#12 channel pipette
Text

12-Channel Adjustable Volume Pipette
12-Channel Adjustable Volume Pipette provides a customizable volume range from 0.5-10 µL. Integrated with individual piston and tip cone assembly that ensures consistency in liquid dispensing. It is autoclavable and able to withstand autoclaving conditions at a temperature of 121℃ under 1 bar pressure for 20 minutes.
0 notes
Text

Labmate Polystyrene Solution Reservoirs are 10 mL containers designed for accurate liquid measurement, pouring, and storage. Crafted from pure polystyrene, they are available in non-sterile or electron beam sterilized versions. Their flat bottoms and volume markings ensure precise measurements. Compatible with 8- and 12-channel pipettes, these reservoirs feature corner spouts and a tapered "V" bottom to minimize waste and maximize recovery.
#Polystyrene Solution Reservoirs supplier#Polystyrene Solution Reservoirs manufracture#Buy Polystyrene Solution Reservoirs
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
Top 5 pieces of lab equipment
Centrifuge. Classic but also essential. Separates your shit with the power of physics aka tell them to get rotated at 5000 rpm, idiots. Comforting hum and sometimes warm air when nicely balanced. Do Not poorly balance your centrifuges around me, I respond to it like nails on a chalkboard that's also abusing a puppy.
Vortexer. Does the opposite of the centrifuge. Literally stimulation go brrrr. Satisfying in a way that's hard to explain if you haven't used one- press test tube on grippy platform, it shakes real good, your shit is now unseparated.
Micropipetter. THE GOOD ONES ie the one pictured below, which is the Gilson Pipetman Classic (tm). I have a powerful bias for these because they're what I had in my very first lab job and the feel of them is just. Better than any of the newer and cheaper ones I've used. If you're pro level you can even main the 8 or 12 channel but Be Careful. I am of course pro level, I LEARNED to pipette loading electrophoresis gels with a multichannel and to this day nothing else has required that level of pipette finesse. You can buy your own single channel Pipetman Classic on Fisher Scientific's website for just $732 ❤

Spectrophotometer/fluorometer. Similar and sometimes combined into one piece of equipment although there are many kinds. Tells you what's in your shit. This is important because, at last in my line of work, the stuff your lab is both paying and being paid big money for all looks like clear water. Because it's very small and suspended in clear water. Is your shit actually in there and how much/what kind is a very important question to know if all your other shit is working. Also in the case of fluorescence generates the data that is what you're actually getting paid for, essentially also answering the question of What's In Your Shit.
Sharpie. Beat out the rest of the competition for its ubiquitousness. You're doing lab work? You need a sharpie. You gotta label a glass beaker with the date your media was made? You gotta label a stack of plastic plates going in the -80 freezer? You gotta write a post it note saying DONT TOUCH TEST IN PROCESS? You gotta draw a diagram of how polymerase chain reaction works on a paper towel for the new kid? You need to write a reminder to yourself to take yesterday's samples out of the incubator at exactly 1:07 on your arm? Sharpie.
#with of course big bias to my own field. lots of other types of labs have cool shit ive never even seen#ive infodumped. enjoy.#science
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Micropipette Guide 2024: Types, Applications and More

Micropipettes or pipettes, are instruments used to measure liquid ranging between volumes of 1-10000 µl and transfer it from one sample container to another. This is a basic liquid-handling instrument for almost all scientific laboratories.
Types of Micropipettes
There is no 1 way to classify micropipettes. It can vary in a number of ways.
1. Number of Channels
Single Channel Micropipettes
A single-channel micropipette has only 1 channel to aspirate and dispense the liquid. It means you can handle only one sample at a time.
Multi-Channel Micropipettes
Multi-channel micropipettes can handle 8, 12 or 16 samples in one go. It can attach multiple tips at the same time and you can get the work done faster especially if working in high-throughput labs.
2. Volume Adjustment
Fixed Volume Micropipettes
Here the volume a pipette can aspirate and dispense remains the same and you don’t have the option to adjust or choose between a range. They offer consistent and accurate results for repetitive pipetting.

Variable Volume Micropipettes
Variable volume pipettes give you the flexibility to choose the volume you want to pipette (within the given range). You need to set the volume manually on the dial. High-performance pipettes also come with a volume lock feature for enhanced safety and reliability.

3. Operating Mechanism
Mechanical Pipettes
These are the standard pipettes widely used in all laboratories. Mechanical micropipettes operate on a piston-driven system, where users manually set the desired volume using a dial and apply thumb pressure on the plunger to aspirate and dispense liquids.

