New Age Makers Institute of Technology (NAMTECH), an Education Initiative of Arcelor Mittal Nippon Steel India (AM/NS India), strives to offer a forward-thinking approach to engineering education, preparing students for the challenges and opportunities presented by the dynamic landscape of Industry 4.0 technologies. Our campus at Research Park, IIT Gandhinagar serves as a hub for excellence, fostering innovation, research, and the development of skills that align with the needs of the evolving industry. NAMTECH’s approach to Inspiring Human Capital is based on the three pillars of:1. Make It Yourself2. Industry Aligned Programs3. Teaching Global Values Website: https://www.namtech.ac/
Last active 2 hours ago
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text

1 note
·
View note
Text
Step into the future of smart manufacturing with NAMTECH’s exclusive 1-year residential iPMP. Tailored for B.E./B.Tech graduates ready to lead innovation in Industry 4.0.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
What You Will Learn in Industrial Automation and Robotics Courses?
Traditional manual processes have now transformed into smart systems that respond with speed and precision. From packaging lines that operate around the clock to robotic arms performing delicate tasks with surgical accuracy, the world of industrial production is evolving. And at the heart of this change lies a new kind of technical literacy, one built through Industrial automation and robotics courses.
But what exactly do these programs teach? And why are they so important today? Let’s explore what students really gain from this kind of education, and how it prepares them to thrive in tomorrow’s industries.
Foundational Engineering Knowledge That Matters
Before students can dive into robots or controllers, they need to understand the language of automation. These courses begin with essential principles: electrical theory, logic design, mechanical fundamentals, and system dynamics. Learners study current flow, sensors, basic circuits, and safety devices. They also explore control systems, how feedback works, what makes a loop stable, and how machines respond to various inputs.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
Programmable Logic Controllers, or PLCs, form the core of most industrial automation systems. Unlike traditional relay setups, these compact computers carry out control tasks instantly by following logic sequences built by engineers. Students gain direct experience working with real hardware, learning to configure, test, and program PLCs using industry-standard languages such as ladder logic, structured text, and function block diagrams.
Courses focus not just on writing code but on solving problems: detecting errors, optimizing sequence flow, and debugging physical setups. Whether it’s running a simulated traffic light or managing conveyor timing, the logic must be precise.
Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) and SCADA Systems
As machines grow smarter, the need for clear communication between systems and humans increases. That’s where HMI and SCADA systems come in.
Students learn to design interactive screens that allow operators to control and monitor processes, from pressure levels in a reactor to the speed of a bottling line. They develop layouts, manage alarms, create trend graphs, and set up data logging.
Equally critical is understanding SCADA architecture, how large-scale systems monitor multiple devices across facilities. These interfaces aren’t just dashboards. They’re lifelines. In high-risk or high-speed environments, the right display can prevent failure.
Robotics: Control, Precision, and Integration
Beyond sensors and switches, industrial robotics introduces a whole new dimension. These machines perform physical tasks with accuracy and consistency, from welding to material handling. In Industrial automation and robotics courses, students explore robotic motion planning, coordinate systems, joint movement, and gripper design.
Training includes simulation as well as real robotic arms. Learners program actions, define tool paths, and calibrate devices to respond to various scenarios. Robotics also demands a sharp eye for safety, understanding fail-safes, emergency stops, and risk analysis becomes part of the curriculum.
Sensor Technology and Instrumentation
In automation, sensing is everything. Machines need to detect position, measure flow, monitor temperature, or determine proximity, all without human input. That’s why students spend time studying sensors in depth.
They learn the theory and application of photoelectric sensors, limit switches, ultrasonic devices, thermocouples, and encoders. Courses often include wiring, calibration, signal processing, and sensor fusion techniques.
It’s one thing to install a sensor. It’s another to ensure its readings are accurate, consistent, and usable within an automation loop. A well-tuned sensing system is the difference between reliable automation and constant failure.
Drives, Motors, and Motion Control
Movement in automation is never random. Whether it’s a robotic arm pivoting or a conveyor transporting items, motion must be controlled, smooth, and predictable.
Students study various types of motors, stepper, servo, induction, and the drives that control them. They learn to manage speed, torque, and direction. Courses also explain PID control, acceleration curves, and how to prevent vibration or misalignment.
Practical lab work allows learners to connect motors, set drive parameters, and test results under different loads. These experiences create engineers who don’t just understand motion, they can manage it with precision.
