Text
Restoring Function Through Hand Surgery

The hands are intricate and vital tools that allow us to perform various daily activities. When hand injuries or conditions affect their functionality, hand surgery becomes a valuable option. Hand surgery encompasses a wide range of procedures aimed at restoring hand function, relieving pain, improving aesthetics, and enhancing overall quality of life. This comprehensive article provides an in-depth overview of hand surgery, including its indications, common procedures, postoperative care, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
Understanding Hand Conditions and Injuries
The hands are susceptible to various conditions and injuries, including fractures, tendon injuries, nerve compression syndromes (such as carpal tunnel syndrome), arthritis, Dupuytren's contracture, trigger finger, and congenital abnormalities. These conditions can cause pain, weakness, stiffness, loss of sensation, and limitations in hand function. Proper diagnosis through physical examination, imaging studies, and other diagnostic tests is essential in determining the need for hand surgery.
Indications for Hand Surgery
Hand surgery may be recommended for a variety of reasons, including:
Traumatic injuries: Hand surgery can address fractures, dislocations, tendon injuries, nerve injuries, and soft tissue injuries resulting from accidents, sports injuries, or trauma.
Nerve compression syndromes: Surgical release of compressed nerves (e.g., carpal tunnel release) can relieve pain, tingling, and numbness in the hand.
Arthritis: Surgical interventions such as joint replacement, joint fusion, or joint reconstruction can alleviate pain, improve joint function, and enhance mobility in arthritic hands.
Tendon and ligament injuries: Surgical repair or reconstruction of damaged tendons and ligaments can restore hand function and stability.
Dupuytren's contracture: Surgery can release the contracted fascia and restore finger extension in this condition characterized by the thickening of tissues in the palm and fingers.
Cosmetic concerns: Hand surgery can address aesthetic issues such as excess skin, prominent veins, or tissue irregularities, improving hand appearance.
Common Hand Surgery Procedures
Hand surgery encompasses a wide range of procedures tailored to the specific condition or injury. Some common hand surgery procedures include:
Fracture fixation: The surgical realignment and stabilization of fractured bones using plates, screws, pins, or wires.
Tendon repair: Surgical reattachment or reconstruction of damaged tendons to restore hand function.
Nerve repair: Microsurgical techniques may be used to reconnect severed or damaged nerves.
Joint replacement: Replacement of damaged joints with prosthetic implants to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
Joint fusion: Surgically fusing the bones of a joint to reduce pain and provide stability in cases of severe joint damage or arthritis.
Carpal tunnel release: The surgical division of the transverse carpal ligament to relieve pressure on the median nerve and alleviate symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Dupuytren's contracture release: Surgical removal or release of the thickened tissue to restore finger extension.
Soft tissue reconstruction: Surgical procedures to restore or reconstruct soft tissues, such as skin grafts or flaps, to improve hand function and aesthetics.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
The postoperative care and rehabilitation process following hand surgery are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. Depending on the procedure performed, patients may require immobilization with splints, casts, or braces to protect the surgical site. Physical therapy or hand therapy is often recommended to promote wound healing, reduce swelling, restore range of motion, and strengthen the hand and fingers. Rehabilitation protocols are tailored to each patient's specific needs and may include exercises, manual therapy, functional activities, and desensitization techniques. Compliance with postoperative care instructions and active participation in rehabilitation are vital for successful recovery.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, hand surgery carries certain risks and potential complications. These may include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, stiffness, loss of sensation, poor wound healing, complex regional pain syndrome, and unsatisfactory functional or aesthetic outcomes. However, with careful surgical technique, appropriate patient selection, and adherence to postoperative care instructions, the risks associated with hand surgery are generally low.
Expected Outcomes
The outcomes of hand surgery depend on various factors, including the specific condition or injury being treated, the patient's overall health, and their commitment to rehabilitation. When performed for appropriate indications, hand surgery can provide significant pain relief, improved hand function, enhanced aesthetics, and a better quality of life. Recovery timelines and expected outcomes vary depending on the complexity of the procedure, the individual's healing capacity, and their commitment to rehabilitation.
Conclusion
Hand surgery plays a crucial role in restoring hand function, relieving pain, and improving quality of life for individuals with hand injuries or conditions. Through a combination of diagnostic expertise, surgical skill, and postoperative rehabilitation, hand surgeons strive to optimize outcomes and help patients regain optimal hand function and aesthetics. If you are experiencing hand pain, functional limitations, or have been diagnosed with a hand condition, consult with a hand surgeon to discuss the available treatment options and determine if hand surgery is appropriate for your specific needs.
