Text
Turn Off Google Maps Location History

WATCHING YOUR EVERY MOVE How to see Google’s creepy map showing EVERYWHERE you’ve ever been – and how to turn it off
Google may have been tracking every movement you make GOOGLE may be keeping a detailed record of your exact movements – and it's easy to find out how. It's also possible that Google is tracking your movements and you didn't even realise you'd signed up for it. If that's the case, we'll reveal how to turn tracking off immediately. Computer Forensics & Mobile Phone Forensics even if the history is turned off we can use this hidden data to aid in Police Investigations or to prove potential innocence. What is Google Location History? Google's Location History is an account-wide service that tracks your movements using your smartphone. It'll record your real-world movements if you're signed into your Google account, Location History is turned on, and Location Reporting is turned on. The idea is that Google can provide you with better services if it knows where you've been. For instance, it can give you more detailed commute advice, recommendations based on places you've visited, and more useful advertisements. You can turn off Google Location Tracking to stop the company recording a detailed map of your travels But not everyone wants Google to keep an ongoing record of their movements. After all, there are major privacy risks when it comes to storing details of everywhere you've ever been online. That's why Google Location History is turned off by default, and is only activated with your permission. However, it's common for users to accidentally enable Google Location History through the Google Maps app, without realising exactly what they've signed up to. Google can map your exact locations over time
How to check your Google Location History There are several ways to check your own Google Location History. The easiest way is to follow the link to the Google Maps Timeline page: https://www.google.com/maps/timeline?pb This lets you see exactly where you've been on a given day, even tracking your methods of travel and the times you were at certain locations. Alternatively, if you've got the Google Maps app, launch it and press the hamburger icon – three horizontal lines stacked on top of each other. Then go to the Your Timeline tab, which will show places you've previously visited on a given day. If you've had Google Location History turned on for a few years without realising, this might be quite shocking. Suddenly finding out that Google has an extremely detailed map of years of your real-world movements can seem creepy – so you might want to turn the feature off. You should be careful about what information you give Google permission to track
How to turn Google Location History off The good news is that it's possible to immediately turn Google Location History off at any time. You can turn off Location History here: Click here However, to truly stop Google from tracking you, you'll also need to turn off Web & Activity Tracking. You can see your tracked location markers here: Click here to see locations You'll also need to turn off Web and App Activity tracking to truly prevent Google from nabbing your location Unfortunately, these location markers are intermingled with a host of other information, so it's tricky to locate (and delete them). To turn it off, simply click the above link then head to Activity Controls. From there, you'll be able to turn off Web & Activity Tracking across all Google sites, apps and services. https://www.thesun.co.uk/tech/8504769/google-maps-location-history-turn-off-timeline/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Stopping Gang Violence with Digital Forensics

Using Mobile Phone, Computer & Digital Forensics to Help Combat Gang Activity
We see them almost every day on the news. The sad stories of yet another innocent bystander shot or stabbed during gang-related activities. Digital Forensics, Computer Forensics & Mobile Phone Forensics are often used in Police Investigations to aid in convictions. …or the child who will never walk again because they were struck by an errant bullet, as a result of another gang shooting. …or the story of another innocent life taken before their time; the violence happening with such stomach-churning repetition that we have now become…with apologies to Pink Floyd, “comfortably numb.” It’s time to bring the power of digital intelligence into the bare-knuckled fight against gang-related crime. As Gang Membership Rises, Violence Follows Statistically, the news is grim. Gang membership worldwide is up: Up to 10-million gang members are reported worldwide More than 33,000 gangs (1.4-million gang members) are said to reside in the US alone And gang-related crimes are not just a US issue with over 5,000 gangs reported operating in Europe in 2017, alone. Not surprising, as the number of gang members rise, the volume of: 50% of homicides in Los Angeles and Chicago are now reported as being gang-related 75% of police agencies report gangs as the No. 1 contributing factor to violent crimes Social Media—The New Spray Paint It took no time for gang members to figure out how to use Social media to their advantage. Now, instead of marking turf by spray-painting walls, gang members are using virtual walls to paint on—threatening revival gang members in “cyber-banging’s” and enticing new recruits to “come see us on Facebook.” Social media has also become a convenient way for gangs to do business with online drug trafficking said to be topping $25-million a month in sales. Encryption Is Making Things More Complex Law enforcement must not only contend with ever-increasing volumes of information online, but gang members are quickly learning how to lock up their mobile devices and use encrypted channels to hide their tracks. Add to this the problems of tracking gang activities internationally across dozens of countries and networks, and the job becomes even more difficult—straining investigative staffs to their limits and leaving more and more team members to feel like they’re drowning in information. Digital Intelligence Simplifies Complexity We can help Law Enforcement agencies around the world fight back with digital intelligence software that can give investigators the edge; helping them to deal with the volume, variety, and velocity at which gang-related data is being exchanged. Services Available: Unlock mobile devices. Access encrypted data. Unify large volumes of data sources and quickly reveal gang networks. Gather intel from known online and social media accounts. Visualize gang member connections, relationships and map their locations. Automatically categorize and analyze media files for quick identification. Tag and share findings to collaborate across jurisdictional boundaries. Keep pace with the growing technological sophistication of organized crime groups. Expedite their investigative strategies. Visually map crime rings. Gather actionable evidence to help prosecutions build solid cases. This allows agencies to more effectively focus their resources on larger, underlying criminal networks rather than on individual crimes—which in turn helps those on the front lines to create a safer world.

Read the full article
0 notes
Text
The reason Tumblr vanished from the App Store: Child pornography that slipped through the filters

In November 2018 Tumblr's app mysteriously disappeared from Apple's App Store
This was due to Indecent Images of Children (IIOC) slipping through their filters Computer Forensics & Mobile Phone Forensics are often used in Police & Defence Cases to Investigate any incident involving Indecent Images of Children (IIOC). Those of you who were looking to download the Tumblr app on your iPhone or iPad were unable to get it in November 2018. But the app's vanishing act isn't the result of a technical issue or glitch. Through independent sources, Download.com learned that the app was removed due to child pornography that got past the site's filters. When Download.com presented these findings to Tumblr, a company spokesperson responded with the following statement: "We're committed to helping build a safe online environment for all users, and we have a zero tolerance policy when it comes to media featuring child sexual exploitation and abuse. As this is an industry-wide problem, we work collaboratively with our industry peers and partners like (NCMEC) to actively monitor content uploaded to the platform. Every image uploaded to Tumblr is scanned against an industry database of known child sexual abuse material, and images that are detected never reach the platform. A routine audit discovered content on our platform that had not yet been included in the industry database. We immediately removed this content. Content safeguards are a challenging aspect of operating scaled platforms. We're continuously assessing further steps we can take to improve and there is no higher priority for our team." This confirmation helps explain why the Tumblr app was removed so suddenly and why there was little explanation from Tumblr or from Apple, since child pornography is a matter that needs to be coordinated with law enforcement. In the following statement sent to Download.com, a spokesperson for the NCMEC explained the role that the organization serves in fighting online child pornography and exploitation "The National Center for Missing & Exploited Children operates the CyberTipline, which serves as the nation's centralized reporting system for online child sexual exploitation. Members of the public and Electronic Service Providers (ESPs) report instances of online child sexual exploitation to the CyberTipline. Last year, NCMEC received more than 10 million reports to its CyberTipline with the vast majority of those reports submitted by ESPs. NCMEC recognizes that global efforts to reduce the proliferation of online child sexual exploitation online requires an industry-wide effort and applauds all ESPs that engage in voluntary efforts to provide content safeguards for their users. In addition to receiving reports from ESPs, any member of the public who comes across suspected child abuse imagery is encouraged to make a CyberTipline report to NCMEC. In a follow-up statement, the NCMEC spokesperson also explained the specific steps that Electronic Service Providers such as Tumblr take to try to block child pornography. "NCMEC offers several voluntary initiatives to ESPs who choose to take extra steps to reduce the distribution of online sexual abuse material on their systems. One of NCMEC's initiatives involves facilitating the sharing of hashes of apparent child pornography images among ESPs. Some ESPs and social networks will participate in this initiative to reduce child sexual exploitation images online and some ESPs will rely on other programs and methods to remove such illegal content from their servers." Tumblr's disappearance was first spotted by PiunikaWeb, which reported on November 16 that users with the iOS parent control features enabled were unable to find the app. Shortly after that, the app vanished completely from the App Store. Tumblr's help center site noted the disappearance in a statement: "We're working to resolve an issue with the iOS app and hope to be fully functional again soon. We really appreciate your patience as we figure this out, and we'll update this article when we have news to share," the company said. Through November 18, the company's message on its help center was that its team was still working on the issue with the app. After this article was first published on November 19, Tumblr updated it to include the statement above that its spokesperson presented to Download.com. Initially, neither Tumblr nor Apple publicly revealed the nature of the "issue." But speculation from a marketing professional on Twitter and 9to5Mac had suggested the app was removed due to inappropriate content in violation of Apple's App Store guidelines. This isn't the first time Tumblr has run into this type of problem. In March 2018, the Indonesian government briefly blocked Tumblr over the company's failure to remove pornographic content from its service. In 2017, South Korea asked Tumblr to take down certain pornographic content. The company initially rejected that request but eventually promised to better monitor the spread of adult content. Download.com contacted Apple and will add to this story with any updates. For now, iOS users who previously downloaded Tumblr may be able to get it again by checking the purchase history on their device. iPhone and iPad owners who want to use Tumblr for the first time will have to wait until the app is reinstated. The app is still available at Google Play for Android users.
Takeaways
The Tumblr app was removed from the Apple App Store because of child pornography that slipped through the company's content filters. Tumblr has removed the offending content and is working with Apple to get the app reinstated. In the meantime, the app remains unavailable to download from the App Store. Computer Forensics & Mobile Phone Forensics are often used in Police & Defence Cases to Investigate any incident involving Indecent Images of Children (IIOC).

https://download.cnet.com/news/the-reason-tumblr-vanished-from-the-app-store-child-pornography-that-slipped-through-the-filters/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Open Source Intelligence - Beyond Salisbury: Identifying Russian intelligence operations

The investigative journalists at Russian news site The Insider are aiming to uncover more Russian military intelligence operations after identifying the GRU agency officers behind the Salisbury chemical weapon attack.
"We're not very focused on Salisbury. We know this will be covered by British authorities," said Roman Dobrokhotov, The Insider's chief editor. Open Source Intelligence / Research, Computer Forensics & Mobile Phone Forensics are often used in Police Investigations to aid in convictions. "They have all the CCTV and from the beginning, they knew real names," he added. It isn't yet clear whether the UK government will release all that they know. In the meantime, The Insider, alongside UK-based investigative organisation Bellingcat, have been filling in the gaps.

Image: Roman Dobrokhotov, chief editor of The Insider They recently revealed the identity of a third GRU operative, Denis Sergeev. They believe Sergeev called the shots during the Salisbury operation and may have been involved in at least one other poisoning in Bulgaria. "What we are interested in is finding other operations of Sergeev or other GRU agents in Europe, trying to piece together their travels with other strange events happening in those countries," he says. He thinks there are more GRU operations that have yet to come to light.

Image: The GRU military intelligence agency is accused of downing the Malaysian airliner MH17 in 2014 "The (Russian) authorities actually helped us with our investigation," Mr Dobrokhotov said. "At first we saw documents of Sergeev on different databases - traffic police and all sorts of other databases, but then suddenly they disappeared. This was another proof for us this person was the right person." It takes guts to expose Russian military intelligence from the centre of Moscow. The Insider is a team of just 13 but they are giving the GRU a run for their money - uncovering their trace in the coup in Montenegro, the downing of Malaysian airliner MH17 and most recently in Salisbury, through meticulous cross-referencing of names, databases, and travel itineraries.

Image: Just thirteen staff work for The Insider Mr Dobrokhotov said that the journalists who work for The Insider "have no real choice" when it comes to avoiding topics that might be considered dangerous, such as uncovering the work of the GRU. "If we want to be journalists and investigate real important topics in our country, we have to touch these stories of MH17, the Salisbury attack, Russian hackers," he said. "We just follow the interesting stories and suddenly at the end, we always see GRU there - we don't hunt GRU, it just happens like this. "Because they're super active, it's a new Russian foreign strategy, when they use their military to interfere in politics in other countries, and they are not very good at conspiracy. That's why we always find them."

Image: GRU headquarters in Russia was used as an address for supposedly covert identities The Russian government's line on Bellingcat is that it is an arm of the British government, drip-feeding false information to slur Russia's name. The Insider is never mentioned. The GRU operatives who are believed to have conducted the chemical weapon attack in Salisbury have gone to ground since their infamous if unconvincing interview on Russian state broadcaster RT.

Image: The GRU operatives went to ground after their RT interview The constant refrain from Russian officials, if one is identifiable in amongst the chorus of conspiracy, is that nothing they've seen so far constitutes proof. They argue that if the UK has more convincing evidence (than CCTV of two Russian men making return trips to Salisbury out of love for its cathedral spire whilst leaving traces of novichok in their wake), then it should be made public. The British ambassador to Russia, Laurie Bristow, told me: "I think the Russian government knows perfectly well what happened in Salisbury. They're using disinformation techniques to obscure what actually happened." But the British government will not reveal the full picture at this stage, he said, partly because the investigation is ongoing and because of evidence that should one day be tested in court.

Image: Mr Bristow said the UK will only present its evidence in court "We have put quite a lot of information out to the public but essentially the administration of justice in the UK takes absolute priority here," Mr Bristow said. "We need to be able to bring those suspects to trial, a fair trial in a court to look at what actually happened and decide whether they were guilty." That's wishful thinking. Russia won't extradite its citizens for trial in the UK. The UK sees no reason to offer up further evidence to Russia. That was entirely clear in the days after Salisbury and nothing has changed since.