Integration Projects: From Concept to Commissioning
Toward the end of most programs, students apply everything they’ve learned in a capstone project. This may involve designing an automated process from scratch, selecting hardware, building control logic, integrating sensors, and testing systems.
It’s not just a test. It’s preparation. It simulates real challenges, including incomplete specs, equipment failure, or changing project goals. The experience builds not only confidence but also the kind of problem-solving mindset employers look for.
Safety, Compliance, and Standards
No system, no matter how efficient, is worth endangering a worker’s life. That’s why safety is woven throughout every topic. They learn how to design systems that prevent unexpected starts, reduce hazards, and shut down when needed.
They also learn to assess risk, calculate safety integrity levels, and implement proper machine guarding. These aren’t theoretical concerns, they’re daily priorities in every automation role.
Final Thoughts
For anyone looking to step into a future-proof career, technical depth and adaptability are essential. Industrial automation and robotics courses offer both. They build an understanding of how machines function, how systems connect, and how processes can be improved through smart engineering. Whether you aim to be a systems integrator, controls engineer, maintenance lead, or robotics programmer, what you learn in these courses is more than skill, it’s your launchpad into a smarter, faster world.
0 notes
Text

Discover how automation robotics courses equip you with cutting-edge skills to thrive in the smart manufacturing revolution of tomorrow.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Step into the world of Industry 4.0 with NAMTECH’s Digital Manufacturing course. Learn how smart factories, automation, and AI-driven systems can accelerate your career growth. Gain hands-on skills, real-world exposure, and a future-ready mindset—because the next generation of engineers isn’t just tech-savvy, they’re digitally empowered.
1 note
·
View note
Text

1 note
·
View note
Text
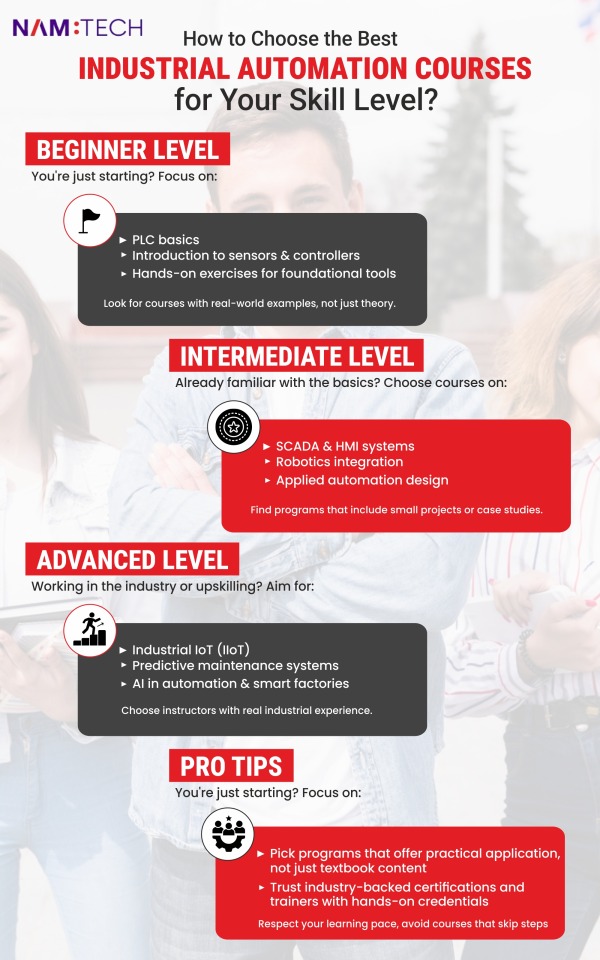
How to Choose the Best Automation Programs Institute for Your Career?
Finding the right institute for automation training isn’t just a box to tick. It’s a career move that decides your future. Whether you're a fresh graduate, a working professional, or someone eyeing a shift into industrial automation, the institute you choose can shape what happens next. But with so many options out there, how do you know which one gets you job-ready, and not just certified?
Let’s walk through what matters when you're choosing an institute.
Start With Your Career Goals
Don’t look for the “top institute.” Look for the one that fits you.
Ask yourself:
Do I want hands-on skills or deeper theory?
Am I aiming for a technician role or an engineering position?
Do I need a quick course or a full-time, structured program?
What industries am I targeting—automotive, manufacturing, energy, or something else?
Once you’ve got your goals in place, it’s easier to narrow down what kind of training you need and which institutes offer it.
