Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Exploring Sensor Innovations: A Journey Through Transportation

In the bustling city, Maya and Priya, two curious friends, ventured into the Auto Expo. Inside, they were greeted by a dazzling array of cars, big and small.
Their first stop was the electric car section. They were amazed by these cars, which ran quietly on electricity instead of gas. It was like stepping into the future!

Next, they discovered the self-driving cars. Maya and Priya's jaws dropped as they watched these cars steer themselves using special sensors and computers. It was like being in a movie!
But what really blew their minds were the fancy features inside the cars. They saw warning systems that beeped when you got too close to another car, and cruise control that could adjust your speed automatically. It was like having a super-smart co-pilot!
As they continued their adventure, they found even more cool gadgets like smart GPS and parking assistants. It was like being in a tech wonderland!

Their trip to the Auto Expo wasn't just fun—it was a learning experience too. They discovered how technology was changing the way we drive cars, and they couldn't wait to see what else was in store for the future of transportation!
In the story, Maya and Priya encountered several sensors used in the showcased technologies, including warning systems, cruise control, self-driving car sensors, smart GPS, and parking assistants.

Through the story of Maya and Priya's adventure at the Auto Expo, we want to show how these advancements are shaping the future of driving. From electric cars to self-driving technology, sensors play a crucial role in making vehicles safer, smarter, and more efficient. By highlighting their importance, we hope to inspire curiosity and spark interest in the incredible possibilities that lie ahead in transportation technology.

Class Activity
0 notes
Text
Unlocking the Digital Revolution: Understanding Digital Logic Families
Introduction
The digital revolution has transformed countless aspects of our lives, from the way we communicate to the way we access information. At the heart of this revolution lies the concept of digital logic families, the building blocks that power our advanced technologies. In this article, we will explore the significance of digital logic families and delve into the intricate world of their evolution, types, practical applications, and future advancements.
What are Digital Logic Families?
In order to comprehend the complexity of digital logic families, it is crucial to first understand the concept of digital logic itself. Digital logic refers to the fundamental building blocks of electronic circuits that manipulate binary signals through logic gates. These logic gates perform operations such as AND, OR, and NOT, allowing for intricate manipulation of binary information.
Digital logic families, on the other hand, are a collection of integrated circuits (ICs) that share similar characteristics and use the same basic principles to process and transmit digital signals. They serve as the foundation for the digital devices we rely on every day, enabling efficient and reliable data processing.
Historical Evolution of Digital Logic Families

The birth of digital logic families can be traced back to the mid-20th century, when scientists and engineers began exploring the possibilities of using electronic circuits to process digital information. Milestones and key advancements during this period include the development of diode-based logic gates and the introduction of the first transistor-based logic gate, the transistor-transistor logic (TTL).
Common Types of Digital Logic Families
Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL)
TTL is one of the earliest and most widely used digital logic families. It utilizes bipolar junction transistors to perform logic operations. TTL has various subfamilies, including low-power Schottky TTL (LS-TTL) and advanced Schottky TTL (AS-TTL). Each subfamily offers different characteristics and trade-offs, such as varying power consumption and switching speed.
Pros of TTL:
High noise immunity
Wide range of operating voltages
Rugged and reliable
Cons of TTL:
Higher power consumption compared to some newer logic families
Limited fan-out capability
Emitter-Coupled Logic (ECL)
ECL is a high-speed logic family that operates on the principle of current steering. It does not rely on voltage levels like TTL does, making it well-suited for high-speed and high-frequency applications. ECL has subfamilies like positive emitter-coupled logic (PECL) and low-voltage positive emitter-coupled logic (LVPECL).
Advantages of ECL:
Extremely fast switching speed
Low power supply noise sensitivity
Excellent signal integrity
Disadvantages of ECL:
Higher power consumption compared to some other logic families
More complex design requirements
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS)
CMOS logic family is widely used in modern digital circuits due to its low power consumption and ability to operate at lower voltages. It consists of complementary pairs of metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). Popular CMOS variants include low-power CMOS (LP-CMOS) and high-speed CMOS (HCMOS).
Overview of CMOS:
Low power consumption
Wide range of operating voltages
Higher resistance to noise
Benefits of CMOS:
Lower power consumption compared to TTL and ECL
Greater noise immunity
Compatibility with various IC technologies
Drawbacks of CMOS:
Reduced speed compared to ECL
Limited driving capability

Practical Applications of Digital Logic Families
Digital logic families find a wide range of practical applications in various devices, particularly through digital integrated circuits (ICs).
Digital integrated circuits (ICs)
ICs play a crucial role in the implementation of digital logic families in diverse devices. They provide the necessary circuitry for processing and transmitting digital signals efficiently. Examples of IC applications utilizing different logic families include microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips, and communication devices.
Role of ICs:
Integration of complex logic functions
Miniaturization of circuitry
Enhanced reliability and performance