Electronic Micropipettes
Electronic micropipettes are more expensive than mechanical ones because they have digital controls, programmability and eliminates the element of human error to a certain extent. It has an electronic display and is ideal for high-throughput labs where reproducibility is paramount.
Components of Micropipette
Plunger
The plunger is one of the main components of the micropipette. Use your thumb to press down on the plunger to aspirate and dispense the liquid.
Then, with a firmer push, sometimes called the “blow-out stop,” it ensures a thorough expulsion of any remaining liquid, guaranteeing accurate measurements—a two-step process of liquid control.
Ergonomics are a key point here since lab professionals will be pipetting repeatedly for long hours. A low-force mechanism which does not require excessive plunge force, will minimize the RSI.
Volume Adjustment Dial
By twisting the volume adjustment dial, you dictate the micropipette’s plunger movement, determining your experiment’s liquid dosage. In micropipettes with adjustable volumes, this feature offers precise measurement control, no matter how small or large the quantity is.
Tip Ejector
Keep your hands and micropipette clean by disposing of used tips promptly. Utilize the convenient tip ejector button to effortlessly remove micropipette tips, ensuring a fuss-free and contamination-free experiment environment.
Tip Cone
The tip cone, also known as the shaft, is the crucial component of a micropipette where the disposable tip is inserted. Its primary function is to ensure a snug fit for the tip, ensuring precision in measurements and preventing air leakage. Its adaptable shape accommodates various sizes and styles of tips, allowing for versatile and secure usage without concerns of detachment or disruptions.
Calibration Screw
Inside the micropipette lies a crucial component, the calibration screw. This is what makes accuracy possible. Twisting this tiny screw adjusts the liquid output, fine-tuning the micropipette’s performance. Regular checks and tweaks, as advised by the manufacturer, ensure precision in your measurements, keeping everything flowing smoothly.
Applications of Micropipettes in Laboratory
Micropipettes are used to measure any small amount of liquid samples for testing and research. They are crucial in lab settings like molecular biology and diagnostics, precisely transferring tiny liquid volumes, facilitating diverse experiments. Mastery of their principles is key to effective scientific research and analysis.
Some common applications include:
1. Molecular Biology
2. Biochemistry
3. Cell Culture
4. Microbiology
5. Analytical Chemistry
6. Clinical Diagnostics
7. Pharmaceutical Research
How does a Micropipette work?
Micropipettes operate on the principle of air displacement. They consist of a plunger connected to an internal piston, which moves to two distinct positions:
Filling Position: When the plunger is depressed to the first stop, the internal piston displaces a volume of air equal to the desired volume shown on the volume indicator dial. This creates a vacuum, drawing the liquid into the tip.
Dispensing Position: The second stop on the plunger is used solely for dispensing the contents of the tip without drawing in additional air.
How to use a micropipette?
1. Start with choosing the right micropipette and micropipette tips
Select the one that is best for your application. While pipettes are similar in the way they function, what sets them apart is the accuracy and precision of the measurement, ergonomics and general durability of the instrument.
Set the volume based on your requirement and ensure the tips match the volume of the pipettes.
2. Attach the micropipette tip to the micropipette
Don’t use excessive force here because good quality pipettes will be quick and seamless to attach to the tips and should provide a leak-proof seal.Immerse the pipette in the liquid at 90 degrees
Be mindful of your posture and keep the position upright.
Aspirate and dispense 2-3 times before actually measuring the liquid
3. Forward or Reverse Pipetting
First let’s talk about forward pipetting:To aspirate the liquid in the tip, press the plunger to the first stop. Immerse the pipette tip vertically in the liquid.
Slowly release the plunger while the tip is immersed. The liquid will be aspirated into the pipette tip.
To dispense the liquid, place the tip on the inner wall of the receiving vessel at a steep angle
Slowly press the plunger to the first stop to dispense the liquid.
To empty the tip completely, press the plunger to the second stop.
Now for reverse pipetting
The reverse technique is suitable for dispensing reagents/solutions that have high viscosity or a tendency to foam easily. It is also recommended for dispensing very small volumes.To aspirate the liquid in the tip, press the plunger to the second stop and immerse the pipette tip vertically in the liquid.
Slowly release the plunger while the tip is immersed. The liquid will be aspirated into the pipette tip.
To dispense the liquid, place the tip on the inner wall of the tube at a steep angle.
Slowly press the plunger to the first stop.
Finally, eject the tip and dispose it off
Calibration of Micropipettes
Calibration is conducted through gravimetric testing, which involves weighing the amount of pure water delivered in a single operation of the pipette. The obtained mass is divided by the density of water to determine its volume. Variable volume pipettes should undergo testing at three or more points across their designated range, typically at maximum volume, 50% of maximum volume, and the lower limit of their range.
Here’s a general guide on how to calibrate a micropipette:
1. Gather MaterialsMicropipette(s) to be calibrated
Appropriate pipette tips
Distilled water or a calibration solution
Weighing balance with appropriate accuracy (usually in milligrams)
Gloves and lab coat for safety
2. Prepare the Micropipette
Ensure the micropipette is clean and free from any residue.
Attach a fresh and compatible pipette tip to the micropipette.
3. Pre-Wet the Pipette Tip (Optional)
For some micropipettes, pre-wetting the tip with the liquid being used can help ensure accuracy. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding pre-wetting.
4. Prepare the Calibration Solution
Use distilled water or a calibration solution recommended by the micropipette manufacturer.
Ensure the calibration solution is at room temperature to minimize density variations.
5. Set the Micropipette to the Desired Volume
Adjust the micropipette to the volume you want to calibrate (e.g., if calibrating a 10-100 μL micropipette, set it to 50 μL).
6. Dispense Liquid into a Weighing Boat or Container
Dispense the liquid from the micropipette into a weighing boat or a container placed on a weighing balance.
Note down the initial weight (W1) of the liquid dispensed.
7. Weigh the Dispensed Liquid
Carefully weigh the liquid dispensed using the weighing balance. Ensure the balance is calibrated and accurate.
Record the final weight (W2) of the liquid.
8. Calculate the Dispensed Volume
Subtract the initial weight (W1) from the final weight (W2) to determine the weight of the liquid dispensed (W).
Convert the weight of the liquid dispensed to volume using the density of the liquid or the known density of the calibration solution.
Calculate the actual volume dispensed using the formula:

9. Compare with Expected Volume
Compare the calculated volume dispensed with the expected volume (e.g., 50 μL for a 10-100 μL micropipette).
Calculate the percent error to assess the accuracy of the micropipette calibration:

10. Adjust if Necessary
If the percent error is within an acceptable range (typically ±2-5%), the micropipette is calibrated. Otherwise, adjustments may be needed.
Consult the micropipette’s user manual for instructions on how to adjust the volume settings. Adjust carefully and recheck the calibration until the desired accuracy is achieved.
11. Record Calibration Data
Keep a record of the calibration process, including the micropipette serial number, date of calibration, volume settings, calibration solution used, measured weights, calculated volumes, and any adjustments made.
12. Final Checks
After calibration, perform a final check to ensure the micropipette is dispensing accurately and consistently across the volume range.
When is micropipette calibration required?
Micropipette calibration is typically required in the following situations:
Initial Use
New micropipettes should be calibrated before their initial use to ensure accuracy and precision.
Scheduled Calibration
Regular calibration intervals are recommended to maintain the accuracy of micropipettes over time. The frequency of calibration depends on factors such as the frequency of use, the criticality of the measurements, and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
After Maintenance or Repair
Calibration should be performed after any maintenance or repair work on the micropipette to verify that it meets the required specifications.
Change in Operating Conditions
If there is a significant change in the operating conditions, such as temperature or altitude, recalibration may be necessary to account for these factors’ effects on the micropipette’s performance.
Compliance Requirements
Laboratories may have regulatory or quality assurance requirements that mandate regular calibration of micropipettes to ensure traceability and compliance with standards.
Where do we get the best micropipette for the lab?
When purchasing a micropipette for your lab, consider key factors such as accuracy, precision, ergonomics, and ease of maintenance. Research the brands and models, compare specifications, and read user reviews to make an informed decision. Evaluate additional features like adjustable volume settings and compatibility with automation systems. Set a budget and balance costs with desired features. Check warranty coverage and customer support options for added peace of mind.
Cleaning and Maintenance of Micropipettes
1. External CleaningRemove and Clean the Tip Ejector: Begin by detaching the tip ejector and giving it a thorough wipe-down.
Wipe Down All Exposed Surfaces: Take a lint-free cloth or tissue and carefully wipe all visible parts of the micropipette, including the body, buttons, operating rod, and tip holder. Be diligent in cleaning any scuffs, marks, or accumulated debris in hard-to-reach areas.
Use a Brush for Stubborn Debris: If there are persistent stains or dirt, consider using a soft-bristled brush to gently scrub the affected areas.
Reassemble and Allow to Dry: Once the exterior surfaces are clean, reattach the tip ejector and ensure it is securely in place. Leave the pipette to air dry completely before further use.
Final Wipe with Cleaning Solution: Finish the cleaning process by wiping down the outer surfaces once more with a cleaning solution to remove any remaining residue. Allow the alcohol to evaporate fully before returning the pipette to service.
2. Internal Cleaning
Cleaning the inside of a pipette should be handled by trained personnel to avoid incorrect reassembly, which can damage the micropipette and affect its performance, leading to decreased accuracy and potential leakage.Disassemble the Micropipette: Carefully take apart the pipette, placing the upper part in a clean, dry area.
Wipe with Alcohol-Coated Wipes: Use alcohol-coated wipes to thoroughly clean the entire interior, including the body, connecting nut, tip holder, O-ring, seal, and the stainless steel surface of the piston. Ensure the piston is completely dry to prevent corrosion.
Allow Alcohol to Evaporate: Let the alcohol evaporate fully from the interior of the pipette.
Check for Lubrication Needs: Refer to the instruction manual to determine if any parts, like the piston assembly and seals, require lubrication. Follow the manual’s guidance for reassembly, ensuring proper alignment and placement of components.
Maintaining Micropipettes
When the pipette is not in use it should be stored in an upright position. The pipette should be inspected prior to use each day for any dust or contamination on outside surfaces. Special attention should be given to the tip cone. No solvent other than isopropanol should be used to clean the pipette. If the pipette is used daily, an internal parts inspection should be performed every three months.
Choosing the right micropipette for your applicationEnsure that the micropipette can accommodate the desired range of liquid volumes for your pipetting needs.
Verify if the micropipette features a universal tip cone to accommodate various types of pipette tips.
Check if the micropipette is autoclavable at the necessary temperature to ensure proper sterilization.
Check if the micropipette is UV resistant so that they can be kept inside the hood even when the UV mode is on.
Assess the ergonomic design of the micropipette for smooth and comfortable handling during use.
Confirm if the micropipette is calibrated to guarantee precise dispensing of liquids.
Evaluate the accuracy and precision of the micropipette’s readings to ensure compliance with ISO standards.
Ergonomics is a key factor in choosing a pipette because repetitive strain injury is common amongst lab personnel who pipette regularly. Low-force tip ejection and minimal plunge force are crucial.
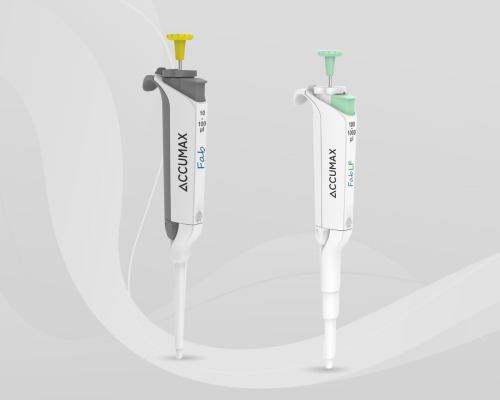
Accumax Lab Devices specializes in manufacturing high-precision liquid handling instruments for top-tier laboratories worldwide. With a focus on innovation, it offers an advanced range of micropipettes designed to enhance user experience within real-world laboratory settings. Especially our range of FAB and FAB LF pipettes, which are specially designed for accuracy and precision with excellent ergonomics to elevate your pipetting experience like never before.
Micropipette FAQs
1. Can I use any brand of pipette tips with my micropipette?
Whether you can use any brand of pipette tips with your micropipette depends on its tip cone design. If your micropipette has a universal tip cone, it means it’s compatible with a wide range of international pipette tip brands, as long as they’re suitable for your micropipette’s volume capacity.
2. What’s the best way to sterilize my pipette before use?
To clean your micropipette before using it, first, check if it can be sterilized using an autoclave. If it can, follow the instructions in the manual to know the right temperature and duration for sterilization. Make sure to consider the type of liquid you’ll be using it for.
3. Is there a simple way to check if my micropipette is calibrated correctly?
Set it to the usual volume, then dispense water five times. Weigh what you piped out on a scale. If it matches up nicely with the ISO standard, your micropipette is good to go. If not, it’s time for a recalibration.
4. How frequently should I recalibrate my micropipette?
For regular use, it’s good to check your micropipette’s calibration every 3 to 6 months. Following the ISO 8655 standard, it’s recommended to have it calibrated annually.
5. How to adjust the volume of a micropipette?
To adjust the volume on your micropipette, look for the display showing numbers indicating the volume range. If you have a fixed-volume micropipette, the range is predetermined. However, if you have a variable volume micropipette, you can adjust it within the given range by using the rotational dial located at the top of the micropipette plunger. Alternatively, you can consult the manual for specific instructions on changing the volume.
6. Why is it important to avoid touching the tips of the micropipette?
When you touch the tips of a micropipette, you risk transferring oils and other substances from your fingers onto them. This can interfere with the accuracy of volume measurements and potentially contaminate your samples. To maintain precision and avoid contamination, it’s best to handle the micropipette tips only with the instrument itself.
7. What happens if I release the plunger of the micropipette too quickly?
Releasing the micropipette plunger too quickly can lead to inadequate liquid draw up and dispensing, causing potential inaccuracies in your measurements.
8. What should I do if my micropipette isn’t working right?
If your micropipette isn’t working properly, it’s time for some troubleshooting. Start by double-checking if it’s properly calibrated and if the volume setting is correct. Ensure that the pipette tips are securely attached and not damaged. If the issue persists, you might need to clean or maintain the micropipette according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If all else fails, it might be time to consult with a colleague or contact technical support for further assistance.
9. Can my micropipette handle different types of liquids?
Your micropipette is designed to handle a variety of liquids, whether they’re watery solutions, viscous substances, or even oils. As long as you’re using the appropriate tip size and technique, your micropipette can smoothly pipette different types of liquids.
This blog originally posted here: Micropipette Guide 2024: Types, Applications and More
0 notes
Text
November 2023 Empties (& Mini Reviews).
Years ago on my old Tumblr, I did a side blog which did reviews & the likes of that sort of thing. One of these things I did was a monthly empties & mini reviews of these products. I've decided to have another try at this (I've also been inspired by various YT channels & IG pages which are based on panning products & also monthly empties). It would also possibly be helpful to me if I see something that I have used & remind me that I did like it considering my memory recently has been terrible.