Image: Members of the military in Salisbury after the March 2018 poisoning Which means UK - Russian relations have seen precious little improvement in the year since the Skripal poisoning. Once the police investigation into Salisbury and Amesbury has wrapped up, the British public has a right to know as much as police are able to tell, whether or not they ever get to see Russia's spire-loving military intelligence officers in the dock. Until then, Bellingcat and The Insider are all we've got shining light on this chemical weapon attack on British soil. This leaves us in a hard place. It is hard to move on after a foreign state uses chemical weapons for attacks on British soil. It is hard to move on after the apparent carelessness of foreign intelligence agents in a plot to assassinate one of their own ends up killing a British citizen. It is hard to move on when this has happened before - the last time with a radiological agent, polonium, which left highly radioactive traces across London. It is hard to move on when the foreign state in question professes to be the injured party, unfairly maligned. "We need to be realistic. Nothing fundamental has changed in Russia", Mr Bristow told me. "It's not going to be possible to create a normal relationship with a country that does this kind of thing, but as the prime minister has said a number of times now that's not the relationship that we want." https://news.sky.com/story/beyond-salisbury-identifying-russian-intelligence-operations-11653304 Read the full article
0 notes
Text
YouTube is disabling comments on all content featuring minors

Recently YouTube has been making a lot of changes to reflect public concerns such as the exploitation of minors, exposure to sexual predators, and spreading incorrect or harmful information
The number of children targeted for grooming and abuse on Instagram has more than tripled - with some of the victims as young as five years old. Recently YouTube has been making a lot of changes to reflect public concerns such as the exploitation of minors, exposure to sexual predators, and spreading incorrect or harmful information such as anti-vaccine theories and flat-earth conspiracies. Apart from reviewing and subsequently deleting countless inappropriate comments and accounts on videos featuring minors last Friday, the video-sharing platform also disclosed plans to disable comments temporarily on thousands of such clips and demonetize them. Today the video-based social media giant announced several new policies that will be implemented in order to further protect underage persons from pedophilic abuse on the platform. One of the steps taken by YouTube in the latest update to its child safety initiative includes blocking the comment section for good on all videos that show younger as well as older minors. Only a select few creators will be allowed to enable comments on their content, subject to the condition that they monitor and moderate the comment section themselves in addition to the pre-existing tools already provided by the platform and "demonstrate a low risk of predatory behavior" as a measure of safety and protection for the children. YouTube is also planning on launching a new comments classifier which will essentially do what the company has been doing itself as well as urging other members of the community to do: scrutinize comments across the platform to search, locate, report and finally remove comments that are inappropriately sexual or predatory in nature. Apparently, the new classifier is twice as better as the previous one, and will not alter the monetization of content in any way. The third and final point made in the blog post was an appeal to the viewers as well as the creators of content on the video-sharing platform, encouraging them to actively participate in protecting underage children by flagging any harmful or dangerous comments, videos or channels that violate YouTube's child safety regulations. Computer Forensics & Mobile Phone Forensics are often used in Police Investigations to aid in grooming convictions. After beginning the process of disabling comments on videos featuring young minors on its platform last week, YouTube have decided to extend the block to those with older minors, in an effort to curb predatory behaviour on its site. Over the past week, YouTube said it suspended comments from tens of millions of videos that had posed risks to such behaviour. The extension, which will see children up to the age of 18 covered, will come into place over the next few months. "A small number of creators will be able to keep comments enabled on these types of videos," YouTube said in a blog post. "These channels will be required to actively moderate their comments, beyond just using our moderation tools, and demonstrate a low risk of predatory behaviour." See also: How to make YouTube Kids safer for your children (CNET) YouTube said it would work with creators directly, with the goal of growing the number over time as it improves its ability to catch inappropriate comments. The Alphabet-owned company is also launching a new comments classifier that will identify and remove predatory comments, with YouTube promising the detection and consequential removal of twice as many comments. Additionally, YouTube said it intends to take action on creators who cause "egregious harm" to the community. "No form of content that endangers minors is acceptable on YouTube, which is why we have terminated certain channels that attempt to endanger children in any way," the blog continued. "Videos encouraging harmful and dangerous challenges targeting any audience are also clearly against our policies. We will continue to take action when creators violate our policies in ways that blatantly harm the broader user and creator community." YouTube has classified the following as harmful content: Sexualisation of minors, which includes sexually explicit content featuring minors and content that sexually exploits minors; harmful or dangerous acts involving minors, such as that showing a minor participating in dangerous activity, or encouraging minors to engage in dangerous activities; infliction of emotional distress on minors, including content that could cause participants or viewers distress; misleading family content, videos misleading viewers by appearing to be family content, but containing sexual themes, violence, obscene, or other mature themes not suitable for young audiences; and cyberbullying and harassment involving minors. If content violates YouTube's policy, it will be removed and an email will be sent to the creator. A warning for a first offence will be given, with no penalty. Once three strikes have been tallied, the channel will be terminated. YouTube last week had already begun limiting the monetisation of videos that include minors, with those flagged as at risk receiving limited or no ads, and made known through the use of a yellow icon. Source: YouTube https://www.neowin.net/news/youtube-is-going-to-disable-comments-on-all-content-featuring-minors https://www.zdnet.com/article/youtube-to-disable-comments-on-videos-featuring-all-minors/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Police figures show that cases of children being groomed on Instagram triple

The NSPCC says the figures are "overwhelming evidence that keeping children safe cannot be left to social networks".
The number of children targeted for grooming and abuse on Instagram has more than tripled - with some of the victims as young as five years old. Figures obtained by the NSPCC suggest there were 5,161 reports of sexual communications with a child recorded in just 18 months. Facebook, Snapchat and Instagram were used in 70% of those incidents. Girls aged 12 to 15 were most likely to be targeted, but roughly one in five victims were under the age of 11. The NSPCC's chief executive, Peter Wanless, has accused social media firms of "10 years of failed self-regulation". He said: "These figures are overwhelming evidence that keeping children safe cannot be left to social networks." The charity obtained freedom of information data from 39 of the 43 police forces in England and Wales. Computer Forensics & Mobile Phone Forensics are often used in Police Investigations to aid in convictions. In incidents where police recorded the method used to contact a child, Instagram was used by groomers 126 times between April and September 2017. This increased to 428 for the same period last year. The figures come amid growing criticism of how social networks protect the children using their platforms. The government is due to release a white paper about online harms, and the NSPCC hopes this will include new laws to tackle grooming. Mr Wanless warned: "We cannot wait for the next tragedy before tech companies are made to act. "It is hugely concerning to see the sharp spike in grooming offences on Instagram, and it is vital that the platform designs basic protection more carefully into the service it offers young people."

Image:Girls aged 12 to 15 were the most likely targets One victim told the NSPCC of how she was groomed by a 24-year-old man when she was just 13. She had met him in person through a friend and he initially said he was 16, then 18, before he added her on Facebook and Snapchat the same evening. The girl said it "escalated very quickly" before he encouraged her to share photos of herself and meet for sex after school. She added: "He drove me somewhere quiet... and took me into the woods and had sex with me. "He drove me in the direction of home straight afterwards, refusing to even talk, and then kicked me out of the car at the traffic lights. I was bleeding and crying." The girl's mother added: "Somebody has got to take responsibility for what happens to children on their platforms. Simply put, if social media didn't exist, this would never have happened." A National Crime Agency spokesman said: "It is vital that online platforms used by children and young people have in place robust mechanisms and processes to prevent, identify and report sexual exploitation and abuse, including online grooming. "Children and young people also need easy access to mechanisms allowing them to alert platforms to potential offending." A spokesperson for Facebook and Instagram said: "Keeping young people safe on our platforms is our top priority and child exploitation of any kind is not allowed. "We use advanced technology and work closely with the police and CEOP to aggressively fight this type of content and protect young people." On Thursday, YouTube announced it is disabling comments on videos featuring children after a vlogger alleged he had found instances of paedophiles targeting videos of young girls on the site. Children as young as five years old are being targeted for grooming on Instagramwhere attempts have more than tripled, the NPCC has warned. More than 5,100 online grooming crimes were recorded by police in just 18 months after a new offence of sexual communication with a child came into force, figures show. In cases where officers recorded how victims were contacted, Facebook, Snapchat and Instagram were used 70 per cent of the time, according to the data obtained by the NSPCC, with Instagram accounting for 33 per cent. The charity’s chief executive, Peter Wanless, accused social media firms of “10 years of failed self-regulation”. “These figures are overwhelming evidence that keeping children safe cannot be left to social networks,” he said. He added: “It is hugely concerning to see the sharp spike in grooming offences on Instagram, and it is vital that the platform designs basic protection more carefully into the service it offers young people.” Facebook was the second most common platform chosen by groomers, used in 23 per cent of offices, followed by Snapchat which was the platform used in 14 per cent of crimes. The data runs from April 2017, when the law was changed, and September 2018 and was obtained through freedom of information requests to 39 of the 43 police forces in England and Wales. In most instances, police forces did not record which particular website or app was used to groom the victim. But where they did, a steep increase in the use of Instagram was observed. In the first six months since the law came into force, from April to September 2017, there were 126 recorded instances of Instagram being used to sexually groom a child. Just one year later during the same time period, that number rose to 428, a 240-per-cent increase. According to the NSPCC data, the most common target of online groomers were girls aged 12 to 15. One in five victims, however, were aged under 11. Children as young as five were recorded as victims in some instances. The government is due to publish a white paper on internet safety before the end of winter and Mr Wanless said it was vital it included tough new regulation. The NSPCC is campaigning for tech firms to be given a legal duty of care to children who use their platforms and for large fines to be imposed on them when they fail to protect under-18s. One mother of a 13-year-old girl who was groomed by a 24-year-old man over Facebook and Snapchat said if social media had not existed her daughter would have been spared her ordeal. “We felt as though we had failed as parents – we knew about these social media sites, we thought we were doing everything we could to ensure our children’s safety when they were online, but we still couldn’t protect her. “Somebody has got to take responsibility for what happens to children on their platforms. Simply put, if social media didn’t exist, this would never have happened to her.” The white paper on internet safety was originally meant to have been published by the end of 2018, although that deadline later slipped to the end of the winter. In February, a spokesperson for the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport, said it had “heard” demands for an internet regulator and statutory duty of care and was “seriously considering all options”. A National Crime Agency spokesperson said: “It is vital that online platforms used by children and young people have in place robust mechanisms and processes to prevent, identify and report sexual exploitation and abuse, including online grooming. “Children and young people also need easy access to mechanisms allowing them to alert platforms to potential offending. “The National Crime Agency helps industry to enhance their reporting tools and where possible, shares knowledge and expertise to support industry to improve standards and security online.” https://news.sky.com/story/instagram-grooming-of-children-as-young-as-five-triples-11651339 https://www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/crime/instagram-grooming-sex-crime-police-report-nspcc-children-a8801876.html Read the full article
0 notes
Text
No evidence of any threat to children from 'Momo challenge' #fakenews

Viral 'Momo challenge' is a malicious hoax, say charities. Groups say no evidence yet of self-harm from craze, but resulting hysteria poses a risk

There is no evidence the so-called "Momo challenge" poses any threat to British children, a minister has said. Speaking in the Commons, Andrea Leadsom pointed out that children's charities have said reports of a ghoulish figure being linked to messages urging recipients to self-harm or take their own lives are a hoax. Conservative MP Douglas Ross raised the matter on Wednesday, asking for a debate on online safety following messages from worried constituents. He said: "Can we have a debate and allow the government to explain what more we can do to protect and educate young people about the scourge of these online dangers?" It comes after a report in The Guardian detailed how the "moral panic" has spread online, fuelled by viral news stories and warnings from police forces and schools. Commons leader Mrs Leadsom said the "appalling" challenge was "one the government is extremely concerned about", adding ministers were drawing up legislation to compel internet companies to take action to safeguard vulnerable users, particularly children. She said charities had told her there was "no confirmed evidence" it had caused any children in the UK to self-harm. It is the most talked about viral scare story of the year so far, blamed for child suicides and violent attacks – but experts and charities have warned that the “Momo challenge” is nothing but a “moral panic” spread by adults. Warnings about the supposed Momo challenge suggest that children are being encouraged to kill themselves or commit violent acts after receiving messages on messaging service WhatsApp from users with a profile picture of a distorted image of a woman with bulging eyes. News stories about the Momo challenge have also attracted hundreds of thousands of shares on Facebook in a 24-hour period, dominating the list of UK news stories ranked by number of interactions on the social network. There have also been claims that the material has appeared in a video featuring Peppa Pig among YouTube’s content aimed at children. But the Samaritans and the NSPCC have dismissed the claims, saying that while there is no evidence that the Momo challenge has initially caused any harm itself, the ensuing media hysteria could now be putting vulnerable people at risk by encouraging them to think of self-harm. The UK Safer Internet Centre called the claims “fake news”. And YouTube said it had seen no evidence of videos showing or promoting the Momo challenge on its platform. The NSPCC said there is no confirmed evidence that the phenomenon is actually posing a threat to British children and said they have received more phone calls about it from members of the media than concerned parents. A Samaritans spokesperson was similarly sceptical, saying: “These stories being highly publicised and starting a panic means vulnerable people get to know about it and that creates a risk.” They recommended media outlets read their guidelines on reporting suicide and suggested press coverage is “raising the risk of harm”. “Currently we’re not aware of any verified evidence in this country or beyond linking Momo to suicide,” said the Samaritans spokesperson. “What’s more important is parents and people who work with children concentrate on broad online safety guidelines.” Child safety campaigners say the story has spread due to legitimate concerns about online child safety, the sharing of unverified material on local Facebook groups, and official comments from British police forces and schools which are based on little hard evidence. While some concerned members of the public have rushed to share posts warning of the suicide risk, there are fears that they have exacerbated the situation by scaring children and spreading the images and the association with self-harm. “Even though it’s done with best intentions, publicising this issue has only piqued curiosity among young people,” said Kat Tremlett, harmful content manager at the UK Safer Internet Centre. The rumour mill appears to have created a feedback loop, where news coverage of the Momo challenge is prompting schools or the police to warn about the supposed risks posed by the Momo challenge, which has, in turn, produced more news stories warning about the challenge. Tremlett said she was now hearing of children who are “white with worry” as a result of media coverage about a supposed threat that did not previously exist. “It’s a myth that is perpetuated into being some kind of reality,” she said. Although the Momo challenge has been circulating on social media and among schoolchildren in various forms since last year, the recent coverage appears to have started with a single warning posted by a mother on a Facebook group for residents of Westhoughton, a small Lancashire town on the edge of Bolton. This post, based on an anecdote she had heard from her son at school, went viral before being picked up by her local newspaper and then covered by outlets from around the world. The supernatural “Momo” image, originally from an artwork made for a Japanese horror show exhibition, has been circulating on the internet for several years but last summer became attached to unverified claims that teenagers were being prompted to kill or harm themselves by messages on WhatsApp. Many campaigners in the child safety sector have been reluctant to issue statements for fear of fanning the flames of the story but are changing direction after seeing the sheer number of dubious stories written to attract clicks on the issue. Hundreds of separate articles have been written on the topic by British news websites in the last three days, dominating the most-read lists on tabloid news sites. These include explainers for concerned parents on how to protect children from the supposed risks of the challenge and claims about the acts that children are supposedly committing after seeing the images. Celebrities such as Stacey Solomon have weighed in and expressed their concerns, creating even more justifications for headlines. Multiple police forces have issued formal warnings about the supposed risks of the Momo challenge, in addition to hundreds of schools. In one example, a Hull primary school posted on its Facebook page an unsourced claim that clips of the Momo challenge image are “hacking into children’s programmes”, with no evidence of what is meant by this claim. A YouTube spokesperson said the claims were completely false: “Contrary to press reports, we have not received any evidence of videos showing or promoting the Momo challenge on YouTube. Content of this kind would be in violation of our policies and removed immediately.” Several outlets, including the Mirror and many local newspapers, have also claimed that the Momo game has been linked to 130 teen suicides in Russia, with no supporting evidence. An identical claim was made in 2017 about a similar supposed viral suicide craze called Blue Whale, which was also linked to exactly 130 teen suicides in Russia. This figures came from a much-criticised single report in the Novaya Gazeta newspaper, with later reporting suggesting that not a single death could be conclusively linked to the game. “We almost need to stop talking about the issue for it to not be an issue any more,” said Tremlett. In the UK, Samaritans can be contacted on 116 123 or email [email protected]. In the US, the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline is 1-800-273-8255. In Australia, the crisis support service Lifeline is 13 11 14. Other international suicide helplines can be found at www.befrienders.org.

