Text
The National UN Volunteers-India
UN SDG: Goal 3 Goal 3: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
SBOAMHSS Coimbatore - Awareness Programme for adolescent girls
Menstrual Hygiene Awareness Programme
Organized by: The National UN Volunteers-India
UN SDG: Goal 3 - Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
Venue: SBOA Matriculation Higher Secondary School, Coimbatore
Date: 24th June 2024.
A Menstrual Hygiene Awareness Programme was conducted for the students of classes VII, VIII, and IX at SBOA Matriculation Higher Secondary School, Coimbatore, on 24th June 2024. This initiative aimed to educate adolescent girls on crucial aspects of menstrual hygiene and overall well-being.
Dr. Lavanya, the school doctor, delivered an insightful lecture covering the anatomy and physiology of the uterus and ovaries. She emphasized the importance of healthy food habits to maintain good circulation and discussed the recommended frequency for changing sanitary pads.
Mrs. Malathi contributed to the programme by explaining the significance of personal hygiene, specifically during the menstrual cycle. She highlighted the importance of drinking adequate water, maintaining a balanced diet, and the consequences of poor hygiene practices.
The event was graced by the presence of the Principal, Mrs. Sabural Banu Ibrahim, who is also the UN Women designate. She witnessed the proceedings and expressed her appreciation for the efforts of the teachers, students, and health professionals involved in organizing this informative session.
This programme underscored the commitment of SBOAMHSS Coimbatore and The National UN Volunteers-India towards promoting health and well-being, in alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 3.

0 notes
Text
The National UN Medical Volunteers - India
PSMA SEMANTHA PROGRAMME
09 JANUARY 2024
PSMA Semantha programme is part of the Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA), which was launched by the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India.
The programme aims to provide assured, comprehensive and quality antenatal care, free of cost, universally to all pregnant women on the 9th of every month.
The programme also engages with private sector doctors who volunteer for the campaign.
We appreciate your dedication and service to this noble cause. You are making a difference in the lives of many mothers and newborns dear Mrs. Milana
We appreciate The Chief Medical Officer Dr. Marutho, Dr. Chandrika, BHE, Lhv Mangala Sister and NGO'S Asha & Nagama, Nagarathna.
God bless you all.
THE NATIONAL UN VOLUNTEERS-INDIA
[Mrs. Milana, Clinical Psychologist serving in Government Hospital, Srirangapatna, Mandya District, Karnataka state, India. She is Medical UN Volunteers-India]

0 notes
Text
Seven Types of Millet Foods and Their Uses.
English
ஏழு வகை தினை உணவுகளும் (Millet) ஏராளமான பயன்களும்!
தினைகளில் அதிகப்படியான கால்சியம், புரதம், நார்ச்சத்து, தாதுக்கள் ஆகியவை அடங்கி உள்ளன. உடல் எடையை குறைக்க விரும்பவர்கள் இந்த தினை வகைகளை உணவாகக் எடுத்துக்கொள்ளலாம். மேலும், சர்க்கரை மற்றும் இருதய நோய்கள் உள்ளவர்களும் தினை வகைகளை எடுத்துக்கொள்ளலாம். சத்து மாவு, ரொட்டிகள், தின்பண்டங்கள் ஆகியவற்றின் மூலம் தினையை நாம் தினமும் எடுத்துக்கொள்ளலாம். சிறுதானிய வகைகள் மொத்தம் ஏழு . அவற்றின் பலன்களைப் பற்றி இந்தத் தொகுப்பில் பார்ப்போம்.
தினை அரிசி (Foxtail millet): தினை அரிசியில் புரதம், வைட்டமின் A மற்றும் B, பாஸ்பரஸ் போன்ற சத்துக்கள் உள்ளன. அரிசி தினை பயன்படுத்தி அதிரசம், இட்லி, பணியாரம், பாயசம், அல்வா போன்ற உணவுகள் செய்து சாப்பிடலாம். இது இதயத்தை ஆரோக்கியமாக வைத்துக்கொள்ளவும், கண் பார்வையை தெளிவாக வைத்துக்கொள்ளவும் உதவும். குறிப்பாக, குழந்தைப் பெற்ற தாய்மார்கள் எடுத்துக்கொண்டால் தாய் பால் நன்றாக சுரக்கும்.
கேழ்வரகு: Finger millet எனப்படும் கேழ்வரகு, அரசி மற்றும் கோதுமையை விட அதிக சத்து மிக்கது. இது எலும்பு தேய்மானம், இரத்த சோகை, மலச்சிக்கல் ஆகியவற்றிற்கு நல்ல தீர்வைத் தரும். மேலும், செரிமான கோளாறு, குடல் புண், மாதவிடாய் கோளாறு பிரச்னைகளில் இருந்து நிவாரணம் பெறுவதற்கு உதவி செய்யும். கேழ்வரகில் இரும்புச் சத்து, பாஸ்பரஸ், சுண்ணாம்புச்சத்து ஆகியவை உள்ளது குறிப்பிடத்தக்கது. கேழ்வரகில் கூழ், அடை, வடை, தோசை, களி ஆகியவை செய்து சாப்பிடலாம்.
சாமை அரிசி: Little millet என அழைக்கப்படும் சாமை அரிசியில் நார்ச்சத்து அதிகம் உள்ளது. ஆகையால், இது சர்க்கரை வியாதிக்கு மருந்தாக இருக்கும். மேலும், வயிற்று கோளாறுகள், மலச்சிக்கல், இரத்த சோகை ஆகியவற்றிற்கு நல்ல பலனைத் தரும். இதில் புலாவ், உப்மா, பொங்கல் ஆகியவை செய்து சாப்பிடலாம்.
குதிரைவாலி: Barnyard Millet எனப்படும் குதிரைவாலியில் இரும்புச் சத்து, நார்ச்சத்து ஆகியவை உள்ளன. இது இதயம் தொடர்பான நோய், இடுப்பு வலி, வயிறு வலி, உயர் இரத்த அழுத்தம் ஆகியவை வரமால் இருக்க உதவும். குதிரைவாலியில் எலுமிச்சை சோறு, கிச்சடி, கொழுக்கட்டை ஆகியவை செய்து சாப்பிட்டால் ருசியாகவும் சத்துமிக்கதாகவும் இருக்கும்.
வரகு அரிசி: Kodo millet என ஆங்கிலத்தில் சொல்லப்படும் வரகு அரிசி புரதம் மற்றும் தாது உப்புக்கள் நிறைந்தவை. உடல் பருமன், இரத்த அழுத்தம், சர்க்கரை நோய் அகியவை குறைவதற்கு உதவி செய்யும். வரகு அரிசி மூலம் வரகு அடை, பாயசம், உப்புமா போன்றவை செய்து உண்டு பயன் பெறலாம்.
கம்பு அரிசி: Pearl millet எனப்படும் கம்பு அரிசியில் அதிகப்படியான வைட்டமின்கள் உள்ளன. ஆகையால் இது உடலை சுறுசுறுப்பாக வைத்துக்கொள்ள உதவும். மேலும், உடல் சூடு, வயிற்றுப்புண், சோர்வு ஆகியவற்றிற்கு கம்பு அரிசி உணவை எடுத்துக்கொள்ளலாம். இது தேவையற்ற கொழுப்புகளை நீக்கவும் உதவுகிறது. கம்பஞ்சோறு, கம்பு அடை, கம்பு தோசை ஆகியவை சுவைமிக்கது.
சோளம்: சோளம் ஆங்கிலத்தில் Sorghum என அழைக்கப்படுகிறது. சோளம் சர்க்கரை நோயை குறைக்கவும், உடல் எடை அதிகரிக்கவும், உடலில் இருக்கும் உப்பை குறைக்கவும் பயன்படுகிறது. சோளத்தில் மாவு சத்து, புரத சத்து, இரும்புச் சத்து ஆகியவை உள்ளன. மேலும் சரும அழற்சி உள்ளவர்கள் சோள உணவு சாப்பிட்டுப் பயன் பெறலாம். சோள முறுக்கு, பாப்கார்ன், சோள அரிசி சாதம் ஆகியவை குழந்தைகளுக்கும் பிடித்த உணவுகளாகும்.
Seven types of millet (Millet) and many benefits!
Millets are rich in calcium, protein, fiber and minerals. People who want to lose weight can take these millets as food. Also, people with diabetes and cardiovascular diseases can also consume millets. We can take millets daily through nutritious flour, breads and snacks. There are seven types of small grains in total. Let's take a look at their benefits in this collection.
Foxtail millet: Millets contain protein, vitamin A and B, and nutrients like phosphorus. You can use rice millet to make dishes like Athirasam, Idli, Paniyar, Payasam and Alva. It helps keep the heart healthy and the eyesight clear. Especially, if taken by mothers who have given birth, the mother's milk will be secreted better.
Finger millet: Finger millet is more nutritious than millet and wheat. It is a good remedy for bone loss, anemia and constipation. Also, it helps to get relief from digestive disorders, intestinal ulcers, menstrual disorders. Kezhvarak contains iron, phosphorus and lime. You can make porridge, adha, vada, dosa, kali and eat it in kelvarak.
Millet Rice: Millet rice also known as Little millet is rich in fiber. Therefore, it can be a cure for diabetes. Also, it is beneficial for stomach disorders, constipation and anemia. Pulao, Upma, Pongal can be made and eaten.
Horsetail: Barnyard Millet contains iron and fiber. It helps to prevent heart related diseases, hip pain, stomach pain, high blood pressure. Lemon rice, khichdi and pudding made from horseradish will be tasty and nutritious.
Millet Rice: Kodo millet is rich in protein and minerals. Helps reduce obesity, blood pressure, and diabetes. Varaku rice can be used to make Varaku Adha, Payasam, Upluma etc.
Rye Rice: Pearl millet is rich in vitamins. So it helps to keep the body active. Also, rye rice food can be taken for body heat, stomach ulcer and fatigue. It also helps in removing unwanted fats. Kampunchoru, Kampu Adha, Kampu Dosa are delicious.
Sorghum: Sorghum is called Sorghum in English. Corn is used to reduce diabetes, increase body weight and reduce salt in the body. Corn contains starch, protein and iron. Also people with dermatitis can benefit from eating corn meal. Sola Murukku, Popcorn and Sola Rice Rice are also favorite foods for children.

