Text
Script
The twelve basic principles of animation were founded some time ago in an age before computer animation, and yet the 7 motion principles are still the building blocks we use today.
Squash and stretch
Squash and stretch add weight and volume to an object, adding exaggeration to make the visuals more realistic. When a ball bounces for example it will squash on impact and stretch during acceleration. Or as can be seen here with this blinking character, simple squash and stretch techniques add life to the face even though it may not be photo-realistic.
Timing
Timing is used in many ways for animation. It can convey realism like in an action sequence with acrobatic movements. Or it can convey emotion like in these head turns. One is fast and shows surprise, the other slow and relaxed.
Arcs
Arcs are the motions in which many natural looking movements take place, be it heads turning or an object being thrown across the room. Nothing ever flies or moves in a completely straight line and it is important to convey this in animation as to have the audience believe the movements they are seeing.
Slow in slow out
Keeping in the theme of realistic body movements, slow in and slow out is another principle that can be seen in this head turn animation as the head slowly starts moving in the beginning and slows down again into its resting position, imitating the acceleration and deceleration seen in realistic movements. These kinds of movements can also be seen in objects like pendulums as can be seen on screen now. The main body section slows, speeds up, and then slows down again between each movement with the tail following behind giving the illusion of weight.
Anticipation
Anticipation is the action that happens before the main action begins, like a lead up to what will happen. Like what can be seen in the jumping animation the body stretches and bends down before performing the jump. This wind-up action further adds to the believability of a jump showing the transfer of energy from standstill to mid-air.
Follow Through
Follow through actions are actions that help imply weight and gravity. For example, when looking at this jump animation it can be seen that once the body lands it does not just stop and stand but impacts and leans into a squatting position before beginning to stand. This adds realism in the fact that the momentum from the jump was carried into the landing and absorbed rather than disappearing entirely.
Secondary Action
Secondary actions are actions that support but do not detract from the main action. Take this rig that only has legs, the main action is that of walking. However, compare that to this full body rig, there is movement in the arms that emphasise the main action of walking but are not the sole focus of the animation.
The next 3 principles deal with appearance, with staging, exaggeration, and appeal playing big roles in an animation coming across as visually sound.
Staging
Staging is the presentation of an animation to give a clear and concise story. This includes the camera angles, long range and closeup shots, as well as including the background scenery. None of these aspects are to take the focus off the animation and draw attention elsewhere. In this scene of a ball jumping over a gap you can see that the background does not have much detail and the camera is set for a longer range shot to capture the whole animation without camera movement.
Exaggeration
Exaggeration is a way to add more life into realistic looking movements in a way that takes away the stiffness of photo-realistic movements. For example, this block pushing animation has exaggerated body movements in the final frames of each push adding the look of exertion even though a realistic looking scene may not have such an extended range of motion.
Appeal
Appeal works using charisma and emotion, having simple and easy to read movements all add to the appeal of an animation making it please to watch. In this push animation it is easy to see the person exerting themself in an easy to see way, whereas an animation with poor design or over-complicated visuals would detract from the main focus and take away form the appeal.
The last two principles of animation deal with methods of animation rather than the animations themselves.
Solid Drawing
Solid drawing is a method in which to add weight, volume, and solidity to an animation to give the sense of 3D space. A very common form of solid drawing in computer animating is the addition of shadows giving the added sense of three dimensions.
Straight-Ahead and Pose to Pose
Straight ahead and pose to pose are 2 differing methods of animation used in different circumstances to reach a desired effect. Straight ahead animation is a great way to add spontaneous and crazy actions where pose to pose is good for creating animations where timing and scale are important. In computer animation, pose to pose is often what is used to create realistic body movements such as jumping, walking, and pushing.
This unit has brought about a greater understanding of these twelve principles using practice exercises that emphasised different principles and has shown that even though they were based on the methods of the past, they are still the building blocks of today’s animation.
0 notes
Video
vimeo
Topic 12
Polished Walk Cycle
Reference
Spider-Man 3. (2007). [film] Directed by S. Raimi. Columbia Pictures.
vimeo
Stepped Key Frames
vimeo
0 notes
Video
vimeo
Topic 11
Walk Cycles
Stepped Key Frames For Legs Rig
vimeo
Polished Full Body Rig
vimeo
Stepped Key Frames For Full Body Rig
vimeo
0 notes
Video
vimeo
Topic 10
Weight Transfer
Stepped Key Frames For Legs Rig
vimeo
Polished Full Body Rig
vimeo
Stepped Key Frames For Full Body Rig
vimeo
0 notes
Video
vimeo
vimeo
Topic 9
Pushing and Lifting
Stepping Key Frames
vimeo
vimeo
0 notes
Video
vimeo
Topic 8
Polished Jump From Last Week
Refined in-betweens
vimeo
0 notes
Video
vimeo
Topic 7
Stepping Key Frames For A Jump
Video Reference
vimeo
0 notes
Video
vimeo
TOPIC 5
Ball jumping over a gap with a tail
EDITING PROCESS -
Blocking: Adding together the aspects of the ball jumping over the gap from topic 4 and adding in the basic rotations for the tail similar to the bouncing ball with a tail.
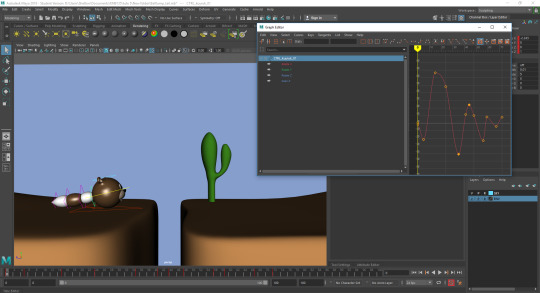
Polishing: Similarly to both the pendulum as well as the bouncing ball with a tail, the offset rotations were added in to each part of the tail to add the realism of the tail being pulled behind and impacted by both the body and the jumps.

