Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Non-woven geotextiles are an important category of geosynthetics used across a wide range of infrastructure and construction applications. This guide provides a deep dive into what non-wovens are, their types, key properties, manufacturing processes, installation methods, advantages, applications, and more.

Introduction to Non-Woven Geotextiles
Geotextiles refer to permeable, polymeric textile materials used in contact with soil or rock in civil engineering applications. They can be woven or non-woven.
Non-woven geotextiles are made by bonding polymeric fibers together through processes like needle punching, heat bonding or resin bonding. The random arrangement of fibres produces a strong, porous and flexible material.
Geotextiles that are non-woven are better than those that are woven. They are better at filtering, draining, and cushioning, and are easier to install. In addition, they are more budget-friendly. These characteristics make non-wovens ideal for many functions like filtration, drainage, separation, and reinforcement.
Needle Punched Non-Woven Geotextiles
Needle-punched non-wovens are a major type of non-woven geotextile produced by mechanically orienting and entangling fibers. Hundreds of fine needles repeatedly penetrate a fibre web to tangle the fibres into a strong, porous and stable fabric.
Compared to other non-wovens, needle-punched variants have high permeability and drainage capacity along with good puncture resistance. This makes them ideal for filtration and drainage applications.
Types of Needle-Punched Non-Woven Geotextiles
Needle-punched non-wovens can be categorized into three main types based on weight and fiber thickness:
Lightweight Needle Punched Wovens
Made from fine fibres and low fiber weights between 20-100 gsm. Mainly used in applications that do not require high strength.
Medium Weight Needle Punched Non Wovens
Heavier fibers and medium basis weights of 100-250 gsm. Provides moderate strength for functions like separation.
Heavyweight Needle Punched Non-Wovens
Very coarse, thick fibres and high basis weights above 250 gsm. Imparts maximum strength for reinforcement uses.
Selections depend on the target function. Non-woven fabrics can be categorized into lightweight and heavyweight variants.
Key Functions and Applications of Non-Woven Geotextiles
Non-woven geotextiles perform various functions that make them indispensable for major infrastructure and construction projects:
Filtration Applications
The porous structure allows water to pass through while blocking soil particles. This filtration ability is useful in:
Roadway drainage systems
Retaining walls
Landfill drainage
Water treatment plants

Drainage Applications
Nonwovens have high water flow rates in the principal direction. This makes them excellent for drainage purposes like:
Landfill drainage layers
Sports field drainage
Retaining wall and slope drainage
Separation Applications
The fabric physically separates dissimilar materials. Key applications include:
Roadway base and subbase separation
Railroad bed separation
Foundations separation
https://www.aakarperiwal.com/blogs/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/geotextile-500x500-3.webp
Reinforcement Applications
Non-wovens provide reinforcement for additional strength when wrapped around soil. Uses include:
Embankments over soft soils
Retaining walls with stacked blocks
Slopes requiring improved bearing capacity
Erosion Control Applications
The fabric acts as a permeable layer to protect against wind and water erosion while allowing water passage. Some uses are:
Covering slopes along railways and highways
Coastal embankments erosion control
Riverbanks and canal protection
Transportation Applications
Within road construction, non-wovens assist with filtration, separation, drainage and stabilization. Common applications:
Separation between sub-base and subgrade
Filtration in edge drains alongside pavements
Soil stabilization for improved load-bearing
Construction Applications
Foundations and walls drainage
Vapor barriers in concrete slabs
Flooring reinforcement and crack prevention

This demonstrates the versatility of non-woven geotextiles across diverse functions in C&I projects. Their adaptive properties drive widespread adoption.
Key Properties of Non-Woven Geotextiles
Non-woven geotextiles exhibit unique properties derived from their material composition, manufacturing method and overall structure:
Raw Materials
Most non-wovens use polypropylene as the raw material which is cost-effective and provides required properties. High-end variants use polyester or a polypropylene-polyester blend.
Basis Weight
Basis weight is the mass per unit area measured in g/m2. Heavier basis weights produce stronger fabrics with higher puncture resistance. Typical range is from 20 g/m2 to 300 g/m2.
Thickness
Thickness depends on fiber density and varies from 1mm to 15mm. Affects permeability, cushioning ability and separation effectiveness.
Hydraulic Properties
Non-wovens have high water permeability (normal to the plane) and adequate transmissivity. Allows swift drainage while blocking soil passage.
