Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Chapter 18 Reflection: Debates & Conclusion
A concept I found the most interesting and useful would be how to balance risk and returns when deciding where to invest, especially the advice that recommended that I employ diversification when investing in order to reduce the risks of holding stocks and eliminate firm-specific risk. It is helpful to remember that the higher average return can only be granted at the price of a higher risk, this is known as the risk-return tradeoff and will be essential when I decide to invest. The concept of inflation and how to protect your savings from devaluation also encouraged me to think about investing more seriously, I have family who always wanted to talk about these concepts and I usually found them boring but now I feel as if I have developed a new interest in protecting my future funds as much as possible from inflation. My favorite reflection was the one that was connected to Chapter 9, as I was able to personalize my response with my goals and incentives for the future while also putting to use the concepts we learned within that chapter. I feel much more confident in the degree I chose as well as how to make better financial decisions!
There is an area where I changed my thinking and it would be that prior to this course I assumed an unemployment rate of 0% was possible and I would often be confused by economic statistics that would say the unemployment rate is at 4% and I automatically assumed that meant our economy would worsen. Now I understand that it’s impossible for the unemployment rate to decrease all the way down to 0% because of the different factors involved in defining why an individual is unemployed. I learned that an unemployment rate below 6% is usually ideal and reflects that our economy is normal. Now when I read news articles based on the economy I will be better able to understand the current situation and the predictions of the future based on economic interactions. Prior to this course, I was also confused by the relationship between inflation and unemployment as described by the Phillips curve, but now I understand the inverse relationship between both variables and the tradeoff faced by policymakers as a result.
The debate that I consider the most significant and interesting would be the Should the Government Fight Recessions with Spending Hikes Rather Than Tax Cuts? debate where I agreed with The Government Should Fight Recessions with Spending Hikes, because when the government increases spending on infrastructure, education, and other programs, demand will be stimulated, and the creation of jobs will occur as well as economic growth as unemployment is reduced. According to a calculation retrieved from economists in the Obama administration, “each dollar of tax cuts increases GDP by $0.99, whereas each dollar of government purchases increases GDP by $1.59,” emphasizing that increases in government spending are more effective than tax cuts.

0 notes
Text
Chapter 17 Reflection: Unemployment and Inflation
The short-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment is a negative relationship as described by the Phillips curve, when unemployment is low, inflation is usually high, on the other hand, when unemployment is high, inflation is typically low. When the economy is growing quickly and unemployment remains low, employers struggle to find workers and usually increase prices to pay their current workers more due to decreased labor supply, leading to higher inflation. During a recession, high unemployment would reduce the prices of goods and services as consumers spend less, leading to lower inflation. There is not a long-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment because the relationship between the variables of inflation and unemployment is not determined by economic activity but instead by the structural factors of an economy, permanently reducing inflation at the cost of allowing higher inflation is not possible. I believe that the short-run lasts about three years to five years, our economy is always fluctuating in response to economic activity so it is expected to contract and expand at various times of the year.
Our current inflation rate is effectively helping to reduce unemployment, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the unemployment rate has diminished since April 2020 when it was at an astounding 14.7% as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. As of March 2023, the unemployment rate is currently at 3.5%, a significant decrease compared to three years ago. In April 2020, the inflation rate for the United States was about 0.3% whereas the inflation rate for March of 2023 was reported to be at 5%, it is clear that the inflation rate right now is effective in reducing unemployment.
Sources:
Civilian unemployment rate (bls.gov)
United States Inflation Rate - March 2023 Data - 1914-2022 Historical - April Forecast (tradingeconomics.com)
Here's the inflation breakdown for March 2023 — in one chart (cnbc.com)
0 notes
Text
Chapter 13 Reflection: 3 Interesting Concepts
Three things I found interesting in Chapter 13: Open-Economy Macroeconomics, of our text, would be that international trade was fostered by technological progress as iit changed the goods and services a country could produce, and the theory of purchasing power parity as well as how government policies aid in increasing international trade.