0 notes
Text
Nourish Your Life: The Vital Importance of Nutrition
💠In our fast-paced lives, it's easy to overlook the significance of proper nutrition. However, the impact of what we consume daily resonates throughout our lives. Adequate nutrition is not just about maintaining a healthy weight; it's about fueling our bodies, enhancing our well-being, and preventing a range of illnesses.
💠Every bite we take provides the building blocks for our body's functions. Nutrients like vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are the essential elements that enable our cells to function optimally. From boosting our immune system to promoting cognitive health, nutrition plays a pivotal role.
💠When we prioritize balanced meals, we ensure a steady energy supply. Carbohydrates offer immediate energy, while proteins aid in muscle repair and growth. Fats support various bodily functions and are crucial for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins.
💠Moreover, the role of nutrition in disease prevention is significant . A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can lower the risk of chronic illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes, certain cancers, digestive disorders etc. Nutrient-dense foods provide antioxidants that combat oxidative stress, reducing the likelihood of cell damage.
💠Nutrition also greatly influences mental health. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, for instance, support brain health.Vit B,C are known to aid in stress management and cognitive function.
💠In children, proper nutrition is vital for growth and development. Nutrient deficiencies during this phase can lead to lifelong health issues.
💠Conversely, a well-balanced diet contributes to stronger bones, better concentration, and overall vitality.
💠Remember, making healthy choices doesn't have to be complicated. Start by incorporating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your meals.
💠Choose whole grains over refined grains, ,and opt for good sources of protein like pulses and lentils.
Hydration is also key – water supports digestion, circulation, and temperature regulation.
💠In conclusion, the importance of nutrition in our day-to-day lives cannot be overstated. It's the foundation for our well-being, vitality, and longevity.
💠By making thoughtful choices and prioritizing a balanced diet, you're investing in a healthier and happier future.
Eat Whole Treat Soul

0 notes
Text
MEDICAL SCIENCES
தமிழில்
Asthma fighter – 5 foods
Asthma is one of the dangerous disordered diseases where it makes the airways and breath pipes to get blocked. Asthma cannot be cured, but it can be managed by taking a regular intake of medicines. Its effects can be reduced by taking the following some of the foods.
Salmon: It is a fish with omega 3 fatty acid oil which will medicate the inflammations in air tubes.
Spinach: This is rich in magnesium, which is helpful for making the respiratory muscles to be relaxed and healthy.
Red Peppers: These are rich in Vitamin c, reduces inflammation.
Onion: Anti-allergic vegetable, which reduces inflammation and produces anti-oxidant to develop the immune system.
Chickpeas: Rich in Vitamin B6, which acts anti-asthmatic food especially for children. It is a stress-relieving nutrient-filled food that reduces stress.
மருத்துவ அறிவியல்
ஆஸ்துமா ஃபைட்டர் - 5 உணவுகள்
ஆஸ்துமா என்பது ஆபத்தான சீர்குலைந்த நோய்களில் ஒன்றாகும், இது காற்றுப்பாதைகள் மற்றும் சுவாசக் குழாய்களைத் தடுக்கிறது. ஆஸ்துமாவை குணப்படுத்த முடியாது, ஆனால் தொடர்ந்து மருந்துகளை உட்கொள்வதன் மூலம் அதை நிர்வகிக்க முடியும். கீழ்க்கண்ட சில உணவுகளை உட்கொள்வதன் மூலம் அதன் தாக்கத்தை குறைக்கலாம்.
சால்மன் மீன்: இது ஒமேகா 3 கொழுப்பு அமிலம் கொண்ட ஒரு மீன், இது காற்று குழாய்களில் ஏற்படும் வீக்கங்களுக்கு மருந்தாகும்.
கீரை: இதில் மெக்னீசியம் நிறைந்துள்ளது, இது சுவாச தசைகள் தளர்வாகவும் ஆரோக்கியமாகவும் இருக்க உதவுகிறது.
சிவப்பு மிளகாயில் வைட்டமின் சி நிறைந்துள்ளது, வீக்கத்தைக் குறைக்கிறது.
வெங்காயம்: ஒவ்வாமை எதிர்ப்பு காய்கறி, இது வீக்கத்தைக் குறைக்கிறது மற்றும் நோயெதிர்ப்பு மண்டலத்தை உருவாக்க ஆன்டி-ஆக்ஸிடன்ட்டை உற்பத்தி செய்கிறது.
கொண்டைக்கடலை: வைட்டமின் பி6 நிறைந்துள்ளது, இது குறிப்பாக குழந்தைகளுக்கு ஆஸ்துமா எதிர்ப்பு உணவாக செயல்படுகிறது. இது மன அழுத்தத்தைக் குறைக்கும் ஊட்டச்சத்து நிறைந்த உணவாகும்.

0 notes
Text
WHAT IS HYPNOPEDIA?
தமிழில்
It consists of talking to your son or daughter for 21 days in a row, while they sleep, when they are already in REM sleep (deep sleep), which is achieved approximately 2 hours after they have fallen asleep) with a soft tone, the purpose you want May your child achieve and always finish the sentence, with a loving word, like I love you.
For example, if you want your daughter or son not to be aggressive, or a fighter with his friends every night you approach him / her and while they sleep you whisper, “my love, tomorrow you will play happy, you will have fun sharing with your classmates, I love you so much".
Important!!!
When the child is sleeping, the words go directly to the unconscious, which hears 1,000 times more than the conscious.
Benefits of Hypnopedia
Helps balance emotional, spiritual and physical energy.
With this tool we can help them to become safer, happier children and to feel tremendously loved by their parents or caregivers.
Let's put this beautiful technique into practice that brings enormous benefits and allows us to be closer to our little ones.
ஹிப்னோபீடியா என்றால் என்ன?
இது உங்கள் மகன் அல்லது மகளுடன் தொடர்ச்சியாக 21 நாட்கள் அவர்கள் தூங்கும் போது, அவர்கள் ஏற்கனவே REM தூக்கத்தில் இருக்கும் போது (ஆழ்ந்த உறக்கம்), அவர்கள் தூங்கி சுமார் 2 மணிநேரம் கழித்து ஒரு மென்மையான தொனியில் பேசுவதைக் கொண்டுள்ளது. நீங்கள் விரும்பும் நோக்கம் உங்கள் குழந்தை அடையட்டும் மற்றும் எப்போதும் வாக்கியத்தை முடிக்கட்டும். (ஐ லவ் யூ போன்ற அன்பான வார்த்தையுடன்)
உதாரணமாக, உங்கள் மகளோ அல்லது மகனோ ஆக்ரோஷமாக இருக்கக்கூடாது என்று நீங்கள் விரும்பினால், அல்லது அவரது நண்பர்களுடன் சண்டையிடுபவர் எனில், ஒவ்வொரு இரவும் அவரை அணுகி அவர்கள் தூங்கும்போது நீங்கள் கிசுகிசுப்பீர்கள், “என் அன்பே, நாளை நீங்கள் மகிழ்ச்சியாக விளையாடுவீர்கள், நீங்கள் வேடிக்கையாகப் பகிர்ந்து கொள்வீர்கள் (உங்கள் வகுப்பு தோழர்களுடன்)
முக்கியமாக!!!
குழந்தை தூங்கும் போது, வார்த்தைகள் நேரடியாக மயக்கத்திற்கு செல்கின்றன, இது நனவை விட 1,000 மடங்கு அதிகமாக கேட்கிறது.
▪️ஹிப்னோபீடியாவின் நன்மைகள்
உணர்ச்சி, ஆன்மீக மற்றும் உடல் ஆற்றலை சமநிலைப்படுத்த உதவுகிறது.
இந்தக் கருவியின் மூலம் அவர்கள் பாதுகாப்பான, மகிழ்ச்சியான குழந்தைகளாக மாறவும், அவர்களின் பெற்றோர் அல்லது பராமரிப்பாளர்களால் பெரிதும் நேசிக்கப்படுவதை உணரவும் நாம் அவர்களுக்கு உதவ முடியும்.
மகத்தான நன்மைகளைத் தரும் இந்த அழகான நுட்பத்தை நடைமுறையில் வைப்போம், மேலும் நம் குழந்தைகளுடன் நெருக்கமாக இருக்க அனுமதிக்கிறது.