0 notes
Text
Ankle Replacement Surgery : Restoring Function

Ankle arthritis and severe ankle injuries can cause debilitating pain and limit mobility. When conservative treatments fail to provide relief, ankle replacement surgery becomes a viable option. Ankle replacement, also known as total ankle arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at replacing the damaged ankle joint with an artificial implant. This article provides a comprehensive overview of ankle replacement surgery, including its indications, surgical techniques, postoperative care, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
Understanding Ankle Arthritis and Injury
The ankle joint is responsible for facilitating movement and providing stability to the foot. However, it is susceptible to arthritis and injuries that can lead to pain, stiffness, swelling, and limited mobility. Common causes of ankle arthritis include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis (due to prior ankle injuries), and avascular necrosis. These conditions can significantly affect an individual's daily activities and quality of life, necessitating surgical intervention.
Indications for Ankle Replacement Surgery
Ankle replacement surgery may be recommended for individuals who experience persistent ankle pain, functional limitations, and decreased quality of life due to ankle arthritis or severe ankle injuries. Candidates for ankle replacement typically have failed conservative treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and ankle bracing. Diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), helps evaluate the extent of joint damage and determine the need for surgery.
Surgical Techniques
Ankle replacement surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia. The surgeon makes an incision along the front of the ankle to access the damaged joint. The damaged bone and cartilage are removed, and the artificial implant components are inserted. The implant typically consists of a metal component fixed to the tibia (shinbone) and a plastic component attached to the talus (ankle bone). These components mimic the natural joint surfaces, allowing for improved mobility and reduced pain.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
After ankle replacement surgery, proper postoperative care and rehabilitation are crucial for optimal recovery and long-term success. Patients are typically required to wear a protective boot or cast to immobilize the ankle initially. Physical therapy and rehabilitation commence soon after surgery to regain strength, range of motion, and balance. The rehabilitation program focuses on weight-bearing exercises, gait training, and functional activities. It is essential to follow the surgeon's instructions regarding weight-bearing restrictions, wound care, and rehabilitation protocols to ensure a successful recovery.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, ankle replacement surgery carries certain risks and potential complications. These may include infection, blood clots, implant loosening, nerve or blood vessel injury, persistent pain, limited range of motion, wound healing problems, and the need for revision surgery. While complications can occur, they are relatively rare, and advancements in surgical techniques and implant design have improved the overall success rate of ankle replacement surgery.
Expected Outcomes
Ankle replacement surgery has shown favorable outcomes in relieving pain, improving mobility, and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with ankle arthritis or severe ankle injuries. Most patients experience a significant reduction in pain, increased ankle function, and improved mobility following surgery. While individual outcomes may vary, the majority of patients can resume daily activities, including walking, cycling, and low-impact exercises, without significant pain or limitations. Regular follow-up appointments with the orthopedic surgeon are important to monitor the progress and longevity of the ankle implant.
Cost in India
On average, the cost of ankle replacement surgery in India ranges from $6,000 to $9,000 USD. This cost typically covers the surgical procedure, hospital stay, surgeon's fees, anesthesia, and post-operative care. However, additional expenses such as pre-operative tests, medications, and rehabilitation sessions may incur separate charges.
Conclusion
Ankle replacement surgery is a valuable treatment option for individuals with ankle arthritis or severe ankle injuries who have not responded to conservative treatments. By replacing the damaged joint with an artificial implant, ankle replacement surgery aims to alleviate pain, restore mobility, and improve the overall quality of life. If you are experiencing persistent ankle pain or have been diagnosed with ankle arthritis, consult with an orthopedic specialist to discuss the available treatment options and determine if ankle replacement surgery is appropriate for your specific condition and needs.
0 notes
Text
Carpal Tunnel Surgery : Procedure
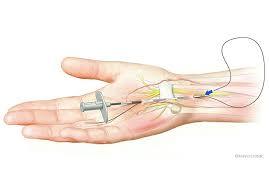
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers. When conservative treatments fail to provide relief, carpal tunnel release surgery becomes a viable option. Carpal tunnel release is a surgical procedure aimed at relieving pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. This article provides a comprehensive overview of carpal tunnel release surgery, including its indications, surgical techniques, postoperative care, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed as it passes through the carpal tunnel—a narrow passageway in the wrist. The compression of the median nerve leads to symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers. CTS is often caused by repetitive hand movements, wrist injuries, certain medical conditions (such as diabetes or arthritis), or anatomical factors that narrow the carpal tunnel.
Indications for Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
Carpal tunnel release surgery may be recommended for individuals with carpal tunnel syndrome who experience persistent symptoms that significantly affect their daily activities and quality of life. Candidates for surgery typically have failed conservative treatments, including wrist splinting, medications, and corticosteroid injections. Diagnostic tests such as nerve conduction studies may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of nerve compression.
Surgical Techniques
Carpal tunnel release surgery can be performed using two main techniques: open carpal tunnel release and endoscopic carpal tunnel release.
