Text
Understanding Obesity: Causes, Risks & Management
Obesity is no longer just a cosmetic concern—it is a serious medical condition that increases the risk of numerous health problems. Globally, both overweight and obesity rates have doubled in the past few decades, becoming a major public health issue. With changing lifestyles, sedentary work, and unhealthy eating habits, more individuals—both adults and children—are affected than ever before.
In this blog, we’ll explore the facts about overweight and obesity, discuss what leads to obesity, and offer insight into diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.

Facts About Overweight and Obesity
Overweight and obesity are defined as excessive fat accumulation that may impair health. The most widely accepted method to measure this is the Body Mass Index (BMI). A BMI over 25 is considered overweight, while a BMI of 30 or higher indicates obesity.
Among the most important facts about overweight and obesity is its rising prevalence across all age groups. Childhood and adolescent obesity have increased significantly, which calls for urgent attention and preventive strategies.
What Leads to Obesity?
There are several contributing factors that explain what leads to obesity:
Poor diet choices high in sugar, refined carbs, and saturated fats
Lack of physical activity and prolonged sitting
Genetic predisposition and family history
Psychological factors such as stress, depression, and emotional eating
Certain medications that promote weight gain
Obesity is a multifactorial condition, and recognizing these causes is key to addressing it effectively.
Tools to Calculate Obesity
Diagnosing obesity involves more than just the number on a scale. Various tools to calculate obesity include:
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Waist circumference
Waist-to-hip ratio
Body fat percentage analysis using calipers or bioelectrical impedance
These methods help healthcare professionals understand fat distribution and health risk levels.
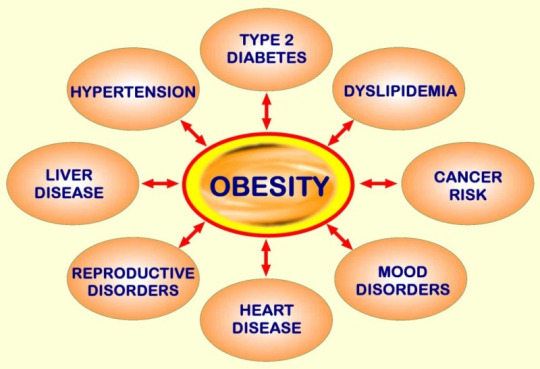
Health Risks Associated with Obesity
The health risks associated with obesity are significant and life-threatening. They include:
Type 2 diabetes
Hypertension and heart disease
Stroke
Sleep apnea
Joint disorders like osteoarthritis
Certain cancers
Obesity also impacts mental health, leading to low self-esteem and depression.
Diagnostic Criteria for Clinical Obesity
The diagnostic criteria for clinical obesity typically start with BMI but also consider other markers like:
Waist circumference above 102 cm (men) or 88 cm (women)
Blood tests for cholesterol, glucose, and liver enzymes
Medical history and lifestyle analysis
Early diagnosis is essential for timely treatment and reducing complications.
Treating and Managing Obesity
A comprehensive plan is needed for treating and managing obesity. It includes:
Dietary changes: Reduced calorie intake, high-fiber foods, and portion control
Physical activity: At least 150 minutes of exercise per week
Behavioral therapy to address emotional eating
Medical treatments: Prescription medications for weight loss
In severe cases, bariatric surgery for obesity may be recommended
All these form part of a long-term plan for weight loss and health improvement.
Cornerstone for Obesity Management
The cornerstone for obesity management lies in prevention. Building healthy habits from a young age, encouraging physical activity, and spreading awareness about nutrition can go a long way. Regular health checkups, early intervention, and family support are also vital.
Obesity in Children and Adolescents
Obesity in children and adolescents is a growing concern. Kids today face increasing exposure to junk food, screen time, and lack of outdoor activity. This not only impacts their physical health but also emotional development. Parents and schools play a key role in creating a healthy environment and instilling active habits early on.

Obesity Prevention Tips
Here are a few simple yet effective obesity prevention tips:
Maintain a balanced, home-cooked diet
Avoid sugary drinks and fast food
Incorporate daily physical activity
Limit screen time and increase outdoor play
Get 7–9 hours of sleep per night
Conclusion: Obesity is preventable, manageable, and treatable with the right strategies. Understanding its causes, risks, and treatment options is the first step toward a healthier life. With awareness, support, and early intervention, we can combat obesity and lead healthier lives—for ourselves and future generations.
0 notes
Text
Tackling Obesity: Clinical Challenges & Realistic Solutions for a Healthier Future
In today’s fast-paced and urbanized world, obesity is no longer just a cosmetic concern—it’s a chronic, complex medical condition with wide-ranging consequences on health, society, and the economy. The alarming rise in global obesity rates demands a closer look into its causes, complications, and, more importantly, clinical solutions that work in the real world.

One of the most comprehensive resources shedding light on this issue is the article titled “Obesity – Clinical Challenges & Sensible Solutions” published on Medtalks. This insightful piece dives deep into the medical, psychological, and lifestyle factors that contribute to obesity and provides actionable solutions backed by clinical expertise.
Why Obesity Demands Immediate Attention
Obesity is linked with a host of serious health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, infertility, sleep apnea, certain cancers, and mental health disorders. What makes it even more challenging is that it doesn’t have a one-size-fits-all cause or solution. Factors such as genetics, environment, food habits, sedentary lifestyle, medications, hormonal imbalances, and stress all play a role in a person’s weight gain journey.
What’s worse—many patients are often stigmatized rather than treated, resulting in delayed care and poor outcomes. That’s why Medtalks’ article stands out. It doesn’t just address clinical aspects but also emphasizes the need for compassionate, long-term obesity management strategies.
Clinical Challenges in Managing Obesity
One of the key highlights from the article is how complex it is for healthcare professionals to address obesity at the root level. Diagnosis, patient motivation, customizing treatments, and managing associated comorbidities require a multidisciplinary approach.
The article explains how doctors often struggle with patient compliance, the psychological burden of obesity, and the limited long-term success of crash diets and quick fixes. It advocates for patient education, realistic goal setting, and continuous behavioral therapy, which are often overlooked in traditional obesity treatment.
Sensible Solutions: A Path Forward
What sets this article apart is its strong emphasis on evidence-based and sustainable interventions. From personalized diet and fitness plans to pharmacological interventions and, in some cases, bariatric surgery, the solutions discussed are practical, scalable, and medically sound.
The piece also underscores the importance of early diagnosis, continuous follow-up, and public health awareness campaigns to manage obesity at a larger scale. It’s not just about losing weight—it’s about creating a healthier, more informed population that can make proactive lifestyle changes.
Final Thoughts
If you're a healthcare professional, a public health policymaker, or even someone battling obesity personally, this article on Medtalks is a must-read. It offers a balanced and medically grounded perspective that’s essential in today’s environment where misinformation and quick-fix solutions are everywhere.
👉 Read the full article here: Obesity – Clinical Challenges & Sensible Solutions
0 notes
Text
Obesity – A Growing Health Concern Worldwide
Obesity is becoming an increasingly common health issue across the globe. But first, let’s understand what is obesity? Obesity is defined as an abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that may impair health. It is usually measured using the Body Mass Index (BMI), where a score of 30 or higher indicates obesity.