Anyway, so far this is the empties for last month that I will also do mini reviews on. If I do another one next month & it has some of these products I won't include them. Anyway, I'll start with the first product:
Simple 10% Vitamin B3 Niacinamide Booster Serum:

I liked this serum! I've used various brands of niacinamide serums over the past few years & I really liked this one. It was nice to apply and it had an almost creamy feel to it. I also preferred it to The Ordinary's serum as that always had a sticky feel to it (though I did like that had the inclusion of zinc to it). I would definetly get this again.
Simple Age Resisting Day Cream with SPF 15:

This was just a simple (no pun intended) moisturiser & does what it says- keeps my skin moisturised. There is no scent to this. I would use this again but I do wish the SPF was higher.
Erbario Toscano Rose Shower Gel:

This smells absolutely gorgeous! I love rose scented things & the smell of this also reminds me of Turkish Delight (not the chocolate one).
It does feel like you need to get a good few squirts for it to foam though. It lasted a while (I got this in August). I would definetly get this again if I see it in TK Maxx.
The Body Shop Lime & Matcha Hair & Body Mist:

This smelt very limey! It's a super refreshing scent and is great scent for throughout the day when you need a pick me up. Sadly though this seems to have been discontinued. I picked this up in TK Maxx for about £6 (I think the original price was either £10 or £12).
Nourish Body Scrub- Rosehip & Coffee:

I got this from (surprise, surprise) TK Maxx. I thought it would have a rose like scent but it didn't- it was a very strong coffee smell (which didn't bother me as I like the smell of coffee).
Its a dry scrub which I'm not used to- I'm used to using ones that lather up. It does an amazing job of exfoilating & left my skin feeling soft. However, I would not purchase this again. It's very harsh (I actually managed to scratch myself with it) & it's incredibly messy.
e.l.f Eye Primer:

This is really good & is also a reasonable price. I've used a Maxfactor or Revlon eye primer in the past & it was horrible; I've also used the Urban Decay one which is brilliant but pricey. Since I've been trying to practice using eyeshadow, I've been using the e.l.f eye primer & it does the job. It does such a good job, I'm on to my second tube.
Cogerie Hyaluronic Anti Age Serum:

I like this serum so so much! It does have a light floral scent so if you don't like scents in your skincare, bear that in mind. My skin always felt soft after using this & it kept my skin hydrated. I also like the design on the bottle, its really pretty.
I do have two problems with this though: the first one being that I always struggle getting the remainder of the serum in bottles that have a pipette in them. The second is I got this from TK Maxx so it's anyone's guess whether they'll have this in stock again. I would definetly get this again though.
Garnier Skinactive Micellar Cleansing Oil Infused Water:

This is the best thing I have ever used to remove my makeup- it gets my Barry M Genie Lipstick off effortlessly and it is great removing waterproof makeup. I get the blue one (the yellow one dries out my hands & makes them sting).
And there you have it- my monthly empties. Do you have any empties that you would get again? Is anything on this list you would try?
I'm also sorry for the appalling photos. Standard lighting and phone camera does not make great ones.
#Monthlempties#empties#November empties#mini reviews#Garnier#micellar water#hyaluronic acid#niacinamide
0 notes
Text
STONYLAB 8-Channel Pipettor Controller
50 to 300 ul
Sold only for $225.39
Featuring ergonomic design and intuitive operating concept, StonyLab 8 Channels Pipettor is ideal to handle multiple samples simultaneously with high accuracy and efficiency
Volume range: 50 to 300 uL; Volume setting is continuously adjustable by turning thumb wheel with a clear volume indicator; minimum increment per single adjustment: 5 uL
Tip cone is autoclavable and can be steam sterilized at 121℃ for up to 20 minutes
Easy to recalibration if needed; Included color caps for conveniently mark different uses of pipettes in lab
Discover more at
💡A multi-channel pipettor, also known as a multi-channel pipette or multi-pipette, is a laboratory instrument used for accurately and efficiently dispensing small volumes of liquid into multiple containers simultaneously. It is commonly used in chemistry and molecular biology labs for tasks such as sample preparation, DNA sequencing, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), and ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay), among others. Multi-channel pipettors come in various configurations, typically with 8, 12, or 16 channels, allowing you to handle multiple samples at once.
0 notes
Text
Innovative multichannel pipettes for handling liquids precisely
Multichannel pipettes have revolutionized the field of laboratory liquid handling by streamlining and expediting pipetting tasks. These versatile instruments are designed to simultaneously transfer multiple samples or reagents, significantly reducing the time and effort required for repetitive pipetting steps. With the ability to handle multiple channels, multichannel pipettes are ideal for scaling up experiments and increasing throughput without sacrificing accuracy and precision.
The most common multichannel pipettes are available in 8- or 12-channel configurations, perfectly spaced to work with 96- or even 384-well microplates. However, larger multichannel options and adjustable spacing versions cater to diverse experimental needs. By leveraging the capabilities of a multichannel pipette, researchers can accomplish in a few steps what would otherwise demand a much larger number of individual pipetting actions.
By employing a multichannel pipette in a scenario requiring 480 pipetting steps, one can accomplish the task with only 40 steps using a 12-channel pipette (5 rows of 8) or 60 steps with an 8-channel pipette (5 columns of 12). This expedited process not only accelerates plate filling but also minimizes the risk of repetitive strain injury (RSI) and the associated mental and physical fatigue. It is crucial to mitigate pipetting errors caused by fatigued analysts as they can compromise accuracy and precision, potentially leading to erroneous or inconclusive results. Consequently, repeating the assay becomes necessary, resulting in the wastage of valuable reagents, samples and reduced productivity.
While multichannel pipettes provide numerous advantages, they also present certain challenges, particularly concerning pipette tip attachment. Loading these tips can be cumbersome and often leads to uneven attachment. Difficulties such as problematic tip attachment, high ejection forces, and increased aspiration forces have impeded the proper utilization of multichannel pipettes. However, recent advancements in multichannel pipette technology have addressed these issues. For instance, electronic pipettes with electronic pistons and/or tip ejection mechanisms have been developed to overcome these challenges. Manufacturing breakthroughs have also improved tip attachment consistency, resulting in enhanced accuracy and precision. Nevertheless, it is important to note that even with these technological advancements, the critical factor for optimal performance lies in the proficiency of a well-trained operator who utilizes a calibrated multichannel pipette for each channel.
Enhancing Pipetting Proficiency: Essential Techniques for Multichannel Pipetting Success
To achieve accurate and reliable results when using multichannel pipettes, proper technique is of utmost importance, as operator variability can quickly lead to errors. Here are essential techniques to consider when utilizing these devices:
Mindful Tip Application: Always opt for manufacturer-approved pipette tips and select those with the smallest air gap. After aspirating the sample, compare the liquid levels within the tips. If uneven, it may indicate inconsistent tip placement across the pipette channels.
Pre-Wet Pipette Tips: Pre-wetting the pipette tips is crucial. This process humidifies the captive air space (air cushion) within the tips, minimizing sample evaporation and the risk of pipette dripping.
Slow and Steady Aspiration: Rapid plunger movements or fast aspiration can introduce unwanted bubbles within the pipette tips. To avoid this, ensure a controlled and gradual aspiration process.
Vertical Aspiration, Minimizing Angles: When aspirating, it is important to maintain a vertical position without tilting or angling the pipette. Angling the pipette in various directions, such as forward-backward or left-right, can result in uneven immersion depths of the pipette tips, leading to inconsistent volume transfer.
Essential Pause After Aspiration: Once the plunger is released, pause for a full second with the tips still immersed in the sample. This pause allows the total sample volume to fully enter each pipette tip, ensuring uniformity across all channels.
Adjusting Dispense Speed: Sometimes, a slower dispense speed may result in residual samples remaining in the pipette tips. If you observe residual droplets, it may indicate the need to adjust the dispense speed to a faster rate. This adjustment ensures that the captive air space above the sample generates enough force to push the entire sample out of the pipette tips.
Tip-Touch or Brush-Off Technique: During dispensing, whenever feasible, gently touch the pipette tips against the side walls of the plate or receptacle. Alternatively, you can dispense the sample on top of the solution. These actions create added surface tension, aiding in complete sample removal and reducing the likelihood of residual sample retention.
By employing these techniques, you can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of multichannel pipetting, ensuring complete sample transfer and minimizing potential sources of error.
0 notes
Photo

Manual Digital Adjustable 12 Channel Option Multichannel Pipette MicroPipette Lab Equipment M12 Series https://a.aliexpress.com/_mMV5cEO https://www.instagram.com/p/CqHeguzpTb5/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Text
Pipette Tip Automatic Plug Cartoning Machine-Introduction to the Classification of Pipette Tips
GST Pipette Tip Automatic Plug Cartoning Machine Manufacturers know that when the tip is used with a pipette, it is mainly used in various pipetting scenarios. Because in the laboratory, the pipetting of liquid is the basic operation of all experiments, so the pipette and its matching tips are the most commonly used consumable products in the laboratory. In order to meet various pipetting needs, its types are also rich and varied. The following introduces some of the more common types of suction heads on the market.