Mechanical Properties
Tensile strength, tear strength, puncture resistance and burst strength are key mechanical properties. Non woven selection depends on the required load capacity.
Endurance Properties
Long-term resistance against environmental exposure, chemicals, microbes and mechanical stresses comes under endurance properties. Requires proper polymer choice.
These characteristics directly impact the effectiveness and lifespan of the non-woven geotextile for its intended function.
Overview of Manufacturing Processes
Non-woven geotextile production involves specialized processes to achieve the desired fiber arrangement and properties:
Web Formation
The first step is creating a uniform web of fibres laid out in overlapping, random orientations using air, mechanical or wet-laid techniques.
Web Bonding
The fiber web undergoes thermal, chemical or mechanical bonding. This interlocks the fibres to impart strength, stability and thickness.
Finishing
Additional treatments enhance properties - for instance, calendering uses heated rollers to achieve smoothness. Fabric edges are trimmed to create rolls.
Testing and Inspection
Extensive testing under certified labs evaluates parameters like strength, permeability, opening size etc. This ensures compliance with specifications.
Keeping manufacturing consistent and monitoring variabilities is vital for non-woven quality assurance. Automation allows scalable production with minimal defects.
Design and Installation Factors for Non-Woven Geotextiles
Proper design, handling and deployment of non-wovens ensures successful project outcomes:

Site Preparation
The installation site must be graded uniformly and cleared of debris/rocks to avoid damage. Burial depth is determined. Subsurface drainage may be added.
Installation Techniques
Non wovens can be unrolled on site and placed loose or tense. Joints are sewn or bonded. Additional layers can be installed to enhance functioning. Fixings like sandbags or pegs may be used.
Seams and Overlaps
Adjoining rolls are overlapped for continuity. End overlaps depend on joint strength. Edges can be sewn, welded, glued or kept loose. Key consideration for soil retention uses.
Design Factors
Careful specifications of geotextile properties like strength, permeability, and opening size based on engineering requirements and testing. Survivability and performance lifetime also key.
Following recommended practices for non-woven deployment optimizes field performance and prevents failures.
Key Benefits and Advantages of Using Non-Woven Geotextiles
Non-woven geotextiles offer numerous benefits that make them advantageous over traditional materials:
Cost-Effectiveness
Made from polypropylene, non-wovens are an affordable alternative to CMP pipe drains or graded aggregates for drainage. Limited overlap joints also reduce the quantity required.
Rapid Drainage Performance
The high porosity provides greater flow capacity compared to sand filters or gravel layers. Useful in applications like retaining walls.
Good Puncture and Burst Resistance
The entangled fibrous structure provides better resistance against punctures during installation compared to woven geotextiles.
Ease of Installation
Flexible, lightweight non-wovens are simpler to install in field conditions compared to rigid materials. No special equipment needed.
Enhanced Properties
Specialized manufacturing processes like calendering and bonding create improved non-wovens with the right balance of filtration, separation, cushioning and strength.
Wider Widths
The ability to produce up to 5m wide rolls compared to just 1m for wovens leads to faster deployment with fewer joints.
These advantages have positioned non-wovens as a material of choice for major construction activities and geotechnical engineering applications.
Applications and Case Studies Demonstrating Non-Woven Geotextiles in Action
Non-woven geotextiles have delivered value across many real-world projects:
Landfill Construction - Needle-punched non-wovens used in leachate collection systems increased design life while reducing clogging through superior filtration compared to gravel layers.
Retaining Wall Drainage - Heat-bonded non-wovens used as wall wraps maintained water drainage and prevented soil washout, keeping 100km of critical rail walls safely stabilized through extreme weather.
Riverbank Protection - Durable non-woven wraps applied on embankments prevented erosion along highly flood-prone rivers through monsoons. Filtered runoff while retaining soil stability.
Roadway Improvement - Calendered non-wovens beneath motorway overpasses provided vital reinforcement to stabilize compressible soil while facilitating drainage and preventing pumping.
Coastal Reinforcement - Wide-width non-wovens encasing sandy coastal cliffs added shear strength and tensile reinforcement. Protected against collapse from rising sea levels and storm surges.
This demonstrates how non-wovens of different compositions can be adapted for specialized needs in infrastructure projects where performance and longevity are critical.