The prevalence of obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, and it now affects people in both developed and developing nations. Some key facts about overweight and obesity underline the gravity of the problem. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight in 2016, and 650 million were obese. This makes obesity one of the most prevalent lifestyle-related health issues globally.
Childhood obesity is another alarming concern. Sedentary lifestyles, fast food culture, and reduced outdoor activities contribute significantly. The effects are not limited to physical health; they also extend to mental health, social well-being, and productivity.
Raising awareness about obesity and promoting healthy living is vital. Public health campaigns and digital platforms like Medtalks can play an essential role in educating people about the risks and prevention strategies. Knowing what is obesity and understanding the facts about overweight and obesity can help individuals take action early.
By promoting accurate information and supporting health education, we can fight this epidemic collectively. Knowledge is the first step toward prevention.
0 notes
Text
The Root Causes Behind the Obesity Epidemic
In recent years, obesity has emerged as one of the most pressing health concerns of the 21st century. But what leads to obesity? It’s not just about overeating. A range of factors contributes to obesity, including genetics, environment, poor dietary habits, hormonal disorders, and sedentary behavior.

Unhealthy diets high in sugar and trans fats, combined with minimal physical activity, are among the primary reasons for excess weight gain. Psychological stress and certain medications can also increase fat accumulation. Understanding what leads to obesity helps in identifying the risk early and taking preventive action.
Beyond appearance, obesity is a serious medical condition with multiple complications. The health risks associated with obesity include heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, fatty liver, certain cancers, and musculoskeletal disorders. It also increases the risk of stroke and mental health issues like depression.
The impact of obesity is far-reaching, affecting quality of life and economic productivity. The more we understand about what leads to obesity and the health risks associated with obesity, the better equipped we are to address it on both personal and societal levels.
0 notes
Text
How to Lose Weight Naturally: Expert Tips & Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s fast-paced world, weight gain and obesity have become significant health concerns. According to WHO, global obesity rates have nearly tripled since 1975, with millions suffering from lifestyle-related health issues. For those wondering how to lose weight naturally, the key lies in sustainable lifestyle changes, not crash diets or extreme workouts. Below, we share some expert-backed weight loss tips and highlight common mistakes to steer clear of during your wellness journey.

Expert Tips on How to Lose Weight Naturally
Eat Mindfully and Choose Whole Foods One of the best weight loss tips is to focus on whole, unprocessed foods. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid sugary drinks, packaged snacks, and trans fats that contribute to unhealthy weight gain and belly fat.
Stay Physically Active Regular physical activity helps burn calories and improves overall health. You don’t need intense workouts—brisk walking, cycling, yoga, or dancing can significantly support obesity prevention and enhance metabolic function.
Drink Enough Water Staying hydrated aids digestion, reduces hunger pangs, and prevents water retention. Drinking water before meals may also reduce calorie intake.
Get Adequate Sleep Poor sleep can lead to hormonal imbalances that increase cravings and reduce energy levels, making weight loss harder. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep to support your natural weight loss journey.
Manage Stress Levels Chronic stress triggers emotional eating and raises cortisol levels, leading to weight gain, especially around the abdomen. Meditation, deep breathing, and spending time in nature can help manage stress effectively.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Natural Weight Loss
Skipping Meals Many believe skipping meals helps shed pounds, but it can slow down your metabolism and lead to binge eating later.
Relying on Fad Diets Detox teas and extreme diets promise quick results but rarely offer long-term success. These methods often cause muscle loss and nutrient deficiencies.
Ignoring Portion Control Even healthy foods can cause caloric surplus if not eaten in moderation. Learning portion sizes is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight.
Overlooking Hidden Sugars Sugar is hidden in many “low-fat” and processed products. Excess sugar intake is a key contributor to childhood obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
Lack of Consistency Natural weight loss is a gradual process. Inconsistency in diet and exercise routines often leads to disappointment and giving up too soon.
Final Thoughts
Losing weight doesn’t have to involve extreme diets or exhausting workouts. Understanding how to lose weight naturally and sticking to simple, science-backed habits can lead to lasting changes. By following these best weight loss tips and avoiding common pitfalls, you not only shed pounds but also protect yourself against obesity-related diseases such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and insulin resistance.
Make small, realistic changes today for a healthier, happier tomorrow. Remember, obesity prevention starts with you.
0 notes
Text
Sedentary Lifestyle & Weight Gain: How to Stay Active at Home
In today’s digital era, many people are tied to their desks for hours—working remotely, binge-watching shows, or scrolling through phones. While convenience has increased, it comes with a downside: a sedentary lifestyle. This modern way of living has become one of the leading contributors to weight gain, obesity, and chronic health issues. The good news? You can still maintain a healthy weight and stay active right from your home. Here’s how.

