https://www.tvgsc.sg/A hiatal hernia, characterized by the protrusion of a segment of the stomach into the thoracic cavity via the diaphragm, poses a complex array of difficulties. In addition to inducing distress, hiatal hernias frequently manifest in conjunction with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), thereby exacerbating their practical implications.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
The Role of Colonoscopy in Colorectal Cancer Prevention
Colorectal cancer often develops without noticeable symptoms in its early stages, making regular screenings a critical component of preventive healthcare. Prevention through screenings not only contributes to individual well-being but also plays a crucial role in public health by reducing the overall burden of colorectal cancer and associated healthcare costs. Emphasising the importance of regular colonoscopy screenings fosters a proactive approach to health, empowering individuals to take control of their well-being and contribute to the prevention of colorectal cancer.
Let us learn more about colonoscopy and its role in preventing colorectal cancer in this article.
Understanding Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is a medical procedure that involves the examination of the colon and rectum using a long, flexible tube with a camera at its end called a colonoscope. It is a common diagnostic and preventive screening tool for various colorectal conditions, including colorectal cancer.
This procedure enables the detection of abnormalities such as polyps, tumours, inflammation, or other signs of colorectal diseases. Colonoscopies are not only diagnostic but also therapeutic, as they allow for the removal of precancerous polyps and the biopsy of suspicious tissues. The ability to both identify and address potential issues makes colonoscopies a crucial tool in colorectal health management and cancer prevention.
Who Should Consider a Colonoscopy?
Colonoscopies are recommended for individuals who fall into certain risk categories or meet specific age and health criteria. The following groups of people should consider a colonoscopy:
Age and Health Criteria
Generally, individuals at average risk for colorectal cancer are advised to start regular screenings, including colonoscopies, at the age of 50. Screening may begin earlier for those with a family history of colorectal cancer or certain hereditary conditions.
Family History
People with a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child) diagnosed with colorectal cancer or certain types of polyps may need to start screening earlier and undergo more frequent colonoscopies.
Personal Medical History
Individuals with a personal history of colorectal cancer, polyps, or certain inflammatory conditions of the colon may require more frequent screenings.
Prior Abnormal Findings
If a previous colonoscopy revealed polyps or abnormalities, the doctor may recommend more frequent screenings.
Genetic Factors
Individuals with known genetic conditions that increase the risk of colorectal cancer, such as Lynch syndrome or familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), may need earlier and more frequent screenings.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate screening schedule based on individual health history and risk factors. Screening recommendations may vary for different individuals, and personalised advice ensures the most effective preventive care.
Preparing for a Colonoscopy
Ensuring a successful and accurate colonoscopy involves careful preparation. This vital screening procedure for colorectal cancer requires specific dietary adjustments and lifestyle modifications in the days leading up to the examination.
Dietary and Lifestyle Adjustments
Preparing for a colonoscopy involves specific dietary and lifestyle modifications to ensure a clear view of the colon during the procedure. Patients are typically advised to follow a low-fibre diet in the days leading up to the colonoscopy. This may include avoiding whole grains, nuts, seeds, and certain fruits and vegetables. Clear liquids, such as broth, gelatin, and clear juices, are often recommended to stay adequately hydrated.
Bowel Preparation Process
Effective bowel preparation is crucial for the success of a colonoscopy. Patients are given a bowel prep kit containing laxatives and clear instructions. The process usually involves drinking a prescribed solution to induce bowel movements, ensuring the colon is thoroughly cleansed. Adequate hydration during this process is essential. Following the provided guidelines meticulously enhances the chances of a successful and accurate examination.
Adhering to the recommended dietary adjustments and following the bowel preparation instructions helps create optimal conditions for the healthcare provider to thoroughly examine the colon and detect any abnormalities. Individuals must communicate openly with their healthcare team and address any concerns or questions they may have regarding the preparation process.
The Colonoscopy Procedure
Let's delve into the step-by-step process of a colonoscopy, its importance in maintaining colon health, and what individuals can expect during this essential medical examination.
Step-by-Step Overview
A colonoscopy is a comprehensive examination of the colon and rectum to detect abnormalities, particularly precancerous or cancerous growths. The procedure involves the use of a long, flexible tube with a camera (colonoscope) that is carefully inserted through the rectum and guided through the entire colon. The camera transmits real-time images to a monitor, enabling the healthcare provider to examine the colon lining thoroughly.
Sedation Options and Patient Experience
Patients may receive sedation to ensure comfort during the procedure. Sedation options can range from mild sedation, where the patient remains conscious but relaxed, to deeper sedation or general anaesthesia, where the patient is unaware of the procedure. The choice of sedation depends on individual preferences, medical conditions, and the complexity of the examination. Most patients experience minimal discomfort, if any, during the procedure.
