SmartCADD is an innovative company with an extensive knowledge of computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) which leverages the use of computers to aid the creation, analysis, modification, and optimization of a design. The application of our services cut across different fields with wide usage.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
In the fast-paced world of construction, clear communication and accurate documentation are vital to ensuring successful project execution. One of the most essential tools in this process is the ISD drawing. Whether you're a project manager, engineer, architect, or contractor, having a solid grasp of ISD drawings and their purpose can significantly improve workflow and reduce costly on-site errors.
0 notes
Text
Understanding ISD Drawings in Construction Projects

In the fast-paced world of construction, clear communication and accurate documentation are vital to ensuring successful project execution. One of the most essential tools in this process is the ISD drawing. Whether you're a project manager, engineer, architect, or contractor, having a solid grasp of ISD drawings and their purpose can significantly improve workflow and reduce costly on-site errors.
In this blog, we’ll break down the ISD drawing meaning, its importance in the construction industry, how it differs from other drawing types like CSD drawings, and why it’s a critical step in project coordination.
What Is an ISD Drawing?
To start, let's define the ISD drawing meaning. ISD stands for Issued for Shop Drawing, and in some contexts, Installation Shop Drawing. An ISD drawing is a detailed technical document that shows how specific elements of a construction project will be fabricated, assembled, or installed. These drawings are prepared after the design drawings are finalized and approved.
The primary function of an ISD drawing is to communicate fabrication or installation-level information to subcontractors, fabricators, or construction crews. These drawings translate the design intent into actionable plans and dimensions, ensuring that what’s built in the field matches what was envisioned by the designers.
ISD Meaning in Construction
The ISD meaning in construction is often interpreted as Issued for Shop Drawing or Issued for Site Drawing, depending on regional or industry-specific terminology. In either case, the intent remains the same: these are documents created to provide more detailed and coordinated information following the initial design phase.
Unlike design drawings, which serve to communicate the overall design to clients and regulatory bodies, ISD in construction focuses on constructability. These drawings resolve design conflicts, provide connection details, and show exact dimensions, materials, and specifications.
Key Features of an ISD Drawing:
Precise dimensions for fabrication
Coordination between different systems (e.g., MEP)
Material specifications
Installation sequences
References to codes and standards
Why Are ISD Drawings Important?
There are several reasons why ISD drawings are vital to construction projects:
1. Improved Coordination
In large-scale construction projects, multiple systems (mechanical, electrical, plumbing, structural) are involved. ISD drawings help coordinate these systems to avoid clashes and ensure seamless integration.
2. Reduction of On-Site Errors
Errors in installation often stem from miscommunication or lack of clarity in design documents. With an ISD drawing, contractors receive detailed instructions, leaving little room for guesswork.
3. Streamlined Fabrication and Installation
Fabricators and installers rely heavily on ISD drawings to guide their work. These drawings provide the precise information needed to pre-fabricate components and install them correctly.
4. Faster Approvals
ISD drawings often undergo internal and external reviews. Once approved, they serve as a reference for inspectors and clients, speeding up the project’s progress and approvals.
ISD Drawing vs. CSD Drawing
A common question arises: how does an ISD drawing differ from a CSD drawing?
CSD Drawing (Coordinated Services Drawing): A CSD drawing focuses on coordination between different services like HVAC, plumbing, and electrical systems. It resolves spatial conflicts before construction begins and ensures that systems don’t interfere with each other.
ISD Drawing (Issued for Shop/Installation Drawing): This goes a step further, converting coordinated design data into a fully detailed fabrication or installation plan. ISD drawings are typically created after CSD drawings and contain more granular information.
In summary, CSD drawings ensure systems can coexist, while ISD drawings ensure those systems can be built and installed accurately.
When Are ISD Drawings Used in a Project Lifecycle?
ISD drawings are usually created after the design and coordination stages and before the actual construction or fabrication begins. Here's how they fit into a typical project lifecycle:
Concept & Design Stage – Architects and engineers produce schematic designs.
Coordination Stage – CSD drawings are developed to avoid service clashes.
Detailing Stage – ISD drawings are created, detailing how each component will be built or installed.
Construction Stage – ISD drawings are issued to site teams or fabricators to execute the work.
As-Built Documentation – Post-construction updates may be made to the ISD drawing to reflect any field modifications.
Common Types of ISD Drawings
ISD drawings span multiple disciplines. Some examples include:
HVAC ISD Drawings: Detailing duct layouts, equipment installation, and airflow routing.
Plumbing ISD Drawings: Showing pipe routes, connection details, and fixture positions.
Electrical ISD Drawings: Indicating conduit runs, cable trays, panel locations, and load schedules.
Structural ISD Drawings: Illustrating steel connections, rebar detailing, and embedded components.
Each drawing type serves to bridge the gap between engineering intent and construction execution.
Challenges in ISD Drawing Creation
While essential, preparing ISD drawings comes with its own set of challenges:
Data Overload: Compiling and updating data from architects, consultants, and suppliers.