Industry Trends and Ongoing Innovations in Non-Woven Geotextiles
Several interesting trends, developments and innovations are shaping the non-woven geotextiles sector:
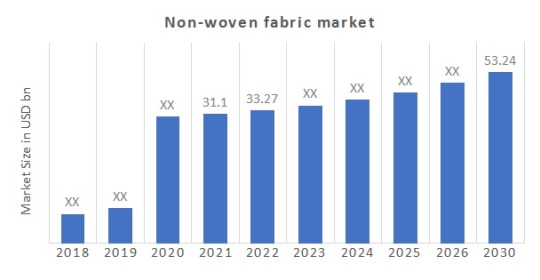
High Growth Potential - The non-wovens market is projected to grow steadily at 6% CAGR driven by major public infrastructure investments and demand from emerging economies.
Raw Material Advances - Enhanced polymers like high-density polypropylene and high-modulus polyester are creating improved non-wovens with greater functionality.
Manufacturing Improvements - Process enhancements and new techniques are allowing more fine-tuned manipulation of fiber properties during production.
Multifunctional Products - Combining non-wovens with drainage nets or reinforcing grids creates single products that provide filtration, separation and reinforcement together.
Application R&D - Ongoing research into novel uses for non-wovens like landfill caps, nuclear waste containment and offshore geotextiles to drive adoption across new domains.
Conclusion
Non-woven geotextiles have become an indispensable resource for civil engineering and infrastructure applications where their high permeability, strength, and versatility can enhance project outcomes and lifespan.
As materials and manufacturing continue evolving, non-wovens are poised to meet more specialized demands. With a thorough understanding of their capabilities, civil engineers can apply these adaptable fabrics for a sustainable future.
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Linux VPS Hosting for Businesses

Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting has become a popular platform for hosting websites, web applications, ecommerce stores and other solutions. A VPS provides isolated virtual server environments with dedicated resources allocated from a physical server.
VPS hosting bridges the gap between shared hosting, where hundreds of accounts run on a single server, and dedicated servers which involve renting an entire physical machine.
With a VPS, businesses get guaranteed resources like CPU cores, RAM, storage and bandwidth allocated only to their virtual machine. This provides greater control, flexibility, security and performance compared to shared hosting.
At the same time, VPS plans are more affordable than dedicated servers since the provider can host multiple VPS instances on powerful physical servers. The pay-as-you-go pricing model also helps optimize costs based on actual usage.
Linux is a very popular operating system choice for VPS hosting, favored by technical users and developers. Compared to Windows, Linux offers key advantages like:
Open source code and access to thousands of free tools
Stability, security and flexibility resulting from worldwide community development
Lower cost than Windows licensing and ability to fully customize the server OS
Scalability to efficiently handle anything from small loads to enterprise-grade web apps
A vast ecosystem of documentation and support resources online
With capabilities like user isolation, configurable resources, root access and support for open source stacks, Linux VPS hosting delivers immense value for businesses at an affordable cost.
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at Linux VPS hosting - its key advantages for businesses, popular use cases and applications, technical factors to consider, criteria for choosing a provider, cost comparisons with other hosting options, frequently asked questions and more.
Key Advantages of Linux VPS Hosting
There are several compelling reasons why Linux is the most preferred platform for VPS deployments. Linux VPS hosting offers businesses the following key advantages:
Flexibility and Customization
One of the biggest draws of a Linux VPS is the immense flexibility it provides to customize the server's configuration and installed software as per the needs of your application or workload.
With full root access, you can choose your preferred Linux distribution, tweak system settings, install required packages, remove unnecessary components, and tailor the VPS for optimal performance.
This level of customization is not possible with shared hosting where you are limited to the web host's server stack. With Linux, you can optimize the server to precisely match your requirements.
Enhanced Performance and Scalability
Linux is designed for efficiency, stability and high performance even under heavy workloads. Resources like CPU cores, RAM, SSD storage, bandwidth can be upgraded seamlessly in real-time to handle spikes in application traffic or usage.
This scalability and ability to fine-tune configurations delivers significantly better performance compared to shared hosting, especially for dynamic websites and web apps.
By isolating applications in their own VPS containers with dedicated resources, performance and uptime are shielded from being impacted by other users on the server.
Improved Security and Isolation
Security is paramount for any business application or platform. Linux provides inherent security advantages over Windows-based VPS options:
Fewer vulnerabilities and malware risks than closed-source Windows
Isolation between VPS instances prevents exploits targeting one site from impacting others
Ability to configure OS-level firewalls, access controls, encryption and other protections
No license costs means more budget can be used for security measures
Known vulnerabilities are quickly patched by the Linux community
This isolation and control over security measures ensures your critical business data and infrastructure are protected on Linux VPS deployments.