0 notes
Text
Human Body – 96 Basic Principles
Siddhars or Siddhas the spiritual scientists of Tamil Nadu (Ancient South India) are the pioneers of this scientific system.
Siddhas fundamental principles never differentiated man from the universe.
According to them, “Nature is man and man is nature and therefore both are essentially one".
"Man is said to the microcosm and the Universe is Macrocosm, because what exists in the Universe exists in man.”
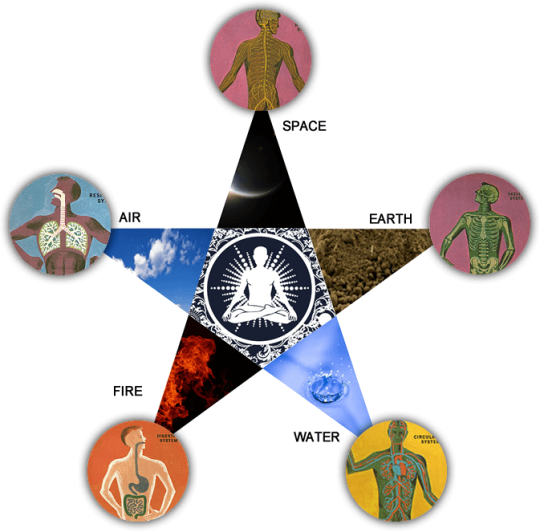
Siddha system trusts that all objects in the universe including human body are combined of five basic primordial elements, namely earth, water, fire, air and space.
Siddhas defined 96 principles as the constituents of Human Being. They comprise Physical, Physiological, Mental and Intellectual mechanisms of a person. They are nothing but the materialization of the “Five Basic Elements “.
The human body is composed of 96 Tattvas (Thathuvam) or basic principles. They are…
⚫Elements – 5
1. Earth
2. Water
3. Fire
4. Air
5. Space
⚫Sense Organs – 5
1. Eye
2. Ear
3. Nose
4. Tongue
5. Skin
⚫Functions Of Sense Organs – 5
1. Vision
2. Hearing
3. Smell
4. Taste
5. Touch
🌑Motor Organs – 5
1. Hands
2. Legs
3. Mouth
4. Rectum
5. Sex Organs
⚫Perception Of Senses – 5
1. Smell
2. Taste
3. Sight
4. Touch
5. Hearing
🌑Intellectual Faculties – 4
1. Mind
2. Intellect
3. Subconscious mind
4. Ego
🌑Arivu – 1
(Wisdom Of Self Realization)
⚫Vital Nerve Force – 10
1. Idakalai
2. Pinkalai
3. Sulumunai
4. Siguvai
5. Purudan
6. Kanthari
7. Atthi
8. Allampudai
9. Sanguni
10. Gugu
⚫Vital Life Force – 10
1. Pranan
2. Abanan
3. Uthanan
4. Samanan
5. Vyanan
6. Nagan
7. Koorman
8. Kirukaran
9. Devadhathan
10. Dhanenjeyan
🌑Visceral Cavities– 5
1. Stomach
2. Small Intestine
3. Large Intestine Especially Rectum
4. Urinary Bladder
5. Seminal Vesicle
⚫States Of The Human Body Or Sheath – 5
1. Physical Sheath
2. Mental Sheath
3. Respiratory Sheath
4. Intellectual Sheath
5. Blissful Sheath
🌑Stations Of Soul – 6
1. Moolatharam
2. Swathistanam
3. Manipooragam
4. Anakatham
5. Visuthi
6. Aakinai
⚫Regions – 3
1. Fire Region
2. Solar Region
3. Lunar Region
🌑Impurities Of The Soul – 3
1. Egoism
2. Karma
3. Maya (Delusion)
⚫Three Humors – 3
1. Vatham = Air + Space
2. Pitham = Fire
3. Kapham = Earth + Water
🌑Physical Bindings– 3
1. Material Bindings
2. Offspring Bindings
3. Worldly Bindings
⚫Cosmic Qualities – 3
1. Sattva (Pure)
2. Rajas (Passion)
3. Tamas (Ignorance)
🌑Acts – 2
1. Good Acts
2. Bad Acts
⚫Passions – 8
1. Desire
2. Hatred
3. Stingy
4. Lust
5. Pride
6. Internal Conflict
7. Mockery
8. Ego
🌑States Of Consciousness – 5
1. Wakefulness
2. Dream
3. Sleep
4. Repose (Tranquil Or Peaceful State)
5. Insensibility To Surroundings
Next to the Tattvas the human body exists of 72000 blood vessels, 13000 nerves and ten main arteries.
4448 diseases can be caused by the imbalance of the three humors.
0 notes
Text
Gall bladder surgery
Most common surgery is removal of gallbladder. Usually many doctors claims that it is an useless organ & removal is not harmful or has no side effect on the body. Let'd understand it's necessity & how important it is.
Most prominent reason of this surgery is gallstones, which is caused by deficiency of bile. If bile juice is sufficiently available gallstones won't occur. Gallbladder does not just stores the bile & releases to other organs but it regulates & concentrates bile. It breakdowns & emulsifies the fat, lubricates colon, alkalizes stomach acid etc.
Without gallbladder whatever amount of bile is produced by the liver it directly passes to intestine & won't be concentrated or regulated.
Here are some complications which may occur after surgery or removal of gallbladder:
1) Imbalanced cholesterol
2) Thyroid disorder
3) Vitamin deficiencies
4) Inefficient toxin removal
5) Constipation/Diarrhea
6) Frequent indigestion
7) Acid reflux/gastritis
8) Inability of absorption of omega3 fatty acid
9) Fatty liver etc.
Before removing of any of the body's organs or part, try to repair it first. And for repair you need to go to the engineer/mechanic, not to a scrap house.