1. Standard suction head
The most common type of tip is also the most widely used tip. It can be used for almost all pipetting operations. This is the most economical type of tip. If there is no special requirement, you can generally use standard tips. Meet most pipetting needs.
Other types of tips are also evolved from standard ordinary tips. There are generally many packaging forms for standard tips, and there are three common types on the market: bagged, boxed, and pre-packed (stacked). Generally speaking, boxed products will provide sterilized finished products, while bags and pre-packed plates will provide less sterilized products. When users use them, if they have special sterilization needs, they can directly purchase sterilized boxes. , or put unsterilized bagged tips into an empty tip box for self-sterilization before use.
Most of the tips and tip boxes on the market are made of PP polypropylene, so they can be processed under high temperature and high pressure in a sterilizer. Among them, the common packaging form of the box is 96 pieces/box, and the specification is 12×8, so as to be used with multi-channel pipettes and 96-well plates.
2. Low adsorption tip
No matter what type of tip you choose, a low residual rate is the key. If we carefully observe the use process of the tip, we will find that when discharging liquid, there is always a part that cannot be discharged and remains inside the tip. No matter what experiment is done, this will cause some error in the results. If this error is within the acceptable range, you can still choose ordinary tips for use.
For experiments with high sensitivity requirements, or precious samples or reagents that are prone to residue, you can choose low adsorption tips to improve the recovery rate, so as to obtain more accurate experimental results and higher recovery rates for precious samples. The surface of the low adsorption tip has been treated with hydrophobicity, which can reduce the surface tension liquid leaving more residue in the tip.
Although this sounds very good, in actual use, this type of suction head is still used less. Because as a kind of product that is used in a large amount in the laboratory, the cost of the tip is also a factor that users will consider. The price of this kind of specially treated tip is indeed more expensive than the standard tip. Of course, from the appearance point of view, there is no difference between the low adsorption suction head and the ordinary shampoo.
3. Filter tip
The filter tip is a kind of consumable designed to avoid cross-contamination, with a filter element on the upper end of the tip. Use the filter tip to pipette the sample so that the sample cannot enter the interior of the pipette, thereby protecting the parts of the pipette from contamination and corrosion, and more importantly, it can also ensure that there will be no cross-contamination between samples.
For example, it can effectively prevent the contamination of the pipette in scenarios where the liquid backflows into the pipette due to misoperation by the experimenter, or in molecular biology experiments where aerosol pollution is likely to occur, and at the same time in pathogen detection In related experiments, the filter tip can better protect the safety of the experimenter.

��Of course, in fact, for filter tips, most ordinary filter elements cannot provide a real barrier function, and can only relatively slow down the process of liquid entering the pipette. Only some high-end tips can provide a real barrier function, to achieve complete isolation. Filter tips are usually pre-sterilized and do not contain DNase/RNase, and are often used in experiments such as molecular biology, cytology, and virology.
4. Flared suction head
The difference between this type of tip and ordinary tips is that its lower end has a larger opening, which is easier to discharge during liquid discharge and provides less mechanical shear. When pipetting viscous substances, conventional tips should have a smaller opening at the lower end, which is not easy to absorb and discharge, and will also cause higher residues. The flared design is more convenient for the processing of such samples. In the face of genomic DNA and fragile cell samples, the opening is too small to easily cause damage to the sample during operation, cell rupture, etc. The opening of the flared tip is about 70% larger than the standard tip, which is the best choice for pipetting fragile samples. Excellent solution.
5. Gel loading tip
The difference from ordinary suction heads is that the bottom end provides a very slender extension. When used for gel loading during electrophoresis, this type of tip can go deep into the sample well of the gel, because the volume of this type of hole is very small, it is difficult for conventional tips to load samples, or it is easy Spilled, gel loading tips are very suitable for such small-volume containers.
6. Extended suction head
Compared with the conventional standard suction head, the length is simply lengthened. Although different brands of tips on the market may have different sizes including length, the extended tip is still much longer than the regular tip. If the container that needs to absorb the solution is very deep, such as the common 15ml centrifuge tube on the market, at this time, the conventional tip cannot absorb the liquid, and the extended tip can complete this operation.

7. Automatic suction head
Unlike the above-mentioned tips, automatic tips are mainly used with a workstation. Compared with traditional manual pipettes, the automated workstation is actually a high-throughput option. It cooperates with various other automated equipment, such as automated cryopreservation tube systems, nucleic acid extractors, etc., to achieve high-throughput experiments. Automation, improving efficiency while liberating manpower.
0 notes
Text
There are pipettes with enhanced electronic feature
In molecular biology where a lot of chemical and cell tests are required, pipettes become imperative in the research. Pipettes are the most useful tool to extract the right amount of samples and introduce the samples into the corresponding laboratory machine. They measure the sample with accuracy and precision that is beyond doubt.
Pipettes do come in several and various designs to facilitate the lab activities easier and better. They come in varied sizes depending on the usage and the objective of the research. There are pipettes with enhanced electronic feature that readily generate sample using vacuum dispersion.
What are the types of pipettes?
Plastic products are lighter and are good to use if you are planning a small portion of the sample object. This can get liquid or dyes from 0.1 cu.m to 0.5 cu.m. Plastic pipettes are affordable and they are disposable as well to facilitate clean jobs.
They are small pipettes that can be used to small amount of liquid or fluid. Pasteur products commonly have glass tubes to enable transparent view of the amount of fluid. Most Pasteur types are used several times because it can be reused with pasteurization process to facilitate cleaning.
Micropipettes are very useful to get samples with correct measurement. It is an adjustable pipette that carries many tubes in it to facilitate any microscopic research in the laboratory. It comes is different sizes but there are macro pipettes that can handle bigger amount of fluid for sampling.
There are pipettes that can readily disperse and get samples with many tubes in it; these are called multi channel pipettes. They may come in various channel codexes. There are 8 channel, 12 channel, 16 channel, 20 channel pipettes present in the market. There are features that include electronic configuration of the pipette.
Automated pipettes are also available; they may come in stationary and in portable types. These pipettes can readily grade the sample while ensuring to get the right amount for the research gathering. Moreover, these automated pipettes are used to generate samples from within the core of the sampled object. It may also use several configuring accessories; computers are the most common component of automated pipettes.
Use to measure the calibrated volume of the fluid. Most graduated pipettes are used in gathering big amount of samples. They may also come in variety of sizes.
These are currently the smallest pipette 10ml serological pipette available today. With enhanced size and strength of the tube it can be use to see the functioning unit of crystallization. It is created by the Brookhaven national Laboratory.
The usage of thes products varies and is very wide. Some pipettes are used to get data sampling in big amounts while others are used in getting small samples and to detect the processes within the sampled object.
They are vital to the correct information gathering that will be produced by the laboratory; being the sample handler, it is the most delicate equipment in the laboratory. Moreover, they facilitate the hardest part of the sampling process by getting the sample at a right measurement.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Flow free bridges yellow pack

