nose blog para refs y cosas
Last active 60 minutes ago
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Note
hi! can you create some dividers for me with a combination of yellow and white... i'd really appreciate it!
hello! I could do that for sure - hope you like these!! 💛🤍










[Free] Masterlist Headers & Dividers!
Please consider liking or reblogging if you use 💕
478 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Create A Villain
The best villains? They don’t even see themselves as the bad guys. They’re 100% convinced that what they’re doing is right, even if it’s messed up. Maybe they’re trying to “save the world” by doing something super questionable, or they think enforcing strict rules is the only way to keep society in check. They truly believe they’re the hero of their own story, which makes them way more interesting and real.
And Yeah, your villain might want power, but the real question is: Why? Were they humiliated in the past and now want control? Did they grow up powerless and now crave it to avoid being vulnerable again? When you dig into their backstory and show us why they’re doing horrible things, it makes them a lot more relatable—even if they’re totally wrong.
Flat, one-note villains are boring. If your antagonist is going to stick with people, they need depth. Show us what’s going on under the surface. Maybe they lie awake at night, doubting their choices, or they’re still haunted by a massive failure that’s pushing them toward their goal. A villain with personal struggles and vulnerabilities feels way more human and way harder to fully
A great Villain doesn’t just fight the hero, they reflect them. They might have totally different goals, but at their core, they share similar traits, maybe ambition, stubbornness, or a tragic backstory. When the hero looks at the villain, they should see a bit of themselves, and that’s what makes the conflict between them so intense.
When the villain finally goes down, it should feel big. Their defeat shouldn’t just be a fight, it should hit them emotionally. Ideally, their downfall comes from their own flaws, maybe they got too arrogant or made a mistake because of their obsessive goal. The best villain defeats leave the audience feeling a little sad or conflicted, not just happy for the hero’s win.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
ultimate character development template
basics
name: meaning of name: nicknames/titles: age: gender: location: birthday: strengths + example where it's shown: weaknesses + example where it's shown: how it affects others:
emotional depth
attachment style + how it manifests in the story: physical fear: emotional/abstract fear: happy memory: sad memory: object of significance: philosophical outlook/belief: what characters are ignorant about themselves: how confident are they: goal: long-term dreams: what they're embarrassed/ashamed to tell others about: regrets: source of pride: source of misery: what they admire above all else: do they believe in fate:
personality
mbti: enneagram: big five: character archetype: star sign: who they pretend to be on the outside: who they actually are/how they feel towards the mask: mental health conditions: how it manifests for them: iq: eq: humour: reputation:
habits
bad habits: mannerisms when stressed: mannerisms when content: mannerisms when scared: mannerisms normally: verbal mannerisms/distinctive speaking style: how do they move across a room: what do they say and what remains unsaid: how they express love: hobbies:
appearance
defining features: eye shape + colour: hair texture + colour: skin texture + tone: vibe: height: build: clothing: any bodily disfigurement (scars, etc.): overall attractiveness: their opinion on their appearance: appeals to:
relationships
who they trust most: what they wish they could do for them: what's holding them back: who they hate most: what they wish they could do to them: what's holding them back: relationship with the protagonist: relationship with the antagonist: siblings: relationship with them: parents/step-parents: relationship with them: previous broken relationships: why did it break: what others expect of them: who believes in them: their mentor character/who they look up to: political/religious/other affiliations: what makes them different from every other character: non-human relationships + why: romantic "type" + why: relationship dynamics:
backstory/background
primary emotion towards their past: primary feelings while in their past: where did they grow up: defining incidents: earliest childhood memory: saddest memory: happiest memory: major accomplishments: their opinion on it: notable people in their backstory: effect on them today: trauma: what have they already lost: financial circumstance:
progression
why are they important (eg. why're they the only one able to do something?): what do they learn about themselves throughout the story: what do they learn about the world: how do they feel towards their newfound knowledge: character arc (positive, negative, neutral): how relationships change because of their actions: what mistakes do they make: what scene is their character highlighted: do they get what they want: why or why not: what happens to them after the story ends:
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
List of 40 character flaws
Stubbornness, Unyielding in one's own views, even when wrong.