International trade benefited as a result of technological progress, including improved transportation, communication technology, and automation advancements. This was interesting from my perspective because it opened my eyes to all the aspects of trade that go hand in hand with productivity levels, for example, communication technology has made it extremely easy to communicate with customers on the opposite side of the world almost instantaneously. Automation advancements led to the creation of robots and artificial intelligence which increased the production of goods in an efficient and cost-effective method, increasing competitiveness. Transportation is a critical aspect of trade that delivers goods from one country to another, previously only a limited number of cargo was allowed on cargo ships, but as time and technological progress improved, cargo ships can carry upwards of 100,00 tons today. Transportation also helps preserve the quality of goods to ensure their quality at arrival, according to Chapter 13: Open-Economy Macroeconomics, “Fresh fruits and vegetables that can grow in the United States only in summer can now be consumed in winter as well because they can be shipped from countries in the Southern Hemisphere,” as another example of how transportation progress has improved international trade.
The theory of purchasing power parity refers to the adjustment of exchange rates between currencies to reflect differences in the relative purchasing power of those currencies. An example of purchasing power parity would be that if an iPhone costs $1000 in the United States and that same iPhone costs 117,800 yen in Japan, the exchange rate should be that the cost of the iPhone is the same in both countries when converted to a common currency. Additionally, the theory of purchasing power parity was interesting to me because it is based on the idea of a globalized economy, when comparing the relative prices of goods, overvalued or undervalued currencies can be identified which is useful in comparing the economic performances of different countries. When a country’s currency is identified as undervalued, it could lead to deflation, whereas when a country’s currency is recognized as overvalued, it could lead to inflation. The theory of purchasing power parity offers economic information on international trading partners which allows economists to infer the future of countries’ economies by identifying whether a currency is undervalued or overvalued.
Government policies can increase international trade, it is reflected in the international agreements of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT). I found this to be an interesting topic of Chapter 13:Open-Economy Macroeconomics because government policies that eliminate or reduce tariffs can make it easier for countries to import and export goods, increasing the amount of trade between countries. Free trade agreements, such as NAFTA, create a framework for trading including reducing trade barriers and promoting investment, this reduces uncertainty between trading countries and encourages businesses to invest in new markets as trading is stable. Trading is essential to the US economy as our world becomes more globalized, so does our world economy. By eliminating trade barriers, the US government is creating international bonds that would benefit the trading partners involved. Governments create a more ideal environment for businesses to participate in international trade when their policies increase trade.

0 notes
Text
Chapter 12 Reflection: Inflation
The costs of inflation as listed in Chapter 12: Money Growth and Inflation of the text include shoe-leather costs defined as the cost of reducing money holdings, menu costs referring to costs of a price adjustment, increased variability of relative prices as the higher the inflation rate the greater the swing in relative prices will be causing prices to vary, and unintended changes in tax liabilities as tax codes ignore inflation. Confusion and inconvenience are also costs of inflation as computing a company's profit becomes difficult as the dollar’s value rapidly changes, as well as arbitrary redistributions of wealth as unexpected alternations in prices redistribute wealth among debtors and creditors. The most important cost of inflation would be shoe-leather cost as people spend time and effort protecting their funds and it’s purchasing power during an inflation, this can include making more frequent trips to the bank to withdraw money or looking around for the best deals, productivity would be diminished as people hold onto the money they receive, taking time away from their days. Deflation refers to a decrease in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time, the value of money increases, but it is a significant consequence for the economy as businesses are hesitant to invest or spend and consumers delay purchasing it can lead to the economic downturn and a loss in job creation as the purchasing power of money increases. Deflation is a problem for everyone, as mentioned in Chapter 12: Money Growth and Inflation of our text, “deflation is often a symptom of deeper economic problems,” which affects every worker, employer, business, and corporation that operates within the United States or with the United States. I would agree that deflation is a bigger issue than inflation because inflation is normal and usually indicates the economy is growing, but prolonged deflation may have negative effects on the economy including diminished economic growth and fewer job opportunities, although inflation is more common.