0 notes
Text
John Korsah from ACCRA-Ghana
Lab scientist
FEVER
Ξ What is fever?
Fever, also known as pyrexia, is a medical condition characterized by an elevation in body temperature above the normal range. In most adults, a fever is typically considered to be present when the body temperature rises to 100.4°F (38°C) or higher. However, the definition of fever can vary depending on factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and the method used to measure body temperature.
Fever is a natural response by the body's immune system to various conditions, such as infections, inflammation, or certain medical conditions.
It is often associated with symptoms like sweating, chills, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, and increased heart rate. Fever itself is not a disease but rather a symptom indicating that the body is fighting off an infection or reacting to an underlying condition.
Fevers are commonly caused by viral or bacterial infections, such as the flu, common cold, urinary tract infections, or pneumonia. Other factors that can contribute to fever include certain medications, vaccinations, heat exhaustion, autoimmune disorders, and some cancers.
In most cases, treating the underlying cause of the fever is the primary approach. Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) can help reduce fever and alleviate associated symptoms.
However, it's important to note that fever itself is not always harmful and can actually be beneficial as it helps the body fight off infections. If a fever persists for an extended period, is accompanied by severe symptoms, or occurs in infants, young children, or individuals with weakened immune systems, it is advisable to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and treatment.
Ξ Types of fever
Fever can be categorized into different types based on their underlying causes or characteristics.
Here are some common types of fever:
1. Infectious Fever: This type of fever is caused by an infection, such as a viral or bacterial infection. Examples include the flu, common cold, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and strep throat.
2. Inflammatory Fever: Inflammation in the body can lead to a fever. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain autoimmune disorders can cause inflammatory fever.
3. Drug-induced Fever: Some medications or drugs can trigger a fever as a side effect. Certain antibiotics, antihistamines, and seizure medications are known to cause drug-induced fevers.
4. Neoplastic Fever: Fevers that are associated with cancers or tumors are referred to as neoplastic fevers. They can occur due to the body's immune response to the presence of cancer cells or as a result of the release of chemicals by the tumor.
5. Recurrent Fever: This type of fever is characterized by recurring episodes of fever that last for a certain period and then resolve, only to return later. Conditions like familial Mediterranean fever, periodic fever syndromes, and certain autoimmune disorders can cause recurrent fevers.
6. Pel-Ebstein Fever: This specific pattern of fever is observed in some cases of Hodgkin's lymphoma, where patients experience alternating periods of fever and normal temperature.
7. Continuous Fever: Continuous fever refers to a sustained fever that remains elevated throughout the day without significant fluctuations.
8. Remittent Fever: This type of fever fluctuates throughout the day but does not return to normal temperature. The variation in temperature is usually more than 2°C (3.6°F).
9. Intermittent Fever: Intermittent fever is characterized by episodes of fever that occur at regular intervals, with temperature returning to normal between episodes. Malaria is a notable example of a disease that causes intermittent fever.
These are just a few examples of the types of fever. It's important to note that the specific type and characteristics of a fever can provide valuable information to healthcare professionals for diagnosing and treating the underlying condition.
Ξ Causes of each fever
Here are some common causes associated with different types of fevers:
1. Infectious Fever:
▪️Viral Infections: Influenza (flu), common cold, viral gastroenteritis, dengue fever, viral hepatitis.
▪️Bacterial Infections: Streptococcal infections (e.g., strep throat), urinary tract infections, pneumonia, tuberculosis, bacterial meningitis.
Inflammatory Fever:
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disease that causes joint inflammation and fever.
▪️Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis can lead to fever during flare-ups.
▪️Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): An autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation in various organs and result in fever.
3. Drug-induced Fever:
▪️Antibiotics: Some antibiotics like penicillins, sulfonamides, and cephalosporins can cause drug-induced fever.
▪️Antihistamines: Certain antihistamines used for allergies can trigger a fever as a side effect.
▪️Antiepileptic Drugs: Medications used to treat seizures, such as phenytoin and carbamazepine, may cause fever in some individuals.
4. Neoplastic Fever:
▪️Cancers: Various types of cancers, such as lymphomas, leukemias, and solid tumors, can cause fever. Fever may occur due to immune response to cancer cells or chemicals released by tumors.
5. Recurrent Fever:
▪️Familial Mediterranean Fever: A hereditary autoinflammatory disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of fever and inflammation.
▪️Periodic Fever Syndromes: Conditions like familial Hibernian fever, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS), and hyper-IgD syndrome can cause recurrent fevers.
6. Pel-Ebstein Fever:
▪️Hodgkin's Lymphoma: Some individuals with Hodgkin's lymphoma may experience fevers that alternate between high and normal temperatures.
It's important to note that these are general examples, and each individual's case may vary. Fever can have various causes, and a healthcare professional should evaluate the specific symptoms and medical history to determine the underlying cause accurately.
Ξ Effects of fever
Fever is a natural response of the body's immune system to fight off infections and other underlying conditions. While fever itself is not typically harmful, it can have certain effects on the body. Here are some common effects of fever:
1. Increased Metabolic Rate: Fever causes an increase in the metabolic rate of the body. This means that the body's processes, such as heart rate, breathing rate, and energy expenditure, are elevated during a fever.
2. Accelerated Immune Response: Fever stimulates the immune system, enhancing the body's defense mechanisms against infections. It can activate immune cells, increase the production of antibodies, and promote the release of cytokines, which aid in fighting off pathogens.
3. Inhibition of Pathogen Growth: Higher body temperatures can inhibit the growth and replication of certain bacteria and viruses. Fever creates an unfavorable environment for pathogens, making it more difficult for them to survive and spread.
4. Increased Heart Rate: Fever can cause an increase in heart rate as the body works to circulate blood and distribute heat evenly throughout the body.
5. Vasodilation: Fever can lead to the dilation of blood vessels in the skin, resulting in flushing or redness. This helps dissipate heat from the body and can contribute to feelings of warmth.
6. Fluid Loss: Fever increases the body's fluid requirements as it can lead to fluid loss through sweating and increased respiratory rate. It is important to stay hydrated during a fever to prevent dehydration.
7. Fatigue and Weakness: Many individuals experience feelings of fatigue, weakness, and decreased energy levels during a fever. This is a natural response as the body redirects its resources to fighting off the underlying cause of the fever.
8. Discomfort and Pain: Fever can be accompanied by symptoms such as headache, muscle aches, and general discomfort. These symptoms are often associated with the underlying condition causing the fever, rather than the fever itself.
It's important to note that in most cases, fever is a temporary and self-limiting condition that resolves as the underlying cause is treated or the infection clears. However, high or persistent fevers, especially in certain vulnerable populations such as young children or individuals with weakened immune systems, may require medical attention.
Ξ How to run lab tests on fever :
1. Purpose
Running lab tests on a person with a fever can help identify the underlying cause of the fever and guide appropriate treatment. The purpose of conducting lab tests is to gather specific information about the patient's condition. Here are some common lab tests that may be conducted during a fever:
▪️Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC provides information about the different types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It can help identify indicators of infection, inflammation, or anemia.
▪️Blood Culture: This test involves collecting a blood sample and incubating it in a laboratory to check for the presence of bacteria or fungi in the bloodstream. Blood cultures help identify a potential bloodstream infection, which could be the cause of the fever.
▪️Urinalysis: A urinalysis involves examining a urine sample to check for signs of infection or inflammation in the urinary tract, which can be a potential source of fever.
▪️Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can be performed to evaluate the condition of the lungs and identify any signs of pneumonia or other respiratory infections, which may cause a fever.
▪️C-reactive Protein (CRP) or Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): These tests measure markers of inflammation in the body. They can help determine the severity of the infection or inflammation contributing to the fever.
▪️Viral Panel: In cases where a viral infection is suspected, specific tests can be conducted to identify the presence of certain viral pathogens, such as influenza, dengue, or respiratory viruses.
▪️Cultures: Depending on the symptoms and suspected source of infection, cultures may be taken from various sites, such as throat swabs, sputum samples, wound swabs, or cerebrospinal fluid, to identify the specific bacteria or fungi causing the infection.
The specific lab tests ordered may vary based on the individual's symptoms, medical history, and clinical presentation. It is important for a healthcare professional to evaluate the patient and determine which tests are necessary to reach a diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment.
2. Procedure
The procedure for conducting lab tests during a fever can vary depending on the specific tests being performed. However, here is a general outline of the steps involved:
▪️Medical History and Evaluation: The healthcare professional will first take a detailed medical history, including information about the patient's symptoms, duration of the fever, and any other relevant information. They will also perform a physical examination to assess the patient's overall condition.
▪️Test Ordering: Based on the medical history, evaluation, and initial assessment, the healthcare professional will determine which lab tests are necessary. They will write an order for the specific tests to be conducted.
▪️Sample Collection: The patient will be directed to the laboratory or a designated collection center for sample collection. The types of samples required may include blood, urine, throat swabs, sputum, or other relevant samples based on the suspected source of infection.
▪️Sample Processing: Once the samples are collected, they are processed in the laboratory according to the specific requirements of each test. This may involve centrifugation, culturing, staining, or other techniques, depending on the test being conducted.
▪️Laboratory Analysis: The collected samples are analyzed using various laboratory techniques and equipment. For example, blood samples may undergo automated analysis, while cultures are incubated to allow for the growth of microorganisms.
▪️Result Interpretation: After the analysis is complete, the results are interpreted by laboratory professionals who generate a report. The report includes the findings for each test conducted, including reference ranges and any abnormalities detected.
▪️Result Communication: The healthcare professional receives the lab report and interprets the results in the context of the patient's clinical presentation. They communicate the results to the patient, explaining any abnormalities or findings and discussing the next steps, such as further diagnostic tests or treatment options.
It is important to note that the specific procedure and timeline for lab tests may vary depending on the healthcare facility, the urgency of the situation, and the specific tests being conducted. The healthcare professionals involved will guide the patient through the process and ensure that the necessary tests are conducted accurately and efficiently.
3. Risks
While lab tests conducted during a fever are generally considered safe, there are some potential risks and considerations to be aware of:
▪️Discomfort or Pain: Certain sample collection procedures, such as blood draws or throat swabs, may cause temporary discomfort or mild pain. However, healthcare professionals aim to minimize any discomfort and ensure patient comfort during the process.
▪️Bleeding or Bruising: In some cases, blood draws may result in minor bleeding at the puncture site or bruising. Healthcare professionals take precautions to minimize these risks, such as using appropriate techniques and applying pressure after sample collection.
▪️Infection: There is a very low risk of infection associated with sample collection, particularly if proper aseptic techniques are not followed. However, healthcare professionals adhere to strict infection control protocols to minimize the risk of infection.
▪️Sample Contamination: Improper handling or contamination of samples can lead to inaccurate results. Laboratory professionals take precautions to ensure proper sample handling, transportation, and storage to minimize the risk of contamination.
▪️Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may have allergies or sensitivities to certain materials or substances used during sample collection or testing, such as adhesive tapes, antiseptics, or latex gloves. Informing healthcare professionals about known allergies or sensitivities can help mitigate this risk.
▪️Psychological Distress: For some individuals, undergoing lab tests may cause anxiety or psychological distress. It is important to communicate any concerns or anxieties to healthcare professionals, who can provide support and address these concerns.
▪️False-Negative or False-Positive Results: Lab tests have a certain degree of sensitivity and specificity. However, false-negative or false-positive results are possible, which means that the test may incorrectly indicate the presence or absence of a condition. Interpretation of test results should always be done in conjunction with the patient's clinical presentation and other diagnostic information.
It is essential to communicate openly with healthcare professionals about any concerns or questions you may have about the lab tests being conducted. They can provide you with information, address your concerns, and help ensure a safe and effective testing process.
4. Medication both in Medicine and Natural ways
Medication can be used to manage various health conditions and symptoms, including fever. It's important to note that specific medications should be prescribed by a healthcare professional based on the underlying cause of the fever and the individual's medical history. Here are some common medications used to treat fever:
▪️Antipyretics: These medications are used to reduce fever by lowering body temperature. Common antipyretics include acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve).
▪️Antibiotics: If the fever is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to target and eliminate the bacteria. However, antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections.
▪️Antiviral Medications: In cases where the fever is caused by a viral infection, specific antiviral medications may be prescribed to help control the viral replication and reduce symptoms.
▪️Anti-inflammatory Drugs: In certain cases, such as fever associated with autoimmune diseases or inflammation, corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory drugs may be used to manage symptoms and reduce fever.
▪️Other Medications: Depending on the underlying cause of the fever, additional medications may be prescribed to address specific symptoms or conditions. For example, antimalarial drugs may be used to treat fever caused by malaria.
While medications prescribed by healthcare professionals are often effective in managing fever, there are also some natural ways to help alleviate fever symptoms:
▪️Rest: Getting plenty of rest allows the body to conserve energy and focus on fighting the underlying cause of the fever.
▪️Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, herbal teas, or clear broths, to stay hydrated and prevent dehydration.
▪️Sponge Bath or Cooling Measures: Applying a damp cloth or sponge soaked in lukewarm water to the forehead, wrists, and ankles can help cool the body. Avoid using cold water or ice as it can cause shivering and may actually increase body temperature.
▪️Room Temperature: Keep the room temperature comfortable and not excessively warm. A cooler environment can help promote comfort during a fever.
▪️Wear Lightweight Clothing: Dress in lightweight and breathable clothing to facilitate heat dissipation from the body.
▪️Herbal Remedies: Some herbal remedies, such as chamomile or peppermint tea, may have mild fever-reducing properties. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional or herbalist before using herbal remedies, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options for fever. They can provide guidance on the most suitable medications or natural remedies based on individual circumstances.

0 notes
Text
➖The Effect Of Eating Fish On Sperm Count
Tobacco use and alcohol consumption are two things you should definitely avoid if you want to increase sperm count. Many men do not understand, nevertheless, that their food can also impact their fertility. The male reproductive system is negatively impacted by processed pork products like bacon and sausages.
You and your partner likely already are aware of the numerous benefits of a healthy diet. However, eating some foods may help his sperm count and quality. You’re less likely to experience pregnancy difficulties if your partner’s sperm are in better health.
➖What is the effect of fish on sperm count?
Men who routinely consume fish have better sperm counts and are more fertile, claims Medicalnewstoday. Due to their high of omega-3 fatty acids, fish may have advantages for the health of sperm. Men with low sperm counts benefit from regularly consuming fatty fish.
Among the top ten vitamins and supplements for boosting sperm count are omega 3s. They are crucial to the structure and development of all cells, sperm cells. Consuming omega 3s can aid to increase sperm count, morphology, and motility.
A Harvard University study found that males who had more than one dish of fatty fish while undergoing reproductive treatments had semen of greater quality. The team examined 156 individuals’ sperm samples and compared them to each volunteer’s food intake as recorded on a food intake questionnaire. Less concentrated and differently shaped sperm were found in processed meat.
According to a different study, males who consume more fatty fish had a significant 65% increase in sperm production. Furthermore, because the results are nearly instantaneous, what you decide to eat for lunch may pay off by the time you try the evening’s few desserts.