Impatience, Difficulty waiting for long-term results.
Self-doubt, Constant uncertainty despite evident abilities.
Quick temper, Excessive reactions to provocations.
Selfishness, Prioritizing one's own needs over others'.
Arrogance, Overestimating one's own abilities.
Trust issues, Difficulty trusting others.
Perfectionism, Setting unreachable high standards.
Fear of change, Avoiding changes.
Haunted by the past, Old mistakes or traumas influencing the present.
Jealousy, Envious of others' successes.
Laziness, Hesitant to exert effort.
Vindictiveness, Strong desire for revenge.
Prejudice, Unfair biases against others.
Shyness, Excessive timidity.
Indecisiveness, Difficulty making decisions.
Vulnerability, Overly sensitive to criticism.
Greed, Strong desire for more (money, power, etc.).
Dishonesty, Tendency to distort the truth.
Recklessness, Ignoring the consequences of one's actions.
Cynicism, Negative attitude and distrust.
Cowardice, Lack of courage in critical moments.
Hotheadedness, Quick, often thoughtless reactions.
Contentiousness, Tendency to provoke conflicts.
Forgetfulness, Difficulty remembering important details.
Kleptomania, Compulsion to steal things.
Hypochondria, Excessive concern about one's health.
Pessimism, Expecting the worst in every situation.
Narcissism, Excessive self-love.
Control freak, Inability to let go or trust others.
Tactlessness, Inability to address sensitive topics sensitively.
Hopelessness, Feeling that nothing will get better.
Dogmatism, Rigidity in one's own beliefs.
Unreliability, Inability to keep promises.
Closed-offness, Difficulty expressing emotions.
Impulsiveness, Acting without thinking.
Wounded pride, Overly sensitive to criticism of oneself.
Isolation, Tendency to withdraw from others.
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Tips Master Post
Edit: Some posts may be deleted
Character writing/development:
Character Arcs
Making Character Profiles
Character Development
Comic Relief Arc
Internal Conflict
Character Voices
Creating Distinct Characters
Creating Likeable Characters
Writing Strong Female Characters
Writing POC Characters
Building Tension
Plot devices/development:
Intrigue in Storytelling
Enemies to Lovers
Alternatives to Killing Characters
Worldbuilding
Misdirection
Consider Before Killing Characters
Foreshadowing
Narrative:
Emphasising the Stakes
Avoid Info-Dumping
Writing Without Dialogue
1st vs. 2nd vs. 3rd Perspective
Fight Scenes (+ More)
Transitions
Pacing
Writing Prologues
Dialogue Tips
Writing War
Writing Cheating
Worldbuilding:
Worldbuilding: Questions to Consider
Creating Laws/Rules in Fantasy Worlds
Book writing:
Connected vs. Stand-Alone Series
A & B Stories
Writer resources:
Writing YouTube Channels, Podcasts, & Blogs
Online Writing Resources
Outlining/Writing/Editing Software
Writer help:
Losing Passion/Burnout
Overcoming Writer's Block
Fantasy terms:
How To Name Fantasy Races (Step-by-Step)
Naming Elemental Races
Naming Fire-Related Races
How To Name Fantasy Places
Ask games:
Character Ask Game #1
Character Ask Game #2
Character Ask Game #3
Miscellaneous:
1000 Follower Post
2000 Follower Poll
Writing Fantasy
29K notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you have any advice for a character who has a sort of sacrificial lamb complex? A savior complex but not as in a hero to save the day, but as in they don't believe they deserve to save themselves?
How to Write a Sacrificial Character
Backstory and Motivation
Traumatic Past: Explore the character’s history. Perhaps they’ve experienced abandonment, betrayal, or loss, leading them to internalize the belief that their worth is tied to suffering for others.
Family Expectations: They may come from a family that emphasizes self-sacrifice or has a history of martyrdom, teaching them that their own needs are secondary to others.