Following a flurry of scare stories, some schools have warned parents about the "momo challenge" - but fact-checkers say it is a hoax. The original tale said a character with bulging eyes would "hack" into WhatsApp and set children dangerous "challenges" such as harming themselves. Charities say there have been no reports of anybody being "hacked" or harming themselves as a result. But the image is now being shared on social media to frighten children. It has been found edited into unofficial copies of children's cartoons such as Peppa Pig on YouTube. "News coverage of the momo challenge is prompting schools or the police to warn about the supposed risks posed by the momo challenge, which has in turn produced more news stories warning about the challenge," said the Guardian media editor Jim Waterson.
What is 'momo'?
In February, versions of the momo story went viral on social media. They attracted hundreds of thousands of shares and resulted in news stories reporting the tale. According to the story, children are contacted on WhatsApp by an account claiming to be momo. Some versions of the tale suggested "hackers" made the image appear on the phone unexpectedly. Children are supposedly encouraged to save the character as a contact and are then asked to carry out challenges, as well as being told not to tell other members of their family. The UK Safer Internet Centre told the Guardian that it was "fake news". However, unofficial copies of cartoons such as Peppa Pig have been uploaded to YouTube with footage of "momo" edited in. Children watching unofficial uploads may therefore be exposed to the distressing images. Several articles claimed the momo challenge had been "linked" to the deaths of 130 teenagers in Russia. The reports have not been corroborated by the relevant authorities. On Wednesday, police in Northern Ireland sought to reassure parents about the doll figure with bulging eyes. The image of momo is actually a photo of a sculpture by Japanese special-effects company Link Factory. According to pop-culture website Know Your Meme, it first gained attention in 2016.
'Urban legend'
Fact-checking website Snopes suggested the story was "far more hype or hoax than reality", but warned the images could still cause distress to children. "The subject has generated rumours that in themselves can be cause for concern among children," wrote David Mikkelson on the site. Police in the UK have not reported any instances of children harming themselves due to the momo meme. The charity Samaritans said it was "not aware of any verified evidence in this country or beyond" linking the momo meme to self-harm. The NSPCC told the Guardian it had received more calls from newspapers than from concerned parents.
What should parents do?
Police have suggested that rather than focusing on the specific momo meme, parents could use the opportunity to educate children about internet safety, as well as having an open conversation about what children are accessing. "This is merely a current, attention-grabbing example of the minefield that is online communication for kids," wrote the Police Service of Northern Ireland, in a Facebook post. Broadcaster Andy Robertson, who creates videos online as Geek Dad, said in a podcast that parents should not "share warnings that perpetuate and mythologise the story". "A better focus is good positive advice for children, setting up technology appropriately and taking an interest in their online interactions," he said. To avoid causing unnecessary alarm, parents should also be careful about sharing news articles with other adults that perpetuate the myth. https://news.sky.com/story/no-evidence-of-any-threat-to-children-from-momo-challenge-says-minister-11651141 https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2019/feb/28/viral-momo-challenge-is-a-malicious-hoax-say-charities https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology-47393510 Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Europol’s Asian City Child Abuse Photographs Geolocated | Bellingcat

Since 2017 the European Union Agency of Law Enforcement Cooperation, better known as Europol, has been crowdsourcing parts of or heavily censored photographs, related to child abuse crimes in their “Stop Child Abuse – Trace an Object” campaign.
Classifying IIOC for both Mobile Phone Forensics and Computer Forensics is a daily activity when it comes to Digital Forensics. Since 2017 the European Union Agency of Law Enforcement Cooperation, better known as Europol, has been crowdsourcing parts of or heavily censored photographs, related to child abuse crimes in their “Stop Child Abuse – Trace an Object” campaign. Within two weeks after the start of their campaign Europol received 10.000 contributions from the public. Bellingcat, among many others, shared this campaign on the crowdsourcing platform Check. Many followers of this campaign have helped by identifying objects and/or geolocating photographs. The location of a photograph in a hotel room was proved to be taken in a hotel on Mauritius within 48 hours after Europol shared the photograph on Twitter. Europol published a press release on the success of their campaign earlier this year and mentioned that out of 70 objects, 25 of them were identified to one country or else to a reasonable number of countries of production and on 1 June 2018, one year after the start of the campaign, a press release describes that Europol received 21.000 tips and more objects and countries of production were identified. Another press release from October 2018makes clear that eight children have been identified and one offender has been arrested because of citizen efforts. Europol shared new images on their website and via Twitter on 15 October 2018. These were mostly of objects that need to be identified, but there were also a few photographs that were taken outside and are possible to geolocate because of recognizable landmarks. Two of these photographs, taken from a roof of a building, show concrete buildings, and were presumably taken in an Asian city. According to Europol, a child was sexually abused in this city. Europol’s investigators need the location of the photograph to be able to trace the abuser and save a victim. The photographs are heavily censored, because of the sensitivity of the material.

Europol’s tweet from 15 October 2018 (left) and the two photographs taken from a roof in an Asian city (right). Geolocation of the Photographs At first glance, the photograph doesn’t seem to contain many recognizable landmarks. No text is displayed on the buildings and the concrete architecture of the buildings only indicates that the photographs have been taken in an Asian city. Many Twitter users responded to the tweet and mentioned a former Soviet Republic, Malaysia, Philippines or Indonesia as possible locations where the photographs were taken, yet the majority of the responses indicated Southern China as the most likely location. Twitter user “Bo” contacted Bellingcat and mentioned the architecture especially shows similarity to the city of Shenzhen in Southern China. Bellingcat responded to Europol’s tweet with this information, included a photograph of similar architecture and an overlay image of the two photographs, mentioning a blue road sign and a structure similar to a satellite receiver on top of a building visible in the photographs. Sixteen days later, on 31 October 2018 Twitter user Olli Enne from Finland geolocated the exact location of the photographs in the Bao’an district of Shenzhen in Southern China. According to Olli, the photographs have been taken from the roof of a building with coordinates 22.722917, 114.053194 and, he explained, several buildings and a hill in the photographs match the buildings visible in satellite imagery. Also, a view line across a building with a blue roof to a building with arch shaped windows in the distance lines up with the view line in satellite imagery. In later tweets, Olli explained that he searched in Shenzhen and other major cities in China for several hours, looking for little green hills and road shapes, and that he draw a map how the area would look on satellite imagery.

Tweet from 31 October 2018 from Olli Enne (left) and the image that explains the geolocation of the photographs (right). The geolocation of the photographs could not be immediately verified by Bellingcat, as it wasn’t easy to match the buildings of the photographs to the buildings visible in satellite imagery, mainly because of the distance from the location where the photographs were presumably taken to these buildings. Yet due to street view on Baidu maps, a Chinese web mapping system, we were able to verify that Olli’s geolocation is a perfect match. A white building visible on the left side in one of the photographs shows strong similarity to a building visible in a 2014 street view on Baidu, just as a white building with several balconies visible on the right side in one photograph shows a match to a building visible in an older street view as well. Also the buildings with red and orange tiles on the roof from the photographs, as well as a blue road sign, are visible street view. A hotel further away, the building with arch shaped windows and several buildings at the end of the road near a hill with trees, one of them demolished in 2017, are all visible in recent or older street views as well. Street view shows a white building with three antennas on the roof, similar to a white building with what looks like three antennas on a roof in the photographs.

Overlay image of Europol’s photographs with enhanced contrast. The distance between the buildings on the left and on the right side, as well as a blue road sign, indicate there’s a bigger road in between these buildings. A smaller street along the white building with balconies crosses this road. Several buildings and also the blue road sign from the photographs are visible in recent or older Baidu maps street views. Also, the building from where the photographs were taken can be geolocated because of the red tiles on the eaves. Street view from 2014shows red tiles and even a pole on the roof, which is similar to a pole visible in one of the photographs.

The location from where the photographs were taken is the roof of a building visible in Baidu street view (red rectangle). Red tiles on the eaves and also a pole on the roof at the same location as in one of the photographs are clearly visible. A Google Earth 3D view of the building the photographs were taken from in the same direction as in those photographs shows the same mountainscape. Particularly the shape of the mountain on the left side of the photographs is very similar to the shape of the mountains in the 3D view. A smaller mountain with a relatively high peak is more difficult to spot, but following a view line in the photographs from the location where they were taken in the direction of that mountain shows the same buildings in the 3D view that are visible in the photographs in that view line. Also the partly visible small green hill at the end of the road is clearly visible in Google’s 3D view.

Google Earth 3D view shows the same mountainscape and the nearby small green hill as visible in the photographs (marked in red rectangles). The green lines are the view lines that show the area that is visible in the photographs, while the yellow line shows the view from the building where the photographs have been taken to the smaller mountain with high peak. Estimating the Year the Photographs Were Taken Because the buildings in the photographs show more similarity to the same buildings in older street view captures, it is clear that the photographs were not taken recently. A 2017 street view shows one of the buildings was even demolished and the buildings near to the location where the photographs were taken have brown netting, i.e. protective constructions for air conditioning. A 2014 street view capture shows GSM antennas on the white building on the left that are not visible in Europol’s photographs. Recent street view shows many GSM antennas and satellite receivers in the area, while the Europol photographs only show one satellite receiver and three antennas. Satellite imagery tells us the photographs had to have been taken after September 2002, as in the photographs one building clearly has a blue painted roof, which is not visible in satellite imagery from September 2002, but is visible in satellite imagery from February 2008. Also, two buildingsvisible slightly in the distance on the right side in one of the two photographs are not visible in 2002 satellite imagery, but are visible in 2008 satellite imagery. A factory and other tall buildings, visible in the photographs behind the building with arch shaped windows were not constructed before February 2003. Satellite imagery from November 2013 shows the construction of a high rise building that should be visible in one of the photographs if they were taken in or after 2013. However, a smaller building is visible in the photograph, but the high rise building that is standing behind it, as visible in 2016 street view, is not visible in the photograph. It is very difficult, perhaps even impossible, to say exactly in which year the photographs were taken. The roughest estimation is between 2003 and 2013, so it’s most likely they were taken around 2008.

Left: two buildings visible on the right side in one of the two photographs that have been constructed after September 2002. Right: A high rise building constructed in 2013 that is not visible in Europol’s photographs, but the smaller building in front is visible.

Satellite imagery of the area visible in the photographs from 2002 compared to imagery of 2008: a blue painted roof (blue square) and two buildings (green rectangle) from the photographs are visible in 2008, but not in the 2002 satellite imagery. The Initial Research The next part describes the initial research of Bellingcat and others, that eventually helped Olli Enne in finding the exact location. This initial research specifies many details, which mainly are added to show our method of working, but also to show which exact steps were needed to come to our results. Bellingcat’s research started when Twitter user “Bo” shared a video filmed in Shenzhen, China, showing very similar architecture as in Europol’s photographs at the 4:17 time mark. Important note: The people in the video have no relation at all to Europol’s campaign, the video is just meant as an illustration of what the architecture in Shenzhen looks like. “Bo,” who is very involved in Europol’s campaign, has cooperated with Bellingcat for this cause and is a member of research collective Serendip, which played an important role in solving one of the biggest child abuse cases in the Netherlands.

A screenshot from a video filmed in Shenzhen, China, showing very similar architecture as in Europol’s photographs. The building on the front from the video has similar windows as a building on the left side in one of the photographs. Also, the smaller buildings in the area with red and orange tiles bear similarities to buildings visible in the photographs. The video doesn’t give much clues as to the several locations where it was filmed, certainly not for people who are not able to read Chinese. One part obviously is filmed in Shekou, a modern harbour area with many high rise buildings and clearly not in the same location as the older buildings. A Cantonese restaurant, visible shortly before the part featuring the older buildings and filmed likely in the same area, is geolocatable for a Chinese speaker. However, text recognition with a OCR-tool didn’t work, because the characters are in a particular style and also not filmed in a straight angle. An earlier part in the video, on the other hand, shows a street with shops. At the wall on the side of one of the shops a small blue sign with a street name is visible, but the same street name and house number is also more clearly visible on the store sign itself. The colon after two characters indicates the name of the street starts after that colon. An aforementioned free online OCR-tool, NewOCR, can be used to recognize text in many languages. However, the tool is quite sensitive in a way that the text has to be straight and no other parts of the image can be included, the smallest deviation results in the tool not recognizing the text. After a few (partly) failed attempts, the tool recognized the text as 南岭东路49号, which (literally) translates as “Nanling East Road 49 number.” Google maps doesn’t display the correct location, but it seems to be the correct area. However, Baidu maps shows the correct location with a search for 南岭东路49 (without word “number”). The stores have changed between the street view date and the date the video was filmed, but it’s obviously the same location.