Cost Savings Compared to Dedicated Servers
Renting dedicated physical servers with fixed hardware capacity can become very expensive for businesses as their infrastructure needs grow. The pay-as-you-go nature of VPS hosting provides huge cost savings:
Only pay for the actual resources used rather than over-provisioning expensive dedicated servers to handle peak loads
Scaling up or down is quick, incremental and aligned to infrastructure needs month-to-month
Migrating to higher configurations or servers is seamless when required
Options like one-year reserved instance plans offer discounted rates
For the vast majority of standard business workloads, Linux VPS provides the right balance of control, resources and affordable costs.
Leverage the Open Source Ecosystem
One of Linux's biggest advantages is that it is open source and maintained collaboratively by a huge global community of developers and users. This provides immense benefits:
Thousands of high quality open source software packages are available for free - web servers, programming languages, databases, monitoring tools etc.
Ability to leverage open source code, modify and contribute back as needed
Active forums provide documentation and support for just about any issue you may face
Avoid expensive proprietary software license fees and vendor lock-in
The thriving Linux ecosystem allows realizing significant cost savings and accelerates development efforts. With Linux VPS, your business has access to a vast open community.
Popular Use Cases and Applications for Linux VPS
The flexibility and performance advantages of Linux VPS make it suitable for hosting a diverse variety of workloads - from lightweight websites to enterprise-grade applications. Some of the most popular use cases include:
Hosting Content Management System (CMS) Platforms
Linux is the go-to choice for hosting popular open source CMS platforms like WordPress, Drupal, Joomla and others. The LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) stack running on Linux servers is ideally suited for these applications.
With a Linux VPS, you can optimize the environment specifically for your CMS, add modules and extensions, and scale up resources seamlessly to handle traffic surges. Many specialized CMS hosting providers offer streamlined Linux VPS configurations optimized for WordPress.
Hosting Dynamic Web Applications
Modern web applications built using frameworks like React, Angular, Node.js etc have dynamic resource requirements. As traffic and usage patterns change, a scalable hosting platform is vital.
With Linux VPS, you can upgrade CPU, RAM, storage and bandwidth on the fly as needed. Advanced capabilities like load balancing across instances and container deployments provide the robust hosting environment needed by data-driven web apps.
Hosting Ecommerce Stores and Platforms
To ensure excellent performance and uptime, ecommerce sites require flexible yet robust hosting infrastructure. A Linux VPS enables effortlessly scaling resources to manage usage spikes during promotions, holiday sales or marketing campaigns.
The security and isolation advantages are also crucial for ecommerce businesses to protect sensitive customer data and transaction information. Linux VPS allows merchants to focus on growing their business without hosting headaches.
Application Development and Testing Environments
For developers, Linux VPS instances provide isolated and portable environments well-suited for developing, testing and staging applications before deployment.
Multiple configurations mimicking production infrastructure can be spun up easily for testing application compatibility and performance on different operating systems, web servers, databases etc. Resources can be tuned to simulate production-scale traffic during load tests.
Game Servers
Linux is the preferred platform for hosting online multiplayer game servers. The high performance and ability to customize Linux to meet the specific requirements of game workloads makes it an ideal choice.
As the player base expands, VPS resources like RAM, CPU and bandwidth can be upgraded in real-time to minimize latency issues and ensure a smooth gaming experience. Many popular titles rely on Linux-based dedicated game server hosting.
Hosting Big Data Platforms
Modern big data frameworks like Hadoop, Spark and distributed data pipelines are designed to run on Linux. The scalable infrastructure provided by VPS matches the demands of big data analytics.
For data science teams, computational resources like CPU cores and RAM can be dynamically added to speed up data processing jobs and workflows as needed. This agility accelerates the pace of development.
Virtualization and Container Deployments
Linux is the go-to platform for open source virtualization solutions like KVM, Xen, Docker, Kubernetes and more that underpin modern cloud-native app architectures.
The hypervisor running on the Linux VPS hosts the guest VMs or provides the management plane for container lifecycle operations. Companies use Linux VPS to build and operate both virtual machine and container-based workloads.
This demonstrates the immense versatility of Linux VPS hosting for meeting a wide variety of workload requirements - from small websites to complex high-traffic web platforms and enterprise apps. The open source foundation enables tailoring the environment to your needs.