Open Carpal Tunnel Release: In this traditional approach, the surgeon makes an incision in the palm of the hand to access the carpal tunnel. The transverse carpal ligament, which forms the roof of the carpal tunnel, is then divided, relieving pressure on the median nerve.
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release: This minimally invasive technique involves the use of a small endoscope—a thin tube with a camera—to visualize the carpal tunnel. The surgeon makes one or two small incisions and inserts the endoscope to guide the release of the transverse carpal ligament using specialized instruments.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Following carpal tunnel release surgery, proper postoperative care and rehabilitation are essential for optimal recovery and symptom relief. The hand may be bandaged or placed in a splint initially to protect the surgical site. Physical therapy or hand therapy may be recommended to promote healing, reduce swelling, and restore hand function. Rehabilitation exercises focus on improving grip strength, range of motion, and flexibility. Patients are typically encouraged to resume light activities soon after surgery, with gradual progression under the guidance of their healthcare provider.
Potential Risks and Complications
Carpal tunnel release surgery is generally safe, but like any surgical procedure, it carries certain risks and potential complications. These may include infection, bleeding, nerve or blood vessel injury, stiffness, scarring, incomplete relief of symptoms, or recurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome. However, serious complications are rare, and the vast majority of patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms and hand function.
Expected Outcomes
Carpal tunnel release surgery has a high success rate in relieving symptoms and restoring hand function. Most patients experience immediate relief from pain and numbness following surgery, while others may take some time to fully recover. The majority of individuals can resume normal daily activities and return to work without significant limitations. Full recovery can vary depending on the severity of the condition, individual healing capacity, and adherence to postoperative rehabilitation.
Cost in India
The cost of carpal tunnel release surgery in India varies depending on several factors such as the city, hospital, surgeon’s experience, and the complexity of the case. On average, the cost of carpal tunnel release surgery in India ranges from $800 to $1,500 USD.
In metropolitan cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore, the cost may be slightly higher compared to smaller cities. The price typically includes pre-operative evaluations, surgeon’s fees, anesthesia charges, operating room costs, and post-operative care.
Conclusion
Carpal tunnel release surgery is a highly effective treatment option for individuals with carpal tunnel syndrome who have not responded to conservative treatments. By relieving pressure on the median nerve, this surgical procedure can alleviate pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand, restoring hand function and improving overall quality of life. If you are experiencing persistent symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, consult with a hand surgeon to discuss your treatment options and determine if carpal tunnel release surgery is appropriate for your specific condition.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Hip Joint Replacement

Hip joint pain and functional limitations can greatly impact an individual's quality of life. When conservative treatments fail to provide relief, hip joint replacement surgery becomes a viable option. Hip joint replacement, also known as total hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at restoring mobility, alleviating pain, and improving overall hip joint function. This comprehensive article provides an in-depth overview of hip joint replacement, including its indications, surgical techniques, postoperative rehabilitation, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
Understanding Hip Joint Degeneration
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint where the femoral head (ball) fits into the acetabulum (socket) of the pelvis. Hip joint degeneration can occur due to various factors, including age, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, and hip fractures. Common symptoms of hip joint degeneration include pain, stiffness, reduced range of motion, and difficulty performing daily activities. Diagnostic techniques such as physical examination, X-rays, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used to assess the extent of hip joint damage and determine the need for surgery.
Indications for Hip Joint Replacement
The decision to undergo hip joint replacement surgery is based on several factors, including the severity of hip joint damage, the impact on the individual's daily activities, and the response to non-surgical treatments. Indications for hip joint replacement include persistent hip pain that limits daily activities, significant functional limitations, decreased quality of life, and radiographic evidence of advanced joint degeneration. Non-surgical treatment options such as medications, physical therapy, assistive devices, and lifestyle modifications may be considered initially, but when these fail to provide sufficient relief, surgery becomes necessary.
Surgical Techniques
Hip joint replacement surgery involves removing the damaged portions of the hip joint and replacing them with artificial components. The surgical procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia. During the surgery, the orthopedic surgeon makes an incision and carefully removes the damaged cartilage and bone. The femoral head is replaced with a metal stem, and a metal or ceramic ball is attached to the stem. The acetabulum is then prepared, and a socket made of metal, plastic, or ceramic is inserted. The artificial components are secured in place, ensuring stability and optimal joint function.
Postoperative Rehabilitation
Postoperative rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the success of hip joint replacement surgery. Physical therapy begins soon after surgery and focuses on regaining mobility, strength, and stability. The rehabilitation program typically involves exercises to improve range of motion, muscle strength, and balance. Patients are instructed on proper techniques for walking, sitting, and performing daily activities to ensure optimal recovery and minimize the risk of complications. Rehabilitation may continue for several weeks or months, depending on the individual's progress and specific needs.