0 notes
Text
John Korsah
ACCRA-Ghana
Understanding blood pressure, types, purpose, procedure and results.
Suggested ways of bringing the abnormalities to normal both in natural ways and the use of medicine.
🍁
1. Understanding blood pressure
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by blood against the walls of arteries as it flows through them. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is usually expressed as two numbers, with the higher number (systolic pressure) over the lower number (diastolic pressure).
For example, a blood pressure reading of 120/80 mmHg would mean a systolic pressure of 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of 80 mmHg.
➖Systolic pressure is the pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts and pushes blood out into the circulatory system, while diastolic pressure is the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
Both numbers are important in determining overall blood pressure and can be affected by various factors such as age, gender, activity level, diet, and medical conditions.
➖High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, occurs when the force of blood against the artery walls is consistently too high. This can put a strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
➖Low blood pressure, on the other hand, can cause symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, and fatigue, and can also be indicative of underlying health problems.
It is important to monitor and maintain a healthy blood pressure range, which is generally considered to be below 120/80 mmHg.
2. Types
There are two primary types of blood pressure: systolic pressure and diastolic pressure.
➖Systolic pressure is the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats and pumps blood out into the circulatory system.
➖Diastolic pressure is the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
Both systolic and diastolic pressures are important in determining overall blood pressure and can be affected by various factors such as age, gender, activity level, diet, and medical conditions.
Blood pressure can also be classified into categories based on the readings:
➖Normal blood pressure: This is when the systolic pressure is less than 120 mmHg and the diastolic pressure is less than 80 mmHg.
➖Elevated blood pressure: This is when the systolic pressure is between 120-129 mmHg and the diastolic pressure is less than 80 mmHg.
➖Hypertension stage 1: This is when the systolic pressure is between 130-139 mmHg or the diastolic pressure is between 80-89 mmHg.
➖Hypertension stage 2: This is when the systolic pressure is 140 mmHg or higher, or the diastolic pressure is 90 mmHg or higher.
➖Hypertensive crisis: This is when the systolic pressure is higher than 180 mmHg or the diastolic pressure is higher than 120 mmHg, and immediate medical attention is required.
3. Tests
Blood pressure can be measured in various ways, including:
➖Manual blood pressure measurement: This involves using a cuff wrapped around the upper arm and a stethoscope to listen to the sounds of blood flow through the arteries as the cuff is inflated and then slowly deflated.
➖Automated blood pressure measurement: This involves using a machine that automatically inflates and deflates the cuff and provides a digital readout of the blood pressure.
➖Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: This involves wearing a portable blood pressure monitor that takes readings automatically at regular intervals over a 24-hour period.
➖Home blood pressure monitoring: This involves using a home blood pressure monitor to take readings at home on a regular basis.
In addition to blood pressure measurements, other tests may be done to help diagnose and manage high blood pressure, including:
➖Urine test: This can help to check for underlying kidney problems that may be contributing to high blood pressure.
➖Blood tests: These can help to check for underlying conditions such as high cholesterol or diabetes that may be contributing to high blood pressure.
➖Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): This can help to check for any abnormalities in heart rhythm or structure that may be contributing to high blood pressure.
➖Echocardiogram: This can help to check for any abnormalities in the structure or function of the heart that may be contributing to high blood pressure.
➖Stress test: This can help to check how well the heart functions under stress and can also help to diagnose underlying heart problems that may be contributing to high blood pressure.
5. Purpose of tests
The purpose of blood pressure tests is to measure the force of blood against the walls of arteries as it flows through them.
This measurement is important because high blood pressure (hypertension) can put a strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
Low blood pressure (hypotension) can also cause symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, and fatigue, and can be indicative of underlying health problems.
The different types of blood pressure tests serve different purposes.
➖Manual and automated blood pressure measurements are the most common methods of diagnosing hypertension and monitoring blood pressure over time.
➖Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring can be used to get a more accurate picture of a person's blood pressure throughout the day and night.
➖Home blood pressure monitoring is useful for people who want to monitor their blood pressure in between doctor's visits.
➖Urine and blood tests, as well as other tests such as an electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and stress test, can help to identify underlying health problems that may be contributing to high blood pressure or affecting the heart and blood vessels.
6. Procedures of tests
The procedures for blood pressure tests can vary depending on the type of test being performed.
Here is a brief overview of the procedures for some of the most common blood pressure tests:
➖Manual blood pressure measurement: A healthcare professional will wrap a cuff around your upper arm and inflate it until it's tight. They will then use a stethoscope to listen to the sounds of blood flow as they slowly deflate the cuff. The point at which the sounds begin and end is used to determine your systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
➖Automated blood pressure measurement: A healthcare professional or automated machine will wrap a cuff around your upper arm and press a button to inflate and deflate the cuff. The machine will provide a digital readout of your blood pressure.
➖Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: A healthcare professional will fit you with a portable blood pressure monitor that you wear for 24 hours. The monitor will take readings at regular intervals throughout the day and night.
➖Home blood pressure monitoring: You will use a home blood pressure monitor to take readings at home on a regular basis. Your healthcare professional will provide instructions on how to use the monitor and how often to take readings.
Other diagnostic tests, such as urine and blood tests, electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and stress test, may involve different procedures. For example, a urine test may involve providing a urine sample at a healthcare facility, while an electrocardiogram may involve attaching electrodes to your chest to monitor your heart's electrical activity.
7. Results
The results of blood pressure tests are typically given as two numbers, representing the systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
The systolic blood pressure is the top number, which represents the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats, while the diastolic blood pressure is the bottom number, which represents the pressure in your arteries when your heart is at rest between beats.
The normal blood pressure reading is generally considered to be less than 120/80 mmHg.
If your blood pressure is consistently high, your healthcare professional may diagnose you with hypertension. Depending on the severity of your hypertension, they may recommend lifestyle changes such as weight loss, exercise, and dietary changes, or medications such as diuretics, beta blockers, or ACE inhibitors to help lower your blood pressure.
If other diagnostic tests, such as urine and blood tests, electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and stress test, are performed, the results may reveal underlying health problems that may be contributing to high blood pressure or affecting the heart and blood vessels. Depending on the results, your healthcare professional may recommend further testing or treatments to address these underlying health problems.
It's important to discuss your blood pressure test results with your healthcare professional, as they can provide guidance on managing and monitoring your blood pressure, as well as any underlying health problems that may be affecting your overall health and wellbeing.
8. Suggested ways of bringing the abnormalities to normal both in natural ways and through medical intervention
There are several ways to bring high blood pressure to normal levels, both through natural methods and medical intervention. Here are some suggestions:
1. Natural methods:
➖Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming or running can help lower your blood pressure.
➖Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of high blood pressure, so it's important to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
➖Reduce salt intake: Consuming too much salt can increase your blood pressure, so try to limit your intake of processed foods and eat more fresh fruits and vegetables.
➖Increase potassium intake: Eating foods rich in potassium, such as bananas, spinach, sweet potatoes, and avocado, can help lower blood pressure.
➖Quit smoking: Smoking can increase blood pressure, so quitting smoking can help reduce your risk of high blood pressure and related health problems.
2. Medical intervention:
➖Medications: There are several medications available to help lower blood pressure, such as diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers.
➖Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be recommended to treat underlying conditions that are causing high blood pressure, such as renal artery stenosis.
➖Lifestyle changes: In addition to natural methods, healthcare professionals may recommend additional lifestyle changes such as limiting alcohol intake and managing stress levels to help lower blood pressure.