Software Compatibility: Ensuring drawings are compatible across multiple platforms like AutoCAD, Revit, or BIM.
Revision Management: Keeping track of version control to ensure the most recent drawings are used on-site.
To overcome these, many companies rely on expert drafting teams or outsource the task to specialized firms.
Conclusion: The Role of SmartCADD in ISD Drawing Services
To summarize, ISD drawings are a cornerstone of modern construction, acting as the link between design and execution. Their value lies in their ability to convey detailed, actionable information to everyone involved in a project—from engineers and fabricators to contractors and inspectors.
Understanding the isd drawing meaning and how it fits into the larger framework of isd in construction allows project teams to plan more accurately, reduce errors, and deliver projects on time and within budget. With the increasing complexity of building systems, the demand for high-quality ISD drawings has never been greater.
That’s where SmartCADD comes in. As a trusted partner in CAD and BIM drafting services, SmartCADD specializes in creating precise, code-compliant ISD drawings tailored to client specifications. Whether you're developing a residential tower or a complex commercial facility, SmartCADD ensures your ISD documentation is accurate, coordinated, and ready for execution.
For construction professionals looking to streamline their projects, reduce errors, and accelerate timelines, partnering with experts like SmartCADD is a smart move—ensuring your construction journey is supported by the drawings that matter most.
0 notes
Text
In the ever-evolving world of sustainable architecture, Building Information Modeling (BIM) is becoming a game-changer. By enhancing collaboration, minimizing waste, and optimizing energy performance, BIM services are reshaping how we approach eco-conscious design. In this guide, we’ll explore how BIM integrates into green building architecture, the benefits it offers, and why it’s essential in today’s Green Building Construction projects.
0 notes
Text
A Guide to BIM in Green Building Design

In the ever-evolving world of sustainable architecture, Building Information Modeling (BIM) is becoming a game-changer. By enhancing collaboration, minimizing waste, and optimizing energy performance, BIM services are reshaping how we approach eco-conscious design. In this guide, we’ll explore how BIM integrates into green building architecture, the benefits it offers, and why it’s essential in today’s Green Building Construction projects.
What Is BIM and Why It Matters in Sustainability?
BIM services refer to the process of creating and managing digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of a building. This virtual model allows stakeholders to collaborate seamlessly, identify design inefficiencies, and make informed decisions early in the construction process.
In the context of Green Building Construction, BIM ensures every aspect of a building—from materials to energy usage—is considered before ground is even broken. This not only saves time and money but also promotes long-term sustainability.
How BIM Supports Green Building Architecture
BIM is central to modern green building architecture. Here’s how it contributes:
1. Energy Modeling
BIM tools simulate energy performance at the design stage, helping teams choose environmentally friendly HVAC systems, optimize natural lighting, and reduce reliance on artificial energy.
2. Material Efficiency
Through accurate quantity take-offs and scheduling, BIM services reduce material waste, which directly supports Green Building Construction principles.
3. Water and Waste Management
Designers can model efficient plumbing systems and predict water usage patterns, aligning with global green standards.
These capabilities align perfectly with the broader goal of how to construct green building frameworks—structures that are sustainable, cost-effective, and future-ready.
BIM Lifecycle and Its Role in Sustainability
The bim lifecycle refers to the complete journey of a building—from initial planning and design through construction and finally to operation and maintenance. At every stage, BIM ensures that sustainability goals are met.
Design: Architects use BIM services to create energy-efficient designs based on climate, orientation, and materials.
Construction: Contractors access real-time updates to minimize errors, waste, and rework, key concerns in Green Building Construction.
Operation: Facility managers use the BIM model to maintain systems, track performance, and schedule energy-saving upgrades.
This lifecycle approach to building management illustrates how to construct green building projects that remain efficient for decades.
Key Benefits of BIM in Green Construction
Collaboration Across Stakeholders
Engineers, architects, and contractors can work from the same data-rich model, ensuring sustainable goals are upheld throughout.
Risk Mitigation
Early detection of design conflicts avoids costly and wasteful fixes later on—an essential benefit in green building architecture.
Regulatory Compliance
Many jurisdictions now require or recommend BIM in public Green Building Construction to meet carbon neutrality goals.
Long-Term Cost Savings
Despite the upfront investment, BIM services provide significant cost savings over the building’s lifespan, especially in energy consumption and maintenance.
How to Construct Green Building Projects Using BIM
If you’re wondering how to construct green building projects efficiently, BIM offers a clear roadmap. Here’s a simple breakdown:
Start with Environmental Analysis
Use BIM tools to assess site conditions, solar angles, wind patterns, and ecological impact.
Set Sustainability Goals
Input performance benchmarks into your BIM model, such as LEED certifications or zero-energy targets.
Simulate and Optimize
Run simulations for lighting, ventilation, and water usage to find the best sustainable options.
Monitor and Adjust
Post-construction, use the digital twin from your BIM model to manage and improve building performance.
