Text

Falling in a straight tunnel through a homogenous Earth would take about 42 minutes, whether the tunnel goes through the center or not. "Shortest-time" tunnels depicted above would transport you between two locations on the surface in 42, 37, and 28 minutes. These tunnels are longer than straight tunnels. But since they start off directly towards the center they make the initial acceleration as large as possible, which develops larger speed and in the end shortens the transit time.
104 notes
·
View notes
Text

Three objects with same mass are going down the large cylinder: small pad slides without friction, while the cylinder and the hoop roll without slipping. The pad looses contact with the surface first, then the cylinder, then the hoop; with cosine of the braking angle to the vertical 2/3, 4/7, and 1/2, respectively, which amounts to about 48, 55, and 60 degrees.
60 notes
·
View notes
Text


This version of a pendulum sees the bead moving without friction on a circular wire that rotates around the vertical axis. With the frame rotating faster and faster, the stable equilibrium position at the bottom becomes unstable while it bifurcates to two stable positions approaching right angles.
39 notes
·
View notes
Text


Jumping off a puck collectively, compared with jumping off individually. Each jump is made with same speed relative to the puck.
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
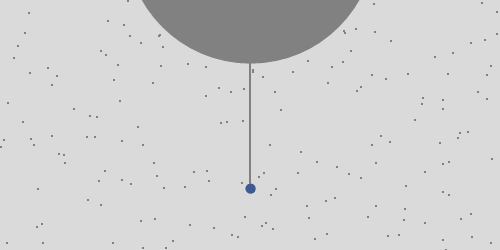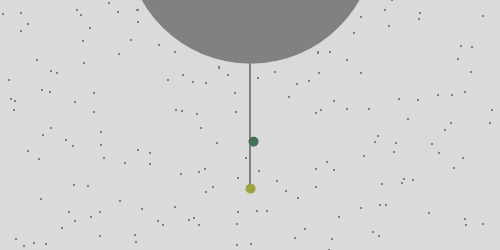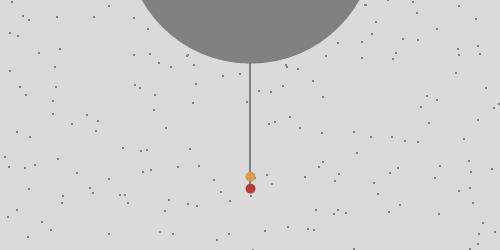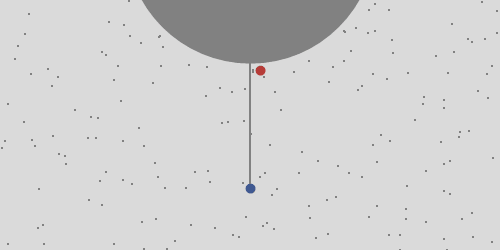
A rock is dropped from a tower one Earth's radius high and observed in the frame of the tower. Perhaps surprisingly the rock doesn't fall at the base of the tower. Ignoring resistance in the atmosphere it lands about 550 km to the East. This is because points closer to the axis move slower and the rock overtakes them. This is Coriolis force, which is not a force of interaction like gravity is. It's a consequence of observing a motion in the rotating frame of the Earth.
170 notes
·
View notes
Text
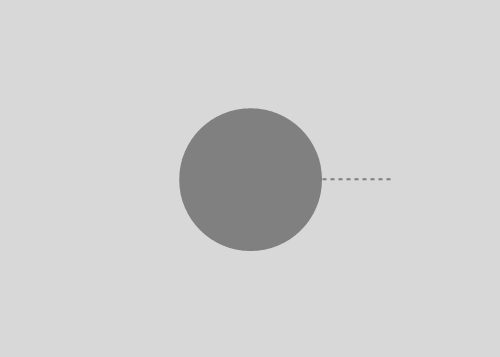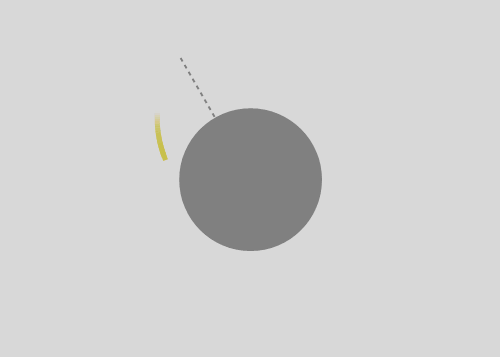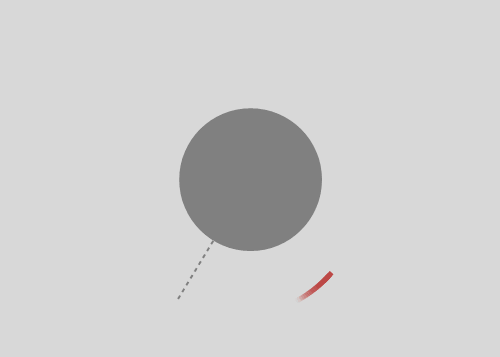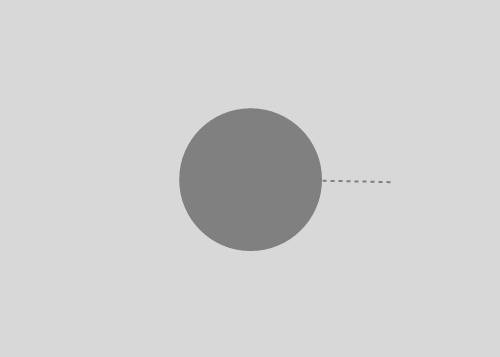
Launching a rock from a tower with height equal to Earth's radius. Air resistance is ignored, but variation of gravitation is not. First rock is just dropped. Then a rock is given some tangential speed. When the initial angular velocity is about five times the angular velocity of the Earth, a rock gets into orbit around the Earth. When this ratio is about six, the orbit becomes circular.
75 notes
·
View notes
Text