Complications and Risks
As with any surgical procedure, hip joint replacement carries certain risks and potential complications. These may include infection, blood clots, dislocation of the artificial joint, implant loosening, nerve or blood vessel damage, leg length discrepancy, and joint stiffness. However, advancements in surgical techniques, infection control measures, and implant materials have significantly reduced the incidence of complications. To minimize risks, patients are advised to strictly follow the postoperative instructions provided by the surgeon and report any unusual symptoms promptly.
Expected Outcomes
Hip joint replacement surgery has a high success rate in terms of pain relief, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life. The procedure aims to restore the individual's ability to perform daily activities and engage in recreational and sports-related pursuits. While individual outcomes may vary, most patients experience significant pain relief and functional improvement within a few months of surgery. The longevity of hip implants has also improved, with many lasting for 15-20 years or more. Regular follow-up with the orthopedic surgeon and adherence to a healthy lifestyle can contribute to the longevity and success of the hip joint replacement.
Cost in India
Hip joint replacement is a common orthopedic procedure that offers significant relief to individuals suffering from severe hip pain and impaired mobility. India has emerged as a popular destination for medical tourism, thanks to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and cost-effective treatments. The cost of hip joint replacement in India is considerably lower compared to many Western countries. On average, the cost of a hip joint replacement in India ranges from $4,500 to $7,500, depending on various factors such as the type of implant, the complexity of the surgery, the hospital chosen, and the city where the procedure is performed.
Conclusion
Hip joint replacement surgery is a well-established procedure that offers a life-changing solution for individuals suffering from severe hip joint degeneration and chronic pain. By restoring mobility, relieving pain, and improving overall hip joint function, this surgical intervention enables patients to regain their quality of life and engage in activities they once enjoyed. The decision to undergo hip joint replacement should be made in consultation with an orthopedic surgeon, considering the individual's specific condition and lifestyle factors. With advancements in surgical techniques, implant materials, and postoperative rehabilitation protocols, hip joint replacement surgery continues to evolve, providing patients with improved functional outcomes and the prospect of long-term joint health.
0 notes
Text
Elbow Arthroscopy's Minimally Invasive Magic

Elbow injuries and conditions can significantly impact a person's daily activities and quality of life. Elbow arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows orthopedic surgeons to visualize and treat various elbow conditions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of elbow arthroscopy, including its indications, surgical techniques, postoperative rehabilitation, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
Understanding Elbow Arthroscopy
Elbow arthroscopy is a procedure that involves inserting a small camera, called an arthroscope, into the elbow joint through small incisions. This allows the surgeon to visualize the structures inside the joint, including the bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. The camera displays real-time images on a monitor, enabling the surgeon to diagnose and treat elbow conditions with precision.
Indications for Elbow Arthroscopy
Elbow arthroscopy is commonly performed to diagnose and treat various conditions, including:
Elbow instability: Arthroscopy helps assess ligament integrity and guide ligament repair or reconstruction procedures.
Elbow fractures: Arthroscopy aids in the reduction and fixation of fractures, promoting optimal healing.
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis): Arthroscopy can remove damaged tissue and perform a release of the extensor tendon.
Golfers elbow (medial epicondylitis): Arthroscopy can remove damaged tissue and perform a release of the flexor tendon.
Elbow arthritis: Arthroscopy can remove loose bodies, smooth rough surfaces, or perform a joint debridement to alleviate symptoms.
Elbow stiffness: Arthroscopy can help release scar tissue and improve range of motion.
Surgical Techniques
Elbow arthroscopy is typically performed on an outpatient basis under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia. The surgeon makes small incisions around the elbow joint to insert the arthroscope and specialized instruments. These instruments allow the surgeon to perform procedures such as debridement, ligament repair or reconstruction, fracture reduction, or removal of loose bodies. Throughout the procedure, the surgeon carefully examines the joint and performs necessary interventions to address the underlying condition.
Postoperative Rehabilitation
Following elbow arthroscopy, a structured rehabilitation program is essential to optimize recovery and restore elbow function. The rehabilitation process typically involves early motion exercises to prevent stiffness and gradually progresses to strengthening exercises. Physical therapy focuses on regaining range of motion, improving muscle strength, and enhancing joint stability. The duration of rehabilitation varies depending on the specific condition treated and individual factors, but most patients can expect significant improvement within a few months.
Complications and Risks
While elbow arthroscopy is considered a safe procedure, there are potential risks and complications to be aware of. These may include infection, bleeding, nerve or blood vessel injury, stiffness, or failure to alleviate symptoms. However, with proper surgical technique, careful patient selection, and adherence to postoperative instructions, the risks associated with elbow arthroscopy are relatively low.