Inflation is considered when I make economic decisions in my life, I try to budget for future inflation keeping in mind that the money I have saved now will probably decrease in value over time, but I also learned that investing is a good way to save the ‘extra’ money we have now in order to gain a return in the future as a way to alleviate the effects of inflation. Specifically considering investments that offer a rate of return greater than the rate of inflation to preserve my savings as much as possible. I budget my paychecks to ensure I have at least 50% to save and 50% to spend on any bills or necessities, but I may alter it to saving 60% and using the remaining 40% for bills or necessities to ensure I can maintain my standard of living through inflation. Inflation usually resonates with higher interest rates, making it expensive to borrow money, therefore I would have to weigh the benefits and the costs of borrowing money to ensure I am making the wisest financial decisions possible.

0 notes
Text
Chapter 10 Reflection: Unemployment
The unemployment rate never falls to zero because the economy is always changing and in response to those changes, workers move toward the industries they are most valued in. When a specific sector of jobs is diminished, the workers of those industries become unemployed and begin the job search process. Minimum wage laws, unions, and efficiency wages also help explain why there is always at least some unemployment. A public policy that affects the unemployment rate would be unemployment insurance, defined in Chapter 10: Unemployment of our text as a program “designed to offer workers partial protection against job loss,” and I think it is intended to be a positive public policy as workers who quit or got fired for a cause were ineligible to receive assistance which minimized the number of people who would take advantage of it. However in reality it turned out to be a negative public policy as it increases frictional unemployment and it diminishes the incentive for people to find work as 50% of their income is covered by unemployment insurance. The “right” amount of unemployment would be below 6% as anything exceeding that would be detrimental to the economy since an unemployment rate of 0% is not possible below 6% is reasonable and healthy.
If I was designing these programs I would consider incentives to work such as providing resources that would aid in financial stability and career advancement, time limits are reasonable because government assistance programs are shared among all people who require it, if there wasn't a time limit, people would take advantage of the monetary assistance and put a strain on the program. Increases in the unemployment rate should be considered a cost to a program, to assess the cost of a program similar to a daycare/preschool program in which subsidized moms could stay home with their children as an alternative to paid care, the cost of that program should be financially supported by the employer of the mother or taxes should be allocated for mothers from their paychecks to the program.
Programs for helping with unemployment should consider the type of unemployment prior to helping with unemployment, there is frictional unemployment which refers to the time it takes for a worker to find a job that best fits their needs and skills and a program idea that would aid in this type of unemployment is resume workshops or free career counseling or resources that would help narrow a specific job down for certain skills an individual may have. Structural unemployment results from the insufficient number of jobs in the labor market that is unable to provide a job for everyone, in order to assist an individual with this type of unemployment a good program would likely offer a workshop where workers can refine their skills and gain new ones to increase the possibilities of jobs that they qualify for.
When the unemployment rate runs below 6% it indicates that the economy is doing well, employers may struggle to find workers for qualified positions which would lead to wage increases and increased prices for consumers or would increase productivity and efficiency through technological innovations. A low unemployment rate usually resonates with inflation and higher interest rates, but it will also lead to economic growth as businesses expand and require more workers to fill positions.

0 notes
Text
Chapter 9 Reflection: Investing in my Future
I save for future emergencies and for my future education. My parents taught me at a young age that just because you have the funds doesn’t mean you should spend it irresponsibly. I “hide” my saved funds in my savings account to prevent myself from seeing them and decreasing my incentive to spend. I have been considering investing when I am more economically stable and my emergency savings are complete, although it can be scary, saving and investment are crucial detriments to economic growth. Firms need to pay you something to use your “extra” money because of the risk involved when they borrow your money, you are accepting the risk of the firm being unable to return the money therefore they also pay you to increase your willingness to let them borrow your funds. Additionally, firms will have to accept an agreed-upon interest rate which is the price of borrowing money.