Microprocessors and microcontrollers
Microprocessors and microcontrollers are key components in modern-day computing systems and embedded devices. They utilize different logic families based on the application's requirements. Logic families commonly employed in microcontrollers include CMOS and TTL, depending on factors like power consumption, speed, and complexity.
Fundamentals of microprocessors:
Execution of instructions
Data processing and manipulation
Interface with peripherals and memory
Comparison of logic families used in microcontrollers:
CMOS: Lower power consumption, compatibility with various IC technologies
TTL: Robustness, easier compatibility with legacy systems
Advancements and Future Trends in Digital Logic Families
The field of digital logic families constantly evolves to meet the demands of emerging technologies and applications.
Recent developments in logic families
Recent advancements in digital logic families include the development of advanced CMOS technologies, such as FinFET and nanosheet transistors, enabling higher performance and energy efficiency. Additionally, research and innovations in emerging technologies, such as quantum computing and neuromorphic engineering, hold promising prospects for future logic families.
Exploring emerging technologies
Emerging technologies, like spin-based computing and molecular electronics, show potential for revolutionizing the field of digital logic families. These cutting-edge technologies aim to overcome the limitations of current logic families and pave the way for faster, smaller, and more energy-efficient digital devices.
Summary and Future Outlook
In summary, digital logic families are the backbone of the digital revolution, providing the essential building blocks for advanced digital technologies. As technology continues to evolve, logic families will play a crucial role in driving further advancements in areas like artificial intelligence, internet of things, and robotics.
Looking ahead, the future of digital logic families holds immense potential for transformative breakthroughs. The continued exploration of emerging technologies and the ongoing pursuit of higher performance and energy efficiency will shape the next chapters of the digital revolution.

FAQs
A. What is the role of propagation delay in digital logic families?
Propagation delay refers to the time taken for a signal to propagate through a logic gate. It affects the overall speed and timing of digital circuits. Minimizing propagation delay is crucial for achieving faster processing speeds and ensuring reliable signal transmission.
B. Which logic family is ideal for high-speed applications?
Emitter-Coupled Logic (ECL) is often preferred for high-speed applications due to its fast switching speed and excellent signal integrity. However, it comes with higher power consumption and more complex design requirements compared to other logic families.
C. How does logic family selection affect signal integrity?
The choice of logic family can have a significant impact on signal integrity. Factors such as noise immunity, voltage levels, and switching characteristics of the logic family influence the quality and reliability of the transmitted signals. Selecting a logic family with better noise immunity and voltage margins improves overall signal integrity.
D. Are there any emerging logic families that might replace the current ones?
The field of digital logic families is constantly evolving, and emerging technologies like spin-based computing and molecular electronics hold the potential to introduce new logic families in the future. While these technologies are still in their early stages of development, they offer promising alternatives that could potentially replace or augment current logic families.
REFERENCE LINKS
https://easyelectronics.co.in/classification-and-characteristics-of-logic-families/
https://limewire.com/studio/image/create-image?model=blue-willow-v4&prompt=%2Fimagine+prompt%3A+An+intricate+digital+illustration+capturing+the+historical+evolution+of+digital+logic+families%2C+showcasing+the+evolution+from+diode-based+logic+gates+to+transistor-transistor+logic+%28TTL%29.+The+artwork+depicts+scientists+and+engineers+working+in+a+laboratory+setting%2C+surrounded+by+electronic+circuits+and+technological+equipment.+The+color+temperature+is+cool%2C+with+a+focus+on+blue+and+silver+tones+to+represent+the+futuristic+nature+of+the+evolution.+The+lighting+is+bright%2C+emphasizing+the+details+of+the+circuitry.+--v+5+--stylize+1000+--ar+16%3A9
https://www.electrically4u.com/classification-and-characteristics-of-digital-logic-family/
https://www.humix.com/video/9db79b2c89a65813caa6594e017ae42ae59f6a5692d0489406dcf4c54a8c70c6
0 notes
Text
Amazon EFS: Empowering Cloud Storage with Ease
Introduction:
Welcome to the world of Amazon Elastic File System (EFS), where scalable and shared file storage becomes a breeze. In this short and easy-to-understand blog post, we'll dive into the superpowers of Amazon EFS, enabling you to conquer file storage challenges in the cloud with simplicity and efficiency.