Guilt and Responsibility: The character might feel an overwhelming sense of guilt for past failures, believing that they owe it to others to endure hardship or take on burdens.
Internal Conflict
Self-Worth Issues: Illustrate their struggle with self-worth. They might dismiss compliments or feel undeserving of happiness, using phrases like “I don’t deserve this” or “I have to earn my place.”
Desire for Connection: While they may push others away, they also yearn for connection and love, creating an internal tug-of-war between wanting to be saved and believing they are unworthy of it.
Sacrificial Actions
Small Acts of Sacrifice: Show them making small sacrifices for friends or loved ones, like skipping meals or taking on additional work, which reinforces their belief that they should suffer for others’ well-being.
Dramatic Moments: Create pivotal scenes where they are put in a position to sacrifice themselves for someone else—physically or emotionally. This can highlight their motivations and lead to significant character development.
Interactions with Others
Supportive Characters: Introduce characters who try to save or help them, but the sacrificial character resists, believing their problems aren’t worth the effort. This can create tension and deepen their internal struggle.
Small Acts of Kindness: Have moments where others go out of their way to help them, reinforcing that they are worthy of care and support. This can include simple gestures, affirmations, or sacrifices made on their behalf.
Conflict with a Mentor or Friend: A mentor figure might challenge this belief, encouraging them to see their value and fight for themselves, leading to moments of growth and resistance.
Gradual Change
Moments of Clarity: Show them having fleeting moments of realization where they understand their self-worth, possibly triggered by a significant event or dialogue with another character.
Catalyst for Change: Introduce a scenario where they must choose between self-sacrifice and self-preservation, forcing them to confront their beliefs head-on.
Life-Altering Experience: Put the character in a situation that forces them to confront their fears, such as a near-death experience or a pivotal choice between saving themselves or others. This moment can act as a wake-up call to their worth.
Acts of Courage: Have them step up in a crisis, leading to a moment where they save someone else and realize their capability and value. This can help them see that they have something to offer.
Turning Point: Create a climactic moment where the character realizes they deserve to save themselves, possibly triggered by witnessing someone else sacrifice themselves for them, prompting a realization of their worth.
Final Confrontation: In the final confrontation (with a villain or personal demon), let them stand up for themselves, verbalizing their worth and challenging the beliefs that have held them back.
Symbolism and Themes
Recurring Motifs: Use symbols that represent sacrifice and self-worth, like broken mirrors (self-perception) or shadows (their past). These can help reinforce their internal struggles visually throughout the narrative.
Redemption Arc: If they ultimately find a way to save themselves or allow others to save them, showcase this as a powerful moment of growth, suggesting that self-worth and love are intertwined.
Emotional Depth
Show Vulnerability: Allow the character to express their fears and doubts, whether through dialogue, journaling, or introspection, making their internal battles relatable and poignant.
Balance with Humor: If appropriate for your story, consider moments of humor or lightness to juxtapose their darker thoughts, showing that they are more than their complex.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Morally Gray Characters in Storytelling
Definition and Core Characteristics:
Complex and Ambiguous Morality: Morally gray characters exhibit traits and make decisions that do not fit neatly into the categories of 'good' or 'evil'. Their actions and motivations often blend aspects of both.
Humanized Flaws: They possess human flaws, which make their actions and decisions relatable and believable. These flaws often drive their complex behavior.
Realistic Motivations: Their motivations are multifaceted and realistic, often stemming from personal experiences, traumas, or societal pressures.
Importance in Storytelling:
Adds Depth: These characters add depth and richness to the narrative, providing a more nuanced and realistic portrayal of human nature.
Creates Tension and Conflict: Their unpredictability and complex morality create tension and conflict, driving the plot and engaging the audience.
Reflects Real Life: By portraying characters with both good and bad qualities, stories can reflect the complexity of real-life moral decisions.
Examples and Their Impact:
Walter White from Breaking Bad: Initially a high school chemistry teacher diagnosed with cancer, Walter turns to manufacturing methamphetamine to secure his family’s future. His descent into criminality and moral compromise makes him a quintessential morally gray character.