Colonoscopy Results and Follow-Up
After undergoing a colonoscopy, the next critical phase involves interpreting the results and establishing a follow-up plan.
Interpreting Findings
The colonoscopy results provide crucial information about the condition of the colon. Normal results indicate a healthy colon lining, while abnormalities may include polyps, inflammation, or other lesions. If polyps are discovered, they are often removed during the procedure for further analysis.
Subsequent Screenings and Recommendations
Based on the findings, the healthcare provider will discuss the next steps. If no abnormalities are detected, the patient receives recommendations for future screenings, typically every 10 years for individuals with normal risk. In cases where polyps are removed, more frequent screenings may be advised. Understanding the results and following up with recommended screenings are vital in maintaining colorectal health and preventing the development of colorectal cancer.
Benefits of Early Detection
Early detection through colonoscopy is a vital component in the proactive prevention of colorectal cancer. This screening method offers a twofold advantage in reducing the risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Firstly, it allows healthcare professionals to identify and remove precancerous polyps during the procedure. Since colorectal cancer often arises from these benign growths, their timely removal significantly decreases the likelihood of malignant transformation.
Secondly, the comprehensive nature of a colonoscopy enables healthcare providers to detect any existing colorectal cancer at an early, more treatable stage. By identifying cancerous lesions in their initial phases, medical interventions, including surgery or other targeted treatments, can be promptly initiated, leading to more favourable outcomes.
Emphasising the benefits of early detection underscores the crucial role that colonoscopies play in maintaining colorectal health, contributing to both preventive measures and timely intervention for those at risk. Regular screenings, therefore, are integral to the comprehensive strategy for maintaining colorectal health.
Summing It Up
Colorectal cancer is often asymptomatic in its early stages. Thus, protecting colorectal health through regular screenings is a proactive and crucial step in maintaining overall well-being.
Screenings, particularly colonoscopies, enable the identification and removal of precancerous polyps, reducing the risk of colorectal cancer development. Embracing routine screenings is an empowering choice, providing an opportunity for timely interventions that can significantly impact health outcomes. Individuals actively contribute to their long-term health by prioritising colorectal screenings, fostering early detection, and prevention, and promoting a proactive approach to colorectal well-being.
#Colonoscopy Singapore#Colonoscopy Screening Singapore#Colonoscopy Screening Procedure#Colonoscopy Procedure Singapore#Colorectal Cancer Screening Singapore
0 notes
Text
Colonoscopy Screening Guidelines: Who Should Get Tested in Singapore?

Colonoscopy screening plays a crucial role in the early detection and prevention of colon cancer, one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in Singapore. This procedure can identify precancerous polyps or early-stage cancer by examining the colon and rectum for abnormalities, allowing for timely intervention and improved outcomes.
Understanding Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a medical procedure that allows a doctor to visually examine the inside of the colon and rectum using a long, flexible tube with a camera and light at the end, called a colonoscope. It is an important screening tool for the early detection of colorectal cancer and other gastrointestinal conditions. During a colonoscopy, the doctor can identify and remove potentially precancerous growths called polyps, as well as detect early signs of cancer.
Early detection through colonoscopy screening also plays a vital role in improving survival rates. When colon cancer is detected at an early stage, before it has spread to other parts of the body, it significantly increases the chances of effective treatment and improves patient outcomes. Additionally, colonoscopy can help identify individuals with a high risk of developing colon cancer due to genetic factors or a family history of the disease.
Who Should Get Tested?
Colonoscopy screening is recommended for individuals who fall into certain risk categories. These include:
Age
One of the primary factors considered in colonoscopy screening guidelines is age. Generally, individuals are advised to undergo their first colonoscopy at the age of 50. This initial screening helps detect any abnormalities or precancerous polyps that may be present in the colon. Subsequent screenings are then recommended at regular intervals based on the initial findings and the individual's overall health.
It's important to note that in some cases, individuals may need to undergo colonoscopy screenings earlier than the recommended age. This is often based on their medical history, family history of colorectal cancer, or the presence of certain risk factors.
Family History
Family history plays a significant role in determining the risk of developing colorectal cancer. Individuals with a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child) who has been diagnosed with colorectal cancer or precancerous polyps may be at an increased risk. In such cases, healthcare professionals may recommend earlier and more frequent colonoscopy screenings to detect and address any potential issues at an earlier stage.
Personal Health History
Personal health history, including a history of inflammatory bowel diseases (such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis), may also influence the colonoscopy screening guidelines. Individuals with a history of these conditions may be at a higher risk of developing colorectal cancer and may require more frequent screenings.
Presence of Symptoms
In some cases, individuals may experience symptoms such as changes in bowel habits, persistent abdominal pain, or unexplained weight loss. These symptoms may prompt healthcare professionals to recommend a colonoscopy, regardless of age, as a diagnostic tool to investigate the underlying cause of these issues.