0 notes
Text
John Korsah
ACCRA-Ghana
1. Liver Function tests, types, purpose, procedure and results.
2. Suggested ways of bringing the abnormalities to normal both in natural ways and the use of medicine.
🍁
1. Liver Function test
Liver function tests (LFTs) are a group of blood tests that are used to assess the health and function of the liver. These tests are often done as part of a routine health checkup or when a person is experiencing symptoms that may suggest liver disease.
The common liver function tests include:
▪️Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): This enzyme is found primarily in the liver and is released into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged. High levels of ALT in the blood can indicate liver damage or disease.
▪️Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): Like ALT, AST is also found in the liver and is released into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged. Elevated AST levels in the blood can also indicate liver damage or disease.
▪️Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): This enzyme is found in many tissues throughout the body, including the liver, bones, and intestines. Elevated levels of ALP in the blood can indicate liver disease, bone disease, or a problem with the intestines.
▪️Total bilirubin: This is a waste product that is produced when red blood cells are broken down in the liver. High levels of bilirubin in the blood can indicate liver disease or a problem with the gallbladder.
▪️Albumin: This is a protein that is produced by the liver. Low levels of albumin in the blood can indicate liver disease or malnutrition.
▪️Prothrombin time (PT): This test measures the time it takes for the blood to clot. The liver produces many of the proteins needed for blood clotting, so changes in PT can indicate liver disease.
It is important to note that LFTs are not a definitive diagnosis of liver disease, and further testing may be needed to confirm a diagnosis.
🔳Types
There are several types of liver function tests that can be used to assess liver health and function. Some of the most common types include:
▪️Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): This test measures the level of ALT in the blood, which is an enzyme that is primarily found in liver cells. Elevated levels of ALT in the blood can indicate liver damage or disease.
▪️Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): Like ALT, AST is also found in liver cells and is released into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged. Elevated levels of AST in the blood can indicate liver damage or disease.
▪️Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): This test measures the level of ALP in the blood, which is an enzyme that is found in many tissues throughout the body, including the liver. Elevated levels of ALP in the blood can indicate liver disease, bone disease, or a problem with the intestines.
▪️Total bilirubin: This test measures the level of bilirubin in the blood, which is a waste product that is produced when red blood cells are broken down in the liver. High levels of bilirubin in the blood can indicate liver disease or a problem with the gallbladder.
▪️Albumin: This test measures the level of albumin in the blood, which is a protein that is produced by the liver. Low levels of albumin in the blood can indicate liver disease or malnutrition.
▪️Prothrombin time (PT): This test measures the time it takes for the blood to clot. The liver produces many of the proteins needed for blood clotting, so changes in PT can indicate liver disease.
▪️Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT): This test measures the level of GGT in the blood, which is an enzyme that is found in liver cells and other tissues. Elevated levels of GGT in the blood can indicate liver disease or heavy alcohol consumption.
▪️Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH): This test measures the level of LDH in the blood, which is an enzyme that is found in many tissues throughout the body, including the liver. Elevated levels of LDH in the blood can indicate liver disease or damage to other tissues in the body.
These tests are often done together as part of a liver function panel to provide a comprehensive assessment of liver health and function.
🔳Purpose
The purpose of liver function tests (LFTs) is to assess the health and function of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that performs many important functions in the body, including:
▪️Filtering and removing toxins from the blood
▪️Producing bile, which helps with the digestion of fats
▪️Regulating the body's metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
▪️Storing vitamins and minerals, such as iron and vitamin D
▪️Producing proteins that are essential for blood clotting
▪️LFTs are used to detect liver damage, inflammation, or disease by measuring the levels of enzymes, proteins, and other substances in the blood that are produced by or indicative of liver cells. Abnormal results from LFTs can help identify liver problems early on and guide further testing and treatment.
🔳Some common reasons for ordering LFTs include:
▪️Monitoring liver function in people with liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis
▪️Assessing liver function in people who are taking medications that can damage the liver
Screening for liver disease in people who have risk factors, such as heavy alcohol use or a family history of liver disease
▪️Evaluating abnormal liver function tests found incidentally during routine blood testing
Investigating the cause of symptoms that may suggest liver disease, such as jaundice, abdominal pain, or unexplained fatigue
Overall, the purpose of liver function tests is to help assess liver health and function, detect liver disease or damage, and guide further testing and treatment.
🔳Procedure
Liver function tests are a blood test that can be performed at a doctor's office, hospital or laboratory.
The procedure for liver function tests is typically as follows:
▪️Preparation: There is no specific preparation required for liver function tests. However, it is important to inform your doctor of any medications or supplements you are taking, as some can affect liver function test results.
▪️Blood collection: A healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from a vein in your arm using a sterile needle. The procedure is quick and usually involves minimal discomfort.
▪️Results: The blood sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis. Results are typically available within a few days, and your doctor will discuss the results with you and any further action needed.
It is important to note that liver function tests are just one tool used to assess liver health and function, and abnormal results do not necessarily mean that you have liver disease.
Further testing and evaluation may be needed to determine the cause of abnormal results and guide appropriate treatment.
Additional information: Some people may experience mild discomfort, bruising, or bleeding at the site of the blood draw. If you experience severe pain, swelling, or bleeding, contact your doctor or healthcare provider immediately.
🔳Results
Interpretation of liver function test results can vary depending on the specific test being performed, the individual's age, sex, and medical history, and other factors.
However, some general guidelines for interpreting common liver function test results are as follows:
▪️Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): Normal levels of ALT are generally between 7 and 55 units per liter (U/L) for men and between 7 and 45 U/L for women. Elevated levels of ALT may indicate liver damage, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis.
▪️Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): Normal levels of AST are generally between 8 and 48 U/L for men and between 7 and 35 U/L for women. Elevated levels of AST may indicate liver damage or other conditions, such as muscle damage or heart disease.
▪️Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): Normal levels of ALP are generally between 44 and 147 U/L for adults. Elevated levels of ALP may indicate liver disease, bone disease, or other conditions, such as pregnancy.
▪️Total bilirubin: Normal levels of bilirubin are generally between 0.1 and 1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for adults. Elevated levels of bilirubin may indicate liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, or other conditions, such as gallbladder disease.
▪️Albumin: Normal levels of albumin are generally between 3.5 and 5.0 grams per deciliter (g/dL) for adults. Low levels of albumin may indicate liver disease or malnutrition.
▪️Prothrombin time (PT): Normal PT values range from 9.5 to 13.8 seconds, depending on the laboratory. Prolonged PT can indicate liver disease or a deficiency of clotting factors.
▪️Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT): Normal levels of GGT are generally between 9 and 48 U/L for men and between 9 and 33 U/L for women. Elevated levels of GGT may indicate liver disease or heavy alcohol consumption.
▪️Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH): Normal levels of LDH are generally between 140 and 280 U/L for adults. Elevated levels of LDH may indicate liver disease or damage to other tissues in the body.
It is important to note that these are general guidelines, and interpretation of liver function test results should always be done by a healthcare professional who can take into account individual factors and medical history.
🔳 Suggested ways of bringing the abnormalities to normal both in natural ways and the use of medicine.
The treatment of abnormal liver function test results depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, lifestyle changes, natural remedies, or medications may be used to help bring the abnormalities back to normal.
Here are some suggested ways to manage abnormal liver function test results:
▪️Lifestyle changes: Making healthy lifestyle choices can improve liver function and help prevent liver damage. These changes may include:
▪️Limiting alcohol consumption or avoiding alcohol altogether, especially if you have liver disease.
▪️Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
▪️Eating a balanced diet that is low in saturated fat, sugar, and salt.
▪️Avoiding exposure to toxins, such as pesticides and industrial chemicals.
▪️Quitting smoking.
Natural remedies: Some natural remedies may help support liver function, such as:
▪️Milk thistle: This herb has been shown to help protect the liver from damage and improve liver function. It can be taken in capsule or tea form.
▪️Turmeric: This spice has anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce liver inflammation. It can be added to food or taken in supplement form.
▪️Dandelion root: This herb has diuretic properties and may help reduce liver congestion. It can be taken in capsule or tea form.
It is important to note that natural remedies should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they may interact with other medications or have side effects.
Medications
Depending on the underlying cause of abnormal liver function test results, medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms or treat the underlying condition.
For example:
▪️Antiviral medications may be used to treat hepatitis B or C.
▪️Corticosteroids may be used to reduce liver inflammation in autoimmune hepatitis.
▪️Medications may be used to manage symptoms of liver disease, such as itching or fatigue.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for abnormal liver function test results, as untreated liver disease can lead to serious complications.
0 notes
Text
John Korsah
ACCRA-Ghana
ESR Test
Detailed aspects of ESR test
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test is a common blood test used to help diagnose and monitor various inflammatory conditions in the body, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancer.
▪️Purpose
The purpose of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test is to measure the rate at which red blood cells (erythrocytes) settle to the bottom of a tube of blood. This test is commonly used to help diagnose and monitor various inflammatory conditions in the body, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancer.
The ESR test indirectly reflects the presence and severity of inflammation in the body. When there is inflammation in the body, certain proteins called acute-phase reactants, such as fibrinogen and C-reactive protein (CRP), are released into the blood. These proteins cause red blood cells to stick together and settle more quickly to the bottom of the tube, resulting in an increased ESR value.
The ESR test is a simple, non-specific test that can provide useful information to healthcare providers in identifying and monitoring inflammatory conditions. However, it is important to note that a high ESR value alone is not diagnostic of any specific condition and needs to be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical and laboratory findings.
▪️Procedure
The ESR test is a simple blood test that can be done at a laboratory or medical clinic. Here is a detailed procedure for the ESR test:
• Preparation: No special preparation is required for the ESR test. However, you may be asked to fast for a few hours before the test if other blood tests are also being done at the same time.
• Blood sample collection: A healthcare professional will collect a small sample of blood from a vein in your arm using a needle and a syringe. The area around the vein may be cleaned with an antiseptic solution, and a tourniquet may be applied to make the vein more visible and easier to access.
• Blood sample processing: The collected blood sample is then placed in a tall, thin tube called a Westergren tube, which is filled with a special anticoagulant to prevent the blood from clotting. The tube is then placed upright and allowed to sit undisturbed for one hour.
• ESR measurement: After one hour, the distance that the red blood cells have settled to the bottom of the tube is measured and reported as the ESR value in millimeters per hour (mm/hr). The ESR value indicates the rate at which the red blood cells have settled to the bottom of the tube.
• Result interpretation: The ESR test result is interpreted by your healthcare provider based on your medical history, physical examination, and other laboratory test results. A high ESR value indicates an increased rate of settling of red blood cells, which is usually due to the presence of inflammation in the body. However, a high ESR value alone is not diagnostic of any specific condition and needs to be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical and laboratory findings.
The ESR test is a simple and safe test that usually takes only a few minutes to perform. However, like any other blood test, it may cause slight bruising or bleeding at the site where the needle was inserted.
▪️Results
The results of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test indicate the rate at which red blood cells (erythrocytes) settle to the bottom of a tube of blood. Here are some important points about the interpretation of ESR test results:
• Normal range: The normal range for ESR values can vary depending on age, gender, and other factors. Generally, a normal ESR value is less than 20 mm/hr for men and less than 30 mm/hr for women.
• High ESR value: A high ESR value indicates an increased rate of settling of red blood cells, which is usually due to the presence of inflammation in the body. However, a high ESR value alone is not diagnostic of any specific condition and needs to be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical and laboratory findings.
• Causes of high ESR: Several conditions can cause a high ESR value, including infections, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and other inflammatory conditions. Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and oral contraceptives, can also affect ESR values.
• Serial ESR measurements: Serial ESR measurements, which are ESR tests done at regular intervals, can be useful in monitoring the course of an inflammatory condition and in assessing the effectiveness of treatment.
▪️Limitations: The ESR test is a nonspecific test that can be affected by several factors other than inflammation. Therefore, it is not a definitive diagnostic tool and needs to be used in conjunction with other tests and clinical findings. Additionally, the ESR test does not provide information about the underlying cause of inflammation, and further tests may be needed to identify the specific cause.
▪️Suggested ways of bringing the abnormalities to normal both in natural ways and with medical interventions
The approach to bringing the abnormalities identified by an ESR test to normal can vary depending on the underlying cause of the abnormality. Here are some suggested ways to bring ESR abnormalities to normal:
Natural ways:
• Lifestyle modifications: Making changes to your lifestyle can help manage inflammation and bring ESR levels to normal. This can include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and managing stress.
• Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources can help reduce inflammation in the body. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, may also help reduce inflammation.
• Herbal remedies: Certain herbs, such as ginger, turmeric, and boswellia, have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce inflammation in the body.
• Supplements: Certain supplements, such as vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, may help reduce inflammation and bring ESR levels to normal. However, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider before taking any supplements.
Medical interventions:
• Medications: Depending on the underlying cause of the abnormal ESR levels, medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be prescribed to help manage inflammation and reduce ESR levels.
• Antibiotics: If the abnormal ESR levels are due to an underlying infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to help treat the infection and bring ESR levels to normal.
• Immunosuppressants: Immunosuppressant medications may be used to treat autoimmune diseases and other conditions that involve chronic inflammation and elevated ESR levels.
• Chemotherapy or radiation therapy: In cases of cancer, chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be used to reduce cancer-related inflammation and bring ESR levels to normal.
It is important to note that the treatment approach for ESR abnormalities will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the abnormality.
It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.