#Flow free bridges yellow pack code#
#Flow free bridges yellow pack trial#
This expansion allows you to have pipes warp from the edge of the map to the other edge of the map. Pair all colors and cover the entire board. Starter, Challenge, Bonus, Classic, Mania, and Jumbo level packs. 9283138 Pipette tips, Eppendorf Combitips advanced® The Eppendorf Combitips have been completely redesigned and optimised so that they are capable of meeting the increased requirements of a modern laboratory to a greater extent than ever before.
#Flow free bridges yellow pack code#
The third expansion, "Flow Free: Warps", was released on August 8, 2017. If you like Flow Free, youll love Flow Free: Bridges Connect matching colors with pipe to create a Flow. Over 900 levels available in Free Play mode. Combitips® advanced 1,0 ml colour code yellow, pac Item No. The gameplay is similar to "Flow Free" except the layout resembles hexagons instead of squares. The second expansion, "Flow Free: Hexes", was released on October 12, 2016, and features both free and paid premium puzzles. In this expansion, pipes can be made to intersect through pre-made bridges. The first expansion, "Flow Free: Bridges", was released on Novemat a fixed price. Expansions īig Duck Games has also released three expansions in the series. Aids to Navigation System and the Intracoastal Waterway. Channels of the ICW are identified by yellow symbols on channel buoys and markers.
#Flow free bridges yellow pack trial#
The app also contains additional paid packs as well as a time trial mode. The Intracoastal Waterway is a chain of local channels linked together to provide an inland passage along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts. Whenever a level is completed, a check mark will appear on the level select icon to indicate that the puzzle is solved, while a star indicates a "perfect" game, where the player finished the puzzle with the fewest moves required. Many grids are "open" and some contain "walls" which must be navigated around. real time access to deck, real time fixed air flow swap ability. Difficulty is primarily determined by the size of the grid, ranging from 5x5 squares (4 colors) to 15x15 squares (14 colors). Vaporesso BilletBox EUC Coils Bridge details Anyone whos used a Billet box will. The objective is to connect dots of the same color by drawing 'pipes' between them such that the entire grid is occupied by pipes. Each puzzle has a grid of squares with pairs of colored dots occupying some of the squares.

0 notes
Text
12-Channel Adjustable Volume Pipette

Labotronics 12-Channel adjustable volume pipette provides a customizable volume range from 0.5-10 µL complies with ISO 8655 standards which offers one-handed operation by simultaneously pipetting across multiple samples with volumes ranging from 0.5~10 µL.The individual piston and tip cone for each channel provide adjustable extracting volume of liquid as per requirment.The adjustable rotating head allows dispensing at desired location.It is completely autoclavable at 121°C. Read more
#measuring equipment#digital measuring tool#sterilizer#12 channel adjustable volume pipette#digital multimeter
0 notes
Text
Polystyrene Solution Reservoirs
Labmate Polystyrene Solution Reservoirs are 10 mL containers designed for accurate liquid measurement, pouring, and storage. Crafted from pure polystyrene, they are available in non-sterile or electron beam sterilized versions. Their flat bottoms and volume markings ensure precise measurements. Compatible with 8- and 12-channel pipettes, these reservoirs feature corner spouts and a tapered "V" bottom to minimize waste and maximize recovery.

#Polystyrene Solution Reservoirs supply#Polystyrene Solution Reservoirs suppliers#Polystyrene Solution Reservoirs supplier
1 note
·
View note
Text
12 Channel Pipettes | Multichannel Micropipette | Microlit USA
Microlit is offering the 12 channel micropipette to improve your testing facility. This Multichannel Pipette have universal tipcone to work with all internationally accepted tips, Lightweight with soft grip to give maximum user comfort and fully autoclavable at 121°C to ensure lab safety from cross contamination. For product inquiry or details, please visit the website https://www.microlit.us/product-category/micropipettes/

#12 channel micropipette#12 channel pipette#mulitchannel micropipette#multichannel pipette#micropipette#pipette#electronic mutlichannel pipette#electronic mutlichannel micropipette#variable volume multichannel pipette#fixed volume multichannel pipette
0 notes
Text
How to Use the Various Types of Pipettes
What is a pipette?
A pipette is a lab instrument used to quantify and move little volumes of fluid precisely. It is ordinarily utilized in science, science, and other logical fields where exact fluid dealing with is required. Pipettes come in different sizes and types, yet they all basically function by bringing up a particular volume of fluid into an expendable tip and afterward administering it somewhere else.
There are two primary kinds of pipettes: air uprooting pipettes and positive removal pipettes. Air relocation pipettes work by making a vacuum over the fluid to be move, permitting it to be drawn up into the tip. These pipettes are ordinarily utilized for general applications and can deal with a large number of volumes.
Positive uprooting pipettes, then again, utilize a dispensable cylinder that comes into direct contact with the fluid. As the cylinder is discouraged, the fluid is drawn up into the tip. These pipettes are often utilized while managing gooey or unstable fluids or when high precision is required.
Pipettes are regularly flexible, permitting the client to set the ideal volume to be moved. They are intended to be exact and precise, with numerous pipettes having adjustment highlights to guarantee predictable and dependable estimations.