Since I have not made any investments yet, I will balance risk and return in the future when I make investments by partaking in the financial advice of diversification, or not investing all my money into one single company to eliminate firm-specific risk and reduce the risks of holding stocks. I would also reflect on the risk-return trade-off, remembering that the higher average return comes at the price of higher risk. To ensure careful consideration pertaining to my future investment, I will obtain information online regarding the stocks of companies specifically keeping in mind the price of the share, the dividend paid to stockholders as portions of the corporations' profit, and their price-to-earnings ratio. I would most likely seek an investment portfolio that is diversified and with low fees as opposed to only a few companies. When I chose my major of political science I did think about the potential jobs or salaries associated with it, I knew there were a lot of opportunities that would open up for me with a Bachelor in Political Science including either law school or the opportunity to work for a government agency, I did not take into account the risks associated with the strength of the economy unfortunately. A job I would be qualified for when I graduate would be a Government Management Analyst, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary in 2021 for this job is $93,000 per year whereas the salary without a degree would be around $40,000 annually, it is a 53,000 difference annually. Using the guide on Forbes to calculate my college education return on investment, the cost of attendance for two years at Colorado Mountain College was covered by the Federal Pell Grant and the cost of attendance at Colorado State University is about $24,000 for the two remaining years of my bachelor's degree, and I do not anticipate taking out any student loans as I am saving the money as I work. My potential return on investment is $93,000 (potential salary after graduation) - $24,000(cost of attendance) = $69,000.
I think I made a good investment, my expected return on investment would be around $69,000 and if I ever wanted to pursue a law degree, my bachelor's in political science would aid in the entrance requirements so I’d stick with my major as there are a variety of jobs that I would qualify for upon completion. The non-monetary aspects of my potential career would include career satisfaction, growth potential, a work-life balance, and the ability to make a social impact, I value both equally and I still believe that political science is the major that best aligns with my passions but also would allow me to find a career that I enjoy.
Sources:
Management Analysts : Occupational Outlook Handbook: : U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (bls.gov)

0 notes
Text
Chapter 8 Reflection: Economic Recessions and Growth
Large annual federal deficits should affect the market for loanable funds as highlighted in Chapter 8: Saving, Investment, and the Financial System of our text, “When the government reduces national saving by running a budget deficit, the interest rate rises and investment falls,” meaning that the supply of loanable funds is reduced by a budget deficit but the demand for loanable funds is not altered. The demand for loanable funds should not be altered because the budget deficit does not influence the amount that households and firms want to borrow at any given interest rate. When the supply of loanable funds decreases, the equilibrium interest rate rises and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds decreases. Inflation is factored into interest rates because as inflation rises, lenders will usually increase interest rates to account for the decrease in the value of money over time as well as to encourage people to spend less and save more, reducing the demand for goods and services and relieving inflation. My expectation with respect to interest rates is that the higher they are, the more people will spend less as consumers and businesses are less likely to borrow funds which means they’ll save their funds over spending them. Consumers and businesses usually do not benefit from high-interest rates, but banks and lending institutions usually benefit from higher interest rates.
The loanable funds market helps define/choose which investment projects are funded each year because as illustrated in Chapter 8: Saving, Investment, and the Financial System of our text, “all income that people have chosen to save and lend out, rather than use for their own consumption,” therefore it is an exchange of funds between borrowers and lenders where the supply and demand determine interest rates. For example, if there is an increase in the demand for the market of loanable funds and the supply of loanable funds remains the same, interest rates will most likely rise. When interest rates rise as a result of a change in the loanable funds market, it makes borrowing more expensive and decreases the possibility of borrowing to fund investment projects. On the other hand, when the supply of loanable funds increases but the demand for loanable funds remains the same, lower interest rates will result and would increase the incentive to borrow to fund investment projects.