Infinite Scalability: With Amazon EFS, your storage can grow effortlessly as your applications demand. Say goodbye to capacity constraints and embrace unlimited scalability.
Seamless Collaboration: EFS allows multiple EC2 instances to access and modify files simultaneously, enabling seamless collaboration and boosting productivity in the cloud.
Lightning-Fast Performance: EFS delivers exceptional performance, ensuring your applications can read and write data with lightning speed, accelerating your workflows.
Rock-Solid Resilience: EFS automatically replicates your data across multiple Availability Zones, providing robust data durability and protection against failures or disasters.
Granular Access Control: EFS integrates with AWS IAM, granting you complete control over access permissions, ensuring data security and compliance.

Conclusion:
Amazon EFS empowers businesses with easy-to-use and scalable file storage in the cloud. Enjoy infinite scalability, collaborate seamlessly, experience lightning-fast performance, safeguard your data with resilience, and maintain granular access control. Let Amazon EFS be your trusted partner as you conquer the world of cloud storage with ease and confidence.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Title: Amazon EC2: Unleash Your Superpowers in the Cloud!
Introduction:
Welcome to the extraordinary world of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), where you can harness the power of the cloud to achieve remarkable feats. In this short and simple blog post, we'll explore the key features and benefits of Amazon EC2, empowering you to become a cloud computing superhero!

Elasticity and Scalability: With EC2, you have the ability to scale your compute resources up or down effortlessly. No task is too big or small as you adapt to changing workloads with ease.
Versatile Instance Types: EC2 offers a wide range of instance types tailored to your specific needs. Choose the perfect fit, whether you require general-purpose instances or high-performance computing clusters.
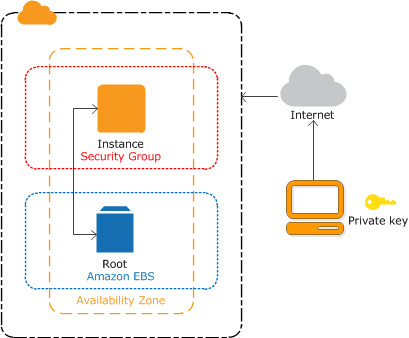
Security and Control: EC2 ensures the utmost security for your applications and data. You have complete control over your instances, including firewall settings and storage encryption, bolstering your defenses against threats.
Storage Options: EC2 provides flexible storage options, including persistent block-level storage (EBS) and scalable file storage (EFS). Leverage these options to securely store and access your data.
Seamless Integration: EC2 seamlessly integrates with other AWS services, allowing you to build comprehensive cloud architectures. Connect with databases, perform scalable data processing, and create a powerful ecosystem.
Conclusion:
With Amazon EC2, you possess the superpowers needed to conquer the cloud. Embrace the elasticity, select the right instance type, secure your applications, leverage storage options, and integrate seamlessly with other services. It's time to unleash your inner superhero and embark on an exciting cloud computing adventure with Amazon EC2!
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Amazon EBS: Reliable Cloud Storage Made Simple
Introduction:
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) is a dependable and flexible storage solution offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It provides persistent block-level storage volumes for your EC2 instances, ensuring data durability and accessibility. Let's explore the key features and benefits of Amazon EBS in a nutshell.

Key Features of Amazon EBS:
Durability and High Availability: EBS replicates your data within availability zones, safeguarding it against hardware failures and ensuring high data durability.
Elasticity and Scalability: EBS allows you to easily resize storage volumes, providing flexibility to accommodate changing storage needs and optimizing costs by paying only for what you use.
Performance Options: With different volume types available, you can choose the optimal balance of cost and performance for your specific requirements, ranging from General Purpose SSD to Throughput Optimized HDD.
Snapshot and Replication: EBS supports creating snapshots of your volumes, allowing you to back up data and restore or create new volumes from these snapshots. It also enables cross-region replication for enhanced data protection and availability.
Integration with AWS Services: EBS seamlessly integrates with other AWS services such as RDS, EMR, and EKS, making it suitable for a wide range of applications including databases, big data analytics, and containerized environments.
Use Cases for Amazon EBS:
Database Storage: EBS provides durable and scalable storage for various database workloads, ensuring reliable data persistence and efficient access.
Big Data and Analytics: With its high throughput and capacity, EBS supports big data platforms and enables processing and analysis of large datasets.
High-Performance Computing (HPC): EBS with Provisioned IOPS offers high I/O performance, making it ideal for demanding computational workloads such as simulations and financial modeling.
Disaster Recovery: Utilizing EBS snapshots and cross-region replication, you can implement robust disaster recovery strategies for your data.
Conclusion:
Amazon EBS is a powerful storage solution within the AWS ecosystem. With its durability, scalability, performance options, and integration capabilities, EBS caters to diverse storage needs, from databases to big data analytics. By leveraging EBS, you can ensure the reliability, availability, and flexibility of your cloud storage infrastructure.
16 notes
·
View notes