0 notes
Video
vimeo
TOPIC 5
Bouncing tail
EDITING PROCESS -
Blocking: Adding the basic movements of the bouncing ball as well as the momentum swinging aspects of the pendulum.
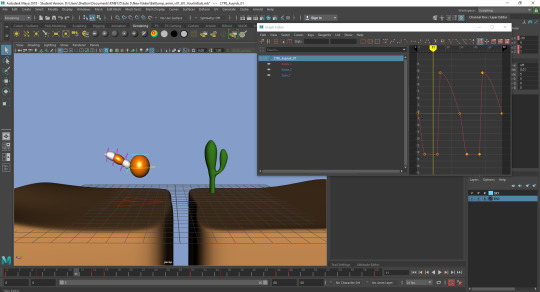
Polishing: Like the pendulum, adding offset rotation to each part of the tail to simulate realism in the tail falling and being pulled behind the balls movements.
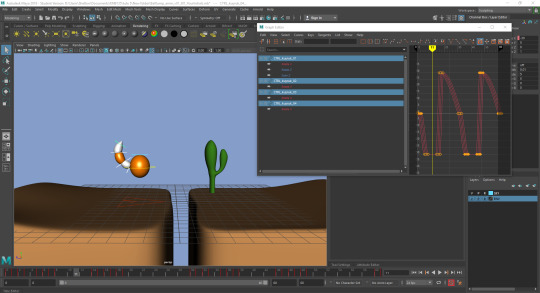
0 notes
Video
vimeo
TOPIC 5
Ultimate pendulum swing
EDITING PROCESS -
Blocking: Adding both side to side movement on the X axis as well as basic rotation from the pendulum around the X axis.

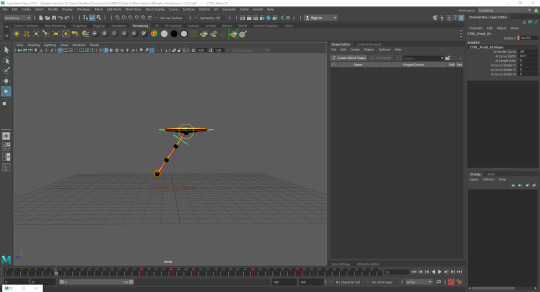
Polishing:Adding in rotation to all parts of the pendulum segmented a frame apart to imitate momentum carrying the pendulum behind the top part each time it moves. Also adding a stopping animation demonstrating the overshooting of the pendulum back and forth until it comes to a stop.

0 notes
Video
vimeo
TOPIC 4
Ball jumping over a gap
EDITING PROCESS -
Blocking: Adding the basic jump movement as well as directional movement over the gap.
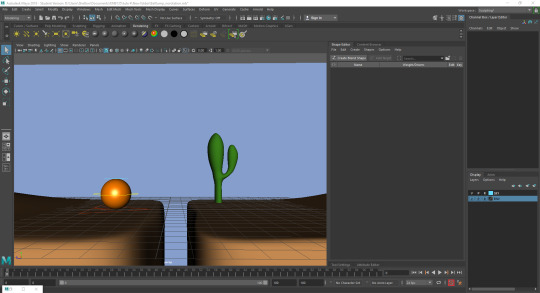


Polishing: Adding squash and stretch as well as rotation to imitate leaning forward and landing as well as adding weight to the ball bounces.
0 notes
Video
vimeo
TOPIC 4
Blinking
EDITING PROCESS -
Blocking: Editing the basic eyelid and eyebrow movement constituted in a blink.