0 notes
Text
John Korsah
ACCRA-Ghana
▪️Coomb test (Direct and Indirect)
The Coombs test, also known as the antiglobulin test, is a laboratory test that detects the presence of antibodies or complement proteins that are bound to the surface of red blood cells. There are two types of Coombs tests: the direct Coombs test and the indirect Coombs test.
➖Direct Coombs test: The direct Coombs test is used to detect antibodies that are already bound to red blood cells in the bloodstream. This test is typically ordered when a patient has symptoms of hemolytic anemia, which is a condition in which red blood cells are destroyed faster than the body can replace them. The test involves mixing a sample of the patient's blood with antiglobulin antibodies, which bind to any antibodies or complement proteins that are already bound to the surface of red blood cells. If the red blood cells agglutinate (clump together), it indicates the presence of antibodies on their surface.
➖Indirect Coombs test: The indirect Coombs test is used to detect antibodies that are present in a patient's blood but have not yet bound to red blood cells. This test is typically ordered when a patient is at risk for developing hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), which can occur when a mother's antibodies cross the placenta and attack the red blood cells of a fetus. The test involves mixing a sample of the patient's blood with a known type of red blood cells, then adding antiglobulin antibodies to the mixture. If agglutination occurs, it indicates the presence of antibodies in the patient's blood that may cause HDN.
The Coombs test is a useful tool for detecting antibodies or complement proteins that are bound to the surface of red blood cells. The direct Coombs test is used to detect antibodies already bound to red blood cells in the bloodstream, while the indirect Coombs test is used to detect antibodies that are present in a patient's blood but have not yet bound to red blood cells.
The results of the Coombs test can be useful in diagnosing and managing conditions such as hemolytic anemia and hemolytic disease of the newborn.
▪️Procedures
The procedures for the direct and indirect Coombs tests are as follows:
➖Direct Coombs test:
A blood sample is collected from the patient and placed in a test tube.
Coombs reagent, which contains antiglobulin antibodies, is added to the blood sample.
The test tube is gently mixed and then incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes to allow the antiglobulin antibodies to bind to any antibodies or complement proteins that are bound to the surface of the patient's red blood cells.
The test tube is then centrifuged to separate the red blood cells from the serum.
The red blood cells are examined under a microscope for signs of agglutination (clumping). If agglutination is present, it indicates the presence of antibodies or complement proteins on the surface of the red blood cells.
➖Indirect Coombs test:
A blood sample is collected from the patient and placed in a test tube.
A known type of red blood cells, such as type A or type B, is added to the test tube.
The test tube is gently mixed and then incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes to allow any antibodies in the patient's serum to bind to the red blood cells.
The test tube is then centrifuged to separate the red blood cells from the serum.
Coombs reagent, which contains antiglobulin antibodies, is added to the test tube.
The test tube is gently mixed and then incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes to allow the antiglobulin antibodies to bind to any antibodies that are bound to the red blood cells.
The test tube is centrifuged again to separate the red blood cells from the serum.
The red blood cells are examined under a microscope for signs of agglutination. If agglutination is present, it indicates the presence of antibodies in the patient's serum that may cause hemolytic disease of the newborn.
▪️Results
The results of the Coombs test can be positive or negative, depending on whether antibodies or complement proteins are detected on the surface of red blood cells.
➖Direct Coombs test:
• Positive result: A positive direct Coombs test indicates the presence of antibodies or complement proteins bound to the surface of the patient's red blood cells. This may indicate the presence of autoimmune hemolytic anemia or a transfusion reaction.
• Negative result: A negative direct Coombs test indicates the absence of antibodies or complement proteins bound to the surface of the patient's red blood cells. However, this does not rule out the possibility of other causes of hemolytic anemia.
➖Indirect Coombs test:
• Positive result: A positive indirect Coombs test indicates the presence of antibodies in the patient's serum that may cause hemolytic disease of the newborn. This is commonly seen in pregnant women who have developed antibodies against their fetus's red blood cells.
• Negative result: A negative indirect Coombs test indicates the absence of antibodies in the patient's serum that may cause hemolytic disease of the newborn. However, this does not rule out the possibility of other causes of hemolytic disease.
It is important to note that the Coombs test is not a definitive diagnostic tool and should be used in conjunction with other tests and clinical evaluation to determine the underlying cause of hemolytic anemia or hemolytic disease of the newborn.
➖Suggested ways of bringing the abnormalities to normal both in natural ways and the use of medicine.
The treatment of abnormalities detected by the Coombs test will depend on the underlying cause of the condition.
Here are some suggested ways to bring abnormalities to normal, both through natural ways and medication:
Hemolytic anemia caused by autoimmune disorders or infections can be treated with corticosteroids, which can suppress the immune system and reduce the destruction of red blood cells. Natural ways to help manage this condition include eating a balanced diet rich in iron and other nutrients that support red blood cell production, staying hydrated, and getting enough rest.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn caused by maternal antibodies can be prevented by administering Rh immunoglobulin (RhIg) to Rh-negative mothers during pregnancy or after delivery. In severe cases, exchange transfusion may be necessary to replace the baby's blood with compatible blood.
If the Coombs test is positive due to a transfusion reaction, stopping the transfusion and administering medication such as antihistamines, corticosteroids, and intravenous fluids may help manage the reaction.
In some cases, treating the underlying condition that caused the abnormality may be necessary. For example, if the Coombs test is positive due to a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection.
In addition to medication and natural remedies, blood transfusions may be necessary to replace the patient's red blood cells in cases of severe hemolytic anemia or hemolytic disease of the newborn.
It is important to note that the treatment of abnormalities detected by the Coombs test should be determined by a healthcare professional based on the individual patient's condition and medical history.

0 notes
Text
John Korsah
ACCRA-Ghana
➖Sickle cell test
The sickle cell test is a diagnostic test that determines whether an individual has sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait. Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body.
This disorder causes red blood cells to be sickle-shaped, stiff, and sticky, leading to decreased oxygen supply to the tissues and organs and potentially causing pain, infections, and organ damage.
Sickle cell trait is a carrier state in which an individual has one copy of the sickle cell gene and one copy of a normal hemoglobin gene.
The sickle cell test is typically performed using a blood sample, and there are several types of tests that can be used to diagnose sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait, including:
• Hemoglobin electrophoresis: This test separates different types of hemoglobin by their electrical charge and can identify the presence of abnormal hemoglobin, such as sickle hemoglobin (HbS).
• Sickle solubility test: This test involves mixing a small amount of blood with a solution that causes sickle hemoglobin to form crystals, which can be seen under a microscope.
• High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): This test separates different types of hemoglobin based on their size and can detect abnormal hemoglobin, including sickle hemoglobin.
The results of the sickle cell test can be positive (indicating the presence of sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait) or negative (indicating the absence of sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait). If the test is positive, further testing may be required to confirm the diagnosis and to determine the type and severity of sickle cell disease.
There is currently no cure for sickle cell disease, but treatment options are available to manage symptoms and complications. These may include pain management, hydration, blood transfusions, bone marrow transplants, and medications to prevent infections and complications. Those with sickle cell trait generally do not require treatment, but should be aware of their carrier status and potential risks associated with having children who may also inherit the trait.
➖Procedure
The sickle cell test is typically performed using a blood sample, and there are several types of tests that can be used to diagnose sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait. The most common procedure for testing for sickle cell disease or trait is:
• Blood sample collection: A healthcare provider will collect a blood sample from a vein in your arm using a needle and syringe. In some cases, a finger prick or heel prick may be used to collect a small sample of blood.
• Laboratory analysis: The blood sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis. There are several tests that can be used to diagnose sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait, including hemoglobin electrophoresis, sickle solubility test, and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The specific test used will depend on the laboratory's protocols and the healthcare provider's preferences.
➖Results
The results of the sickle cell test can be positive or negative, depending on the presence or absence of sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait.
A positive result indicates the presence of sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait. Sickle cell disease is diagnosed when an individual has two copies of the sickle cell gene (one from each parent), while sickle cell trait is diagnosed when an individual has one copy of the sickle cell gene and one copy of a normal hemoglobin gene.
A negative result indicates the absence of sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait. However, it is important to note that a negative result does not rule out the possibility of being a carrier for the sickle cell gene. In some cases, further testing may be recommended, especially if there is a family history of sickle cell disease or if symptoms of sickle cell disease are present.
It is important to interpret the results of the sickle cell test in conjunction with other clinical findings and to discuss the results with a healthcare provider or a genetic counselor to determine the appropriate next steps.
➖Suggested ways of bringing the abnormalities to normal both in natural ways and the use of medicine for sickle cell test
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic condition that affects the structure and function of red blood cells. The abnormal shape of sickle cells can lead to blockages in blood vessels, causing pain, organ damage, and other complications. While there is currently no cure for SCD, there are several ways to manage the symptoms and prevent complications.
Some suggested ways of bringing the abnormalities to normal both in natural ways and the use of medicine for sickle cell disease:
1. Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids helps to prevent dehydration, which can trigger sickle cell crises. It's recommended to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water or other fluids every day.
2. Get enough rest: Fatigue and exhaustion can trigger sickle cell crises. Getting enough rest and sleep can help to reduce the frequency of crises.
3. Avoid extreme temperatures: Both extreme cold and heat can trigger sickle cell crises. Try to stay in a comfortable temperature-controlled environment as much as possible.
4. Manage stress: Stress can also trigger sickle cell crises. Try to find ways to manage stress, such as through relaxation techniques, exercise, or therapy.
5. Take prescribed medications: There are several medications that can help manage the symptoms of sickle cell disease, such as hydroxyurea, which can reduce the frequency and severity of sickle cell crises.
6. Blood transfusions: In some cases, regular blood transfusions may be necessary to manage the symptoms of sickle cell disease.
7. Bone marrow transplant: For some people with severe sickle cell disease, a bone marrow transplant may be an option. This involves replacing the bone marrow with healthy donor cells, which can produce healthy red blood cells.
It's important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan for sickle cell disease.
They can help you determine the best course of action based on your individual needs and medical history.