Interest rates are related to return on investments (ROI) because when interest rates are high, investors may potentially earn a higher return on their investment but higher interest rates can also make borrowing more expensive. Interest rates are considered carefully when determining the return on investment, the demand of money during a recession usually rises, at times to alleviate the economic effects of a recession lower interest rates can occur, and lower interest rates usually result in a lower return on investment. During a boom, the demand for money often decreases as businesses and consumers are willing to invest and spend and are less worried about economic uncertainty in the future, leading to higher interest rates to prevent inflation. Higher interest rates can reduce investments as it becomes more expensive to borrow, usually slowing down economic growth. Lower returns on investment decrease the incentive for businesses and consumers to invest, which can also affect economic growth negatively in the long run. Lower interest rates and higher returns on investment can encourage businesses to invest or borrow, leading to positive economic growth in the long run. After reading Chapter 8: Saving, Investment, and the Financial System, my financial plans were affected as I realized the variables that result in economic growth and economic downturns. Important variables include interest rates and expected returns on investment. Interest rates can be influenced by inflation, economic growth, the supply and demand of the loanable funds market, and international factors such as war. During inflation and economic growth, interest rates are usually higher, when the demand for loanable funds increases and the supply remains the same, interest rates will also be higher. When the supply for loanable funds increases and the demand remains the same, interest rates will be much lower. Higher interest rates also relate to international factors such as war, as emphasized in Chapter 8 of our text. Returns on investment are affected by economic conditions such as interest rates, economic growth, and inflation. Low interest rates can make it difficult to generate a higher return on investment whereas inflation diminishes the value of investments. It made me realize that every action is dependent on the results of economic growth in the United States, when economic growth is diminished, interest rates and returns on investment will reflect that, it can be hard to predict my future personal plans when I have no idea what will happen in the future, whether another pandemic will slow down economic growth or whether a war will.

0 notes
Text
Chapter 5 Reflection: GDP
Is GDP an accurate measure of evaluating a country’s economy? Do countries with high GDPs display the entirety of well-being in a country?
GDP or gross domestic product is the total value of all goods and services produced by a country within that country usually in the given time period of a year, and it allows economists to measure a country’s economic output which determines the size, health, and stability of a country’s economy. GDP can be calculated by adding consumer goods, investments, government spending, and exports and then subtracting the value of imports, it is a useful indicator of a country’s economic growth. Some countries, such as the United States, China, Japan, Germany, and India maintain the highest GDPs around the world, while others such as Burundi, South Sudan, Somalia, and others have some of the lowest GDPs. Countries with a higher GDP may have a higher level of human capital present within their societies as it leads to more productive workers, they may also have access to natural resources, stable political systems, and technological innovation which promotes economic investment and growth and leads to an increase in productivity and competitiveness displaying a larger GDP. GDP is only one economic measure used to determine the economic well-being of a country, but there are others that should also be considered, such as quality of life, poverty, income distribution, and human development, therefore countries that display high GDPs are not always economically stable or growing, it is just one measure although being significantly useful for economists and policymakers. A current event that focuses on the concept of GDP in the United States was highlighted in the article 4Q GDP Rose 2.9%, Better Than Expected, Despite Recession Talk written by Tim Smart and published on USNews, the article highlights “consumer spending rose 2.1% in the quarter, down from 2.3% in the third quarter but still a good reading…inflation increased by 3.2%, meeting expectations but falling from 4.8% in the prior three-month period,” emphasizing that prices are not rising as quickly as expected. This is beneficial for consumers; however, it could have negative effects on businesses or investors, consumers can buy more than expected with the same amount of money therefore their money goes further than expected. Investors or businesses may see smaller profits and returns than expected as the real inflation rate fell short of expected inflation.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, the current GDP is +1.1% for the first quarter of 2023, compared to the first quarter of 2022 which held the GDP at -1.4%, the GDP is therefore growing. The growth of the United States’ GDP matters because it is an important measure of a country’s economic health. When our GDP grows it means the economy is also growing, allowing businesses to produce more goods and services which also leads to job growth and an increased standard of living for people in the United States. The shrinking of our GDP is significant because it means that the economy is contracting which usually results in job losses, a decrease in living standards, and lower wages. It can also alert us when a recession is on the rise as well as any other economic downturns. GDP is related to health, countries with GDP growth usually correlate with higher standards of living including access to healthcare which prevents the onset of diseases or sicknesses in the future as health is monitored. We are currently still seeing the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the United States GDP as it caused interference to businesses and corporations resulting in a decline of economic activity, this caused chain supply issues, labor shortages, and uncertainty within the US economy. On a personal note, working in the hospitality industry all practices are still not back to normal, our services provided are significantly different, and as a result of the pandemic, many hospitality services were forced to either close down for a short period of time or diminish the number of guests served which did impact the profits of such businesses.