Sorts of pipettes
There are a few sorts of pipettes accessible for various applications. Here are a few ordinarily employed types:
Micropipettes: Micropipettes are the most widely recognized kind of pipette utilized in research centres. They are intended for exact and precise estimation of little volumes, regularly going from microliters (μL) to milliliters (mL). Micropipettes are accessible as flexible or fixed-volume pipettes.
Multichannel Pipettes: Multichannel pipettes are like micropipettes; however, they have numerous channels, ordinarily going from 8 to 12 channels. They consider synchronous exchange of fluid in numerous wells or tests, saving time and expanding productivity, especially in high-throughput applications, for example, plate measures.
Pasteur Pipettes: Pasteur pipettes, otherwise called droppers or moving pipettes, are expandable plastic or glass pipettes with tight tips. They are regularly utilized for moving little volumes of fluid or for universally useful fluid handling.
Serological Pipettes: Serological pipettes are for some time, graduated pipettes with a wide tip and an enormous bulb at the top. They are principally utilized for estimating and moving bigger volumes of fluid, normally going from 1 mL to 100 mL. Serological pipettes are usually utilized in cell culture, sub-atomic science, and different applications where bigger volumes are taken care of.
Volumetric Pipettes: Volumetric pipettes are profoundly exact and exact pipettes utilized for estimating a solitary fixed volume of fluid. They have a solitary graduation mark close to the tip, considering exact estimations of a particular volume. Volumetric pipettes are regularly utilized in logical science and in the readiness of standard arrangements.
Dispensable Pipettes: This is the most essential pipette; it’s anything but a mind-boggling piece of research centre hardware and ought to just be utilized for unpleasant estimations. While using an expendable pipette, notwithstanding, utilizing a customary pipetting technique is basic. Suction fluid at a 90-degree point, administer at a 45-degree point and tap off to guarantee all fluid is administered.
Single-channel pipette: A solitary channel pipette is a non-dispensable device, commonly of the air-relocation assortment, that gives dependable estimation results with the utilization of a solitary expendable tip. Single-channel pipetting is usually associated with two strategies:
Forward Procedure: This is the expected capability and the most utilized pipette estimating method. To utilize this methodology, first press the unclogger to pause and marginally lower the pipette tip in the fluid, then, at that point, suction your deliberate volume by leisurely delivering the unclogger to keep away from bubbles. Place the tip against the repository’s side, then cautiously press the unclogger through the main stop to the last brush-out position while “igniting” the last drop from the tip.
Switch Procedure: While working with thick arrangements or arrangements inclined to bubbles, we have the choice of utilizing an opposite pipetting way to deal with lessened impedance from air bubbles. To utilize this methodology, press the unclogger right down to the third stop position (right down), somewhat lower in fluid, and gradually return the unclogger to the top to suction the fluid into the tip. Place the pipette tip against the container’s wall and press the unclogger to the main stop, then pull out the tip from the repository. You presently have an example of fluid in the tip that isn’t important for the estimation. You can then rehash it.
Rehash unimposing method: An expert can utilize this pipette to set and administer a predefined volume into a few containers without being in the middle between administrators. This limit of multi-dispensing saves time and work. The recurrent pipette gadget isn’t similar to a customary fab pipette. The differentiation is between a filling and administering switch and an unclogger. Follow these moves toward effectively utilizing a rehashing pipette:
Slide the filling switch right down.
Raise the locking clasp to the top.
Close the switch in the wake of embedding the needle-type tip into the barrel until it fits properly.
Drench the tip at a 90-degree point in the fluid.
Slide the filling switch gradually vertically to fill the tip totally.
Take action by disposing of the fluid from the first administration.
The recurrent pipette is currently prepared to work.
These are a portion of the primary sorts of pipettes utilized in labs. The decision of pipette relies upon the expected volume range, exactness, accuracy, and explicit application.
Original Source: https://nboxoffice.com/how-to-use-the-various-types-of-pipettes/
0 notes
Text
Home
Everything You Required To Understand About TNF Alpha Elisa Kit Antibody
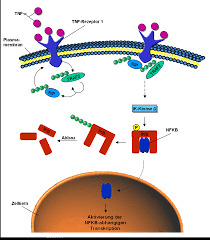
Whenever you are thinking about TNF Alpha Elisa kit antibody, it is the multifunctional pro-inflammatory cytokine that belongs to the (TNF) tumor necrosis factor superfamily. TNF Alpha is really involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, immune cells, apoptosis, differentiation, coagulation, as well as likewise lipid metabolism.
Elisa Kit is actually the widely used innovation, specifically in the enzyme immunoassay technology. This enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (Elisa) is also called EIA (Enzyme Immunoassay). It is basically the biochemical technique mainly used in immunology in order to find the presence of an antigen or antibody in a particular sample.
Primary Features Of Human TNF Alpha Elisa Kit:
- TNF Alpha Elisa kit is actually in the size of 96 wells/kit along with the removable strips. The sample types for this kid consist of serum & plasma such as heparin, citrate, & EDTA, and also cell culture supernatants.
- The individuals must require to store this kit at 4 degrees Celsius for around six months as well as also at -20 degrees Celsius for around 12 months. You have to avoid several freeze-thaw cycles.
- This specific kit is utilizing the Boster Biological Technology for providing the complete benefits of Elisa kit for antibodies.
- When considering the immunogen, it has the expression system for basic E.coil immunogen sequence V77-L233 with less than 1 pg/ml sensitivity.
- The assay range is about 15.7 pg/ml to 1000 pg/ml and there is no founded cross reactivity with any other relevant proteins.
- This EK0525 TNF Alpha Elisa kit is extremely reactive to TNF in the human samples.
- Whenever you want to find out about the validated sample types, they consist of serum, plasma, and also cell culture supernatants.
More Concerning Necessary Materials To Utilize This Kit:
The following are the very required materials to efficiently use this TNF Alpha Elisa Kit however not included in its package. You should have a microplate reader which is capable of reading absorbance at 450 nm. Some other required points are pipettes & pipette tips which are capable of exactly dispensing 0.5 microlitres via 1 ml volumes of the liquid solutions, automated plate washer, as well as multi-channel pipettes which are recommended for the greater quantity of samples. In these materials, an automated plate washer is not compulsory and also it is entirely optional. At the same time, the users of this kit must also need to have 500 ml graduated cylinders, deionized or distilled water, or test tubes for dilution. This alpha kit is generally utilized to measure the protein in human plasma, serum, and also culture media.
Likewise, it is using their proprietary simple action Elisa technology with particular sensitivity. This specific innovation is using capture antibodies that are conjugated to a similarity tag which is highly determined by the monoclonal antibody employed to coat the plates of Elisa kit. This specific approach to sandwich Elisa allows the antibody analyte sandwich complex formation just within a single step most significantly to reduce the assay time. This single wash protocol decreases the assay time to about 90 mins or less. You can click here to recognize more details concerning Elisa kit online.
1 note
·
View note