Check the Curriculum: Is It Aligned With Industry Needs?
This part’s big. You’re not learning automation for fun—you want skills that matter at work. So flip through the course content. Make sure it includes things like:
PLC programming (e.g., Siemens, Allen-Bradley)
SCADA and HMI systems
Robotics and motion control
Pneumatics, hydraulics, and sensors
Industrial communication protocols
IoT and smart manufacturing basics
If a course skips the tools companies use, it's outdated.
Also, look for project work. A good institute doesn’t just talk theory. It lets you do things.
Look Into the Instructors
The people teaching you should have been where you’re heading.
Here’s what to check:
Do they have real-world industry experience?
Have they worked on factory floors or automation systems?
Can they explain complex tools in a way that makes sense?
You’ll learn faster and smarter when your trainers know what it’s like to solve problems, not just talk about them.
Prioritize Hands-On Learning
Automation isn’t something you can fully grasp through lectures alone. You need labs. Simulators. Equipment.
Look for institutes that offer:
Real PLC kits (Siemens, ABB, Delta, etc.)
SCADA software with real-time setup
Industrial robots or robotic arms
Practice environments that mirror factory systems
If you're learning online, check if they offer remote access to labs or virtual simulators. The key is simple: if you can’t apply what you’re learning, you won’t retain it.
Find Out Who’s Hiring Their Graduates
You’re not just paying for training. You’re investing in outcomes. So dig into the institute’s placement record.
Ask questions like:
Which companies hire from this institute?
Are alumni working in core automation roles, or just stuck in support jobs?
Do they offer help with interviews, resumes, and certifications?
Even better, connect with a few past students. Their experiences will tell you more than any brochure ever could.
Check Certification and Industry Partnerships
Some institutes offer certifications linked to big names in automation. These can give your resume extra weight.
Look for:
Courses endorsed by Siemens, Rockwell, or Schneider Electric
Certification from industry bodies like ISA or NSDC
MOUs or ties with actual manufacturing companies
It’s not just about the logo—it’s about credibility. Certifications show that your training meets recognized standards.
Don’t Ignore the Batch Size and Support
A great trainer can't help 50 students at once. The smaller the batch, the better your chances of asking questions, getting feedback, and building your skills.
Also, check if they provide post-course support:
Can you reach out to mentors later?
Do they guide you on career paths?
Is there a community or alumni group you can join?
8. Compare the Costs
You’ll find automation courses that range from a few thousand to over a lakh. Here’s what to keep in mind:
What’s included in the fee?
Are there lab sessions, toolkits, or internships?
Will this course help you get a job or promotion?
Sometimes, a slightly more expensive course offers way more value—better tools, smarter trainers, stronger industry links. So weigh the cost against what you’re getting.
Location and Learning Mode
Not everyone can move to another city for training. Thankfully, many institutes now offer online or hybrid programs.
Choose what fits your life:
Full-time classroom courses – Best for immersive learning
Online learning – Great for working professionals
Hybrid models – A flexible mix of both
Trust Your Instinct
Once you’ve narrowed your options, contact the institute. Talk to them. Ask real questions:
What’s the trainer-to-student ratio?
How often do they update the curriculum?
Do they help with job placement or internships?
Can I speak to a former student before enrolling?
Final Thoughts
Choosing the best automation programs institute isn’t about chasing rankings or flashy websites. It’s about alignment. You don’t need dozens of options. You need one that works for you. When in doubt, trust the basics: practical learning, expert instructors, and clear outcomes. If an institute delivers on those, you're already on the right track.
0 notes
Text

Discover how NAMTECH Industry 4.0 program equips you with the future-ready skills demanded by today’s smart manufacturing landscape. From automation and data analytics to robotics and cyber-physical systems, our curriculum bridges theory with real-world application. Learn how our hands-on approach, industry collaborations, and cutting-edge labs empower you to thrive in a tech-driven manufacturing environment and lead innovation in the era of digital transformation.
#Industry 4.0 program#Industry 4.0#NAMTECH#Industry 4.0 Smart Manufacturing#Smart Manufacturing Program#Smart Manufacturing
1 note
·
View note
Text

Prices vary by city, institute, course content, and delivery mode. Always compare reviews, trainers, and curriculum before enrolling.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Explore NAMTECH automation courses across all price ranges — from affordable to premium — with a clear comparison of key features, hands-on training, industry exposure, and career outcomes.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Smart Manufacturing Engineering is at the forefront of this transformation, integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and robotics to create highly efficient, flexible, and sustainable production systems.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How a Course in Digital Manufacturing Prepares You for Industry 4.0?