0 notes
Text
Chapter 4 Reflection
Ride-sharing Companies Market vs Taxi Service Market
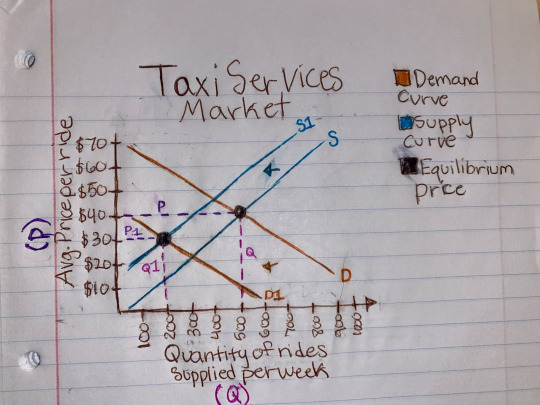
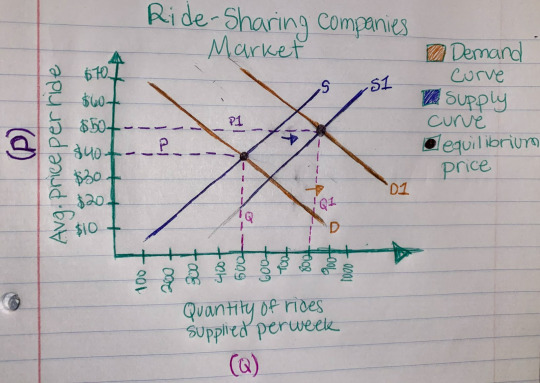
Yes, I would expect Uber, Lift, and other ride-sharing companies to affect the prices of taxi trips. When a consumer is in need of transportation to a specific location it may be more convenient to request a ride from the ease of their fingertips on Uber or Lyft, whereas taxis require the consumer to be physically outside and visible, signaling them that they are in need of a ride. The convenience of Uber and Lyft would most likely decrease the prices of taxi trips as they become the new ‘taxi’ transportation system, Uber and Lyft also show the price of the trip and it is set (besides the optional tip) unlike taxis where the prices could vary each ride (many charge by the minute).
Taxi Services Market
Ride-Sharing Companies Market
The emergence of Lyft and Uber would shift the demand curve to the left for the market of taxis. Lyft and Uber become more convenient alternatives to taxi services increasing the demand for Lyft and Uber and decreasing the demand for taxi services. In the taxi service market, it would cause the equilibrium price to decrease. The quantity supplied, or the supply curve as a result would decrease as well due to the law of supply as mentioned in Chapter 4, this is a shift of the supply curve to the left.
The market for ride-sharing services would see a shift in the demand curve to the right as they become more popular and convenient than taxis, gaining more consumers to receive their services. As the demand for taxis decreases, the demand for ride-sharing services increases. The demand curve would shift to the right to represent the market for ride-sharing services, causing the equilibrium price to increase slightly which results in a higher quantity provided of services, shifting the supply curve to the right.
Minimum Wage
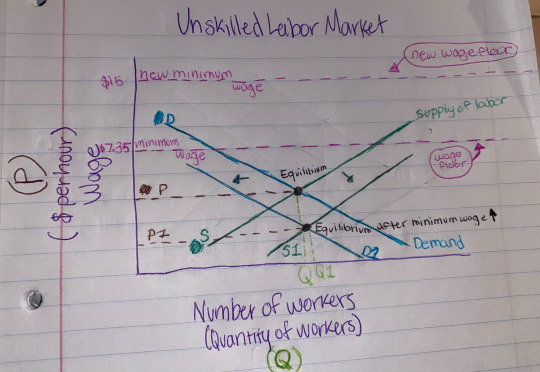
The quantity demanded of labor usually decreases when the minimum wage is increased as it increases the cost of labor for employers who will then reduce the number of workers they hire and/or reduce the number of hours of current workers to alleviate the increased cost of labor.