0 notes
Text
John Korsah
ACCRA-Ghana
Lipid profile test,
A lipid profile test, also known as a lipid panel or cholesterol panel, is a blood test that measures the levels of different types of lipids (fats) in the blood.
The test typically measures the levels of the following:
1. Total cholesterol: This is the total amount of cholesterol in the blood, including both high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (also known as "good" cholesterol) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (also known as "bad" cholesterol).
2. HDL cholesterol: This is the "good" cholesterol that helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transports it to the liver for processing and removal.
3. LDL cholesterol: This is the "bad" cholesterol that can build up in the walls of arteries and form plaques, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
4. Triglycerides: These are another type of fat found in the blood that can also contribute to the development of heart disease.
A lipid profile test is often used to assess a person's risk for developing heart disease and to monitor the effectiveness of lifestyle changes or medication in lowering cholesterol levels. High levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, as well as low levels of HDL cholesterol, are associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
➖Purpose
The purpose of a lipid profile test is to assess a person's risk of developing heart disease.
The test is often used to:
1. Identify people who have high cholesterol levels, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
2. Monitor the effectiveness of lifestyle changes or medication in lowering cholesterol levels.
3. Determine the risk of developing heart disease in people who have other risk factors, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or a family history of heart disease.
4. Help guide treatment decisions, such as whether to start cholesterol-lowering medication.
By identifying and monitoring lipid levels, a lipid profile test can help healthcare providers develop a personalized plan to manage a person's risk of heart disease.
This may include lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet, exercise, and smoking cessation, as well as medication, if necessary.
➖Procedure
The procedure for a lipid profile test typically involves the following steps:
1. Preparation: The patient may be asked to fast for 9-12 hours before the test. This means avoiding food and drink, except for water, during this time.
2. Blood sample collection: A healthcare provider will collect a blood sample from the patient, usually by inserting a needle into a vein in the arm. The sample will be collected in a tube and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
3. Analysis: The laboratory will analyze the blood sample to measure the levels of total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. The results will be reported to the healthcare provider who ordered the test.
4. Interpretation: The healthcare provider will interpret the test results and discuss them with the patient. If the results show high cholesterol levels or other risk factors for heart disease, the healthcare provider may recommend lifestyle changes or medication to help manage the risk.
The lipid profile test is a simple and safe procedure that can be done in a doctor's office or a laboratory.
The test does involve a needle stick, which may cause some discomfort, but most people tolerate it well.
➖Results
The results of a lipid profile test typically include measurements of the following:
1. Total cholesterol: The desirable level of total cholesterol is less than 200 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) for adults. Higher levels may indicate an increased risk of heart disease.
2. HDL cholesterol: The desirable level of HDL cholesterol is 60 mg/dL or higher for both men and women. Low levels of HDL cholesterol may increase the risk of heart disease.
3. LDL cholesterol: The desirable level of LDL cholesterol is less than 100 mg/dL for adults. Higher levels may indicate an increased risk of heart disease.
4. Triglycerides: The desirable level of triglycerides is less than 150 mg/dL for adults. Higher levels may indicate an increased risk of heart disease.
In addition to these measurements, the lipid profile test may also include calculations of other ratios, such as the total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio or the LDL cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio, which can provide additional information about a person's risk of heart disease.
It is important to note that the interpretation of lipid profile test results may vary depending on a person's individual risk factors for heart disease, such as age, family history, and other medical conditions. Healthcare providers use these results, along with other information about the patient's health, to develop a personalized plan for managing their risk of heart disease.
➖Suggested ways of bringing the abnormalities to normal in natural ways
1. High levels of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides, as well as low levels of HDL cholesterol, can increase the risk of heart disease. There are several natural ways to help manage these abnormalities and bring lipid levels back to normal. Some suggestions include:
2. Dietary changes: Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in saturated and trans fats can help lower cholesterol levels. This includes consuming more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Foods that are high in fiber, such as oatmeal and beans, can also help lower LDL cholesterol levels.
3. Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can help increase HDL cholesterol levels and lower triglycerides. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week for adults.
4. Weight loss: Losing excess weight, especially around the waistline, can help lower LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels and increase HDL cholesterol levels.
5. Quitting smoking: Smoking can lower HDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. Quitting smoking can help improve lipid levels and overall heart health.
6. Managing stress: Chronic stress can increase cortisol levels, which can raise triglyceride levels. Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help lower lipid levels.
7. Supplements: Some supplements, such as fish oil, niacin, and plant sterols, may help lower cholesterol levels. However, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements to ensure they are safe and effective for the individual.
It is important to note that these natural approaches may not be sufficient for everyone and may need to be combined with medication or other medical treatments, depending on the severity of the lipid abnormalities and individual health factors.
Therefore, it is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for managing lipid levels and reducing the risk of heart disease.
➖Suggested ways of bringing the abnormalities to normal in medication
If natural approaches to managing lipid abnormalities are not effective or not sufficient, medication may be necessary to lower lipid levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Some common medications used to treat lipid abnormalities include:
1. Statins: These medications work by reducing the amount of cholesterol produced by the liver and can lower LDL cholesterol levels by up to 60%. Examples of statins include atorvastatin (Lipitor), simvastatin (Zocor), and rosuvastatin (Crestor).
2. Bile acid sequestrants: These medications work by binding to bile acids in the intestine, preventing them from being reabsorbed into the bloodstream and reducing LDL cholesterol levels. Examples of bile acid sequestrants include cholestyramine (Questran) and colestipol (Colestid).
3. Ezetimibe: This medication works by blocking the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine and can lower LDL cholesterol levels by up to 20%. It is often used in combination with a statin.
4. PCSK9 inhibitors: These medications work by blocking the action of PCSK9, a protein that breaks down LDL receptors in the liver, leading to increased LDL cholesterol removal from the bloodstream. Examples of PCSK9 inhibitors include evolocumab (Repatha) and alirocumab (Praluent).
5. Fibrates: These medications work by lowering triglyceride levels and increasing HDL cholesterol levels. Examples of fibrates include fenofibrate (Tricor) and gemfibrozil (Lopid).
It is important to note that medication should be used in conjunction with lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, to achieve optimal lipid levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
It is also important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage based on individual health factors and any potential side effects.

0 notes
Text
John Korsah
ACCRA-Ghana
CALCIUM OXALATE CRYSTALS.
Detailed understanding of calcium oxalate crystals.
Calcium oxalate crystals are tiny, crystalline structures made up of calcium and oxalate molecules that can be found in various biological tissues, including plant cells, urinary tracts, and kidney stones. These crystals are formed through a process known as crystallization, which occurs when there is an excess of calcium and oxalate ions in the urine or other body fluids.
In plants, calcium oxalate crystals play a role in calcium regulation, storage, and defense against herbivores. They can be found in various plant tissues, including leaves, stems, and roots. In some plants, these crystals may also contribute to the development of colors, such as in the colorful petals of hibiscus flowers.
In humans and other animals, calcium oxalate crystals can be found in the urinary tract and can contribute to the formation of kidney stones. When urine becomes concentrated with calcium and oxalate, these substances can crystallize and form small stones that can cause pain and discomfort when passing through the urinary tract.
Types: There are two main types of calcium oxalate crystals found in kidney stones: calcium oxalate monohydrate and calcium oxalate dihydrate. Calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals are harder and more common in kidney stones, while calcium oxalate dihydrate crystals are softer and less common.
Factors: There are various factors that can increase the risk of developing calcium oxalate kidney stones, including a diet high in oxalate-rich foods (such as spinach, rhubarb, and beets), low fluid intake, and certain medical conditions that affect the urinary tract, such as hypercalciuria and hyperoxaluria.
Treatments: Treatment for calcium oxalate kidney stones typically involves pain management and hydration to help pass the stones, as well as dietary changes and medications to prevent the formation of future stones. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the stones.
➖Suggested ways of bringing abnormalities to normal both in natural ways and the use of medicine
The approach to treating abnormalities will depend on the specific condition and underlying causes. However, here are some general suggestions for bringing abnormalities to normal:
1. Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle changes can be a natural way to help bring certain abnormalities back to normal. This may include adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, getting adequate sleep, reducing stress levels, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
2. Medications: In some cases, medications may be necessary to help bring abnormalities back to normal. For example, if you have high blood pressure, your doctor may prescribe medications such as diuretics or ACE inhibitors to help lower your blood pressure to normal levels. It is important to follow your doctor's instructions when taking medications and to report any side effects.
3. Surgery: For some conditions, surgery may be necessary to bring abnormalities back to normal. For example, if you have a herniated disc in your spine, surgery may be necessary to repair the damage and relieve the associated pain and discomfort.
4. Alternative Therapies: Some people may find relief from abnormalities through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, or chiropractic care. However, it is important to discuss any alternative therapies with your doctor before trying them, as they may not be appropriate for your specific condition.
5. Monitoring and Management: In some cases, abnormalities may not require treatment but rather monitoring and management. For example, if you have a mild case of high cholesterol, your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes to help manage the condition and prevent it from worsening.
A combination of lifestyle changes, medications, surgery, alternative therapies, and monitoring and management may be necessary to achieve the best results.

0 notes