Through each of these steps, BIM services ensure your project aligns with the highest standards in Green Building Construction.
Real-World Applications of BIM in Green Architecture
Across the globe, forward-thinking firms are using BIM to lead the way in green building architecture. Notable examples include:
Passive House Designs: Leveraging BIM to achieve airtightness and thermal efficiency.
Smart Campuses: Institutions integrating the bim lifecycle to manage entire building portfolios.
Carbon-Neutral Workspaces: Offices designed entirely through BIM simulations to minimize emissions.
These projects not only showcase how to construct green building infrastructure, but also highlight BIM's role as the backbone of a greener future.
Final Thoughts
The journey toward sustainable architecture is complex—but with BIM services, it becomes more navigable, efficient, and impactful. By integrating BIM into your Green Building Construction strategy, you're not just building smarter—you're building greener, from the foundation to the rooftop.
Whether you’re designing an office tower or a single-family home, incorporating green building architecture through BIM can help you meet today's sustainability challenges with confidence.
SmartCADD is proud to be at the forefront of this movement, delivering cutting-edge BIM services that empower clients to create sustainable spaces that are as innovative as they are responsible.
#bim services#Green Building Construction#How to construct green building#Green building architecture#bim lifecycle
0 notes
Text
Today, clients, governments, and communities are demanding cleaner, smarter, more resilient buildings.
The reason? Most traditional construction workflows simply weren’t built for that kind of complexity.
That’s where BIM services are quietly revolutionizing the way we work, especially when it comes to green building construction.
0 notes
Text
BIM in electrical engineering refers to the use of intelligent 3D models to design, document, and manage electrical systems throughout a building’s lifecycle. It allows engineers to simulate, analyze, and coordinate electrical components such as lighting, power distribution, cable trays, fire alarm systems, and communication networks—all within a unified digital environment.
0 notes
Text
BIM Electrical Essentials: A Beginner’s Guide for Electrical Engineers
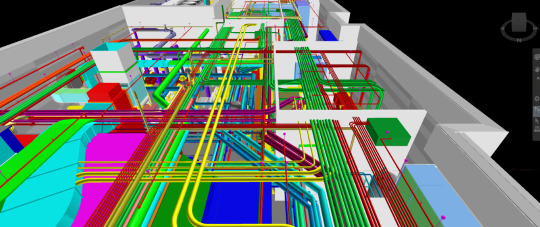
As the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry continues to adopt digital transformation, Building Information Modeling (BIM) has emerged as a powerful tool. While BIM is often associated with architectural and structural elements, its impact on electrical engineering is equally profound. This blog explores BIM electrical essentials—key concepts and tools that every electrical engineer should know to stay competitive and efficient in today’s digital construction landscape.
What Is BIM in Electrical Engineering?
BIM in electrical engineering refers to the use of intelligent 3D models to design, document, and manage electrical systems throughout a building’s lifecycle. It allows engineers to simulate, analyze, and coordinate electrical components such as lighting, power distribution, cable trays, fire alarm systems, and communication networks—all within a unified digital environment.
This digital representation goes far beyond simple drafting. It includes critical data such as load calculations, panel schedules, and circuiting, making BIM for electrical engineers a comprehensive approach to modern design and construction.
Why Electrical Engineers Should Embrace BIM
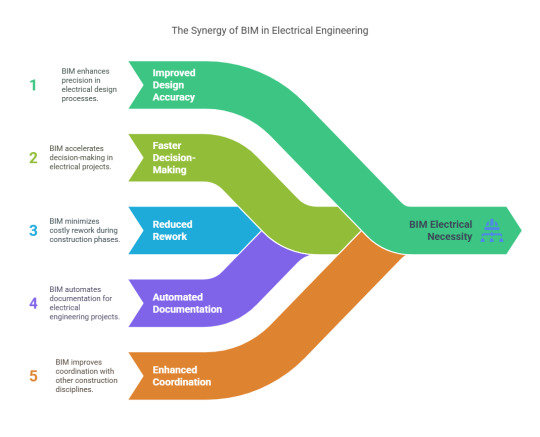
In the traditional workflow, electrical design is often siloed, leading to miscommunication, design errors, and costly changes during construction. BIM bridges these gaps by creating a collaborative environment where multiple disciplines can work together in real time.
For an electrical engineer, the benefits of BIM electrical workflows include:
Improved design accuracy
Faster decision-making
Reduced rework on-site
Automated documentation
Enhanced coordination with other disciplines like HVAC and plumbing
These advantages make BIM electrical not just a trend but a necessity in today’s BIM in AEC industry.
Roles and Responsibilities of a BIM Electrical Engineer
A BIM electrical engineer is more than just a designer. They play a crucial role in integrating electrical systems into the BIM workflow. Their responsibilities often include:
Creating and managing 3D models of electrical systems
Ensuring compliance with codes and standards
Coordinating with MEP teams to avoid conflicts
Performing load and circuit calculations
Extracting material quantities and construction documents
Using simulation tools for energy and lighting analysis
The role demands both engineering knowledge and BIM proficiency, making the BIM electrical engineer a valuable asset in multidisciplinary teams.