Understanding Sedentary Lifestyle Risks
A sedentary lifestyle refers to long periods of inactivity—particularly sitting or lying down—with minimal physical movement. It poses several health risks such as:
Obesity and weight gain
Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
High blood pressure and cholesterol
Poor posture and joint pain
Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases
People who sit for extended periods are more likely to develop belly fat and struggle with metabolism-related conditions, even if they maintain a moderate diet.
How to Lose Weight Without Exercise
If you're wondering how to lose weight without exercise, lifestyle adjustments and mindful habits can still deliver results:
Eat Smart & Eat Light Focus on a nutrient-rich diet with fewer calories. Choose lean proteins, fiber-rich vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats to reduce overall fat accumulation.
Stay Hydrated Drinking enough water boosts your metabolism and keeps hunger cravings at bay.
Practice Portion Control Overeating—even healthy food—can lead to weight gain. Mindful eating helps reduce calorie intake.
Stand Up Often Set reminders to stand or walk every 30 minutes. Small breaks throughout the day can counter the effects of sitting.
Prioritize Sleep Lack of sleep contributes to weight gain by disrupting hunger hormones. Aim for at least 7-8 hours of quality sleep.
Best Home Workouts for Obesity
If you can dedicate just 15–30 minutes a day, you’ll experience noticeable health benefits. Here are some of the best home workouts for obesity that require no equipment and can be modified for beginners:
Walking in Place or around the house
Chair Squats for lower body strength
Modified Push-ups (against the wall or on knees)
Seated Leg Raises for obese beginners or elderly
Step-ups using stairs or a low platform
Stretching and Yoga to improve flexibility and reduce stress
Dance Workouts – fun and cardio-friendly
Resistance Band Exercises (optional for added challenge)
These home workouts not only promote calorie burning but also improve mobility, heart health, and mental well-being.
Final Thoughts
While physical inactivity may seem inevitable in a work-from-home or desk job setup, small steps can lead to significant health benefits. Understanding sedentary lifestyle risks is the first step toward making better choices. Whether you’re looking for how to lose weight without exercise or the best home workouts for obesity, the key lies in consistency and awareness.
Remember, your health doesn’t depend solely on the gym—it depends on your daily habits. Stay active, stay aware, and take charge of your health from the comfort of your home.
0 notes
Text
Top 10 Superfoods to Fight Obesity & Burn Belly Fat
Obesity has become one of the most pressing health concerns worldwide, leading to an increased risk of diabetes, heart disease, high cholesterol, and other lifestyle disorders. If you're on a mission to shed extra pounds and adopt a healthier lifestyle, your diet is a great place to start. Incorporating nutrient-dense, metabolism-boosting foods can support your journey. Here’s a list of the best foods for weight loss that also act as powerful foods to reduce belly fat and support overall obesity prevention.

1. Avocados
Rich in monounsaturated fats and fiber, avocados help you feel full longer and reduce unhealthy cravings. They’re excellent for weight management and are one of the best foods for weight loss due to their healthy fat content.
2. Green Tea
Packed with antioxidants and metabolism-boosting catechins, green tea increases fat burning, especially around the belly area. It’s a staple in many effective obesity diet tips.
3. Berries
Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are low in calories and high in fiber and antioxidants. They regulate blood sugar levels and support digestion, making them ideal foods to reduce belly fat.
4. Leafy Greens
Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are low-calorie, high-volume foods that fill you up without adding inches to your waistline. They are rich in nutrients and play a vital role in reducing abdominal fat and promoting a balanced diet.
5. Oats
High in soluble fiber and slow-digesting carbohydrates, oats help reduce hunger and stabilize insulin levels. They are excellent for people dealing with obesity and high blood sugar.
6. Nuts & Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds offer protein, fiber, and healthy fats. These nutrient-packed snacks help control appetite and prevent overeating, a common trigger for obesity.
7. Greek Yogurt
With high protein content and probiotics, Greek yogurt boosts metabolism, supports gut health, and reduces bloating. It’s a smart addition to any obesity-fighting diet.
8. Fatty Fish
Salmon, tuna, and mackerel are loaded with omega-3 fatty acids and protein. These help reduce inflammation and promote the loss of visceral fat, which is linked to obesity-related diseases.
9. Quinoa
A complete protein and gluten-free whole grain, quinoa is rich in fiber and essential amino acids. It promotes satiety and reduces cravings, helping with long-term weight loss goals.
10. Apples
Low in calories and high in fiber, apples are one of the best foods for weight loss. Their natural sweetness helps curb sugar cravings, while pectin content aids digestion and fat breakdown.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right foods is essential in your fight against obesity. These superfoods not only aid in burning belly fat but also support a healthy metabolism, balanced hormones, and long-term health. Following these obesity diet tips, combined with regular physical activity and good sleep, can make a significant difference in your weight loss journey.
Remember, beating obesity is not about starving your body—it’s about nourishing it right. Fill your plate with these wholesome foods, stay consistent, and embrace a lifestyle that supports your well-being from the inside out.
0 notes
Text
(Serum Glutamate Pyruvate Transaminase) SGPT: A Key Indicator of Liver Health
Introduction Serum Glutamic-Pyruvic Transaminase (SGPT) also known as Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), is a key enzyme primarily found in the liver. It plays a critical role in diagnosing liver health and detecting underlying conditions. With liver diseases on the rise globally, understanding SGPT levels and their implications has become crucial. If you’re looking for the latest information on liver health, this blog will guide you through the essentials of SGPT, its significance, and trending solutions for managing liver enzymes effectively.