Technical Considerations for Linux VPS Hosting
While a Linux VPS provides immense flexibility, optimally configuring, securing and managing it involves making some key technical decisions:
Choosing the Right Linux Distribution
Hundreds of Linux distributions exist, but some popular options for VPS hosting include:
Ubuntu - Considered one of the most user-friendly. Long term support releases ideal for stability. Extensive packages.
CentOS - Derived from Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Stable, secure and perfect for servers. Reduced costs.
Debian - Known for being robust and versatile. Strict focus on free open source software.
Fedora - Backed by Red Hat. Features latest upstream releases. Regular incremental updates.
When choosing a distro, factor in support timelines, availability of security updates, hardware compatibility, ease of configuration, and the types of software packages required.
Provisioning Optimal Server Resources
The right-sized specifications like number of CPU cores, RAM size, SSD storage, network bandwidth etc. ensure your Linux VPS provides optimal performance for the expected workload and allows future growth.
Over-provisioning resources adds unnecessary costs while under-provisioning results in poor performance. Monitor utilization using tools like htop and resize as needed.
Understanding Virtualization Technologies
Hypervisors like KVM, Xen, VirtualBox etc handle the virtualization layer, turning physical resources into isolated VPS instances. The choice of hypervisor impacts performance and scalability.
Evaluate different virtualization technologies before choosing a Linux VPS provider. Look for hyper-converged infrastructure delivering high performance, availability and resource utilization.
Effectively Managing the Linux Server
Mastering command line skills and using tools like webmin or Cockpit simplifies managing the VPS - creating users, configuring firewalls, system monitoring and more.
Alternatively, many providers offer fully managed VPS solutions if you prefer offloading server administration tasks to experts. This allows focusing on apps instead of infrastructure.
Migrating Applications to the VPS
For smoother migrations, assess compatibility of existing apps and their dependencies with the target Linux distribution chosen.
Test and validate the complete migration process on a staging server before the actual switchover. Plan downtime windows carefully to minimize disruption for users.
Implementing Security Best Practices
Harden your Linux VPS by disabling unneeded services, using SSH keys for authentication, installing fail2ban, enabling the firewall, automating security patches and other measures.
Monitor user activity, implement role-based access control, take regular backups, use VPNs and consider DDoS protection to further strengthen security.
Leveraging Infrastructure Automation Tools
Automation tools like Ansible, Chef, Puppet and Terraform allow programmatically managing the Linux VPS lifecycle - provisioning resources, installing and configuring software, deploying apps etc.
Storing infrastructure-as-code templates in GitHub enables version control and collaboration for environment consistency. Automation aids efficiency.
Monitoring and Optimizing Performance
Use tools like New Relic, Datadog or open source options such as Prometheus to gain visibility into how your VPS and applications are performing under real workloads.
Monitor metrics like CPU usage, disk I/O, bandwidth etc. to proactively optimize and right-size the infrastructure. Set alerts for critical thresholds.
While Linux provides endless possibilities, making prudent technical choices is key to unleashing the full potential of Linux VPS hosting for your workloads.
How to Select a Reliable Linux VPS Hosting Provider
Choosing the right hosting provider is as important as optimizing the VPS itself. Some key criteria to evaluate when selecting a Linux VPS provider:
Robust and High-Performance Infrastructure
The data center, network architecture, and hardware forming the backbone of the VPS infrastructure impacts speed and reliability.
Look for providers using cutting-edge components - fast multi-core CPUs, SSD storage, premium memory etc. Minimum 1 Gbps network links demonstrate strong connectivity.
Managed Support Services
Look for 24x7 fast response support via live chat, phone and ticketing. Platform management services like migrations, monitoring, optimization etc further improve uptime and performance.
Flexible and Instant Scaling of Resources
The ability to upgrade compute, memory, storage and bandwidth on demand provides true pay-as-you-grow economics. Avoid providers restricting flexible resource expansion.
Reliable Data Protection and Backup
Proactively safeguard against data loss and disasters through regular encrypted VPS backups. Verify backup frequency, retention policies and restoration processes.
Global Infrastructure Across Regions
Having a geographically diverse network of data centers close to users improves performance and redundancy.
Ensure the provider has an infrastructure presence suitable for your target markets.
Competitive Yet Transparent Pricing
Upfront published pricing allows accurate cost planning. Beware of hidden fees. Look for pricing models that offer flexibility and maximize value for money.