What Does an Electrical BIM Modeller Do?
An electrical BIM modeller is typically responsible for the hands-on creation of the BIM model. Working under the guidance of an engineer, they develop detailed 3D representations of electrical systems, ensuring accuracy and constructability. Key tasks include:
Modeling conduits, cable trays, switches, and panels
Embedding data like voltage, circuit IDs, and cable types
Tagging and annotating electrical elements
Reviewing designs for clash detection
Exporting plans and schedules for construction
A skilled electrical BIM modeller is not just a drafter—they understand design intent and how electrical systems function within a building.
MEP BIM Modeling: Where Electrical Fits In
MEP BIM modeling encompasses the mechanical, electrical, and plumbing disciplines in a building. Within this collaborative environment, electrical systems must work in harmony with HVAC ducts, plumbing pipes, and other elements.
This is where BIM truly shines—by enabling interdisciplinary coordination. Electrical engineers can:
Share models with mechanical and plumbing teams
Identify and resolve spatial conflicts through clash detection
Plan routing that minimizes space usage and maximizes efficiency
Ensure compliance with codes for clearances and accessibility
By participating in MEP BIM modeling, electrical engineers avoid costly errors and enhance overall project performance.
Clash Detection: A Core Benefit of BIM Electrical
One of the most valuable features of BIM in electrical engineering is clash detection. This process uses BIM software to identify and highlight conflicts between electrical components and other building systems before construction begins.
For example, if a cable tray conflicts with a duct or structural beam, the BIM model flags the issue. Engineers and modellers can then make adjustments in the design phase—saving time, money, and effort during construction.
Clash detection leads to:
Fewer change orders
Lower labor and material costs
Faster project timelines
Increased stakeholder confidence
For an electrical BIM modeller, performing clash detection is a daily task that adds real value to the project.
Common BIM Tools for Electrical Engineers
Several BIM software platforms cater to electrical engineering. Here are the most commonly used tools:
Autodesk Revit: Industry-standard for BIM electrical design and modeling.
Navisworks: Used for model coordination and clash detection.
AutoCAD MEP: Useful for 2D/3D MEP designs, though Revit is more advanced.
ETAP, Dialux, and Relux: Often integrated for load calculation and lighting simulation.
Becoming proficient in these tools is essential for any aspiring BIM electrical engineer.
Real-World Applications of BIM Electrical
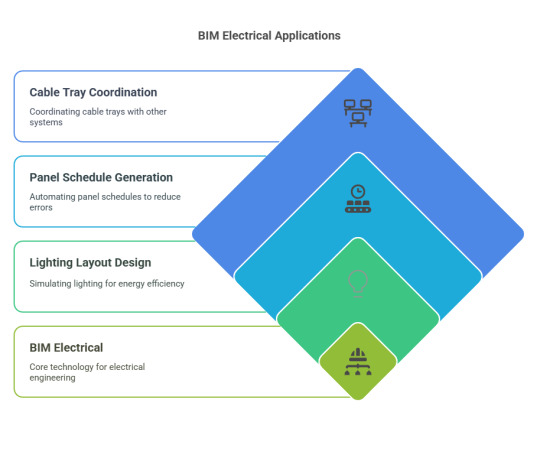
To understand the value of BIM for electrical engineers, let’s look at a few practical applications:
Lighting Layout Design
Engineers can simulate daylight and artificial lighting in a 3D environment, optimizing energy usage and placement.
Panel Schedule Generation
BIM can auto-generate accurate panel schedules based on the circuiting in the model, reducing manual errors.
Cable Tray Coordination
Routing trays around HVAC systems and structural components becomes easier, thanks to real-time visibility across trades.
Facility Management
After construction, the BIM model serves as a digital twin. Electrical teams can use it for maintenance, upgrades, and energy audits.
These use cases demonstrate how BIM electrical adds value throughout the building lifecycle—not just during design.
BIM in the AEC Industry: A Collaborative Future
The integration of BIM in AEC industry practices has reshaped the way buildings are designed, constructed, and maintained. No longer can electrical engineers work in isolation. BIM demands collaboration, communication, and a digital-first mindset.
As governments and clients increasingly mandate BIM deliverables, electrical professionals who lack BIM skills risk falling behind. Conversely, those who embrace BIM gain a competitive edge, delivering smarter designs with greater efficiency.
Tips for Beginners: Getting Started with BIM Electrical
If you're new to BIM electrical, here are some practical steps to begin your journey:
Learn Revit MEP: Start with basic tutorials, then focus on electrical components.
Understand Electrical Systems: Solid grounding in electrical engineering principles is still essential.
Study BIM Standards: Familiarize yourself with ISO 19650, LOD (Level of Development), and other BIM-related standards.
Join BIM Communities: Participate in forums, webinars, and online courses.