What is SGPT? SGPT is an enzyme that facilitates amino acid metabolism. Elevated SGPT levels in the bloodstream usually indicate liver damage, as this enzyme leaks into the blood when liver cells are damaged. Regular health check-ups and liver function tests often include SGPT readings to evaluate overall liver health.
Why is Monitoring SGPT Levels Important? Keeping a tab on your SGPT levels is vital as it can:
Detect liver conditions early, such as hepatitis or fatty liver disease.
Monitor the effectiveness of treatments for liver disorders.
Provide insights into overall health and lifestyle effects.
Causes of Elevated SGPT Levels
Some common reasons for high SGPT levels include:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A condition linked to obesity and poor lifestyle choices.
Alcoholic Liver Disease: Prolonged alcohol consumption significantly affects SGPT levels.
Hepatitis Infections: Viral infections like Hepatitis A, B, or C.
Medications and Toxins: Certain drugs and toxic substances.
Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise and stress can also contribute.
Symptoms to Watch For Elevated SGPT levels may not always manifest symptoms initially, but watch for:
Persistent fatigue
Jaundice
Nausea or vomiting
Swelling in the abdomen
Dark urine
How to Manage and Lower SGPT Levels?
Adopt a Healthy Diet: Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants, such as green leafy vegetables, berries, and nuts. Avoid processed and fatty foods.
Exercise Regularly: Engage in moderate activities like walking or yoga to maintain a healthy liver.
Stay Hydrated: Water aids in detoxifying the liver and flushing out toxins.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol is detrimental to liver health.
Consult a Doctor: Seek medical advice for persistent high SGPT levels.
Latest Trends in SGPT Management
Plant-Based Supplements: Natural remedies like milk thistle and turmeric are gaining popularity.
Personalized Health Monitoring: Wearable devices now include liver function tracking.
Telemedicine Consultations: Access to online liver health consultations has increased significantly.
Gut-Liver Connection Research: Studies are exploring how gut health impacts liver enzymes.
Conclusion: Maintaining healthy SGPT levels is integral to overall well-being. By adopting a balanced lifestyle, regular check-ups, ps and staying updated with the latest trends in liver health, you can ensure optimal liver function. Make liver care a priority and take proactive steps to manage your SGPT levels effectively.
0 notes
Text
Fatty Liver & SGPT-SGOT: How Are They Connected?
Introduction
The liver is essential for digestion, metabolism, and detoxification. However, unhealthy lifestyle choices can lead to fatty liver disease (FLD), a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver. A key indicator of liver health is the levels of SGPT (Serum Glutamate Pyruvate Transaminase) and SGOT (Serum Glutamic-Oxaloacetic Transaminase), which are enzymes released into the bloodstream when the liver is damaged. In this blog, we will examine the connection between fatty liver and elevated SGPT and SGOT levels, as well as their causes, symptoms, and potential treatments.

Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is classified into two main types:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Caused by obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, or poor diet, NAFLD is common among individuals who do not consume alcohol in excess.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): This is triggered by excessive alcohol consumption, which leads to fat buildup in liver cells.
Both conditions can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) or cirrhosis, causing severe liver damage if left untreated.
What Are SGPT and SGOT?
SGPT (ALT - Alanine Aminotransferase): An enzyme found primarily in the liver. When liver cells are damaged, SGPT levels increase in the blood.
SGOT (AST - Aspartate Aminotransferase): Found in the liver, heart, and muscles, SGOT is another enzyme that indicates liver damage when present in high amounts.
A normal SGPT and SGOT range is crucial for optimal liver function. Elevated levels may indicate liver inflammation, fatty liver, or liver cirrhosis.
How Fatty Liver Affects SGPT-SGOT Levels
When fat builds up in the liver, it leads to inflammation and cell damage, prompting the liver to release SGPT and SGOT enzymes into the bloodstream. This is how fatty liver contributes to elevated enzyme levels:
Inflammation and Liver Cell Damage: Fatty deposits in the liver cause inflammation, leading to enzyme leakage into the blood.
Liver Overload: The liver struggles to process fats efficiently, increasing stress on liver cells.
Progression to NASH: Persistent fat accumulation leads to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a severe form of fatty liver disease that significantly raises SGPT-SGOT levels.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver & High SGPT-SGOT Levels
Fatty liver is often referred to as a "silent disease" because it may not present symptoms in the early stages. However, some individuals might experience:
Fatigue and weakness
Abdominal discomfort or pain (upper right side)
Unexplained weight gain or loss
Jaundice (in severe cases)
Swelling in legs or abdomen (late-stage liver disease)
Elevated liver enzymes (SGPT-SGOT levels) detected in blood tests
If you have any of these symptoms, it's crucial to get a liver function test (LFT) to assess your enzyme levels.
Causes of Elevated SGPT-SGOT Levels in Fatty Liver
Many factors contribute to the development of fatty liver and the elevation of liver enzyme levels.:
Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle – Excess fat accumulation leads to liver dysfunction.
Unhealthy Diet – High sugar, processed foods, and trans fats worsen liver health.
Alcohol Consumption – A leading cause of liver inflammation and enzyme elevation.
Diabetes and Insulin Resistance – Directly linked to fatty liver and high SGPT levels.
Viral Hepatitis – Infections like Hepatitis B and C increase liver damage.
Certain Medications – Painkillers, antibiotics, and cholesterol-lowering drugs can stress the liver.
How to Lower SGPT-SGOT Levels and Treat Fatty Liver
The positive aspect is that fatty liver and elevated SGPT-SGOT levels can be reversed through lifestyle changes and appropriate medical treatment. Here are effective ways to enhance liver health.:
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A liver-friendly diet can help reduce liver fat and enzyme levels:
Eat fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Include healthy fats like olive oil, nuts, and seeds.
Consume lean proteins such as fish, chicken, and plant-based proteins.
Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excess carbs.
Reduce alcohol consumption to prevent further liver damage.
2. Exercise Regularly
Engaging in regular physical activity helps reduce excess fat and enhances liver function. Aim for at least 30 minutes of cardio exercises daily, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling.
3. Hydration & Detoxification
Drinking plenty of water helps eliminate toxins from the liver. Herbal teas, such as green tea and dandelion tea, aid in liver detoxification.
4. Weight Management
Losing 5 to 10 percent of body weight can significantly lower SGPT and SGOT levels while reducing fat accumulation in the liver.
5. Avoid Harmful Medications
Certain medications can place extra stress on the liver. Consult your doctor before taking painkillers, antibiotics, or cholesterol-lowering medications.
6. Try Natural Remedies
Milk Thistle: Known for its liver-protecting properties.
Turmeric: Contains curcumin, which helps reduce liver inflammation.
Amla (Indian Gooseberry): Rich in Vitamin C, supports liver detoxification.
When to See a Doctor?
If your SGPT and SGOT levels remain elevated despite lifestyle changes, consult a hepatologist for further evaluation. Tests such as ultrasound, liver biopsy, and FibroScan can help determine the extent of liver damage.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease and elevated SGPT and SGOT levels are closely related and indicate liver distress. However, with the right diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes, you can reverse fatty liver and maintain healthy liver function. Regular liver function tests (LFTs) can help monitor your SGPT and SGOT levels, allowing for early intervention and improved liver health.
If you suspect you have fatty liver disease, take proactive steps today to protect your liver and enhance your overall well-being!
0 notes
Text
Overcoming Obesity: A Holistic Approach to Better Health
Obesity is a growing global health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. It is not merely a cosmetic issue but a complex medical condition associated with various health risks, including diabetes, heart disease, and joint problems. Effective weight management strategies and understanding underlying health conditions such as hypothyroidism can play a crucial role in overcoming obesity. This article explores the causes of obesity, the role of hypothyroidism, and practical weight management strategies to achieve a healthier life.