Expected Outcomes
The success rates of elbow arthroscopy depend on various factors, including the underlying condition, patient characteristics, and adherence to rehabilitation. When performed for appropriate indications, elbow arthroscopy can provide significant pain relief, improved joint function, and a return to normal activities. However, it is important to note that individual outcomes may vary, and full recovery may take several months.
Conclusion
Elbow arthroscopy is a valuable tool in diagnosing and treating a range of elbow conditions. By utilizing a minimally invasive approach, orthopedic surgeons can visualize and address specific issues within the elbow joint. With advances in surgical techniques and rehabilitation protocols, elbow arthroscopy offers patients the potential for improved pain relief, functional recovery, and a return to an active lifestyle. If you are experiencing elbow pain or have been diagnosed with an elbow condition, consult with an orthopedic specialist to determine if elbow arthroscopy is a suitable option for you.
0 notes
Text
Knee Replacement Surgery For Relieving Pain

Chronic knee pain and limited mobility can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. When conservative treatments no longer provide relief, knee replacement surgery becomes a viable option. Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure designed to restore functionality and alleviate pain in individuals with severe knee joint damage. This comprehensive article provides an in-depth overview of knee replacement surgery, including its indications, surgical techniques, rehabilitation process, potential risks, and long-term outcomes.
Understanding Knee Degeneration
The knee joint is a complex structure consisting of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons that work together to facilitate smooth movement. Knee degeneration can occur due to various factors, including age, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, previous injuries, and other medical conditions. Common signs and symptoms of knee joint damage include pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited range of motion. Diagnostic techniques such as physical examination, X-rays, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used to assess the extent of knee degeneration and determine the need for surgery.
Indications for Knee Replacement
The decision to undergo knee replacement surgery is typically based on the severity of the knee joint damage and the impact it has on the individual's daily activities and quality of life. Factors influencing the decision-making process include the individual's age, overall health, pain levels, functional limitations, and response to non-surgical treatments. Non-surgical treatment options such as medications, physical therapy, assistive devices, and lifestyle modifications may be considered initially but may not provide sufficient relief in advanced cases.
Preoperative Preparation
Before undergoing knee replacement surgery, a thorough consultation with an orthopedic surgeon is essential. The surgeon will evaluate the patient's medical history, perform a physical examination, and order necessary preoperative evaluations and tests, such as blood work and imaging studies. Preparing for surgery includes discussing the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes with the surgeon. Patients may also receive instructions regarding medication management, fasting guidelines, and arrangements for postoperative care and rehabilitation.
Surgical Techniques
Knee replacement surgery can involve total knee replacement or partial knee replacement, depending on the extent of joint damage. Total knee replacement involves replacing the entire knee joint with artificial components made of metal alloys and high-quality plastic. Partial knee replacement, on the other hand, replaces only the damaged portion of the knee joint, leaving healthy structures intact. The surgical procedure generally involves making an incision, removing damaged bone and cartilage, and affixing the artificial components securely. Minimally invasive techniques and computer-assisted navigation may be utilized to enhance precision and reduce tissue trauma during surgery. In some cases, additional procedures such as ligament repair or realignment may be performed to optimize joint stability and function.
Postoperative Rehabilitation
Following knee replacement surgery, a structured rehabilitation program is crucial for optimal recovery and functional outcomes. The immediate postoperative care focuses on pain management, wound care, and mobility assistance. As the recovery progresses, physical therapy exercises are introduced to improve range of motion, muscle strength, and joint stability. The rehabilitation program also emphasizes gait training and functional exercises to help patients gradually return to their desired activities. The duration and intensity of the rehabilitation process may vary depending on the individual's progress, but most individuals can expect significant improvement within a few months.
Complications and Risks
Like any surgical procedure, knee replacement surgery carries certain risks and potential complications. These can include infection, blood clots, implant loosening or dislocation, nerve or blood vessel damage, and stiffness in the joint. However, with advances in surgical techniques, implant design, and infection control measures, the incidence of complications is relatively low. Factors that can influence the occurrence of complications include the patient's age, overall health, smoking habits, and adherence to postoperative instructions. To minimize risks, it is crucial to follow the surgeon's guidance regarding postoperative care, including wound care, medication management, physical therapy protocols, and activity restrictions.
Long-Term Outcomes
The success rates of knee replacement surgery are generally high, with the majority of patients experiencing significant pain relief and improved mobility. Knee replacement surgery can greatly enhance the individual's quality of life, allowing them to engage in activities that were once restricted due to knee pain and limitations. The longevity of knee implants has also improved, with many lasting for 15-20 years or more. However, the long-term outcomes can be influenced by various factors, including the patient's age, overall health, weight management, adherence to rehabilitation protocols, and the presence of other medical conditions. Regular follow-up with the orthopedic surgeon and appropriate lifestyle modifications can contribute to the longevity and success of the knee replacement.