Screenshots from the video showing a Cantonese restaurant (left) and shops on Nanling East Road nr. 49 (right). The name of the street including house number is marked with a blue rectangle and this part of the image was used to read the text with an OCR-tool. A short part of the video shows a drone shot from the area and suggests the Cantonese restaurant is one of the buildings visible in the drone shot. The area of the drone shot is found easily near to the location of the shops on Nanling East Road. Particularly, a building with a blue and white roof is very recognizable.

Screenshot from the video showing a drone shot (left) and the same location on Google Earth (right). From here, the exact location of the buildings visible on 4:17 in the video is also not hard to find, as it is just a bit further south from the drone shot area. The high rise buildings visible in the video, but also the area in the video at 4:20 (showing a green edge and a small building with a blue roof next to a higher building) is visible in satellite imagery. A closer look at the part of video that shows the Cantonese restaurant at 3:43 shows the same green edge in the distance and the same buildings visible at 4:17. Bellingcat contacted a person living in Shenzhen about the location of the restaurant and the spelling in Chinese characters. This individual told us that the name of the restaurant is spelled 金沙湾茶餐厅, which translates as Golden Sands Bay Tea Restaurant. The restaurant is displayed on Google maps in the correct street, but the map doesn’t match the satellite imagery exactly. The map, in fact, moves the restaurant 500 meters to the east of the real location on satellite imagery. Baidu mapsshows the restaurant almost at the right location and displays a few reviews, as well as an older photograph of the restaurant. The address of the restaurant, 深圳市龙岗区樟树布新村一巷10, which translates very odd, is in fact the first alley on nr. 10 of that neighbourhood (Yushubu new village) in Longgang district, Shenzhen.

The exact location marked by a red dot where the video is filmed from at the 4:17 mark: the buildings with similar architecture as in Europol’s photographs and the high rise buildings are visible to the east from the red dot. The green edge and small building with a blue roof are to the south-southwest of the red dot. The Cantonese restaurant is marked in an orange square. Unfortunately, no match was found between this eastern suburb of Shenzhen and Europol’s photographs, although the mountainscape in eastern direction seems to be a match. After finding many more areas in Shenzhen with similar architecture and mountain scapes, no precise match to the photographs was found. We realized that the chance to find the exact location in a city of 2000 square kilometers (compare it to London, with 1500 square kilometers) is like trying to find a needle in a haystack. At that time it was not even clear the location is in Shenzhen, as other major cities in the area like Dongguan, Guangzhou and likely many more cities in China have similar architecture. Yet the Bellingcat team found another clue that the photographs possibly were taken in a northern or eastern suburb of Shenzhen: a video filmed from a tram in Shenzhen shows a building with three antennas on the roof, very similar to what looks like three antennas on top of a building in one of the photographs. We also noticed many satellite receivers on the roofs of many buildings in the same area. By following the direction of the tram in the video simultaneously to the street view in Baidu we were able to find the exact location of the building with three antennas. In this area, we also could not find an exact match with Europol’s photographs, but we noticed again the similarity between the architecture of this area and the photographs. A few days later, when the exact location was found by Twitter user Olli Enne, we realized how close we were to the exact spot: 1.2 kilometer as the crow flies or a 20 minute, 1.5 kilometer walk. The tram in the video stops at Xinlan, which is even less than a kilometer from the exact photograph’s location.

A screenshot of a video filmed from the Qinghu-Xinlan tram in Shenzhen shows three antennas on a roof of a building with a similar shape as a structure visible in Europol’s photographs and a satellite dish is also visible. A street view of the same area shows many more satellite dishes. Conclusion This research shows that in a complex investigation tiny details can be very important. The architecture, the tiles with red and orange colors, the blue roof and the mountainous area narrowed down the research to Southern China. Details in a video lead us to an eastern suburb of Shenzhen with similar architecture. Another video shows us GSM antennas and a satellite dish, also visible in the photographs, and lead us to a northern suburb of Shenzhen. Tiny details as buildings that are not visible in the photographs, but are visible in satellite imagery, and GSM antennas missing in the photographs, but which are visible in street view, show the photographs are at least five years old, likely even older. It takes hours of research, and a complex investigation as this one clearly can not be solved by one person or a small team; a crowdsourced wisdom is required to solve cases like this. When even with crowdsourcing a location or an object can’t be found, it can feel very frustrating. Yet, when a photograph is geolocated or an object is recognized, you realize that there is a chance that the case will be solved and someone will get arrested for a serious crime — and it was you who contributed to that. Research by Daniel Romein and Timmi Allen, editing by Natalia Antonova. https://www.bellingcat.com/resources/case-studies/2018/11/08/europols-asian-city-child-abuse-photographs-geolocated/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Open Source Monitoring of historic NATO Trident Juncture Exercises & GPS Hacking

Russia denies claim it meddled with Finnish GPS during NATO war games
The Trident Juncture Excercise was the largest NATO exercise in decades and involved 31 countries - including non-member allies. Russia has denied suggestions that it was responsible for Finland having its GPS signal disrupted during NATO war games. Finnish Prime Minister Juha Sipila revealed on Sunday that air navigation services across the country had to issue traffic warnings due to the interruption last week, which is believed to have been deliberate. Norway posted a similar warning about the loss of GPS signals for pilots in its own airspace at the end of October, when the NATO exercise off its Trondheim coast got under way.

Image:Thirty-one countries took part in the war games Mr Silipa appeared to point the finger at the Russians during an interview with Finnish public broadcaster Yle, noting that the Kremlin "is known to possess such capabilities". The Kremlin has developed a strong CEMA (cyber and electromagnetic activity) military capability which NATO has been focusing on counteracting in recent years.

Image:Two German Eurofighter jets simulate the interception of a plane over the Baltic sea during the drill Russia has said it has "no information" about the allegation, which has not been made by any of the other 31 countries that had forces taking part in the war games - military exercises used to test tactics and equipment. The so-called Trident Juncture was the largest NATO exercise in decades and came to a close last Wednesday, with some non-member nations - including Finland - joining in as allies. It took place close to Russia in an area stretching from the Baltic Sea to Iceland. Finland has a testing history with Russia, with which it shares an 833-mile (1,340 km) border, and part of the reason why it has not signed up to NATO is to avoid any potential confrontation with its eastern neighbour. Russia’s massive annual military exercises, which are named after cardinal directions (e.g. Vostok for east, Zapad for west), garner a tremendous amount of international attention and intense scrutiny. While in some rare circumstances Russian military exercises parlayed into larger international conflicts, such as the July 2008 Kavkaz military exercises that were followed the following month by the Russo-Georgian War, they are usually just opportunities for Russia to showcase its military hardware, ensure its combat readiness, and practice various scenarios — the same as most other states’ and alliances’ military exercises. Meanwhile, from October 25 to November 23 of this year, NATO is carrying out its own military exercises, dubbed the “Trident Juncture Exercises,” in Norway and the North and Baltic Seas. About 50,000 participants are involved, from all NATO members along with Norway’s neighbors of Finland and Sweden. With such a range of participants, there is an abundance of potential open source material to gather and analyze as related to these exercises. This article will provide some methodology to anyone interested in monitoring and analyzing the exercises, along with some basic findings on the exercises thus far.
Satellite Monitoring of Exercises
Much like the Russian Zapad exercises in Belarus in Russia, the NATO Trident Juncture Exercises are quite spread out, but with a few locations that have an especially high density of activity. A map provided by the Norwegian Armed Forces shows a rough estimate of the largest locations used to host the exercises throughout Norway:

The largest location detailed by this map is the Rena Camp in Hedmark County, followed by the Haltdalen-Røros-Brekken location in Trøndelag County — these two spots make a good starting location to begin monitoring the exercises. The Haltdalen-Røros-Brekke location is relatively spread out, as it is a winter training camp that specializes in teaching winter warfare to soldiers, making it a poor candidate to monitor with low-resolution satellite imagery. The Rena Camp is the largest military camp in Norway, and is located just northeast of the small Norwegian town of Rena. The most recent satellite image of the camp on Google Earth is from July 2014. However, imagery from Planet Labs allows for the monitoring of large-scale changes during the lead-up to the exercises and the exercises themselves. The 25 October 2018 satellite image can be seen in a higher resolution here. August 21 and October 25, 2018 (©2018 Planet Labs, Inc. cc-by-sa 4.0)


The “Nordland County” location in Bodø would be a good candidate for satellite monitoring, with sixty aircraft reportedly present for the training, but there is no imagery available on Planet Labs that is not without heavy cloud cover. NOTE: If any of our readers have locations that they would like to have checked with Planet Labs imagery, please leave coordinates and possible dates in the comments of this article.
Social Media Monitoring of Exercises
Soldiers who take part in large-scale exercises, regardless of nationality, love to share photographs of their trip on social networks. While social network use is relatively restricted among Russian soldiers, thanks to a series of embarrassments in Ukraine in 2014-5 and recent legislation, it is hard to stop a 19-year-old conscript or new contract soldier from sharing photographs on Instagram of themselves in interesting locations surrounded by impressive military hardware. The same can be said for NATO exercises, which, when compared with the Russian and Belarusian Armed Forces during the recent Zapad exercises, has a much more open, public relations-focused mindset about their demonstrations of armed strength. The first place to start to find participants sharing photographs and videos of the exercises is with popular hashtags, including #TridentJuncture and #NATO. The top results for these hashtags will be glossy, professional photographs shared by various press services, public figures, and official accounts, including from Lasse Løkken Matberg (arguably NATO’s most photogenic exercises participant), the official NATO Instagram account, and the official British Army account. These official and press service accounts, while sometimes providing interesting tidbits of information, are not the subject of this article, as anyone with basic Google skills can easily find all of the materials from these accounts across all social and sharing platforms. Instead, we will highlight some interesting findings from accounts without blue check marks that could be useful, and detail search strategies to find useful information. Downloading Full-Resolution Instagram Photographs A photograph uploaded by Teleplan Globe, a small company assisting with Trident Juncture, shared a photograph of the “combat room” for the exercises. On its own, there is not a lot that can be gleaned from the photograph; however, by pulling the full-resolution copy of the photograph from Instagram, we can decipher the displays on the screens of the “combat room”.

(Source) First, on Chrome, open up “Developer Tools” from the options.

Second, click the “Select an element in the page to inspect it” icon on the top-left of developer tools.

Third, highlight and then click the photograph that you want to pull in its highest-available resolution from the Instagram servers.
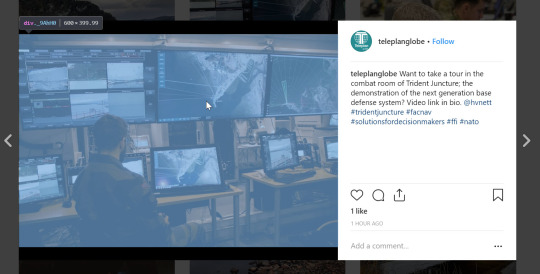
After clicking on the image, a line from the Elements part of developer tools will be highlighted, showing us where the web page is pulling the image from. You may need to expand (click the arrow facing right) near the field. Here, it is under the field, right above the “_9AhH0” line that was highlighted after we clicked the image.

Four URLs are visible here, indicating different resolutions. The URL that we are interested in is the final one, between “src=” and “style”. This JPG file is the photograph in the highest resolution available. Double-click this URL to highlight it, then copy-paste it into the URL field of your web browser.
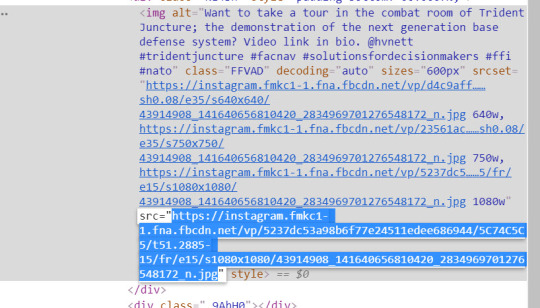
The image will now appear in your browser and can be saved by right-clicking, rather than taking a screenshot at a lower resolution of the photograph on its Instagram page.

While the resolution of the photograph is not quite high enough to discern the text on the screens, we can still cross-reference the satellite imagery and CCTV footage visible in the “combat room.” For example, the port visible in the center of the photograph on two monitors is located in Stjørdal, east of Trondheim.

The satellite image on the right-most large screen is the same port, but at a rotated angle.

Finding Instagram Location Labels With thousands of soldiers from dozens of countries in Norway, we cannot expect a uniform behavior with geotagging photographs. While many oversharing soldiers may use the correct geotag that Instagram provides, many — especially those who cannot understand Norwegian — will likely use incorrect location names. For an accurate example of geotagging, a German soldier used the general “Haltdalen” geotag when conducting winter training near the Haltdalen Training Center.

After clicking on the hyperlink over Haltdalen, we can find all of the recent Instagram photographs using this geotag. However, this is the only one related to the exercises with this location. Another photograph that we can discover through relevant hashtags (#TridentJuncture2018) is a Norwegian soldier drinking a bottle of Coke near “Hedmark” — a location with numerous photographs and videos showing military equipment and soldiers involved in the exercises.

This geotag, nevertheless, is extremely broad, ranging across hundreds of square kilometers. While the Haltdalen geotag was fairly narrow, as it is a single village in a very remote region, Hedmark encompasses a much larger area, and many photographs taken within this region use other geotags generated by Instagram other than “Hedmark.” There is no surefire method (that Bellingcat is aware of) to gather all geotags within a particular area, but one solution is via search for Instagram cross-posts on Twitter, with geotags added. This search will provide potential geotags that are provided to users uploading photographs within a certain radius, thus providing a list of likely geotags for relevant photographs. Firs, grab the coordinates for an area that you are interested in. For us, the Rena Camp in Hedmark county is the most likely place that the geotagged “Hedmark” photos are coming from, meaning we should find the coordinates for this place. Be sure to use the decimal coordinates, without any degree symbols, as those are the only ones that work with Twitter searches. The fastest way to gather coordinates for a location is to navigate to it on Google Maps, then pull the decimal coordinates from the URL (or, alternatively, right click a spot, select “What’s here?”, and copy the coordinates).