Understanding ObesityObesity is characterized by an excessive accumulation of body fat that negatively impacts health. It is typically measured using the Body Mass Index (BMI), where a BMI of 30 or higher indicates obesity. Several factors contribute to obesity, including genetic predisposition, sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary choices, and underlying medical conditions.
Common Causes of Obesity
Unhealthy Diet: Consumption of high-calorie, processed foods rich in sugar and unhealthy fats leads to weight gain.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity reduces calorie expenditure, contributing to fat accumulation.
Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in determining an individual’s likelihood of obesity.
Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like hypothyroidism can slow metabolism and lead to weight gain.
Emotional Factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression often trigger overeating and unhealthy food choices.
Lack of Sleep: Poor sleep patterns can affect hunger hormones, increasing cravings for unhealthy foods.
The Link Between Hypothyroidism and ObesityHypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland produces insufficient hormones, can contribute to weight gain. The thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) play a crucial role in regulating metabolism. When these hormone levels drop, metabolism slows down, making it harder for the body to burn calories efficiently.
How Hypothyroidism Affects Weight
Slower Metabolism: Reduced hormone levels lower the body’s ability to burn fat.
Water Retention: Many people with hypothyroidism experience bloating and fluid retention, increasing weight.
Fatigue: Low energy levels make it difficult to engage in physical activities, leading to further weight gain.
Managing Weight with Hypothyroidism
Medication: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy (e.g., levothyroxine) can help normalize metabolism.
Balanced Diet: Consuming nutrient-dense foods supports thyroid function and aids in weight loss.
Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities like walking, yoga, and strength training can help manage weight effectively.
Effective Weight Management StrategiesLosing weight requires a combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, and behavioral changes. Here are some practical strategies:
1. Nutrition and Diet
Eat Whole Foods: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains in your diet.
Reduce Sugar and Processed Foods: Cutting back on refined carbohydrates and sugary drinks can help prevent weight gain.
Increase Protein Intake: Protein helps in muscle building and keeps you full for longer.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water aids digestion and helps control hunger.
Practice Portion Control: Eating smaller meals throughout the day prevents overeating.
2. Physical Activity
Engage in Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Strength Training: Builds muscle mass, which helps in burning more calories even at rest.
Cardio Workouts: Activities like brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming help in fat loss.
Yoga and Meditation: Reduces stress, which is often linked to emotional eating.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Prioritize Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to regulate hunger hormones.
Manage Stress: Practicing mindfulness, deep breathing, and engaging in hobbies can reduce stress-related weight gain.
Set Realistic Goals: Weight loss is a gradual process; aim for sustainable changes instead of quick fixes.
Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting a nutritionist or doctor can provide personalized advice.
ConclusionObesity is a complex condition influenced by various factors, including lifestyle, genetics, and medical conditions like hypothyroidism. However, with the right approach—combining a balanced diet, regular exercise, proper sleep, and stress management—it is possible to achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Understanding the role of hypothyroidism and adopting effective weight management strategies can help individuals lead healthier and more active lives. If you struggle with obesity, consulting a healthcare professional for tailored guidance is the first step toward sustainable weight loss.
0 notes
Text
Effective Strategies to Lower Elevated SGOT and SGPT Levels
SGOT (Serum Glutamic Oxaloacetic Transaminase) and SGPT (Serum Glutamic Pyruvic Transaminase) are important liver enzymes that indicate liver health. Elevated levels of these enzymes can be a sign of liver inflammation, damage or disease. While various factors including alcohol consumption, obesity, fatty liver disease and medications can lead to increased SGOT and SGPT levels, adopting a healthier lifestyle can help regulate them effectively. In this blog, we will explore actionable strategies to reduce elevated SGOT and SGPT levels naturally and maintain optimal liver health.