Practice with Real Projects: Nothing beats hands-on experience. Try small-scale models or volunteer for BIM tasks in your team.
As a BIM electrical engineer, continuous learning is part of the job. The more you engage with BIM, the more valuable your skills become.
Final Thoughts
The future of electrical engineering lies in digital, integrated workflows—and BIM electrical is at the heart of this transformation. Whether you're an aspiring electrical BIM modeller, a seasoned engineer looking to upskill, or a student entering the field, understanding the essentials of BIM for electrical engineers is your first step toward staying relevant and impactful.
By mastering tools, processes, and collaboration techniques, you'll not only design better systems—you'll help shape smarter, more sustainable buildings.
At SmartCADD, we believe in empowering professionals with the skills and knowledge needed to lead in the digital age of construction. Ready to electrify your career with BIM? Now’s the time to plug in.
#bim electrical#electrical bim modeler#bim electrical engineer#mep bim modeling#bim for electrical engineers#bim in electrical engineering#bim#BIM in AEC Industry#clash detection
0 notes
Text
BIM in the AEC industry has changed the way projects are being approached. BIM for electrical engineers is an important tool that simplifies the overall workflow and improves accuracy and teamwork. Using Electrical BIM modeling leads to a better construction process and ensures smooth project execution.
0 notes
Text
One critical aspect of this transformation is the role that construction documentation plays within the BIM process. Construction documentation refers to all the necessary drawings, plans, and details that guide a construction project from start to finish. In this article, we’ll explore why construction documentation is crucial in the BIM process and how it contributes to successful project delivery.
0 notes
Text
AS-built modeling is a process to generate a digital replica of buildings/structures after they are built. These digital models provide all the details, including changes made throughout the construction process.
0 notes
Text
Why Construction Documentation is Crucial in the BIM Process

In the world of modern construction, the implementation of Building Information Modeling (BIM) has transformed the way projects are designed, managed, and executed. One critical aspect of this transformation is the role that construction documentation plays within the BIM process. Construction documentation refers to all the necessary drawings, plans, and details that guide a construction project from start to finish. In this article, we’ll explore why construction documentation is crucial in the BIM process and how it contributes to successful project delivery.
Understanding the BIM Process
Before delving into the importance of construction documentation, it’s essential to understand what the BIM process entails. Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of a building’s physical and functional characteristics. It provides a comprehensive and collaborative approach to designing, constructing, and managing buildings.
BIM integrates all aspects of the construction process into a single 3D model that includes design, structural elements, and mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems. This collaborative approach allows all stakeholders—architects, engineers, contractors, and owners—to have access to the same set of information, ensuring coordination and reducing errors.
Within the BIM process, construction documentation plays a vital role in translating the information from the model into detailed, actionable plans that can be followed during construction. Without proper documentation, even the most detailed and well-thought-out BIM model can lead to confusion, delays, and errors on the construction site.
What are Construction Documents?
Construction documents are the formal written and visual documentation created throughout the lifecycle of a construction project. These documents include construction drawings, specifications, and contracts, all of which help guide the construction team. Construction documents are essential for communication between all stakeholders and provide the necessary legal and technical details to carry out the project successfully.
Some of the most common types of construction documents include:
Construction Drawings: Detailed visual representations of the project, including floor plans, elevations, sections, and other construction details.
Specifications: Written descriptions that outline the materials, standards, and procedures required for construction.
Schedules: Timeframes for various project milestones and the overall completion of the project.
In the BIM process, these documents are not static; they evolve as the model is refined and updated. Construction documentation is generated directly from the BIM model, ensuring that the design intent is accurately captured and communicated.
The Importance of Construction Documentation in BIM
Construction documentation is a critical component of the BIM process for several reasons. Let’s explore some of the key ways it adds value to construction projects.
1. Facilitating Communication and Coordination
One of the most significant benefits of construction documentation in the BIM process is its ability to facilitate communication among all project stakeholders. The construction drawings generated from the BIM model serve as a clear and precise means of conveying design intent and construction requirements.
In large, complex projects, miscommunication or lack of coordination can lead to costly errors and delays. Construction project documentation ensures that everyone, from architects and engineers to contractors and subcontractors, is on the same page. These documents act as a reference point throughout the construction process, providing guidance on installation methods, materials, and timelines.
2. Streamlining the Construction Process
In the past, construction teams often had to rely on paper drawings and manual processes to manage projects. This led to inefficiencies, delays, and errors. However, with construction documentation created through the BIM process, teams can access real-time, digital updates to the construction drawings and other documents.
Digital documentation reduces the likelihood of errors caused by outdated or inaccurate information, ensuring that the project is completed according to the most up-to-date specifications. The BIM process also allows for more precise planning and coordination, reducing the chances of rework and streamlining the construction timeline.
3. Accurate Record Keeping for Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Construction projects must adhere to various legal and regulatory requirements. Construction documentation helps ensure compliance with local building codes, zoning laws, and other regulations. The detailed construction drawings and specifications generated in the BIM process serve as a comprehensive record of the design, materials, and methods used on the project.