With these coordinates, we need to conduct a Twitter search with the following query. If you have a Twitter account, you can do this by typing it into the “Search Twitter” field on the top-right of the user interface. Anyone, with or without a Twitter account, can enter the same search here. geocode:XX.XXXXX,YY.YYYYY,RADIUS instagram.com geocode:61.1499048,11.3966162,25km instagram.com

This search function looks for all tweets with location data at the entered coordinates, plus a radius, plus the word “Instagram.com”. Note that there are no spaces in the search query before Instagram.com, so delete any possible space between the X and Y coordinates. We add Instagram to the search in order to find cross-posted photographs from Instagram that could have geotags on them, which will broaden our search capabilities in noting potential geotags that are used by soldiers and locals involved with or observing the NATO exercises near these coordinates. One of the search results seems promising — there is clear location data on Twitter, plus a link to an Instagram upload that the user presumably made.

The uploaded photograph has a geotag for “Rena, Norway”, which would not have come up if we were to only search for “Hedmark.”

Following the hyperlink on Rena, Norway, we find a motherload of geotagged photographs relating to the ongoing exercises.

While it would probably be easy enough to guess that photographs near the Rena military camp would be tagged Rena, Norway, we have to consider that users will use different languages and auto-suggested options that may not be the most obvious choices. For example, another photograph is in the results for our Twitter geocode search is seen below, and obviously is related to the Trident Juncture Exercises.

Clicking through to the Instagram upload, we see a geotag that uses Norwegian: “Regionfelt Østlandet” (Eastern Norway Region).

Like with the “Rena, Norway” hashtag, we can find many relevant photographs with this geotag, as seen below.

Some American soldiers participating in the area may use this geotag if it is an autosuggested option, but they also may not, as most probably do not know enough Norwegian to understand what it means. Under the same logic, they may choose incorrect hashtags, such as for a nearby hotel or park, if it were to be the first or second suggested option by Instagram for a geotag. By running a geocode search on Twitter, you can find some of these locations, and then check recently geotagged photographs for those locations to see if any interesting materials were incorrectly tagged.
Naval and Aircraft Monitoring of Exercises
With heavy naval and aerial components, it is easy to find and monitor the aircraft and naval vessels involved in ongoing NATO exercises in the North and Baltic Seas. At each of the airstrips and ports used in the exercises (seen on the map on the third page of this document), we can look at current and historic data from a number of free and premium tracking sites, including Marine Traffic, ADS-B Exchange, FlightAware, and VesselFinder. Note that for many of these services, viewing real-time data is free, but a membership or fee can be required to view historical data. https://www.bellingcat.com/news/uk-and-europe/2018/11/06/open-source-monitoring-nato-trident-juncture-exercises/ https://news.sky.com/story/russia-denies-claim-it-meddled-with-finnish-gps-during-nato-war-games-11552466 Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Here's How Hackers Could Have Spied On Your DJI Drone Account

Cybersecurity researchers at Check Point have revealed details of a potentially dangerous vulnerabilities in the DJI Drone web app
If you require Digital Forensic assistance in examining Drone systems of importance to an Investigation get in touch now - Drone Forensics Cybersecurity researchers at Check Point today revealed details of a potential dangerous vulnerability in DJI Drone web app that could have allowed attackers access user accounts and synced sensitive information within it, including flight records, location, live video camera feed, and photos taken during a flight. Thought the vulnerability was discovered and responsibly reported by the security firm Check Point to the DJI security team in March this year, the popular China-based drone manufacturing company fixed the issue after almost six months in September. The account takeover attack takes advantage of a total of three vulnerabilities in the DJI infrastructure, including a Secure Cookie bug in the DJI identification process, a cross-site scripting (XSS) flaw in its Forum and a SSL Pinning issue in its mobile app. The first vulnerability, i.e. not having the "secure" and "httponly" cookie flag enabled, allowed attackers to steal login cookies of a user by injecting a malicious JavaScript into the DJI Forum website using the XSS vulnerability. "To trigger this XSS attack all the attacker need do is to write a simple post in the DJI forum which would contain the link to the payload," the researchers explained in a report published today. "A user who logged into DJI Forum, then clicked a specially-planted malicious link, could have had his or her login credentials stolen to allow access to other DJI online assets," Once captured, the login cookies, which include authentication tokens, can then be re-used to take complete control over the user's DJI Web Account, the DJI GO/4/pilot Mobile Applications and account on its centralized drone operations management platform called DJI Flighthub. However, to access the compromised account on the DJI mobile apps, attackers have to first intercept the Mobile application traffic after bypassing its implementation of SSL pinning by performing man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack to the DJI server using Burp Suite. "We also carried out further research and found that by parsing flight logs files we can get much more information such as location and angle of every picture taken during the drone’s flight, the drone’s home location, last known location and more," researchers said. DJI classified the vulnerability as "high risk—low probability," because successful exploitation of the flaw required a user "to be logged into their DJI account while clicking on a specially-planted malicious link in the DJI Forum."

DJI also said the company did not find any evidence of the flaw being exploited in the wild. Check Point researchers reported the vulnerability to the DJI through its bug bounty program, but declined to reveal the financial reward offered to them. The DJI bug bounty program offers up to $30,000 in rewards for single vulnerabilities. DJI has been facing scrutiny in the United States after the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) released a memo late last year accusing the company of sending sensitive information about the U.S. infrastructure to China through its commercial drones and software. However, the drone maker denied the allegations, saying that the memo from the US government office was based on "clearly false and misleading claims." Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Researchers successfully bypass hardware encryption in Samsung and Crucial SSDs

Researchers from the Netherlands discovered several vulnerabilities in various SSDs from Crucial and Samsung. The embedded hardware encryption can be bypassed.
If you require Digital Forensic assistance in gaining access to Encrypted, PIN or Password Locked Devices get in touch now - Advanced Data Recovery Before we begin, the researchers have only tested a small number of Samsung and Crucial SSDs, it's likely more widespread to other brands as well. They gents not only have they been able to bypass encryption, they also simply download the firmware, reverse engineered it and found out how the security measures work for the SSD manufacturers. Carlo Meijer and Bernard van Gastel explain that the hardware data encryption technologies built into modern SSDs is easy to bypass making even Bitlocker ineffective. SSDs use native encryption solutions like AES and the researchers found that many hardware implementations with native encryption reveal security weaknesses, allowing for complete recovery of the data. They have published a paper on their findings which you can read here, Samsung already responded with an online notice.
Vulnerability CVE-2018-12037 shows up on the Crucial MX100, MX200 and MX300, the external Samsung T3 and T5 ssds and the Samsung 840 Evo and 850 Evo. The researchers obtained the right entry to security, by buffer overflows and the JTAG debug interface. According to Van Gastel, there are also other ways of enabling the execution of code on the controller, such as via power glitching. Vulnerability, CVE-2018-12038 shows an issue with wear leveling at the chip on which the key is stored. SSDs are delivered without a password at factory default, by default everything is encrypted with the key stored unprotected. When changing a password, a protected key is still written, but due to wear leveling, the unprotected data could still reside on other sectors. The key without a password can thus be read in that other location, although it is logically impossible to extract it. This was the case with the Samsung 840 Evo. The researchers warn that Windows BitLocker can automatically choose hardware encryption if a drive with TCG Opal support is present. Only a completely new installation, with reformatting the disk, forces software encryption. "The command to see if Windows outsources the encryption to the disk is' manage-bde-status' in the Command Prompt or PowerShell. If 'Hardware Encryption' is behind 'Encryption Method', the encryption will be outsourced to the SSDs', according to Van Gastel. The flaws can be found in the encryption mechanism of various types of solid state drives (SSDs) (listed below) by two major manufacturers, namely Samsung and Crucial. The vulnerabilities occur both in internal storage devices (in laptops, tablets and computers) and in external storage devices (connected via a USB cable). The affected storage media include popular models that are currently sold a lot. Researcher Bernard van Gastel: "The manufacturers involved were informed half a year ago in accordance with current professional practice. The results will be made public today so that organizations and consumers involved can protect their data properly. ' Researcher Carlo Meijer: 'This problem mainly requires action from organizations that store sensitive data on these devices. And also of some consumers who use this form of data protection. However, most consumers do not yet use this form of data protection. ' Recommendations If sensitive data needs to be protected, it is advisable to use software encryption in any case and not only rely on hardware encryption. One of the possible options is to use the free VeraCrypt open source software package, but there are other solutions as well.

Background Encryption (encryption) is the most important mechanism for data protection. This can be done via software and via hardware, for example in SSDs. In modern operating systems, software encryption is generally used for the entire storage. However, it is possible that such a control system decides to rely solely on hardware encryption (if supported by their storage medium via the TCG Opal standard). BitLocker, the encryption software built into Microsoft Windows, can make such a switch to hardware encryption, but in these cases it does not offer effective protection. Encryption software built into other operating systems (such as macOS, iOS, Android and Linux) seems unaffected when these switches are not executed. Methods used The researchers found these vulnerabilities with the aid of public information and around € 100 of evaluation equipment. They bought the SSDs that they researched through the normal sales channels. The vulnerabilities are quite difficult to discover. However, once the nature of the vulnerabilities is known, there is a risk that exploitation of these defects will be automated by others, making abuse easier. The researchers at Radboud University will not release such exploitation resources. Products involved The models where actual vulnerabilities have been demonstrated are: the Crucial (Micron) MX100, MX200 and MX300 internal hard drives; the Samsung T3 and T5 external USB drives; the Samsung 840 EVO and 850 EVO internal hard drives. Windows computers On computers with Windows, a software component called BitLocker provides encryption of the data from the computer. Within Windows, the type of encryption that BitLocker uses is set via the so-called Group Policy. Only a completely new installation, including reformatting the internal drive, will force software encryption. Changing the default value does not solve the problem immediately because it does not re-encrypt existing data. More information about the Group Policy setting can be found in the left section below. Responsible disclosure Both manufacturers were informed in April 2018 via the National Cyber Security Center (NCSC). The university has provided the data to both manufacturers so that they can adjust their product. The manufacturers themselves will provide detailed information to their customers about the models concerned; the necessary links are at the bottom. When discovering a security error, there is always the dilemma of how to deal with this information. Immediate publication of the data can encourage attacks and cause damage. Long-term secrecy of the error can mean that the necessary steps to prevent vulnerability are not taken while people and organizations are still at risk. In the security community, it is common practice to look for a certain balance and to wait for defects to be exposed up to 180 days after the manufacturer of the product concerned has been informed. This procedure of responsible disclosure is used by Radboud University as standard. The protection of digital data has become a necessity, especially in the light of the new European general data protection regulation (AVG). Radboud University wants to contribute to this through its computer security research, both by developing new security mechanisms and by analyzing the power of existing mechanisms. Publication The researchers are now about to publish the scientific aspects of their findings in the scientific literature. Today, November 5, 2018, a preliminary version (pdf, 757 kB) of these findings will be published. After the end of the peer review process, a definitive version will appear in the scientific literature. This publication is not a guide to breaking into SSDs. https://www.guru3d.com/news-story/researchers-successfully-bypass-hardware-encryption-in-samsung-and-crucial-ssds.html Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Forensic Video Analysis | Expert: Acosta video distributed by White House was doctored

Video footage released by the Whitehouse from a Press Event appears to be doctored according to Experts
If you require Digital Forensic assistance in Forensic Video Analysis or Enhancement get in touch now - Advanced Data Recovery The Independent - Frame by Frame analysis of footage:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8TSpgB0QS0gSarah Sanders tweeted out a video of CNN's Jim Acosta pushing a White House intern's arm away and revoked his press pass on the grounds of assault. Following rumours the footage was doctored we looked into it to find out if it was true. A video distributed by the Trump administration to support its argument for banning CNN reporter Jim Acosta from the White House appears to have been doctored to make Acosta look more aggressive than he was during an exchange with a White House intern, an independent expert said Thursday. White House press secretary Sarah Sanders tweeted the video, which shows Acosta asking President Donald Trump a question on Wednesday as the intern tries to take his microphone away. But a frame-by-frame comparison with an Associated Press video of the same incident shows that the one tweeted by Sanders appears to have been altered to speed up Acosta’s arm movement as he touches the intern’s arm, according to Abba Shapiro, an independent video producer who examined the footage at AP’s request. Earlier, Shapiro noticed that frames in the tweeted video were frozen to slow down the action, allowing it to run the same length as the AP one. The tweeted video also does not have any audio, which Shapiro said would make it easier to alter. It’s also unlikely the differences could be explained by technical glitches or by video compression — a reduction in a video’s size to enable it to play more smoothly on some sites — because the slowing of the video and the acceleration that followed are “too precise to be an accident,” said Shapiro, who trains instructors to use video editing software. An independent video production trainer tells the AP a video tweeted by the White House on an interaction between CNN reporter Jim Acosta and an intern appears to have been manipulated to make the reporter's actions look more aggressive. (Nov. 8) Sanders, who hasn’t said where the tweeted video came from, noted that it clearly shows Acosta made contact with the intern. In her statement announcing Acosta’s suspension, she said the White House won’t tolerate “a reporter placing his hands on a young woman just trying to do her job.” While the origin of the manipulated video is unclear, its distribution marked a new low for an administration that has been criticized for its willingness to mislead. The White House News Photographers Association decried the sharing of the footage. “As visual journalists, we know that manipulating images is manipulating the truth,” said Whitney Shefte, the association’s president. “It’s deceptive, dangerous and unethical. Knowingly sharing manipulated images is equally problematic, particularly when the person sharing them is a representative of our country’s highest office with vast influence over public opinion.” CNN has labelled Sanders’ characterization of Acosta’s exchange with the intern as a lie. Its position has been supported by witnesses including Reuters White House correspondent Jeff Mason, who was next to Acosta during the news conference and tweeted that he did not see Acosta place his hands on the White House employee. Rather, he said he saw him holding on to the microphone as she reached for it. “The irony of this White House video involving Jim Acosta is that if it is found to be doctored, it will show the administration to be doing what it accuses the news media of doing — engaging in fake information,” said Aly Colon, a professor in journalism ethics at Washington & Lee University. Several journalists and organizations — including the American Society of News Editors, the Associated Press Media Editors and the Online News Association — demanded Acosta’s press pass be reinstated. “It is the essential function of a free press in every democracy to independently gather and report information in the public interest, a right that is enshrined in the First Amendment,” said Julie Pace, AP’s Washington bureau chief. “We strongly reject the idea that any administration would block a journalist’s access to the White House.” The New York Times editorialized in favour of restoring Acosta’s pass, saying it signalled Trump’s view that asking hard questions disqualifies reporters from attending briefings. The newspaper said that if Sanders was so offended by physical contact, “what did she have to say when her boss praised as ‘my kind of guy’ Rep. Greg Gianforte of Montana, who was sentenced to anger management classes and community service for body-slamming a Guardian reporter last spring?” CNN has been a frequent target of the president, who has characterized journalists as enemies of the people and who routinely accuses the mainstream media of spreading “fake news.” And Acosta has been one of the more visible thorns in the side of the White House. During their verbal altercation on Wednesday, Trump called Acosta a “terrible person.” Still, it’s rare for the White House to pull the so-called hard passes from journalists. During Lyndon Johnson’s presidency, the Secret Service denied clearance to Robert Sherrill, a reporter for The Nation who had gotten into physical fights with government officials. During the George W. Bush presidency, Trude Feldman, who worked for various news outlets, was suspended for 90 days after security cameras recorded her looking through a press aide’s desk late one night. In the 1970s, President Nixon tried to get Washington Post reporters banned from the White House. Despite losing his White House pass, Acosta is expected to travel to Paris this weekend to cover Trump’s trip to meet with world leaders. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
[Case Study] Mobile Phone Forensics: Apple Enhanced USB Restricted Mode in iOS 12