Preparing for a Colonoscopy
Before undergoing a colonoscopy, proper preparation is essential to ensure accurate and effective results. Patients are usually provided with detailed instructions on how to cleanse their colon before the procedure. This typically involves dietary restrictions and bowel preparation to clear the colon of any stool that may interfere with the examination.
What to Expect During a Colonoscopy
During a colonoscopy, the patient is usually given sedation to ensure comfort throughout the procedure. The doctor will insert a flexible tube with a tiny camera into the rectum and guide it through the colon, examining the lining for any abnormalities. If any polyps or suspicious areas are found, the doctor may remove them or take tissue samples for further analysis. The procedure typically takes around 30 minutes to an hour, and most patients can return home the same day.
Post-Colonoscopy Care
After the procedure, patients are monitored until the sedation wears off, and they are deemed fit to leave the medical facility. It's common for patients to experience some bloating or mild discomfort, which usually subsides shortly after the procedure. The results of the colonoscopy are then shared with the patient, along with any necessary recommendations for follow-up screenings or additional medical interventions.
Benefits of Early Detection through Colonoscopy Screening
By identifying and removing precancerous polyps or detecting early-stage cancer, colonoscopy can significantly reduce the risk of developing advanced colorectal cancer. Therefore, this results in improved treatment outcomes and quality of life for individuals and their families.
Additionally, colonoscopy screening can help identify individuals with a high risk of developing colon cancer due to genetic factors or a family history of the disease. For these individuals, regular screenings can provide peace of mind and allow for early intervention if any abnormalities are detected. By taking proactive steps to protect their health, individuals can potentially prevent the development of colon cancer altogether or catch it at its earliest and most treatable stage.
Colonoscopy screening is a vital tool in the prevention and early detection of colon cancer in Singapore. Following the recommended guidelines for screenings can help identify precancerous polyps or early-stage cancer, enabling timely intervention and improved outcomes.
By understanding who should get tested and the importance of early detection, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and potentially save lives. Consult your doctor to discuss the possibility of undergoing a colonoscopy screening. Remember, early detection is the key to fighting colon cancer and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
#colonoscopy singapore#colonoscopy services#colonoscopy services singapore#colonoscopy doctor singapore#colonoscopy screening singapore#colonoscopy screening procedure#colonoscopy procedure singapore#colonoscopy clinic singapore#colorectal cancer screening singapore#colonoscopy centre singapore
0 notes
Text
Hiatal Hernia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

What is Hiatal Hernia?
A hiatal hernia manifests when the upper portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm, the muscular partition between the chest and abdomen. This occurrence can trigger discomfort and digestive issues, as stomach acid may reflux into the esophagus, leading to symptoms such as heartburn.
Root Causes
While the precise cause of many hiatal hernia repair remains elusive, several factors may contribute, including:
Changes related to Age: The natural weakening of the diaphragm muscle with age increases the susceptibility to hernia development.
Injury: Trauma or accidents causing damage to the diaphragm can create weak spots conducive to hernia formation.
Congenital Factors: Some individuals are born with an unusually large opening in the diaphragm, elevating the risk of hiatal hernia.
Lifestyle Factors: Activities exerting pressure on the diaphragm, such as coughing, vomiting, heavy lifting, and straining during bowel movements, can contribute.
Smoking: Smoking is a major factor since it weakens various muscles in the body, including the diaphragm.
Types of Hiatal Hernia
Two primary types of hiatal hernias exist:
Sliding Hiatal Hernia: Accounting for about 95% of cases, the stomach's part connecting to the esophagus slides up into the chest cavity through the weakened diaphragmatic area.
Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia: Less common but potentially more severe, in this type, the stomach pushes up beside the esophagus through the diaphragm, increasing the risk of complications like strangulation.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms vary based on hernia size, location, and individual factors. Common symptoms of hiatal hernia may include:
Heartburn - A burning sensation in the chest and throat due to stomach acid reflux.
Regurgitation - Food or liquid coming back into the mouth.
Difficulty Swallowing - Challenges in swallowing food or liquids.
Chest Pain - Discomfort in the chest or upper abdomen.
Early Satiation - Feeling full quickly after consuming small amounts.
Belching - Frequent and louder than normal burping.
Hiccups - Persistent and difficult-to-control hiccups.
While not everyone with a hiatal hernia experiences symptoms, prompt medical attention is crucial if you experience any of these symptoms in major degrees.
How is it Diagnosed?
Physicians may use various tests for hiatal hernia diagnosis, including:
Barium Swallow - Involves drinking a chalky liquid visible on X-rays.
Endoscopy - Inserts a thin tube with a camera down the throat to examine the esophagus and stomach.
Esophageal Manometry - Measures pressure and muscle contractions in the esophagus.
