuable relationships.
Top Bug Bounty Platforms
Bug bounty platforms act as intermediaries between organizations seeking to improve their cybersecurity and ethical hackers looking to identify vulnerabilities. Here are some of the top bug bounty platforms
HackerOne
HackerOne is one of the most well-known and widely used bug bounty platforms. It connects organizations with a community of skilled hackers and offers a range of features to streamline the bug bounty process.
Bugcrowd
Bugcrowd provides a platform for crowdsourced security testing, allowing organizations to tap into a diverse pool of security researchers to find and fix vulnerabilities.
Synack
Synack combines human intelligence with machine learning to provide a scalable and effective approach to cybersecurity testing. They focus on a managed crowd of skilled ethical hackers.
Open Bug Bounty
Open Bug Bounty takes a unique approach by offering a public bug bounty platform where ethical hackers can report vulnerabilities even if the organization doesn't have a bug bounty program in place.
Cobalt
Cobalt offers a Penetration Testing as a Service (PTaaS) platform, connecting organizations with a global community of certified ethical hackers to find and remediate vulnerabilities.
YesWeHack
YesWeHack is a European bug bounty platform that connects organizations with a community of over 21,000 ethical hackers to enhance cybersecurity.
Intigriti
Intigriti is a European bug bounty platform that focuses on providing continuous security testing to help organizations identify vulnerabilities and improve their security posture.

BugHunt
BugHunt offers a bug bounty platform that caters to organizations of all sizes, connecting them with a community of ethical hackers to identify security issues.
Detectify
Detectify offers automated web application security scanning and monitoring services, with the ability to report vulnerabilities to organizations
Zerocopter
Zerocopter offers a platform that combines continuous security testing, vulnerability management, and coordinated disclosure to help organizations secure their digital assets.
You will find a lot of bug bounty platforms differing from each other in some points but still doing the same target which is helping corporates to secure their software assets and using the skills of security researchers in an ethical way. Sometimes bug bounty becomes very competitive with many people applying to the same bug on the same site or same program. That's why most programs start private to limit the number of testers and then become public when they believe most of the vulnerabilities have been patched which is not always the real case.
Please keep in mind that the Ethical Hacking takes in the future may vary depending on market dynamics, customer demands, and technological advancements. To get the most up-to-date information on Ethical Hacking future technologies and strategies.
I recommend to visit the ACTE Institute training programs covering all aspects of Ethical Hacking, providing valuable support for individuals aspiring to become Ethical Hacker.
I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Institution because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline. Take things step by step and consider enrolling in a course if you’re interested.
For More Update Just Follow My Account
2 notes
·
View notes