Additionally, construction project documentation provides a valuable record for future maintenance, renovations, or legal disputes. The digital nature of BIM makes it easier to store and retrieve documentation, improving accessibility and reducing the risk of lost or misplaced documents.
4. Supporting Installation Services Drawings
For a construction project to be successful, it’s not enough to have detailed design plans; it’s also necessary to provide clear and actionable instructions for the installation of various systems and components. Installation services drawings are a critical part of construction documentation, detailing how specific elements of the building—such as HVAC systems, electrical systems, and plumbing—should be installed.
Through the BIM process, installation services drawings can be seamlessly integrated into the overall project documentation. These drawings are automatically updated as changes are made to the BIM model, ensuring that installation teams have the most accurate information. This level of detail reduces errors and ensures that installation is completed correctly and on time.
5. Ensuring Cost and Schedule Control
One of the biggest challenges in construction is staying within budget and meeting deadlines. Proper construction documentation can help mitigate these challenges. By using BIM, construction teams can create accurate cost estimates and schedules that are based on the detailed information provided in the construction documents.
BIM allows for more accurate material takeoffs and quantity surveying, reducing the risk of unexpected costs due to inaccurate estimates. Additionally, construction documentation helps track project milestones and timelines, ensuring that the project stays on schedule.
6. Enhancing Collaboration Across Disciplines
The BIM process enables real-time collaboration between various disciplines involved in a construction project, including architects, engineers, contractors, and suppliers. Construction documentation generated through BIM ensures that all stakeholders are working with the same set of data, minimizing the risk of errors or misinterpretations.
For example, the construction drawings can be reviewed and updated by the entire team as the project progresses. Engineers can ensure that their designs align with architectural plans, while contractors can confirm that the installation methods are feasible and aligned with the documentation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, construction documentation is essential to the success of any construction project, particularly in the context of the BIM process. By providing clear, accurate, and up-to-date information, construction documentation ensures that all stakeholders are aligned, reduces the risk of errors, supports legal and regulatory compliance, and enhances the overall efficiency of the construction process.
At SmartCADD, we understand the importance of high-quality construction documentation and its role in delivering successful construction projects. Our team is dedicated to providing cutting-edge construction drawing services and construction project documentation that streamline the BIM process, enhance collaboration, and ensure the timely and cost-effective completion of every project.
By leveraging the power of BIM and accurate construction documentation, we aim to contribute to a more efficient and sustainable future in the construction industry.
#construction documentation#construction drawings#construction documents#construction project documentation#what are construction documents#construction drawing services#bim process#CSD Drawings#ISD Drawings
0 notes
Text
Have you ever wondered how building construction projects run so smoothly every time? How are the lights always perfect? How are elevators always ready when you need them? You might not know that there is a BIM facility management system that keeps everything in control.
0 notes
Text
Introduction to BIM in Facilities Management

Building Information Modeling (BIM) is transforming the way we design, construct, and manage buildings. It’s a digital approach that integrates various aspects of a building’s lifecycle, from planning and construction to operation and maintenance. In facilities management, BIM is revolutionizing how buildings are maintained, operated, and optimized. This article provides an introduction to BIM in facility management, exploring its role, benefits, and how it is shaping the future of building management, with a particular focus on BIM and facilities management for SmartCADD.
What is BIM?
BIM, or Building Information Modeling, is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure. Unlike traditional 2D blueprints, BIM encompasses all aspects of a building’s lifecycle, including architectural, structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems (often referred to as MEP). BIM allows for the creation and management of digital models that include not just geometry, but also data about materials, systems, and operational details.
BIM’s core purpose is to support decision-making throughout the lifecycle of a building, from conception to demolition. It allows architects, engineers, and construction teams to collaborate more efficiently, minimizing errors and reducing costs. As BIM technology has evolved, its role has expanded into facility management, helping building owners and facility managers to optimize building performance and streamline maintenance processes.
What is Facility Management?
Facility management refers to the operations, maintenance, and oversight of buildings and infrastructure. The role of a facility manager is to ensure that the building’s systems (such as HVAC, lighting, plumbing, etc.) operate efficiently, safely, and cost-effectively. Facility management includes a wide range of responsibilities, from ensuring regulatory compliance and maintaining equipment to managing space utilization and responding to tenant needs.
Facility management is crucial in both residential and commercial buildings, as it impacts operational costs, energy efficiency, and occupant satisfaction. Traditionally, facility management relied on manual record-keeping, paper-based maintenance logs, and outdated techniques for scheduling repairs and replacements. However, with the advent of BIM, facility management is undergoing a significant transformation, becoming more data-driven, efficient, and proactive.
The Role of BIM in Facility Management
As buildings evolve over time, facility managers need accurate, up-to-date information to operate and maintain the systems efficiently. This is where BIM in facility management comes in. By integrating BIM into facilities management, building owners and managers can make more informed decisions, automate workflows, and improve the overall performance of a building.