1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
Your diet plays a crucial role in managing SGOT and SGPT levels. Incorporating liver-friendly foods and avoiding harmful ones can significantly improve your liver function.
Increase Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Fruits and vegetables like berries, oranges, papaya, spinach and carrots are packed with antioxidants that help detoxify the liver.
Consume More Leafy Greens: Green vegetables such as kale, lettuce and broccoli aid in reducing liver inflammation.
Eat Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats and quinoa support liver function and help regulate enzyme levels.
Reduce Processed Foods: Avoid packaged and junk foods that contain artificial additives, preservatives and unhealthy fats.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out toxins and supports liver detoxification.
2. Reduce Alcohol Intake
Excessive alcohol consumption is a leading cause of liver enzyme elevation. Since alcohol is metabolized by the liver, heavy drinking can strain its function and lead to damage. To lower SGOT and SGPT levels:
Limit alcohol intake or eliminate it altogether.
Opt for liver-friendly beverages like green tea, which contains catechins that aid liver detoxification.
Hydrate adequately to flush toxins from the body.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity and excess fat accumulation in the liver can contribute to elevated SGOT and SGPT levels. A well-balanced diet combined with regular physical activity can help in weight management.
Engage in at least 30 minutes of exercise five days a week.
Incorporate aerobic activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling.
Add strength training to build muscle and enhance metabolism.
Avoid crash diets and focus on sustainable weight loss.
4. Manage Blood Sugar Levels
High blood sugar can contribute to fatty liver disease, leading to increased SGOT and SGPT levels. Regulating blood sugar is essential for liver health.
Reduce sugar intake, especially refined sugars found in sweets and sodas.
Opt for complex carbohydrates instead of simple sugars.
Monitor blood sugar levels regularly, especially if you have diabetes.
5. Take Liver-Supporting Supplements
Certain natural supplements have been found to support liver function and reduce enzyme levels.
Milk Thistle: Contains silymarin, which protects liver cells and promotes regeneration.
Turmeric: Curcumin, its active compound, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties beneficial for the liver.
Dandelion Root: Helps detoxify the liver and improve digestion.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil and flaxseeds, these help reduce liver fat accumulation.
6. Stay Active and Reduce Stress
A sedentary lifestyle and high-stress levels can contribute to poor liver function. Exercise and stress management techniques can support liver health.
Yoga and Meditation: Help reduce stress, which can indirectly improve liver function.
Regular Physical Activity: Promotes overall well-being and reduces inflammation.
Adequate Sleep: Ensures proper bodily functions and aids liver detoxification.
7. Avoid Unnecessary Medications
Certain medications, especially painkillers and antibiotics, can impact liver health and elevated enzyme levels. If your SGOT and SGPT are high:
Avoid self-medication and consult a doctor before taking pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Opt for natural remedies for minor health issues whenever possible.
Always take medications as prescribed and do not exceed the recommended dosage.
8. Detox Your Liver Naturally
Detoxifying your liver naturally can help lower enzyme levels and improve liver function.
Drink lemon water in the morning to kickstart detoxification.
Consume beetroot juice, which contains betaine that helps in liver detox.
Increase fiber intake to support digestion and toxin elimination.
Try intermittent fasting to allow the liver to cleanse itself effectively.
9. Regular Health Check-Ups
Routine health check-ups help monitor SGOT and SGPT levels and identify any underlying liver conditions early.
Get a liver function test (LFT) at least once a year.
If diagnosed with fatty liver or other liver-related issues, follow your doctor’s advice strictly.
Monitor cholesterol and triglyceride levels as they are linked to liver health.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy liver is essential for overall well-being. Elevated SGOT and SGPT levels can be managed effectively through lifestyle changes, including a nutritious diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, and proper hydration. Avoiding alcohol, unnecessary medications, and processed foods also plays a significant role in keeping your liver enzymes in check. By adopting these strategies, you can improve liver health and ensure a healthier life. If your SGOT and SGPT levels remain persistently high, it is advisable to seek medical advice for further evaluation and treatment.
0 notes
Text
Obesity vs. Overweight: What’s the Difference & Why It Matters?
In today’s health-conscious world terms like obesity vs. overweight are often used interchangeably. However, they represent two different conditions that have distinct health implications. Understanding the difference between obesity vs. overweight, their causes and the associated obesity health risks is crucial for maintaining optimal well-being. One of the primary indicators of weight-related health concerns is BMI (Body Mass Index), which helps categorize individuals based on their weight relative to their height.

This blog will explore the key differences between obesity vs. overweight, why it matters, and how one can manage their weight effectively.
Understanding BMI and Its Role
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a simple numerical value derived from a person’s height and weight. It helps determine whether an individual falls within a healthy weight range or is categorized as overweight or obese. The BMI categories are as follows:
Underweight: BMI below 18.5
Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
Obesity: BMI of 30 or higher
While BMI is a useful screening tool, it does not account for muscle mass, bone density or fat distribution. Therefore, additional health assessments are often required to determine the real impact of excess weight.
Obesity vs. Overweight: What’s the Difference?
The distinction between obesity vs. overweight lies in the extent of excess body weight and fat accumulation. While both conditions indicate excessive weight, obesity is characterized by a significantly higher percentage of body fat compared to being overweight.
Overweight: Individuals in this category have a BMI of 25-29.9 and may have excess weight due to muscle mass, fat or a combination of both. It does not necessarily indicate poor health.
Obesity: This condition is marked by a BMI of 30 or higher and involves excessive fat accumulation, which significantly increases the risk of various health complications.
Why Does It Matter? The Health Risks of Obesity and Overweight
Both obesity vs. overweight are linked to various health issues, but obesity carries a significantly higher risk of developing serious conditions. Understanding the obesity health risks can help individuals take preventive measures to improve their overall well-being.
Health Risks Associated with Overweight
Increased risk of high blood pressure
Higher likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes
Greater strain on joints and muscles, leading to discomfort
Higher chance of developing cardiovascular diseases
Risk of fatty liver disease
Health Risks Associated with Obesity
Severe cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes
Type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance
Joint and mobility issues like osteoarthritis
Increased risk of cancer including breast, colon and liver cancer
Sleep apnea and breathing difficulties
Mental health concerns such as depression and anxiety
Liver diseases including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Weakened immune system making individuals more prone to infections
Causes of Overweight and Obesity
Several factors contribute to excess weight gain. While some causes are lifestyle-related, others may involve genetic, metabolic or hormonal influences.
Lifestyle Factors
Poor diet high in processed foods, sugar and unhealthy fats
Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle
Emotional eating and stress-related binge eating
Irregular sleep patterns, which impact metabolism
Genetic and Medical Factors
Family history of obesity
Hormonal imbalances such as hypothyroidism
Metabolic disorders including insulin resistance
Certain medications that promote weight gain
How to Prevent and Manage Obesity and Overweight?
While obesity vs. overweight both present health concerns, the good news is that they can be managed and prevented through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions when necessary.
1. Adopting a Healthy Diet
Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins.
Reduce intake of processed foods, sugary beverages and unhealthy fats.
Control portion sizes and practice mindful eating.
Increase fiber intake to aid digestion and promote satiety.
2. Increasing Physical Activity
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
Incorporate strength training to improve metabolism and muscle mass.
Stay active throughout the day by walking, stretching or doing household chores.
3. Managing Stress and Mental Well-being
Practice stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga or deep breathing exercises.
Get adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night) to regulate metabolism and hormones.
Seek mental health support if stress eating or emotional eating is a concern.
4. Medical and Professional Guidance
Consult a nutritionist or dietitian for a personalized diet plan.
Visit a doctor for regular health check-ups and weight management advice.
Consider medical treatments like weight loss medications or bariatric surgery in severe obesity cases.
Understanding the difference between obesity vs. overweight is essential for recognizing the health risks and taking appropriate measures for prevention and treatment. While overweight individuals may still be at risk for health complications, obesity health risks are significantly higher, requiring immediate attention and lifestyle adjustments.
By monitoring BMI, adopting a healthy lifestyle, staying physically active and seeking professional guidance, individuals can manage their weight effectively and reduce the risks associated with obesity vs. overweight. Prioritizing overall well-being ensures a healthier, longer and more fulfilling life.
0 notes
Text
अपने परिवार को एचएमपीवी से सुरक्षित रखे: सभी उम्र के लोगों के लिए उपाय
ह्यूमन मेटान्यूमोवायरस (एचएमपीवी) (Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), एक श्वसन वायरस है जिसकी पहचान वर्ष 2001 में की गई थी। यह विशेष रूप से छोटे बच्चों, बुजुर्गों और कमजोर प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली वाले व्यक्तियों में महत्वपूर्ण बीमारी का कारण बन सकता है। यह एक घातक वायरस है जो कि गई गंभीर स्थितियों को जन्म दे सकता है। ऐसे में यह समझना आवश्यक है कि अपने परिवार को एचएमपीवी से कैसे बचाया जाए, विशेष रूप से श्वसन संक्रमण के चरम मौसम के दौरान। मौजूदा लेख में आप एचएमपीवी के लक्षणों की पहचान और इसके प्रसार को रोकने के लिए क्या सरल उपाय हैं उनके बारे में विशेष जानकारी प्राप्त करेंगे।
0 notes
Text
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that has recently garnered attention due to a surge in cases, particularly in East Asia. Despite its increased prevalence, health experts emphasize that HMPV is a known virus and does not pose an unusual threat.
What is HMPV?
HMPV is a virus that typically causes respiratory symptoms similar to the common cold, including cough, fever, runny or stuffy nose, sore throat, wheezing and shortness of breath. Most individuals experience mild illness, but young children, older adults and those with weakened immune systems may develop more severe conditions such as bronchiolitis or pneumonia.