Visibility into Usage and In-Depth Monitoring
The ability to track fine-grained VPS utilization metrics helps optimize workloads and infrastructure efficiency. Robust monitoring is invaluable.
Reputation and Technical Expertise
Verify testimonials, client reviews and the provider's track record in managing Linux VPS infrastructure at scale. Technical expertise inspires confidence.
Prioritizing these parameters helps evaluate offerings and select a Linux VPS provider that best matches your application needs and business priorities.
Linux VPS vs Other Hosting Options - A Cost Comparison
Deciding between Linux VPS and alternate hosting approaches depends on your workload requirements and budget. Here is a cost comparison across different types of hosting:
Shared Hosting
With shared hosting, hundreds of accounts share the resources of a single physical server. This allows web hosts to offer basic shared plans cheaply starting at just 21 INR/mo. per month.
However, you have no control or ability to customize the server environment. Performance is unpredictable due to other users impacting resources. Limited isolation and risk of overloading makes shared hosting suitable only for low-traffic personal sites.
Windows VPS
A Windows Server VPS provides the flexibility to run Windows-only proprietary software. However, Windows licensing results in significantly higher costs compared to open source Linux distros.
The monthly price for entry-level Windows VPS plans starts at 225 INR/mo. and upwards. There are also fewer open source app options on Windows. Use cases are limited unless Windows-only compatibility is mandatory.
Dedicated Server Hosting
Renting an entire physical server gives full control but involves major upfront investment starting at $100 per month for entry configurations. Resources are trapped on expensive hardware even when unused.
With cloud VPS, you pay only for actual usage and can RIGHTSIZECORES, RAM etc cost-efficiently. Dedicated servers are overkill for most needs.
Cloud Virtual Machine Instances
Cloud platforms like AWS EC2 also offer pay-as-you-go VMs. But additional charges for data transfers, load balancing and managed services make costs add up faster.
The complexity of directly handling cloud infrastructure makes managed VPS solutions simpler for most use cases. Cloud VMs are ideal for large-scale, complex deployments.
Managed Kubernetes Clusters
Container orchestration systems like Kubernetes abstract away the underlying VPS/VM infrastructure complexity entirely. This simplifies app deployment but reduces visibility.
Kubernetes is ideal for cutting-edge microservices-based apps. But traditional monolithic apps may not benefit as much from the added complexity unless you need auto-scaling.
For a majority of standard business workloads, Linux VPS strikes the right balance between performance, control and affordability. The savings from open source and ability to RIGHTSIZE resources deliver the best ROI for many use cases.
Popular Linux VPS Hosting Providers
Many leading hosting providers offer Linux VPS solutions catering to personal and business users. Some reputed ones include:
Vultr
Vultr is a popular IaaS platform providing high-performance Linux VPS hosting across 19 geo-locations.
Key Features
Bare metal KVM and SSD-based storage for maximum performance
Fast automated VPS setup within 60 seconds
Global private network between all Vultr locations
plans start at $5/month for 1 vCPU, 1 GB RAM, 25 GB SSD
Usage-based hourly and monthly billing
DDoS protection and IPv6 support
Scalable resources and real-time provisioning
Averthost
Averthost delivers developer-friendly Linux VPS powered by advanced cloud infrastructure across 10 locations.
Key Features
Instant provisioning of resources through API/automation
Access to latest Intel processors up to 32 cores
Local NVMe SSD disks rather than remote storage
Customizable high grade hardware for CPU, RAM, storage, network
Bare metal performance with dedicated resources
Pricing from 21 INR/month for entry-level plans
Frequently Asked Questions About Linux VPS Hosting
Q1. Is Linux VPS right for me?
Linux VPS is recommended for users comfortable using command-line administration and wanting greater control over the hosting environment than shared plans provide. It is suitable for developers, agencies, tech startups and SMBs running production workloads.
Explore More From : solve the network
We hope you found this blog post informative and engaging. If you're hungry for more great content, be sure to check out our other websites and explore a world of knowledge and entertainment:
Averthost - Discover cutting-edge web hosting solutions and tips to enhance your online presence.
Solve The Network - Dive into the world of networking and find solutions to common network-related challenges.
Akar Periwal - Explore the creative works and insights of Akar Periwal, an artist and visionary.
IT News DB - Stay updated with the latest developments in the world of Information Technology and cybersecurity.
1 note
·
View note