Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Link
#iit#iit jee#jee mains#jee advance#jee advanced exam#jee advanced 2021#jee#ncert exemplar#ncert#ncert solutions#ncert books#ncert syllabus#cbse#cbse board exams#cbse 2021#neet#neet2021#neetpreparation#class 12#class 10
0 notes
Text
What is the surface area of a sphere?
There are various geometrical figures that the students often come across. The sphere is one such concept that helps the students to learn and to compute the solutions as well.
Few of the interesting facts that we all see is:
The geometrical shape of the sphere is always round and this can always be represented in the three dimensional space.
This is often defined as a flat figure as it does not have any sides and is a flat surface.
The volume of the sphere is calculated as 4/3 πr3
The volume of the sphere will always be equal to the surface area of the sphere and will be calculated by the formula 4πr2
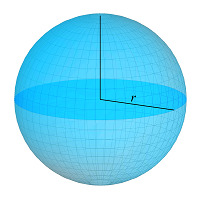
We can see the general representations of the sphere where we assume the distance from the center to the sides of the sphere as “R”.phere The other parameters are calculated based on the values.
Definition
In the geometrical applications, there are different other parameters also that we often see to define the sphere and the geometrical importance. So, a sphere is also defined as a geometrical round shape in three dimensional spaces. The sphere usually does not have any flat surface as we are not being able to define the sphere in terms of dimensions as in the length or breadth.
Unlike circle, that can also be explained in a plane shape or flat shape that is usually being defined in XY plane, in case of the sphere is defined in three dimensions, i.e. x-axis, y-axis and z-axis.
Important Facts:
A sphere is a symmetrical object that has all the dimensions defined in the same plane.
When we calculate the surface points of sphere they are at equidistant from center
A sphere as a geometrical shape has only curved surface, no flat surface, no edges and no vertices.
Properties of a sphere
The sphere as a geometrical figure has few of the important features. These are also called attributes of sphere.
A sphere is a perfectly symmetrical shape that is represented in a 3D space.
It is not a polyhedron in nature.
All the points marked on the surface will be equidistant from the center.
The sphere does not have a surface of centers and will have a constant mean curvature
In case of the sphere there is a constant value for the width and circumference.
Shape of Sphere
The shape of a sphere is round where it does not have any faces. It should be noted that sphere is a geometrical three dimensional solid that have got curved surface. Like other solids, such as cuboid, cube, cone and cylinder, it does not have any flat surface or a vertex or an edge.
Now let us have a look at the real-life examples of sphere which are:
Basket balls
World Globe
Marbles
Planets
Moon
Equation of a Sphere
In the field of analytical geometry, if “r” is considered the radius, (x, y, and z) is said to be the locus of all points and (x0, y0, z0) is the center of a sphere, and then the equation of a sphere can be written as:
(x -x0)2 + (y – y0)2 + (z-z0)2 = r2
Formulas
As per statistics, the diameter is twice the radius. Therefore, diameter of a sphere is given as:
D = 2r units
Since we know that all the three-dimensional objects have the surface area and the volume, the surface area well as the volume of the sphere is explained so that we will be able to understand the system.
Surface Area of a Sphere
As the sphere is always represented in the 3D space, so a there is a mechanism to calculate the surface area... The formula of surface are is given by:
The Surface Area of a Sphere (SA) = 4πr2 Square units
Where “r” is considered the radius of the sphere.
Volume of a Sphere
This is so very important that we should be able to calculate the volume of the square as well. This is often being defined as the amount of space occupied by the object three-dimensional object. The volume is to be calculated in many of the mathematical calculations as this will be able to give us the value addition and also the perfect representation on a scheduled space.
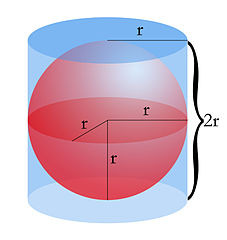
So, if we are to apply the Archimedes Principle, the volume of a sphere is given as,
The volume of Sphere (V) = 4/3 πr3 Cubic Units
The concepts are better explained in the online contents by
www.doubtnut.com It provides the latest materials to study along with online video tutorials that will help the students to understand the concept with ease. Moreover, there are doubts clearing sessions that are conducted that helps the students to identify their weakness and also build in the confidence. With their beautifully explained topics, Doubtnut are able to provide the students with the required materials to top up on their concept of learning and building in confidence.
#iit#iit jee#jee mains#jee advance#jee advanced exam#jee advanced 2021#ncert#ncert exemplar#ncert books#ncert solutions#ncert syllabus#cbse#cbse board exams#cbse 2021
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
WHAT IS AN ELIMINATION REACTION?
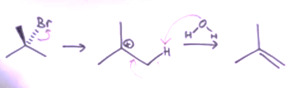
DEFINITION OF EIMINATION REACTION
Any from the class of organic chemicals reaction where a pair of atoms or group of atoms are removed from a molecule, usually through the action of acids, metals, or bases and, in some cases, by heating it to a high temperature is known as elimination reaction. Elimination reaction is the principal by which organic compounds that contain only single carbon-carbon bonds or also known as saturated compounds are transformed into compound that contain double or triple carbon-carbon bonds or also known as unsaturated compounds. The group of atoms that leave the molecule are what elimination reactions are commonly known by. For example, dehydrohalogenation is the removal of a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom. While, dehalogenation is the reaction when both the atoms that are leaving are halogens. Similarly, dehydration is the reaction when the elimination of a water molecule, usually from an alcohol takes place. Dehydrogenation is the reaction when both the leaving atoms are hydrogen atoms. Depending on the reaction kinetics, elimination reactions are also classified as E1 and E2. The reaction rate is proportional to the concentration of the substance to be transformed in an E1 reaction. On the other hand, the reaction rate is proportional to the concentrations of both the substrate and eliminating agents, in an E2 reaction.