The quantity supplied of labor will usually increase when the minimum wage is also increased, the higher minimum wage attracts more workers and encourages them to enter the labor market giving employers more hiring options based on a wider range of skills.
The wage floor is drawn above the equilibrium wage because the equilibrium wage is defined as the wage at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity of labor demanded. The wage floor depicts the situation where minimum wages are set above the equilibrium wage level and it is the lowest legal price that can be paid in a market for goods and services or labor.
The position of the wage floor with respect to the equilibrium wage will change when the minimum wage rises from $7.35 to $15, when it is raised to $15 the new minimum wage will become the equilibrium wage, and the wage floor will be increased to $15 as opposed to 7.35 which it was previously. Employers can legally pay at least $15 per hour in the unskilled labor market, which may or may not incentivize workers to enter the labor market but with diminished job approval results as employers become weary of hiring new workers or have a wider variety of workers to choose from as there is more competition in the labor market for those without a job.
0 notes
Text
Chapter 3 Reflection
A concept from Chapter 3 that surprised me the most was the concept of comparative advantage and its function in trade, benefitting everyone in society as it allows people to specialize in producing goods and services efficiently. It surprised me the most because Chapter 3 mentions, “it is impossible for one entity to have a comparative advantage in both goods,” as the comparative advantage is based on opportunity cost. Opportunity cost is the cost of giving up one good to produce another good, since resources are limited and a country/entity cannot produce an unlimited amount of goods, countries tend to specialize in the goods in which they have a comparative advantage. I would like to do more research on how economic sanctions affect a country’s trade system and finally their economy as well, as I know that sanctions take resources and finances away from countries affecting the stability of their economies. I can look for more information within our textbook or at educational institutions' resources that highlight economic concepts.
We can’t think about trade with China and trade with Wyoming in the same way, since China is a foreign and sovereign country and Wyoming is a state within the United States, trade with China is considered international trade, and trade with Wyoming is considered domestic trade. They are different because China has an immensely large economy which complicates trade with China compared to trade with Wyoming, including tariffs, quotas, and other barriers, trade with China can also be more expensive than trade with Wyoming. Trade with China and Wyoming is similar because they both still involve the exchange of goods and services in order to obtain goods and services they could not easily produce domestically. Trade with China and trade with Wyoming are similar as they both employ the concepts of supply and demand, where market forces drive the price of goods and services, also involving comparative advantage, in which each trading party specializes in the goods and services that provide the lowest opportunity cost.
An example of a recent purchase I made that was primarily produced overseas would be roasted coffee beans I purchased from a coffee estate in Mexico after finding their social media advertising on TikTok, there are locally produced options that roast coffee beans but none that grow and produce the actual coffee beans in Colorado. I did some research and found a few nearby coffee shops promoted “sustainably sourced coffee beans” or “local fresh roasted coffee beans” but none really mentioned growing the coffee beans, it makes me wonder where they also source their beans. Although I still could’ve bought the locally sourced options, I did not as I didn’t know they really sold any, and I automatically assumed they may have purchased their coffee beans similarly to how I did, from large coffee bean estates. I defined local as within 4 hours of my location, Glenwood Springs, although local may vary among people and I may not have the same definition of local that others do.

0 notes
Text
Chapter 2 Reflection
I decided to focus on Ilhan Omar, who is a representative for Minnesota's 5th congressional district since 2019. A normative statement made by Ilhan Omar includes “In America, no one should die because they can’t afford healthcare.” during an introduction to a plan that would lower drug prices, since it is prescriptive and makes a statement as to how America should be this is a normative statement. A positive statement made by Ilhan Omar includes “our homelessness is not a crisis of scarcity, but a crisis of moral clarity”, which she tweeted on Twitter on January 28th, 2019, this was a descriptive statement as it spoke about how the world is. It matters whether his statement is normative or positive because although a positive statement provides a clear description of what has happened or what is happening, a normative statement would be how a person wants to address a topic or issue in the way that best aligns with their moral values or views on humanity. Despite positive statements actually offering what is happening, normative statements offer a view into an individual's perspective on a certain issue or topic with an additional insight on their values and their moral compass.