Treatments for Hiatal Hernia
Treatment depends on symptom severity, hernia size, and location. Lifestyle changes, medications, and surgery are viable options.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting certain habits can alleviate symptoms and prevent hernia progression:
Dietary Adjustments - Avoiding trigger foods, reducing caffeine and alcohol, and consuming smaller, more frequent meals.
Maintaining Healthy Weight - Excess weight exacerbates symptoms by adding pressure on the diaphragm.
Elevating Bed Head - Prevents nighttime reflux by discouraging stomach acid backup.
Smoking Cessation - Quitting smoking helps fortify the weakened diaphragm and reduces esophageal irritation.
Through Medications
Medications, oral and intravenous, also play a role in relieving symptoms. These include:
Antacids - Neutralize stomach acid, offering quick relief from heartburn.
H2 Blockers - Reduce stomach acid production.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) - Potent medications effectively controlling acid reflux symptoms.
Hernia Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary, with options such as:
Nissen Fundoplication - Commonly recommended, this surgery wraps the stomach's top around the lower esophagus, reinforcing the valve and preventing acid reflux.
Open Hernia Surgery - Reserved for larger or more complex hernias, involving a larger abdominal incision.
Endoluminal Fundoplication (ELF) - A less invasive procedure performed through the mouth using a thin tube with a camera and tiny instruments.
Recovery and Prognosis
Recovery duration varies based on surgery type. Aftercare involves adhering to medical advice, maintaining a balanced diet, ample rest, pain management, and regular follow-up appointments.
The prognosis for hiatal hernia patients is generally positive. Proper TVGSC hernia treatment often leads to significant symptom relief and improved quality of life. However, recurrences can happen, necessitating additional treatment.
For any concerns about hiatal hernias, it is recommended to consult with a hernia surgeon for accurate diagnosis and treatment plans tailored to a patient’s specific needs.
#hernia repair Singapore#hernia operation#Singapore hernia operation#hernia surgery#hernia surgery Singapore#Singapore hernia treatment#hernia surgeon#hernia surgeon Singapore#hernia repair surgery#hernia repair surgery Singapore
1 note
·
View note
Text
Hernia Repair in Singapore 2024
TVGSC hernia management. Regular health checkups play a crucial role in swiftly identifying and addressing hernias at their initial stages, allowing for targeted interventions before complications arise. Timely detection not only alleviates discomfort but also enhances the quality of life by enabling less invasive treatments.

#hernia repair Singapore#hernia operation#Singapore hernia operation#hernia surgery#hernia surgery Singapore#Singapore hernia treatment#hernia surgeon#hernia surgeon Singapore#hernia repair surgery#hernia repair surgery Singapore
0 notes
Text
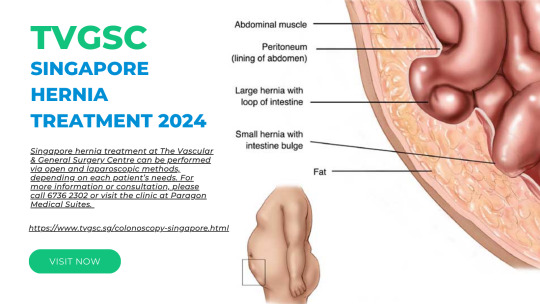
TVGSC Singapore Hernia Treatment 2024
Singapore hernia treatment at The Vascular & General Surgery Centre can be performed via open and laparoscopic methods, depending on each patient’s needs. For more information or consultation, please call 6736 2302 or visit the clinic at Paragon Medical Suites.
0 notes
Text
Hiatal Hernia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options 2024
The muscular partition between the thorax and abdomen, known as the diaphragm, is traversed by the upper portion of the stomach. a hiatal hernia develops. As gastric acid may reflux into the esophagus, this may result in digestive issues and discomfort, including heartburn and other symptoms.

0 notes
Text
Hiatal Hernia Repair Comprehensive Guide 2024
A hiatal hernia, characterized by the protrusion of a segment of the stomach into the thoracic cavity via the diaphragm, poses a complex array of difficulties. In addition to inducing distress, hiatal hernias frequently manifest in conjunction with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), thereby exacerbating their practical implications.

0 notes
Text
Importance of Colonoscopies: A Preventive Approach
A colonoscopy detects inflammation, bleeding, and polyps in the rectum and large intestine. It is the most common colon cancer screening in Singapore and detects IBD and diverticular disease. Before a colonoscopy, the intestines must be empty. To be more specific, your doctor will specify things to eat and avoid before therapy.

0 notes
Text
hernia repair Singapore
A hiatal hernia, characterized by the protrusion of a segment of the stomach into the thoracic cavity via the diaphragm, poses a complex array of difficulties. In addition to inducing distress, hiatal hernias frequently manifest in conjunction with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), thereby exacerbating their practical implications.
hernia #herniarepair #herniaoperation #herniaoperation #herniaoperation #herniasurgery
1 note
·
View note