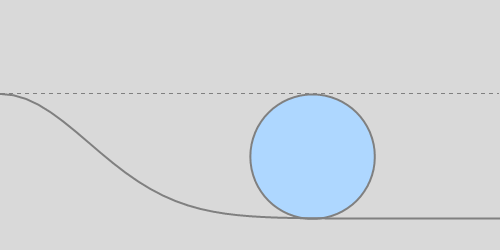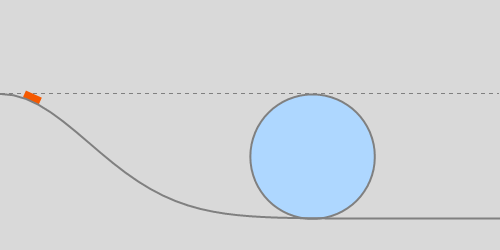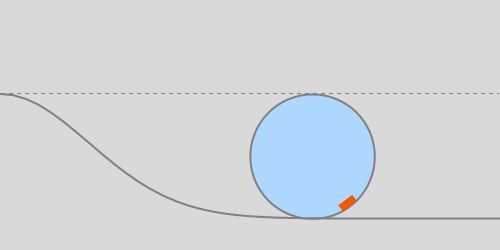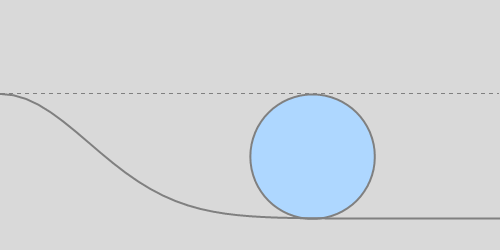
Continuing, the break-off angle of an accelerating sphere is smaller. Three values of acceleration are depicted, relative to g: 0.1, 0.5, and 2.0.
46 notes
·
View notes
Text

Rolling of a wheel can be viewed as a combination of translation and rotation about the centre of mass. Or as pure rotation about the instantaneous axis that is where the wheel touches the ground.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
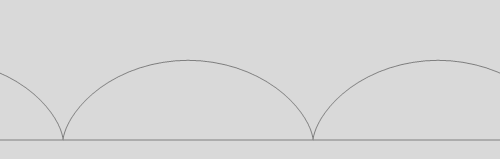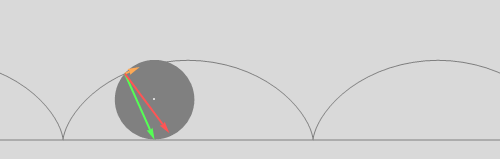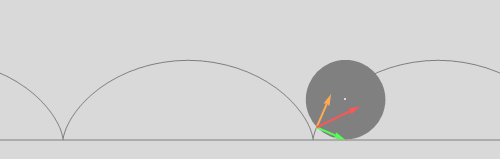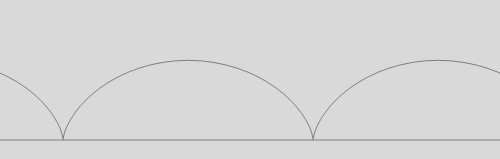
A wheel rolls on a horizontal surface without slipping. Also rolling is the acceleration vector (red). It has two components. Tangential acceleration (orange) changes the magnitude of the velocity vector of a point on the rim of the wheel. Normal acceleration (green) changes its direction.
Note: this is from Irodov, problem 1.52., where it says that acceleration is constant in magnitude and pointing permanently towards the center of the wheel. I humbly disagree. Please comment.
76 notes
·
View notes
Text

Animating polygon-by-polygon previously I realized I can simplify my code and construct a tower with an arbitrary number of polygons. What's the smallest and what's the largest height of a tower?
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Triangle must be the top. (after szimmetria-airtemmizs)
405 notes
·
View notes
Text

This GIF has 10 frames, 8 colors, and 26 kilobytes.
105 notes
·
View notes