Conclusion
Knee replacement surgery is a well-established procedure that offers significant relief to individuals suffering from severe knee joint damage and chronic pain. By restoring mobility and alleviating pain, this surgical intervention enables patients to regain their quality of life and engage in activities they once enjoyed. The decision to undergo knee replacement surgery should be made in consultation with an orthopedic surgeon, taking into account the individual's specific condition and lifestyle factors. With advancements in surgical techniques, implant design, and postoperative rehabilitation protocols, knee replacement surgery continues to evolve, providing patients with improved functional outcomes and the prospect of long-term joint health. Find everything about Knee Replacement Surgery costs in India that range from 2200 - 10000 USD.
0 notes
Text
Understanding ACL Reconstruction Surgery

The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a vital structure in the knee joint that provides stability during movement. Unfortunately, ACL injuries are common, often occurring during sports or physical activities involving sudden stops, changes in direction, or direct blows to the knee. When the ACL is torn or severely damaged, it can greatly affect an individual's mobility and quality of life. ACL reconstruction surgery is a widely recognized and effective procedure for restoring stability to the knee joint. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of ACL reconstruction surgery, including its indications, surgical techniques, rehabilitation process, and expected outcomes.
Understanding ACL Injuries
The ACL is a key ligament that runs diagonally across the knee joint, connecting the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). Its primary function is to prevent excessive forward movement of the tibia relative to the femur. ACL injuries often occur during sports activities such as football, basketball, and skiing, or due to sudden twists or hyperextension of the knee joint. Common signs and symptoms of an ACL tear include a popping sensation at the time of injury, immediate swelling, severe pain, and difficulty in bearing weight on the affected leg. Diagnostic techniques such as physical examination, imaging studies (MRI), and arthroscopy are used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the injury.
Indications for ACL Reconstruction
The decision to undergo ACL reconstruction surgery depends on several factors, including the individual's age, activity level, and desired functional outcomes. Generally, surgery is recommended for individuals who experience persistent instability, recurrent giving way of the knee, or those involved in high-demand sports or activities that require pivoting and jumping. However, in certain cases, non-surgical treatment options such as physical therapy and bracing may be considered, particularly for individuals with low activity levels or minimal instability.
Preoperative Preparation
Before undergoing ACL reconstruction surgery, a thorough consultation with an orthopedic surgeon is essential. The surgeon will evaluate the patient's medical history, perform a physical examination, and order necessary preoperative evaluations and tests, such as blood work and electrocardiogram. Preparing for surgery includes discussing the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes with the surgeon. Patients may also receive instructions regarding medication management, fasting guidelines, and arrangements for postoperative care.
Surgical Techniques
ACL reconstruction surgery involves replacing the torn ligament with a graft, which can be obtained from the patient's own body (autograft) or a donor (allograft). Autograft options commonly used include the patellar tendon, hamstring tendon, and quadriceps tendon. Allograft options include the Achilles tendon and tibialis anterior tendon. The surgery is typically performed arthroscopically, utilizing small incisions and specialized instruments. During the procedure, the surgeon removes the torn ligament remnants, prepares the bony tunnels, and secures the graft in place using screws or other fixation devices. In some cases, additional procedures such as meniscus repair or cartilage restoration may be performed simultaneously.
Postoperative Rehabilitation
Following ACL reconstruction surgery, a structured rehabilitation program is crucial for optimal recovery and functional outcomes. The rehabilitation process is divided into several phases, including the early stage, intermediate stage, and late stage. In the early stage, the focus is on reducing pain and swelling, regaining range of motion, and strengthening the surrounding muscles. As the recovery progresses, physical therapy exercises are introduced to improve balance, stability, and overall knee strength. The rehabilitation program also includes functional training and sport-specific exercises to help patients gradually return to their desired activities. The timeline for recovery varies, but most individuals can expect to resume normal activities within 6 to 9 months.
Complications and Risks
As with any surgical procedure, ACL reconstruction surgery carries certain risks and potential complications. These can include infection, bleeding, blood clots, graft failure, and knee stiffness. However, with advancements in surgical techniques, such complications are relatively rare. Factors that can influence the occurrence of complications include the patient's age, overall health, smoking habits, and adherence to postoperative instructions. To minimize risks, it is crucial to follow the surgeon's guidance regarding postoperative care, including wound care, medication management, and physical therapy protocols.
Long-Term Outcomes
The success rates of ACL reconstruction surgery are generally high, with the majority of patients experiencing improved stability, reduced pain, and a return to pre-injury activity levels. However, the long-term outcomes can be influenced by various factors, including the patient's age, level of physical activity, associated injuries, and commitment to postoperative rehabilitation. It is important to note that while ACL reconstruction surgery significantly restores knee stability, it does not guarantee complete protection against future injuries. Patients should continue to engage in proper conditioning, warm-up exercises, and use appropriate protective gear to minimize the risk of re-injury.