BIM provides facility managers with a centralized digital model that includes real-time information about the building’s systems, equipment, and spatial configurations. The BIM facility management model serves as a comprehensive repository for all building data, enabling facility managers to track asset conditions, plan maintenance schedules, and monitor energy consumption.
Key Benefits of BIM in Facility Management
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
BIM enhances efficiency by providing facility managers with immediate access to accurate, detailed building data. This eliminates the need to sift through paper records or outdated systems. With BIM, managers can easily access information about building components, from structural details to equipment specifications, enabling faster decision-making and quicker response times for maintenance and repairs.
Proactive Maintenance and Reduced Downtime
BIM helps facility managers identify potential issues before they escalate. For example, BIM allows for predictive maintenance, where sensors in a building’s systems can send real-time data to the BIM model. This enables managers to detect wear and tear or system inefficiencies early, thus preventing costly emergency repairs and minimizing downtime. With BIM, facility managers can schedule maintenance activities based on real-time data rather than relying on outdated or reactive approaches.
Better Space Management
Space management is one of the most critical aspects of facility management. With BIM, facility managers can monitor how space is being utilized and optimize layouts for better space planning. 3D BIM offers a detailed 3D representation of building layouts, allowing managers to visualize spaces, track occupancy, and allocate resources more efficiently. This is especially useful for large facilities with multiple tenants or departments that require dynamic space planning.
Enhanced Energy Management
Energy efficiency is a top priority for many organizations. BIM provides valuable data on building systems and energy consumption patterns. By analyzing this data, facility managers can optimize HVAC systems, lighting, and other utilities, resulting in significant energy savings. BIM models can also simulate energy consumption scenarios, helping managers identify the best solutions for reducing the building’s carbon footprint.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
BIM fosters collaboration among various stakeholders involved in facility management, from architects and contractors to maintenance teams. Since BIM stores all building data in a centralized model, team members can access the same information and collaborate in real-time. This minimizes misunderstandings and ensures everyone is on the same page when it comes to repairs, upgrades, and general building operations.
Compliance and Documentation
Keeping track of regulatory compliance is essential for facility managers, particularly in buildings that require frequent inspections or adhere to strict standards. BIM facilitates compliance by maintaining an up-to-date, digital record of all inspections, maintenance tasks, and system configurations. Facility managers can easily generate reports and track all necessary documentation for regulatory purposes.
BIM and Facilities Management for SmartCADD
As BIM technology continues to evolve, software solutions like SmartCADD are playing a pivotal role in helping facility managers implement BIM in their operations. SmartCADD is a powerful platform that integrates BIM into facility management workflows, offering several key features to optimize building management.
SmartCADD Features for Facility Managers
Real-Time Data Integration
SmartCADD provides facility managers with real-time integration of building systems and equipment, which is critical for effective decision-making. The platform allows for the seamless collection of data from building systems, such as temperature, humidity, and energy usage, and integrates this data directly into the BIM model. This allows facility managers to monitor performance and detect issues proactively.
Automated Maintenance Scheduling
With SmartCADD, facility managers can automate maintenance schedules based on real-time data from the BIM model. The platform can send alerts and reminders when specific maintenance tasks are due, ensuring that tasks are never missed and equipment remains in optimal working condition. Automated scheduling helps reduce manual errors and ensures that the building operates smoothly.
Asset Management
Asset management is an essential part of facility management, and SmartCADD makes it easier than ever to track and manage building assets. The platform allows managers to store detailed information about each asset, including manufacturer details, maintenance history, and expected lifespan. This simplifies asset tracking and helps ensure that the right decisions are made when it comes to replacing or repairing equipment.
Visualization and Reporting Tools
SmartCADD’s advanced visualization tools provide facility managers with an interactive 3D representation of their building, making it easier to navigate through different systems and components. With the ability to view building data in 3D, facility managers can gain a clearer understanding of how the building operates and identify potential issues faster. Additionally, SmartCADD’s reporting tools generate detailed, customizable reports for maintenance activities, compliance checks, and more.
Conclusion
The integration of BIM in facility management is revolutionizing how buildings are managed, operated, and maintained. By providing facility managers with accurate, real-time data, BIM enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and improves the overall performance of a building. The benefits of BIM in facility management are far-reaching, from proactive maintenance to energy optimization and space planning.
As organizations continue to embrace BIM, platforms like SmartCADD are making it easier for facility managers to leverage the full potential of BIM technology. With its real-time data integration, automated scheduling, and advanced asset management tools, SmartCADD is empowering facility managers to streamline operations and enhance building performance.
In summary, BIM and facilities management are a powerful combination that is shaping the future of building management. As technology continues to evolve, the role of BIM in facility management will only become more critical in optimizing building operations, enhancing sustainability, and delivering long-term value for building owners and occupants.
0 notes
Text
With the BIM Process, digital representations of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility are created and managed. Unlike traditional Computer-Aided Design (CAD), which mainly involves drafting, BIM encompasses geometry, spatial relationships, geographic information, and quantities of building components.