How Does HMPV Spread?
HMPV spreads through close contact with infected individuals, primarily via respiratory droplets released during coughing or sneezing. The virus can also survive on surfaces for short periods, making hand hygiene crucial in preventing transmission.
HMPV Symptoms
The symptoms of HMPV are often similar to those of the common cold and may include:
Cough
Fever
Runny or stuffy nose
Sore throat
Wheezing
Shortness of breath
Rash
These symptoms typically appear 3 to 6 days after exposure and usually last about 2 to 5 days. In most cases, individuals recover without complications.
When to Worry About HMPV
While HMPV generally causes mild illness, certain groups should be more cautious:
Infants and young children: They are at higher risk for severe respiratory issues like bronchiolitis and pneumonia.
Older adults: Especially those over 65, who may experience more severe symptoms.
Individuals with weakened immune systems: They are more susceptible to complications.
If symptoms worsen or persist beyond a week, or if there is difficulty breathing, it's important to seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnostic Techniques for HMPV
Diagnosing HMPV involves several methods:
Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR): This sensitive test detects viral RNA and is considered the gold standard for HMPV diagnosis.
Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR): Used for detecting HMPV-specific cDNA, though less sensitive than RT-qPCR.
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): An isothermal method that allows for rapid detection without the need for complex equipment.
In some cases, chest X-rays or bronchoscopy may be utilized to assess the extent of respiratory involvement.

Preventing HMPV Infection
Preventing the spread of HMPV involves several key measures:
Hand hygiene: Regularly wash hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
Avoid close contact: Stay away from individuals who are sick and if you're ill, limit contact with others.
Disinfect surfaces: Clean and disinfect frequently touched objects and surfaces.
Respiratory etiquette: Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing.
Currently, there is no vaccine for HMPV, making these preventive measures essential.
Protecting Your Family from HMPV
To safeguard your family:
Educate: Ensure all family members understand the importance of hygiene practices.
Monitor health: Keep an eye on symptoms, especially in vulnerable individuals like young children and the elderly.
Seek medical advice: Consult healthcare providers if symptoms escalate or if there's a concern about exposure to HMPV.
By staying informed and adhering to preventive strategies, you can effectively protect your family from HMPV and contribute to reducing its spread within the community.
0 notes
Text
Tackling Obesity: A Comprehensive Approach to a Healthier Life
Introduction Obesity has emerged as a global epidemic, with its prevalence skyrocketing in recent decades. Defined as an excessive accumulation of body fat, obesity increases the risk of several chronic diseases, including diabetes, heart disease and certain cancers. If you’re looking for sustainable and trending weight management strategies, this blog offers a detailed guide to understanding obesity and overcoming it effectively.