Identifying which statement falls into which category does make me approach and interpret the information or statement differently, I would not hold normative statements as important academically or as professionally as I would hold positive statements, however ethically and if I wanted to truly understand an individual better, I would take into consideration their normative statements more than their positive statements. This is because I feel that normative statements allow us to understand why an individual may hold a certain belief as to how it has to be, whereas positive statements simply offer what the situation is or what is happening. From a political perspective, it’s necessary to understand the clear distinction between both positive and normative statements because politicians more than anyone offer normative statements to national issues, “we should do this”, “it should be done like this”, “if we did it like this it would work better” and especially to win votes and to convince the general public that they can do what they think is right as long as people vote them into office. Political campaigns are rooted in normative statements, and I think I just realized now!
As I looked through the table of propositions about which most economists agree I did not find many I strongly disagreed with, however I slightly disagree with #16 “The United States should not ban genetically modified crops,” but not from an economist's perspective because I bet it must be cheaper and more efficient to grow genetically modified crops meaning I agree from an economic standpoint, but I disagree from my moral perspective. It’s just hard to understand what is going into our crops and if agricultural companies are willing to take shortcuts for the most production possible. I strongly agreed with #11 “The gap between Social Security funds and expenditures will become unsustainably large within the next years if current policies remain unchanged” because last semester in my algebra class we had an activity where we basically tried to find out how much money we would have saved up after 60 years that would be necessary for retirement and even consistently saving money isn't enough because inflation in 60 years will make a dollar worth about 20 cents (I'm estimating). It was an eye-opener because I realized how many people are unprepared for retirement and think they have many years to save up or social security benefits will be waiting for them once they retire, it’s not the reality. I also strongly agree with #12 “Cash payments increase the welfare of recipients to a greater degree than do transfers-in-kind of equal cash value.” and #14 “The redistribution of income in the United States is a legitimate role for the government.” because it reinforces Principle 7 of governments that can sometimes improve market outcomes and in my microeconomics class last semester we talked about how direct cash was more beneficial to families who are on welfare support than credits or equal to cash value support. I also do believe that it is the United States’ government's responsibility to minimize income inequality and to address negative externalities like pollution to ensure the well-being of their citizens.
0 notes
Text
"Although the invisible hand is powerful, it is not omnipotent."

0 notes
Text
Chapter 1 Reflection
As I read Chapter 1: Ten Principles of Economics a concept that made me rethink my previous beliefs would be principle 7: governments can sometimes improve market outcomes. Previously, I knew that government policies played a role in the economy however I didn’t grasp in which ways the government prevents market failures. If people didn’t feel like their efforts and hard work were valued and protected, they wouldn’t be willing to participate in the economic market as there is no guarantee that their goods and services will be compensated. Governments can impose policies and laws and enforce them to improve market outcomes, ensuring that participants in the market are protected in return for producing and selling goods and services. Governments can also impose tariffs on companies that violate any environmental regulations, a specific quote that stuck with me throughout this chapter would be, “although the invisible hand is powerful, it is not omnipotent,” which is why the government has to step in and allocate resources to prevent market failures and to address externalities that the market alone fails to take environmental costs into account.
A common debate I always hear is, “the government needs to leave the economy alone” however, I don’t think many people take into consideration that the government tries to remedy market failures and promote economic equality to encourage workers and increase productivity, as we learned in Chapter 1 from the Ten Principles of Economics, principle 8 states “In nations where workers can produce a large number of goods and services per hour, most people enjoy a high standard of living,” a country’s standard of living depends on its ability to produce goods and services. I took Microeconomics last semester and had a difficult time understanding the Principles of Economics. Still, the more I try to understand it and work with it, applying it to real life, I understand why they’re prominent principles and how each one helps us better understand the economy around us and the stability of other countries' economies.
New questions I have now about the US economy based on Chapter 1 include how does the United States tax policy compare to other countries? Is individual income taxed higher than in other countries or lower? I always hear complaints about how much income is taxed every pay period, but I never understood why. I’d also like to learn more about how federally collected taxes are distributed and how it compares to other countries.
1 note
·
View note