0 notes
Text
With the BIM Process, digital representations of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility are created and managed. Unlike traditional Computer-Aided Design (CAD), which mainly involves drafting, BIM encompasses geometry, spatial relationships, geographic information, and quantities of building components.
0 notes
Text
Ensure seamless collaboration and error-free construction with BIM Coordination Services. From MEP BIM Coordination to BIM Clash Detection, streamline your projects with accuracy and efficiency.
#BIM Coordination Services#MEP BIM Coordination#Revit BIM Coordination#BIM Clash Detection#BIM Services#Building Information Modeling
0 notes
Text
Streamline Your Projects with Expert BIM Coordination Services

Construction projects can get complicated fast. Different teams work on different parts, and if they’re not in sync, mistakes happen. That’s where BIM Coordination Services come in. They help architects, engineers, and contractors work together smoothly, reducing errors and keeping things on track.
What Are BIM Coordination Services?
Simply put, BIM Coordination Services make sure all the parts of a building project fit together. These services help teams detect design clashes early, improve efficiency, and keep construction moving without unexpected problems. By integrating various BIM Services, teams can visualize the project in 3D, identify potential issues, and resolve them before they become costly on-site problems.
Key Parts of BIM Coordination
MEP BIM Coordination: Ensures mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems don’t interfere with each other. Proper integration helps avoid installation issues that can delay the project.
Revit BIM Coordination: Uses Revit software to create detailed 3D models for better design accuracy. These models allow teams to analyze structures before actual construction begins.
BIM Clash Detection: Finds and fixes design conflicts before construction starts. This process helps avoid costly on-site changes.
Project Collaboration: Keeps communication clear so everyone stays on the same page. When architects, engineers, and contractors coordinate well, projects move forward smoothly.
Cost Estimation: Helps with budgeting by giving accurate material and labor estimates. Having a precise forecast helps teams manage finances better and avoid unexpected costs.
Why BIM Coordination Matters
1. Fewer Design Mistakes
Using Revit BIM Coordination, teams can see a 3D model of the project, making it easier to catch errors before construction starts. This prevents delays and costly changes during the building phase.
2. No More Last-Minute Fixes
Revit Clash Detection helps spot issues in the design phase so they don’t turn into costly surprises later. For example, detecting a clash between electrical wiring and plumbing early can prevent major rework.
3. Faster, More Efficient Work
With BIM Services, teams can plan better, avoid delays, and save money. Improved coordination reduces downtime, keeping the project on schedule.
4. Better Teamwork
MEP BIM Coordination helps different teams work together, leading to fewer misunderstandings and better results. When all departments collaborate effectively, projects are completed with higher precision.
5. Stay on Budget
By predicting costs accurately, BIM Coordination Services help prevent unexpected expenses. A clear financial roadmap ensures that resources are used efficiently.
6. Follow the Rules
Using BIM Services ensures your project meets all legal and safety standards, reducing compliance risks. Following industry regulations helps avoid legal complications later.
How BIM Coordination Supports Your Project
Early Clash Detection: With BIM Clash Detection, design conflicts can be resolved before construction begins, preventing unnecessary delays.
Better Visualization: Revit BIM Coordination provides a clear picture of the final project, allowing teams to make informed decisions.
Streamlined Workflow: MEP BIM Coordination ensures that mechanical and electrical layouts are properly aligned, preventing rework during installation.
Real-Time Collaboration: BIM Services enhance communication, ensuring that all project stakeholders are updated on changes instantly.
Budget Control: Cost Estimation features help teams stay within budget and allocate resources more effectively.
Regulatory Compliance: By adhering to local building codes, projects avoid compliance issues that could cause legal trouble down the road.
Why Choose SmartCADD for BIM Coordination?
Working with professionals makes a huge difference. SmartCADD provides tailored BIM Coordination Services to make sure your project runs smoothly, with fewer errors and delays. Our experienced team leverages the latest tools to deliver seamless project execution.
Success Stories: How SmartCADD Made a Difference
Case Study 1: High-Rise Commercial Project
A commercial building faced significant coordination challenges due to complex mechanical and electrical systems. By implementing MEP BIM Coordination, our team identified over 200 clashes before construction started, preventing costly adjustments later.
Case Study 2: Residential Development
For a multi-unit residential project, our Revit BIM Coordination approach optimized space utilization. The result? A 15% reduction in material waste and improved design accuracy.
Case Study 3: Industrial Expansion
An industrial plant required detailed BIM Clash Detection to integrate new systems with existing structures. Our team resolved all potential conflicts, ensuring a smooth expansion process.
Ready to Get Started?
Need BIM Coordination Services for your project? Contact us today and let’s make your construction process easier and more efficient!
#BIM Coordination Services#MEP BIM Coordination#Revit BIM Coordination#BIM Clash Detection#BIM Services#Building Information Modeling
0 notes