Apple is known for their continuous efforts to make their user’s private data secured. I believe the news that Apple enhanced USB restricted mode in iOS 12 has already become a hot spot in the Digital Forensics community.
If you require Digital Forensic assistance in gaining access to PIN or Password Locked iPhone or Samsung handsets get in touch now - Advanced Data RecoveryIf you are a police officer, a law enforcement investigator, this is grave news for you. So today, forensic experts will talk about iOS USB restricted mode, we’ll see what is USB restricted mode, what does it do, what enhancement has been made in iOS 12 and how are they going to have an impact on our works.
What is USB Restricted Mode? The USB Restricted Mode was first introduced in iOS 11.4.1. USB Restricted Mode prevents USB accessories that plug into the Lightning port from making data connections with an iPhone, iPad, or iPod Touch if your iOS device has been locked for over an hour. This seemingly small change goes a long way in blocking tools used by law enforcement to crack passcodes and circumvent Apple’s encryption and built-in measures designed to shield sensitive user data. Actually Apply has never said as much it, but it’s believed that USB Restricted Mode is Apple’s effort to combat forensic devices that are specially designed to help law enforcement crack an iOS device’s passcode and retrieve data that would normally be guarded by encryption. iOS has built-in security features that prevent constant passcode guesses — such as when it locks down your device after several incorrect attempts. But of course, this would not stand in the way of forensic solution providers, some companies have seemingly found a way of avoiding those safeguards via USB and the Lightning port. Now, Apple is trying to eliminate this method of gaining entry to a recovered or confiscated device.
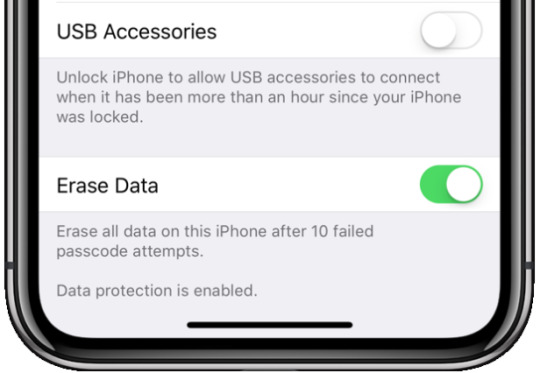
What does USB Restricted Mode do? Once USB Restricted Mode is engaged on a device, no data communications occur over the Lightning port. A connected computer or accessory will not detect the iPhone as a “smart” device. USB Restricted Mode works like this: after an hour of your iPhone, iPad, or iPod Touch sitting without being unlocked, iOS will basically cut off the Lightning port and limit it to charging only. This hour timeout should theoretically stop forensic devices (which plugs into an iPhone and cracks the passcode within a few hours) from working successfully. So, USB restricted mode effectively deters the ability of third-party forensic tools to crack iPhone’s passcodes.

What enhancement has been made in iOS 12? According to Apple itself, the additional security measures were required because “the USB accessory ecosystem doesn’t provide a reliable way to identify accessories before establishing a data connection”. Below is a brief summary of USB Restricted Mode in iOS 12. In iOS 12, USB Restricted Mode engages if any of the following conditions are met: One hour after the phone is locked, or one hour since the phone was disconnected from a USB accessory (whichever is later). Basically, one hour since last unlock/last disconnect. Immediately after the phone is locked if 72 hours or more have passed since the phone last established connection with a USB device. If the 72 hours have passed, USB Restricted Mode will engage immediately every time the iPhone’s screen is locked. After S.O.S. mode If the iPhone is in a state where it requires a passcode to re-enable biometric authentication (“Your passcode is required to enable Touch ID/Face ID” message is displayed); basically, USB Restricted Mode now engages under the same rules as Touch ID/Face ID expiry. Is there a solution to crack USB Restricted Mode? Actually, merely plugging in nearly any device (not just ones that have previously been connected to that phone), such as Apple’s Lightning to USB 3 Camera Adapter, will disable the one-hour limitation. This would give a forensic inspector enough time to bring the device to a lab and then work on it for as much time as they’d like. The problem likely lies in Apple’s Lightning communication protocol — in other words, the way the iPhone “talks” to devices that are plugged into it. When you connect the iPhone to a computer, the two devices exchange cryptographic keys and establish trust. Many Lightning accessories, however, don’t have the capability to do that, so the iPhone just trusts them by default. If this is indeed a bug and not intended behaviour, it might be hard for Apple to fix it. A fix could render numerous Lightning accessories useless — though it might be possible to make sure the iOS device only communicates with devices that were previously plugged into it. Conclusion The iOS 12 update brings additional challenges to our forensic works. But of course, we, digital forensic solution providers, are also making continuous efforts to catch up with the rapid developing private data security technologies. Check out our website and see what forensic solutions we offer. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Home Secretary: Advertisers are unwittingly funding online child abuse

Sajid Javid has told tech giants that he will "not be afraid to take action" against them if they do not tackle abuse.
Dealing with IIOC (Indecent Images of Children) for both Mobile Phone Forensics and Computer Forensics is a daily activity when it comes to Digital Forensics.Internet adverts for well-known brands could be funding the sexual exploitation of children online by unwittingly appearing on websites hosting child abuse, the home secretary will warn today. Sajid Javid, who is meeting with tech giants bosses in the US this week, has set up a task force and commissioned new research to look at how advertising is funding online abuse of children. The Home Secretary has asked the Internet Watch Foundation to investigate how advertising may be funding online sexual abuse in an effort to both understand the scale of the problem and possible remedies.

Image:Sajid Javid says tech companies must take their responsibilities seriously Mr Javid, who has made stamping out online abuse his "personal mission" as Home Secretary, is also chairing a new task force of ad agencies and brands. "It is vital tech companies take their responsibility seriously," Mr Javid said ahead of his trip to Seattle and Silicon Valley. "I have demanded action and will be discussing the progress industry has made during my visit to the US - as well as seeing the latest tools being developed to detect online child grooming." It comes amid concerns that offenders are duping online advertisers and brands to access funding streams. "Using a variety of sophisticated techniques to avoid detection, offenders are exploiting online advertising networks to monetise their distribution of child sexual abuse material," said Susie Hargreaves, chief executive of the Internet Watch Foundation. "It is our mission to identify the methods offenders are employing to share this disturbing material, enabling us to most effectively disrupt its distribution." Last year, the government, along with some of the world's largest brands pulled millions of pounds in marketing from YouTube after an Times newspaper investigation showed brand ads were unwittingly appearing next to extremist context and funding the videos' creators. Mr Javid has warned tech giants that he will "not be afraid to take action" against them if they do not tackle abuse - although he has refused to discuss what new legislation might look like. As well as meeting tech bosses, the Home Secretary will also visit Microsoft's headquarters in Redmond, Washington where engineers are working on solutions to tackle online grooming. Work is also going on to try to improve the capabilities of the Child Abuse Image Database to help police both search for indecent images and identify victims. The National Crime Agency estimates that around 80,000 people in the UK pose some kind of sexual threat to children online. Referrals of child abuse images to the NCA have jumped 700% increase since 2013. https://news.sky.com/story/home-secretary-advertisers-are-unwittingly-funding-online-child-abuse-11545926 Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Forensic Analysis Of The μTorrent Peer-to-Peer Client In Windows | Forensic Focus

The μTorrent software client is the most popular BitTorrent peer-to-peer software application worldwide.
If you require Digital Forensic assistance in the examination of exhibits suspected of sharing illegal material in uTorrent get in touch now - Computer Forensics The μTorrent software client is the most popular BitTorrent peer-to-peer software application worldwide . Contraband files such as copyrighted movies and music, child pornography and pirated content, are frequently acquired through the peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing protocol BitTorrent. This research will include the digital forensic analysis of the μTorrent client, specifically, the free (Basic) version 3.5.3 for Windows released on utorrent.com. The μTorrent client is based on the same architecture of the original, less popular client, itself named BitTorrent (bittorrent.com). In fact both software applications are owned by BitTorrent, Inc. Although the same artifacts have been identified in all versions of μTorrent, any examination of other versions should be tested by the examiner. μTorrent is available for Windows, Mac, Linux, Android, and iOS (only with a jailbroken device). A computer running μTorrent can be paired with external devices for viewing (iOS and Android mobile devices, USB storage drives, and certain streaming devices). A user can remotely and securely manage μTorrent running on a computer. Their μTorrent client can then be accessed from another computer or mobile device equipped with a web browser . BitTorrent uses trackers to allow clients to find peers, known as seeds. Rather than downloading a file from a single source (node), the BitTorrent protocol allows users to join a swarm of hosts to upload and download content from each other. A seed is a node that possesses an entire file being distributed. A user who wants to distribute a file must first create a small torrent descriptor file that contains only metadata and has a .torrent file extension. The .torrent files are distributed through one or more Torrent websites, called an Indexer, that allows users to search for particular content and download applicable .torrent files. The .torrent files include specific tracker information. A tracker is a server that keeps track of what peers and seeds have the pieces of the files to be distributed. The creation of the distributed hash table (DHT) method for “trackerless” torrents make the trackers redundant . Users with the .torrent file loaded into their BitTorrent client can establish connections among other BitTorrent nodes (peers or seeds) via the DHT communications feature of BitTorrent. The file being distributed is divided into segments (pieces), as each new peer receives a new piece, that peer now becomes a distributor of that piece. Every piece is protected by a cryptographic hash (SHA1). The BitTorrent client will identify what pieces are needed in order to obtain a complete file. Once a peer has downloaded a complete file, it then becomes a distribution seed. BitTorrent does not ensure the anonymity of its participants. The IP of connected peers can be readily identified through the client user interface or via the netstat Windows command that will display the connected peers and seeds. The standard ports for BitTorrent, including the μTorrent client, are TCP/UDP ports 6881-6889 (6969 for the tracker port).
The μTorrent Client
The default installation will place all files for the μTorrent client in the user’s application data directory as follows: C:\Users\\AppData\Roaming\uTorrent\ The following configuration files include relevant information regarding application setting and history: resume.dat settings.dat dht.dat (distributed hash table) rss.dat If the client is shut down, the above DAT files are backed up and .old is appended as the new file extension. The below graphics are of the μTorrent directory following a fresh installation in Windows 10. After installation but prior to launching the application is shown on the left. On the right is the application files after first launch of μTorrent, adding TEST.torrentto the client, then shutting it down.
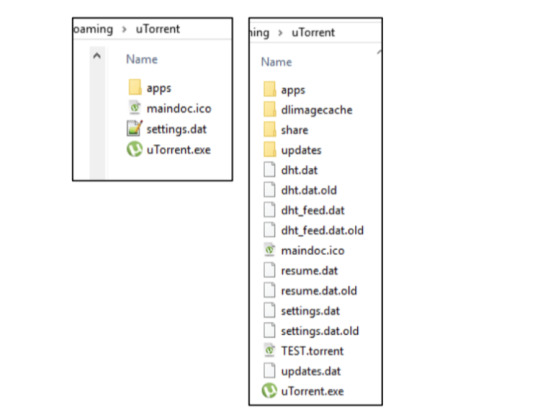
BEncode Editor
The DAT files and .torrent files are written in BEncode. Therefore, to view the contents, a tool capable of decoding BEncode files must be used, such as BEncode Editor. When viewing these files in the BEncode Editor, data will appear with an indicator showing the data type adjacent to each heading: Byte strings: (b) Integers: (i) (base 10 ASCII characters) Lists: (l) Dictionaries: (d) A number surrounded by brackets: , will represent a quantity based on the data type (byte string, integer, list or dictionary): Byte strings: number of bytes or characters Integers: number of digits Lists and Dictionaries: number of items in the list or dictionary Below is the contents of a settings.dat file viewed with BEncode Editor.
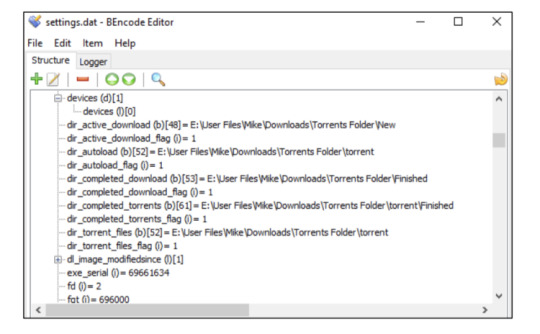
μTorrent DAT Files
settings.dat Contains settings and configuration data autostart=: 0=OFF, otherwise there will be no entry ct_hist : Number of .torrent files created by this client (within brackets), includes path and name of files/folders that the user used to create the .torrent file; good indicator of knowledge and intent; may point to external media or other storage drive/directory locations born_on=13036184115: Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) time, or FILETIME, number of 100 nanosecond intervals since 1 Jan 1601 UTC – must add 7 trailing zeroes in EpochConverter devices: Paired devices will be listed here with device name, USB VID&PID and serial number auto_transfer=: 0=OFF/1=ON usb_id: contains the USB device vendor ID (VID) and product ID (PID), along with USB device electronic serial number and possibly the device friendly name