What Causes Obesity? The primary causes of obesity include:
Poor Diet: Overconsumption of high-calorie, low-nutrient foods.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes significantly.
Genetics: Family history can predispose individuals to obesity.
Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like hypothyroidism can lead to weight gain.
Psychological Factors: Stress and emotional eating.
Health Risks Associated with Obesity Obesity is linked to numerous health complications, such as:
Type 2 diabetes
Hypertension
Sleep apnea
Osteoarthritis
Fatty liver disease
Identifying Obesity Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common method used to classify obesity:
Underweight: BMI < 18.5
Normal weight: BMI 18.5–24.9
Overweight: BMI 25–29.9
Obese: BMI ≥ 30
Trending Weight Management Strategies
Intermittent Fasting (IF): Alternating eating and fasting periods to reduce calorie intake.
Plant-Based Diets: Focus on whole foods like fruits, vegetables and legumes.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense exercise followed by rest periods.
Gut Microbiome Research: Exploring probiotics and prebiotics for weight management.
Behavioral Therapy: Addressing emotional eating and building healthy habits.
Practical Tips for Weight Loss
Set Realistic Goals: Aim for gradual and consistent weight loss.
Track Your Progress: Use apps or journals to monitor food intake and activity.
Increase Physical Activity: Engage in activities you enjoy to stay consistent.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking water can reduce hunger and calorie consumption.
Get Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep is linked to weight gain.
Medical Interventions For severe cases, medical treatments include:
Prescription Medications: FDA-approved weight loss drugs.
Bariatric Surgery: Surgical procedures like gastric bypass for weight loss.
Non-Surgical Options: Endoscopic therapies are gaining traction.
The Role of Technology in Fighting Obesity
Smart Devices: Fitness trackers monitor activity levels and calories burned.
AI-Driven Diet Plans: Apps provide personalized meal suggestions.
Telehealth Consultations: Access to dietitians and fitness experts online.
Conclusion Combating obesity requires a multi-faceted approach that combines lifestyle changes, medical guidance and the latest technological advancements. With determination and the right resources, achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is possible. Stay informed about the latest trends in weight management and take proactive steps to lead a healthier, more fulfilling life.
0 notes
Text
Understanding SGPT: A Vital Indicator of Liver Health
Introduction Serum Glutamic-Pyruvic Transaminase (SGPT) also known as Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), is a key enzyme primarily found in the liver. It plays a critical role in diagnosing liver health and detecting underlying conditions. With liver diseases on the rise globally, understanding SGPT levels and their implications has become crucial. If you’re looking for the latest information on liver health, this blog will guide you through the essentials of SGPT, its significance and trending solutions for managing liver enzymes effectively.

What is SGPT? SGPT is an enzyme that facilitates amino acid metabolism. Elevated SGPT levels in the bloodstream usually indicate liver damage, as this enzyme leaks into the blood when liver cells are damaged. Regular health check-ups and liver function tests often include SGPT readings to evaluate overall liver health.
Why is Monitoring SGPT Levels Important? Keeping a tab on your SGPT levels is vital as it can:
Detect liver conditions early, such as hepatitis or fatty liver disease.
Monitor the effectiveness of treatments for liver disorders.
Provide insights into overall health and lifestyle effects.
Causes of Elevated SGPT Levels
Some common reasons for high SGPT levels include:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A condition linked to obesity and poor lifestyle choices.
Alcoholic Liver Disease: Prolonged alcohol consumption significantly affects SGPT levels.
Hepatitis Infections: Viral infections like Hepatitis A, B or C.
Medications and Toxins: Certain drugs and toxic substances.
Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise and stress can also contribute.
Symptoms to Watch For Elevated SGPT levels may not always manifest symptoms initially, but watch for:
Persistent fatigue
Jaundice
Nausea or vomiting
Swelling in the abdomen
Dark urine
How to Manage and Lower SGPT Levels?
Adopt a Healthy Diet: Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants, such as green leafy vegetables, berries and nuts. Avoid processed and fatty foods.
Exercise Regularly: Engage in moderate activities like walking or yoga to maintain a healthy liver.
Stay Hydrated: Water aids in detoxifying the liver and flushing out toxins.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol is detrimental to liver health.
Consult a Doctor: Seek medical advice for persistent high SGPT levels.
Latest Trends in SGPT Management
Plant-Based Supplements: Natural remedies like milk thistle and turmeric are gaining popularity.
Personalized Health Monitoring: Wearable devices now include liver function tracking.
Telemedicine Consultations: Access to online liver health consultations has increased significantly.
Gut-Liver Connection Research: Studies are exploring how gut health impacts liver enzymes.
Conclusion: Maintaining healthy SGPT levels is integral to overall well-being. By adopting a balanced lifestyle, regular check-ups and staying updated with the latest trends in liver health, you can ensure optimal liver function. Make liver care a priority and take proactive steps to manage your SGPT levels effectively.
0 notes
Text
The Esthetic Clinics® Attracts 15 Global Patients to India Amid Cosmetic Surgery Medical Tourism Boom MedTalks News
MedTalks News features The Esthetic Clinics® as a leading destination in India's thriving Cosmetic Surgery medical tourism industry. Over 15% of its patients are from international locations, making the clinic chain a trusted choice for advanced cosmetic surgery procedures at competitive prices. Led by Dr Debraj Shome, an internationally recognised expert in facial plastic surgery, and Dr Rinky Kapoor, a noted cosmetic dermatologist, The Esthetic Clinics® offers a wide range of advanced cosmetic and plastic surgery procedures. These include blepharoplasty and eyelid surgeries, hair transplants and restoration surgeries, facial plastic surgery for cancer and scars, cosmetic rhinoplasty, laser treatments, non-surgical facelifts, skin laser treatments, weight loss treatments, body and breast contouring surgeries, and injectables like Botox, fillers, skin whitening treatments, and Ulthera. Each treatment is meticulously planned and executed for optimal outcomes. Dr Debraj Shome is the only American Board Certified Facial Cosmetic Surgeon in India and serves as the Governor At Large of the Indian Chapter of the American College of Surgeons. A recent success story at The Esthetic Clinics® is Ashley Baker, a transgender woman from the US who underwent facial feminisation surgery (FFS). FFS is essential for transgender women and non-binary individuals, transforming masculine facial features into a more feminine appearance. For Ashley, who faced prohibitive costs for surgery in the US, The Esthetic Clinics® provided a comprehensive transformation with a deep plane facelift, abdominal sculpting, liposuction, and hairline restoration. Sharing her experience, Ashley Baker said, "The care and expertise I received at The Esthetic Clinics® were unparalleled. The transformation has been life-changing, allowing me to align my physical appearance with my gender identity thereby boosting my confidence. The cost was also a fraction of what I would have paid back home, making this high-quality care accessible to me." Headquartered in Mumbai, The Esthetic Clinics® operates ten centres across major cities, including New Delhi, Bengaluru, and Kolkata. Equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and staffed by skilled professionals, these centres deliver precise, excellent care. The blend of advanced techniques and affordability has cemented India's status as a premier destination for medical tourism, with The Esthetic Clinics® leading this growth. About MedTalks: MedTalks (www.medtalks.in) is a healthcare and patient education platform offering resources across 100+ medical specialties. Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h0WJ1K751pQ
Source: https://www.theweek.in/wire-updates/business/2024/12/13/dcm54-medtalks.html
0 notes