Severus Snape from Harry Potter: Snape’s actions and allegiances are ambiguous throughout much of the series. His ultimate loyalty and sacrifices reveal a deeply complex character motivated by love and regret.
Creating a Morally Gray Character:
Blend Virtues and Vices: Give your character a mix of admirable qualities and significant flaws. This balance helps create a sense of realism.
Motivations Over Actions: Focus on the character’s motivations rather than just their actions. Understand why they make certain decisions, even if those decisions are morally questionable.
Consequences and Growth: Show the consequences of their actions and allow for character growth or regression. This evolution keeps the character dynamic and engaging.
Impact on the Audience:
Empathy and Engagement: Morally gray characters can evoke empathy from the audience, as they see parts of themselves in the character’s struggles and decisions.
Moral Reflection: These characters prompt audiences to reflect on their own moral beliefs and the complexities of right and wrong.
Discussion and Debate: The ambiguous nature of morally gray characters often sparks discussion and debate, making stories more engaging and thought-provoking.
By understanding and effectively using morally gray characters, storytellers can craft richer, more engaging narratives that resonate deeply with their audience.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
how to write creepy stories
over describe things
under describe things
short sentences in rapid succession build tension
single sentence paragraphs build dread
uncanny valley = things that aren't normal almost getting it right
third person limited view
limited expressions
rot, mold, damage, age, static, flickering, espsecially in places it shouldn't be
limited sights for your mc - blindness, darkness, fog
being alone - the more people there are, the less scary it is
intimate knowledge, but only on one side
your reader's imagination will scare them more than anything you could ever write. you don't have to offer a perfectly concrete explanation for everything at the end. in fact, doing so may detract from your story.
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
20 Emotional Wounds in Fiction That Make Readers Root for the Character
Abandonment: Characters who have been abandoned by loved ones or caregivers can evoke sympathy from readers.
Betrayal: Being betrayed by someone close can create deep emotional wounds that make readers empathize with the character.
Loss of a Loved One: Whether through death or separation, the loss of a loved one can be a powerful emotional wound.
Rejection: Characters who experience rejection, whether in relationships or by society, can be relatable and evoke empathy.
Abuse: Physical, emotional, or psychological abuse can create complex wounds that shape a character's personality and behavior.
Neglect: Characters who have been neglected, especially in childhood, can evoke sympathy from readers.
Failure: Experiencing a significant failure or loss can create emotional wounds that make characters more relatable.
Guilt: Characters who carry guilt for past actions or decisions can be compelling and evoke empathy from readers.
Shame: Feelings of shame can create internal conflict and make characters more relatable and sympathetic.
Injustice: Characters who have experienced injustice or unfair treatment can evoke strong emotions from readers.
Trauma: Characters who have experienced traumatic events, such as war or natural disasters, can be sympathetic and relatable.
Loneliness: Characters who feel lonely or isolated can evoke empathy from readers who have experienced similar feelings.
Fear: Characters who face their fears or struggle with phobias can be relatable and evoke empathy from readers.
Self-doubt: Characters who struggle with self-doubt or low self-esteem can be relatable and evoke sympathy.
Identity Crisis: Characters who are grappling with questions of identity or struggling to find their place in the world can be sympathetic.
Addiction: Characters who struggle with addiction can be complex and evoke empathy from readers.
Betrayal of Trust: Characters who have had their trust betrayed can be sympathetic and relatable.
Unrequited Love: Characters who experience unrequited love can be sympathetic and evoke empathy from readers.
Isolation: Characters who feel isolated or disconnected from others can be relatable and evoke sympathy.
Fear of Failure: Characters who struggle with a fear of failure can be relatable and evoke empathy from readers.
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
20 Compelling Positive-Negative Trait Pairs
Here are 20 positive and negative trait pairs that can create compelling character dynamics in storytelling:
1. Bravery - Recklessness: A character is courageous in the face of danger but often takes unnecessary risks.
2. Intelligence - Arrogance: A character is exceptionally smart but looks down on others.
3. Compassion - Naivety: A character is deeply caring but easily deceived due to their trusting nature.
4. Determination - Stubbornness: A character is persistent in their goals but unwilling to adapt or compromise.
5. Charisma - Manipulativeness: A character is charming and persuasive but often uses these traits to exploit others.
6. Resourcefulness - Opportunism: A character is adept at finding solutions but is also quick to exploit situations for personal gain.