The graphic below shows the μTorrent Devices interface with two devices connected: iPhone/iPod and Apple iPhone 3GS.
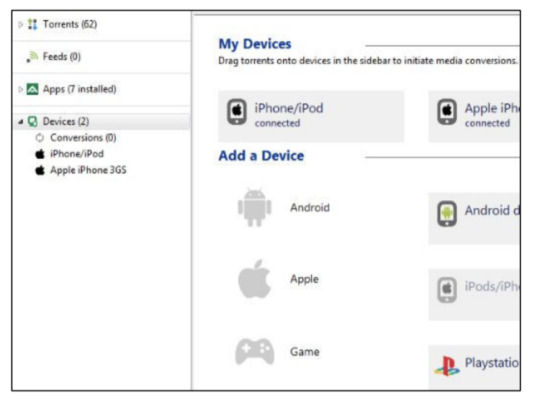
dir_last entry is the directory selected by the user to download a Torrent file when the user added the associated .torrentfile and selecting the “choose save dir” option (see below graphic). The dir_last entry is updated for each new .torrent file added in this manner.
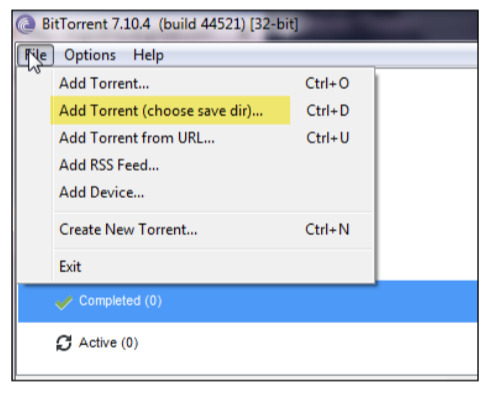
*dir_active_download: Location set by user to save new downloads *dir_autoload: Location set by user to autoload Torrent files *dir_completed_torrents: Location set by user to store completed downloads *dir_completed_torrents: Location set by user to archive completed .torrent files *dir_torrent_files: Location set by user to store torrent files downloaded by the client

(*) The above settings will be present only if the user changed the default location for that particular directory using the Preferences menu (see below image), otherwise no entry will be present.
runs_since_born: Number of times the program started and closed since install runtime_since_born_secs: Number of seconds the program has run search_list: List of Torrent search sites used in the μTorrent toolbar, can be added by the user, results in user’s web browser loading the search site so check Internet History settings_saved_systime: Last time client settings were changed, UNIX time
Remote Access
A system configured for Remote Access will allow a user to control the uTorrent client running on the remote system using a web interface. To initiate Remote Access, the user will navigate to https://remote.utorrent.com and enter the previously configured computer name and password. After authenticating, the user is presented with a web interface that appears nearly identical to the uTorrent client status on the remote system. The below image depicts the Remote Access web interface (top) and the actual uTorrent client (bottom).
Below are the more relevant entries in settings.dat that will be present if the client is set to be operated via Remote Access connection using the Preferences > Remote menu settings. A unique name must be provided and any password will be accepted. The below image shows the Remote Access setting enabled:
upnp.external_ip: Last external (routable) IP of the computer the client is installed on will be stored here; see image below upnp_cached_host: Universal plug and play(upnp) URL of the IGDdevicedesc.xml file on the local network; will include the local network gateway IP and port; used to facilitate network connectivity
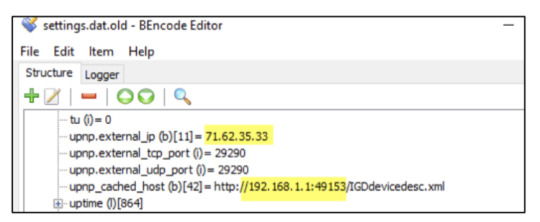
upnp.external_ip: External (routable) IP of the computer that the client is installed on webui.ssdp_uuid: Universal unique identifier (last 6 characters represent the MAC address of the network interface) webui.ucinnect_hashword: Salted SHA-1 hash of the login password for Remote Access webui.ucinnect_username: Name of the computer assigned by the user in Preferences > Remote
resume.dat
Stores status info when client is shut down added_on=: Time Torrent was added to the client (UNIX time) completed_on=: Time Torrent was completely downloaded or created (UNIX time) created_torrent=: 1=client created torrent, 0=client did not create torrent download_url=: If client used ‘add torrent from URL’ function downloaded=: Bytes of the file downloaded so far last_seen_complete=: Last time client was seeding the complete file (UNIX time) last_active=: Last time the file was being seeded or shared by this client (UNIX time) path=: Path where incoming files are saved, number of files for this Torrent in brackets runtime=: Time file has been downloading in the client (or seeding time following download) seedtime=: Seconds that client has been seeding file started=: File status when client last exited (0=stopped, 1=force started, 2=started, 3=running/not downloading) uploaded=: Total uploaded (shared) bytes of data for that specific file uploaded=: Total uploaded (shared) bytes of data for that specific file peers6 =: IP and Port of peers sharing this file at time client exited (includes the client’s local and external IP, both IPv4 and IPv6), see below for the procedure to convert the data to identify the IP addresses. Use the following procedure to view the IP address of each Peer: o The peers6 field of the resume.dat file contains the IP addresses of each peer the client is communicating with in order to participate in the sharing of content via the BitTorrent protocol. o In the peers6 field of the resume.dat file, select display options to “Raw BEncoded Data” and “as Binary.” o Convert from Hex to Decimal to get the IP. o The last 4 hex characters represent the port (Big Endian). o Follow the below steps to translate the data in order to identify the IP address of each peer. Open the data field adjacent to the peers6 entry:

Copy and paste this hex data into Notepad++ and create a new line with 36 characters each. Each line will display the IPv6 (all zeros if no IPv6 is present), followed by IPv6 port (FFFF if no IPv6), followed by the IPv4 (8 characters) and the IPv4 port (4 characters):
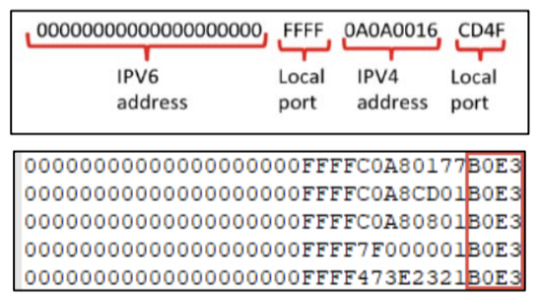
Byte string (36 characters): 00000000000000000000FFFFC0A80177B0E3 IPv4 IP and Port: FFFFC0A80177B0E3 IPv4 address (convert from hex to decimal): C0A80177:E3B0 C0=192 A8=168 01=1 77=119 Port (Little Endian): E3B0=58,288 (port) Converted: 192.168.1.119:58288
dht.dat
Contains data used by the client when connecting to the Distributed Hash Table (DHT) network for sharing contact information, so users engaged in downloading the same file(s) can discover each other. This file also stores the client’s outwardly facing IP address. This is a useful artifact as most Windows artifacts only store the local, non-routable IP address. Be sure and review dht.dat.old as this is the previous version of the file from the last shutdown of the μTorrent client for this user. age: Time last updated, or when client shut down (UNIX decimal), good indicator of associating the client’s IP to a date/time. ip: Represents the client’s routable IP address in hex (assigned by the client’s service provider), follow the below steps to translate the data to identify the outwardly facing client IP. Double click the text data to the right (below example: G>#!):

Select display options: “Raw BEncoded Data” and “as Binary”:
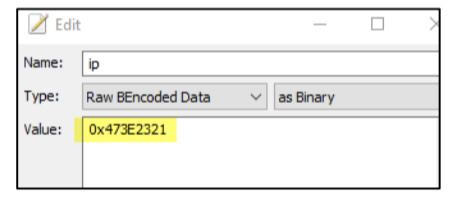
Convert hex to decimal: 47=71 3E=62 23=35 21=33

Converted IP: 71.62.35.33 In the above test example, visiting the website www.whatismyipaddress.com disclosed the correctly translated IP address, rather than just the local IP, of the test Windows computer system. nodes: Contains the IP addresses (IPv6 and IPv4) of each peer the client is communicating with in order to participate in the sharing of content via the BitTorrent protocol. To convert the data, follow the steps below. 26-byte (52 hex digits):

To determine the total number of peers that the client is communicating with, divide the number in brackets (10036, in the example below) by 26 (hex bytes in the string) to determine the total number of IP addresses contained in the data (386 IPs in the example below) – display Type “Binary / as Binary” as depicted below.
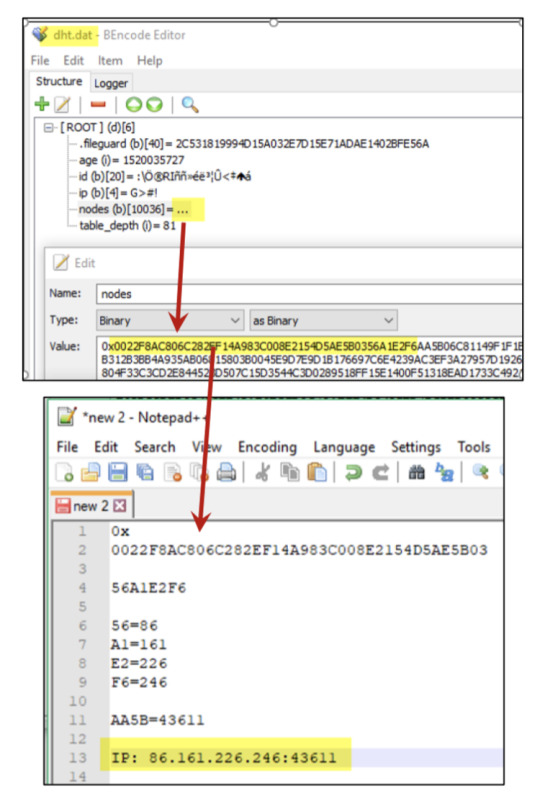
id (b)=: Contains the unique ID of the client’s node, 20 hex character pairs. To display the data, select: “Raw BEncoded Data” and “as Binary”:
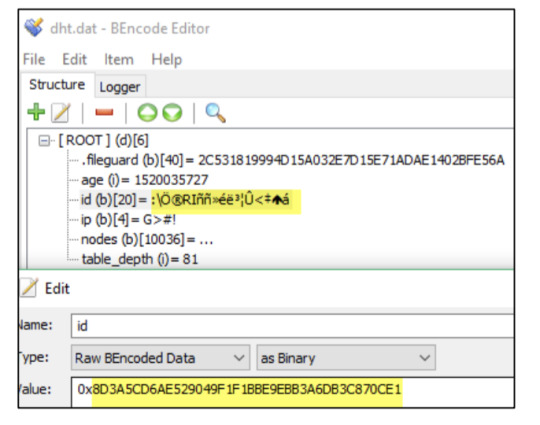
Torrent files
To distribute files using the BitTorrent protocol, a .torrent file will need to be created and seeded. In the client, .torrent files can be created using the following procedure. In μTorrent, select FILE Create Torrent
Select either a single file, or the contents of a directory containing the files that will be associated with the torrent file Add or change the torrent tracker URL information Add any comments regarding the torrent contents as desired Check Start seeding Select Create Provide a name for the torrent file, and be sure the file type is Torrent files:
A BEncode viewer (BEncode Editor) is necessary to view the content of a .torrent file. announce: URL of the tracker site announce-list: A new key, contains a list of URLs of all trackers for this torrent
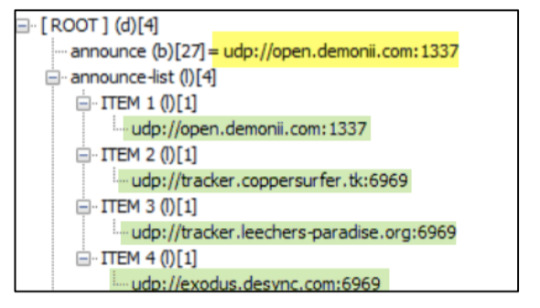
o Tiers of announces will be processed sequentially o All URLs in each tier must be checked before the client goes on to the next tier o The first successful connection with a tracker will cause it to be moved to the front of the tier info: Contains an entry for each file that is included in the torrent: ITEM 1 (d): Indicates which file by number, with the number in brackets referring to the number of items contained in this section (2) length (i)=: Number of bytes of the file path (i): Name of the file name (b)=: Name of the torrent (not to be confused with the name of the .torrent file itself) piece length (i)=: The number of bytes that each piece of the torrent file was split into, arrived at by adding all of the file sizes, and dividing this number by 2,040 pieces (b): Includes the complete SHA1 characters of all pieces strung together, n = total bytes of SHA1 concatenated hashes
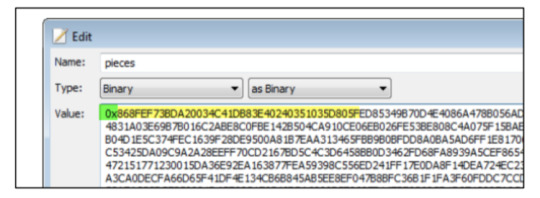
The below graphic explains the contents of the info section of a torrent file. Each file is combined into one stream, then split into fixed piece lengths for efficient transfer using the BitTorrent protocol.
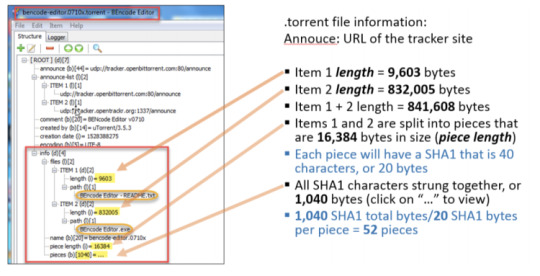
Once a .torrent file has been generated, it will need to be seeded so that others can locate the file based on a search using keywords. The below image displays the Info tab of TEST.torrent showing that there is one member of the swarmwith one peer connected (both are the test client), and the content is included in 33 pieces, each 1 MB in size. TEST.torrent was created by μTorrent v 3.5.3 at 14:15:01, 2 Mar 18.
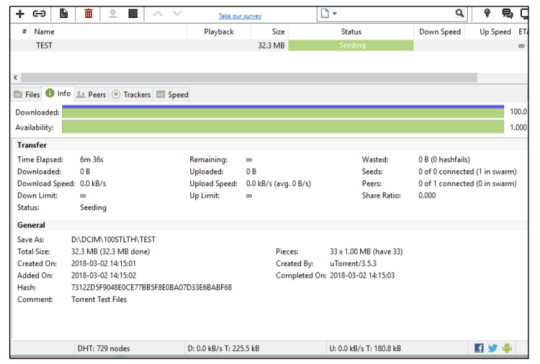
μTorrent statistics
In μTorrent, select Help –> Show Statistics The entire μTorrent directory from the suspect’s system can be exported, and installed in test VM having the same OS in order to emulate (view) the suspect’s μTorrent state at time of last shutdown:

Install same version of μTorrent on the destination system first (look for the .exe file in the updates folder for the version installed). Note that this ‘emulation’ will increment the statistics to include your testing (e.g., program launch time +1), so use VM snapshots and restore as needed.
μTorrent Search Tool
In μTorrent, users can search for content and torrent file indexer site results will display. The search activity will be captured in Web History as it uses the default browser to run the searches.
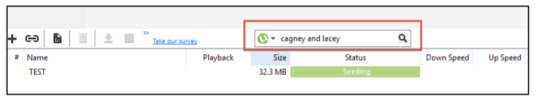
μTorrent Windows Registry Artifacts
The following Windows Registry entries are associated with the installation and use of μTorrent: ntuser.dat\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\uTorrent
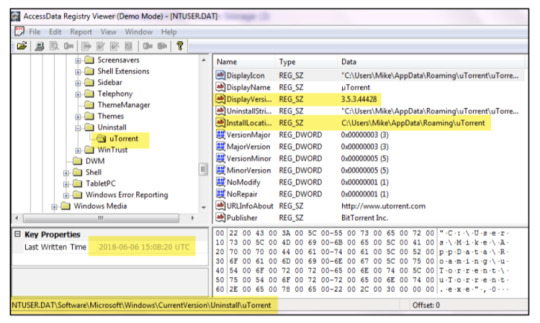
ntuser.dat\Software\BitTorrent\uTorrent
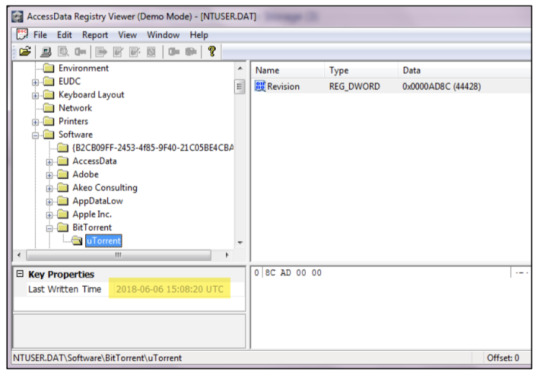
ntuser.dat\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\ FileExts\.torrent\OpenWithList Will show which BitTorrent client type was preferred if multiple clients have been installed (and when) Value = letter representing the order of assigned programs
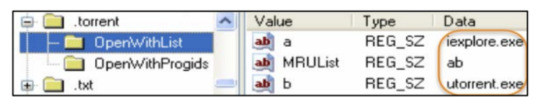
ntuser.dat\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\ RecentDocs\.torrent – Shows recent Torrent files accessed ntuser.dat\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\ComDlg32\ OpenSavePidlMRU\torrent – Shows Torrent files opened or saved via the Windows dialog shell usrclass.dat\Local Settings\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Shell\MuiCache – When an applications is executed, Windows retrieves the application name and stores it – Shows applications that have been executed
Using Notepad++
Notepad++ can be used to assist in translating the raw data retrieved from the encoded data stored in the DAT files or torrent files. To force a string into new lines after every nth character: Copy and paste data to Notepad++ Remove any leading ‘x0’ in byte string data) Select CTRL+H to enter the find and replace menu Enter: ^.{n} in ‘Find what’ Enter: $0\r\n in ‘Replace with’ Replace the {n} with the number of characters before each line (in the below example, {20} is used) o Use 36 for peers6 (resume.dat) – IP/Port o Use 52 for nodes (dht.dat) – Node ID/IP/Port o Use 40 for pieces (.torrent files) – SHA1 characters Select Regular expression Results can then be copied to Excel
Alan Henry, Most Popular BiTorrent Client: μTorrent; https://lifehacker.com/5813348/five-best-bittorrent-applications/1705622513 (May 2015) Ernesto, BitTorent Inc Buys uTorrent, https://torrentfreak.com/bittorrent-inc-buys-%C2%B5torrent/ (Dec 2006) Lauren Hockenson, μTorrent Pro Tips: How to Pair Your Android Device, http://blog.utorrent.com/2015/02/20/%CE%BCtorrent-pro-tips-how-to-pair-your-android-device μTorrent Remote; https://www.utorrent.com/remote Ben Jones, https://torrentfreak.com/common-bittorrent-dht-myths-091024 (Oct 2009) by Michael R. Godfrey https://articles.forensicfocus.com/2018/11/02/forensic-analysis-of-the-%CE%BCtorrent-peer-to-peer-client-in-windows/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
iPhone Lockscreen Exploit Discovered in Apple's Latest iOS Update

It's only been a few hours since Apple releases iOS 12.1 and an iPhone enthusiast has managed to find a passcode bypass hack, once again, that could allow anyone to see all contacts' private information on a locked iPhone.
If you require Digital Forensic assistance in gaining access to PIN or Password Locked iPhone or Samsung handsets get in touch now - Advanced Data RecoveryAlmost as soon as Apple released iOS 12.1 on Tuesday, a Spanish security researcher discovered a bug that exploits group Facetime calls to give anyone access to an iPhone users’ contact information with no need for a passcode. Jose Rodriguez discovered the iOS exploit and first sent the information to The Hacker News. He’s uploaded a video (embedded below) to YouTube demonstrating how the passcode bypass works and Gizmodo has verified that all the conditions he outlines are legitimate. A bad actor would need physical access to the phone that they are targeting and has a few options for viewing the victim’s contact information. They would need to either call the phone from another iPhone or have the phone call itself. Once the call connects they would need to: Select the Facetime icon Select “Add Person” Select the plus icon Scroll through the contacts and use 3D touch on a name to view all contact information that’s stored. Making the phone call itself without entering a passcode can be accomplished by either telling Siri the phone number or, if they don’t know the number, they can say “call my phone.” We tested this with both the owners’ voice and a strangers voice, in both cases, Siri initiated the call. This isn’t a critical security flaw and a random hacker would have some hurdles to clear for this to be of any use, but it could put domestic abuse victims or political dissidents at risk. A truly dedicated hacker could use email and phone number information from a victim’s network to construct a more elaborate hacking campaign through techniques such as phishing. We’ve contacted Apple for comment on the issue but did not receive a reply. We’ve seen virtually identical methods used to bypass the lockscreen in previous versions of iOS and there’s not a whole lot that anyone can do about it until Apple decides to add a fix in future updates. Until then, you could disable Siri to add an extra level of protection but that won’t solve the whole problem. Jose Rodriguez, a Spanish security researcher, contacted The Hacker News and confirmed that he discovered an iPhone passcode bypass bug in the latest version of its iOS mobile operating system, iOS 12.1, released by Apple today. To demonstrate the bug, Rodriguez shared a video with The Hacker News, as shown below, describing how the new iPhone hack works, which is relatively simple to perform than his previous passcode bypass findings. Instead, the issue resides in a new feature, called Group FaceTime, introduced by Apple with iOS 12.1, which makes it easy for users to video chat with more people than ever before—maximum 32 people.
How Does the New iPhone Passcode Bypass Attack Work?
Unlike his previous passcode bypass hacks, the new method works even without having Siri or VoiceOver screen reader feature enabled on a target iPhone, and is trivial to execute. Here are steps to execute the new passcode bypass hack: Call the target iPhone from any other iPhone (if you don't know the target's phone number, you can ask Siri "who I am," or ask Siri to make a call to your phone number digit by digit), or use Siri to call on your own iPhone. As soon as the call connects, initiate the "Facetime" video call from the same screen. Now go to the bottom right menu and select "Add Person." Press the plus icon (+) to access the complete contact list of the targeted iPhone, and by doing 3D Touch on each contact, you can see more information. "In a passcode-locked iPhone with latest iOS released today Tuesday, you receive a phone call, or you ask Siri make a phone call (can be digit by digit), and, by changing the call to FaceTime you can access to the contact list while adding more people to the Group FaceTime, and by doing 3D Touch on each contact you can see more contact information," Rodriguez told The Hacker News. Also, it should be noted that since the attack utilizes Apple's Facetime, the hack would only work if the devices involved in the process are iPhones. The new passcode bypass method seems to work on all current iPhone models, including iPhone X and XS devices, running the latest version of the Apple mobile operating system, i.e., iOS 12.1. Since there's no workaround to temporarily fix the issue, users can just wait for Apple to issue a software update to address the new iPhone passcode bypass bug as soon as possible. Rodriguez has previously discovered a series of iPhone passcode bypass hacks. Around two weeks ago, he found an iPhone bypass hack that works in 12.0.1 and takes advantage of Siri and VoiceOver screen reader to get through your phone's defenses, allowing attackers to access photos and contacts on a locked iPhone. Rodriguez discovered a similar bug in iOS 12 in late last month that also takes advantage of Siri and VoiceOver screen reader, and allows attackers with physical access to your iPhone to access your contacts and photos. http://www.gizmodo.co.uk/2018/11/iphone-lockscreen-exploit-discovered-in-apples-latest-ios-update/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Is Data Recovery Possible after a Ransomware Attack?

"Specialists from foreign countries and other users started to seek advice after reading this article. Turns out, not all of you understand when forensics engineers can help recover data. In this article, we will consider typical questions and give answers based on own experience."
If you require assistance following a Ransomware Attack get in touch now - Advanced Data Recovery Frequently asked questions: Are the files encrypted or a whole partition? We have had both cases in our experience. If files are encrypted, we recommend you recover data from FreeSpace partition (ransomware usually misses this area). Why will it succeed? Data copies could be deleted, moved or create temporary files. So it’s necessary to make analysis. It’s a difficult case when a partition is entirely encrypted. In the future it will occur rarely. Why do we think so? The volume of storage devices increases. As a result, time spent for encryption will increase as well. This will make it more difficult for hackers to achieve their goals. Is it possible to recover data if a whole partition is encrypted? If the algorithm of encryption is cryptographic and the key is unknown, we won’t be able to help. How can you determine whether an algorithm is cryptographical or not? Usually the algorithm of encryption is unknown. So it’s difficult to give a definitive answer. There’s a choice to search markers.

In this case, we define XOR with some additions. How to determine XOR is used? It’s necessary to take two or three files of same type and compare them. The presence of coinciding parts and further analysis will let us make a conclusion about the algorithm used.

A frauder sent the name of algorithm of encryption in a text file. Will it help to decrypt?

It’s difficult to answer. There are many variations of cryptographic algorithms. The task of key search is the most important. I know a new extension of files that ransomware created. Will it help? It’s not important what kind of extension it is. There are many options, but they systematize poorly. Most important is what is inside the file.

How can you find the encryption key? It’s a direct key brute-force or heuristic analysis. But there are few chances. If there’s ransomware (for example, an email with an infected file), it’s possible to make a test case with prepared PC with a huge volume of data (we need to buy some time). Run a ransomware. While it’s encrypting data, we make some dumps of RAM in short intervals. Compare them and seek patterns. Have you succeeded in key searching with the help of RAM dumps? Not yet. It’s just a hypothesis. We can’t check it because users are not ready to pay for such expensive work. So when is it possible to help if a virus has encrypted data? It’s possible if files are not entirely encrypted.

How can you determine that? You need to find an unencrypted copy of an encrypted file (on another device, for example) and compare them. This procedure should be repeated on some examples. It’s necessary to determine the length and location of encrypted areas better. If there’s no coincidence, file will be entirely encrypted. The only decision is a key search (vide supra). If there’s coincidence, part of the user’s data is not encrypted. What size of file should be taken for comparison? The more the better. A file’s size has to be more than 10 MB. One of the versions of well-known Petya (NotPetya) encryptor had encrypted only the first MB of data. Files of up to 1 MB were entirely encrypted. Files of more than 1 MB were partly recovered. Look at the fifth figure. How can you recover data if a file is not entirely encrypted? There’s no single algorithm for the problem. Everything depends on data file type, length and location of encrypted areas. It’s a creative work for data recovery specialists. What do you do when you get a case with ransomware? The algorithm we follow: to check FreeSpace area to investigate the ransomware we open uncompressed files, for example doc, xls (don’t confuse with docx, xlsx). If you don’t have a correct header of a file, so this file is possibly encrypted we search a code 0x00000000 (for example). Such code is often used in uncompressed files and it’s not used in encrypted fragment.

we ask the customer to provide unencrypted copies of encrypted files from another PC, if possible compare them and define the areas of encryption in this example at 6th pic ransomware encrypts with blocks 8192 bytes in size. Encrypt area Unchanged area Encrypt area Unchanged area Encrypt area Unchanged area … ID key ransomware


We try to decrypt using various combinations of ID key ransomware and known algorithms of encryption (AES 256, for example). We know that there are a few chances but let’s try. we suggest RAM investigation if there’s ransomware; we define more exactly what kind of data should be recovered and whether partial data recovery will help the customer; we suggest an individual solution depending on a file type. https://www.digitalforensics.com/ Read the full article
0 notes