Conclusion
ACL reconstruction surgery is a well-established procedure for individuals suffering from ACL injuries. By restoring stability to the knee joint, this surgical intervention allows patients to regain mobility, reduce pain, and resume their active lifestyles. While the road to recovery requires dedication and commitment to rehabilitation, the long-term outcomes of ACL reconstruction are generally favorable. It is crucial for patients to consult with an orthopedic surgeon to determine the best course of action and to receive individualized care throughout the surgical process. With advancements in surgical techniques and postoperative rehabilitation protocols, ACL reconstruction continues to evolve, providing patients with improved functional outcomes and a brighter future. Find everything about ACL Reconstruction Surgery costs in India that range from 2000 - 6500 USD.
0 notes
Text
Pacemaker Implantation: Enhancing Cardiac Function

Pacemaker implantation is a common medical procedure used to treat individuals with abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) and to improve their cardiac function and overall quality of life. A pacemaker is a small electronic device that helps regulate the heart's electrical activity and ensures that it beats at a steady and appropriate pace. In this article, we will explore the process of pacemaker implantation, indications for the procedure, types of pacemakers, the implantation procedure itself, recovery and follow-up care, and the potential benefits and considerations associated with pacemaker implantation.
Indications for Pacemaker Implantation:
Pacemakers are recommended for individuals with various heart rhythm abnormalities, including:
a. Bradycardia: A slow heart rate, typically defined as fewer than 60 beats per minute, which can result in dizziness, fainting, fatigue, and other symptoms.
b. Heart Block: An interruption or delay in the electrical signals that regulate the heartbeat, leading to an irregular heart rhythm and potential symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
c. Arrhythmias: Certain types of arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, may require a pacemaker to help manage the heart's rhythm.
Types of Pacemakers:
Pacemakers can be categorized based on their functionality and features. The two main types are:
a. Single-Chamber Pacemakers: These pacemakers have one lead (wire) that connects the device to either the right atrium or the right ventricle of the heart, depending on the specific needs of the patient.
b. Dual-Chamber Pacemakers: Dual-chamber pacemakers have two leads—one positioned in the right atrium and the other in the right ventricle. This allows for more synchronized pacing and coordination between the upper and lower chambers of the heart.
Pacemaker Implantation Procedure:
a. Preoperative Evaluation: Before the pacemaker implantation procedure, the patient undergoes a thorough evaluation, which includes a medical history review, physical examination, and potentially additional tests, such as electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, or electrophysiological studies. These tests help determine the appropriate pacemaker type and placement.
b. Anesthesia and Incision: Pacemaker implantation is usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation. A small incision is made, typically in the upper chest, where the pacemaker generator is placed. The leads are then inserted into the veins and guided to the appropriate heart chambers.
c. Lead Placement and Testing: The leads are carefully positioned within the heart chambers and connected to the pacemaker generator. Once the leads are in place, their position and functionality are tested to ensure proper pacing and sensing capabilities.
d. Closure and Recovery: After confirming the correct functioning of the pacemaker system, the incision is closed with stitches or surgical tape. The patient is then monitored in a recovery area before being transferred to a hospital room or discharged home on the same day or the following day.
Recovery and Follow-Up Care:
a. Healing and Incision Care: Following pacemaker implantation, it is important to keep the incision clean and dry, as directed by the healthcare provider. The patient should avoid strenuous activity and heavy lifting for several weeks to allow for proper healing.
b. Medications and Monitoring: The patient may be prescribed medications, such as antibiotics or pain relievers, as needed. Routine follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor the pacemaker's functioning, adjust settings if necessary, and ensure the patient's overall well-being.
c. Lifestyle Considerations: After pacemaker implantation, most individuals can resume their normal activities, including exercise and driving, once they have fully recovered. However, certain precautions and considerations may be advised, such as avoiding intense electromagnetic fields or undergoing regular device checks to ensure optimal performance.
Potential Benefits and Considerations:
a. Improved Heart Function: Pacemakers help regulate the heart's rhythm, ensuring that it beats at an appropriate rate. By doing so, they alleviate symptoms associated with bradycardia, heart block, and certain arrhythmias, improving overall heart function and quality of life.
b. Symptom Relief: Pacemaker implantation can significantly reduce symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath that are often associated with abnormal heart rhythms.
c. Long-Term Management: Pacemakers provide long-term management for individuals with chronic heart rhythm disorders, allowing them to lead active and fulfilling lives.
d. Risks and Considerations: While pacemaker implantation is generally a safe procedure, it carries certain risks, including infection, bleeding, lead dislodgement or malfunction, and complications associated with anesthesia. The healthcare provider thoroughly discusses the individualized risks and benefits with the patient before proceeding with the procedure.