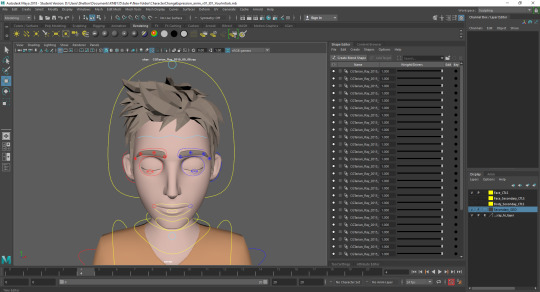
Polishing: Adding a squash and stretch effect to add life to the simply but important animation.
0 notes
Video
vimeo
TOPIC 3
Surprised head turn
EDITING PROCESS -
Blocking, Refining, and Polishing with the same methods as the relaxed head turn. The main difference in the animation being the speed of the head turn as well as the varied expression imitating shock.
0 notes
Video
vimeo
TOPIC 3
Relaxed head turn
EDITING PROCESS -
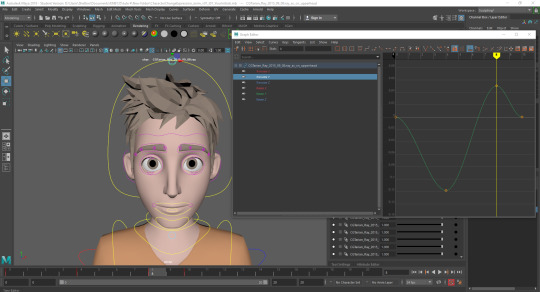
Blocking: Starting with basic movement between poses, start and finish.
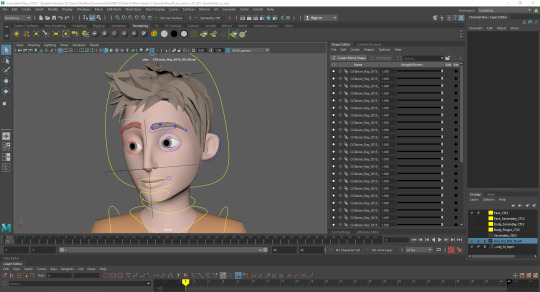
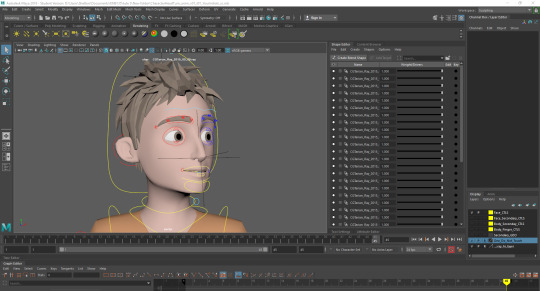
Refining: Adding poses between the first and last to add life into the character with eyelid and eyeball movement as eyebrows and head tilt.

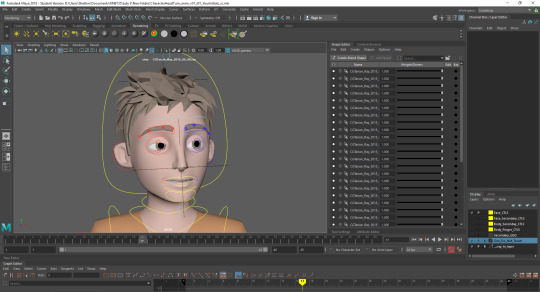
Polishing:Editing the movement curves to bring the main part of the head turn down to a few frames leaving the rest of the time to accentuate the relaxed nature of the characters movements. Also adding in head squash during the turn to add more life into the animation as well as add a moving hold at the end.

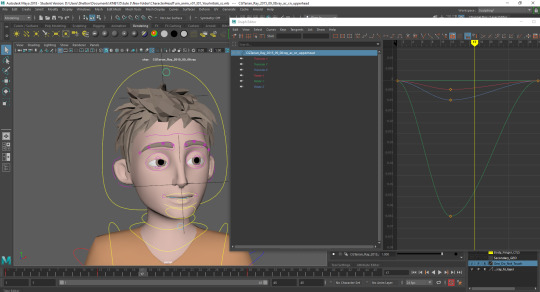
0 notes
Video
vimeo
TOPIC 3
Pendulum Swing
EDITING PROCESS -
Blocking: Adding rotation around the Z axis to mimic a pendulum motion from left to right and back again.

Polishing: Editing the motion curves to make the pendulum slower in the peaks of each swing to give the impression of losing and gaining momentum.

0 notes
Video
vimeo
TOPIC 2 (CONTINUED)
Ping-pong ball bouncing across screen. (above)
Soccer ball bouncing across screen. (below)
vimeo
Bowling ball bouncing across screen.
vimeo
EDITING PROCESS -
Taking the previous bouncing on the spot animation, movement was added to the X axis and then refined to have the ball slow down towards the end of the movement mimicking a loss of momentum.

0 notes