7. Loyalty - Blind Obedience: A character is fiercely loyal but follows orders without question, even when they're wrong.
8. Optimism - Denial: A character remains hopeful in difficult times but often ignores harsh realities.
9. Humor - Inappropriateness: A character lightens the mood with jokes but often crosses the line with their humor.
10. Generosity - Lack of Boundaries: A character is giving and selfless but often neglects their own needs and well-being.
11. Patience - Passivity: A character is calm and tolerant but sometimes fails to take action when needed.
12. Wisdom - Cynicism: A character has deep understanding and insight but is often pessimistic about the world.
13. Confidence - Overconfidence: A character believes in their abilities but sometimes underestimates challenges.
14. Honesty - Bluntness: A character is truthful and straightforward but often insensitive in their delivery.
15. Self-discipline - Rigidity: A character maintains strong control over their actions but is inflexible and resistant to change.
16. Adventurousness - Impulsiveness: A character loves exploring and trying new things but often acts without thinking.
17. Empathy - Overwhelm: A character deeply understands and feels others' emotions but can become overwhelmed by them.
18. Ambition - Ruthlessness: A character is driven to achieve great things but willing to do anything, even unethical, to succeed.
19. Resilience - Emotional Detachment: A character can endure hardships without breaking but often seems emotionally distant.
20. Strategic - Calculative: A character excels at planning and foresight but can be cold and overly pragmatic in their decisions.
These pairs create complex, multi-dimensional characters that can drive rich, dynamic storytelling.
---
+ If you find my content valuable, consider Support This Blog on Patreon!
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
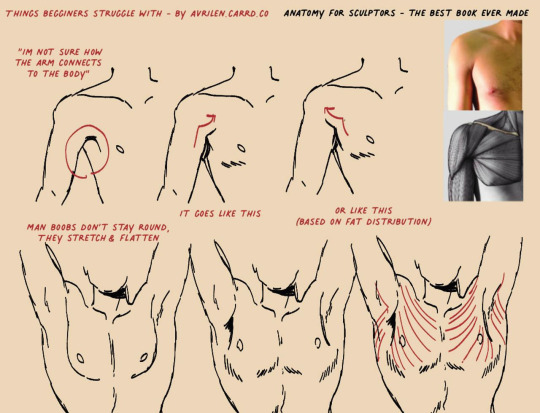
A small guide for people who struggle with this area
26K notes
·
View notes
Note
Can you draw more aph denmark x aph iceland? :3
aaaaa Long time without draw the otpp ;;;;;;;;i WILL DO IT...WHEN I HAVE TIME......I MISS THEM SO MUCH
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
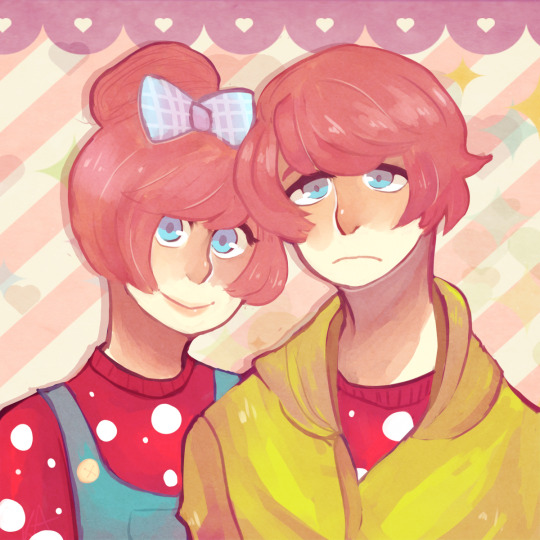

My part for an ArtTrade with miyalin!
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Some doodles of this nerds
someday I'll present them.
7 notes
·
View notes