E2 REACTIONS
In any elimination reaction two groups from adjacent carbons are removed and are replaced by a double bond between those two carbons. So, let’s take a bromopropane for example.
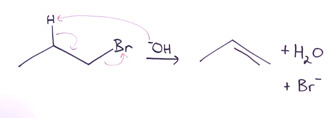
You can see the hydrogen and the bromine; these are the two adjacent carbons. So, what is going on is some nucleophile, let us say hydroxide, in this case instead of doing a substitution reaction, what we are going to do is an acid-base reaction, which means that a proton will be extracted, you can see the arrow in the picture goes from the hydroxide directly to the proton, and then the electrons that are in the carbon-hydrogen bond are going to go and form the double bond between the two carbons, then just as with substitution reaction, a leaving group has to leave. So, what is left is propene and then we have the water and the bromide ion, and then hence, basically one thing that is very important to keep in mind in an elimination reaction is that it is a beta elimination, which means, if the bromine is the leaving group here then the alpha position and the beta position are right behind it. It is a proton on the beta carbon that is removed because removing the proton at the alpha position is not going to work out as those electrons will have nowhere to go, instead what happens is that the carbon in the alpha position is able to receive the electrons in the carbon-hydrogen bond which in turn are the electrons that form the pi bond as that carbon can also lose the electrons that are there which now belong to the bromine.
The transition state – just like the SN2 reactions, the 2 is referring to a bimolecular transition state, meaning that the substrate is attached to both the leaving group and the proton that is being extracted at the same time, making this a concerted reaction, which happens all at once or in one step.
E1 REACTIONS
The E1 reaction is to the E2 reaction what the SN1 reaction is to the SN2 reaction. Basically, as mentioned above, the E1 reaction is going to be two steps with a unimolecular transition state. The first step in the E1 reaction is that the leaving group leaves.

If you look at the substrate here, the bromine is going to leave, which leaves a tertiary carbocation. It is very important to understand that in this substrate, the carbon is sp3 hybridized and therefore has tetrahedral geometry. Anytime a carbon that is sp3 hybridized losing as electron domain, since this bromine is leaving with the electrons in that bond, now the next carbon atom has only three electron domains, and anything that is surrounded by three electron domains will exhibit trigonal planar geometry. So, in this case, the methyl group is now flat, this is now a flat molecule with respect to the carbons. So, there is a formal positive charge, meaning even a weak nucleophile such as water can go ahead and do an acid-base reaction, and grab the proton, you can see in the image the oxygen reacting with the hydrogen proton, then the electrons in that carbon-hydrogen bond are the ones that go to form the carbon-carbon pi bond in the product. To learn more about topics like elimination reactions, and other such interesting topics in chemistry, check out www.doubtnut.com You will find all the information that you need for your studies.
#iit#iit jee#jee mains#jee main exam 2021#jee advance#jee advanced exam#jee advanced 2021#neet#neetpreparation#ncert#ncert exemplar#ncert syllabus#ncert solutions#ncert books#cbse#cbse board exams#cbse 2021
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
When one delves into the causes of magnetic properties, one should be aware of the basic concept of magnetism. Magnetism is an occurrence by the virtue of which a material exerts an either attractive or repulsive force on another. The basic cause of magnetic force is the movement of electrically charged particles. Therefore, the understanding of magnetic behavior of a material can be understood by deciphering the structure of atoms. Electrons that are present in atoms have an orbital motion, as they go around the nucleus.
#iit#iit jee#jee#jee mains#jee advance#jee advanced exam#jee advanced 2021#neet#neet2021#cbse#cbse 2021#cbse board exams#class 12#class 10#chemistry#physics#maths#biology
0 notes
Link
Ionization enthalpy is defined as the least amount of energy necessary to remove the most loosely attached electron from an isolated neutral gaseous atom or molecule in physics and chemistry. Ionization energy is measured in several units in physics and chemistry. The amount of energy necessary to remove a single electron from a single atom or molecule, given in electronvolts, is the unit in physics. The molar ionization energy or roughly enthalpy, given in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol), is the amount of energy necessary for all of the atoms in a mole of material to lose one electron apiece. How to determine the ionization energy?
#iit jee#iit#jee#jee mains#jee advance#jee advanced exam#jee advanced 2021#ncert#jee advanced postponed#ncert exemplar#ncert solutions#ncert books#ncert syllabus#cbse#cbse board exams#cbse 2021#class 12#class 10
0 notes
Link
HC Verma Physics books are the most popular among CBSE students, especially in classes 9 to 12, and practically every student can be found referring to the chapters in the books, as well as the practise questions at the end of each chapter. Students in class 12 must adhere to these texts religiously, as many questions from them appear on exams. Students can get incredibly useful practise material online for such renowned books. There are various sources where students can acquire full answers to all of the questions in the HC Verma books, and can clear their doubts with the help of these solutions.
#iit jee#jee mains#jee advance#jee advanced exam#jee advanced 2021#jee#neet#neet2021#ncert#ncert exemplar#ncert solutions#ncert books#ncert syllabus#ncert textbooks#cbse#cbse board exams#cbse 2021
0 notes