Conclusion:
Pacemaker implantation is a valuable intervention for individuals with abnormal heart rhythms. It helps regulate the heart's electrical activity, alleviates symptoms, and improves overall cardiac function. With advancements in technology and surgical techniques, pacemaker implantation has become a routine and effective procedure. If you or a loved one is experiencing heart rhythm abnormalities, consulting with a cardiologist or cardiac electrophysiologist can provide valuable insights and guidance on whether pacemaker implantation is a suitable treatment option. The procedure, coupled with appropriate postoperative care and regular follow-up, can lead to significant improvements in cardiac health and quality of life. Find everything about Pacemaker Implantation costs in India that range from 3000 - 7500 USD.
0 notes
Text
Advancements in Robotic Heart Surgery
Robotic heart surgery represents a groundbreaking advancement in the field of cardiac surgery. This innovative technique combines the expertise of cardiac surgeons with the precision and dexterity of robotic technology to perform complex procedures with enhanced accuracy and minimal invasiveness. In this article, we will explore the principles, benefits, procedure, applications, and potential considerations associated with robotic heart surgery.
The Principles of Robotic Heart Surgery:
Robotic heart surgery involves the use of a surgical robot, controlled by the cardiac surgeon, to perform intricate procedures with unmatched precision. The robot consists of robotic arms equipped with specialized surgical instruments and a high-definition camera, providing a magnified, three-dimensional view of the surgical field. The surgeon operates the robot from a console, controlling the instruments with hand movements and foot pedals.
Advantages and Benefits of Robotic Heart Surgery:
a. Enhanced Precision and Visualization: The robotic system offers superior visualization, providing the surgeon with a detailed, magnified, and high-resolution view of the surgical site. This improved visualization enables precise manipulation of tissues and delicate structures, enhancing surgical accuracy.
b. Minimally Invasive Approach: Robotic heart surgery is typically performed using small incisions, which significantly reduces trauma to the chest and minimizes scarring. This minimally invasive approach results in less pain, reduced blood loss, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stays compared to traditional open-heart surgery.
c. Reduced Risk of Complications: The robotic system's precise movements and improved visualization contribute to a reduced risk of complications such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues. Additionally, the smaller incisions used in robotic surgery lead to fewer wound-related complications.
d. Faster Recovery and Improved Quality of Life: Patients who undergo robotic heart surgery often experience a faster recovery time, allowing them to resume normal activities and enjoy an improved quality of life sooner compared to traditional surgery.
Robotic Heart Surgery Procedures:
a. Mitral Valve Repair or Replacement: Robotic-assisted surgery is particularly advantageous for mitral valve procedures. The surgeon can access the heart through small incisions, repair or replace the valve with precision, and restore optimal valve function.
b. Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): Robotic CABG involves using robotic instruments to perform bypass grafts on the blocked coronary arteries, improving blood flow to the heart muscles. This technique allows for greater precision and reduces the need for large incisions.
c. Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) Repair: ASD repair involves closing a hole between the upper chambers of the heart. Robotic surgery enables precise suturing and closure of the defect through small incisions, resulting in improved cosmetic outcomes.
d. Atrial Fibrillation Surgery: Robotic surgery can be used to treat atrial fibrillation, a common arrhythmia. The surgeon uses the robot to create precise lesions or perform ablation to restore normal heart rhythm.
Considerations and Potential Limitations:
a. Cost and Accessibility: Robotic heart surgery can be more expensive than traditional surgery due to the initial investment in robotic systems and ongoing maintenance costs. Additionally, access to robotic surgery may be limited in some regions or healthcare settings.
b. Learning Curve: The adoption of robotic heart surgery requires specialized training for cardiac surgeons to become proficient in operating the robotic system. The initial learning curve may impact procedure times and patient outcomes during the early stages of implementation.
c. Patient Selection: Not all patients are suitable candidates for robotic heart surgery. Factors such as the complexity of the procedure, patient comorbidities, and individual anatomical considerations need to be assessed by the surgical team to determine the appropriateness of robotic-assisted surgery.
Conclusion:
Robotic heart surgery represents a remarkable advancement in cardiac surgical techniques, offering enhanced precision, minimal invasiveness, and improved patient outcomes. The combination of robotic technology and the expertise of cardiac surgeons opens new horizons for complex procedures such as mitral valve repair, coronary artery bypass grafting, and atrial septal defect closure. While considerations such as cost, accessibility, and the learning curve exist, the continued evolution of robotic systems holds promise for expanding the availability and benefits of robotic heart surgery. Collaborations between cardiac surgeons, healthcare institutions, and technological innovators will continue to shape the future of cardiac surgery, revolutionizing patient care and improving outcomes in the field of cardiovascular medicine. Find everything about Robotic Heart Surgery costs in India that range from 15000 - 58000 USD.
1 note
·
View note