The manufacturing world’s getting a huge makeover thanks to Industry 4.0 transforming old production techniques. By mixing in automation, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT), companies are switching to smarter manufacturing processes. For professionals and students wanting to keep up in this fast-changing industry, switching to a digital manufacturing program could be a smart move.
This article explores how such a course equips you with the necessary skills to thrive in the age of Industry 4.0.
Understanding Industry 4.0 and Its Impact on Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 represents a shift toward digitized and interconnected production systems. Traditional manufacturing relied on mechanical and manual operations, but today’s factories are leveraging real-time data, cloud computing, and advanced robotics.
Companies that adopt these technologies enhance productivity, reduce waste, and improve product quality. A well-structured program in digital manufacturing covers these critical aspects, ensuring that learners understand how Industry 4.0 technologies integrate into modern production lines.
With manufacturing becoming more reliant on intelligent systems, professionals need specialized knowledge to navigate this transition effectively.
Core Skills You Gain from a Digital Manufacturing Course
A comprehensive course in digital manufacturing prepares you with both technical and strategic skills. Some of the key competencies you develop include:
1. Automation and Robotics
Learn how to integrate automated systems into production lines.
Understand robotic programming and human-robot collaboration.
Gain insights into industrial automation tools and processes.
2. Data Analytics in Manufacturing
Discover how data is collected, processed, and used to improve efficiency.
Learn predictive maintenance techniques using real-time analytics.
Explore machine learning applications in manufacturing optimization.
3. Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
Study the role of 3D printing in modern production.
Learn about materials and techniques used in additive manufacturing.
Understand the cost and efficiency benefits of digital fabrication.
4. Cyber-Physical Systems and IoT
Gain expertise in integrating IoT devices within industrial environments.
Understand how smart sensors enhance production efficiency.
Learn about cloud computing and digital twins in manufacturing.
5. Supply Chain Digitization
Explore how digital tools optimize supply chain management.
Learn about real-time tracking and inventory control systems.
Understand the role of blockchain in secure and transparent transactions.
Practical Applications: Bridging Theory and Industry Needs
A program in digital manufacturing does not only focus on theory. Many courses incorporate hands-on training through industry collaborations, lab work, and real-world case studies. This practical approach helps bridge the gap between classroom learning and workplace expectations.
For example:
Students work on digital twin simulations to test production efficiencies before implementation.
Hands-on robotics training allows learners to develop automation workflows.
Case studies on successful smart factories provide valuable industry insights.
By engaging with real-world applications, students develop problem-solving skills and gain direct experience with cutting-edge technologies.
Career Opportunities in Digital Manufacturing
With Industry 4.0 driving significant changes in production methods, companies are actively seeking professionals with expertise in digital manufacturing. Graduates from such programs find roles in various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods.
Some career paths include:
Manufacturing Engineer – Designs and optimizes production processes using digital tools.
Automation Specialist – Implements robotics and automated systems in factories.
Industrial Data Analyst – Uses data-driven insights to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
IoT Specialist – Develops and manages smart factory solutions.
Supply Chain Manager – Leverages digital tools to streamline logistics and inventory management.
The demand for professionals with digital manufacturing expertise continues to grow, making it a promising career choice for those looking to work at the forefront of technological advancements.
Choosing the Right Digital Manufacturing Course
Not all programs in digital manufacturing offer the same depth and specialization. When selecting a course, consider the following factors:
Curriculum – Ensure the course covers key Industry 4.0 topics, including automation, AI, and IoT.
Faculty and Industry Ties – Look for programs that offer instruction from experienced professionals and partnerships with leading manufacturers.
Hands-on Learning – Opt for courses that provide laboratory sessions, internships, or industry projects.
Global Recognition – Choose an institute with a strong reputation in the manufacturing industry.
Final Thoughts
A program in digital manufacturing is more than just a course—it is a gateway to future-proofing your career in an industry undergoing rapid technological advancements. With Industry 4.0 shaping the future of production, acquiring expertise in automation, data analytics, and smart manufacturing will place you at the forefront of industrial innovation.
0 notes
Text

Smart advanced manufacturing is revolutionizing industries by integrating automation, AI, IoT, and real-time analytics to create highly efficient and data-driven production systems.
1 note
·
View note


